Period cramp feeling 35 weeks pregnant
Pregnancy at week 35 | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Pregnancy at week 35 | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
Your baby
Your baby now weighs more than 2.3kg and measures about 32cm from head to bottom. They are quite cramped and their legs are bent up into their chest, but they can still change position and kick you. They can swallow about a litre of amniotic fluid every day, which is passed as urine.
Don’t worry if your baby is still in the breech position (head up, feet down) – most babies will gradually turn into the head-down position during the last month. If your baby is still in the breech position during the next week or two, your doctor or midwife may try to turn them using a procedure known as External Cephalic Version (ECV).
Your baby at 35 weeks
| Length: | 32cm (head to bottom) |
| Weight: | 2.3kg |
Your body
You may be having a lot of Braxton Hicks contractions by now. They feel like a tightening or cramping in your tummy, and they can happen as often as every 10 to 20 minutes in late pregnancy. They are your body’s way of preparing for the birth and are nothing to be worried about. You can tell if they’re Braxton Hicks and not real contractions because they normally go away if you move position.
They may be real contractions if:
- they get stronger or closer together
- they last longer as time goes by
- they are stronger when you walk
- you feel pain or pressure in your pelvis, abdomen or lower back
If you went into labour now it would be considered premature labour and you would need medical attention straight away. If you’re in doubt, contact your doctor or midwife.
If you’re in doubt, contact your doctor or midwife.
Things to remember
If your pregnancy is high risk, your doctor or midwife will probably want to see you more often from now on.
One serious complication that can develop in late pregnancy is pre-eclampsia. This is usually diagnosed if your doctor notices you have high blood pressure or protein in your urine.
See your doctor straight away if you develop:
- a bad headache
- pain in the tummy
- blurry vision
- sudden swelling of your hands or feet
Read next
Your pregnancy at 36 weeks
Learn about your pregnancy journey and what is happening to you and your baby.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Raising Children Network (Pregnancy week-by-week), Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (Breech Presentation at the End of your Pregnancy), NHS (You and your baby at 35 weeks pregnant), Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (Labour and birth)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: August 2020
Back To Top
Need more information?
Pregnancy at week 34
As at the start of your pregnancy, you’re probably feeling tired and emotional. The baby doesn't have much room to move, but you might feel them kick and roll.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 39
Your baby's weight gain should slow down since they are now ready to be born. You might soon start to notice the early signs of labour.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy and travel - Better Health Channel
Travelling to developing nations is not encouraged during pregnancy, due to the risk of disease and the standard of medical facilities.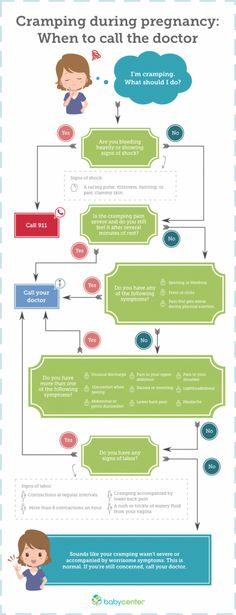
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Multiple birth - triplets or more
If you are pregnant with triplets or more, the birth will need careful planning. The main risk is that your babies will be born prematurely. Find out more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Episiotomy
An episiotomy is a procedure performed during labour to assist with the delivery of your baby.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
The role of exercise in improving fertility, quality of life and emotional wellbeing
Being in the healthy weight range reduces the risk of infertility and improves the chance of conceiving spontaneously and with assisted reproductive technology (ART).
