Nuchal folds test
Nuchal translucency test Information | Mount Sinai
Nuchal translucency screening; NT; Nuchal fold test; Nuchal fold scan; Prenatal genetic screening; Down syndrome - nuchal translucency
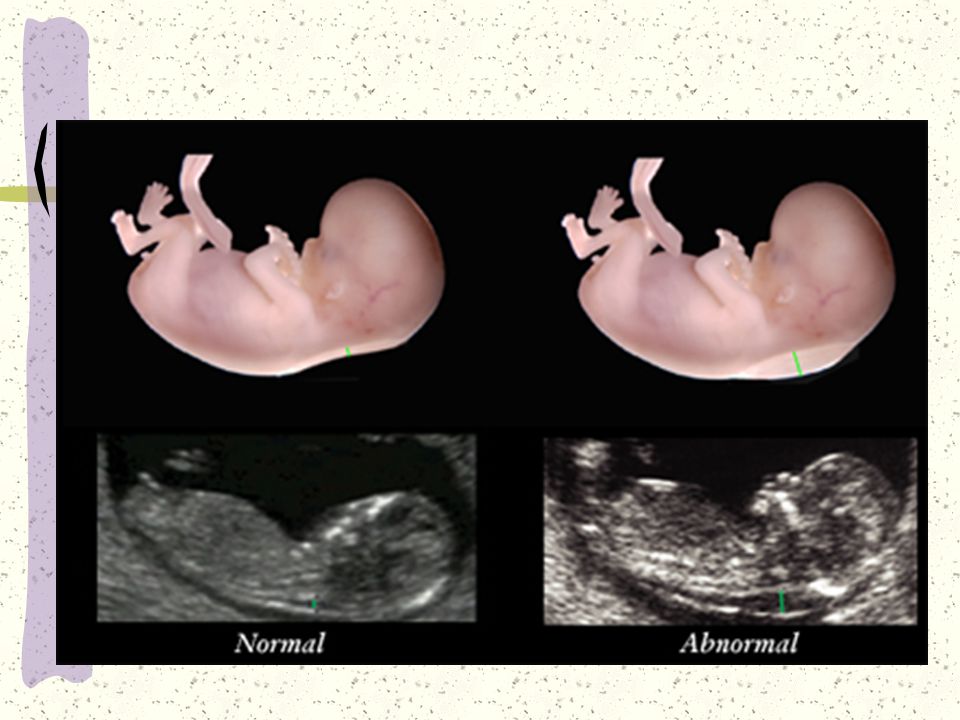
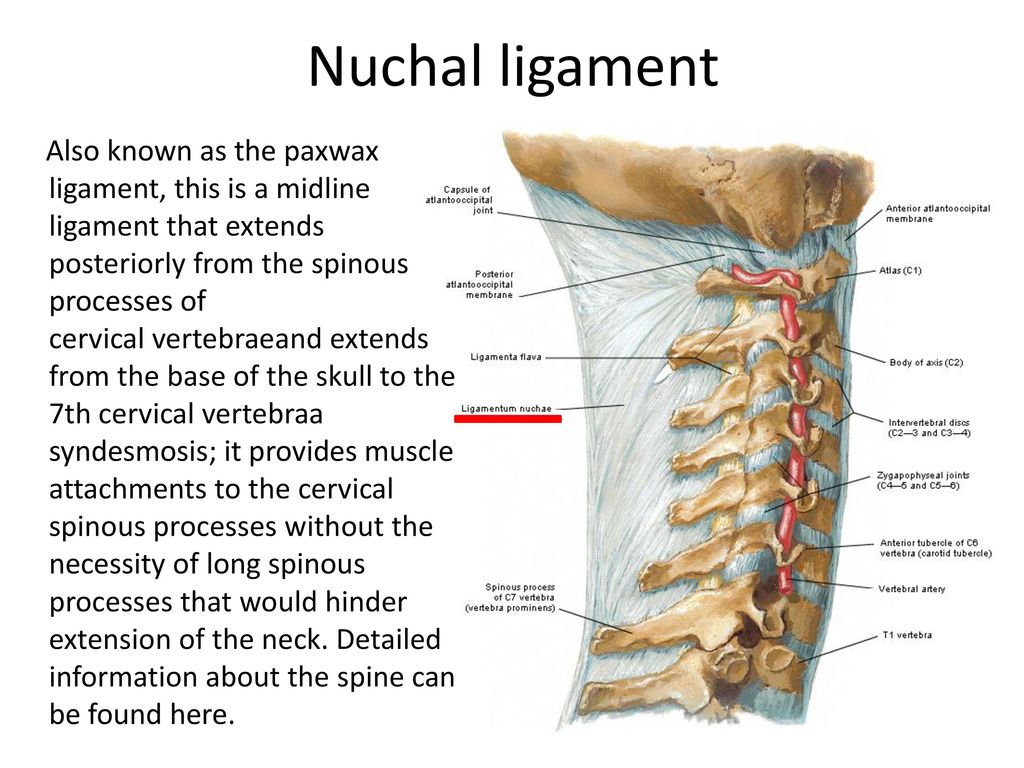
The nuchal translucency test measures the nuchal fold thickness. This is an area of tissue at the back of an unborn baby's neck. Measuring this thickness helps assess the risk for Down syndrome and other genetic problems in the baby.
