Passing grey tissue during pregnancy
Miscarriage - what you might actually see and feel
Miscarriage - what you might actually see and feel | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content7-minute read
Listen
WARNING — This article contains some graphic descriptions of what you might see during a miscarriage.
A miscarriage requires prompt medical care. If you think you are having a miscarriage, call your doctor or midwife for advice and support. Go to the Emergency Department if:
- you are bleeding very heavily (soaking more than 2 pads per hour or passing clots larger than golf balls)
- you have severe pain in your tummy or shoulder
- you have a fever (a temperature above 38 degrees C)
- you are dizzy, fainting or feel like fainting
- you notice fluid coming from your vagina that smells bad
- you have diarrhoea or pain when you have a bowel motion (do a poo)
Miscarriage is a very unfortunate and sad outcome of pregnancy that takes a significant emotional and physical toll on a woman. It also happens more frequently than many people think. It's important to recognise that there's no right or wrong way to feel about a miscarriage.
Despite close to one in 5 pregnancies ending in miscarriage, what actually happens and what a woman needs to know and do when faced with a possible miscarriage are subjects that rarely get discussed.
This article aims to give you an idea of what happens and what a woman needs to know and do at different stages in her pregnancy.
Please call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 if you have any concerns or wish to discuss the topic further.
What might I feel during a miscarriage?
Many women have a miscarriage early in their pregnancy without even realising it. They may just think they are having a heavy period. If this happens to you, you might have cramping, heavier bleeding than normal, pain in the tummy, pelvis or back, and feel weak. If you have started spotting, remember that this is normal in many pregnancies — but talk to your doctor or midwife to be safe and for your own peace of mind.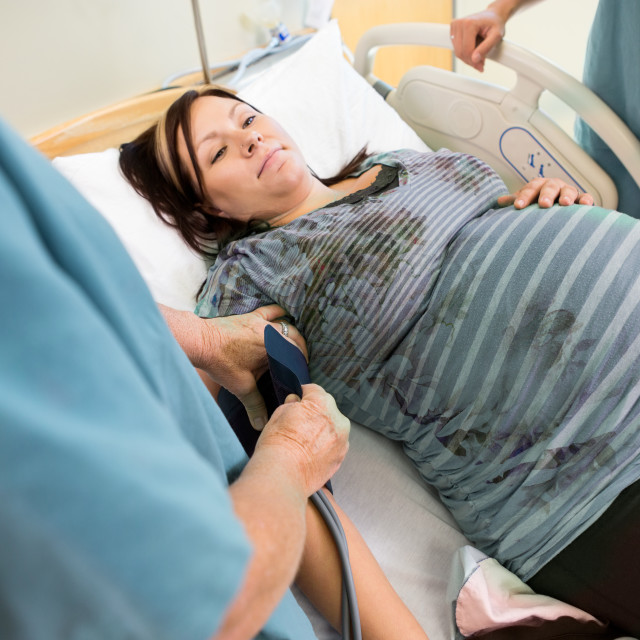
Later in your pregnancy, you might notice signs like cramping pain, bleeding or passing fluid and blood clots from your vagina. Depending on how many weeks pregnant you are, you may pass tissue that looks more like a fetus, or a fully-formed baby.
In some types of miscarriage, you might not have any symptoms at all — the miscarriage might not be discovered until your next ultrasound. Or you might just notice your morning sickness and breast tenderness have gone.
It is normal to feel very emotional and upset when you realise you’re having a miscarriage. It can take a while to process what is happening. Make sure you have someone with you, for support, and try to be kind to yourself.
What happens during a miscarriage?
Unfortunately, nothing can be done to stop a miscarriage once it has started. Any treatment is to prevent heavy bleeding or an infection.
Your doctor might advise you that no treatment is necessary. This is called 'expectant management', and you just wait to see what will happen. Eventually, the pregnancy tissue (the fetus or baby, pregnancy sac and placenta) will pass naturally. This can take a few days or as long as 3 to 4 weeks.
Eventually, the pregnancy tissue (the fetus or baby, pregnancy sac and placenta) will pass naturally. This can take a few days or as long as 3 to 4 weeks.
It can be very hard emotionally to wait for the miscarriage because you don’t know when it will happen. When it starts, you will notice spotting and cramping and then, fairly quickly, you will start bleeding heavily. The cramps will get worse until they feel like contractions, and you will pass the pregnancy tissue.
Some women opt to have medicine to speed up the process. In this case, the pregnancy tissue is likely to pass within a few hours.
If not all the tissue passes naturally or you have signs of infection, you may need to have a small operation called a ‘dilatation and curettage’ (D&C). You may need to wait some time for your hospital appointment. The operation only takes 5 to 10 minutes under general anaesthetic, and you will be able to go home the same day.