Read more on Your Fertility website
Undescended testicles - Better Health Channel
Undescended testicles means that one or both testicles are missing from the scrotum.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Baby, Symptoms & Cramping • Kopa Birth®
Welcome to week 35 pregnancy! You are likely busy getting ready for your little one’s arrival, and it’s finally right around the corner. Let’s talk about your baby, your pregnancy symptoms, and discuss cramping you may experience late in pregnancy and when you should take it seriously.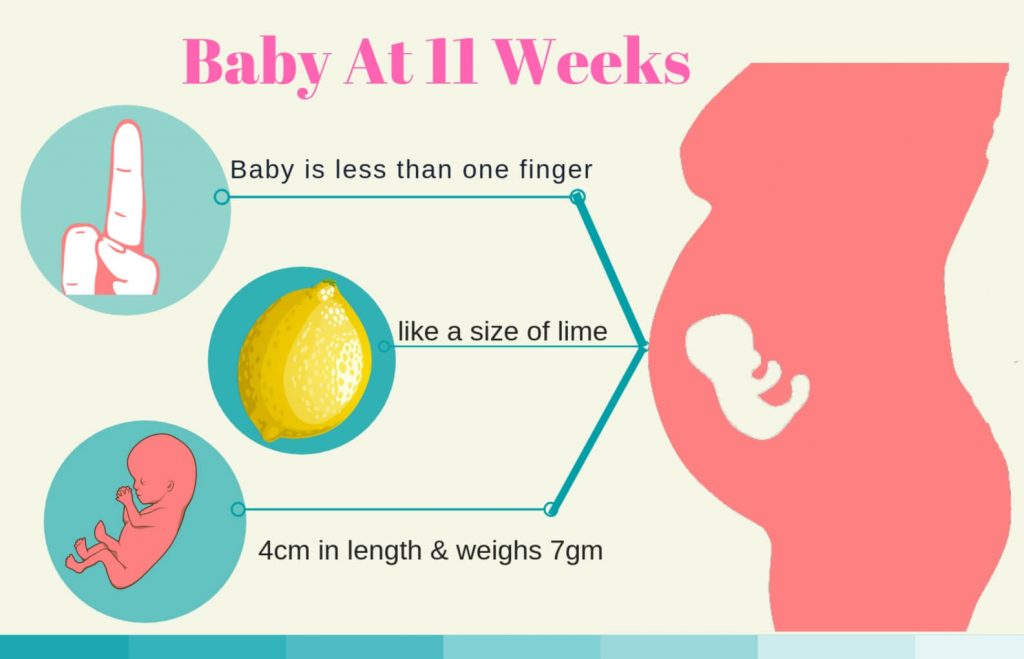
Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
Updated August, 24, 2021
Table of contents
- Week 35 Pregnancy: Baby
- Variation in Baby’s Size
- Week 35 Pregnancy: Symptoms
- Leg and Foot Swelling
- When is Swelling a Problem?
- Numbness
- Snoring
- Pelvic Pain or Pressure
- Leg and Foot Swelling
- Week 35 Pregnancy: Cramping
- Preterm Labor Cramps
- When to Call Your Doctor
- Preterm Labor Cramps
Week 35 Pregnancy: Baby
Your baby is getting so big! At 33 weeks from conception, he or she now weighs over 5 1/4 pounds, and is about 13 1/4 inches from crown to rump or 18 1/4 inches in total length (1).
In other week 35 baby news:
- The lungs are getting close to maturity
- The circulatory system is complete
- The musculoskeletal system is complete (2)
You continue to grow right along with baby! You have probably gained between 24 to 29 pounds, and your uterus now reaches 6 inches above your belly button.
Variation in Baby’s Size
As we’ve talked about baby’s size through your pregnancy, we’ve used general numbers that approximate baby’s size at each stage. These are more accurate in the beginning, as babies all begin development on the same schedule.
Later in pregnancy, though, there is more variation. Your baby’s genetics are a factor — if all members of your family are tall, your baby may be longer than average length already. Weight also varies, and your baby may especially be heavier if you gained more weight than average or if you have untreated gestational diabetes. Baby’s size is almost never a problem for a natural delivery, but if your doctor has any concern, he or she may use ultrasound to get a general idea of baby’s weight. But please note, estimates of baby’s weight performed late in pregnancy are often inaccurate and can lead to unnecessary labor inductions or cesarean sections.
Read more: Natural Childbirth, Large Baby: Worried? Read This.
Week 35 Pregnancy: Symptoms
Leg and Foot Swelling
Most pregnant women experience swelling in their legs and feet during pregnancy. By week 35 of your pregnancy, it’s probably a symptom that you’re quite familiar with. You may feel like you don’t have ankles anymore or that your feet look like swollen sausages. Your skin may feel tight and uncomfortable.
To relieve the swelling, stay off of your feet as much as possible, and when you do sit or lie down, prop your legs up (2). This is the time to opt for comfortable shoes. Slip-ons may be easier than shoes you need to tie as it becomes harder for you to bend and reach your feet. You also want to make sure that your shoes have enough room to accommodate your feet by the end of the day when they may be swollen and larger than in the morning.
When is Swelling a Problem?
Sudden, severe swelling can be a symptom of preeclampsia, a serious problem. Call your doctor or midwife right away if you notice sudden swelling, swelling in your face, or swelling that’s accompanied by pain, a headache that won’t go away, or blurry vision.
