16 weeks pregnant contractions
Braxton Hicks contractions | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Braxton Hicks contractions | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
If you feel tightening or cramping in your abdomen during your pregnancy, you may be having Braxton Hicks contractions. This is normal and not a sign that you’re ready to give birth.
Braxton Hicks contractions are sometimes called ‘false’ or ‘practice’ contractions.
What are Braxton Hicks contractions?
Braxton Hicks contractions are a tightening in your abdomen that comes and goes. They are contractions of your uterus in preparation for giving birth. They tone the muscles in your uterus and may also help prepare the cervix for birth.
Braxton Hicks contractions don’t cause labour and aren’t a sign that labour is beginning.
If you’re not sure whether what you’re experiencing is Braxton Hicks contractions or actual labour, contact your doctor or midwife. They will be able to tell by doing a vaginal examination — if there are no signs that your cervix is changing, it is not labour.
What do they feel like?
Braxton Hicks contractions feel like muscles tightening across your belly, and if you put your hands on your belly when the contractions happen, you can probably feel your uterus becoming hard.
The contractions come irregularly and usually last for about 30 seconds. While they can be uncomfortable, they usually aren’t painful.
If the pain or discomfort of your contractions eases off, they’re probably Braxton Hicks contractions.
When do you get them?
Braxton Hicks contractions occur from early in your pregnancy but you may not feel them until the second trimester. If this is your first pregnancy, you might start to feel them from about 16 weeks. In later pregnancies, you may feel Braxton Hicks contractions more often, or earlier. Some women won’t feel them at all.
Some women won’t feel them at all.
In late pregnancy, you may experience Braxton Hicks contractions more often — perhaps as much as every 10 to 20 minutes. This is a sign that you are preparing for labour — known as prelabour.
How are Braxton Hicks contractions different from labour pain?
There are some differences between Braxton Hicks contractions and true labour contractions that will help your doctor or midwife decide whether you are in labour:
Braxton Hicks contractions:
- don’t result in your cervix thinning and opening
- usually last for about 30 seconds
- can be uncomfortable, but usually aren’t painful
- come and go at irregular times
- usually occur no more than once or twice an hour (until late in the pregnancy), a few times a day
- usually stop if you change position or activity or go for a walk
- usually go if you have a warm bath or shower
Real labour contractions:
- result in your cervix thinning and opening
- last 30 to 70 seconds
- become very regular
- get closer together
- last longer as time goes by
- get stronger or come more often when you walk
- get stronger over time
Should I call my doctor or midwife?
If you are less than 37 weeks pregnant, contractions can be a sign of premature labour. Contact your doctor or midwife immediately if:
Contact your doctor or midwife immediately if:
- you feel pain, pressure or discomfort in your pelvis, abdomen or lower back
- the contractions become stronger, closer together and more regular
- there is fluid leaking or gushing from your vagina
If you are full-term, you may choose to wait until a bit later in your labour, depending on what you have arranged with your doctor or midwife. If your waters break, or your contractions are strong and 5 minutes apart, it’s time to go to the hospital.
As any stage of pregnancy, you should contact your doctor or midwife immediately if you:
- you have persistent pain in your abdomen
- you have vaginal bleeding
- you notice your baby’s movements have slowed or stopped
- you feel very unwell
If you are in doubt, don’t hesitate to call your doctor or midwife for advice.
How can I ease the discomfort?
Braxton Hicks contractions are normal and don’t need treatment.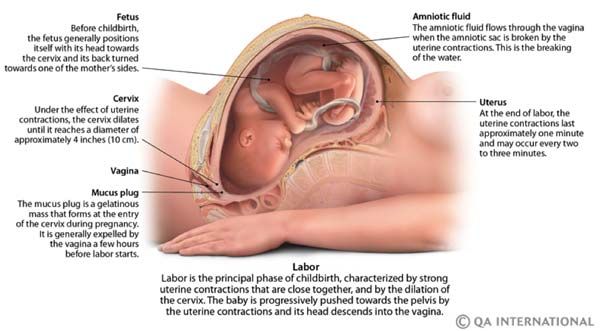 But if you feel uncomfortable, you can try:
But if you feel uncomfortable, you can try:
- lying down
- taking a walk
- relaxing in a warm bath
- having a massage
It may help to practise your breathing exercises during your Braxton Hicks contractions.
