Mucus in stool and pregnant
Mucus In Stool During Pregnancy? Should you be worried? Is it Normal? Reasons
Pregnancy brings about various physiological changes in the body. There are some common problems faced by pregnant women like nausea, vomiting, fatigue, changes in dietary preference, etc. which are caused due to the widespread changes going on in the body. However, sometimes pregnant women may face some uncommon symptoms which may put them to worry. Presence of mucus is one such condition that most pregnant women do not know of and hence, it is necessary to be more aware of it.
Book an appointment online to consult with Dr. Ritambhra Bhalla for gynecological issues.
What causes mucus in stool?
Mostly, mucus in stool is caused due to some digestive problems. Common causes of mucus in stool in pregnant women are:
- Hormonal changes can result in the presence of mucus in stool.
Since during pregnancy, there are high hormonal fluctuations taking place in the body, there is an increased chance of finding mucus in stool.
- The increase in the size of the uterus during pregnancy disrupts the intestine which may also lead to excretion of mucus.
- Dehydration can also lead to mucus in stool.
- Infection in the stomach or other parts of the digestive tract may also result in mucus.
- Food allergies can also result in mucus excretion.
Must Read: How To Tackle Backaches During Pregnancy
- Many doctors recommend various vitamin supplements to women before or during pregnancy. This can also cause mucus in stool, especially if the vitamins have an excess of iron or calcium.
Is it normal?
Though rather uncommon, it is completely okay to find some mucus in your stool during pregnancy. Especially during the first trimester, when the body is undergoing a lot of changes, there is an increased risk of mucus excretion which is completely normal. Also, if your doctor prescribes supplements, there is an increased chance of finding mucus in stool and is nothing to worry about.
Especially during the first trimester, when the body is undergoing a lot of changes, there is an increased risk of mucus excretion which is completely normal. Also, if your doctor prescribes supplements, there is an increased chance of finding mucus in stool and is nothing to worry about.
Want to consult a doctor? Book Online Consultation with Doctor, consult the best Gynecologist in India
Join our Cloudnine Community to discuss further regarding - Pregnancy Daily Care, Pregnancy Nutrition, Pregnancy Fitness, Nutrition.
Prevention:
There are certain guidelines which can help in reducing the risk of mucus excretion during pregnancy like:
- Staying hydrated helps in prevention of mucus and various other health problems during pregnancy.
 Drink plenty of water during pregnancy, and if needed, use hydration salts too.
Drink plenty of water during pregnancy, and if needed, use hydration salts too. - Performing light exercises which are suitable for pregnant women (with the prior recommendation of your doctor) can also help.
- Maintaining a healthy diet is also important, not just for mucus prevention but for a healthier pregnancy in general.
To know more About Uterine rupture during pregnancy
When to see a doctor?
Mostly the presence of mucus in stool is not a cause of worry. However, if you notice additional symptoms like the presence of blood along with the presence of mucus, it is highly advisable to contact your health provider.
Moreover, if you have extreme abdominal pain or haemorrhoids, it is also advisable to contact a maternity doctor. Additionally, excretion of very high quantities of mucus or persistent presence of mucus in the stool should also be not taken lightly.
Good news, now you can shop right away from wide range of products on Cloudnine Momeaze.
Watch Video on Do's and Don'ts of Pregnancy
Cloudnine is one of the leading maternity and childcare hospitals in the country. When it comes to pregnancy and maternity, we are renowned for providing world-class facilities and care. Our specialists are extremely qualified and experienced and are dedicated to providing you with the best possible treatment and care.
Do you have questions in your mind like How Many Weeks Pregnant Am I? Check out Cloudnine's Pregnancy Due Date Calculator now!
Our customers had a few questions regarding this blog, check them out now!
Stomach upset during pregnancy?
Constipation during pregnancy?
Have Similar Questions?
Get answers from our Experts, browse through hundreds of Q&A, attend live sessions, and much more
Ask your question!
Want to consult the best gynecologists in India? Please find the links below.
- Best Gynecologists in Bangalore
- Best Gynecologists in Chennai
- Best Gynecologists in Mumbai
- Best Gynecologists in Pune
- Best Gynecologists in Chandigarh
- Best Gynecologists in Gurgaon
- Best Gynecologists in Noida
Want to consult the best Maternity Packages in India? Please find the links below.
- Best Maternity Packages in Bangalore
- Best Maternity Packages in Chennai
- Best Maternity Packages in Mumbai
- Best Maternity Packages in Pune
- Best Maternity Packages in Chandigarh
- Best Maternity packages in Gurgaon
- Best Maternity Packages in Noida
Mucus In Stool During Pregnancy: Causes And Treatment
It should not cause worry unless there is pain, blood, or discomfort in passing stool.
Research-backed
MomJunction believes in providing reliable, research-backed information to you. As per our strong editorial policy requirements, we base our health articles on references (citations) taken from authority sites, international journals, and research studies. However, if you find any incongruencies, feel free to write to us.
Image: iStock
Excess mucus in stool during pregnancy may occur due to gastrointestinal issues or pregnancy-related factors, such as hormonal changes. Gastric mucus is produced in the stomach and helps in the motility of the digested food in the gastrointestinal tract. We excrete some mucus in stools usually. However, pregnancy may increase the amount of mucus excreted, making it more noticeable (1).
Excess mucus due to underlying issues is treatable. Read this post to learn the various causes and treatment options for excess mucus in stool during pregnancy.
Is It Normal To Have Mucus In Stool During Pregnancy?
You may sometimes pass mucus in the stool due to multiple gastrointestinal issues (2) (3). We pass a small amount of mucus in the stool, which is generally unnoticeable. Pregnant women may pass excess mucus in their stool during the first trimester.
We pass a small amount of mucus in the stool, which is generally unnoticeable. Pregnant women may pass excess mucus in their stool during the first trimester.
The appearance of mucus in stool is due to the rapid changes in your body during the gestational period. Safety measures and precautions may be taken if there is an excess of mucus secretion or followed by pain and bleeding. You may consult a doctor to help determine the cause of the condition.
Related: Bleeding During Pregnancy: Causes, Diagnosis And Treatment
What Causes Mucus in Stool During Pregnancy?
Some possible causes of secretion of excess mucus in stool during pregnancy are (3) (4) (5) (6):
- Dehydration: Hydration is for a healthy gut and mind. During pregnancy, water intake is crucial for the mother and her fetus. Dehydration might be one of the prime factors for the excretion of mucus in the stool.
Related: 12 Signs Of Dehydration During Pregnancy And Ways To Avoid It
- Irritatable bowel syndrome: Change in routine, stress, and infection may cause irritable bowel syndrome.
 The symptoms may include mucus in stool, abdominal pain, and alternating diarrhea and constipation.
The symptoms may include mucus in stool, abdominal pain, and alternating diarrhea and constipation. - Hormonal change: Various hormonal changes occur in your body during the gestational period. Some pregnancy-specific hormones may directly or indirectly regulate the mucus secretion in the stool during pregnancy.
- Infection in the stomach: Bacterial or viral infection in the gastrointestinal tract may result in excess mucus secretion in the stool. Intestinal parasites such as tapeworms, hookworms, amoeba, and pinworms could be the reasons.
Some symptoms of stomach infection that may accompany the secretion of mucus in the stool are diarrhea, cramping, vomiting, nausea, and fever - Food allergies: Lactose intolerance and specific food allergies may also result in mucus secretion in the stool.
- Intestine blockage: The fetus might be pushing against the intestine wall, resulting in blocked intestine and constipation.
 The body might be oversecreting mucus in the stool to ease constipation.
The body might be oversecreting mucus in the stool to ease constipation. - Medications or vitamins: Prenatal intake of vitamins fortified with iron or calcium during pregnancy may be associated with excess mucus excretion in stool.
- Hemorrhoids: Piles or hemorrhoids are swollen veins around the anus usually accompanied by constipation during pregnancy. During pregnancy, hemorrhoids may occur due to constipation and pressure from the growing baby.
- Other gastrointestinal conditions: These include Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, colon polyps, and diverticulitis.
Related: Crohn's Disease And Pregnancy: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
What Are The Treatment Options And Ways To Prevent Mucus In Stool?
Identifying the cause behind mucus secretion is essential for the treatment. Some treatments options available for reducing mucus in the stool during pregnancy are (7) (8) (9 ):
- Stay hydrated: Taking plenty of water during pregnancy may help reduce dehydration-induced constipation.