Numbness
You may notice numbness or tingling in your hands, fingers, or toes. It’s a strange feeling, but not worrisome. It’s a result of your body’s tissues swelling due to extra the extra fluids of pregnancy, and then pressing on your nerves (2). Some women even develop carpal tunnel syndrome, which is caused by the compression of a nerve within the carpal tunnel in the wrist. (We discuss carpal tunnel syndrome in our Week 30 Pregnancy article.) These feelings of numbness, tingling, and pain usually go away after your baby is born and your tissues return to normal.
Snoring
More than a third of women snore during pregnancy (1). Snoring is caused by your upper airway relaxing and closing partway during sleep, making it harder to get air in and out. Pregnancy adds the extra factor of swollen nasal passages, which exacerbates the problem. You may find that it helps to sleep partly upright, like in a recliner, which makes gravity work for you instead of against you.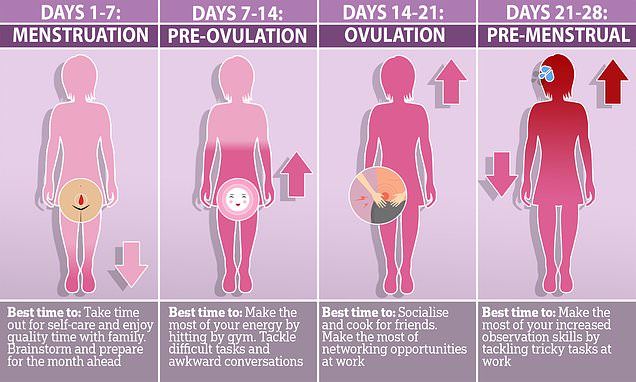 If you have concerns about your snoring or feel like you’re struggling to breathe properly, talk to your healthcare provider.
If you have concerns about your snoring or feel like you’re struggling to breathe properly, talk to your healthcare provider.
Pelvic Pain or Pressure
You may be feeling an increase in pressure or even pain in your pelvis. A couple of things may be happening that could cause these sensations. First, as you get into the final stretch of pregnancy, the joints throughout your body loosen even more. This loosening will help your baby fit through the birth canal, so it’s beneficial to you. However, it also means that you may feel increased aches and pains throughout your body, especially in your pelvis and lower back. (The increasingly loose joints paired with the ever-growing bump may also make you feel like your walk has turned into a waddle.)
In the last month or so of pregnancy, baby may also settle lower in your pelvis, which is called lightening or the baby dropping. For some women, this doesn’t occur until labor, but for others, it happens weeks before baby is born.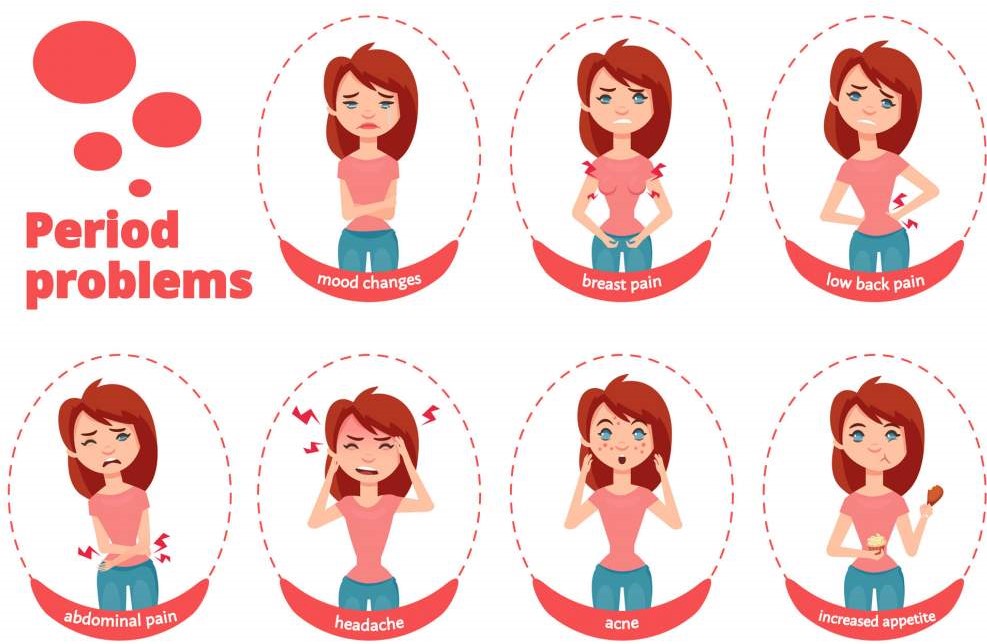 You may see a distinct difference in the shape of your baby bump. And you may feel a difference in your ability to take a deep breath or eat a meal without discomfort (thanks to baby moving lower and therefore not pushing up into your lungs and stomach.) Unfortunately, the downside is that around 20% of women have pelvic pain (4) as baby’s large, bony head sits lower the your pelvis, putting pressure on both bones and nerves. You may find it helpful to rest with your feet up, lie down when you have the chance, and wear a pregnancy support belt.
