Miscarriage should i go to hospital
Miscarriage - NHS
A miscarriage is the loss of a pregnancy during the first 23 weeks.
Symptoms of a miscarriage
The main sign of a miscarriage is vaginal bleeding, which may be followed by cramping and pain in your lower abdomen.
If you have vaginal bleeding, contact a GP or your midwife.
Most GPs can refer you to an early pregnancy unit at your local hospital straight away if necessary.
You may be referred to a maternity ward if your pregnancy is at a later stage.
But bear in mind that light vaginal bleeding is relatively common during the first trimester (first 3 months) of pregnancy and does not necessarily mean you're having a miscarriage.
Causes of a miscarriage
There are potentially many reasons why a miscarriage may happen, although the cause is not usually identified.
The majority are not caused by anything you have done.
It's thought most miscarriages are caused by abnormal chromosomes in the baby.
Chromosomes are genetic "building blocks" that guide the development of a baby.
If a baby has too many or not enough chromosomes, it will not develop properly.
In most cases, a miscarriage is a one-off event and most people go on to have a successful pregnancy in the future.
Preventing a miscarriage
The majority of miscarriages cannot be prevented.
But there are some things you can do to reduce the risk of a miscarriage.
Avoid smoking, drinking alcohol and using drugs while pregnant.
Being a healthy weight before getting pregnant, eating a healthy diet and reducing your risk of infection can also help.
What happens if you think you're having a miscarriage
If you have the symptoms of a miscarriage, you'll usually be referred to a hospital for tests.
In most cases, an ultrasound scan can determine if you're having a miscarriage.
When a miscarriage is confirmed, you'll need to talk to your doctor or midwife about the options for the management of the end of the pregnancy.
Often the pregnancy tissue will pass out naturally in 1 or 2 weeks.
Sometimes medicine to assist the passage of the tissue may be recommended, or you can choose to have minor surgery to remove it if you do not want to wait.
After a miscarriage
A miscarriage can be an emotionally and physically draining experience.
You may have feelings of guilt, shock and anger.
Advice and support are available at this time from hospital counselling services and charity groups.
You may also find it beneficial to have a memorial for the baby you lost.
You can try for another baby as soon as your symptoms have settled and you're emotionally and physically ready.
It's important to remember that most miscarriages are a one-off and are followed by a healthy pregnancy.
How common are miscarriages?
Miscarriages are much more common than most people realise.
Among people who know they're pregnant, it's estimated about 1 in 8 pregnancies will end in miscarriage.
Many more miscarriages happen before a person is even aware they're pregnant.
Losing 3 or more pregnancies in a row (recurrent miscarriages) is uncommon and only affects around 1 in 100 women.
Page last reviewed: 09 March 2022
Next review due: 09 March 2025
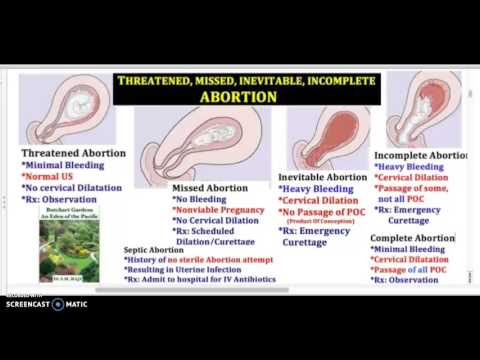
Treating miscarriage | The Royal Women's Hospital
If a miscarriage has begun, there is nothing that can be done to stop it. Any treatment you have will be aimed at avoiding heavy bleeding and infection.
A discussion with the doctor or nurse will help you to work out which treatment options are best and safest for you.
On this page:
- No treatment (expectant management)
- Treatment with medicine
- Surgical treatment (curette)
- Waiting for treatment
- After a miscarriage
No treatment (expectant management)
You can choose to wait and see what will happen. This is called 'expectant management'. If nothing is done, sooner or later the pregnancy tissue will pass naturally. If it is an incomplete miscarriage (where some but not all pregnancy tissue has passed) it will often happen within days, but for a missed miscarriage (where the fetus or embryo has stopped growing but no tissue has passed) it might take as long as three to four weeks.
