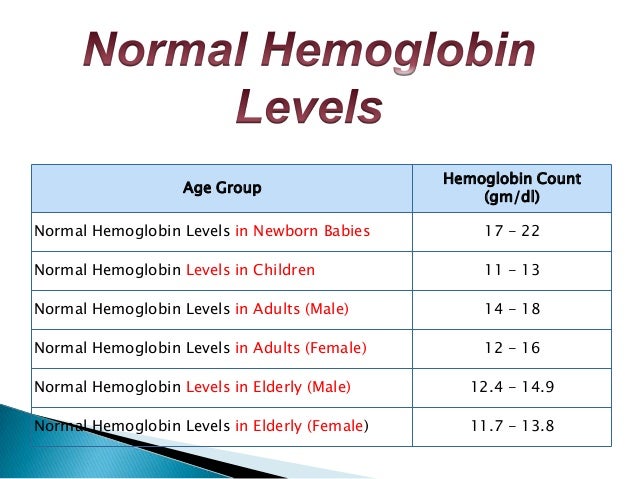
Normal pregnancy blood levels
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
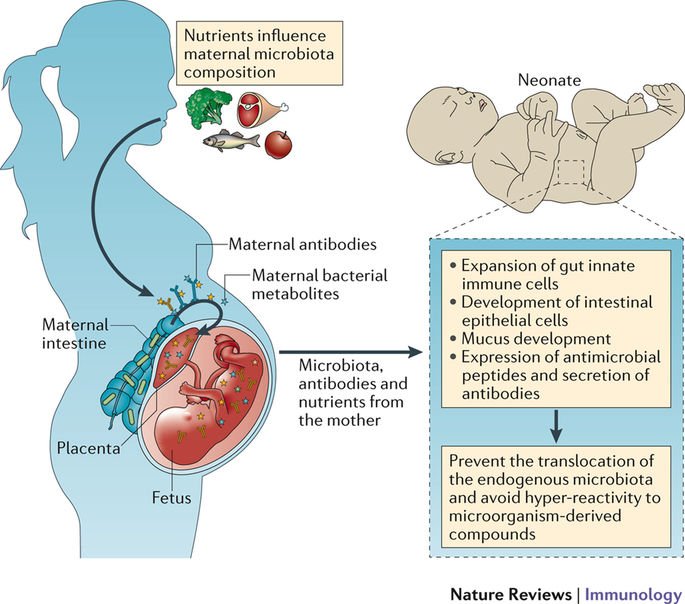
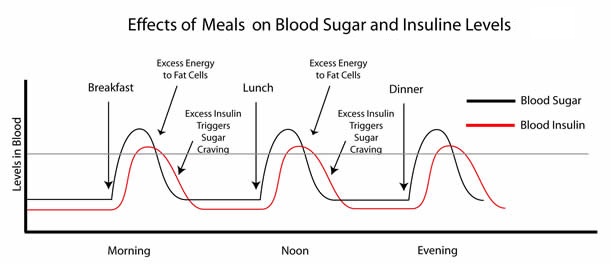
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone normally produced by the placenta. If you are pregnant, you can detect it in your urine. Blood tests measuring hCG levels can also be used to check how well your pregnancy is progressing.
Confirming pregnancy
After you conceive (when the sperm fertilises the egg), the developing placenta begins to produce and release hCG.
It takes about 2 weeks for your hCG levels to be high enough to be detected in your urine using a home pregnancy test.
A positive home test result is almost certainly correct, but a negative result is less reliable.
If you do a pregnancy test on the first day after your missed period, and it’s negative, wait about a week. If you still think you might be pregnant, do the test again or see your doctor.
hCG blood levels by week
If your doctor needs more information about your hCG levels, they may order a blood test. Low levels of hCG may be detected in your blood around 8 to 11 days after conception. hCG levels are highest towards the end of the first trimester, then gradually decline over the rest of your pregnancy.
The average levels of hCG in a pregnant woman’s blood are:
| 3 weeks | 6 – 70 IU/L |
| 4 weeks | 10 - 750 IU/L |
| 5 weeks | 200 - 7,100 IU/L |
| 6 weeks | 160 - 32,000 IU/L |
| 7 weeks | 3,700 - 160,000 IU/L |
| 8 weeks | 32,000 - 150,000 IU/L |
| 9 weeks | 64,000 - 150,000 IU/L |
| 10 weeks | 47,000 - 190,000 IU/L |
| 12 weeks | 28,000 - 210,000 IU/L |
| 14 weeks | 14,000 - 63,000 IU/L |
| 15 weeks | 12,000 - 71,000 IU/L |
| 16 weeks | 9,000 - 56,000 IU/L |
| 16 - 29 weeks (second trimester) | 1,400 - 53,000 IU/L |
| 29 - 41 weeks (third trimester) | 940 - 60,000 IU/L |
The amount of hCG in your blood can give some information about your pregnancy and the health of your baby.