 It can also avoid the accumulation of various toxins in the body. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends drinking around 8 to 12 cups (64 to 96 ounces) of water every day. Excess fluids, including more fresh juices in your diet, are beneficial. Water also helps absorb water-soluble vitamins (vitamins B and C) from the diet into the body.
It can also avoid the accumulation of various toxins in the body. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends drinking around 8 to 12 cups (64 to 96 ounces) of water every day. Excess fluids, including more fresh juices in your diet, are beneficial. Water also helps absorb water-soluble vitamins (vitamins B and C) from the diet into the body. - Take a healthy diet: A healthy and balanced diet rich in green leafy vegetables and fiber supplements can help reduce constipation during pregnancy.
- Change medication: If you have mucus secretion in the stool followed by vitamin intake, you may consult your physician. It might be possible to change the particular medication to help you relieve mucus in the stool.
- Use laxatives: In constipation, your health care provider may suggest a laxative or a stool softener. The laxatives are over-the-counter medication and may help reduce constipation and mucus secretion in the stool.

- Get the infection cured: If the origin of mucus in the stool is an infection, your doctor may suggest an antibiotic regime to control the infection. It is best practice to complete the course of antibiotics for complete recovery and reduce recurrence.
- Avoid allergic food: In case of food allergies, try to identify and avoid the allergen in your food. Abstaining from the source of allergy may help regain a healthy gut and reduce mucus secretion in the stool. It is always good to limit junk and spicy foods for better health during pregnancy.
- Include mild exercises: Exercising during pregnancy can help you stay healthy and fresh. A little warmup followed by movement exercise will keep your gut healthy. It may help ease constipation-induced mucus secretion. Mild exercises and physical activities are safe during the pregnancy. Walking and jogging may keep you active and aid digestion.
Related: 17 Safe Pregnancy Exercises And Workouts For Women
When Should You Call The Doctor?
Mucus in stool is not a sign to worry about. You may improve your lifestyle and undertake preliminary measures to reduce the excess secretion of mucus in stool.
You may improve your lifestyle and undertake preliminary measures to reduce the excess secretion of mucus in stool.
When stool has an excess amount of visible mucus during pregnancy, it may be due to health conditions, such as (10) (11) :
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn’s disease
One may take note of the symptoms and consult a doctor in the following cases:
- There is an excess amount of mucus in the stool
- Blood or pus in the stool
- Pain while passing stool
- Having stomach pain, cramping, or bloating
- Sudden changes in stool frequency, consistency, or color
1. Can probiotics cause mucus in stool?
Research indicates that probiotics may alter the composition and volume of stool, causing gassiness and increased mucus secretion in stools. If you notice these symptoms after consuming probiotics during pregnancy, you should talk to your gynecologist or nutritionist (12).
2. Can anxiety cause mucus in stool?
Anxiety may increase mucus secretion in stool in some individuals (13). However, the underlying reason is not known, and it may not happen to everyone.
Mucus in the stool during pregnancy can make you worried at times. However, it is generally acceptable to have mucus in stool during pregnancy. It could be due to dehydration and constipation induced by various body changes during pregnancy. Understanding of your health and proactively working towards it during pregnancy may help your gut stay healthy, fit and reduce mucus secretion in the stool.
Key Pointers
- Pregnant women may pass mucus in their stool during the first trimester due to dehydration, hormonal changes, stomach infections, and other issues.
- Some treatment options that may relieve the condition are proper hydration, a healthy diet, mild exercises, and avoiding allergic foods.
- Consult a doctor if you notice excess mucus, pus, or blood in the stool or experience pain, cramps, or bloating.

References:
MomJunction's articles are written after analyzing the research works of expert authors and institutions. Our references consist of resources established by authorities in their respective fields. You can learn more about the authenticity of the information we present in our editorial policy.
- The gastrointestinal mucus system in health and disease.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3758667/ - Gastrointestinal Infections in Pregnancy.
https://patient.info/doctor/gastrointestinal-infections-in-pregnancy - Bladder and bowel problems during pregnancy.
https://www.pregnancybirthbaby.org.au/bladder-and-bowel-problems-during-pregnancy - Hormones in pregnancy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3640235/ - Piles in pregnancy.
https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/related-conditions/common-symptoms/piles/ - Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).

https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/irritable-bowel-syndrome-ibs - Nutrition Column An Update on Water Needs during Pregnancy and Beyond.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1595116/ - How much water should I drink during pregnancy?
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/experts-and-stories/ask-acog/how-much-water-should-i-drink-during-pregnancy - Constipation in Pregnancy.
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-health-wellness/constipation-during-pregnancy/ - The Diagnosis and Treatment of Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2695363/ - The Effect of Phloroglucinol in Patients With Diarrhea-predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Trial.
https://www.jnmjournal.org/journal/view.html?uid=1563&vmd=Full&
The following two tabs change content below.
- Reviewer
- Author
Anshuman Mohapatra is a biotechnology scientist with more than six years of research experience in analytical chemistry and biotechnology. He has submitted his PhD thesis at the Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati (IIT Guwahati) and served as a research fellow (JRF/SRF) during his PhD tenure. His research interest includes analytical chemistry, neurobiology and lipid disorder diseases. Three of his research... more
Dr. Miguel Razio Osorio began his career in 2004. After two years of internship and social service, he decided to specialize in G&O. Since 2013, Dr. Razo has dedicated his training and practice to improve his patients' obstetric and gynecological health, getting his degree as a certified specialist in 2017. He then began working at the different health systems in... more
Dog Allergy In Babies: Symptoms,..
Dog Allergy In Babies: Symptoms,..
Masturbation In Pregnancy: Safety,.
 .
.Masturbation In Pregnancy: Safety,..
12 Symptoms Of Egg Allergy In Babies..
12 Symptoms Of Egg Allergy In Babies..
Zantac (Ranitidine) For Babies: Its..
Zantac (Ranitidine) For Babies: Its..
Custard Apple (Sharifa) During..
Custard Apple (Sharifa) During..
7 Causes Of Dry Skin On Baby, Symptoms,..
7 Causes Of Dry Skin On Baby, Symptoms,..
How To Teach A Baby To Chew And Swallow..
How To Teach A Baby To Chew And Swallow..
Yeast Infection In Toddlers: How To..
Yeast Infection In Toddlers: How To..
6 Causes Of Watery Eyes In Babies,..
6 Causes Of Watery Eyes In Babies,..
White mucus in stool what does it mean
Mucous membrane, which promotes digestion and absorption of nutrients, lines the inner surface of the gastrointestinal tract. To protect against mechanical injury, from exposure to acids and alkalis, its cells secrete mucus that envelops the stomach and intestines from the inside.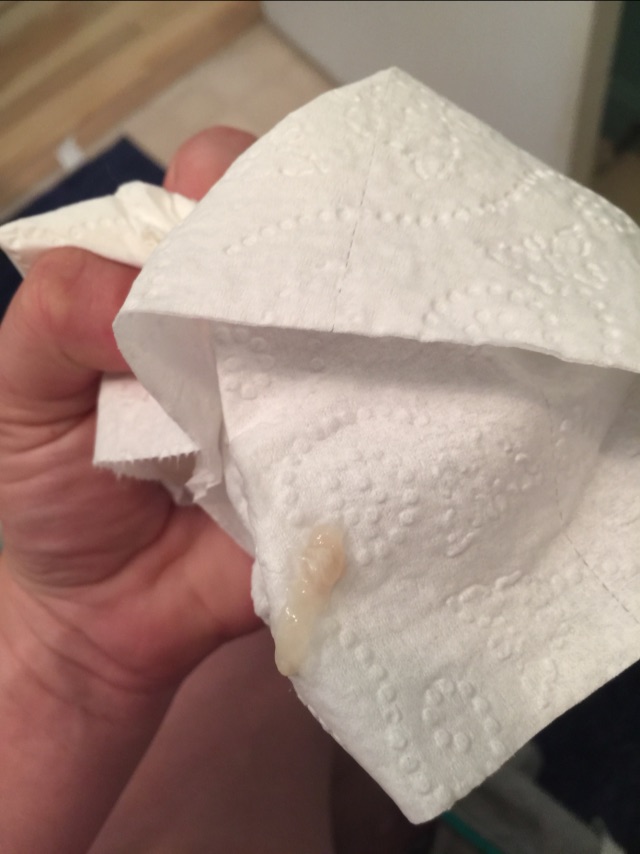
What does white mucus in stool indicate?