Sources:
Raising Children Network (23 weeks pregnant), RANZCOG (Labour and birth), Elsevier Patient Education (Braxton Hicks Contractions)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: October 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Giving birth - stages of labour
- Health professionals involved in your pregnancy
- Signs of premature labour
Need more information?
Pregnancy at week 22
By week 22, some parts of your baby’s body are fully formed, while some women experience Braxton Hicks contractions about now.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 35
You'll probably be having lots of Braxton Hicks contractions by now. It's your body's way of preparing for the birth. They should stop if you move position.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Giving birth - contractions
Contractions are when the muscles in your uterus tighten and then relax. They occur throughout the later stages of your pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
What happens to your body in childbirth
During childbirth, your body's hormones, ligaments and muscles, as well as the shape of your pelvis, all work together to bring your baby safely into the world.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Anatomy of pregnancy and birth - uterus
The uterus is your growing baby’s home during pregnancy. Learn how the uterus works, nurtures your baby and how it changes while you are pregnant.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Preterm labour - MyDr.com.au
Going into labour before your 37th week of pregnancy is called preterm labour, or premature labour. Find out what it means for you and your baby.
Read more on myDr website
38 weeks pregnant | Raising Children Network
38 weeks pregnant? In this pregnancy week by week guide, find out how your baby is growing, how your body is changing and how to look after yourself.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
26 weeks pregnant | Raising Children Network
26 weeks pregnant? In this pregnancy week by week guide, find out how your baby is growing, how your body is changing and how to look after yourself.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Giving birth - early signs of labour
You can know the early signs of labour, even if you cannot predict when your labour will begin. Find out also what to do if something appears to be wrong.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Anatomy of pregnancy and birth
From conception to giving birth, a woman's body goes through many physical changes. Learn what happens to your body during pregnancy and labour.
Learn what happens to your body during pregnancy and labour.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Braxton Hicks | What Do They Feel Like?
What do Braxton Hicks feel like?Named after Doctor John Braxton Hicks, who did extensive studies on them, Braxton Hicks contractions are the tightening and relaxing of your uterus during pregnancy. Braxton Hicks contractions aren't painful, but they maybe uncomfortable if you aren’t expecting them.
Braxton Hicks symptoms include mild, early contractions, when the womb contracts and tightens, and your bump may become a little harder to touch than normal. Some mums believe that Braxton Hicks is just your body’s way of practicing before the big day, but it’s important to remember that Braxton Hicks is not the onset of labour. Braxton Hicks are not harmful to you or your little one, so if you begin to feel these early contractions, the best thing to do is relax. Chances are they will pass quickly.
Are Braxton Hicks painful?For many women Braxton Hicks are uncomfortable rather than painful. As you near the end of your pregnancy, they might begin to feel a little more intense, especially if your baby is in the head-down position and pressing on your cervix. Some women don’t feel Braxton Hicks at all, but might notice their bump becoming very tight before it softens again. Each Braxton Hicks contraction should pass quite quickly, but they are very irregular. If you are in any doubt, call your midwife or maternity triage - don’t worry, they are there to help and would rather you and your little one were safe and happy in the knowledge that nothing is wrong.
If you are in any doubt, call your midwife or maternity triage - don’t worry, they are there to help and would rather you and your little one were safe and happy in the knowledge that nothing is wrong.
Not all women experience Braxton Hicks. For those that do, they may start to feel them around the halfway point of pregnancy, although they can be felt as early as 16 weeks. In fact, your body has been performing Braxton Hicks from as early as seven weeks into your pregnancy, but you will not have felt them this early. Most women who experience them feel them from around week 20, and as your due date nears, they will become a little more common.