- Higher than expected levels: you may have multiple pregnancies (for example, twins and triplets) or an abnormal growth in the uterus
- Your hCG levels are falling: you may be having a loss of pregnancy (miscarriage) or risk of miscarriage
- Levels that are rising more slowly than expected: you may have an ectopic pregnancy – where the fertilised egg implants in the fallopian tube
hCG levels and multiple pregnancies
One of the ways of diagnosing a multiple pregnancy is by your hCG levels. A high level may indicate you are carrying multiple babies, but it can also be caused by other factors. You will need an ultrasound to confirm that it’s twins or more.
Levels of hCG in your blood don’t provide a diagnosis of anything. They can only suggest that there are issues to look into.
If you have any concerns about your hCG levels, or wish to know more, speak to your doctor or maternity healthcare professional. You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436.
Sources:
UNSW Embryology (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin), Elsevier Patient Education (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin test), SydPath (hCG (human Chorionic Gonadotrophin), Pathology Tests Explained (Human chorionic gonadotropin), NSW Government Health Pathology (hCG factsheet)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: December 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Due date calculator
- Pregnancy tests
- Early signs of pregnancy
Need more information?
Human chorionic gonadotropin - Pathology Tests Explained
Why and when to get tested for hCG
Read more on Pathology Tests Explained website
Pregnancy testing - MyDr.
 com.au
com.au Pregnancy testing can be done from around the time that your period is due, and involves testing your urine for the pregnancy hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Read more on myDr website
Pregnancy tests
Find out how a home pregnancy test works.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy testing - Better Health Channel
Sometimes, a home pregnancy test may be positive when a woman isn’t pregnant.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Molar pregnancy
A molar pregnancy is a type of pregnancy where a baby does not develop. A molar pregnancy can be either complete or partial.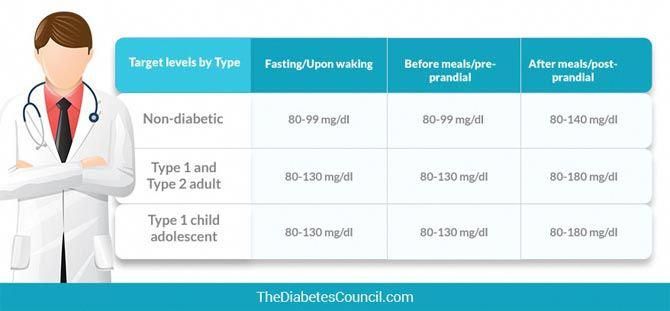
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Beta HCG Test | HealthEngine Blog
A Beta HCG (BHCG or Blood Pregnancy Test) May Be Performed by Your Doctor If They Suspect That You May Be Pregnant, or if You Suspect Pregnancy Yourself!
Read more on HealthEngine website
5 weeks pregnant: Changes for mum
Week 5 of pregnancy is probably when you’ll know that you’re pregnant because your period is missing. There are also subtle changes in your body which are symptoms of pregnancy such as changes to your breasts, and pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and pregnancy heartburn. These changes are caused by pregnancy hormones, like hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, produced by the placenta) which is the hormone detected by a pregnancy test.
Read more on Parenthub website
4 weeks pregnant: Key points
When you are 4 weeks pregnant your body and your new baby are undergoing rapid changes. The placenta forms and begins producing a hormone called human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), which is the substance a pregnancy test detects to confirm you are pregnant. The cells which are growing into your new baby establish membranes which connect them to the placenta and prepare themselves for differentiation into different types of cells, which will occur next week when you are 5 weeks pregnant. These developments may cause you to experience unusual emotions and also cause changes in your body such as darkening of the areolas of your nipples.
Read more on Parenthub website
Week by week pregnancy- 6 weeks pregnant
6 weeks pregnant is a time when embryo development is occurring rapidly and pregnant women often start experiencing pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness. Pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), the hormone a pregnancy test detects, is usually evident in the woman’s blood in the sixth week of pregnancy. Antenatal care should be provided at a doctor appointment for women who have not already checked their pregnancy health. Find out more about the pregnancy changes which occur this week.
Pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), the hormone a pregnancy test detects, is usually evident in the woman’s blood in the sixth week of pregnancy. Antenatal care should be provided at a doctor appointment for women who have not already checked their pregnancy health. Find out more about the pregnancy changes which occur this week.
