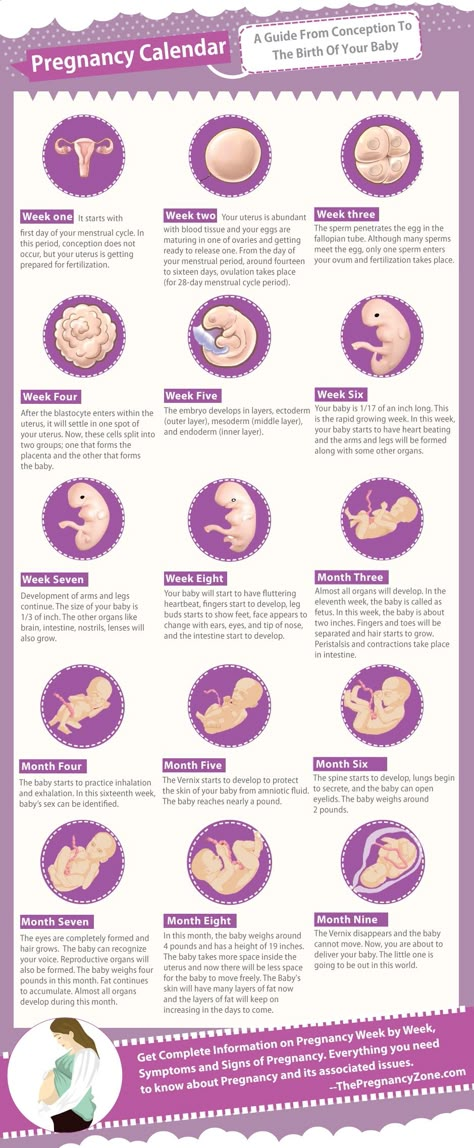
Vitamin k while pregnant
Vitamin K during pregnancy | How Much Do You Need? | AptaclubVitamin K in Pregnancy – Prenatal Nutrition
Read time: 1 minute
Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and helping wounds heal properly. It’s important to make sure you and your baby get enough in preparation for labour and your recovery afterwards. Although vitamin K deficiency is rare, an injection is given to all babies just after they’re born to minimise this risk.
Learn more about the importance of vitamin K in pregnancy, how much you need and which foods are the best sources.
Why is vitamin K so important during pregnancy?
As well as playing a key role in blood clotting, vitamin K is also needed for healthy bone development and protein formation in the liver1. This is particularly important during labour and just after you’ve given birth, when your body is recovering and starting to heal2.
Sufficient levels of vitamin K are also crucial for your baby immediately after birth, and while vitamin K deficiency in babies is very rare, it can lead to a condition called haemorrhagic disease that increases their risk of bleeding too much2.
Free 'Eating for 2' recipe e-book
Healthy, tasty recipes by chef Lorraine Pascale and our team of nutritionists
Join now for FREE
How much vitamin K do you need when you’re pregnant?
You should easily be able to get all the vitamin K that you and your baby need by eating a healthy, balanced pregnancy diet. The nutrient content of vitamin K-rich foods isn’t usually affected by cooking, and because it’s a fat-soluble vitamin, your body can build up stores of it in your liver, ready for when you need it.
It’s worth noting that some medical conditions and medications can affect your ability to absorb nutrients like vitamin K. If there’s a risk you’re not getting enough, you may need to take a supplement. If you have any concerns, talk to your GP or midwife, as taking a supplement unnecessarily can affect your baby3.
The exact amount of vitamin K you need depends on your size. According to the NHS, adults need approximately 1mcg a day of vitamin K for each kilogram of their body weight. So if you weigh 65kg, you need 65mcg of vitamin K each day1. Just half a cup of cooked broccoli contains 116mcg of vitamin K4.
According to the NHS, adults need approximately 1mcg a day of vitamin K for each kilogram of their body weight. So if you weigh 65kg, you need 65mcg of vitamin K each day1. Just half a cup of cooked broccoli contains 116mcg of vitamin K4.