While you are waiting for a miscarriage to finish, it’s best to rest at home — but you can go to work if you feel up to it. Do what feels right for you. You can use paracetamol for any pain. If you are bleeding, use sanitary pads rather than tampons.
Do what feels right for you. You can use paracetamol for any pain. If you are bleeding, use sanitary pads rather than tampons.
What might I see during a miscarriage?
In the first month of pregnancy, the developing embryo is the size of a grain of rice so it is very hard to see. You may pass a blood clot or several clots from your vagina, and there may be some white or grey tissue in the clots. The bleeding will settle down in a few days, although it can take up to 2 weeks.
At 6 weeks
Most women can’t see anything recognisable when they have a miscarriage at this time. During the bleeding, you may see clots with a small sac filled with fluid. The embryo, which is about the size of the fingernail on your little finger, and a placenta might be seen inside the sac. You might also notice something that looks like an umbilical cord.
At 8 weeks
The tissue you pass may look dark red and shiny — some women describe it as looking like liver. You might find a sac with an embryo inside, about the size of a small bean. If you look closely, you might be able to see where the eyes, arms and legs were forming.
If you look closely, you might be able to see where the eyes, arms and legs were forming.
At 10 weeks
The clots that are passed are dark red and look like jelly. They might have what looks like a membrane inside, which is part of the placenta. The sac will be inside one of the clots. At this time, the developing baby is usually fully formed but still tiny and difficult to see.
At 12 to 16 weeks
If you miscarry now, you might notice water coming out of your vagina first, followed by some bleeding and clots. The fetus will be tiny and fully formed. If you see the baby it might be outside the sac by now. It might also be attached to the umbilical cord and the placenta.
From 16 to 20 weeks
This is often called a 'late miscarriage'. You might pass large shiny red clots that look like liver as well as other pieces of tissue that look and feel like membrane. It might be painful and feel just like labour, and you might need pain relief in hospital. Your baby will be fully formed and can fit on the palm of your hand.
After the miscarriage
You will have some cramping pain and bleeding after the miscarriage, similar to a period. It will gradually get lighter and will usually stop within 2 weeks.
The signs of your pregnancy, such as nausea and tender breasts, will fade in the days after the miscarriage. If you had a late miscarriage, your breasts might produce some milk. You will probably have your next period in 4 to 6 weeks.
Remember, it’ll be normal to feel very emotional and upset at this time.
More information
Read more about miscarriage:
- What is a miscarriage?
- What happens after a miscarriage
- Emotional support after miscarriage
- Fathers and miscarriage
- Experiencing a pregnancy loss
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
KidsHealth (Understanding miscarriage), The Royal Women's Hospital (Treating miscarriage), Pink Elephants Support Network (Sorry for your loss), Women’s and Children’s Health Network (Miscarriage), Patient.com (Miscarriage and bleeding in early pregnancy), Pink Elephants Support Network (Treatments and procedures), New Kids Center (Blood Clots of Miscarriage: What It Looks Like?), Babycenter Australia (Understanding late miscarriage)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: March 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Fathers and miscarriage
- Emotional support after miscarriage
- What happens after miscarriage
- Miscarriage
- Experiencing a pregnancy loss
Need more information?
Miscarriage
Miscarriage Despite being common and widespread, miscarriage can be a heartbreaking experience – with up to one in five pregnancies ending before week 20
Read more on Gidget Foundation Australia website
Miscarriage
A miscarriage is the loss of a baby, usually during the first three months or first trimester of pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Fathers and miscarriage
A miscarriage can be a time of great sadness for the father as well as the mother.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Emotional support after miscarriage
It is important to know that there is no right or wrong way to feel after experiencing a miscarriage.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
What happens after miscarriage
There are a number of things you may need to consider after a miscarriage.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Miscarriage | SANDS - MISCARRIAGE STILLBIRTH NEWBORN DEATH SUPPORT
Helping you understand the complex range of emotions you may experience during fertility treatment or after miscarriage or early pregnancy loss
Read more on Sands Australia website
Miscarriage: a guide for men | Raising Children Network
This Dads Guide to Pregnancy covers miscarriage, the grief men might experience after miscarriage, and how to support partners after pregnancy loss.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
The Pink Elephants Support Network - Medical Options for Recurrent Miscarriage
In some cases, a medical reason for miscarriage or recurrent miscarriage can be found through testing
Read more on Pink Elephants Support Network website
New research on vitamin B3 and miscarriages
Pregnant women are being warned not to start taking vitamin B3 supplements, despite a recent study that suggests it might reduce the risk of miscarriages and birth defects.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy: miscarriage & stillbirth | Raising Children Network
Have you experienced a miscarriage or stillbirth? Find articles and videos about coping with the grief of losing a pregnancy or having a stillbirth.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
What does a miscarriage look like? Symptoms and seeking help
Miscarriage, or pregnancy loss, can look and feel different for each person. Common symptoms include bleeding and cramping.