Read more on Parenthub website
5 weeks pregnant: Key points
The fifth week of pregnancy begins around the time your menstrual bleeding is due and is a good time to take a pregnancy test to confirm that you are pregnant. You are also likely to begin experiencing pregnancy symptoms like fatigue, morning sickness and changes to your breasts this week. Your baby is still only about 1.5mm long but it is developing rapidly and taking on a more human form. If you have not already visited your doctor the 5th week of pregnancy is a good time to do so.
Read more on Parenthub website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.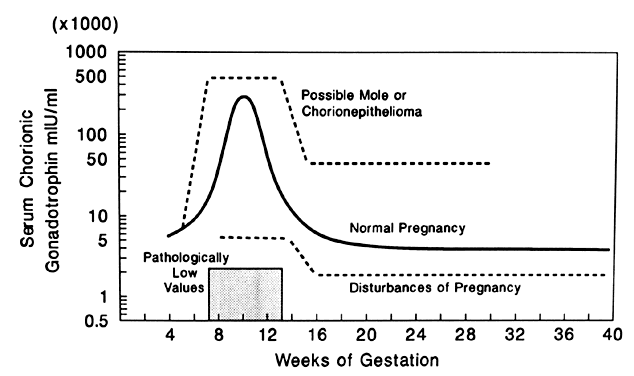
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
hCG Levels | The American Pregnancy Association
HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) is often called the pregnancy hormone because it is made by cells formed in the placenta, which nourishes the egg after it has been fertilized and becomes attached to the uterine wall. Levels can first be detected by a blood test about 11 days after conception and about 12-14 days after conception by a urine test.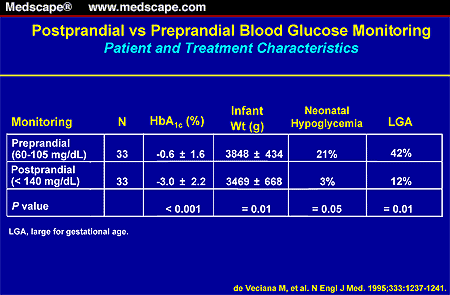
Typically, the hCG levels will double every 72 hours. The level will reach its peak in the first 8-11 weeks of pregnancy and then will decline and level off for the remainder of the pregnancy.
- As you get further along in pregnancy and the hCG level gets higher, the time it takes to double can increase to about every 96 hours.
- Caution must be used in making too much of hCG numbers. A normal pregnancy may have low hCG levels and result in a perfectly healthy baby. The results from an ultrasound after 5 -6 weeks gestation are much more accurate than using hCG numbers.
- An hCG level of less than 5 mIU/mL is considered negative for pregnancy, and anything above 25 mIU/mL is considered positive for pregnancy.
- An hCG level between 6 and 24 mIU/mL is considered a grey area, and you’ll likely need to be retested to see if your levels rise to confirm a pregnancy.
- The hCG hormone is measured in milli-international units per milliliter (mIU/mL).
- A transvaginal ultrasound should be able to show at least a gestational sac once the hCG levels have reached between 1,000 – 2,000 mIU/mL. Because levels can differentiate so much and conception dating can be wrong, a diagnosis should not be made by ultrasound findings until the hCG level has reached at least 2,000 mIU/mL.
- A single reading is not enough information for most diagnoses. When there is a question regarding the health of the pregnancy, multiple testings of hCG done a couple of days apart give a more accurate assessment of the situation.
- The hCG levels should not be used to date a pregnancy since these numbers can vary so widely.
- There are two common types of hCG tests. A qualitative test detects if hCG is present in the blood. A quantitative test (or beta) measures the amount of hCG actually present in the blood.
Guideline to hCG levels in weeks during pregnancy
* These numbers are just a guideline – every woman’s level of hCG can rise differently. It is not necessarily the level that matters, but rather the change in the level.
It is not necessarily the level that matters, but rather the change in the level.
What Does a Low hCG Level Mean?
A low hCG level can mean any number of things and should be rechecked within 48-72 hours to see how the level is changing. A low level can indicate:
- Miscalculation of pregnancy dating
- Possible miscarriage or blighted ovum
- Ectopic pregnancy
Is a High hCG Level a Bad Thing?
A high level of hCG can also mean a number of things and should be rechecked within 48-72 hours to evaluate changes in the level. A high level can indicate:
- Miscalculation of pregnancy dating
- Molar pregnancy
- Multiple pregnancies
Should I Check My hCG level Regularly?
It’s not common for doctors to routinely check your hCG levels unless you are showing signs of a potential problem.
A health care provider may recheck your levels if you are bleeding, experiencing severe cramping, or have a history of miscarriage.
What Can I Expect After a Pregnancy Loss?