If it is an incomplete miscarriage (where some but not all pregnancy tissue has passed) it will often happen within days, but for a missed miscarriage (where the fetus or embryo has stopped growing but no tissue has passed) it might take as long as three to four weeks.
While you are waiting you may have some spotting or bleeding, much like a period. When the pregnancy tissue passes, you are likely to have heavier bleeding with crampy, period-like pains. You can use sanitary pads and take pain relieving tablets, such as paracetamol.
If your miscarriage is incomplete, with just a small amount of pregnancy tissue remaining, it’s probably best to take a wait and see approach. But if there is heavy bleeding or signs of infection you will need treatment.
If the tissue does not pass naturally or you have signs of infection, the doctor will recommend a dilatation and curettage (D&C). You and the doctor can discuss and decide the preferred option for you.
Things to know
- There are many reasons why some women prefer to wait and see.
 It may feel more natural, it may help with the grieving process or it may give you more of a sense of control.
It may feel more natural, it may help with the grieving process or it may give you more of a sense of control. - Some women become worried or frightened when the bleeding gets heavier, especially if blood clots, tissue or even a recognisable embryo is passed.
- Usually, the wait and see approach takes longer than any other approaches such as surgery or medication. Sometimes bleeding can last for up to four weeks.
- Although excessive bleeding and blood transfusion are very rare, they are slightly more common with expectant management than with surgery.
- A few women still need to have surgery – sometimes urgently – if they develop infection, bleed heavily or if the tissue does not pass naturally.
- The waiting time can be emotionally draining for some women.
Treatment with medicine
Medicine is available that can speed up the process of passing the pregnancy tissue. For an incomplete miscarriage, the medicine will usually encourage the pregnancy tissue to pass within a few hours. At most it will happen within a day or two. For a missed miscarriage, it may happen quickly, but it can take up to two weeks and, occasionally, longer.
At most it will happen within a day or two. For a missed miscarriage, it may happen quickly, but it can take up to two weeks and, occasionally, longer.
- Medication is not suitable if there is very heavy bleeding or signs of infection. It is usually not recommended for pregnancies that are older than about nine weeks.
- If the tissue does not pass naturally, eventually your doctor will recommend a dilatation and curettage (D&C).
Things to know
- The pregnancy tissue will pass between four to six hours after taking the medicine, during which time you may be in hospital. After a few hours, if the pregnancy hasn’t passed, you may be sent home to wait. This will depend on where you are and which hospital you are in.
- The medicine has side effects which usually pass in a few hours but can be unpleasant, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, fever and chills. The tablets can be swallowed or dissolved under the tongue, or inserted in the vagina.
- After receiving the medication there may be some spotting or bleeding like a period. When the pregnancy tissue passes, you are likely to notice heavier bleeding and clots with strong cramping, period-like pains. You can use sanitary pads and take pain relieving tablets such as paracetamol.
- Some women may need stronger pain killers or a pain relieving injection.
- A few women still need to have surgery, sometimes urgently, if they develop infection, bleed heavily or if the tissue does not pass.
Surgical treatment (curette)
A D&C (or ‘curette’) is a minor operation. The full name is dilatation and curettage. It is done in an operating theatre, usually under general anaesthetic. There is no cutting involved because the surgery happens through the vagina. The cervix (neck of the uterus) is gently opened and the remaining pregnancy tissue is removed so that the uterus is empty. Usually the doctor is not able to see a recognisable embryo.
The actual procedure usually only takes five to ten minutes, but you will usually need to be in the hospital for around four to five hours. Most of this time will be spent waiting and recovering.
You may have to wait a day or two to have a curette and sometimes, while you are waiting, the pregnancy tissue will pass on its own. If this happens and all of the tissue is passed you may not need to have a curette.
A curette is done in the following circumstances:
- You have heavy or persistent bleeding and/or pain.
- The medical staff advise that this is a better option for you; this may be because of the amount of tissue present, especially with a missed miscarriage.
- This is an option you prefer.
Things to know
The risks of a D&C are very low, but include:
- some pregnancy tissue remains in uterus. This can cause prolonged or heavy bleeding and the operation may need to be repeated
- infection needing antibiotics
- damage to the cervix or uterus.