It is important to note that bleeding is common during pregnancy — especially in early pregnancy. It does not necessarily mean that anything is wrong.
The only way to accurately identify a pregnancy loss is to test pregnancy hormone levels and have an ultrasound of the uterus.
Read on to learn more about what pregnancy loss can look and feel like.
According to a 2016 study, not all pregnancy losses involve bleeding. Overall, they do not follow a single pattern. This is why it is crucial to seek medical care for bleeding and any unusual symptoms during pregnancy.
Pregnancy loss during the first trimester may involve:
- heavy bleeding
- bleeding that starts light and gets heavier
- passing blood clots or tissue
- cramping, which may come in waves
- a gush of fluid from the vagina
If a person takes a pregnancy test after experiencing a pregnancy loss during the first trimester, the result may be negative, or the test may have a positive line that gets fainter.
Experiencing pregnancy loss later in the first trimester and beyond will involve passing more tissue.
Second-trimester pregnancy loss can also cause intense cramping and sometimes even contractions.
In addition to bleeding and cramping, some people may notice larger blood clots.
According to a 2019 meta-analysis, one-quarter of pregnant women experience bleeding during the first trimester. Another study from 2016 puts that percentage higher, at closer to 20–40%.
A large-scale 2010 study found that about 12% of pregnant women experienced pregnancy loss, and about two-thirds of that group reported bleeding during their pregnancy.
Some differences between bleeding due to a pregnancy loss and other types of bleeding during pregnancy include:
- Amount of blood: Heavy bleeding is more likely to signal a pregnancy loss.
- Bleeding pattern: Bleeding that gets progressively heavier may indicate a pregnancy loss.
- Pain: Cramping, especially when it occurs in a clear pattern, is more likely to signal a pregnancy loss.

- Passing tissue: Some — not all — people who experience a pregnancy loss pass large blood clots or tissue.
For people who do experience bleeding during a pregnancy loss, the duration tends to depend on how far the pregnancy has progressed.
Pregnancy losses that occur in the first weeks of pregnancy tend to cause bleeding that lasts a few days. Those that occur later may cause bleeding that lasts for as long as 4 weeks.
Sometimes, the bleeding stops and starts again. Over time, it should get lighter.
A very early pregnancy loss is sometimes called a chemical pregnancy. These pregnancies are lost shortly after the embryo implants, usually within a few days or weeks.
A chemical pregnancy may be detectable by a pregnancy test, but it would likely not be seen on an ultrasound.
In many cases, early pregnancy losses can happen before a person knows they are pregnant.
In fact, around 80% of early pregnancy losses occur in the first trimester, or in weeks 0–13. The end of these early pregnancies may be mistaken for a period because the symptoms are similar.
The end of these early pregnancies may be mistaken for a period because the symptoms are similar.
For example, both a period and an early pregnancy loss can involve bleeding and cramping. Pregnancy tissue that passes out of the vagina may look like typical blood clots that occur during a period.
It is possible that a person will not realize they have missed a period. Instead, they may mistake the symptoms of a pregnancy loss for those of a menstrual period.
Pregnancy losses and periods can both cause:
- vaginal bleeding
- passing blood clots or tissue
- abdominal pain
However, a pregnancy loss will often cause additional symptoms that set it apart from a period, especially if the pregnancy loss occurs several weeks into the pregnancy. These symptoms include:
- larger clots or pregnancy loss tissue
- more clots than typical periods
- lower abdominal cramping
- back pain
- passing a significant amount of clear or pinkish fluid
- sudden heavy bleeding, or heavier bleeding than a typical period
- longer bleeding
- sudden easing of some early pregnancy symptoms, such as nausea and breast tenderness
It is important to remember that bleeding during the first weeks of a pregnancy is not uncommon, and it is not always a sign of pregnancy loss or a problem with a pregnancy.
However, if a person experiences other symptoms of pregnancy loss, they should seek care from a doctor.
A “missed miscarriage” refers to a delay between the loss of the pregnancy and any bleeding or passing of tissue.
During a missed miscarriage, an embryo dies but does not leave the uterus for several weeks. In fact, a pregnant person may not realize the pregnancy has ended until an ultrasound finds no heartbeat.
When the embryo does leave the uterus, the blood, tissue, and clots may be dark brown. The tissue has had time to deteriorate, so bright red blood or heavy bleeding may not occur. The bleeding may last several days to several weeks.
