How to become a child custody lawyer
How to Become a Child Custody Lawyer -
Degree CompletedHigh School Diploma/GEDSome CollegeAssociate DegreeBachelor's DegreeMaster's DegreeDoctorate Degree
Desired DegreeDiploma/CertificateAssociate DegreeBachelor's DegreeMaster's DegreeDoctorate
Program of InterestAll Criminal Justice ProgramsCriminal JusticeCyber SecurityEmergency ManagementForensicsHomeland SecurityInternational Relations/Global AffairsLaw & ParalegalLaw EnforcementSocial Work
Sponsored Content
Becoming a child custody attorney falls under the category of family law. These types of lawyers represent families that have become embittered in all types of volatile situations. There is no shortage of cases and work available for family attorneys, especially those who specialize in child custody. This is an ever-expanding field has more lawyers are becoming involved primarily in family law. This can be a rewarding option as the services of a child custody lawyer could bring justice for families in tough predicaments. There is also a specific process to follow on the way to becoming a child custody lawyer.
Child Custody Lawyer Education
Before seeking out a specialization in what type of law you would like to practice, there exists the initial requirement of completing an undergraduate program. In order to become a child custody attorney, there is no required major at the undergraduate level. However, a bachelor’s degree is required to move on to law school.
Featured Law School:SPONSORED
Request Information
Washington University in St. Louis
Featured Program: Top-20 law school - 1-Year Online Master of Legal Studies, No GRE/LSAT required
Request Info
Purdue University Global
Featured Program: Online Bachelor's in Legal Support and Services - Paralegal Concentration
Request Info
Rasmussen University
Featured Program: Online Paralegal Associate Degree and Post-Degree Certificate Programs
Request Info
American University
Featured Program: Online Master of Legal Studies- No GRE/ LSAT Req'd, Five Concentrations Available, Bachelor's Required
Request Info
Pepperdine University
Featured Program: Online Master of Legal Studies Program, Bachelor's Required
Request Info
Search Paralegal Programs
You know you’re ready to make the move to become a Paralegal. All you need is the training to make it happen. Learn more about flexible training options and the cost of programs in your area.
All you need is the training to make it happen. Learn more about flexible training options and the cost of programs in your area.
FIND SCHOOLS
Sponsored Content
Once a bachelor’s degree is earned, the next part of the process involves getting accepted to an accredited Law School. Admissions are very competitive, which emphasizes the need to build an impressive resume throughout one’s undergraduate career. The more accolades and experience students can acquire, the better their chances are of being accepted. Also, much of the decision-making process revolves around an applicant’s LSAT scores.
The LSAT is the first step to entering a law school. The acronym stands for Law School Admission Test as students prepare rigorously in an effort to achieve the highest possible score. There are four parts of the test, which include reading comprehension, analytical reasoning, logical reasoning, as well as a writing sample. Because law school admissions have become so competitive, LSAT scores are extremely important.
Getting admitted to an accredited Law School allows students to continue their pathway to becoming a child custody lawyer. Law School curriculums cover a three-year span and most students attend to on a full-time basis. There’s an extensive amount of reading involved in these curriculums, which is why it is important to choose an undergraduate major that prepares for this type of workload.
Achieving a Juris Doctor Law Degree comes at the end of this three-year increment. However, students will need more than just a law degree to take the Bar Examination in their respective state. The next step in the process is taking and passing the MRPE, which stands for the Multistate Professional Responsibility Examination. Only two States, Maryland and Wisconsin, make this test a non-requirement. In the other 48 states, those looking to take the Bar Examination will need to take and pass the MRPE, which focuses on ethics.
Passing the Bar Examination is the final step in a child custody lawyer’s education. Many candidates take months to prepare for this examination, even after they have graduated from law school. It is a rigorous exam, which encompasses all facets of the law. Different formats are used on a state to state basis and they include the MBE (Multistate Bar Examination), MPT (Multistate Performance Test), MEE (Multistate Essay Examination) and UBE (Uniform Bar Examination).
Many candidates take months to prepare for this examination, even after they have graduated from law school. It is a rigorous exam, which encompasses all facets of the law. Different formats are used on a state to state basis and they include the MBE (Multistate Bar Examination), MPT (Multistate Performance Test), MEE (Multistate Essay Examination) and UBE (Uniform Bar Examination).