With injury and inflammation of the mucous membrane, mucus secretion increases. In the normal state, the mucus is not noticeable in the feces, it is evenly mixed with the feces. With irritation of the mucous membrane, an increased amount of mucus can be easily determined by visual inspection of the products of defecation, during the coprogram.
Coprogram - a study of feces that allows you to determine the state of the gastrointestinal tract, the presence of processes of digestion and absorption, diseases of the stomach and intestines.
Parameters determined by the coprogram:
Color and consistency of feces;
Presence of epithelium, starch, mucus;
Number of erythrocytes and leukocytes;
Presence of connective tissue, muscle fibers;
Volume of iodophilic flora, fatty acids.
The color and structure of the mucus found in the feces depends on the cause of its hypersecretion and the nature of the damage:
Yellow and green mucus - the presence of a bacterial process, an admixture of pus;
Clear mucus - catarrh;
Admixture of blood, pinkish tint of mucus - the presence of an ulcer of the mucous membrane, hemorrhagic inflammation.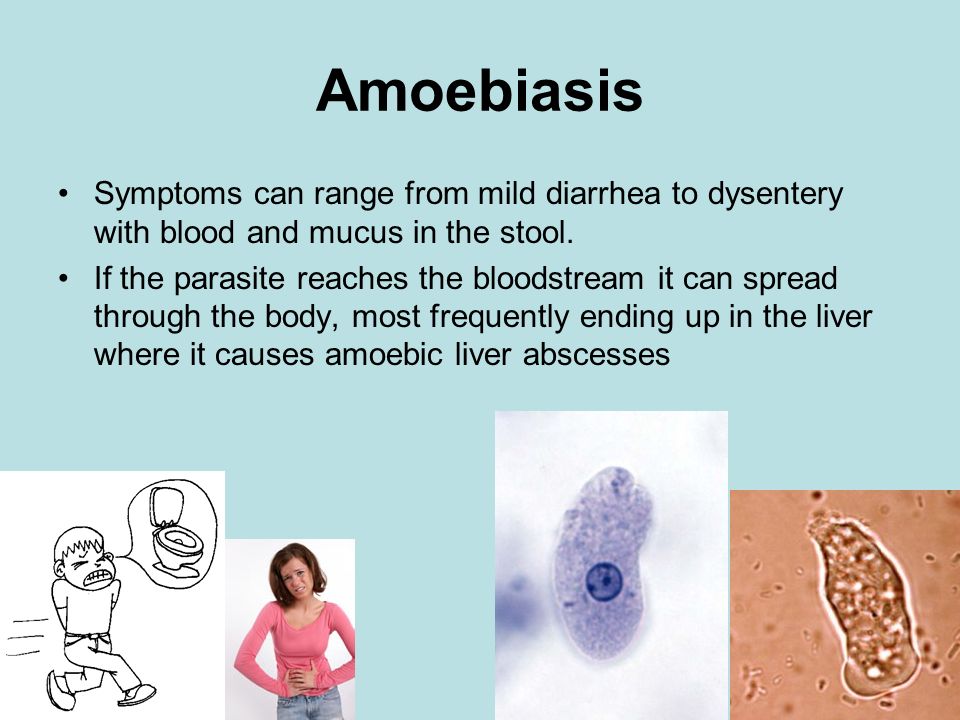
Reasons for the appearance of white mucus in the feces
Depending on the cause of hypersecretion of mucus, its consistency and therapy of the pathological process depend.
Factors affecting the appearance of mucus in the stool:
SARS. With a respiratory infection caused by adeno- and enterovirus, parainfluenza viruses, catarrh of the intestinal wall occurs. In addition, the patient swallows the mucous discharge of the nasopharynx. Mucus in the feces with ARVI has a transparent consistency, its volume is small. For the treatment of this condition, antiviral drugs are prescribed - Interferon, Arbidol.
Side effects of certain drugs and products. A small amount of clear mucus may result from taking NSAIDs, flatulence medications, smoking, drinking coffee. After the abolition of the above drugs, the condition returns to normal.
Intestinal infectious diseases. Bacterial infections provoke the release of a large amount of mucus of various structure and consistency.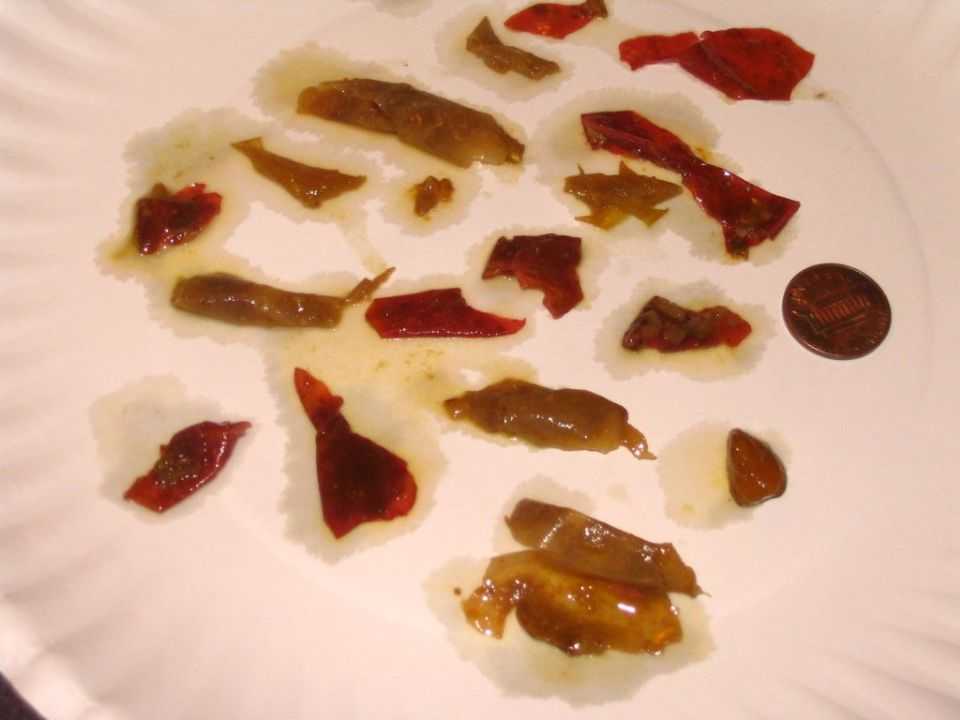 With salmonellosis, a small amount of mucus accompanies frequent swamp-colored stools. With dysentery, the mucus becomes green, it contains pus and an admixture of blood. During a staph infection, mucus accompanies frequent, bloody, frothy stools.
With salmonellosis, a small amount of mucus accompanies frequent swamp-colored stools. With dysentery, the mucus becomes green, it contains pus and an admixture of blood. During a staph infection, mucus accompanies frequent, bloody, frothy stools.
Treatment of intestinal infections - taking drugs from the nitrofuran group (Furazolidone, Ercefuril, Eneterofuril) or from the cephalosporin group.
Viral intestinal infections. With colienterocolitis, yellow mucus with whitish impurities is found in the feces against a watery yellow-green color. With rotavirus infection, which causes malabsorption and digestion, mucus accompanies frequent stools with symptoms of dehydration. Therapy - taking Viferon, Kipferon, drugs for rehydration (Gidrovit, Regidron), solutions for parenteral administration.
Parasitic infections. Mucus in the feces with helminthiases accompanies frequent stools with an admixture of blood and pain in the abdomen. Additionally, a decrease in appetite, anemia, and allergic manifestations are diagnosed. Therapy of parasitic infections is carried out with Mebendazole, Niridazole, Piperazine, Meironidazole, Tinidazole, Chloxil.
Therapy of parasitic infections is carried out with Mebendazole, Niridazole, Piperazine, Meironidazole, Tinidazole, Chloxil.
Candidiasis. Entering the intestinal lumen of the mycelium of the fungus of the genus Candida causes the release of white mucus into the feces. Treatment - taking Griseofulvin, Amphotericin.
Autoimmune intestinal inflammation (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease). Mucus with blood and pus is secreted against the background of diarrhea, fever, pain along the intestines. Treatment - taking drugs from the group of cytostatics, glucocorticoids, sulfalazines.