A doctor may prescribe medication to help the person who has had the pregnancy loss bleed and pass the tissue. Surgery may also be necessary.
It is not possible for healthcare professionals to stop a pregnancy loss once it starts.
Call a doctor and schedule an appointment within 24 hours if any of the following occur:
- vaginal bleeding
- a fever
- intense pain or cramping
- bleeding that stops and starts again
- any other changes in the pattern of bleeding, even if a doctor has already addressed the cause
- bleeding that lasts for longer than 7 days, even if a doctor has already confirmed pregnancy loss
Pregnant people should receive emergency medical attention if they:
- experience heavy bleeding during the second trimester and cannot reach their doctor
- bleed heavily enough to soak through more than one pad per hour for more than 2 hours
- feel faint, lightheaded, or confused
- experience contractions, amniotic fluid leakage, the water breaking, or other signs of premature labor
Most pregnancy losses pass on their own.
In some cases, the fetus dies without causing any bleeding. When this happens, the person carrying the fetus may want to wait for the pregnancy to pass on its own or want it to be over as quickly as possible.
If a person wants to expedite a pregnancy loss, a doctor can supply medication that helps with passing the pregnancy at home. This approach is safest during early pregnancy.
A healthcare professional can also perform surgery to remove the remains of the embryo or fetus.
Sometimes a pregnancy loss is incomplete, leaving behind tissue that can lead to infection or other health problems. When this happens, a doctor may recommend medication or surgery.
Doctors used to advise couples to wait 1 month, or sometimes much longer, before trying to conceive again after a pregnancy loss.
However, research now shows that there is no medical justification for this recommendation. If a couple feels ready, it is safe to begin trying to conceive again right away.
A 2017 study indicates that fertility may even be slightly higher immediately following a pregnancy loss.
Sometimes, however, it takes a while for a menstruating person’s cycle to resume following a pregnancy loss.
This can make it difficult to time sexual intercourse for conception and to accurately date a pregnancy — especially if a person becomes pregnant before the first menstrual period after a pregnancy loss.
To improve accuracy, it can be helpful to:
- monitor basal body temperature
- use ovulation tests
- try other ways to predict fertility
Early pregnancy losses can sometimes result from chromosomal irregularities. This means that the developing embryo or fetus has an irregular number of chromosomes.
These irregularities usually occur at random, meaning they are unlikely to reoccur. In other words, experiencing one pregnancy loss does not increase the likelihood of experiencing another.
A 2017 study finds that 15. 7% of women with a previous pregnancy loss had another during the 2-year study period.
7% of women with a previous pregnancy loss had another during the 2-year study period.
Meanwhile, a 2016 study finds that women were more likely to become pregnant in the 3 months following a pregnancy loss.
Many people become pregnant again shortly after a pregnancy loss, and a smaller number experience multiple losses in a row.
The risk of repeat pregnancy losses increases with age, according to a 2019 study. The risk is also higher among people with a history of:
- preterm labor
- gestational diabetes
- stillbirth
- cesarean delivery
A 2017 study found that 15.7% of participants whose most recent pregnancy ended in a pregnancy loss went on to have a second pregnancy loss.
A 2018 study focused on women who had three or more pregnancy losses. This study found that 64.5% of those women had a live birth within 5 years. Some of these participants may have received fertility treatments.
Pregnancy loss is one of the less common causes of bleeding during pregnancy, especially when the bleeding occurs early on.
But bleeding in early pregnancy is not always a sign of pregnancy loss.
Some other signs of pregnancy loss include cramping and passing blood clots or tissue.
Only a healthcare professional can accurately identify a pregnancy loss. For this reason, it is important to consult a doctor or nurse midwife about any bleeding during pregnancy.
What does an early miscarriage look like?
Bleeding is common in the early weeks of pregnancy. That is why bleeding alone should not be seen as an indication of an early pregnancy loss.
In addition to bleeding, an early pregnancy loss may cause a person to experience:
- a gush of clear or pale pink fluid from the vagina
- passing blood clots or tissue
- a sudden decrease in pregnancy symptoms (such as nausea and morning sickness)
- a negative result on a pregnancy test, or a positive sign that is very faint
How do I know if I’m miscarrying?
The signs and symptoms of a pregnancy loss will remain largely the same, no matter the week. But the further along a person is, the greater the amount of tissue loss during the miscarriage.
But the further along a person is, the greater the amount of tissue loss during the miscarriage.