How the Test is Performed
Your health care provider uses abdominal ultrasound (not vaginal) to measure the nuchal fold. All unborn babies have some fluid at the back of their neck. In a baby with Down syndrome or other genetic disorders, there is more fluid than normal. This makes the space look thicker.
A blood test of the mother is also done. Together, these two tests will tell if the baby could have Down syndrome or another genetic disorder.
How to Prepare for the Test
Having a full bladder will give the best ultrasound picture. You may be asked to drink 2 to 3 glasses of liquid an hour before the test. DO NOT urinate before your ultrasound.
How the Test will Feel
You may have some discomfort from pressure on your bladder during the ultrasound.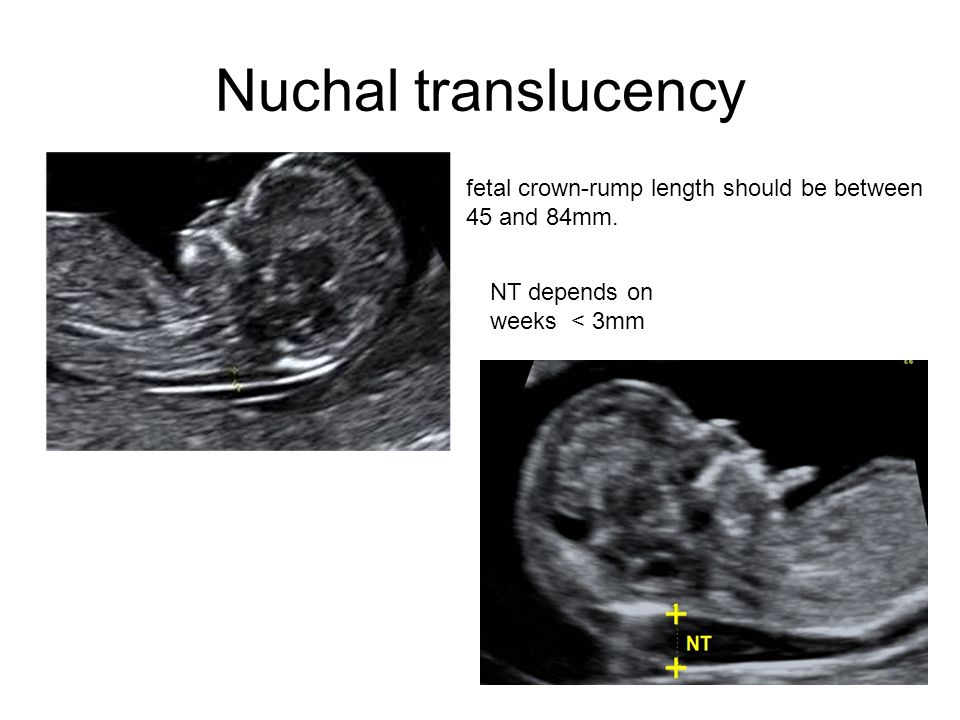 The gel used during the test may feel slightly cold and wet. You will not feel the ultrasound waves.
The gel used during the test may feel slightly cold and wet. You will not feel the ultrasound waves.
Why the Test is Performed
Your provider may advise this test to screen your baby for Down syndrome. Many pregnant women decide to have this test.
Nuchal translucency is usually done between the 11th and 14th week of pregnancy. It can be done earlier in pregnancy than amniocentesis. Amniocentesis is another test that checks for birth defects.
Normal Results
A normal amount of fluid in the back of the neck during ultrasound means it is very unlikely your baby has Down syndrome or another genetic disorder.