Most women can expect their levels to return to a non-pregnant range about 4 – 6 weeks after a pregnancy loss has occurred.
This can differentiate by how the loss occurred (spontaneous miscarriage, D & C procedure, abortion, natural delivery) and how high the levels were at the time of the loss.
Healthcare providers usually will continue to test hCG levels after a pregnancy loss to ensure they return back to <5.0.
What Can Interfere With My hCG Levels?
If you get a positive test result, you are most likely pregnant. False positives are extremely rare. However, there are some conditions that may cause a false positive, such as certain types of cancer and early miscarriage. Some antibodies may also interfere with test results.
Medications that contain hCG may interfere with hCG levels, as well.
These medications are often used infertility treatments, and your health care provider should advise you on how they may affect a test.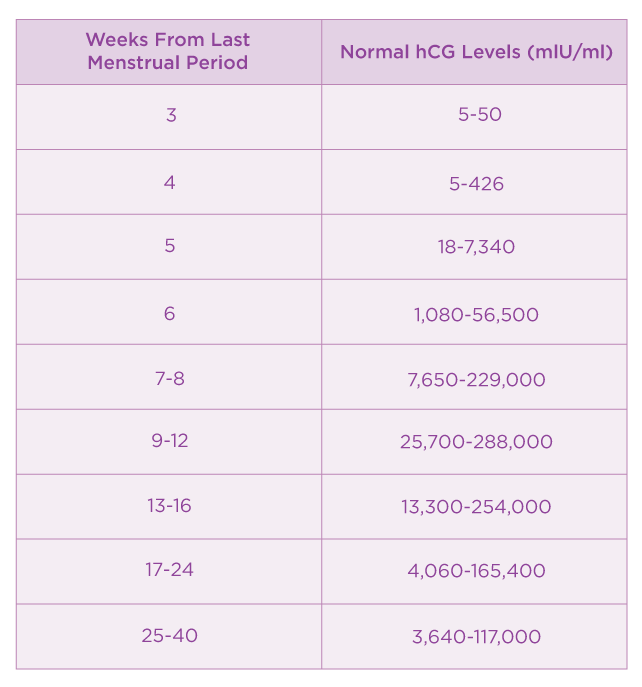
All other medications such as antibiotics, pain relievers, contraception or other hormone medications should not have any effect on a test that measures hCG.
Want to Know More?
- Pregnancy Calculator
- Calculating Gestation Age
- Concerns Regarding Early Fetal Development
Compiled using information from the following sources:
1. U.S. Food and Drug Administration
www.fda.gov
2. Bashir, I; Ihenetu, K; Miller, J.J.; Gim, M.; Lippmann, S. A Positive Pregnancy Test in the Post-Menopausal Psychiatric Patient — What to Think? Psychiatry (Edgemont). Feb. 2006.
Gestational diabetes in pregnancy - treatment and diagnosis of diabetes in pregnant women in Moscow, Clinical Hospital on Yauza
Consult a gynecologist
Service in two languages: Russian, English.
Leave your phone number and we will call you back.
Contents
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0006
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0006
Specialists of the Yauza Clinical Hospital diagnose and treat gestational diabetes and its complications. For a comfortable pregnancy and the safety of the expectant mother and baby, we exercise strict control over the blood sugar level of a pregnant woman, if necessary, prescribe a specially designed diet and medications.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
- About 7% of pregnant women have manifestations of gestational diabetes. In 50% of cases, the disease is asymptomatic
- Gestational diabetes in pregnancy significantly increases the risk of pregnancy complications for both mother and fetus
- Perinatal mortality increases by 2-3% with a combination of diabetes mellitus and pregnancy
Pregnancy diabetes (gestational diabetes) is an increase in blood glucose that first occurs during pregnancy but is not high enough to warrant a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. These are hidden disorders of carbohydrate metabolism that threaten to develop into diabetes mellitus. nine0006
These are hidden disorders of carbohydrate metabolism that threaten to develop into diabetes mellitus. nine0006
Pregnant blood glucose norm
During pregnancy, all women experience changes in insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance. This is fine. The difference between the norm and pathology in the degree of change.
Blood tests for diabetes during pregnancy - norm and pathology
- If the test of venous blood taken on an empty stomach shows a glucose level of more than 5.1 mmol / l, this is the norm for pregnant women.
nine0022 From 5.1 to 7.0 mmol / l - gestational diabetes. - If 7.0 mmol / l or more - diabetes mellitus.
- Testing capillary blood (taken from a fingerstick) for the diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus is not recommended.
- If during an oral glucose tolerance test (when 75 g of glucose is taken orally during the study) after an hour the glucose level is more than 10.