What’s the difference between Braxton Hicks and contractions?An excellent question, and one that many midwives and doctors have had to explain to expectant mums. Whilst it’s easy to mistake Braxton Hicks contractions for going into labour, particularly if it is your first baby, or you’re not used to the symptoms, they are very different from the real deal. Towards the end of your pregnancy Braxton Hicks are often referred to as ‘false labour’. The following points outline some of the differences between Braxton Hicks and labour contractions:
Towards the end of your pregnancy Braxton Hicks are often referred to as ‘false labour’. The following points outline some of the differences between Braxton Hicks and labour contractions:
- Braxton Hicks are not painful, while labour contractions tend to be.
- Braxton Hicks occur randomly rather than regularly. Labour contractions last longer and become more and more regular the further along you are into labour.
- Labour contractions often come with other indicators, like water breaking or a show. For some women this can happen late in labour, but for others, their water might not break at all, and their baby is born in the sac. The show can occur during pregnancy, prior to labour starting. So it is possible for a woman to have a show and Braxton Hicks without labour starting. If you’re in any doubt get in touch with a midwife.
- Braxton Hicks tend to stay at the same level of intensity, whereas labour contractions become increasingly more painful as they develop.

- Labour contractions are often accompanied by lower back pain and/or cramping.
- Labour contractions can come with the onset of diarrhea and nausea, whereas Braxton Hicks tend not to.
Braxton Hicks contractions can vary in length, are typically infrequent and irregular.
How to relieve Braxton HicksFor many women it is simply a case of letting them run their course. But there are a few things you can do if Braxton Hicks are painful:
- Trying going for a pee. This can relieve some of the pressure around your uterus and can often stop Braxton Hicks.
- Drink some water. Dehydration is often a cause of Braxton Hicks.
- Try changing position. If you’ve been sitting in the same position for a while - and if you are heavily pregnant, this is more than likely - then a gentle walk can help relieve Braxton Hicks contractions.
- If you have been doing anything strenuous, then have a sit-down and a little rest.

- If all else fails, run yourself a nice warm bath. The warm water will help relax your muscles.
There is nothing the midwife can do about Braxton Hicks contractions, but if you are worried or concerned as to whether you are experiencing Braxton Hicks or labour, then you should definitely call your midwife or maternity triage. If nothing else, they will be able to put your mind at ease.
A mum’s view of Braxton Hicks"I didn't have Braxton Hicks contractions with my first baby, so experiencing them for the first time with my second one was a bit of a surprise. The main difference between Braxton Hicks and actual labour contractions is my labour pains started as a bit of a dull ache, and gradually got more and more painful. Braxton Hicks contractions have been a little sharper and come in much shorter waves than labour. Thankfully, they are also over much quicker than labour!" - Julia, soon-to-be mum of two.
Join the club
Ready to stop worrying about what other people think and do what feels right to you? We’ll give you the support you need to follow your instincts and enjoy parenthood to the max:
*Weaning is recommended at around 6 months. Please speak with a healthcare professional before introducing solid foods.
Join the club
Ready to stop worrying about what other people think and do what feels right to you? We’ll give you the support you need to follow your instincts and enjoy parenthood to the max:
Helpful emails
Non-judgemental support
Free weaning plan*
Tips from real parents
Join now
*Weaning is recommended at around 6 months. Please speak with a healthcare professional before introducing solid foods.
More from pregnancy
How to distinguish real contractions from training ones?
Shemyakina Natalya Nikolaevna, head of the obstetric department of the Leleka maternity hospital will help you figure it out.
Training contractions, or as they are also called, fake, or Braxton-Hicks contractions, are irregular contractions that do not have increasing intensity. The uterus may tone up, but normally, it should pass quickly.
For example, the tone appeared once in half an hour and the uterus relaxed rather quickly. Then the tone reappeared only after two hours and again passed. These are training contractions, they do not increase in intensity and do not become more frequent. nine0005
Training bouts are physiologically provided by our body. So the uterus is preparing to do the hard work in the process of childbirth. Normally, training contractions appear in terms of pregnancy close to childbirth - from the 37th week of pregnancy.