Nuchal translucency measurement increases with gestational age. This is the period between conception and birth. The higher the measurement compared to babies the same gestational age, the higher the risk is for certain genetic disorders.
The measurements below are considered low risk for genetic disorders:
- At 11 weeks -- up to 2 mm
- At 13 weeks, 6 days -- up to 2.8 mm
What Abnormal Results Mean
More fluid than normal in the back of the neck means there is a higher risk for Down syndrome, trisomy 18, trisomy 13, Turner syndrome, or congenital heart disease. But it does not tell for certain that the baby has Down syndrome or another genetic disorder.
If the result is abnormal, other tests can be done. Most of the time, the other test done is amniocentesis.
Risks
There are no known risks from ultrasound.
Driscoll DA, Simpson JL. Genetic screening and diagnosis. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 10.
Walsh JM, D'Alton ME. Nuchal translucency. In: Copel JA, D'Alton ME, Feltovich H, et al, eds. Obstetric Imaging: Fetal Diagnosis and Care. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 45.
2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 45.
Wapner RJ, Dugoff L. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital disorders. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 32.
Last reviewed on: 4/19/2022
Reviewed by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Nuchal Translucency Ultrasound Screening Test In 1st Trimester
Written by R. Morgan Griffin
Reviewed by Traci C. Johnson, MD on December 15, 2020
Who Gets the Test?
The first trimester screening is a safe, optional test for all pregnant women. It's a way of checking your baby's risk of certain birth defects, such as Down syndrome, Edward's syndrome (trisomy 18), trisomy 13, and many other chromosomal abnormalities, as well as heart problems.
Women carrying twins may be less likely to get the full first trimester screening. The results aren't as accurate as they are with single babies.
What the Test Does
The screening involves two steps. A blood test checks for levels of two substances -- pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) and human chorionic gonadotropin. A special ultrasound, called a nuchal translucency screening, measures the back of the baby's neck. At times, the nuchal translucency test may add on ultrasound markers, such as measuring a baby's nasal bone.
The combined result of the blood tests and the ultrasound gives you a sense of your baby's risk. However, it's not a diagnosis. Most women who have an abnormal first trimester screening go on to have healthy babies.
Whether you get this test is your choice. Some women want the test so they can prepare. Others don't. They may decide that knowing the results wouldn't change anything. Or they feel that the test could result in unnecessary stress and invasive testing.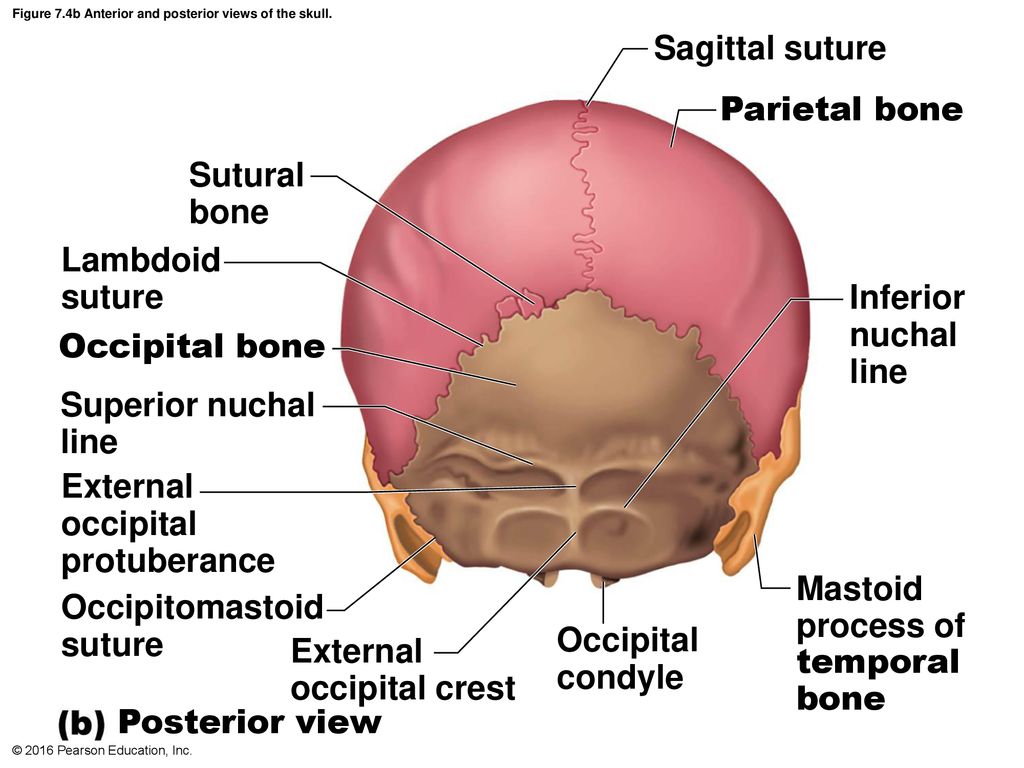 However knowing of possible risks would allow for increased monitoring during your pregnancy as well as giving you delivery options (special hospital, pediatric surgeon availability).