You may see a distinct difference in the shape of your baby bump. And you may feel a difference in your ability to take a deep breath or eat a meal without discomfort (thanks to baby moving lower and therefore not pushing up into your lungs and stomach.) Unfortunately, the downside is that around 20% of women have pelvic pain (4) as baby’s large, bony head sits lower the your pelvis, putting pressure on both bones and nerves. You may find it helpful to rest with your feet up, lie down when you have the chance, and wear a pregnancy support belt.
Week 35 Pregnancy: Cramping
This late in pregnancy, moms often scrutinize every cramp carefully, wondering if it may be the beginning of labor. Although cramping most often isn’t always related to labor contractions, it’s a good idea to pay attention to your body’s signals as you approach the last few weeks of pregnancy.
Preterm Labor Cramps
Preterm labor is one that begins before week 37 of pregnancy. At 35 weeks, baby may still be immature and underdeveloped, so it’s often best to halt labor contractions at this point in the pregnancy.
Preterm labor cramps can be difficult to distinguish. You might experience mild to moderate abdominal cramping, similar to menstrual cramps. This may or may not be accompanied by discomfort in your thighs (3). This feeling may come and go. It may eventually progress into distinct contractions, or it may stop altogether.
When to Call Your Doctor
When it comes to preterm labor, it’s best to err on the side of caution. Call your doctor or midwife if you’re experiencing any 2 of the following symptoms:
- At least 6 contractions in an hour
- Menstrual-like cramps that are continuous or come and go, and are accompanied by a feeling of pressure
- A dull lower back ache that won’t go away
- Intestinal cramping without any diarrhea
- A noticeable change in vaginal discharge (blood-tinged, lots of mucus, etc.)
Also, pick up the phone if cramping is severe, comes with a fever or dizziness, or is accompanied by bleeding.
Check back in soon to learn all about week 36 of your pregnancy!
Kopa Birth’s online birthing classes allow you to prepare for a natural hospital birth from the comfort of your own home, 24/7. Enroll today in our free online childbirth class and start preparing for your natural birth!
Enroll today in our free online childbirth class and start preparing for your natural birth!
References:
- Glade, B.C., Schuler, J. (2011). Your Pregnancy Week by Week, 7th edition. First Da Capo Press
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2010). Your Pregnancy and Childbirth Month to Month, 5th edition
- Simkin, P. (2010). Pregnancy, Childbirth and the Newborn, 4th edition. Meadowbrook Press
- Pennick V, Liddle SD. Interventions for preventing and treating pelvic and back pain in pregnancy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 8. Art. No.: CD001139. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001139.pub3.
Here are some other birth articles and stories we know you’ll love.
33-36 weeks of pregnancy
33 weeks of pregnancy
How does the baby develop?
This week, the baby continues to actively grow and gain weight, his height is already about 44 cm, and the weight of a tiny body is approximately 1800-1900 g. During this period, the baby is no longer so easy to turn around, it takes up more space, which is why and his movements. This week, the baby sleeps a lot and therefore moves less, and the amplitude of his movements also decreases. The muscles become stronger, so the pushes, although rare, are quite strong and more concentrated. For a mother, baby movements can be very sensitive and painful, causing internal organs to suffer. The blood vessels of the baby are already expanding and contracting, their walls are becoming thicker, and the tone is higher. Brain cells undergo a process of adhesion. The skin of the crumbs turns pink, and due to the increase in subcutaneous fat, all wrinkles on the body are smoothed out. On the head of the crumbs, the hairs become darker and thicker, and the hairs covering the body become less and less. This fluffy hairiness is called lanugo. At 33 weeks, the baby's skin is covered with a special lubricant that protects it and ensures an easier delivery. Lubrication most of all covers the face, back, folds under the arms, groin and neck.