 0 mmol/l, and after two hours the blood glucose level is in the range of 7.8-8.5 mmol/l - then for pregnant women this is a normal indicator. nine0023
0 mmol/l, and after two hours the blood glucose level is in the range of 7.8-8.5 mmol/l - then for pregnant women this is a normal indicator. nine0023
To better understand what gestational diabetes, or diabetes in pregnancy, is, you need to talk a little about hormonal changes in the body in pregnant women.
Causes of gestational diabetes
Hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy are associated with increased production of large amounts of steroid hormones. Some of them, such as cortisol and progesterone, have a significant effect on cell receptors, increasing their resistance to insulin. nine0005 This leads to an increase in blood glucose levels and requires a significant increase in insulin production by the pancreas. In cases where the compensatory capacity of the pancreas is not enough, sugar metabolism gets out of control and a condition called gestational diabetes or gestational diabetes develops.
This condition occurs quite often. Between 3 and 10% of pregnant women develop pathological insulin resistance leading to gestational diabetes. nine0005 Unlike diabetes mellitus diagnosed before pregnancy, pathological insulin resistance that occurs during pregnancy does not cause fetal malformations and in most cases does not require insulin treatment. But, nevertheless, uncompensated gestational diabetes can significantly complicate the course of pregnancy.
nine0005 Unlike diabetes mellitus diagnosed before pregnancy, pathological insulin resistance that occurs during pregnancy does not cause fetal malformations and in most cases does not require insulin treatment. But, nevertheless, uncompensated gestational diabetes can significantly complicate the course of pregnancy.
Specialists of the Yauza Clinical Hospital diagnose, treat and prevent diabetes in pregnant women and its complications, such as impaired fetal growth. The doctors of the Clinical Hospital on the Yauza strictly control the blood sugar level of a pregnant woman, if necessary, prescribe a specially designed diet. This ensures a comfortable pregnancy and the safety of the expectant mother and baby. nine0006
Pregnancy diabetes - consequences for the child
Large disproportionate fruit. The most important and frequent complication of gestational diabetes is fetal growth failure. Developing in conditions of increased blood glucose levels, which penetrate the fetoplacental barrier, the fetus is forced to compensate for the increased sugar level with its own insulin.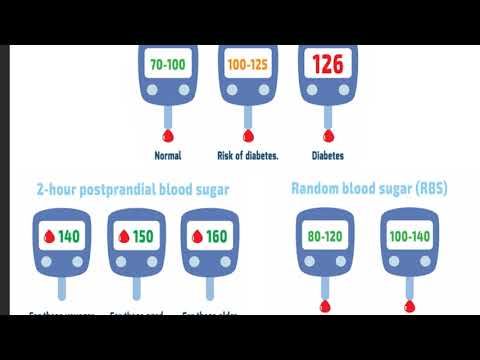 Due to the fact that the structure of insulin and growth hormone are very similar, high levels of insulin stimulate the growth of the fetus. The problem is that a large fetus develops. In such a fetus, body proportions differ from those of normally developing newborns, in which the volume of the head is larger than the volume of the shoulder girdle. In fetuses with uncompensated gestational diabetes, the size of the shoulder girdle predominates, and the size of the abdomen increases. This leads to the fact that during childbirth after the fetus's head passes through the birth canal, the shoulders can get stuck (shoulder dystocia) and the child, along with the mother, can be severely injured or die. nine0006
Due to the fact that the structure of insulin and growth hormone are very similar, high levels of insulin stimulate the growth of the fetus. The problem is that a large fetus develops. In such a fetus, body proportions differ from those of normally developing newborns, in which the volume of the head is larger than the volume of the shoulder girdle. In fetuses with uncompensated gestational diabetes, the size of the shoulder girdle predominates, and the size of the abdomen increases. This leads to the fact that during childbirth after the fetus's head passes through the birth canal, the shoulders can get stuck (shoulder dystocia) and the child, along with the mother, can be severely injured or die. nine0006
Polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios. In addition, in gestational diabetes, the balance of the amount of amniotic fluid can be disturbed and either polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios develops. This is a serious risk factor for intrauterine fetal death or premature birth.
Underdevelopment of the lungs. In gestational diabetes, the lungs of the fetus mature later, as the production of surfactant (a special lubrication of the inner walls of the alveoli, where oxygen is exchanged in the lungs) is disrupted. Therefore, premature birth in gestational diabetes is especially dangerous. nine0006
Hypoglycemia and metabolic disorders in the fetus. Due to the constant increased production of its own insulin during pregnancy, immediately after birth, the child is in a state of hypoglycemia with electrolyte imbalance, which threatens his life.
All this dictates the need for the earliest possible detection of gestational diabetes in pregnant women, the level of sugar in the blood of a pregnant woman and to prevent the development of complications.