The practice of law can only begin after a Bar Examination has been passed with an acceptable score. Below is a checklist that can be used in route to becoming a child custody lawyer:
- Receive a Bachelor’s Degree
- Take the LSAT
- Gain admission to a Law School
- Receive a Juris Doctor Law Degree
- Complete and pass the MRPE
- Pass the Bar Examination in your respective state
Job Description and Skills
A child custody lawyer operates under family law. In situations where parents cannot agree on custody of their child, the matter is settled in a court of law. In that setting, parents enlist a child custody lawyer to represent them throughout the process. Child custody lawyers provide legal counsel, advice and instructions on how to navigate through the process. There are a lot of details involved in child custody hearings as it accounts for the primary caretaker of a child, any special needs, potential interactions with members of the household, the existence of abuse, as well as the overall adjustment of a child to the environment.
In that setting, parents enlist a child custody lawyer to represent them throughout the process. Child custody lawyers provide legal counsel, advice and instructions on how to navigate through the process. There are a lot of details involved in child custody hearings as it accounts for the primary caretaker of a child, any special needs, potential interactions with members of the household, the existence of abuse, as well as the overall adjustment of a child to the environment.
Child custody lawyers work closely with parents and often prepare them for courtroom experience. Child custody lawyers also handle mediation, which is recommended in many states. Courts may order mediation in which family members and their respective lawyers will attempt to resolve the custody matter in a controlled setting.
Child custody cases arise when parents cannot agree on various components of a child’s welfare. A child custody lawyer is recommended during the following occurrences:
- Expected or documented abuse of a minor
- Contested proceedings involving child
- Visitation rights
- Parental right termination
- Adoption
Child custody lawyers may work for parents or other family members who have custody of a child. The situation may call for the need to enforce an existing order. In many instances, child custody agreements are violated and that requires the expertise of a lawyer to help mitigate this process. Any changes in child custody also have to be done legally in a court of law.
The situation may call for the need to enforce an existing order. In many instances, child custody agreements are violated and that requires the expertise of a lawyer to help mitigate this process. Any changes in child custody also have to be done legally in a court of law.
Child custody cases are sometimes part of a divorce. That is why child custody lawyers are often well-versed in a variety of areas of family law. A family lawyer can typically handle all facets of a divorce which may include child custody, child support and other necessary components. Those interested in becoming a child custody lawyer would assume a career that includes the following duties:
- Investigating the specifics of custody arrangement
- Conducting negotiations
- Gathering records involving parents and children
- Making hearing requests
- Producing evidence to support their client
- Collection of child support payments
- Communicated child’s preferences to a court
- Offering recommendations while in court
Child custody lawyers may also be required when a parent passes away. There are even instances when grandparents, other family members or even close friends of a family will attempt to gain custody of a child. Those attempts will be assisted by a child custody attorney with proficient knowledge in family law. All parents should understand their legal rights when it comes to their children and a child custody lawyer can shed light on the specifics.
There are even instances when grandparents, other family members or even close friends of a family will attempt to gain custody of a child. Those attempts will be assisted by a child custody attorney with proficient knowledge in family law. All parents should understand their legal rights when it comes to their children and a child custody lawyer can shed light on the specifics.
Salary
The salary of a child custody lawyer typically averages more than six figures, although it is not the highest-ranking salary among lawyers. The nature of the work indicates that financial compensation does not come in great abundance with every case. Unlike some high-profile civil cases, those who are involved in child custody battles are not always the most affluent members of society. This can influence what child custody lawyers can expect to receive in regular fees from clients who reside in their immediate area. Geographic location factors greatly into the amount of annual earnings a child custody lawyer can expect to earn. Those who are located in areas with higher poverty rates will typically make less money than those located in more affluent areas.
Those who are located in areas with higher poverty rates will typically make less money than those located in more affluent areas.
The annual median salary of a lawyer in the United States is $120,910, according to the U. S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. However, there are salaries that exceed that median amount, as well salaries that are below that amount. Child custody lawyers can expect their annual income to be adjusted by numerous factors that include the size of the firm they work for, their overall experience, past client reviews, and overall record.