Which foods contain vitamin K?
Foods rich in vitamin K include5:
- Green leafy vegetables – such as kale and spinach
- Broccoli
- Brussels Sprouts
- Asparagus
- Vegetable oils
- Cereal grains
Protecting your baby with vitamin K at birth
Although a significant deficiency is unlikely, babies are sometimes born with low vitamin K levels. They’ll usually be given a booster injection shortly after they’re born, just to be on the safe side6. If you don’t like the idea of your baby being injected, they can have an oral dose instead.
Try increasing your intake with these vitamin K-rich snacks and meals:
- A bowl of vitamin K- fortified breakfast cereal
- Roast asparagus with a poached egg
- Steamed broccoli with your favourite salad dressing
- Oven-baked kale crisps
- Sesame-crusted tuna steaks with quinoa and baby spinach
View references
1. NHS UK. Vitamin K [Online]. 2012. Available at: www.nhs.uk/Conditions/vitamins-minerals/Pages/Vitamin-K.aspx[Accessed June 2014]
NHS UK. Vitamin K [Online]. 2012. Available at: www.nhs.uk/Conditions/vitamins-minerals/Pages/Vitamin-K.aspx[Accessed June 2014]
2. Shahrook S et al. Vitamin K supplementation during pregnancy for improving outcomes. The Cochrane Library, 2014.
3. Stazi AV, Mantovani A. A risk factor for female fertility and pregnancy: celiac disease. Gynecoll Endocrinol 2000;14(6):454-463.
4. Puckett RM, Offringa M. Prophylactic vitamin K for vitamin K deficiency bleeding in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4, 2000.
Read next
- Aptaclub home
- Pregnancy
- Diet & nutrition
- Key vitamins and nutrients
- Importance of vitamin k
The ABCs of vitamins in pregnancy
Prenatal vitamins are important to good nutrition during pregnancy. They promote proper development of the growing baby and the health of the mother. When taken in proper amounts, vitamins are beneficial. However, taken in excess, vitamins can be harmful. It’s important to know what extra vitamin supplements — if any — are needed during pregnancy.
They promote proper development of the growing baby and the health of the mother. When taken in proper amounts, vitamins are beneficial. However, taken in excess, vitamins can be harmful. It’s important to know what extra vitamin supplements — if any — are needed during pregnancy.
Your doctor can help you decide: Find a Sanford physician
Most nutritional advise for pregnant women is based on reports from the Institute of Medicine and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Recommended dietary allowances (RDA) are levels of vitamins and nutrients recommended by expert panels based on extensive scientific evidence.
Multi-vitamin supplements are recommended for pregnant women who do not consume an adequate diet. Groups at increased risk for vitamin and nutrient deficiencies include:
- Women with multiple gestations
- Heavy smokers
- Vegetarians
- Women with a history of bariatric surgery
- Substance abusers
- Women with Crohn disease or bowel resection
- Adolescents
- Women with lactase deficiency
These women should have a consultation with a dietitian at the beginning of pregnancy to determine the proper diet and necessary vitamin supplements.
Amounts of prenatal vitamins
The amount of vitamin in each prenatal pill or multi-vitamin supplement can vary depending on the product used, making it important to check your vitamins and not exceed the upper safe limits of daily intake.
The following is a list of the recommended dietary allowance and tolerable upper limits for pregnant women:
Vitamin A
Coming in forms that include retinal, retinyl esters, retinol and retinoic acid — the most common, Vitamin A is required for:
- Cell growth
- Genes
- Development of the vertebrae, spinal cord, limbs, heart, eyes and ears
Because the foods Americans eat contain sufficient amounts, vitamin A deficiency is rare in the United States. Women of lower socioeconomic status should consume more foods with vitamin A rather than use vitamin A supplements.
The daily requirement of vitamin A is 770 micrograms.
Some over-the-counter multivitamins can contain too much vitamin A, so it is important to check the amount and make sure you are not taking more than 3,000 micrograms of vitamin A daily. Taking too much vitamin A has been linked to birth defects of the baby involving the head, face and heart.