. nine0006
Diagnosis of diabetes in pregnant women at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
Signs of diabetes in pregnant women
Gestational diabetes in pregnancy is not usually associated with the classic symptoms of diabetes, such as thirst or excessive urination (polyuria).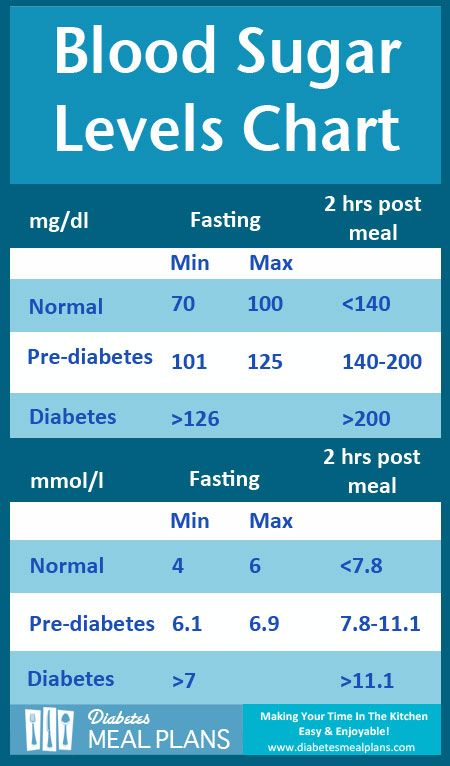
Pregnancy tests for diabetes mellitus
First phase. At the first visit of a pregnant woman to a doctor at any time, she is tested for glucose levels in venous blood - fasting glucose, regardless of food intake, glycated hemoglobin. This is the first phase of research to detect diabetes mellitus or gestational diabetes in pregnant women. If diabetes mellitus is detected, the patient is referred for observation and treatment to an endocrinologist. nine0006
Second phase. For a period of 24-28 weeks, all patients who did not show identified disorders of carbohydrate metabolism at the first study are called for a glucose tolerance test (PGTT) to detect "hidden diabetes". This is done because the occurrence of gestational diabetes is associated with the development of insulin resistance under the influence of hormones produced by the placenta. Therefore, in the vast majority of cases, gestational diabetes develops in the second half of pregnancy after 24 weeks, when there is a peak in the production of placental hormones.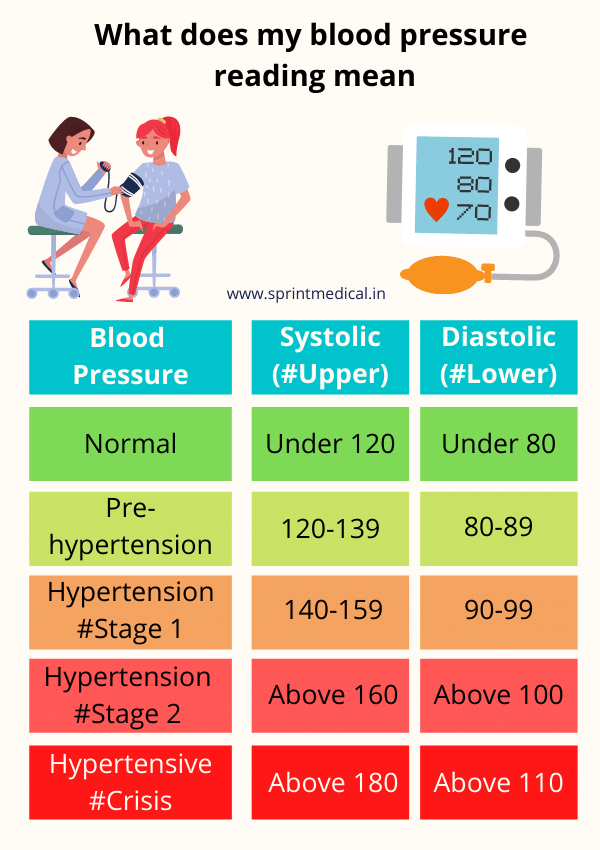 nine0006
nine0006
Glucose tolerance test
It is carried out to detect pathological insulin resistance, characteristic of latent diabetes in pregnant women. Pregnant women undergo a two-hour test, only in the laboratory.
During the 3 days leading up to the test, the woman should eat her usual diet, including carbohydrates (>150 g of carbohydrates per day), maintain her usual physical activity. The evening before testing, dinner should include 30-50 grams of carbohydrates. nine0005 On the day of the study, before the analysis, you should not smoke and take medications that can affect the level of glucose (vitamins, glucocorticoid hormones, iron preparations, which include carbohydrates, beta-agonists, beta-blockers). You can drink water.