 This is very rare (around 1 in 1000) and, when it does happen, it is usually a small hole or tear which will heal itself
This is very rare (around 1 in 1000) and, when it does happen, it is usually a small hole or tear which will heal itself - excessive bleeding (very rare)
- anaesthetic risks. These are very low for healthy women, but no anaesthetic or operation is without risk.
Waiting for treatment
If you have heavy bleeding with clots and crampy pain, it is likely that you are passing the pregnancy tissue. The bleeding, clots and pain will usually settle when most of the pregnancy tissue has been passed. Sometimes the bleeding will continue to be heavy and you may need further treatment.
You should go to your nearest emergency department if you have:
- increased bleeding, for instance soaking two pads per hour and/or passing golf ball sized clots
- severe abdominal pain or shoulder pain
- fever or chills
- dizziness or fainting
- vaginal discharge that smells unpleasant
- diarrhoea or pain when you open your bowels.

What to do while you are waiting
- You can try to rest and relax at home.
- Usual activity that is not too strenuous will not be harmful. You can go to work if you feel up to it.
- If you have pain you can take paracetamol.
- If there is bleeding, use sanitary pads rather than tampons.
After a miscarriage
- It is usual to have pain and bleeding after a miscarriage. It will feel similar to a period and will usually stop within two weeks. You can take ordinary painkillers for the pain. Your next period will usually come in four to six weeks after a miscarriage.
- See a doctor or attend a hospital emergency department if you have strong pain and bleeding (stronger than period pain), abnormal discharge, (especially if it is smelly), or fever. These symptoms may mean that you have an infection or that tissue has been left behind.
- Try and avoid vaginal sex until the bleeding stops and you feel comfortable.

- Use sanitary pads until the bleeding stops (do not use tampons).
- All contraceptive methods are safe after a miscarriage
- See a GP (local doctor) in four to six weeks for a check-up.
Anti-D injection after a miscarriage
It is important to have your blood group checked. If you’re RhD negative and the fetus is RhD positive this can cause problems for future pregnancies. This is because the fetus’s blood cells have RhD antigen attached to them, whereas yours do not. If small amounts of the fetus’s blood mixes with your blood, your immune system may perceive this difference in blood cells as a threat and produce antibodies to fight against the fetus’s blood. Once your body has made these antibodies they can’t be removed. This is unlikely to have caused your miscarriage and is more likely to affect future pregnancies. Women with a negative blood type usually need an Anti-D injection, which will stop the antibodies forming.
Future pregnancies after a miscarriage
One of the most common concerns following a miscarriage is that it might happen again. However, if you have had one miscarriage the next pregnancy will usually be normal.
However, if you have had one miscarriage the next pregnancy will usually be normal.
If you do try for another pregnancy, try and avoid smoking, alcohol and excess caffeine as they increase the risk of miscarriage. It is recommended that all women take folic acid while trying to conceive, and continue until three months of pregnancy. In your next pregnancy you are encouraged to see your GP and have an ultrasound at about seven weeks. If ultrasound is done too early in pregnancy the findings are often uncertain and cause unnecessary worry.
Feelings and reactions
There is no ‘right’ way to feel following a miscarriage. Some degree of grief is very common, even if the pregnancy wasn’t planned. Partners may react quite differently, just as people can respond differently to a continuing pregnancy. Feelings of loss may persist for some time and you may have mixed feelings about becoming pregnant again. Some friends and family may not understand the depth of emotion that can be attached to a pregnancy and may unreasonably expect for you to move on before you are ready.
Some couples decide that they want to try for a pregnancy straight away, while others need time to adjust to their loss. If you feel anxious about a possible loss in future pregnancies, you may find it helpful to talk to someone about this. If it’s difficult to speak with your friends and family about these issues, your doctor, community support group and counsellors can provide information and assistance.
Related Health Topics
-
- Treatment for miscarriage
Treatment for miscarriage is aimed at avoiding heavy bleeding and infection. It is also aimed at looking after you, physically and emotionally.
-
- (English) PDF (302 KB)
- Treatment for miscarriage
The Women’s does not accept any liability to any person for the information or advice (or use of such information or advice) which is provided on the Website or incorporated into it by reference. The Women’s provide this information on the understanding that all persons accessing it take responsibility for assessing its relevance and accuracy. Women are encouraged to discuss their health needs with a health practitioner. If you have concerns about your health, you should seek advice from your health care provider or if you require urgent care you should go to the nearest Emergency Dept.