However knowing of possible risks would allow for increased monitoring during your pregnancy as well as giving you delivery options (special hospital, pediatric surgeon availability).
How the Test Is Done
The first trimester screen won't harm you or your baby. A technician will take a quick blood sample from your arm or fingertip. The nuchal translucency screening is a normal ultrasound. You'll lie on your back while a technician holds a probe against your belly. It will take between 20 to 40 minutes.
What to Know About Test Results
You should have the results in a few days. If your results are normal, your baby has a low risk of these birth defects. If they're abnormal, your doctor may suggest further tests to rule out problems. These could include ultrasounds or invasive procedures, like CVS or amniocentesis.
Try not to worry if your results are abnormal. Remember: This test can't diagnose birth defects. It only shows if your baby has a greater risk than average.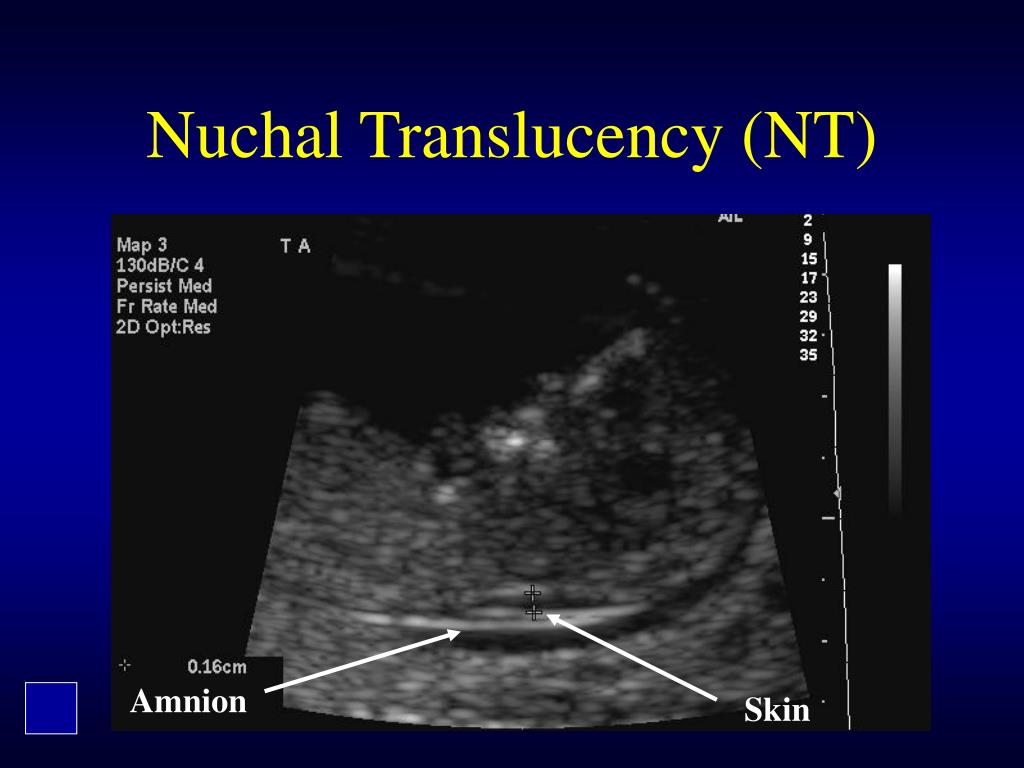
Sometimes your test results are combined with a second trimester screening. In that case, you may not get test results until your second trimester. Or you may get the results, and then get combined results after the second test.
How Often the Test Is Done During Your Pregnancy
You would get the first trimester screen once between the 11th and 13th week.
Other Names for This Test
Nuchal test, integrated screening
Tests Similar to This One
Triple screen, quad screen, MSAFP, sequential screening
Screening for the detection of congenital diseases of the fetus during pregnancy
Category: Reminders for the population .