Venous blood is taken on an empty stomach (after 8-14 hours of fasting, usually in the morning, before breakfast).
Then the patient takes a glucose solution (75 g).
And they take blood in an hour and two after the sugar load. Normally, the level of glucose in the blood after a sugar load should not exceed an hour later - 10 mmol / l, after 2 hours - 8.5 mmol / l. nine0005 If manifest diabetes mellitus is detected, the patient is referred to an endocrinologist, gestational diabetes mellitus is treated by an obstetrician-gynecologist or therapist.
Normally, the level of glucose in the blood after a sugar load should not exceed an hour later - 10 mmol / l, after 2 hours - 8.5 mmol / l. nine0005 If manifest diabetes mellitus is detected, the patient is referred to an endocrinologist, gestational diabetes mellitus is treated by an obstetrician-gynecologist or therapist.
Glucose tolerance test contraindications
- Strict bed rest for a pregnant woman (until doctor's approval).
- Pronounced toxicosis of pregnant women (with nausea and vomiting).
- Acute infectious or inflammatory disease. nine0023
- Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis.
- Dumping syndrome (syndrome of resected stomach).
Prenatal diabetes monitoring
Blood glucose monitoring, self-monitoring diary
When diagnosing gestational diabetes, it is necessary to establish strict control of sugar levels throughout the subsequent pregnancy and during childbirth. To do this, regularly examine the blood for sugar (glucose). In addition, the patient conducts self-monitoring using a glucometer. nine0006
In addition, the patient conducts self-monitoring using a glucometer. nine0006
It is recommended that a pregnant woman keep a diary of observations in which to record:
- blood glucose level (normal <5.1 mmol/l),
- the presence of ketone bodies in the urine, which is determined by test strips sold in a pharmacy (normally, ketone bodies are absent),
- blood pressure readings (normal <130|80 mmHg),
- fetal movements,
- body weight, nine0022 diet.
Expert ultrasound
Conducting an expert ultrasound examination reveals signs of intrauterine suffering of the fetus (diabetic fetopathy), polyhydramnios. Most often, this is a sign of chronically elevated blood glucose levels, penetrating into the blood of the fetus. This requires urgent correction of the diet and normalization of the level of glycemia (blood sugar). If necessary, insulin therapy.
Make an appointment nine0006
Treatment of gestational diabetes
Diet for gestational diabetes
In most cases, it is sufficient to follow a special diet recommended by a nutritionist based on the body mass index of the pregnant woman and her taste preferences. The effectiveness of diet therapy is determined by the maintenance of normal blood glucose levels. Diet in pregnancy diabetes recommends:
The effectiveness of diet therapy is determined by the maintenance of normal blood glucose levels. Diet in pregnancy diabetes recommends:
- Avoid simple carbohydrates - sweets, pastries, white bread, honey, sugar, jam, sweet drinks and fruits, ice cream. nine0023
- Limit complex carbohydrates - cereals (semolina, rice - exclude), potatoes, corn, legumes, durum wheat pasta. Distribute their intake evenly over several meals throughout the day to eliminate starvation (causes the formation of ketone bodies).
- Eat enough protein - meat, fish, seafood, poultry, mushrooms, eggs, hard cheese, dairy and sour-milk products of medium fat content (3-5%).
- It is necessary to enrich the diet with fiber and vitamins - greens, vegetables (except for boiled carrots and beets), sweet and sour berries (excluding grapes). nine0023
- Correctly choose fats, do not exceed their amount recommended by the doctor - vegetable oils (add to ready-made meals), nuts, seeds.
 Animal fats (butter, sausages) - limit.
Animal fats (butter, sausages) - limit. - When cooking, boil, stew, steam and bake dishes. Don't fry. Do not deep fry.
A detailed menu for a pregnant woman with gestational diabetes will be compiled by a doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of each particular woman. nine0005 It is not worth using table No. 9 in its pure form for pregnant women with diabetes mellitus due to a significant restriction of its calorie content.
In detail, what you can eat with diabetes in pregnant women will be told by the doctor at an in-person consultation.
Pharmacotherapy
In cases where the diet fails to achieve the desired control of the level of glycemia in the blood, there are signs of a negative effect on the fetus - they resort to prescribing drugs - insulin. In case of diabetes in pregnant women, antidiabetic drugs in tablets should not be used. Insulin therapy is prescribed by an endocrinologist. Pregnant women with diabetes who are on insulin therapy are jointly managed by an endocrinologist, an internist and an obstetrician-gynecologist. nine0006
nine0006
Physical activity
Patients are recommended regular physical activity - walking in the fresh air (at least 150 minutes per week), swimming.