The Women’s provide this information on the understanding that all persons accessing it take responsibility for assessing its relevance and accuracy. Women are encouraged to discuss their health needs with a health practitioner. If you have concerns about your health, you should seek advice from your health care provider or if you require urgent care you should go to the nearest Emergency Dept.
Miscarriage. What to do after a miscarriage?
When a woman finds out about her pregnancy, she changes her rhythm of life, especially if the pregnancy is desired. However, depending on many circumstances, miscarriage , that is, a natural termination of pregnancy, may occur. Statistics say that up to 20 percent of pregnancies end in pathological abortions. Often a woman may not know that she was pregnant, as a miscarriage sometimes occurs at a very early stage and seems to be just a normal delay in menstruation followed by heavy discharge. nine0005
If a woman finds out that she is pregnant and wants to become a mother, she should be very attentive to her condition.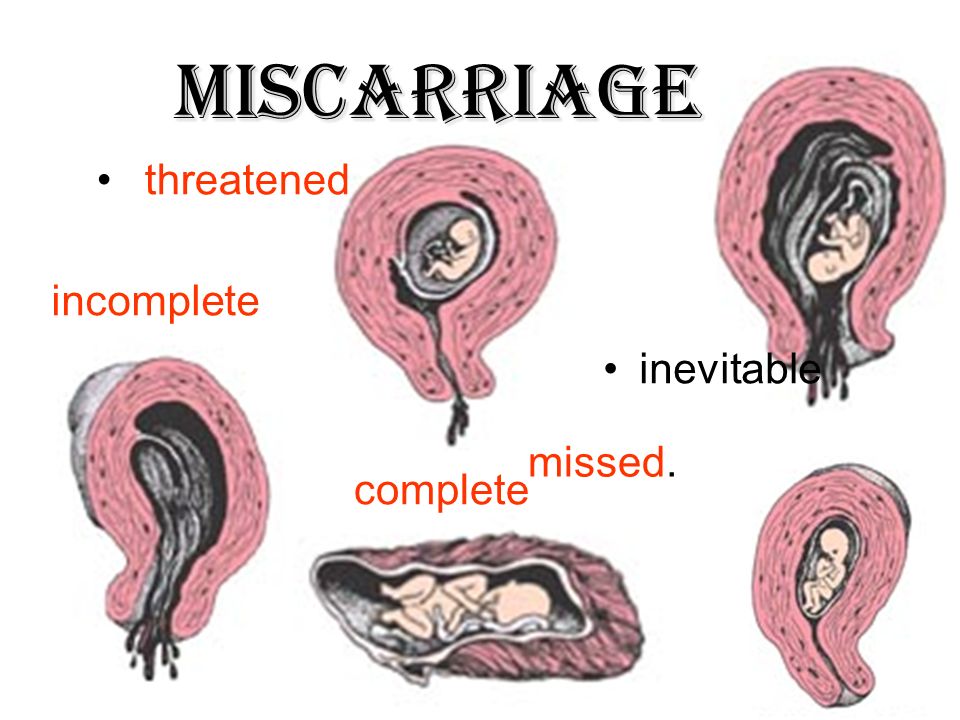 The threat of miscarriage often occurs in the early stages of pregnancy and therefore it is necessary to know what symptoms and signs precede a sudden miscarriage.
The threat of miscarriage often occurs in the early stages of pregnancy and therefore it is necessary to know what symptoms and signs precede a sudden miscarriage.
Signs
The main sign of a suspected miscarriage is bleeding from the uterus. They happen not abundant, pale scarlet or gray-brown. The discharge most often gradually increases and is characterized by sudden spasms or pulling pains in the lower abdomen. These symptoms may last for some time. nine0005
The pains are often so mild that the woman simply does not pay attention to them. They are able to be interrupted, and the woman simply forgets about them, especially if the discharge also stopped, and before that they were insignificant. Meanwhile, the very first symptoms should alert you and you should urgently go to the gynecologist for examination and consultation. Even if the process has stopped, after a few days you can feel a sharp deterioration in health, and then you can no longer save the life of the unborn child. Be sure to pay attention to what exactly comes out with the discharge, if there are tissue fragments, it means that miscarriage has already occurred. Therefore, one should not hesitate to go to the doctor, the fetus may come out, in whole or in parts, there may be white particles or a round gray bubble. When the body is completely cleansed, the pain will subside, but before that it may continue for some time.