Symptoms of pregnancy loss include:
- sudden bleeding, sometimes heavy
- a gush of clear or pink fluid from the vagina
- mild to severe back pain and abdominal cramping
- contraction-like pain
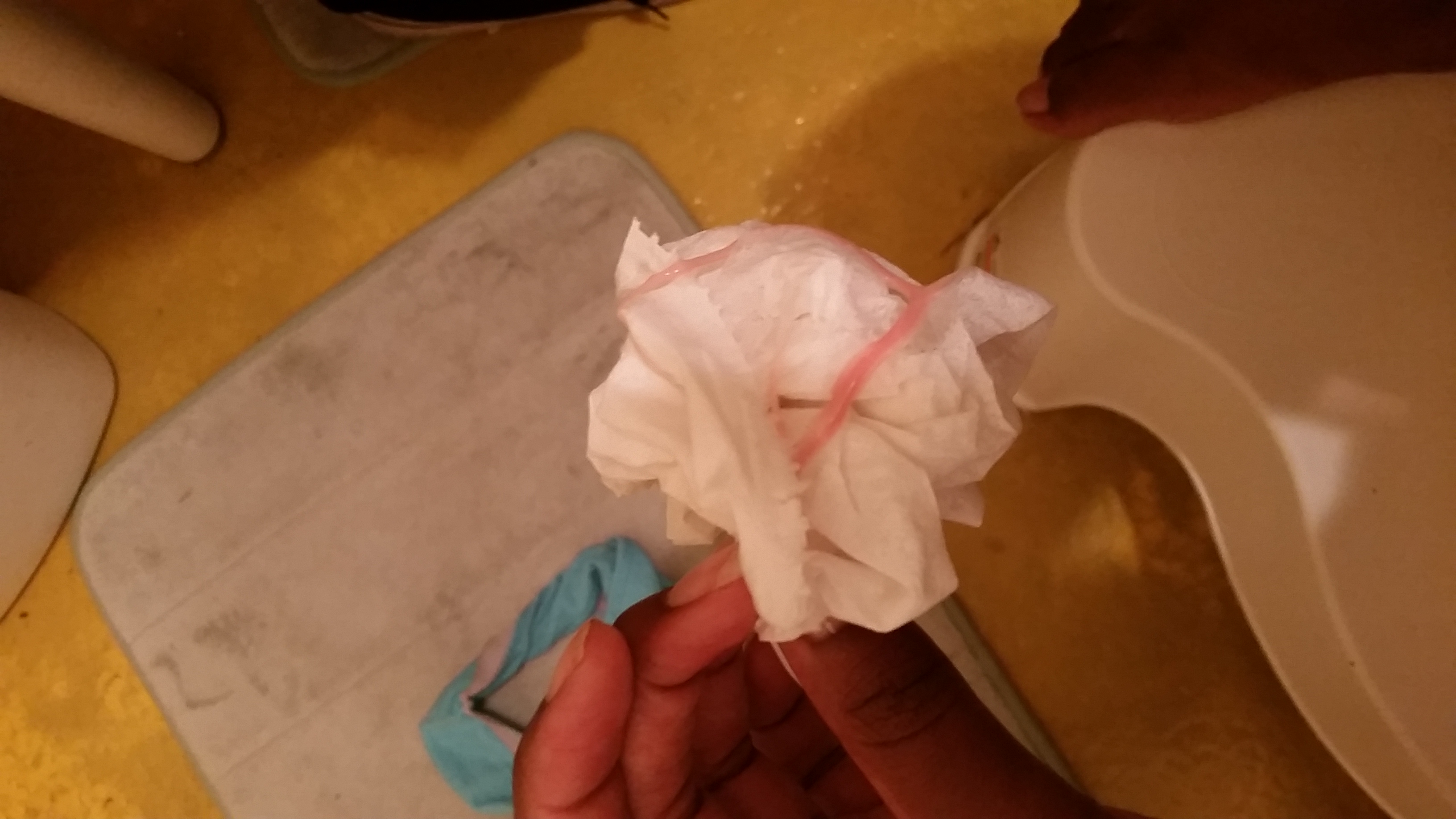
What does miscarriage tissue look like?
The clots and tissue passed during a pregnancy loss may look like typical period clots, or they may be larger.
Pregnancy loss tissue includes:
- the fetus or embryo
- gestational sac
- placenta
When a pregnancy is more advanced (after 6 to 8 weeks), the gestational sac may be noticeable. Before that, it may be too small to see.
The tissue passed during a pregnancy loss may be:
- brown
- black
- dark red
- bright red or pink
- white or gray, in some cases
If the pregnancy began to deteriorate before the start of bleeding, the clots may be smaller and darker. This is common with a missed miscarriage.
This is common with a missed miscarriage.
What does miscarriage tissue vs. a blood clot look like?