Taking too much vitamin A has been linked to birth defects of the baby involving the head, face and heart.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is important for the health of your bones and the absorption of calcium. During pregnancy, vitamin D is also important for the growth of your baby and low vitamin D during pregnancy can result in a small baby, preterm birth and bone fractures.
Women who should take extra vitamin D during pregnancy include those who:
- Are strict vegetarians
- Have limited exposure to sunlight
- Avoid dairy foods
You can have your vitamin D level checked at the beginning of a pregnancy by asking for a 25-hydroxy-D level from your doctor. The recommended dose during pregnancy is 600 international unites (IU) and most prenatal vitamins contain 400 IU of vitamin D. However, some contain as little as 200 IU or as much as 1,000 to 1,2000 IU.
There are different forms of vitamin D in multivitamin supplements and prenatal vitamins — check to see what type of vitamin D your multivitamins contain. Many non-prescription vitamins labeled vitamin D contain ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) rather than cholecalciferol (vitamin D3). Vitamin D3 is better absorbed into your body and more effective at increasing your vitamin D level.
Many non-prescription vitamins labeled vitamin D contain ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) rather than cholecalciferol (vitamin D3). Vitamin D3 is better absorbed into your body and more effective at increasing your vitamin D level.
Taking as much as 1,000 to 4,000 IU per day of vitamin D is safe during pregnancy. However, unless your diet is deficient in vitamin D and your 25-hydroxy-D level is low, studies have shown no proof that taking extra vitamin D routinely during pregnancy helps lower preeclampsia, preterm birth or low birth weight.
Vitamin C
An antioxidant that functions to keep you healthy, vitamin C also helps you absorb iron. Women who smoke should take extra vitamin C in their diet. Pregnant women should take 85 mg per day.
There is no evidence that taking extra amounts of vitamin C helps prevent preeclampsia, stillbirth, preterm birth or low birth weight.
Vitamin E
There is no need to take extra vitamin E during pregnancy, as studies have shown no benefit in lowering stillbirth, preterm birth, preeclampsia or low birth weight.
Some studies have reported patients having more abdominal pain and premature rupture of membranes at term when taking vitamin E supplements during pregnancy. Taking too much vitamin E can cause platelet and bleeding problems.
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is important in your metabolism and in the formation of red blood cells. Taking extra vitamin B6 during pregnancy helps relieve nausea and vomiting associated with morning sickness.
It is uncommon to find a deficiency in Vitamin B.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is responsible for fat and carbohydrate metabolism and protein synthesis. Poor diets and strict vegetarian diets can cause deficiency, resulting in anemia and neurologic abnormalities.
Vitamin K
Vitamin K is important in helping blood clot. Though extra vitamin K is not needed during pregnancy, women who are pregnant and using anti-seizure medications are at increased risk of vitamin K deficiency in their baby. These women should take oral vitamin K, at a rate of 10 mg daily, from 36 weeks until delivery.
Folate
Taking an adequate amount of folate is important to help your baby from having the birth defect spina bifida. Folate is a vitamin important in making the body’s DNA and RNA.
Folate deficiency is the most common vitamin deficiency in pregnancy, with low folate levels caused by poor diet and genetic factors.
You should be taking an adequate level of folate one month prior to conception and continue through at least the first trimester.
Good sources of folate in your diet include:
- Fruits
- Green vegetables
- Beans
- Nuts
- Bread
Folate requirements are increased in pregnancy with the recommendation that women take 400 to 800 micrograms (0.4 to 0.8 mg) of folate prior to becoming pregnant and continue throughout pregnancy.