Spastic colitis. Mucus with blood is accompanied by constipation and diarrhea with a spastic component. Treatment - intestinal sanitation with Enterofuril, Furozolidone, taking antispasmodics, probiotics, Enterol.
Dysbacteriosis. The pattern of colonization of the intestine with Clostridium includes mucus on the background of unstable stools, abdominal pain, loss of appetite. Treatment of the disease is carried out with intestinal antiseptics (Furazolidone, Enterofuril, Metronidazole), probiotics (Linex, Bifiform, Bifikol, bifidumbacterin).
Raw food diet, starvation. Violations of the diet cause mucosal depletion, atrophy and irritation with coarse food, which provokes the release of copious amounts of mucus.
Pancreatitis. Mucus hypersecretion is caused by mucosal irritation with large amounts of pancreatic enzymes. Treatment - infusion of Furosemide, Diakarba, enzyme intake, diet, surgery.
Diverticulosis intestine. Protrusions of the intestinal wall cause brown mucus in the background of small bleeding in the small intestine. Therapy - surgical treatment after intestinal sanitation and restoration of its microflora.
Proctitis, proctosigmoiditis. Mucus and blood in the feces appear along with pain on the background of irritations with enemas, chemical and mechanical damage. Therapy - antibacterial, anti-inflammatory drugs, taking antispasmodics and laxatives.
Malignant tumors of the intestine. With oncological lesions of the intestine, mucus with an admixture of blood appears in the stool against the background of intestinal obstruction and chronic pain syndrome. Treatment - removal of the neoplasm, radiation and chemotherapy.
Causes of white mucus in the feces of a newborn
Immediately after birth, the gastrointestinal tract of a newborn is sterile. In the first days of life, it is populated by microorganisms, the biocenosis of which contains both valuable lacto- and bifidobacteria, as well as saprophytes and conditionally pathogenic microorganisms.
During the first 2-3 weeks of a baby's life, a balance between different types of bacteria is established in his intestines. Transitional stool contains mucus, has a greenish tint. Once an equilibrium is established, the consistency of the stool may change, as well as its color and frequency.
Factors affecting the appearance of mucus in the stool in infants:
Intestinal dysbacteriosis. The predominance of enterobacteria, clostridia, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella over lactic acid bacteria causes flatulence, constipation, and the release of a large amount of mucus streaked with blood. If the mucus takes on a reddish tint, this is a sign of ulceration on the mucous membrane. Therapy of dysbacteriosis - taking Enterofuril, bacteriophages, Stop Diara, a course of treatment with probiotics (Linex, Normoflorin, Bifiform, Primadophilus). To prevent recurrence of dysbacteriosis, you need to carefully care for the baby.
The predominance of enterobacteria, clostridia, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella over lactic acid bacteria causes flatulence, constipation, and the release of a large amount of mucus streaked with blood. If the mucus takes on a reddish tint, this is a sign of ulceration on the mucous membrane. Therapy of dysbacteriosis - taking Enterofuril, bacteriophages, Stop Diara, a course of treatment with probiotics (Linex, Normoflorin, Bifiform, Primadophilus). To prevent recurrence of dysbacteriosis, you need to carefully care for the baby.
Bacterial and viral intestinal infections. When salmonella, dysentery bacillus, toxic infections are introduced into the child's body, inflammation of the intestinal mucosa develops. This circumstance causes the release of a large amount of mucus with clots. Diagnosis of infections - bacteriological culture of feces. These conditions are dangerous in that the child can quickly die from dehydration caused by diarrhea and vomiting.
Medicines for flatulence. Drugs - defoamers (Bobotik, Espumizan, Bebicalm) can imitate mucus in the stool in an infant. After stopping the medication, the admixture of mucus is no longer noted.
Drugs - defoamers (Bobotik, Espumizan, Bebicalm) can imitate mucus in the stool in an infant. After stopping the medication, the admixture of mucus is no longer noted.
Violation of the rules for the introduction of complementary foods. The introduction of certain vegetables into the diet can provoke the release of a large amount of stool. The consistency of the stool changes, it becomes liquid or, conversely, more dense, becomes green.
Lactase deficiency . Deficiency of the enzyme lactase, which ferments milk, causes fermentative dyspepsia. Its symptoms are the release of a large amount of mucus, the admixture of milky inclusions in the feces, gases, loose stools, and abdominal pain. Diagnosis - a study of feces for carbohydrates, treatment - a diet for a nursing mother, the introduction of lactase preparations to an infant, a lactose-free mixture is chosen for artificial feeding.
Allergy, atopic dermatitis. External manifestations in the form of weeping skin, peeling of the skin of the cheeks, may be accompanied by irritation of the intestinal mucosa. As a result, an increased amount of mucus is secreted.
As a result, an increased amount of mucus is secreted.
Runny nose. Swallowed mucus from the nasopharynx enters the intestine and is diagnosed in the feces of a child who cannot blow his nose on his own.
Intestinal invaginitis. When a part of the child's intestines is squeezed by another part, severe pain appears, gushing vomiting, loose bloody stools with an admixture of mucus. A day after the first symptoms of intestinal vaginitis appear, the feces are converted into lumps of mucus mixed with blood. Emergency surgeon assistance is required - a barium enema to straighten the intestines, otherwise the child may die from pain shock.
What to do if white mucus appears in the stool?
If mucus in the stool appears in children episodically, most likely, its appearance is not associated with any pathology. Eliminating the cause of this condition, most often a violation of the diet, will completely eliminate the problem. The increase in this symptom and the addition of pathology with other symptoms is a reason to see a doctor.
Examinations to clarify the diagnosis:
Micro- and macroscopic examination of feces;
Bacterial culture of feces;
Ultrasound and X-ray of intestines, stomach;
General and biochemical analysis of blood.
According to the results of the study, treatment is prescribed, the scheme of which is determined by the cause of the pathology. If it is based on an infectious factor, antibiotics, absorbents, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. With dysbacteriosis, the balance of the intestinal microflora is restored. To normalize the production of mucus, a special diet is prescribed that contains foods that do not provoke hypersecretion of mucus.
Author of the article: Volkov Dmitry Sergeevich | PhD surgeon, phlebologist
Education: Moscow State University of Medicine and Dentistry (1996). In 2003 he received a diploma from the educational and scientific medical center for the administration of the President of the Russian Federation.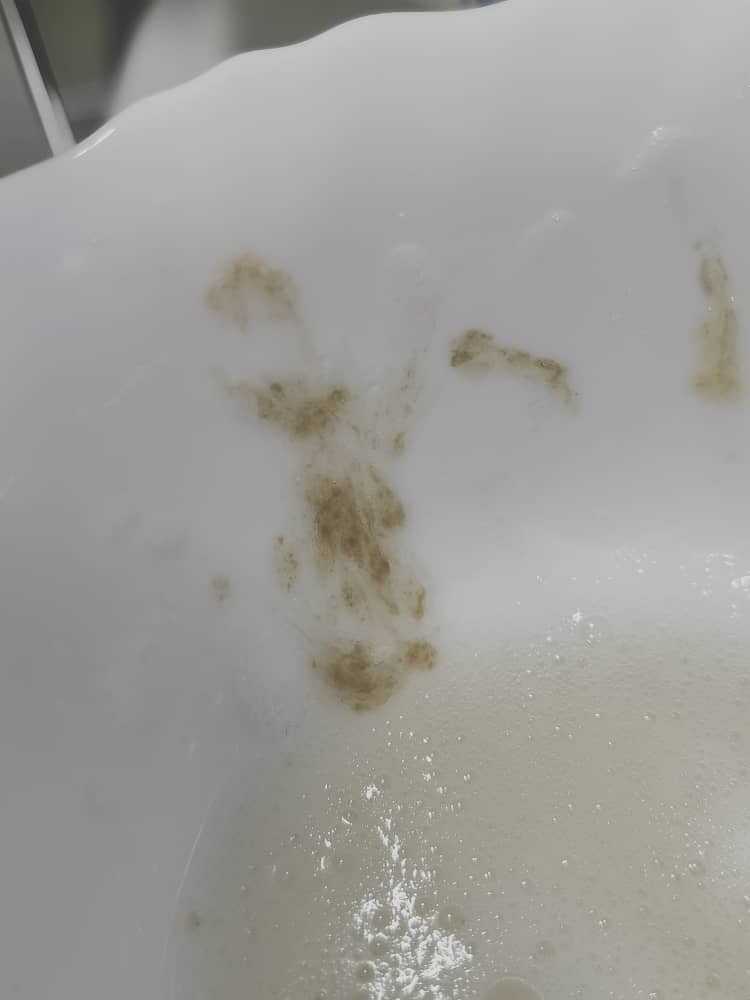
Our authors
Editor and medical expert — Harutyunyan Mariam Harutyunovna.