Pregnancy screening is a whole range of studies that allows parents and doctors to get the most complete information about the health of an unborn baby. Screening reveals many congenital and physical characteristics. How and when is pregnancy screening done?
What is pregnancy screening and why is it done
Screening during pregnancy is a complex of examinations, which includes ultrasound and biochemical analysis of venous blood for hormones. As a rule, screening is carried out three times - in the first, second and third trimester.
As a rule, screening is carried out three times - in the first, second and third trimester.
Early detection of pathologies is very important. This makes it possible to start treating genetic diseases as early as possible and, if not completely cure them, then at least stop the symptoms as much as possible. If the doctor notices any abnormalities during the examination, the pregnancy is monitored especially carefully, which makes it possible to prevent the development of complications or premature birth. If the detected pathologies turn out to be too severe and incompatible with life, the doctor will refer the patient to terminate the pregnancy for medical reasons. nine0003
Pregnancy screening is harmless for both mother and baby. This is a fairly accurate study, although it should be clearly understood that it does not give a 100% guarantee. The accuracy of screening depends on many factors - the professionalism of the researchers, the woman's compliance with the rules for preparing for the examination, and other factors.
First pregnancy screening
The first screening during pregnancy is carried out between the 11th and 13th weeks. It makes no sense to undergo this examination earlier - before the 11th week of pregnancy, many indicators are practically indeterminate. nine0003
The study includes two medical tests - an ultrasound and a blood test.
ultrasound
With the help of ultrasound, the doctor determines the exact gestational age, evaluates the baby's physique, its dimensions (head circumference, limb length, height), the work of the heart muscle, the symmetry of the brain, the volume of amniotic fluid, the structure and size of the placenta, as well as the condition and tone of the uterus. For each of these parameters, there are normal indicators with which the doctor will compare the results. For an 11-13 week pregnancy, these rates are:
- KTP (coccygeal-parietal size, that is, the length of the fetus from the crown to the tailbone) is 43–65 mm.
 If this figure is more than normal, then the child will be large. A downward deviation indicates slow development (the reason for this state of affairs is often a hormonal imbalance or infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother), genetic pathologies or fetal death (in this case, the heart will not be auscultated). However, this may also be due to a banal mistake in determining the timing of pregnancy. nine0030
If this figure is more than normal, then the child will be large. A downward deviation indicates slow development (the reason for this state of affairs is often a hormonal imbalance or infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother), genetic pathologies or fetal death (in this case, the heart will not be auscultated). However, this may also be due to a banal mistake in determining the timing of pregnancy. nine0030 - BDP (biparietal size, that is, the distance from the temple to the temple) - 17-24 mm. A high BDP means a large fetus, but only on the condition that all other indicators say the same. Otherwise, we can talk about a herniated brain or hydrocephalus. Low BDP indicates slow brain development.
- TVP (collar space thickness) - 1.6–1.7 mm. Deviation from this norm (TVP above 3 mm) is considered a sign of some severe chromosomal pathologies - Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, etc. However, one should not panic ahead of time - no one will make such a serious diagnosis only on the basis of TVP.
 To confirm, you need to take a blood test for hormones and take a biopsy of the outer dense shell of the embryo for further research. nine0030
To confirm, you need to take a blood test for hormones and take a biopsy of the outer dense shell of the embryo for further research. nine0030
The length of the nasal bone is 2–4.2 mm. Too small a nose bone can indicate pathology or simply that the baby's nose will be snub-nosed. HR (heart rate) - 140-160 beats per minute. A small (up to 40 beats per minute) deviation in one direction or another is considered a variant of the norm.
The size of the chorion, amnion and yolk sac. The chorion is the outer shell of the fetus, which will eventually become the placenta. If it is located on the lower wall of the uterus, they speak of chorion previa. This is a potentially dangerous situation, fraught with miscarriage, and in this case, bed rest is recommended for the pregnant woman. nine0003
The amnion is the inner membrane that holds the amniotic fluid. The normal volume of amniotic fluid at 11–13 weeks is 50–100 ml.