During this period, the baby is no longer so easy to turn around, it takes up more space, which is why and his movements. This week, the baby sleeps a lot and therefore moves less, and the amplitude of his movements also decreases. The muscles become stronger, so the pushes, although rare, are quite strong and more concentrated. For a mother, baby movements can be very sensitive and painful, causing internal organs to suffer. The blood vessels of the baby are already expanding and contracting, their walls are becoming thicker, and the tone is higher. Brain cells undergo a process of adhesion. The skin of the crumbs turns pink, and due to the increase in subcutaneous fat, all wrinkles on the body are smoothed out. On the head of the crumbs, the hairs become darker and thicker, and the hairs covering the body become less and less. This fluffy hairiness is called lanugo. At 33 weeks, the baby's skin is covered with a special lubricant that protects it and ensures an easier delivery. Lubrication most of all covers the face, back, folds under the arms, groin and neck.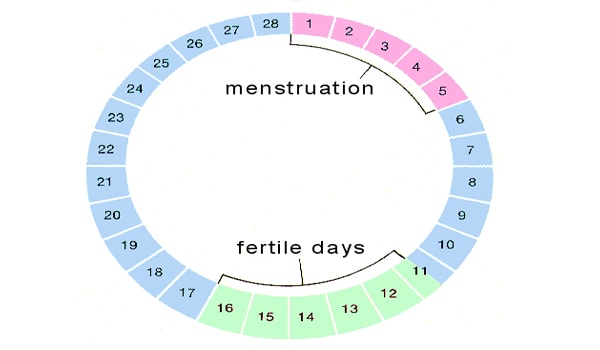 nine0007
nine0007
How does mother feel?
The uterus of the expectant mother rises higher and higher, at a distance of up to 34 cm from the pubis, and the tummy grows significantly. This is due to the large weight of the crumbs, amniotic fluid and placenta. At the same time, it is harder for the mother to squat and make other movements. Strong and sharp jolts of the baby, as well as an enlarged uterus, can cause pain. But the expectant mother can already determine what exactly pushed her baby: with her knee or fist. If the tremors are light, this may indicate that the baby is hiccuping. At this time, a woman is recommended light physical activity, which allows you to take frequent breaks. Walking or fitness is best. Due to the fact that the enlarged uterus puts pressure on many organs, the mother may experience temporary discomfort, which is not related to any diseases. A high load is placed on the spine, causing pain in the sacrum, lower back and pelvis. In a pregnant woman, the volume of circulating blood increases by a liter, which has a strong effect on the functioning of the kidneys, oppressing the bladder and causing frequent urination. Sometimes mom can get up to six times a night. The cause of heaviness in the stomach, heartburn and nausea is the pressure of the uterus on the stomach. In this case, frequent meals in small portions will help to alleviate the condition. nine0007
Sometimes mom can get up to six times a night. The cause of heaviness in the stomach, heartburn and nausea is the pressure of the uterus on the stomach. In this case, frequent meals in small portions will help to alleviate the condition. nine0007
34 weeks pregnant. How does the baby develop?
At this time, the baby has grown significantly, the weight of his small body reaches 2100 g, and the length is 45 cm. The body of the baby is already proportional and it is difficult to distinguish it from a newborn child. There are no wrinkles and folds on the face, the skin is smooth and even. The baby already often sucks his finger, developing a sucking reflex, so his cheeks are already formed and visible. Bones become denser, muscle mass also grows significantly. You can already see even the facial muscles on the face. By this time, the baby has already finally settled down in his mother's tummy and he is unlikely to be able to change the position of the body now. The bones of the skull, which are filled with connective tissue, remain very soft. nine0007
nine0007
The baby's internal organs continue to develop. He swallows amniotic fluid many times throughout the day. Water passes through the digestive tract and stimulates the muscles. The pancreas and liver process the dense part of the amniotic fluid, which consists of vellus hairs, lubrication, and small skin flakes. The liquid component of the water is excreted by the kidneys. The body thus processes about half a liter of water. Bile continues to accumulate in the gallbladder, providing preparation for the activities of the organs after birth. There is an intensive preparation for the appearance of the crumbs into the world, his head shape may change. With the onset of childbirth during this period, the lungs of the baby are able to provide the body with the necessary amount of oxygen. nine0007
How does mother feel?
This week of pregnancy requires conscientious control of the condition of the expectant mother. This is just the period when a woman can feel false contractions. Painful sensations appear in the upper part of the uterus and gradually subside. With the increase in the duration of pregnancy, contractions become more pronounced. They resemble short muscle contractions lasting from a few seconds to five minutes. Thus, the body prepares for the upcoming birth. This process with varying intensity accompanies the pregnancy of every woman. Experts call it Braxton-Hicks contractions. How can a future mother distinguish labor pains from precursors, especially if she is expecting a baby for the first time? nine0007
Painful sensations appear in the upper part of the uterus and gradually subside. With the increase in the duration of pregnancy, contractions become more pronounced. They resemble short muscle contractions lasting from a few seconds to five minutes. Thus, the body prepares for the upcoming birth. This process with varying intensity accompanies the pregnancy of every woman. Experts call it Braxton-Hicks contractions. How can a future mother distinguish labor pains from precursors, especially if she is expecting a baby for the first time? nine0007
Consider the main differences:
- Preparatory contractions are characterized by a high interval between them, which varies in duration. And prenatal contractions are regular, with a gradually decreasing interval.