Views: 692 306
Date last updated: 05/25/2022
Average reading time: 10 minutes
Small amounts of mucus are always present in feces 8 - normally it is produced by the inner lining of the large intestine 1 . However, profuse mucus discharge, especially in combination with diarrhea in a child, usually indicates the presence of pathology 2. The parent may notice films, flakes or shreds on the surface of the feces, sometimes even dense lumps or tubes 8 .
This should alert parents. What diseases develop mucous diarrhea and what parents need to do in this case, read the article.
Causes
Diarrhea with mucus is a symptom that indicates damage to the digestive system. Excessive mucus secretion is characteristic of diseases of the large intestine - colitis. This is due to the fact that there are many more goblet cells in the wall of the colon, which are responsible for the production of mucous secretion 1.
The causes of diarrhea with mucus in a child can be divided into infectious and non-infectious 2 .
Infectious causes
Intestinal infections last 1-3 weeks 2 . Infectious factors include viruses, bacteria and pathological fungi that affect the intestinal mucosa and cause diarrhea 2. Mucous diarrhea is also often a manifestation of active activity of parasites in the intestines 2 . In addition to mechanical injury to the intestinal wall, worms can have a toxic effect on the body by the substances they secrete. Parasites can provoke allergies and maintain constant inflammation in the digestive tract 9.
Depending on the mechanism of development, the following types of diarrhea are distinguished:
- Secretory . At the heart of diarrhea of secretory origin is enteritis - damage to the wall of the small intestine, primarily of viral origin. With such a pathology, the feces become liquid, watery 14.
- Invasive diarrhea.
 Invasive is associated with damage to the large intestine by pathogenic bacteria - for example, Salmonella, Shigella or Escherichia. They penetrate the intestinal wall and cause active inflammation - colitis, which is manifested by the appearance of diarrhea with mucus 14
Invasive is associated with damage to the large intestine by pathogenic bacteria - for example, Salmonella, Shigella or Escherichia. They penetrate the intestinal wall and cause active inflammation - colitis, which is manifested by the appearance of diarrhea with mucus 14
It is the large intestine that normally ensures the formation of fecal masses, therefore, a violation of its function leads to the appearance of loose stools with abundant mucus content 1 .
Non-infectious causes
Non-infectious diarrhea lasts more than 3 months and becomes chronic 2 .
Mucous diarrhea in a child is often the result of an allergic reaction 2,11. In young children, the main food allergens are cow and goat milk proteins. The list of allergens is expanding as new dishes are introduced, and schoolchildren and adolescents are already often allergic to eggs and gluten-containing foods 10 . An unbalanced diet, frequent or, conversely, too rare meals can provoke the appearance of a food allergy.
Liquid, non-abundant feces mixed with mucus and blood is observed in the following cases 2 :
- Ulcerative colitis is a disease in which there is an active lesion of the mucous and submucosal layer of the large intestine with the formation of ulcers. It is based on a violation of the body's immune response, which leads to chronic inflammation 16 .
- Crohn's disease is a pathology with a long course, occurring with exacerbations. Unlike ulcerative colitis, this disease can affect all parts of the digestive system. In children and adolescents, the disease begins in the large intestine. In this case, chronic inflammation affects all layers of the intestinal wall 16,17.
- Juvenile polyposis - the formation of multiple polyps in the small and large intestine, in which the epithelial glands that produce mucus are actively working 5 .
Irritable bowel syndrome
Another cause of diarrhea in children and adolescents is irritable bowel syndrome. It develops due to functional dysfunction of the digestive system. In this case, the child usually has mucous diarrhea with particles of undigested food 1.
It develops due to functional dysfunction of the digestive system. In this case, the child usually has mucous diarrhea with particles of undigested food 1.
In most cases, symptoms appear in the morning, immediately after breakfast, for example, on the way to school. This phenomenon is called "morning onslaught syndrome". In this case, the teenager first leaves the shaped stool, then the feces become mushy or liquid feces are released. After a bowel movement, the child feels well and, as a rule, diarrhea does not recur during the day 1.
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea in children
Separately, antibiotic-associated diarrhea is a stool disorder that occurs while taking antimicrobials or several months after a course of treatment 2 . Against the background of the use of drugs, the composition of the intestinal microflora is disturbed - dysbacteriosis develops. Against its background, clostridia actively multiply, and pseudomembranous colitis develops. This causes the child to develop excruciating repeated diarrhea with mucus or blood 6,15 .
Symptoms of diarrhea with mucus
Diarrhea is not an independent disease, but a separate symptom. When it appears, it is important for parents to pay attention to the frequency of the child's stool, its abundance and consistency.
Normally, a child older than a year should not pass stools more than 1-2 times a day. The feces are usually dark brown in color, formed, hard. There should be no visible impurities. Diarrhea causes stool to thin, sometimes to the point of complete absence of solid particles 13 .
Diarrhea with green mucus is most often caused by a bacterial infection 3 . With damage to the large intestine, stools are usually multiple, but not too plentiful. In addition to mucus, it sometimes contains blood or pus 2,7.
Food allergy may present with colicky abdominal pain, loose stools with vitreous mucus 11 . Persistence of liquid stools is a reason to suspect more serious problems, primarily of a non-infectious nature 2.
With an intestinal infection, diarrhea is accompanied by pain in the abdomen - usually they are quite strong, cramping.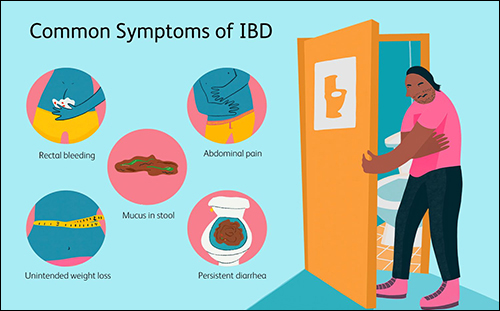 It is painful for the child to go to the toilet, sometimes he has a false urge to defecate - tenesmus 3.
It is painful for the child to go to the toilet, sometimes he has a false urge to defecate - tenesmus 3.
The situation requires close attention from the parents if loose, mucous stools are accompanied by additional symptoms 7 :
- Vomiting of undigested food or bile, sometimes with blood;
- Fever - fever;
- Chill and weakness;
- Infrequent urge to urinate;
- Flatulence - bloating;
- Body aches, muscle pains;
- Skin rash;
- Loss of appetite;
- Drowsiness or, conversely, emotional arousal;
- Black feces.
Children with severe diarrhea become dehydrated and complain of extreme thirst. Due to malabsorption of nutrients against the background of diarrhea, the child loses weight 7 .
If episodes of diarrhea with mucus recur, and other alarming symptoms join them, it is necessary to show the child to the pediatrician 7 . The doctor will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.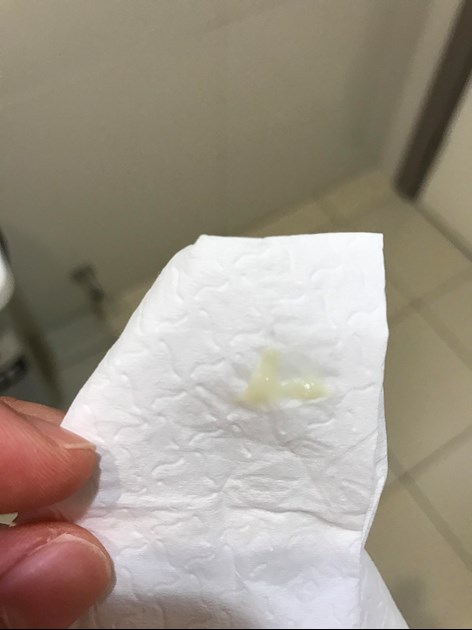
How is the child examined?
In most cases, diarrhea with mucus does not require any specific examination 7 . The doctor assesses the condition of the child, examines him and, based on this, makes recommendations for treatment. To distinguish infectious causes of mucous diarrhea from non-infectious ones, the pediatrician prescribes laboratory tests and instrumental methods of investigation 4,7.