The appearance of training contractions in the early stages of pregnancy is not the norm
The uterus can tone up with an active lifestyle, physical activity, with a change in body position, but this tone should quickly pass. Normally, the uterus should not often come into tone. And even more so, contractions, as such, should not be until the 37th week of pregnancy. nine0015 Braxton Hicks contractions in the early stages are a threat of preterm labor. If a woman has contractions periodically during the day: after an hour, after 2, then again after an hour, (even if they are not regular), for periods up to 37 weeks, such a tone should alert the expectant mother.
And even more so, contractions, as such, should not be until the 37th week of pregnancy. nine0015 Braxton Hicks contractions in the early stages are a threat of preterm labor. If a woman has contractions periodically during the day: after an hour, after 2, then again after an hour, (even if they are not regular), for periods up to 37 weeks, such a tone should alert the expectant mother.
Because this is not the norm, but the threat of premature birth. This is an occasion to contact a specialist and change your rhythm of life, put on a bandage. The causes of premature birth are most often internal, caused by hormonal disorders and a violation of the physical health of a woman. But significant physical activity and stress can also cause premature birth. nine0005
Labor pains
Unlike training contractions, labor pains are regular. The uterus comes to tone first once every 15 minutes, and after a while - once every 7-10 minutes. Contractions gradually become more frequent, longer and stronger. And already occur every 5 minutes, then 3 and finally every 2 minutes.
And already occur every 5 minutes, then 3 and finally every 2 minutes.
True labor pains are contractions every 2 minutes, 40 seconds. If within an hour or two the contractions intensify - pains that begin in the lower abdomen or in the lower back and spread to the stomach - most likely, these are real labor pains. nine0005
Training contractions are NOT so much painful as unusual for a woman. When the expectant mother sees how the stomach comes into tone, its shape changes and it becomes dense, like an inflated ball. This might scare you a little. But a woman must understand that in real, labor pains, there must be a clear periodicity, intensification and acceleration over a certain period of time. Real fights never stop, but practice fights do. The uterus then comes to tone, then relaxes. nine0015 Often women confuse contractions with tone, which is caused by other physiological processes in the body. For example, increased intestinal peristalsis, intestinal infections, colic, etc.
What else should alert a woman?! If within an hour or two the uterus periodically comes into tone and mucous, bloody (streaked with blood or brown) discharge appears, then most likely there are structural changes in the cervix - it opens. Also an important sign to seek help is the discharge of the mucous plug long before childbirth. Her departure in terms of childbirth, a week or two before childbirth is normal. nine0005
Tracking labor pains
There are several methods for determining the types of contractions. A woman can do this herself, writing down the frequency and duration of contractions on paper or tracking them using special programs for a computer and phone. Or you can contact a doctor at antenatal clinic or at the maternity hospital, where a specialist will conduct fetal monitoring (fetal CTG). With the help of 2 sensors, the fetal heartbeat, uterine contractions are monitored and it is determined whether these are training contractions or labor. nine0005
nine0005
When should I go to the maternity hospital?
If within an hour or two there is an increase and intensification of pain, its intensity increases, the frequency of contractions is clear and regular, you can go to the maternity hospital. A woman can make a mistake, but it’s better to come and make sure for sure whether these are labor or training contractions.
If the amniotic fluid breaks, you can slowly pack up and go to the maternity hospital. Since, normally, after this labor activity should begin.
The main thing is that a woman should not panic. nine0025 The latent phase of labor can last 8-10 hours until the cervix is fully dilated. Labor activity does not proceed in 30 seconds. In the process of labor, the cervix of the uterus in women giving birth for the first time opens about 1 cm in an hour. She needs to open up to 10 cm, that is, a woman has about 10:00 by the time the baby is born.
Happy pregnancy and childbirth!