- Preparatory contractions may stop immediately after rest or a change in the position of the expectant mother's body, and labor gradually intensifies regardless of the change in position.
- Pain is also different.
 Labor pains are accompanied by severe pains that become more and more noticeable. Preparatory contractions are characterized by either sharp pain, or they can be completely painless. nine0026
Labor pains are accompanied by severe pains that become more and more noticeable. Preparatory contractions are characterized by either sharp pain, or they can be completely painless. nine0026 - False contractions may stop with the use of medically approved antispasmodics. While such drugs will not have any effect on labor pains or it will be minimized.
- A woman can feel false contractions in various places. This may be the lower abdomen, the side walls of the uterus, the entire abdomen. Pain during labor pains can resemble premenstrual pain. Also, pain can begin in the lower back, gradually covering the front of the abdomen. nine0026
It is very important for a woman with such symptoms to ensure a sense of security, in case of any contractions, it is necessary to inform the gynecologist of the pregnant woman.
35 weeks pregnant. How does the baby develop?
Every baby reaches their weight and height this week. Approximately, his body weight is approximately 2,300 g, and his height is up to 47 cm. Starting this week, the height and weight of the crumbs will gradually increase by 250 g. But these parameters depend on genetics and individual characteristics of the organism. By this period, the formation of all systems and organs of the baby is already ending, and cardinal changes in the body are not expected. The amount of mucus that covers the baby's skin gradually decreases. The hair fluff practically disappears from the body, and even if it remains, it completely disappears after birth. The body becomes pink, the muscles are stronger, and the shoulders become rounded. The baby already almost completely occupies the uterine cavity, its arms and legs are in a bent state. The baby is already very crowded and the mother can feel his every movement. The baby often changes his facial expression, closing his eyelids and contracting facial muscles. Small nails appear on the fingers. This week, the formation of the genitourinary and nervous system ends. The fact that the bones of the skull have not yet fused will make it easier to pass through the birth canal.
Starting this week, the height and weight of the crumbs will gradually increase by 250 g. But these parameters depend on genetics and individual characteristics of the organism. By this period, the formation of all systems and organs of the baby is already ending, and cardinal changes in the body are not expected. The amount of mucus that covers the baby's skin gradually decreases. The hair fluff practically disappears from the body, and even if it remains, it completely disappears after birth. The body becomes pink, the muscles are stronger, and the shoulders become rounded. The baby already almost completely occupies the uterine cavity, its arms and legs are in a bent state. The baby is already very crowded and the mother can feel his every movement. The baby often changes his facial expression, closing his eyelids and contracting facial muscles. Small nails appear on the fingers. This week, the formation of the genitourinary and nervous system ends. The fact that the bones of the skull have not yet fused will make it easier to pass through the birth canal. It is important during this period to control the number of movements of the baby. For half a day, approximately 10 movements should be recorded. If the movements are much more or less, the mother should consult a doctor. nine0007
It is important during this period to control the number of movements of the baby. For half a day, approximately 10 movements should be recorded. If the movements are much more or less, the mother should consult a doctor. nine0007
How does mother feel?
Mom has difficulty breathing during this period. This is caused by the growing uterus, which pushes the lungs first. The lungs cannot fully expand, making breathing difficult. Also, an enlarged uterus pushes the bladder and intestines aside. This week, almost every pregnant woman feels short of breath, she has shallow and rapid breathing and a constant desire to take a deep breath. The cause of shortness of breath during this period can be a long walk or climbing stairs, as well as a long stay in the supine position. Proper alternation of rest and physical activity will help to alleviate the condition. The bottom of the uterus rises 35 cm from the pubis and 15 cm from the navel, this is the highest point for the entire period of bearing a baby. It feels like one of the hardest weeks of pregnancy. The body of the expectant mother is actively preparing for the upcoming birth, all ligaments become more extensible and elastic. It can also lead to an increased risk of injury and falls. During this period, doctors do not recommend flights and long trips. If you need to go somewhere, the presence of a loved one and a mandatory change of position approximately every 15 minutes is important. Mom needs to rest more often this week. Special physical exercises that will help reduce back pain will be useful. nine0007
It feels like one of the hardest weeks of pregnancy. The body of the expectant mother is actively preparing for the upcoming birth, all ligaments become more extensible and elastic. It can also lead to an increased risk of injury and falls. During this period, doctors do not recommend flights and long trips. If you need to go somewhere, the presence of a loved one and a mandatory change of position approximately every 15 minutes is important. Mom needs to rest more often this week. Special physical exercises that will help reduce back pain will be useful. nine0007
36 weeks pregnant. How does the baby develop?