The yolk sac is an embryonic organ that, in the first weeks of a fetus's life, plays the role of some internal organs that will be formed later.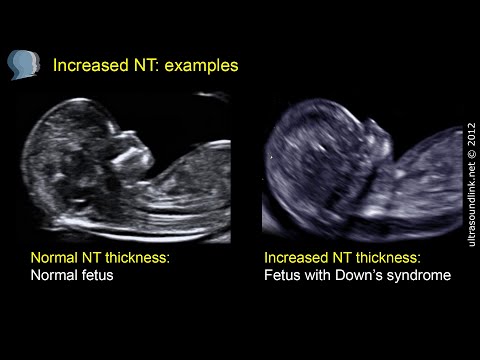 By the time of the first screening, the yolk sac should practically disappear (then the examination form will indicate “not visualized”). If its size is about 6 mm, then the fetus may have certain pathologies. nine0003
By the time of the first screening, the yolk sac should practically disappear (then the examination form will indicate “not visualized”). If its size is about 6 mm, then the fetus may have certain pathologies. nine0003
Cervix. Normally, its length by the time of the first screening is 35–40 mm. A shorter cervix means a risk of preterm labor.
Ultrasound is performed in two ways - transabdominal, in which the sensor of the ultrasound machine is located on the abdomen, and transvaginal, in which it is inserted into the vagina. Transvaginal ultrasound provides more complete and accurate information, but it is usually performed only in the first trimester. This method is usually used when examining overweight women, since the fat layer in the abdomen does not allow the fetus and uterus to be examined in detail. nine0003
It is necessary to properly prepare for an ultrasound. Before a transabdominal ultrasound, it is advised to drink about a liter of water so that the bladder is full at the time of the examination - then the uterus will shift slightly towards the abdomen and the picture will be clearer. With transvaginal ultrasound, the degree of fullness of the bladder does not matter, however, before the examination, it is better to go to the toilet - it will be more comfortable. Before the examination, you need to take a shower or freshen up with wet wipes. The accumulation of gases can distort the results of ultrasound, no matter what method it is carried out. Therefore, expectant mothers suffering from flatulence are advised the day before the examination to take remedies for flatulence and not eat anything that produces gas. nine0003
With transvaginal ultrasound, the degree of fullness of the bladder does not matter, however, before the examination, it is better to go to the toilet - it will be more comfortable. Before the examination, you need to take a shower or freshen up with wet wipes. The accumulation of gases can distort the results of ultrasound, no matter what method it is carried out. Therefore, expectant mothers suffering from flatulence are advised the day before the examination to take remedies for flatulence and not eat anything that produces gas. nine0003
Blood test
Biochemical screening, also called a dual test, is done to determine the level of two hormones (hence the name) - free b-hCG and PAPP-A.
- b-hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) begins to be produced from the first days of pregnancy. Its amount gradually increases until about the 9th week, and then begins to gradually decrease. On average, for a period of 11–13 weeks, 50,000–55,000 mIU / ml is considered the norm.
 An elevated level of hCG may indicate a multiple pregnancy, or, in the worst case, genetic pathologies of the fetus or the presence of diabetes in the mother. Reduced hCG is typical of miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, fetal death, or certain malformations (Patau syndrome and Edwards syndrome). nine0030
An elevated level of hCG may indicate a multiple pregnancy, or, in the worst case, genetic pathologies of the fetus or the presence of diabetes in the mother. Reduced hCG is typical of miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, fetal death, or certain malformations (Patau syndrome and Edwards syndrome). nine0030 - PAPP-A is an A-plasma protein. The content rate for a period of 11–13 weeks is 0.79–6.01 mU / l. Low PAPP-A is a sign of chromosomal pathologies such as Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome, fetal death and miscarriage, fetal malnutrition (underweight) and preeclampsia.
- A high PAPP-A is a sign of multiple pregnancies, large fetuses, or a low placenta.