Child Custody Lawyer Job Outlook
Child custody lawyers practice under family law, which currently has a high demand. The divorce rate in the United States indicates that child custody lawyers will continue to have a favorable outlook for the future. However, more unwed couples are giving birth to a high number of children. Pew Research statistics indicate that one out of every four parents in the United States are not married. Those statistics also show that one out of every five children is living with a single female parent.
Those statistics also show that one out of every five children is living with a single female parent.
FIND SCHOOLS
Sponsored Content
With the number of unmarried parents on the rise, there remains a high demand for child custody hearings. Even when parents are amicable towards one another, child custody becomes an integral part of raising a child. Many couples opt to have this matter resolved in a court of law, which typically comes with the hiring of a child custody attorney.
The job outlook for child custody lawyers is reflected more in the trends associated with marriage and single parents, as opposed to overall lawyer job projections. Child custody is evolving into an ongoing legal contract, which means acquiring legal representation has also become part of the process.
Degree CompletedHigh School Diploma/GEDSome CollegeAssociate DegreeBachelor's DegreeMaster's DegreeDoctorate Degree
Desired DegreeDiploma/CertificateAssociate DegreeBachelor's DegreeMaster's DegreeDoctorate
Program of InterestAll Criminal Justice ProgramsCriminal JusticeCyber SecurityEmergency ManagementForensicsHomeland SecurityInternational Relations/Global AffairsLaw & ParalegalLaw EnforcementSocial Work
Sponsored Content
Child Custody Lawyer - Job Description, Education, Salary, Employment
Child custody is the term used to describe a parent’s rights and obligations towards their child. When two unmarried people have a child, or a married couple divorces, decisions must be made about who will care for and support that child. When the parents are unable to agree, the courts must decide. A child custody lawyer can determine what is in the child’s best interest, and assist you with the legal process. Keep reading to learn more about the child custody lawyer.
When two unmarried people have a child, or a married couple divorces, decisions must be made about who will care for and support that child. When the parents are unable to agree, the courts must decide. A child custody lawyer can determine what is in the child’s best interest, and assist you with the legal process. Keep reading to learn more about the child custody lawyer.
What Does a Child Support Lawyer Do?
Child custody can be the most difficult aspect of a divorce, especially if the parents are not on the same page about custody, child support, and visitation. When the parents are unable, or unwilling to work it out amongst themselves, the court will decide who will have custody. Custody is not an issue that pertains only to divorcing parents, however. Unmarried couples with a child are also subject to child custody cases as are family members of a relative that is an unfit parent.
There are two main types of child custody: legal and physical. Legal custody refers to the rights and responsibilities of a parent by specifying who can make major decisions for the child when it comes to education, medical needs, healthcare, and overall welfare.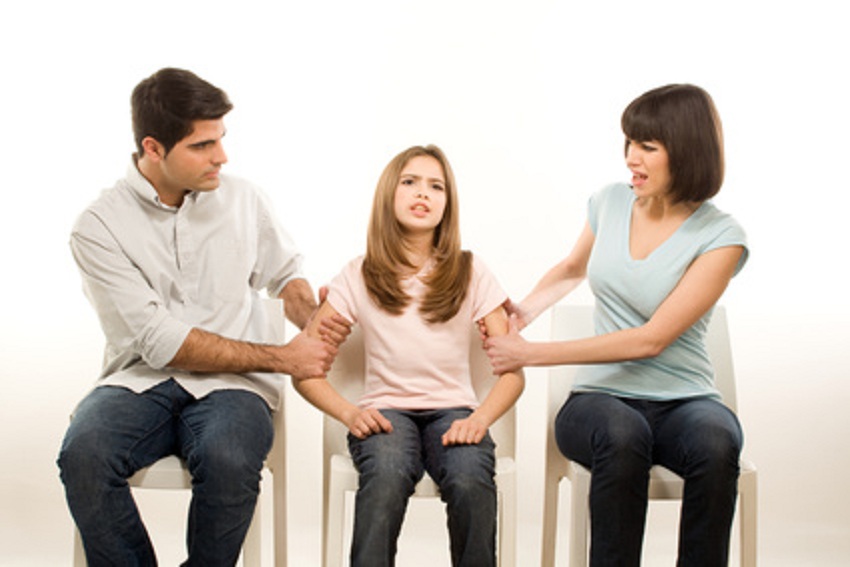 It is becoming more common for judges to order joint legal custody, which involves both parties making decisions about the child’s life.