Be sure to pay attention to what exactly comes out with the discharge, if there are tissue fragments, it means that miscarriage has already occurred. Therefore, one should not hesitate to go to the doctor, the fetus may come out, in whole or in parts, there may be white particles or a round gray bubble. When the body is completely cleansed, the pain will subside, but before that it may continue for some time.
Terms of miscarriages
A miscarriage is classified as early if it occurred before twelve weeks from the onset of pregnancy. Starting from the 22nd week, if a spontaneous miscarriage has occurred, it is considered late. If the termination of pregnancy occurred before thirty-seven weeks, then this is already called premature birth. All subsequent fetal rejections are called term births and are generally considered normal, since during this period, mostly able-to-survive children are born. In modern medicine, children born after 22 weeks are nursed and subsequently do not differ from those born at term with normal weight. nine0005
nine0005
Types of miscarriages
Specialists have identified several types of miscarriages.
- Complete or inevitable - characterized by pain in the lower back and dilatation of the cervix, hemorrhages from it. The fetal membrane necessarily bursts, and the pregnancy is terminated. The fetus comes out of the uterus, and all discomfort in the form of pain and bleeding stops.
- Miscarriage is different in that the fetus died, but remained in the mother's body. This can be detected by a doctor when examining a woman and when listening to the fetal heartbeat. nine0050
- Repeated miscarriage is rare, it occurs only some time after the first and can occur up to three times in a row in the early stages.
Causes of spontaneous abortion
The vast majority of women, having learned about their pregnancy, want to give birth to a healthy baby. And if there is a spontaneous miscarriage , then for a failed mother this is a real tragedy. Many, having experienced an abortion, try to conceive a child faster again, but first you need to know the reasons for what happened in order to save the fetus in the future. According to statistics, the largest number of miscarriages occurs precisely in the early stages. nine0005
And if there is a spontaneous miscarriage , then for a failed mother this is a real tragedy. Many, having experienced an abortion, try to conceive a child faster again, but first you need to know the reasons for what happened in order to save the fetus in the future. According to statistics, the largest number of miscarriages occurs precisely in the early stages. nine0005
There are several reasons for this:
- Violations in genetics.
This is the most common cause of miscarriage. This is not due to heredity, it is a consequence of the mutation of parent germ cells, which accidentally ended up in unfavorable conditions. This is also the influence of radiation, poisoning, viruses, that is, temporary situations that affected the quality of germ cells. The body thus gets rid of a weak non-viable fetus. It is impossible and unnecessary to prevent such spontaneous abortion. It is only necessary, having decided to become pregnant, to try to cleanse your body of possible harmful influences. nine0005
nine0005
- Hormonal disorders
The cause of miscarriage at a very early stage also lies in the lack of the hormone progesterone, or in the fact that a woman has an excess of male sex hormones that suppress the production of estrogen and progesterone in her body. In this case, the fetus can be saved medically by administering the necessary medicines to the woman. The work of the adrenal glands, as well as the thyroid gland, affects the production of hormones, so a lot depends on the work of these glands throughout the pregnancy process. nine0005
- Immunological causes .
In this case, the vitality of the fetus is directly affected by the Rh conflict. The embryo will inherit the positive Rh of the man, and if the partner has a negative Rh, then her body simply rejects cells that are foreign to him. A similar situation can be prevented by injecting the expectant mother with a variety of progesterone, a process called immunomodulation.
Sexually transmitted infections such as toxoplasmosis, syphilis, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and others are of great danger. External infection: bacteria and viruses infect the fetal membranes, and the body will inevitably reject the embryo. Therefore, before becoming pregnant, you should be examined to know for sure that there are no infections, and if the result is positive, undergo treatment. nine0005
In addition, all inflammatory processes, various diseases of the internal organs, which are accompanied by a persistent high temperature, can also lead to unexpected rejection of the fetus. Rubella is especially dangerous, and viral hepatitis is common. But even a sore throat, mild pneumonia, appendicitis sometimes play a key role and lead to a miscarriage, so the expectant mother must undergo a thorough examination even before the child is conceived, and then beware of all kinds of infections and weakening of the body. nine0005
- Medical abortion.