In order for the blood test to give the most accurate information, it must be taken on an empty stomach, at least 8 hours after the last meal. 2-3 days before the analysis, you should refrain from fried, fatty, spicy, smoked foods, chocolate, nuts, seafood. It is also recommended not to have sexual intercourse.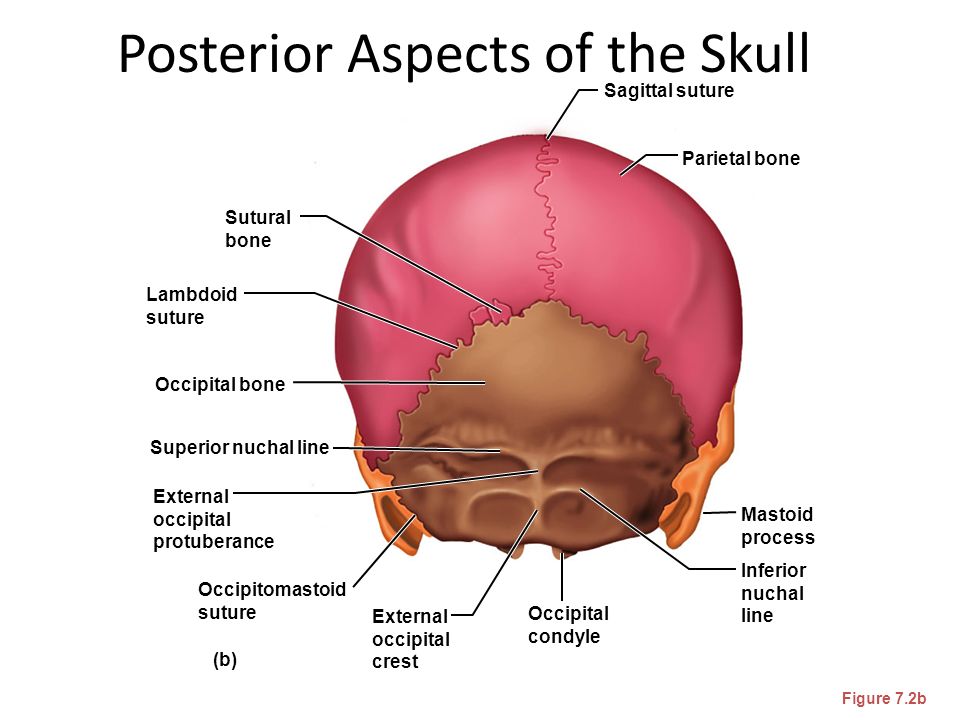 All this is not so significant, but it can affect the result in one way or another. nine0003
All this is not so significant, but it can affect the result in one way or another. nine0003
Second pregnancy screening
The second screening during pregnancy is carried out at 16-20 weeks. Like the first one, it consists of the same two stages - ultrasound and blood test.
ultrasound
This time, the doctor determines not only the size, but also the position of the fetus and its bone structure, the condition of the internal organs and the place of attachment of the umbilical cord, as well as the volume of amniotic fluid. Here are the approximate main indicators of the norm for a period of 16-20 weeks:
- BPR - 26–56 mm.
- DBK (length of the femur) - 13-38 mm.
- DPC (length of the humerus) - 13-36 mm.
- OG (head circumference) - 112-186 mm.
IAF (amniotic fluid index, that is, the volume of amniotic fluid) - 73-230 mm. Oligohydramnios can adversely affect the condition of the child's bone structure and the development of his nervous system.
Localization of the placenta. There is some risk only when the placenta is located on the anterior wall of the uterus - with such localization, detachment of the placenta is possible. nine0003
Umbilical cord. One of the most important parameters is the place of attachment of the umbilical cord. Marginal, split or sheath attachment is fraught with fetal hypoxia and difficulties during childbirth, often it becomes an indication for caesarean section. The umbilical cord is fed through 2 arteries and 1 vein, although sometimes only one artery is available. This can cause fetal hypoxia, heart disease, disorders in the child’s cardiovascular system, and cause a baby’s low body weight. However, if all other analyzes and examinations do not show deviations from the norm, you should not worry. nine0003
Cervix. The length of the cervix at this time should be 40–45 mm. A short cervix means a threatened miscarriage.
Visualization. Unsatisfactory visualization can be caused both by the peculiarities of the position of the fetus or the excess weight of the expectant mother, and by edema or hypertonicity of the uterus.
Blood test
As during the first screening, during the second, a blood test for b-hCG is taken, the level of free estriol and AFP is also checked. Here are the norms for their content at the 16th-20th weeks of pregnancy:
- b-hCG - 4.67-5-27 ng / ml.
- Free estriol is a hormone whose level can be used to judge the state of the placenta. The norm is 1.17–3.8 ng / ml. Elevated estriol is characteristic of multiple pregnancy or a large fetus. Reduced - for threatened miscarriage, placental insufficiency, anencephaly and Down's syndrome.
- AFP is a protein that is produced in the gastrointestinal tract of the fetus. Norm - 15-27 U / ml. A slightly lower AFP may mean that the gestational age was determined incorrectly (slightly underestimated). If the AFP is very low, the cause may be Edwards or Down syndrome, the threat of miscarriage or fetal death. High AFP is characteristic of neural tube pathologies, esophageal atresia, Meckel's syndrome.