It is becoming more common for judges to order joint legal custody, which involves both parties making decisions about the child’s life.
Physical custody addresses who will have day-to-day responsibility for the child. It determines where a child will reside and, whenever possible, the court orders joint physical custody so that the child spends time in both parents’ homes. If a person is awarded sole physical custody, the child resides with that parent full-time, but may visit the other parent on a scheduled basis.
All states try and base custody arrangements on what is in the best interest of the child. Whenever possible, courts favor joint custody as this gives the child an opportunity to build a strong relationship with both parents. It has many other benefits including lessening the sense of rejection and loss that a child can experience during a divorce.
When handling custody cases, the courts consider a number of factors when determining who gets custody including:
- Who the primary caretaker is
- Physical and mental health of parents
- Special needs of the child
- Interactions and relationships with other household members
- Evidence of drug or alcohol abuse
- Adjustment to school and the community
Many states require mediation or parenting classes in custody cases. Under court ordered mediation, parents meet with a family mediator to work through the details of custody and visitation.
Under court ordered mediation, parents meet with a family mediator to work through the details of custody and visitation.
A child custody lawyer, also known as a “family law attorney,” will advocate for their client and help create a custody agreement that is in the child’s best interest. If the parents cannot come to an agreement, the attorney petitions the court for custody on the client’s behalf. A lawyer experienced in child custody cases will also guide you through the legal process and paperwork, represent you should the case go to court, and negotiate child support rates.
Professional Requirements to Become a Child Custody Lawyer
The process to become a child custody lawyer takes hard work and commitment. The first step involves completing an undergraduate program to earn a bachelor’s degree. There is no specific field of study required for admission to law school, but in general, pre-law students major in political science, criminal justice, or business administration.
After receiving a bachelor’s degree, one must take the Law School Admissions Test (LSAT). Undergraduate GPA and LSAT score are two of the main factors when it comes to law school admission. If the student passes the LSAT and is admitted into law school, they will spend three years studying law before receiving a Juris Doctorate (J.D.) degree. They can also complete internships, clerkships, or legal clinics during this time to gain experience and broaden career prospects.
Once the individual has a J.D. degree, he must take the Multistate Professional Responsibility Examination (MPRE) (this does not apply to residents of Maryland, Wisconsin, and Puerto Rico). This exam ensures an individual’s conduct and professionalism meet the American Bar Association (ABA) standards. If they pass the MPRE, the last step required to become a child custody lawyer is taking passing the bar exam. This two-day exam is broken down into state and multistate sections. If a lawyer wants to practice law in additional states, he must take the bar exam in each one of those states.
Additional Education and Experience
After completing law school, one can continue their education and receive a Master of Laws (LL.M.) degree. This internationally recognized program gives students a deeper understanding of the law as well as global credibility.
Additional Licensing Requirements
In all states, there are additional licensure requirements for practicing child custody lawyers. Continuing Education is the most common, as this keeps attorneys up-to-date with the laws and case precedent. The amount of hours required varies by state. Generally, these Continuing Education courses must be completed every one to three years.
Where Can You Work as a Child Custody Lawyer
There are multiple options when it comes to where you can work as a child custody lawyer. You can work in a large firm, or as a solo practitioner. Typically, attorneys working at a firm or in a private practice earn a higher salary than solo practitioners.
Another option is to become an attorney for the state government. In child custody cases involving neglect and/or abuse, the court may appoint an attorney to represent the child(ren) or involved. This court appointed attorney advocates on behalf of the child by assessing the situation and providing the court with an unbiased view of what would be in the child’s best interest.
In child custody cases involving neglect and/or abuse, the court may appoint an attorney to represent the child(ren) or involved. This court appointed attorney advocates on behalf of the child by assessing the situation and providing the court with an unbiased view of what would be in the child’s best interest.
You can also work as a public interest attorney for a non-profit organization. This type of lawyer often works with civil legal services organizations to provide free or reduced representation to low-income individuals.