For a correct diagnosis, tell the doctor about the child's eating habits, recent medications, allergies 2 .
Treatment
Diarrhea in a child should be treated by a specialist pediatrician or pediatric gastroenterologist. Only a doctor can adequately assess the severity of the patient's condition and prescribe rational therapy.
If the disease is mild, the child is given more liquids to drink to quickly replenish the deficiency. If a severe degree of dehydration (dehydration) develops, hospitalization and the introduction of saline solutions intravenously will be required 3,7.
Diet therapy
In order for the bowel function to recover faster, it is important to monitor the child's nutrition. If the diarrhea is not pronounced, and there are no signs of intoxication, in older children it is necessary to reduce the amount of food by 15-20%. Food should be well cooked, it is better to serve the dish in a pureed or mashed form. From 3-5 days you can return to the previous diet. With moderate diarrhea in the first days, the amount of food is reduced by 20-30%, within 4-6 days they gradually return to the usual menu 14 .
Avoid foods that increase diarrhea. Food containing tender fiber should be added to the menu 14.
Diet for diarrhea with mucus in a child 14
Foods to avoid
Drug therapy
Treatment should be comprehensive and aimed at eliminating the cause of diarrhea with mucus 1 3 . In addition to the main therapy, drugs are used to combat diarrhea 7 .
Imodium® can be used as a symptomatic treatment in children from 6 years of age. The active ingredient of the drug is loperamide, which slows down peristalsis and reduces the frequency of stools 12 . Imodium® is recommended for use in acute and chronic diarrhea that develops on the background of allergies, changes in diet or medication. As an adjuvant, Imodium® can be included in the complex therapy of infectious diarrhea 12 .
The active ingredient of the drug is loperamide, which slows down peristalsis and reduces the frequency of stools 12 . Imodium® is recommended for use in acute and chronic diarrhea that develops on the background of allergies, changes in diet or medication. As an adjuvant, Imodium® can be included in the complex therapy of infectious diarrhea 12 .
Imodium® does not directly affect the cause of frequent and altered stools. The remedy only alleviates the symptoms, due to which the child's condition improves. The use of Imodium® must be agreed with the doctor, as the medicine has contraindications. It is contraindicated for use in children under 6 years of age 12 .
Diarrhea with mucus in a child is an alarming symptom. Its appearance often indicates the presence of a serious pathology of the digestive system. Therefore, it is important for parents to consult a doctor in time. The specialist will help determine the cause of the appearance of loose stools and choose the appropriate treatment.
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional medical advice. For diagnosis and treatment, contact a qualified specialist.
Gastrointestinal pathologies occur in almost every person. Deviations from the norm occur in 95% of the population. Most often, people are concerned about pain in the gastrointestinal tract, digestive disorders, etc. Particularly noteworthy are the conditions that are called tenesmus. This is a painful and unpleasant urge to empty the bowels. In this case, defecation, as a rule, does not occur. With tenesmus, mucus may pass from the rectum instead of feces, and sometimes there is spotting or pus. A person with such a pathology experiences pain. The place of localization of discomfort is the area of the anus, perineum, sacral region. Still pain is sometimes felt in the gastrointestinal tract. Some patients described this uncomfortable condition as follows. There is a feeling of distension of the intestines from feces.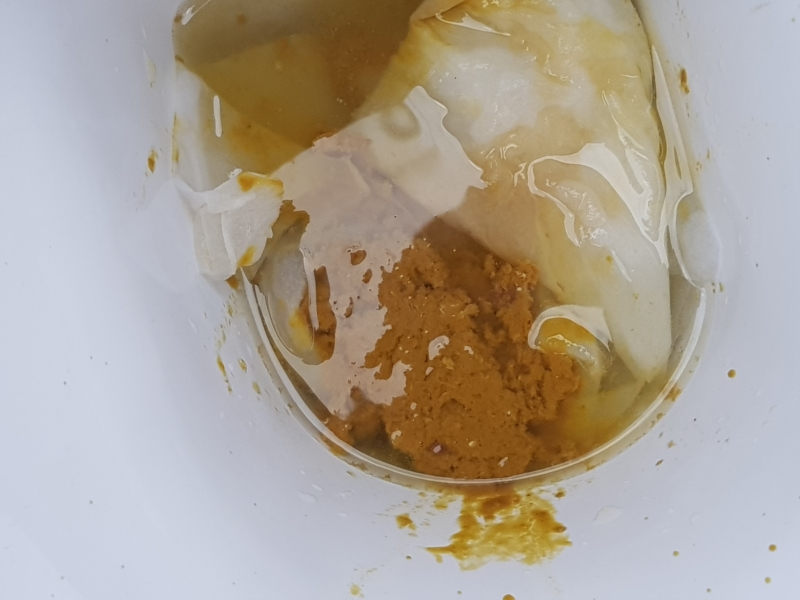 However, after visiting the toilet there are no results - defecation does not occur. Cal, if it comes out, then in small quantities.
However, after visiting the toilet there are no results - defecation does not occur. Cal, if it comes out, then in small quantities.
This condition is characterized as uncomfortable when there is an urge to empty the large intestine, but defecation is not observed. This phenomenon is sometimes associated with disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, other dangerous pathologies, up to cancer. Inflammatory processes in the intestines, colorectal cancer, as well as irritable bowel syndrome are capable of provoking false urges to empty. Tenesmus can also be caused by problems in the urogenital area, etc. To accurately determine the cause of this phenomenon, you need to undergo diagnostic procedures in a medical institution.
Causes and symptoms
Tenesmus has a variety of causes. Presumably, the occurrence of pathology is promoted by inflammatory processes in the large intestine. Moreover, inflammation can be both infectious and non-infectious in nature.
The phenomenon may be temporary or permanent. Short-term manifestations disappear after going to the toilet. Constant discomfort can manifest itself in the patient even in a calm state. As mentioned earlier, tenesmus is a manifestation of a particular pathology of the gastrointestinal tract or urogenital area.
Short-term manifestations disappear after going to the toilet. Constant discomfort can manifest itself in the patient even in a calm state. As mentioned earlier, tenesmus is a manifestation of a particular pathology of the gastrointestinal tract or urogenital area.
Inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract sometimes provokes narrowing, blockage, perforation or scarring of the intestinal walls. As a result, the promotion of feces is difficult, there are false urges to defecate.
We list the main reasons due to which this anomaly of intestinal motility occurs:
- ulcerative colitis;
- intestinal infections;
- Crohn's disease;
- rectal gonorrhea;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- colorectal cancer;
- hemorrhoids and others.
As you can see, intestinal tenesmus has a variety of causes, so you should be examined by a specialist in time to find out the causes of the pathology.
What to do in case of symptoms of pathology
It is important not to self-medicate, but to seek qualified help. It is necessary to undergo an examination in the clinic as soon as possible, the following manifestations of the pathology make themselves felt:
It is necessary to undergo an examination in the clinic as soon as possible, the following manifestations of the pathology make themselves felt:
- blood in stool;
- a person can shiver, have a fever;
- pain syndrome in the gastrointestinal tract;
- nausea, vomiting.
All this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the intestines. With these manifestations, you need to get medical help urgently.
When to call an ambulance urgently
An ambulance should be called if bowel obstruction is suspected. That is, in addition to tenesmus, a person has symptoms such as the inability to empty the intestines for a long time, strong and cramping pain, or slowly increasing pain in the intestines. The symptoms are also dangerous if the patient has vomiting, frequent tenesmus with blood and no discharge of flatus, feces even after enemas.
Before the ambulance arrives, put the person on the bed, apply cold to the stomach and do not give any food. In this condition, the patient should not take painkillers and laxatives. Also, you can not apply a heating pad to the stomach.
In this condition, the patient should not take painkillers and laxatives. Also, you can not apply a heating pad to the stomach.
When to see a doctor
You should see a doctor if you have difficulty with bowel movements, especially when they are accompanied by intense pain. Why is it better to start treatment immediately? If the symptoms do not change within a few days, then without quality medical care, complications of the patient's condition may occur.
Treatment
If a person experiences tenesmus, treatment is prescribed depending on the causes of the pathology, the severity of the condition, etc. It is very important to correctly determine the cause of the phenomenon. If a patient has colorectal cancer, it is best to detect it as early as possible. With such a disease, complex treatment is prescribed, which includes a variety of methods. It is also necessary to start treatment for inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract as soon as possible. Early diagnosis of these pathologies is the key to successful treatment outcomes.