It is not always easy to tell the difference between pregnancy loss tissue and a blood clot. Both may look like typical period clots, though it is not uncommon for them to be larger than normal.
Actual pregnancy tissue may not be discernible until after the eighth week. Then, the tissue may look like pink, white, or gray tissue. A person may also be able to see a fluid-filled sac in the passed tissue.
Physiological changes in the body during pregnancy
From the very first days of pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes profound transformations. These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body. During pregnancy, many internal organs undergo significant restructuring. These changes are adaptive in nature, and, in most cases, are short-lived and completely disappear after childbirth. Consider the changes in the basic systems of the vital activity of a woman's body during pregnancy.
Consider the changes in the basic systems of the vital activity of a woman's body during pregnancy.
The respiratory system during pregnancy works hard. The respiratory rate increases. This is due to an increase in the need of the mother and fetus for oxygen, as well as in the limitation of the respiratory movements of the diaphragm due to an increase in the size of the uterus, which occupies a significant space of the abdominal cavity.
The mother's circulatory system during pregnancy has to pump more blood to ensure an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. In this regard, during pregnancy, the thickness and strength of the heart muscles increase, the pulse and the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute increase. In addition, the volume of circulating blood increases. In some cases, blood pressure increases. The tone of blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for increased supply of tissues with nutrients and oxygen. During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply. On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure.
During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply. On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure.
And changes in the blood system. During pregnancy, blood formation increases, the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, plasma and bcc increases. BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%. Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period.
Kidneys work hard during pregnancy. They secrete decay products of substances from the body of the mother and fetus (the waste products of the fetus pass through the placenta into the mother's blood).
Changes in the digestive system are represented by increased appetite (in most cases), cravings for salty and sour foods. In some cases, there is an aversion to certain foods or dishes that were well tolerated before the onset of pregnancy. Due to the increased tone of the vagus nerve, constipation may occur.
The most significant changes, however, occur in the genitals of pregnant women. These changes prepare the woman's reproductive system for childbirth and breastfeeding.
The uterus of a pregnant woman increases significantly in size. Its mass increases from 50 g - at the beginning of pregnancy to 1200 g - at the end of pregnancy. The volume of the uterine cavity by the end of pregnancy increases by more than 500 times! The blood supply to the uterus is greatly increased. In the walls of the uterus, the number of muscle fibers increases. The cervix is filled with thick mucus that clogs the cavity of the cervical canal. The fallopian tubes and ovaries also increase in size. In one of the ovaries, there is a "corpus luteum of pregnancy" - a place for the synthesis of hormones that support pregnancy. Walls vaginas will loosen and become more elastic. External genitalia (labia minor and major), also increase in size and become more elastic. The tissues of the perineum are loosened. In addition, there is an increase in mobility in the joints of the pelvis and a divergence of the pubic bones. The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth.
In the walls of the uterus, the number of muscle fibers increases. The cervix is filled with thick mucus that clogs the cavity of the cervical canal. The fallopian tubes and ovaries also increase in size. In one of the ovaries, there is a "corpus luteum of pregnancy" - a place for the synthesis of hormones that support pregnancy. Walls vaginas will loosen and become more elastic. External genitalia (labia minor and major), also increase in size and become more elastic. The tissues of the perineum are loosened. In addition, there is an increase in mobility in the joints of the pelvis and a divergence of the pubic bones. The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth.
Skin in the genital area and in the midline of the abdomen usually becomes darker in color. Sometimes "stretch marks" form on the skin of the lateral parts of the abdomen, which turn into whitish stripes after childbirth.
Sometimes "stretch marks" form on the skin of the lateral parts of the abdomen, which turn into whitish stripes after childbirth.
Mammary glands increase in size, become more elastic, tense. When pressing on the nipple, colostrum (first milk) is released.
Changes in the bone skeleton and muscular system . An increase in the concentration of the hormones relaxin and progesterone in the blood contributes to the leaching of calcium from the skeletal system. This helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the bones of the pelvis and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Also, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus.
It should be noted that calcium compounds are washed out of all bones of the maternal skeleton (including the bones of the foot and spine). As shown earlier, a woman's weight increases during pregnancy by 10 -12 kg. This additional load against the background of a decrease in bone stiffness can cause foot deformity and the development of flat feet. A shift in the center of gravity of the body of a pregnant woman due to an increase in the weight of the uterus can lead to a change in the curvature of the spine and the appearance of pain in the back and pelvic bones. Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women).
As shown earlier, a woman's weight increases during pregnancy by 10 -12 kg. This additional load against the background of a decrease in bone stiffness can cause foot deformity and the development of flat feet. A shift in the center of gravity of the body of a pregnant woman due to an increase in the weight of the uterus can lead to a change in the curvature of the spine and the appearance of pain in the back and pelvic bones. Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women).