How do Child Custody Lawyers Get Paid
Child custody lawyers almost always charge an hourly rate, though they may simply prepare documents for a flat fee. In the case of an hourly rate, a retainer fee is likely to be requested. The retainer is an advanced payment that is placed in a special account for the lawyer to use as he works on the case. The amount of retainer requested will depend on the overall estimated costs.
Flat rate fees are often reserved for uncontested child custody cases. In uncontested cases, the parties involved work out an agreement in regard to custody, visitation, and child support. This usually gets the case moving more quickly through the legal system and reduces the costs involved. It also allows attorneys to predict with reasonable certainty how long it will take to close the case.
In uncontested cases, the parties involved work out an agreement in regard to custody, visitation, and child support. This usually gets the case moving more quickly through the legal system and reduces the costs involved. It also allows attorneys to predict with reasonable certainty how long it will take to close the case.
When a custody case is contested, or complicated in some other manner, it is more common for an attorney to charge an hourly rate. For this type of arrangement, the client is charged for the actual amount of time the lawyer has spent working on the case.
The amount charged by a family attorney, whether it’s hourly or flat-rate, depends on several factors including experience and geographical location. Attorneys with experience are usually more familiar with different areas of the law, with the attorneys likely to represent the other parent, and with the family court judges, and charge higher fees for their services. Location also plays a role in how much child custody lawyers get paid since those practicing larger cities cost more on average than those in rural areas.
Child Custody Lawyer Salary
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (“BLS”) Occupational Outlook Handbook, the median annual salary for child custody lawyers is $119,250 ($57.33/hr.) as of 2018. Unfortunately, this is the average for all lawyers as the BLS does not list the average salary for each field of practice separately.
Lawyers working with large firms or private practices tend to earn more on an annual basis than solo practitioners or public interest attorneys.
Employment Outlook for Child Custody Lawyer
According to the BLS, the employment rate for lawyers is expected to increase around 8%, between 2016 and 2026. This is the average rate for all occupations in the United States.
Hiring a Child Custody Lawyer
For most people, divorce or separation is a very stressful event, and even more so if children are involved. With emotions already running high, disagreements over child custody can intensify the conflict between the parents. Naturally, parents want to keep their child with them, but this may not be in their best interest. A child custody lawyer can help parents come up with an arrangement that is beneficial to all parties involved.
Naturally, parents want to keep their child with them, but this may not be in their best interest. A child custody lawyer can help parents come up with an arrangement that is beneficial to all parties involved.
Since the outcome of a child custody case can significantly impact not your family’s future, hiring a family lawyer with experience and expertise is vital. The lawyer you hire should also be familiar with state custody laws, have great communication skills, and be willing to stand up for your rights.
The attorney representing you will likely learn personal details about your life, so it is essential to hire one that you feel comfortable with. You should choose a lawyer that you trust, and that you feel you can build a strong rapport with. It may take meeting with several attorneys before you find the one that is best for your case.
How to Find the Right Child Custody Lawyer
Finding the right child custody lawyer entails more than a quick internet search or flip through a phone book. It requires knowing where to look and then meeting with potential attorneys to decide if they will be an asset to your case.
It requires knowing where to look and then meeting with potential attorneys to decide if they will be an asset to your case.
Asking family, friends, and other professionals in your life for recommendations of a family lawyer is perhaps your best option. You can also ask a lawyer you know, even if they practice in a different area of the law. Many know other lawyers in the area and whether they are reputable or not.
If unable to get personal or professional recommendations, another way to find the right child custody lawyer is by visiting online attorney databases. These databases have a list of practicing lawyers and you can narrow the choices by selecting your location and the area of law. The bar association website for each state also provides a list of attorneys.