Early diagnosis of these pathologies is the key to successful treatment outcomes.
The doctor at the appointment will make a complete picture of the occurrence of the disease. The examination may include the following activities:
- blood tests;
- colonoscopy;
- stool culture;
- CT scan of the abdominofield region;
- screening for sexually transmitted diseases.
The treatment regimen will depend on which pathology has caused intestinal tenesmus. If the cause of tenesmus in adults is an inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal tract, then the treatment regimen will be the same. With infectious diarrhea, completely different methods are already being used, etc.
Home treatment
Diseases that produce false bowel movements can often be treated at home. However, it should be noted that any use of medicines, including traditional medicine preparations, must be agreed with the attending physician. For example, in addition to the main treatment, auxiliary phytotherapeutic agents are also prescribed to the patient at home.
For example, in addition to the main treatment, auxiliary phytotherapeutic agents are also prescribed to the patient at home.
Here are some examples. To achieve temporary relief of the patient's condition, baths with herbal decoctions are sometimes prescribed. Enemas are often used using sea buckthorn and rose hips (for ulcerative colitis). With dysentery, painful symptoms are eliminated by bed rest, a special diet, drinking plenty of water, and taking medication prescribed by a doctor.
Prevention of tenesmus
Preventive measures for this pathology are as follows:
- high fiber diet;
- intake of sufficient quantity of clean drinking water;
- moderate physical activity;
- reduction of stressful situations at home, at work, etc.
A high fiber diet may not be beneficial for all patients. This preventive measure is very effective for false tenesmus, but is contraindicated in patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. You can’t take high-fiber foods yet in such cases:
You can’t take high-fiber foods yet in such cases:
- period of exacerbation of chronic gastrointestinal disease;
- severe narrowing of the intestinal lumen.
Those people who are not prohibited from such a diet can alleviate their condition by eating:
- legumes;
- nuts;
- vegetables, fruits;
- lentils;
- seeds;
- whole grains, etc.
It is equally important to drink at least 2-3 liters of water per day. This is important for normal and timely defecation. Moderate physical activity, sports help to improve digestion, restore intestinal motor function and eliminate false urges to defecate.
It is important to keep a calm state of mind in any situation, as the intestines (and stomach) are very sensitive to stress. For this, relaxation methods, meditation, yoga, psychotherapy, etc. are used.
Which doctor to contact in case of a symptom
For the timely start of treatment, it is necessary to contact a coloproctologist who will examine the patient, prescribe the necessary diagnostic tests and develop an effective treatment regimen.
You can make an appointment with the specialists of JSC "Medicina" (clinic of academician Roitberg) by phone +7 (495) 775-73-60 or using the online form on the website.
Answers to some popular questions
Many people are interested in the question of what is urinary tenesmus. Tenesmus is a false urge to both defecate and urinate. Therefore, there are intestinal false spasms, and there are also tenesmus of the bladder. Accordingly, with such spasms, there is a tonic contraction of the muscles of the rectum or bladder. Spasmodic contraction of the sphincters may also occur simultaneously. In both cases, false spasms do not allow either the intestines or the bladder to empty, that is, they are ineffective. Such phenomena are uncomfortable, may be accompanied by severe pain.
Another popular question from patients is how to get rid of tenesmus? The success of treatment depends on correct diagnosis. The rate of recovery of the patient will depend on how quickly and correctly the doctor determines the cause of the pathology. In cases where false urges cause tumors in the rectum, inflammatory, infectious diseases in the gastrointestinal tract, treatment should be started as early as possible. Then the result of therapy will be positive, and the process of recovery from the disease will take less time. Therefore, at the first symptoms of tenesmus, one should not hesitate, but undergo an examination in a professional clinic.
In cases where false urges cause tumors in the rectum, inflammatory, infectious diseases in the gastrointestinal tract, treatment should be started as early as possible. Then the result of therapy will be positive, and the process of recovery from the disease will take less time. Therefore, at the first symptoms of tenesmus, one should not hesitate, but undergo an examination in a professional clinic.
Everything that flows from the rectum (except stool) needs attention. Mostly it is mucus or pus. You will notice them on underwear, toilet paper, and sometimes in feces. Discharge from the rectum is found in a number of severe intestinal diseases. Sometimes this is the first sign of a problem.
Starting treatment at this stage will stop the progression of the disease and give much better results. Therefore, if you notice a discharge from the intestines, be sure to consult a doctor.
And now about the diseases that should be suspected when there is a discharge from the rectum.
Proctitis discharge
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum is called proctitis. Discharge is one of its leading symptoms. Discharges are mucous, sometimes purulent.
The pathology is accompanied by bleeding from the rectum, pain in the back of the body or in the left side of the abdomen, a feeling of fullness in the intestines, diarrhea, painful defecation. Sometimes the symptoms disappear quickly, sometimes they last chronically. The main task of diagnosing the disease is to determine the cause of proctitis. The treatment and its result depend on it.
Proctitis is caused by a number of diseases. In the presence of discharge from the rectum, it is necessary to exclude them all.
Proctitis
Proctitis is more common in people with inflammatory bowel disease (this name combines Crohn's disease with ulcerative colitis). According to statistics, 30 out of a hundred patients with inflammatory bowel disease develop proctitis. This disease is manifested by severe diarrhea, sometimes by alternating diarrhea and constipation, abdominal pain, and general weakness.
This disease is manifested by severe diarrhea, sometimes by alternating diarrhea and constipation, abdominal pain, and general weakness.
Another cause of proctitis is a sexually transmitted infection: gonorrhea, chlamydia, genital herpes. The likelihood of getting sick after risky sexual behavior is especially high. Anal sex is one of the main risk factors. However, microbes in the rectum can also move from the genitals.
Other microbes can also affect the intestines: salmonella, shigella, campylobacter. Note: They cause foodborne infections. Infection can be identified by nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps.
Be careful with antibiotics too. As you know, antibiotics also kill beneficial bacteria, as a result of which the pathogenic microbe Clostridium is activated, which begins to multiply in the rectum. This also leads to the development of proctitis.
It is possible that proctitis may develop as a result of radiation therapy for cancer if the radiation affected the rectum or adjacent areas. Radiation proctitis begins during radiation therapy and usually lasts several months after the end of treatment, sometimes even bothering the patient for years.
Radiation proctitis begins during radiation therapy and usually lasts several months after the end of treatment, sometimes even bothering the patient for years.
Occasionally, proctitis occurs after surgery performed on the large intestine - excision and removal of part of the intestine, after the installation of the stoma. This form is called subversive proctitis.
The disease causes a number of complications. they are:
- Anemia. Its cause is chronic bleeding from the intestines. Anemia is manifested by headache, weakness, dizziness, shortness of breath, nausea;
- Ulcer - chronic inflammation that damages the mucous membrane and causes open sores;
- Fistula - if the ulcer has damaged the entire depth of the intestinal wall, a fistula will develop. Perforation results in an abnormal connection between the intestines and the skin or other organs, most commonly between the bladder and vagina.
Anal abscess discharge
An anal abscess is a purulent focus located in the anus. This is the result of an acute infection of the internal glands of the anus in nine out of ten cases. The internal glands of the anus produce fluid. When their ducts become blocked, fluid accumulates, becomes infected, and forms an abscess.
This is the result of an acute infection of the internal glands of the anus in nine out of ten cases. The internal glands of the anus produce fluid. When their ducts become blocked, fluid accumulates, becomes infected, and forms an abscess.
Anal abscess
An abscess can also form as a result of an injury or sexually transmitted infection. It is also possible that the root cause of the problem may be Crohn's disease or diverticulitis. The disease can affect people of both sexes at any age.
The risk is increased with immunodeficiency, diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, chemotherapy, long-term use of steroids.
Anal abscess discharge clearly purulent. Accompanied by throbbing pains, aggravated by defecation, coughing, sitting. Possible constipation, fever, chills, night sweats, weakness, fatigue. The area around the anus is red and sore.
The disease is diagnosed by rectal examination. During the diagnosis, attention is paid to an increase in body temperature, redness and painful swelling in the anus. On examination, a defect is found, from which pus, blood or feces are released. Proctosigmoidoscopy or other tests may be performed to rule out other diseases.