This week the baby begins to actively prepare for the birth. All organs of the baby are already almost completely mature and can function independently. The weight of the baby reaches 2,500 g, and its height is approximately 46 cm. This period is preparatory for the birth of the baby. By the beginning of this week, the baby is already in its final position in the uterus. In the vast majority of cases, it is located facing the back of the mother and head down. This position is the safest during the passage of the birth canal and the most convenient. If there is a breech presentation of the baby, a caesarean section is possible. In this case, it all depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. But this week, it is possible to change the position of the body only from the pelvic to the head, since the baby's head is heavier and this part of the body outweighs. The baby constantly sucks his finger and his cheeks become chubby. The baby also receives oxygen through the umbilical cord and also makes respiratory and swallowing movements. The baby at this time looks the way it is born, and the bones of the skull still remain pliable and soft to facilitate passage through the birth canal. nine0007
In the vast majority of cases, it is located facing the back of the mother and head down. This position is the safest during the passage of the birth canal and the most convenient. If there is a breech presentation of the baby, a caesarean section is possible. In this case, it all depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. But this week, it is possible to change the position of the body only from the pelvic to the head, since the baby's head is heavier and this part of the body outweighs. The baby constantly sucks his finger and his cheeks become chubby. The baby also receives oxygen through the umbilical cord and also makes respiratory and swallowing movements. The baby at this time looks the way it is born, and the bones of the skull still remain pliable and soft to facilitate passage through the birth canal. nine0007
How does mother feel?
During this period, a pregnant woman feels very tired. The tummy becomes heavier, making it difficult to choose the position of the body. The baby begins to sink lower, preparing for childbirth, and it becomes easier for the mother to breathe. But this increases the pressure on the bladder, causing more frequent urination. The uterus is located at a distance of 36 cm from the pubis. This is the highest point throughout the entire period of pregnancy. The body of the expectant mother is being rebuilt, leading intensive preparation for childbirth. Hormonal changes cause an increase in hormone levels. The pelvic bones soften under the influence of hormones, trying to make it as easy as possible for the baby to pass through the birth canal. At the same time, contractions intensify and more abundant vaginal discharge appears. A pregnant woman needs to listen more to her body this week and carefully monitor it. With pulling pain in the lower abdomen, as well as pain in the lower back, attention should be paid to its duration and frequency. If you have all the indicators, you should immediately contact a gynecologist: premature birth this week is not uncommon, so it is important to respond to body signals in time.
The baby begins to sink lower, preparing for childbirth, and it becomes easier for the mother to breathe. But this increases the pressure on the bladder, causing more frequent urination. The uterus is located at a distance of 36 cm from the pubis. This is the highest point throughout the entire period of pregnancy. The body of the expectant mother is being rebuilt, leading intensive preparation for childbirth. Hormonal changes cause an increase in hormone levels. The pelvic bones soften under the influence of hormones, trying to make it as easy as possible for the baby to pass through the birth canal. At the same time, contractions intensify and more abundant vaginal discharge appears. A pregnant woman needs to listen more to her body this week and carefully monitor it. With pulling pain in the lower abdomen, as well as pain in the lower back, attention should be paid to its duration and frequency. If you have all the indicators, you should immediately contact a gynecologist: premature birth this week is not uncommon, so it is important to respond to body signals in time. Mom should be very careful: do not make sudden movements, control posture, moderate walks and sitting time. During this period, sleep is disturbed, so the body is also preparing for the night feeding of the baby. This week, mom can fully feel what puffiness is. It is necessary to control edema, which can cause disruption of the organs. nine0007
Mom should be very careful: do not make sudden movements, control posture, moderate walks and sitting time. During this period, sleep is disturbed, so the body is also preparing for the night feeding of the baby. This week, mom can fully feel what puffiness is. It is necessary to control edema, which can cause disruption of the organs. nine0007
How to distinguish between PMS and pregnancy symptoms?
The symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and early pregnancy are quite similar. In this regard, a woman may have difficulty in determining her condition.