Essential Information
| Degree Level | Juris Doctor (J.D.), Master of Laws (LL.M.) is optional |
| Degree Field(s) | Law |
| License/Certification | Licensure in state of practice |
| Key Skills | Critical thinking, negotiation, verbal and written communication, familiar with family law, ability to research, analytical, compassionate |
| Number of Jobs (2016) | 792,500 |
| Job Outlook (2016-2026) | 8% growth rate (average growth rate) |
| Median Salary (2017) | $119,250* |
| On the Job Training | Moderate term of on-the-job training |
| Top Earners | Top earners in the field are generally employed by large law firms |
(*Source: the BLS)
Custody and guardianship - Lawyer in Samara and Moscow
At any stage in the development of human society, the most natural and most optimal environment for raising a child was the family. It was she who was the most important tool for integrating the child into society, and so far there are no institutions that can replace the family in this. The upbringing of a child in the birth family most fully meets his interests. The right of a child to live and be brought up in a family is enshrined both in domestic legislation and at the international level. For example, the Convention on the Rights of the Child provides that cases of separation of a child from his parents are unacceptable, except in cases where this is contrary to the interests of the child. Priority is given to the family upbringing of children.
It was she who was the most important tool for integrating the child into society, and so far there are no institutions that can replace the family in this. The upbringing of a child in the birth family most fully meets his interests. The right of a child to live and be brought up in a family is enshrined both in domestic legislation and at the international level. For example, the Convention on the Rights of the Child provides that cases of separation of a child from his parents are unacceptable, except in cases where this is contrary to the interests of the child. Priority is given to the family upbringing of children.
However, it does not always happen that a child can objectively be brought up in his own family and this will meet the interests of his upbringing and development. When a family cannot properly fulfill its social function, state assistance is needed. Thus, the law provides for the possibility of removing a child from the family in case of a threat to his life and health.
The functions of the state to protect the rights and interests of children are implemented by guardianship and guardianship authorities. To achieve this goal, the bodies are vested with a number of powers:
- Identification and registration of children left without parental care;
- Establishment of guardianship and guardianship over children;
- Supervision of guardians, custodians, organizations that house children left without parental care;
- Issuance of permits for transactions with the property of the ward;
- Representing the interests of minors in relations with state and other bodies and organizations, if the actions of legal representatives of minors are contrary to the interests of children or they refuse such representation;
- Actions aimed at the placement of children left without parental care, supervision of the performance by guardians and trustees of their duties in raising children transferred to them.

Guardianship and guardianship authorities are also vested with a number of powers in relation to incapacitated and partially capable citizens.
As already mentioned, the primary form of raising children is the birth family. If this is impossible due to objective circumstances, then the most desirable is the adoption of the child, since this provides him with the same legal protection of his interests as education in the birth family. However, if this is not possible, then guardianship or guardianship may be established over the child. Guardianship is established over children under the age of 14, guardianship - over minors aged 14 to 18 years. The scope of their rights also differs. So, the guardian acts in civil circulation on behalf of the ward, the trustee only gives consent to the commission of certain transactions by the ward. If guardianship has been established over a child, then when he reaches the age of 14, it is automatically replaced by guardianship.
In contrast to adoption, which is established by a court order, the decision of the guardianship and guardianship authority is required to place a child under guardianship or guardianship.
Guardianship and trusteeship is established by agreement and is paid. Certain funds are allocated for the maintenance of the child, however, the guardian or trustee has the right to spend his personal funds on the maintenance of the child.
A guardian or custodian may be appointed only with his written consent. He is appointed within a month from the day when the body of guardianship and guardianship revealed the need to establish guardianship or guardianship. If within a month guardianship or guardianship has not been established, the duties of these persons are temporarily performed by the guardianship and guardianship bodies themselves.
In practice, it is preferable that the guardian or guardian is a relative of the child, but this can be any person who has expressed his desire.
Citizens who have expressed their consent to become guardians and trustees are subject to registration. It also provides for the obligation to prepare them by educational organizations, medical organizations, organizations providing social services, or other organizations, including organizations for orphans and children left without parental care, exercising the indicated powers of guardianship and guardianship authorities.
One of the powers of the guardianship and trusteeship authorities is to examine the living conditions of a person who has agreed to become a guardian or trustee. During the examination, in particular, the following circumstances are revealed:
- Personal qualities of the applicant;
- The motives that prompted him to become a guardian or custodian;
- Living conditions;
- Relationships with family members.
A person who has expressed a desire to become a guardian or trustee, along with other documents, must provide documents confirming his income level and health status, allowing him to fulfill the duties of raising a child.
Based on the above information, the guardianship and guardianship authority makes a decision to appoint a person as a guardian or trustee or to register a person as a citizen who has expressed a desire to become a guardian.