16 weeks pregnant - what's going on, fetal development, feeling, what the belly looks like
WHAT'S HAPPENING
At the 16th week of pregnancy, the length of the fetus will reach 11 - 11. 5 cm, and weight - 80 g. All life processes are actively going on in the body of a little man: the heart is working hard, the kidneys are regularly excreting urine, the development of the central nervous system continues. By the period of 15-16 weeks of pregnancy, the composition of the blood of the fetus has already taken shape: it, as it should be, consists of lymphocytes, erythrocytes and monocytes. It contains fetal (or "fetal") hemoglobin: it is needed for a better supply of oxygen to cells, and in a newborn its share is about 80 - 85% of the total. However, already at this time, “adult” hemoglobin also appears - within six months after the birth of a child, it will replace the fetal one. nine0005
5 cm, and weight - 80 g. All life processes are actively going on in the body of a little man: the heart is working hard, the kidneys are regularly excreting urine, the development of the central nervous system continues. By the period of 15-16 weeks of pregnancy, the composition of the blood of the fetus has already taken shape: it, as it should be, consists of lymphocytes, erythrocytes and monocytes. It contains fetal (or "fetal") hemoglobin: it is needed for a better supply of oxygen to cells, and in a newborn its share is about 80 - 85% of the total. However, already at this time, “adult” hemoglobin also appears - within six months after the birth of a child, it will replace the fetal one. nine0005
By the 16th week of pregnancy, the baby's muscles have already grown strong enough, he has learned to hold his head evenly and turn it from side to side, move his fingers and legs. Your baby is very active: he smiles, frowns, yawns, swallows, spits, sucks his thumb and even tries to play with what he finds nearby: he grabs the umbilical cord, touches his arms and legs. And if there is more than one baby in the mother's belly, the children communicate with each other.
And if there is more than one baby in the mother's belly, the children communicate with each other.
YOUR FEELING
During the 15-16th week of pregnancy, the uterus grows and stretches the muscles and ligaments in the lower abdomen, due to which you may feel slight pain. Now the uterus has grown so much that it is already palpable: to do this, empty your bladder, lie on your back and relax. Now try using your fingertips to carefully examine the area in the middle of the abdomen just above the pelvic bone. The protruding zone is your unborn child. If all else fails and you do not find the uterus, ask your doctor to teach you how to do it right. nine0005
At the 16th week of pregnancy, due to squeezing the intestines, problems with going to the toilet "in a big way" may appear. If it were only about discomfort, it would not be so scary, but prolonged constipation can increase the risk of miscarriage. Therefore, it is necessary to reconsider your diet and include in it products that have a laxative effect. To prevent problems with peristalsis at the 15th - 16th week of pregnancy, it is advisable to perform simple physical exercises daily and take a walk in the fresh air, it is also a good idea to visit the pool. nine0005
To prevent problems with peristalsis at the 15th - 16th week of pregnancy, it is advisable to perform simple physical exercises daily and take a walk in the fresh air, it is also a good idea to visit the pool. nine0005
Your breasts continue to grow, the areolas become even larger and darker. The hormonal surge is over, and your appetite has increased. However, we must try not to overeat and constantly control body weight. Normal weekly weight gain varies from 300 to 500 g.
And at the stage of 15 - 16 weeks of pregnancy, your temperature may rise by 1 - 2 degrees. Do not worry: the body "overheats" due to intense work, and with the help of increased sweating and a feeling of heat, the body cools itself. The amount of vaginal discharge may also increase. Increased secretion is a kind of preparation of the genital tract for childbirth. nine0005
In general, the 16th week of pregnancy is a period when the emotional state of a woman normalizes and energy returns to her. There is a thirst for vigorous activity: I want to start repairs, large-scale shopping or even moving. But the expectant mother should be careful not to lift weights and not overwork, because this can adversely affect the health of her baby.
There is a thirst for vigorous activity: I want to start repairs, large-scale shopping or even moving. But the expectant mother should be careful not to lift weights and not overwork, because this can adversely affect the health of her baby.