If a woman had an abortion in a hospital and then became pregnant and decided to give birth, there is a danger that she will have a miscarriage. Abortion is a stress factor for the body, ovarian dysfunction is often observed, inflammatory processes in the female genital organs can begin, and all this will lead, at best, to miscarriage and subsequent repeated miscarriages, and at worst, to infertility. Therefore, you need to think very seriously before going for an abortion. nine0005
- Medicines and certain herbs.
It is advisable for a pregnant woman not to take any medication at all, especially during the first three calendar months. Medicines and herbs can cause various defects in the fetus, which in turn will lead to its rejection. Analgesics and uncontrolled hormonal contraceptives are especially dangerous. Parsley and nettle should be eaten with caution - they cause a high tone of the uterus, which in turn can reject the fetus. nine0005
nine0005
- Stress.
It is no coincidence that in ancient times, pregnant women were protected from unrest, they were created comfortable conditions, and they tried to give as many positive emotions as possible. Now the direct dependence of the health of the unborn baby on the mental state during pregnancy has already been proven. Any stress, fear and overstrain can cause an unexpected termination of pregnancy. If you have a problem (death of a loved one, divorce, etc.), you need to find sedatives with the help of a doctor, they will help you cope with this period. nine0005
- Unhealthy lifestyle.
Of course, the intake of alcoholic beverages, an unhealthy lifestyle, smoking, even coffee consumption in large quantities, improper diet - all this can lead to a transient miscarriage. Therefore, the expectant mother should prioritize and change her rhythm of life in advance in order to give birth to a healthy child.
- Sexual intercourse, falling, heavy lifting. nine0063
-
woman's age. At the age of 20-30 years, the risk of spontaneous miscarriage is 9-17%, at 35-40 years old - 20%, at 40-45 - 40%;
-
alcohol abuse;
nine0050 -
abuse of caffeine;
-
smoking;
-
drug use;
-
chronic diseases of the mother;
-
maternal infections;
-
use of medications incompatible with pregnancy;
- nine0002 history of spontaneous abortion.
 The risk of subsequent pregnancy loss in women with one miscarriage in history is 18-20%, with two - 30%, with three - 43%.
The risk of subsequent pregnancy loss in women with one miscarriage in history is 18-20%, with two - 30%, with three - 43%.
All of these factors can affect the fetus, so you should protect yourself and your baby by avoiding these activities.
What to do after a miscarriage?
Having experienced the tragedy of losing a child, parents often intend to immediately conceive a new baby, but they are afraid that everything will happen again. In this case, you do not need to make independent decisions, but consult a doctor. And first of all, it is necessary to identify the cause that led to the miscarriage. For this, the expectant mother needs to undergo as thorough an examination as possible. nine0005
If no obvious cause is found, the fetus most likely has a chromosomal abnormality. In this case, you should not worry, since the next conception will occur with a different set of chromosomes, which means that there will be no repeated miscarriage. If the miscarriage was repeated, it is necessary to contact a geneticist and conduct a study of the set of chromosomes of both parents. If it turns out that the cause was an infection, then it is necessary to fully recover. If we are talking about sexual infections, then both parents need to undergo therapy. It is necessary to take tests for hormonal studies, hemostasis systems and determine the immune status. nine0005