Before taking a child into custody, the potential guardian must personally get to know the child and establish contact with him. He can obtain information about the child, his state of health and relatives.
If a person has been appointed a guardian or custodian, an agreement is concluded with him. This agreement is paid and terminates when the ward reaches the age of 18 years.
The property of the ward is separated from the property of the guardian. The disposal of such property is possible solely in the interests of the child and with the consent of the guardianship and guardianship authority. Any transactions with the property of the ward, entailing its reduction are prohibited: donation, sale, lease, and so on. A special nominal bank account is opened in the name of the ward, where payments to the minor are to be credited. Funds from such an account are spent by the guardian without the consent of the body of guardianship and guardianship. The law also provides for the prohibition of transactions between the guardian (custodian) and the ward, with the exception of donation or gratuitous use in favor of the ward.
Funds from such an account are spent by the guardian without the consent of the body of guardianship and guardianship. The law also provides for the prohibition of transactions between the guardian (custodian) and the ward, with the exception of donation or gratuitous use in favor of the ward.
Thus, guardianship and guardianship is an institution designed to partially fulfill the obligations of the family in raising a minor. This form of placement is not life-long, unlike adoption, but it is able to compensate for the child's lack of a family and ensure his physical and moral development. Guardians and trustees must themselves declare their desire, and also undergo special training and examination by the guardianship and guardianship authorities. The above actions ensure that the child will live and be brought up in proper conditions. The guardian and custodian may be removed in case of non-performance and dishonest performance of their duties. If the child does not have a family, guardianship and trusteeship is an effective tool that allows them to perform their functions until the ward reaches the age of 18 years.
Sincerely, Attorney Anatoly Antonov, Managing Partner of Antonov & Partners Law Office.
Do you have questions for a lawyer?
Ask them right now here , or call us by phone in Moscow +7 (499) 288-34-32 or in Samara + 281263 (24/7), or come to our office for a consultation (by appointment)!
Relevance date of the material: 11/21/2018
To make an appointment for a consultation, call the round-the-clock number +7 (846) 212-99-71 or leave a request below
Child custody lawyer in Yekaterinburg.
Registration of guardianship/trusteeship is a complex procedure that requires knowledge and practical skills. Only a professional lawyer will be able to provide legal support at any stage.
Get advice
Get advice
11000 +
Legal advice provided
1250 +
Dispute resolution
%
cases won
Lawyers and lawyers
Child custody legal services
- Legal advice;
- Building a defense strategy in court and supervisory authorities;
- Drafting documents;
- Evidence collection;
- Expertise.

Taking custody of a child in Russia is not as easy as it seems at first glance. Children occupy a special place in the country, therefore, when applying for guardianship or guardianship, documents, the state of physical and mental health of potential guardians and trustees, housing conditions, and the amount of earnings are carefully checked. A small child will not be given to persons suffering from drug addiction or alcoholism.
Taking a child into custody is not a way to earn money, it is a huge responsibility and great material costs. People who dare to take such an action need to consult a professional lawyer who will explain all the nuances of the registration procedure and the consequences of such a step.
For whom guardianship/guardianship is possible
Guardianship or guardianship is possible for a child left without parental care and in the absence of adoptive parents.
Who can become a guardian/trustee
Citizens who have reached the age of majority and have full legal capacity, as well as who:
- have not been deprived of parental rights, are appointed guardians or trustees.

- Do not suffer from alcoholism or drug addiction.
- Not removed from the duties of guardians (custodians).
- No criminal record.
- Not married to a person of the same sex.
Sisters, brothers, grandparents, and other relatives have the priority right to be guardians or trustees over other people. In this case, the above conditions must be met.
Differences between guardianship and guardianship
Guardianship is established over persons under the age of 14 and completely incompetent citizens. On behalf of these persons, guardians have the right to carry out all legally significant actions in order to protect the wards.
Guardianship, in turn, is issued for persons who have reached the age of 14, but not yet of legal age, and for persons with limited legal capacity. At the same time, the main task of the trustee is to protect the rights of the wards from encroachment by third parties and to provide consent (disagreement) to the commission of legally significant actions by the wards.





:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/2785562/original/028627600_1556001360-shutterstock_1019963743.jpg)