Changes in the nervous system . In the first months of pregnancy and at the end of it, there is a decrease in the excitability of the cerebral cortex, which reaches its greatest degree by the time of the onset of childbirth. By the same period, the excitability of the receptors of the pregnant uterus increases. At the beginning of pregnancy, there is an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve, in connection with which various phenomena often occur: changes in taste and smell, nausea, increased salivation, etc.
In the first months of pregnancy and at the end of it, there is a decrease in the excitability of the cerebral cortex, which reaches its greatest degree by the time of the onset of childbirth. By the same period, the excitability of the receptors of the pregnant uterus increases. At the beginning of pregnancy, there is an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve, in connection with which various phenomena often occur: changes in taste and smell, nausea, increased salivation, etc.
Active endocrine glands there are significant changes that contribute to the proper course of pregnancy and childbirth. Changes in body weight. By the end of pregnancy, a woman's weight increases by about 10-12 kg. This value is distributed as follows: fetus, placenta, membranes and amniotic fluid - approximately 4.0 - 4.5 kg, uterus and mammary glands -1.0 kg, blood - 1.5 kg, intercellular (tissue) fluid - 1 kg , an increase in the mass of adipose tissue of the mother's body - 4 kg.
Diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles and diastasis of the womb. Solvable problems of pregnancy. Interview with Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor M.A. Chechnyova
— What is muscle diastasis and what is pubic diastasis?
— Pregnancy is an amazing and wonderful time, but it is also a period of additional loads, which undoubtedly becomes a test of strength for the female body.
The previously existing everyday point of view that pregnancy rejuvenates and gives strength is not confirmed by anything. During the bearing of a child, significant additional loads are placed on the mother's body, which often lead to the manifestation of problems that were invisible before pregnancy.
Diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles is a divergence of the inner edges of the muscles along the white line of the abdomen (connective tissue structure) at a distance of more than 27 mm. Pubic diastasis is one of the manifestations of pregnancy-associated pelvic girdle pain. This pathology affects the entire pelvic ring, sacroiliac joints and symphysis. And they certainly have common causes for the appearance.
This pathology affects the entire pelvic ring, sacroiliac joints and symphysis. And they certainly have common causes for the appearance.
The formation of such problems is facilitated by a decrease in the strength of collagen in the connective tissue. One of the reasons is an innate predisposition, the so-called connective tissue dysplasia, when the tissues are very elastic, extensible. During pregnancy, the body of a woman increases the production of the hormone relaxin, which reduces the synthesis of collagen and enhances its breakdown. This is provided by nature to create maximum elasticity of the birth canal. However, other structures, such as the anterior abdominal wall and the pubic symphysis, also fall under the action of relaxin.
— How does diastasis of the muscles and diastasis of the pubis affect pregnancy and childbirth?
— The divergence of the rectus abdominis muscles is observed in about 40% of pregnant women. During pregnancy, it does not give serious complications that threaten the life of the mother or the condition of the fetus. However, the inferiority of the work of the rectus abdominis muscles forces the redistribution of the load on the back muscles, which can lead to lumbar-pelvic pain and, accordingly, discomfort in the back. During childbirth, the abdominal muscles are involved in attempts, and the violation of their anatomy and function can affect the birth act.
However, the inferiority of the work of the rectus abdominis muscles forces the redistribution of the load on the back muscles, which can lead to lumbar-pelvic pain and, accordingly, discomfort in the back. During childbirth, the abdominal muscles are involved in attempts, and the violation of their anatomy and function can affect the birth act.
With diastasis of the pubis, things are more complicated. As already mentioned, this is only one of the manifestations of a violation of the structure and function of the pubic joint (symphysiopathy) during pregnancy. It occurs in about 50% of pregnant women in varying degrees of severity: in 25% of cases it leads to restriction of the mobility of the pregnant woman, in 8% - to severe disorders up to disability.
With symphysiopathy, the ligaments of the pubic articulation and cartilage that connect the pubic bones suffer. All this leads to severe pain in the pubic joint, pelvic bones, lower back, as well as to a violation of gait and the inability to stand up or lie down without outside help. Women with pelvic girdle pain syndrome experience significant levels of discomfort, disability, and depression, with associated social and economic problems. These include impaired sexual activity during pregnancy, chronic pain syndrome, risk of venous thromboembolism due to prolonged immobility, and even seeking early induction of labor or caesarean section to stop pain.
Women with pelvic girdle pain syndrome experience significant levels of discomfort, disability, and depression, with associated social and economic problems. These include impaired sexual activity during pregnancy, chronic pain syndrome, risk of venous thromboembolism due to prolonged immobility, and even seeking early induction of labor or caesarean section to stop pain.