General symptoms of PMS and pregnancy
- Changes in mood: irritability, anxiety, tearfulness. With PMS, these symptoms disappear after the onset of menstruation. Signs of pregnancy will be the persistence of this condition and the absence of menstruation. It is worth noting that a depressed mood can be a sign of depression. If the symptoms do not disappear within 2 weeks, you should consult a doctor.
 nine0026
nine0026
- Constipation. Hormonal fluctuations slow down bowel movements, which is a common cause of constipation. In pregnant women, this symptom is noted during the first two trimesters. With PMS, constipation goes away after the onset of menstruation.
- Changes in the chest. These changes may include:
- pain;
- sensitivity;
- swelling;
- size increase.
With PMS, these symptoms are usually most pronounced just before menstruation and disappear immediately after it ends. nine0007
In the early stages of pregnancy, the breasts become tender and enlarge. Veins may protrude on the surface of the breast and there may be pain around the nipples.
- Fatigue. This symptom is associated with the action of one of the sex hormones - progesterone. With PMS, the condition returns to normal after the end of menstruation.
Fatigue is also a common sign of early pregnancy. The duration of this symptom depends on the individual characteristics of the woman's body. In addition, fatigue can be a sign of iron deficiency anemia. nine0007
The duration of this symptom depends on the individual characteristics of the woman's body. In addition, fatigue can be a sign of iron deficiency anemia. nine0007
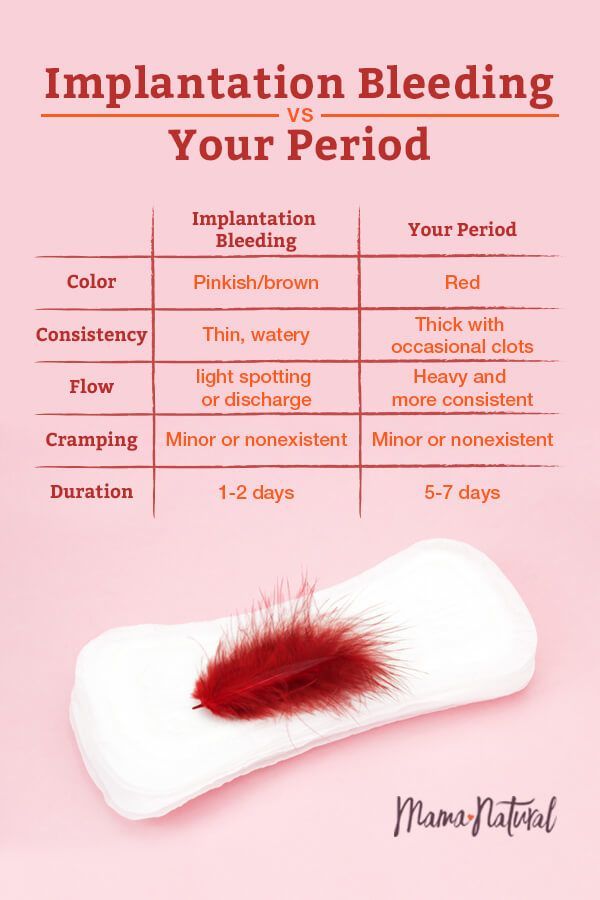
- Bleeding. As you know, menstruation is accompanied by a period of bleeding, which lasts an average of 4-5 days.
In early pregnancy, light bleeding may also occur, which is usually associated with the period of embryo implantation (10-14 days after fertilization).
- Spasms. This symptom is characteristic of both PMS and pregnancy. However, in the case of pregnancy, cramps occur closer to the stomach. They can appear throughout the entire pregnancy. This is due to the process of embryo implantation and expansion of the uterus. nine0026
- Headache and back pain. These symptoms are characteristic of both the PMS period and pregnancy.
- Appetite changes. Increased appetite is a common pregnancy symptom, but it is also common during PMS.

Cravings for sugary or fatty foods are associated with fluctuations in sex hormones such as estrogen and progesterone.
Symptoms most likely to indicate pregnancy include:
- cessation of the menstrual cycle. This is one of the most obvious symptoms that indicates pregnancy, but there are other reasons for changing the menstrual cycle:
- stress;
- low body weight;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- thyroid disease or diabetes mellitus;
- menopause;
- Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms in early pregnancy. They are observed in 80% of pregnant women; nine0026
- nipple changes. If the areola, the area around the nipple, becomes darker or larger, it may indicate pregnancy. Such changes can occur as early as 1-2 weeks after conception.
When should I see a doctor?
Women who experience the above symptoms should have a home pregnancy test.