RISK FACTORS
If pregnancy develops without pathologies and complications, there should not be any special unpleasant sensations at this time. With prolonged physical exertion, you may experience pain in the lower back or legs, but in no case in the lower abdomen. nine0005
At the 16th week of pregnancy, the risk of developing iron deficiency anemia increases. This is due to an increase in the volume of circulating blood and a decrease in the number of red blood cells in it. To compensate for the lack of iron, the gynecologist may prescribe medications containing this element. Also, in the blood of the expectant mother, when the period has reached 16 weeks of pregnancy, a lack of calcium and magnesium is often found, which is fraught with the appearance of cramps in the legs (most often at night). In this situation, special magnesium preparations will help, and to fill the daily need for calcium, it is enough to eat a little cottage cheese every day and drink a glass of kefir or milk. nine0005
In this situation, special magnesium preparations will help, and to fill the daily need for calcium, it is enough to eat a little cottage cheese every day and drink a glass of kefir or milk. nine0005
Allocations for a period of 16 weeks of pregnancy are white or yellowish, practically do not smell. When they cause itching, have a pungent odor and turn green, these may be symptoms of a genital infection that must be treated. And if the discharge turns brown, pink or red, this is a cause for serious concern. In combination with cramping pains, a feeling of tightness in the lower back and a “petrified” abdomen, they can be a sign of uterine hypertonicity. Take a supine position and immediately call an ambulance. nine0005
MEDICAL SUPERVISION
At the 16th week of pregnancy, in addition to a complete blood and urine test, you may have to donate blood for a coagulogram (to determine its clotting), free estriol, AFP and hCG. In diseases such as Down's syndrome, craniocerebral hernia and anencephaly, the level of these substances will deviate from the norm.
Usually, an ultrasound scan is not done at 16 weeks of gestation, but if it is prescribed, the expectant mother will be able to observe on the monitor not only the movements of her baby, but also his facial expressions. This time, using a conventional ultrasound machine, you can also determine the sex of the child, unless, of course, your baby turns to the right side. nine0005
In some cases, an amniocentesis is prescribed at the 16th week of pregnancy. For this study, the amniotic membrane is punctured and a small amount of amniotic fluid is removed with a needle. A diagnostic test allows you to determine with almost absolute certainty whether the fetus has this or that pathology. With this study, several hundred genetic defects can be identified. But this procedure is not safe: according to statistics, in one case in a thousand, infection occurs, and the risk of miscarriage as a result of amniocentesis is approximately 0.5 - 1%. Therefore, without extreme necessity, it is better not to do a puncture of the amniotic membrane at the 15th - 16th week of pregnancy. nine0005
nine0005
RECOMMENDATIONS
- For the 16th week of pregnancy, the recommendations remain the same. Now it is important for you to monitor weight gain. And in order to avoid obesity, it is necessary to exclude “fast” carbohydrates from the diet (buns, cakes, chocolate, sweets). Extra pounds can lead to complications and negatively affect the process of childbirth. When you are already 16 weeks pregnant, eat right: do not give up breakfast, choose nuts, fruits, biscuits, natural sugar-free yoghurts as snacks. And at night you can drink herbal tea with honey or a glass of kefir; nine0091
- Some pregnant women are interested in the question of whether it is possible to visit a bath or sauna for a period of 15 - 16 weeks of pregnancy. You should not do this: like a hot bath or shower, bath procedures can harm the child, because if your body temperature rises even for a few minutes, great damage will be done to the baby's body.
Pregnancy: 4 months
Child nutritionVitamins and minerals during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Putting order in our knowledge about what vitamins and minerals and in what quantity are necessary for the health of the child, and what foods contain them.
What is the use of sports during the period of expectation of a baby and which sport to choose?
Pregnancy and childbirthWork during pregnancy
How to work during pregnancy? What benefits and guarantees does the expectant mother have? nine0005 Pregnancy and childbirth
Sex during pregnancy
Is it possible to have sex during pregnancy, what should be taken into account, what positions to choose?
Pregnancy and childbirthTests and examinations during pregnancy
Pregnancy and childbirthEating Right During Pregnancy
How to create a healthy diet for a pregnant woman, what vitamins should be present in the diet, how much liquid should be drunk, what drinks to prefer and what to avoid, what foods are considered harmful for pregnant women and how to keep weight under control while staying in a good mood.