Read more
- 10 things to expect in your second trimester
- Learn secrets for an easier labor and delivery
- Becoming a mom at Sanford Health
…
Posted In Health Information, Pregnancy, Women's
Vitamins and pregnancy - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Albitskaya Elena Vladimirovna
Ultrasound doctor
Clinical hospital Lapino-1 "Mother and Child"
One of the most frequent questions that pregnant women ask their doctor is what vitamins should be taken during pregnancy? Let's say right away whether expectant mothers need to drink pharmaceutical vitamins or not - there is no unequivocal answer to this question. Some doctors believe that the necessary nutrients should be obtained from natural products. Others are in favor of taking pharmaceutical multivitamins. It can only be said unequivocally that vitamins and microelements must necessarily enter the body of a pregnant woman. We will tell you which of them are most important for the expectant mother.
Some doctors believe that the necessary nutrients should be obtained from natural products. Others are in favor of taking pharmaceutical multivitamins. It can only be said unequivocally that vitamins and microelements must necessarily enter the body of a pregnant woman. We will tell you which of them are most important for the expectant mother.
Folic acid
Other names for this vitamin are vitamin B 9 or B c . This vitamin is necessary for cell division and reproduction, so it is especially important in the first trimester of pregnancy, when all organs and systems of the child are being laid. Folic acid plays an important role in the synthesis of hemoglobin, and with its deficiency, anemia can develop. And folic acid also helps to reduce the likelihood of spinal defects in a child, takes care of the correct formation of his psyche and intellect. It is better to start taking folic acid three months before the planned conception, since a small supply of this vitamin will only be useful for both the expectant mother and the baby. If the pregnancy has come unplanned, then folic acid must be taken as soon as the woman finds out about her situation. On average, the dosage of this vitamin is from 0.4 to 0.8 mg per day.
If the pregnancy has come unplanned, then folic acid must be taken as soon as the woman finds out about her situation. On average, the dosage of this vitamin is from 0.4 to 0.8 mg per day.
Calcium
An expectant mother needs about 1200–1400 mg of calcium daily, while an ordinary woman needs 800–1000 mg of this trace element. Why? During pregnancy, the amount of calcium in the body of the expectant mother is significantly reduced, since it is also spent on the growth and development of the child. Especially a lot of calcium is needed in the third trimester, when the baby's skeleton is calcified. But calcium is needed not only for the growth of bones and teeth of a child - with its help, his nervous system, his heart, muscles, skin tissues, eyes, ears, hair and nails are formed. A pregnant woman needs calcium for the full functioning of the kidneys, the prevention of muscle pain, constipation, osteoporosis, caries and toxicosis. In addition, this trace element protects the expectant mother from stress and nervous overload.
Vitamin E
This vitamin is involved in the process of tissue respiration, it helps oxygen to penetrate into every cell of the body. At the same time, vitamin E is an excellent antioxidant: it protects cells from the formation of free radicals that can provoke various diseases. This protective function is especially important at the stage of embryo formation. In addition, vitamin E helps to normalize the hormonal balance of the body. In the early stages, it participates in the formation of the placenta, and also protects against abortion. The dose of vitamin E during pregnancy is 15 mg.
Vitamin E is found in vegetable oils, not less than this vitamin in lettuce, tomatoes, rose hips, parsley, spinach and peas. Some vitamin E is found in meat, eggs and milk.
Magnesium
Magnesium is involved in all metabolic processes, helps to cope with stress, normalizes the functioning of the cardiovascular system and blood pressure, keeps blood vessels in good shape. Due to a lack of magnesium in the body, cramps in the muscles (usually in the calves) may appear. And since the uterus is also a muscular organ, with a lack of magnesium during pregnancy during gestation, the excitability of the myometrium increases, which leads to active uterine contractions. Therefore, with hypertension and the threat of abortion, magnesium is often prescribed.
Due to a lack of magnesium in the body, cramps in the muscles (usually in the calves) may appear. And since the uterus is also a muscular organ, with a lack of magnesium during pregnancy during gestation, the excitability of the myometrium increases, which leads to active uterine contractions. Therefore, with hypertension and the threat of abortion, magnesium is often prescribed.