If the miscarriage was repeated, it is necessary to contact a geneticist and conduct a study of the set of chromosomes of both parents. If it turns out that the cause was an infection, then it is necessary to fully recover. If we are talking about sexual infections, then both parents need to undergo therapy. It is necessary to take tests for hormonal studies, hemostasis systems and determine the immune status. nine0005
After a miscarriage, should be treated, if necessary, and pause between conceptions. During pregnancy, you should not take medications to prevent re-spontaneous pathological termination of pregnancy. Therefore, you can become pregnant only after the end of the course of treatment. If the cause was hormonal abnormalities, then the expectant mother should take special drugs to stabilize the background, and at this time she should never become pregnant. During the pause, you need to choose contraceptives with the help of a doctor. You can go to a specialized clinic where you will be prescribed a full course of rehabilitation. nine0005
nine0005
The first week after a miscarriage women often experience pain in the lower abdomen, heavy bleeding, so you should refrain from sexual intercourse with a man. If there is severe bleeding, acute pain in the lower abdomen, convulsions, high fever, palpitations, nausea, vomiting, then you should immediately consult a doctor to identify the cause of this condition. It is necessary to plan a subsequent pregnancy not earlier than three months after this situation, but preferably six months later. Until that time, it is worth reconsidering your outlook on life, giving up hard work, eating right and wisely, taking vitamins, exercising, losing weight if you are overweight, stop smoking, drinking alcohol, think over your daily routine. nine0005
It is very important during this recovery period to have a positive attitude and confidence that the next attempt will be successful. This is harder to do than to say, because after a miscarriage the woman is in a depressed state and is afraid of a repetition of the situation.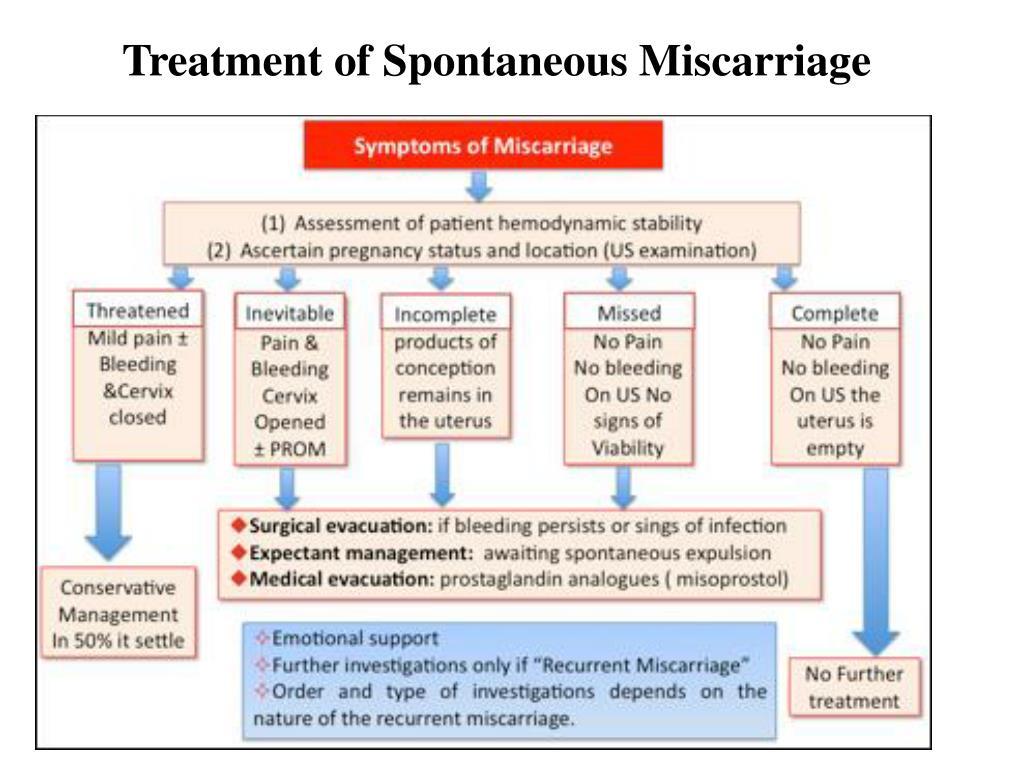 You can’t get hung up on your problem, during this period it’s better to do some favorite thing, relax, change the situation, travel, visit the city more often. The modern ecological situation in cities has a bad effect on women's health, so private trips to nature, a trip to the sea, to friends in another city can distract from painful thoughts. An important role in this case is played by the woman's relatives and, above all, the husband, who can surround her with care and attention, creating peace of mind. nine0005
You can’t get hung up on your problem, during this period it’s better to do some favorite thing, relax, change the situation, travel, visit the city more often. The modern ecological situation in cities has a bad effect on women's health, so private trips to nature, a trip to the sea, to friends in another city can distract from painful thoughts. An important role in this case is played by the woman's relatives and, above all, the husband, who can surround her with care and attention, creating peace of mind. nine0005
You may need to contact a counseling psychologist or psychotherapist. Yoga classes, self-education, visiting theaters, exhibitions and temples have a very beneficial effect on the psyche of a woman and help to distract from her problems. Helping others who have a difficult life situation, caring for the sick can also have a beneficial psychological effect and help you look at your problems from the outside.