On examination, a defect is found, from which pus, blood or feces are released. Proctosigmoidoscopy or other tests may be performed to rule out other diseases.
The anal abscess itself is rare. Also, antibiotics alone rarely help. Most cases require surgery.
Treatment of the pathology usually involves draining the abscess. This can be done on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. The need for deeper anesthesia is not ruled out.
Immunocompromised individuals who are at risk of developing a severe infectious disease should be hospitalized.
Anal fistula discharge
If left untreated, an abscess will form - pus will accumulate and eventually come out through the skin. An anal fistula is a small tube between the infected anal area and the skin. Develops in half of patients with abscess.
Rarely, a fistula is formed against the background of tuberculosis, sexually transmitted infection, chronic bowel disease.
Anal fistula is characterized by pain, redness, swelling around the anus, bleeding, painful urination and defecation, fever and discharge.
Sometimes a fistula closes on its own and then reappears, although this should not be allowed to occur as it can lead to a serious, life-threatening complication. Therefore, if any of the above complaints occur, you should definitely contact a specialist. The fistula is treated surgically.
Hemorrhoid discharge
Varicose veins of the lower rectum cause discharge from the back of the body. Allocations are not a mandatory sign of hemorrhoids, but they happen more often.
Hemorrhoids are indicated by bleeding during defecation, severe itching around the anus, pain around the anus, swelling, the presence of a nodule in the anal canal.
Hemorrhoid discharge
Hemorrhoids are a very common disease. The likelihood of its development increases under the influence of factors that increase pressure in the intestine. These include chronic constipation, pregnancy, and prolonged sitting.
Complex treatment of hemorrhoids. In the early stages, the problem can be solved by changing lifestyle and regulating bowel function. Conservative treatment may also be required. In more complex cases, surgeons are involved. Today, there are many effective methods of treating hemorrhoids.
Conservative treatment may also be required. In more complex cases, surgeons are involved. Today, there are many effective methods of treating hemorrhoids.
Remember that bleeding is a characteristic of many other diseases. Some of them pose a serious threat to health, so self-diagnosis is, to put it mildly, reckless behavior. Be sure to consult your doctor.
Discharge from anal cancer
One of the diseases that the patient can mistake for hemorrhoids is anal cancer. It is a rare form of cancer, although its prevalence has increased in recent years. Increased risk of developing the disease - impaired immunity, risky sexual behavior, female sex, smoking.
Human papillomavirus infection is considered the strongest risk factor. This microorganism is detected in 91% of cancer cases. The risk of developing anal cancer increases if the patient also has a papilloma virus-associated tumor in another location. In women it is cancer of the cervix and vagina, in men it is cancer of the genital organs.
The diagnosis of anal cancer is most often reported around the age of 60, and very rarely before the age of 35. At first, the disease resembles hemorrhoids - discharge and bleeding from the rectum, itching, pain, changes in bowel function, swollen lymph nodes in the anal area.
If you notice these symptoms, see your gastroenterologist. Most of them really give hemorrhoids, but it is possible that we are dealing with a malignant disease, and early diagnosis will prevent a tragic outcome.
To confirm cancer, the doctor will examine the anus and perform laboratory or instrumental tests - anoscopy, proctoscopy, biopsy. The prognosis depends on the stage of the disease and the general condition of the patient. In accordance with this, treatment is carried out, which includes surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
You can make an appointment by calling the free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or fill out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Mucus in the stool: white, yellow or brown mucus in the stool causes mucus in the stool
Mucus is a thick, slippery substance that is produced in various human organs. In the intestines, it is needed in order to moisturize the mucous membrane and ensure the free passage of feces. Therefore, a small amount of mucus in the stool is not a cause for concern. But mucus in the stool in an adult in large quantities, especially in combination with other symptoms, may indicate some diseases of the digestive tract. Sometimes malignant tumors appear this way.
Causes of mucus in the stool
An increase in the amount of mucus in the stool can be associated with various pathologies. Some of them are chronic and pose a serious threat. Most often it is associated with inflammatory processes. For example, mucus in the feces combined with diarrhea is a classic manifestation of many intestinal infections. The appearance of blood impurities and pain in the abdomen may indicate more serious diseases, such as Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, or a malignant neoplasm.
Symptoms to look out for when mucus appears in the stool
A serious illness can be indicated by a large amount of mucus (sometimes even patients themselves describe this symptom as "mucus instead of feces") and its frequent appearance in stool, as well as a combination this symptom with other manifestations:
- blood in the stool;
- black tarry stool - melena;
- diarrhea - frequent and loose stools;
- abdominal pain.
If jelly-like mucus in the stool is combined with these signs, you need to visit a doctor and get an examination.
Most often, mucus is excreted with feces. But sometimes it appears in the intervals between bowel movements. When mucus is released without feces in an adult, this may indicate an inflammatory process in the intestines and a low tone of the sphincter - a circular muscle in the rectum.
What diseases cause mucus in the stool?
Irritable bowel syndrome - a functional disorder, when there are no pathological formations in the intestine, but its work is disturbed. The main manifestation is constipation, diarrhea, or their alternation. The appearance of such a symptom as feces with mucus in an adult is also very typical.
The main manifestation is constipation, diarrhea, or their alternation. The appearance of such a symptom as feces with mucus in an adult is also very typical.
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disease that can be severe and lead to the development of malignant tumors. The lesion can spread to all parts of the digestive tract - starting with the oral cavity and ending with the rectum. At the same time, there is often clear mucus in the feces of an adult.
Ulcerative colitis also belongs to the group of inflammatory bowel diseases and leads to the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane. They bleed, secrete pus and mucus - all these impurities are present in the stool. Other characteristic symptoms of the disease: pain and cramps in the abdomen, diarrhea.
Proctitis - inflammation in the rectum. It develops as a result of various infections (including sexually transmitted infections), injuries, hemorrhoids, and inflammatory bowel diseases. White mucus in the stool in an adult is one of the characteristic symptoms.
White mucus in the stool in an adult is one of the characteristic symptoms.
Pseudomembranous colitis is a serious infectious disease affecting the rectum. It is caused by the microorganism clostridioides difficile, usually after the normal intestinal microflora has been destroyed by antibiotics. Pseudomembranous colitis can cause severe, even life-threatening diarrhea, with mucus in adult stools and foul-smelling stools.
Food poisoning usually presents with flu-like symptoms, blood and mucus in the stool. It usually goes away within a few days, but in some cases it can be serious.
Intestinal infections and helminths can also cause mucus in the faeces.
Colon and rectal cancer. The leading symptom of the disease is the admixture of blood in the feces. But feces with white mucus may also appear.
Anal fistulas or rectal ulcers . Ulcers are mucosal defects, and fistulas are pathological communications between the gut and the skin surface. In both cases, feces often have an unpleasant odor, and mucus is excreted with it in large quantities.
In both cases, feces often have an unpleasant odor, and mucus is excreted with it in large quantities.
Allergic colitis most often occurs in young children as a reaction to cow's milk. In this case, feces often contain a lot of mucus.
When should I see a doctor?
Mucus in the feces and other bowel symptoms do not always indicate a malignant tumor. Most often, other, less dangerous, diseases manifest themselves in this way. But you can find out the exact diagnosis and exclude oncological pathology only after the examination. Therefore, if thick mucus appears in the stool, you should not delay a visit to the doctor.
Examination for the appearance of mucus in the stool
To find out why mucus appeared in the feces, the doctor may prescribe the following diagnostic methods:
- Complete blood count.
- Fecal analysis - coprogram.
- Fecal analysis for infection, helminth eggs.
- Fecal occult blood test.

- Colonoscopy is an endoscopic procedure in which the lining of the rectum and colon is examined using a thin, flexible tube (colonoscope) inserted through the anus.
- Sigmoidoscopy - endoscopic examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon.
- Endoscopic examination of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
- Video capsule endoscopy is an alternative to classic endoscopic studies of the digestive tract. The patient is asked to swallow a small capsule containing miniature video cameras. This capsule will pass through the intestines, "examine" its mucous membrane and leave the body naturally.
- CT, MRI.
Whatever disease causes mucus in the feces, it is better to diagnose it at an early stage. You can check the condition of your digestive organs using the comprehensive program "Gastrointestinal tract" at the Euroonco clinic. This program includes all the main instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods, as well as consultations from our leading specialist doctors.