Magnesium is found in whole grains and whole grain breads, figs, almonds, seeds, dark green vegetables and bananas.
iodine
Pregnant women are usually prescribed iodine in the first trimester. Up to 16 weeks of pregnancy, the development of the child and the laying of all its organs and systems are "under the protection" of the mother's thyroid gland. And if a woman has little iodine, then this means that some system or organ of the baby may suffer. And even when the child’s own thyroid gland is formed and starts working, she can still take iodine only from the mother’s body. Its daily dose is 250 mg per day.
Its daily dose is 250 mg per day.
Iodine is most easily obtained from seafood and sea or iodized salt. A lot of iodine is found in sea fish, seaweed, squid, persimmon, feijoa, dates, dried figs, dairy products and meat. However, iodine is destroyed by temperature effects, which means that after heat treatment, the amount of iodine in the products decreases sharply.
Iron
Iron is needed primarily to prevent anemia. After all, it is part of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen throughout the body of the mother and child. In addition, iron is involved in protein synthesis, which is involved in the formation of muscle tissue. And iron deficiency can lead to increased uterine tone. The average daily dosage of iron is 30–60 mg. In some cases, if the woman's iron supply was initially reduced, the dosage may be higher.
Iron is found in meat, especially in veal, turkey, hare, pork and beef. There is iron in plant foods, but from there it is absorbed much worse. Iron is best absorbed when taken together with vitamin C.
Iron is best absorbed when taken together with vitamin C.
If a pregnant woman eats properly and varied, eats a lot of fruits and vegetables, then she may not need an additional complex of vitamins for pregnant women. It may be necessary to drink some vitamins separately, but this should be determined by the doctor. If, before pregnancy, a woman had signs of vitamin deficiency, she eats incorrectly or poorly, then multivitamins cannot be dispensed with.
Inset
Vitamin B 9 (folic acid) found in animal liver, spinach, asparagus, lentils, Brussels sprouts, beans and wholemeal flour. However, it is absorbed very poorly from food, no more than 50%. That is why it is prescribed to almost all pregnant women
At one time, our body will not be able to absorb more than 500 mg of calcium. Therefore, you should not try to get the entire daily norm of this trace element in one meal. Try to eat foods containing calcium in small portions several times a day
To increase magnesium concentration in tissues, vitamin B 6 (pyridoxine) is needed, which facilitates its absorption and acts as a conductor of magnesium into the cell. Therefore, magnesium and vitamin B 6 are often prescribed together.
Therefore, magnesium and vitamin B 6 are often prescribed together.
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Albitskaya Elena Vladimirovna
Lapino-1 Clinical Hospital "Mother and Child"
Diagnostics
By clicking on the submit button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select a clinic
Clinical Hospital MD GROUPClinical Hospital Lapino-1 "Mother and Child"Clinic KG "Lapino" in Odintsovo (branch)Clinic "Mother and Child" Khodynskoye PoleClinic "Mother and Child" KuntsevoClinic "Mother and Child" SavelovskayaClinic "Mother and Child" Yugo-ZapadMother and Child Clinic NovogireyevoMother and Child Clinic Lefortovo
All directionsSpecialist consultations (adults)Specialist consultations (children)Laboratory of molecular geneticsGeneral clinical examinationsProcedural roomTelemedicine for adultsTherapeutic examinationsUltrasound examinations for adults
01.
Specialist consultations (adults)
02.
Specialist consultations (children)
03.
Laboratory of molecular genetics
04.
General studies
05.
Procedure room
06.
Television and adults
07.
Therapeutic studies
08.
Ulzvous Valzvous Studies. adults
Nothing found
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to timely update the price list posted on the website, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to clarify the cost of services and the timing of the tests by calling
Vitamins and pregnancy - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Al Sabunchi Omar Majidovich
Surgeon, Endoscopist, Plastic Surgeon
MD GROUP Clinical Hospital
The problem of rational provision of vitamins and minerals to pregnant and lactating women remains the object of focused attention of physicians around the world.
The lack of vitamins in such an important life period is a condition much more serious than many people think and, alas, is very common at the present time. After all, now you are responsible not only for yourself - the health of the unborn baby is in your hands. He receives all the vital nutrients only from his mother. The need for vitamins during this period almost doubles.