Remember, the human body is a self-healing system, it just needs a little help. nine0005
nine0005
Miscarriage due to miscarriage | Articles by EMC doctors about diseases, diagnosis and treatment
What is a miscarriage?
According to medical statistics, miscarriage is the most common complication during pregnancy. About 10-20% of all recorded pregnancies end in miscarriage. Miscarriage is a sporadic, sudden, termination of pregnancy, which is accompanied by complete or partial emptying of the uterus. nine0005
Missed pregnancy loss (MP) can be seen on ultrasound. It consists in confirming the non-viability of the fetus without bleeding. The ST can end in a miscarriage, when the body gets rid of the dead fetus on its own, or in a medical abortion, when medical or surgical manipulations are used to clean the uterine cavity.
Causes of miscarriage and miscarriage
80% of miscarriages occur in the first trimester before 12 weeks. In 50% of cases, this occurs due to genetic defects in the fetus. The threat of miscarriage due to chromosomal abnormalities decreases with the course of pregnancy: by 20 weeks it is 10-20% versus 41-50% in the first trimester. The main cause of genetically determined early miscarriages are autonomous trisomies - when three homologous chromosomes are present in the cells instead of two. Such defects occur at the time of conception and are not subject to correction. They lead to miscarriage or to the development of severe genetic diseases. In addition to genetics, immunological, endocrine and infectious causes are distinguished. nine0005
The main cause of genetically determined early miscarriages are autonomous trisomies - when three homologous chromosomes are present in the cells instead of two. Such defects occur at the time of conception and are not subject to correction. They lead to miscarriage or to the development of severe genetic diseases. In addition to genetics, immunological, endocrine and infectious causes are distinguished. nine0005
In the second trimester, various diseases and disorders in the mother's body become the main cause of miscarriage.
There is a list of factors that can trigger early pregnancy loss:
Symptoms and signs of miscarriage
You can suspect a miscarriage by sudden spotting and sharp pain in the lower abdomen. If these symptoms appear, seek immediate medical attention. The doctor must conduct an ultrasound diagnosis. Transvaginal scanning (TVS) is considered the gold standard for diagnostics - when the sensor is inserted into the uterus through the vagina. If TVS is not available, a transabdominal scan can be applied - through the anterior abdominal wall. nine0005
Missed pregnancy may be asymptomatic and not manifest until the next scheduled ultrasound.
How does a miscarriage occur?
The miscarriage process has four stages. This does not happen overnight and lasts from several hours to several days.
The first stage - the threat of miscarriage. Among the symptoms: pulling pains in the lower abdomen, scanty blood discharge, increased uterine tone. The process of detachment of the placenta from the place of attachment in the uterus begins. The internal os is closed. The main thing is to seek help in time, then with proper therapy if there is a chance to stop the miscarriage and save the pregnancy. nine0005
The process of detachment of the placenta from the place of attachment in the uterus begins. The internal os is closed. The main thing is to seek help in time, then with proper therapy if there is a chance to stop the miscarriage and save the pregnancy. nine0005
The second stage - the beginning of a miscarriage. Strong discharge, the cervical canal is ajar, the doctor diagnoses the final detachment of the placenta.
Third stage - miscarriage in progress. You can feel the regular contractions of the uterus, the outcome of the fetus, placenta and uterine contents, profuse blood discharge has begun.
The last fourth stage is a complete miscarriage. The pregnancy is interrupted, the uterine cavity does not contain the fetus and products of conception.
nine0204 How to determine ST? It should be remembered that a miscarriage can be diagnosed only during an ultrasound examination. Home tests will not give reliable results. Ultrasound will show the presence or absence of a heartbeat in the fetus.