During childbirth, such a patient may have a rupture of the pubic symphysis, may require surgery to restore it.
— How to prevent the development of muscle and pelvic diastasis during pregnancy and childbirth? What factors increase the likelihood of its development?
- There is no recipe that will be one hundred percent. There is a wonderful term in the medical literature called "lifestyle modification". Whatever diseases we study, be it symphysiopathy, diabetes mellitus or preeclampsia, the risk group for pathology is always overweight women. You need to prepare for pregnancy, you need to be in good physical shape. During pregnancy, weight gain should be monitored. The recommendation to "eat for two" is not just wrong, but extremely harmful. Pregnant women should maintain reasonable physical activity. Weak and flabby abdominal muscles, combined with the large size of the fetus, undoubtedly increase the risk of diastasis.
During pregnancy, weight gain should be monitored. The recommendation to "eat for two" is not just wrong, but extremely harmful. Pregnant women should maintain reasonable physical activity. Weak and flabby abdominal muscles, combined with the large size of the fetus, undoubtedly increase the risk of diastasis.
The risk factors for symphysiopathy in numerous studies are hard physical labor and previous injuries of the pelvic bones. Factors such as time elapsed from previous pregnancies, smoking, use of hormonal contraception, epidural anesthesia, mother's ethnicity, number of previous pregnancies, bone density, weight and gestational age of the fetus (post-term fetus) are not associated with an increased risk of symphysiopathy.
— How to diagnose diastasis recti and diastasis pubis?
— In most cases, diastasis rectus abdominis can be diagnosed clinically. It happens that inspection, palpation and simple measurements are enough.
In the standing position, you can see the divergence of the muscles when the woman does not have subcutaneous fat. In this case, diastasis is defined as a vertical defect between the rectus muscles.
In this case, diastasis is defined as a vertical defect between the rectus muscles.
With tension of the abdominal press, a longitudinal protrusion is observed in the diastasis zone. Such a protrusion is especially noticeable if the patient in the supine position is asked to raise her head and legs. If necessary, you can measure the width of the defect simply with a ruler.
Ultrasound may be the most accurate diagnostic method. With ultrasound, the inner edges of the rectus muscles are clearly visible and the distance between them at different levels can be measured.
Computed tomography is used in the diagnosis of diastasis extremely rarely, mainly in scientific research.
For the diagnosis of symphysiopathy and diastasis pubis there is no one test as a "gold standard".
The first place, of course, is the questioning and examination of the patient. We pay attention to the gait of the pregnant woman, to how she sits down, lies down and how she gets up. Symphysiopathy is characterized by a “duck gait”, when a pregnant woman rolls from foot to foot. On palpation in the area of the womb, pain and swelling are noted. The so-called pain provocative tests are used, for example, a mat-test (pulling up an imaginary rug, mat with your foot towards you).
Symphysiopathy is characterized by a “duck gait”, when a pregnant woman rolls from foot to foot. On palpation in the area of the womb, pain and swelling are noted. The so-called pain provocative tests are used, for example, a mat-test (pulling up an imaginary rug, mat with your foot towards you).
The following questionnaires are used to assess quality of life, pain and disability: Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQL), Oswestry Disability Index (ODI), Disability Rating Index (DRI), Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale (EPDS), Pregnancy Mobility Index (PMI), and Pelvic Ring Score (PGQ).
Of the instrumental methods, ultrasound is the most widely used, less often computed or magnetic resonance imaging. Ultrasound allows you to assess the condition of the ligaments of the pubic joint and the interpubic disc, the severity of the changes and the risk of natural childbirth.
— What is the treatment for diastasis recti or pubis?
— Primary prevention: when planning and during pregnancy, it is necessary to strengthen all muscle groups of the pelvic girdle, as well as the pelvic diaphragm.
More often, diastasis of the rectus muscles disappears on its own during the first months after childbirth. Special physical exercises to correct the work of muscles, to tone them and restore their basic functions should be performed under the guidance of a competent instructor. There are types of physical exercises that can, on the contrary, worsen the situation with diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles. In some cases, when there is no effect from physiotherapy exercises, it is necessary to resort to surgical correction of the defect. Currently, both endoscopic and open surgery are practiced. The choice of method depends on the size and localization of the defect.
In case of symphysiopathy, therapeutic exercises reduce back and pelvic pain. Acupuncture and wearing a pelvic bandage have a positive effect on symphysiopathy.
Initial treatment for pubic symphysis should be conservative even if symptoms are severe. Treatment includes bed rest and the use of a pelvic brace or corset that tightens the pelvis.