For the full development and birth of a healthy child, doctors recommend taking care of him in advance - at the stage of pregnancy planning, long before the baby is born.
Many people are confused about this. Why take vitamins before pregnancy?
It is during the first weeks of pregnancy that the formation of all organ systems of the fetus takes place, the “foundation” is laid, on which the further development of your child depends, and without which the birth of a healthy baby is impossible. Therefore, the expectant mother should be “ready” for a “meeting” with her baby. After all, the energy requirement of a pregnant woman from the first days after conception increases by 25%! It is during this period that sufficient supply of the fetus with vitamins and minerals is vital. But most modern women learn about their "interesting position" much later, when such an important stage has already been passed. Therefore, most doctors recommend that both spouses start taking vitamins several months before the planned conception.
But most modern women learn about their "interesting position" much later, when such an important stage has already been passed. Therefore, most doctors recommend that both spouses start taking vitamins several months before the planned conception.
Vitamins are essential nutrients, that is, they are not formed in the body, and at the same time, a person cannot exist without them. Vitamin A (retinol) is "responsible" for the formation of the skin and organs of vision. Vitamin C is the main “building block” involved in the maturation of all organs and systems; in its absence, the development of a baby is simply impossible. B vitamins are indispensable for the nervous system. Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant, a natural natural "defender" of the baby from radiation, harmful chemicals, industrial poisons, which is so important in a modern metropolis. Vitamin D is indispensable for the normal development of the skeleton and teeth. Folic acid is "responsible" for the formation of the central nervous system and blood cells - erythrocytes.
An important role is played by trace elements, which are an essential component of all biochemical reactions in the human body. The expectant mother needs not only potassium, sodium, calcium or iron, which we have heard about and are used to, but also microelements such as silicon, magnesium, copper, and selenium. Magnesium has the ability to reduce the tone of the smooth muscles of the uterus, is indispensable for building bone and cartilage tissue, muscle development. Its deficiency can lead to uterine hypertonicity and the threat of abortion. Without iron, the formation of blood cells is impossible. By the end of pregnancy, the mother "transfers" to the child about 350-400 mg of iron. During the period of breastfeeding - about 300 mg! A low content of this mineral leads to a weakened immune system and makes your baby more vulnerable to viruses and bacteria. Deficiency of copper and zinc leads to disruption of cell division, malformations of the nervous system, heart. Therefore, in the early stages of pregnancy, when all vital organs are laid down, the presence of these trace elements is extremely important. Iodine is one of the most important trace elements, without which the development of the thyroid gland and the full mental development of the child in the future is impossible. According to WHO, about 1 billion people on Earth suffer from iodine deficiency. Entire regions suffering from a lack of this microelement have been identified. Moscow has long and confidently been the leader in this list.
Iodine is one of the most important trace elements, without which the development of the thyroid gland and the full mental development of the child in the future is impossible. According to WHO, about 1 billion people on Earth suffer from iodine deficiency. Entire regions suffering from a lack of this microelement have been identified. Moscow has long and confidently been the leader in this list.
Calcium is essential for the normal formation of muscles, bones and teeth. According to the current recommendations in the Russian Federation, the rate of calcium intake during pregnancy and lactation is 1000-1200 mg per day. The richest source of calcium is milk and dairy products (cottage cheese, cheese, yogurt, kefir, etc.). However, to get the required 1000-1200 mg of calcium per day, a woman needs to drink 1.0-1.5 liters of milk per day or eat about a kilogram of cottage cheese daily! But not everyone loves dairy products. In addition, in the early stages of pregnancy, when toxicosis worries, and morning sickness does not allow you to even enjoy your favorite yogurt, it is quite difficult to decide on such experiments. As a result, the intake of calcium from food in most women is often insufficient.
As a result, the intake of calcium from food in most women is often insufficient.