Prenatal diabetes - childbirth
With a compensated course of gestational diabetes, normal development of the fetus and the condition of the woman, childbirth is carried out in time in a natural way. The question of early delivery, caesarean section may arise if there are relevant indications from the mother or fetus. nine0006
Specialists of the Yauza Clinical Hospital have included mandatory fetal development screenings and tests to diagnose sugar metabolism disorders in the pregnancy monitoring program. Recommendations are given on a special diet for women with manifestations of gestational diabetes. If necessary, strict glycemic control is carried out throughout pregnancy, ensuring its successful completion and the birth of a healthy child.
Make an appointment nine0006
Cost of services
Prices for services you can see in the price list or check by phone listed on the site.
Attention! Website prices may vary.
Please check the current cost with the administrators by phone.
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT. WE WORK WITHOUT DAYS OFF
Service in two languages: Russian, English.
Leave your phone number and we will call you back. nine0006
Advantages of the clinic
More appears during pregnancy in women who did not have diabetes before.
Outside of pregnancy, blood glucose levels up to and including 6.0 mmol/L are considered normal. But pregnant women are different. The level of sugar becomes lower, due to the costs of the developing fetus, a decrease in the formation of glucose in the liver and other processes. Therefore, the value of glucose in a pregnant woman on an empty stomach of 5.1 mmol / l and higher (but up to 7.0 mmol / l), even with a single determination, indicates gestational diabetes mellitus. nine0006
Above 7.0 mmol/l is manifest diabetes, which requires immediate contact with an endocrinologist and initiation of insulin therapy. Often this means that diabetes was before pregnancy, but was not detected.
Often this means that diabetes was before pregnancy, but was not detected.
Gestational diabetes is dangerous because it can cause a number of complications during pregnancy and childbirth, namely: stillbirth, miscarriage, high risk of obesity and the development of diabetes later. nine0006
For a woman, this condition is also unsafe: the risks of preeclampsia, the need for a caesarean section and the development of diabetes mellitus after childbirth increase.
Fortunately, all these consequences can be avoided if you consult a doctor and start treatment.
Gestational diabetes is usually asymptomatic, but can sometimes present with excessive fatigue, constant thirst, frequent urination, and blurred vision. All this can be attributed to stress and weather. Therefore, it is possible to accurately diagnose with the help of tests. nine0006
After the 6th week of pregnancy, blood glucose is tested from a vein.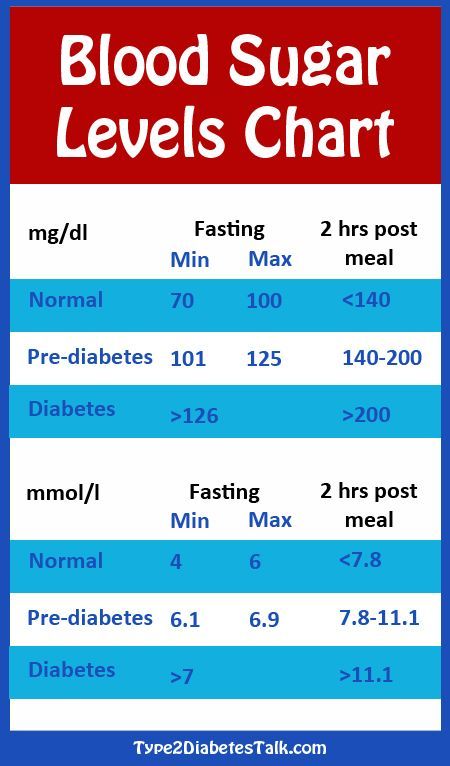 Normally, the result is up to 5.0 mmol / l inclusive. An increase in sugar to 5.1 mmol / l or more requires intervention - a consultation with an endocrinologist who will talk about the need to change diet, lifestyle, regular self-monitoring of blood sugar, in some cases, insulin treatment is prescribed.
Normally, the result is up to 5.0 mmol / l inclusive. An increase in sugar to 5.1 mmol / l or more requires intervention - a consultation with an endocrinologist who will talk about the need to change diet, lifestyle, regular self-monitoring of blood sugar, in some cases, insulin treatment is prescribed.
At 24-28 weeks, all pregnant women with normal blood glucose are given an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) to detect underlying disorders. OGTT is included in the list of examinations that are carried out as part of the MHI. nine0006
You can reduce your risk of gestational diabetes by making lifestyle changes. To do this, you need:
- have a BMI less than 25,
- switch to a healthy diet,
- 150 minutes of physical activity per week,
- stop smoking.
Our endocrinologists act within the framework of clinical recommendations, Russian and international, and do not prescribe unnecessary tests and drugs.