 High AFP is also possible in women who have had an infectious disease during pregnancy. nine0030
High AFP is also possible in women who have had an infectious disease during pregnancy. nine0030
Third pregnancy screening
The third screening during pregnancy is carried out at the 30th-43rd week. Based on the results of this screening, the doctor decides on the need for a caesarean section or the possibility of a natural birth. The basis of the third screening is the same ultrasound. Sometimes dopplerography is prescribed - a study of the work of blood vessels. Here are the approximate norms for a given gestational age:
ultrasound
nine0028 The thickness of the placenta is 23.9–43.8. Too thin placenta is not a particularly dangerous deviation from the norm. The reason may be the miniature physique of a woman, her infectious diseases, hypertension. An excessively thick placenta is a sign of anemia, diabetes, Rh conflict. Such an indicator as the degree of maturity of the placenta is also taken into account - at a period of 30–35 weeks, the 1st degree of maturity is considered normal. With too rapid thickening and aging of the placenta, premature birth, fetal hypoxia and its slow development are possible. nine0003
An excessively thick placenta is a sign of anemia, diabetes, Rh conflict. Such an indicator as the degree of maturity of the placenta is also taken into account - at a period of 30–35 weeks, the 1st degree of maturity is considered normal. With too rapid thickening and aging of the placenta, premature birth, fetal hypoxia and its slow development are possible. nine0003
Prenatal screening is very important and should not be neglected. Timely detected pathologies and deviations from the norm can save the life and health of your child. This is worth remembering, especially for those parents who refuse to be examined out of fear of learning that the development of the baby is not going according to plan.
Collar space at 12 weeks: thickness, norm of fetal TVP
Girls, how much collar space do you have for a period of 12 weeks, as I understood everything up to 3 mm is the norm. This is the most important screening indicator! nine0003
Here's what they write on the Internet.
One of the most important parameters measured at the first scheduled ultrasound is the thickness of the collar space (or cervical fold), designated TVP . Evaluation of TVP is a fairly accurate (but by no means 100%!) method for the early diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and other fetal malformations.
nuchal space is a subcutaneous collection of fluid in the occipital region of the neck, which appears as an anechoic (black) band on ultrasound. Evaluation of TVP is informative at terms from 11 to 13 weeks, with a coccygeal-parietal size of 45-84 mm, since during the second trimester the accumulation of subcutaneous fluid resolves. nine0003
In addition, the thickness of the cervical fold during measurement can be affected by the position of the fetus - when the head is extended, it can increase by 0.6 mm, and if the chin is pressed to the chest, decrease by 0.4 mm. Therefore, two measurements, even taken on the same day, may give slightly different results.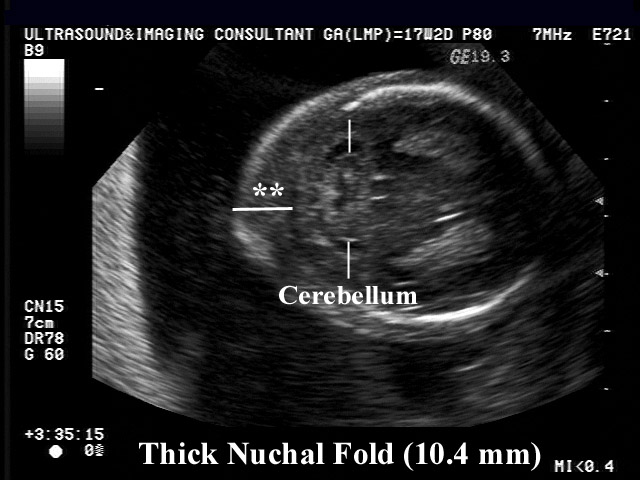 Correct measurement must be made with the head in neutral position.
Correct measurement must be made with the head in neutral position.
Normal thickness of the collar space is less than 3 mm. Its thickening does not indicate a pathology, but reveals a risk group among pregnant women, which should undergo additional examinations. First of all, it is necessary to assess the degree of risk, taking into account other "soft" signs of chromosomal abnormalities (the length of the nasal bone, hyperechoic focus in the heart, blood flow disturbances in the venous duct) and the age of the pregnant woman. Based on these data, a geneticist may recommend a chorionic villus biopsy or amniocentesis, performed already at the end of the first trimester, or a triple test at 16 weeks, and based on its results, decide on an invasive diagnosis. Early amniocentesis (before 15 weeks) can cause miscarriage, so it is performed only at a very high risk of genetic pathologies. However, this is the only accurate diagnostic method, unlike ultrasound and a triple test.