In order to “cover” the body's increased need for vitamin C (that same ascorbic acid), you need to eat about a kilogram of sour apples a day or drink 3-5 (!) Liters of apple juice. A daily dose of B vitamins can be obtained by eating about 1000 g of black bread daily. Thus, it is almost impossible to provide the body with the right amount of all the necessary vitamins and minerals, relying only on food.
Unfortunately, the results of a study conducted by the Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences are disappointing and indicate a widespread vitamin deficiency among pregnant and lactating women. For example, a deficiency of B vitamins was found in 20-100% (!) of women, vitamin C - in 50%!
What are the consequences of vitamin deficiency?
Deficiencies in essential nutrients, when they are most needed, cause serious and sometimes irreparable damage to the health of mother and child. Insufficient supply of vitamins and minerals to the fetus leads to growth retardation, weight loss and even malformations. The lack of vitamins already in the womb creates unfavorable conditions for the future health of the baby long before he is born.
Insufficient supply of vitamins and minerals to the fetus leads to growth retardation, weight loss and even malformations. The lack of vitamins already in the womb creates unfavorable conditions for the future health of the baby long before he is born.
Where to get the necessary amount of vitamins and minerals?
To effectively solve this difficult task, along with a proper balanced diet, a reliable help to meet the increased needs of the body can be the use of multivitamin complexes specially designed for pregnant women and nursing mothers.
By supplementing the diet with the missing amount of these valuable substances, the necessary conditions are created for the normal course of pregnancy and the birth of a strong and healthy baby.
The benefits of taking vitamins during pregnancy and breastfeeding are undeniable and undeniable. Recently, a lot of preparations containing a complex of vitamins and minerals for pregnant women have appeared on the domestic market, which poses a certain problem of choice for women.
Since in our country the deficiency of such elements as calcium, iron, magnesium, iodine is most common, preference should be given to precisely those complexes that primarily contain precisely these minerals. Not all drugs meet these requirements. The multivitamin-mineral complexes Vitrum Prenatal Forte (Unipharm, Inc., USA) and Elevit (La Roche, Switzerland) have proven themselves well and enjoy well-deserved attention both among doctors and among patients. They are designed on the principle that taking just one tablet a day contains 100% of the recommended daily allowance and fully covers the needs of the body of a woman and a growing baby. These drugs have been clinically tested both in our country and abroad, in which their effectiveness has been proven and confirmed. In the course of research, a decrease in the number of pregnancy complications, such as anemia, the threat of termination, has been established, which positively affects the course and outcome of pregnancy.
How often should I take vitamins?
Most doctors agree that it is advisable to take these drugs constantly, throughout pregnancy and lactation, without interruption. Indeed, in the first months of life, the baby receives all the necessary nutrients only with mother's milk.
There is an opinion that "synthetic" vitamins do not correspond to "natural, natural" and therefore are not absorbed by the body. Statements of this kind are nothing more than a delusion. All "vitamins in tablets" are completely identical in their chemical structure and biological activity to natural ones. Moreover, the assimilation of vitamins from preparations is often higher than from foods in which they are usually found in a “bound”, inactive form. Remember that vitamins do not show themselves by their presence, but by their deficiency.
By clicking on the send button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select a clinic
To clarify the current cost, select a clinic
Clinical Hospital MD GROUPClinical Hospital Lapino-1 "Mother and Child"Clinic KG "Lapino" in Odintsovo (branch)Clinic "Mother and Child" Khodynskoye PoleClinic "Mother and Child" KuntsevoClinic "Mother and Child" SavelovskayaClinic "Mother and Child" Yugo-ZapadMother and Child Clinic NovogireyevoMother and Child Clinic Lefortovo
All directionsSpecialist consultations (adults)Specialist consultations (children)Laboratory of molecular geneticsGeneral clinical examinationsProcedural roomTelemedicine for adultsTherapeutic examinationsUltrasound examinations for adults
01.
Specialist consultations (adults)
02.
Specialist consultations (children)
03.
Laboratory of molecular genetics
04.