Mild contractions at 34 weeks
34 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms and Baby Development
34 Weeks Pregnant: Your Baby’s Development
At 34 weeks pregnant, your baby is getting bigger, and there’s less room in your womb for those cartwheels! As a result, you may notice that his movements feel different — possibly a little less forceful now — but you’ll still sense his wiggles and stretches.
Around this time, your baby may also be dropping deeper into your pelvis as he gets ready to make his grand entrance. As early as this week, or maybe in the weeks following, if you have an ultrasound or checkup with your healthcare provider, you may learn that your baby has moved into a head-down position in preparation for birth.
Wondering what color eyes your baby will have when he's born? Eye color depends on the amount of the pigment melanin that's present. Babies born with little or no pigment will have blue eyes, but that color may change over the first year or two. If your little one has darker eyes at birth, the color is less likely to change. You can read more about when do baby’s eyes change color here.
Speaking of birth, your due date is fast approaching, and you'll want to get a head start on those final preparations. Take this quiz to find out how close you are to being ready for your baby’s arrival.
If you’re expecting a boy, his testicles are likely to have dropped into the scrotum by now. Sometimes, one or both of the testicles don’t descend before birth. If this is the case for your little one, the testicles are likely to drop by the time your baby is 6 months old.
RELATED PREGNANCY TOOL
Baby Name Generator
By gender:
Unisex
By theme:
Nature
Mythology
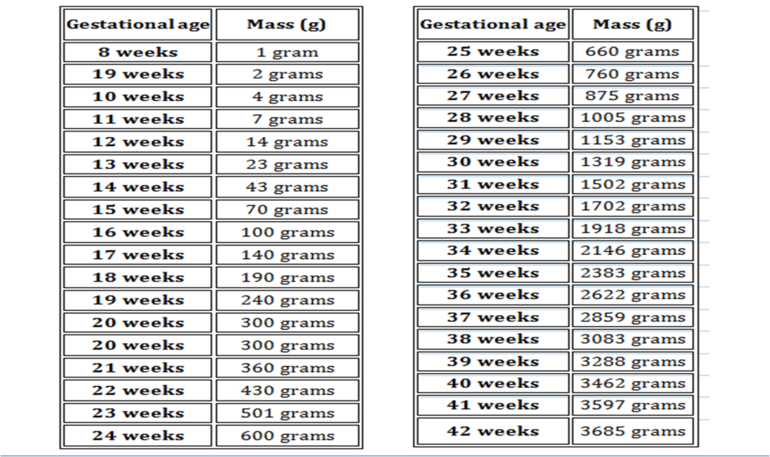
The Size of the Fetus at 34 Weeks Pregnant
At 34 weeks, the average fetus is about the size of a cantaloupe. He may measure nearly 12 inches long, crown to rump, and weigh more than 4 1/2 pounds. Check out the illustration below for a rough idea of what your little one might look like and how your baby may be positioned at 34 weeks.
Check out the illustration below for a rough idea of what your little one might look like and how your baby may be positioned at 34 weeks.
Mom's Body at 34 Weeks Pregnant
Wondering how many months pregnant you are at 34 weeks? As pregnancy doesn't fit neatly into full months, you could be around seven or eight months pregnant. In the coming weeks, it’s a good idea to watch out for the signs of preterm labor. Preterm labor is when labor starts before 38 weeks of pregnancy. Preterm labor and preterm birth are of concern because babies born too early may not be developed enough and are at high risk of having serious health problems. Some of the signs of preterm labor include
mild abdominal cramps with or without diarrhea
increased vaginal discharge
change in vaginal discharge — watery, bloody, or with more mucus
constant dull backache in the lower back
regular or frequent contractions
your water breaking, which could be a large flow or just a slow stream.
If you’re 34 weeks pregnant with twins, it's especially important to watch for these signs. When you're expecting twins or multiples, you have about a 50 percent greater chance of going into early labor than if you're having just one baby. Don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns, and learn more about your babies in our twin pregnancy week-by-week guide.
34 Weeks Pregnant: Your Symptoms
At 34 weeks pregnant, here are some of the symptoms you may be experiencing:
Braxton Hicks contractions. As you near your due date, Braxton Hicks contractions — also known as prelabor or practice contractions — are more likely to get stronger and occur more often. It’s most likely nothing to worry about if these cramping sensations come at irregular intervals and subside when you change positions, but if you suspect that you are having preterm labor contractions, contact your healthcare provider right away.
 Although your provider is the best person to assess your symptoms, take the time to learn more about the difference between Braxton Hicks contractions and true labor contractions as it might help put your mind at ease.
Although your provider is the best person to assess your symptoms, take the time to learn more about the difference between Braxton Hicks contractions and true labor contractions as it might help put your mind at ease. Enlarged breasts. Your breasts are probably becoming even fuller as you roll into the last few weeks of the third trimester. This could cause some discomfort as the skin stretches and becomes itchy. By this time, you’re no stranger to the bit of relief a good moisturizing lotion can provide, but don’t forget that a properly fitting bra can also help. Many specialty underwear shops and department stores have bra fitting specialists who can help you find a bra that fits correctly and gives you maximum support. You may also have to adjust the strap length or use a bra clasp extender as the weeks progress as well as in the first few months of motherhood. Learn even more about breast changes during pregnancy.
Pelvic pain. At 34 weeks, as your baby drops lower into your pelvis in preparation for birth, you might experience some pelvic pain, lower-back discomfort, or pressure on your bladder.
 On the bright side, because your baby has dropped, you may feel less pressure on your diaphragm and lungs, making it easier to breathe. To help relieve any pelvic pain, try to stay off your feet when you feel most uncomfortable. A soak in a warm bath may also give you some relief. If these ideas don’t work, speak to your healthcare provider for further advice on what to do.
On the bright side, because your baby has dropped, you may feel less pressure on your diaphragm and lungs, making it easier to breathe. To help relieve any pelvic pain, try to stay off your feet when you feel most uncomfortable. A soak in a warm bath may also give you some relief. If these ideas don’t work, speak to your healthcare provider for further advice on what to do.
Swollen ankles and feet. It’s not uncommon for women to have swelling in their ankles and feet at this stage of pregnancy. One way to help relieve the swelling is to reduce standing time as much as you can. Plus, when you’re sitting down, you can prop up your legs on a pillow. For those times when you’re feeling discomfort from the swelling and you can’t sit, wearing supportive shoes might help.
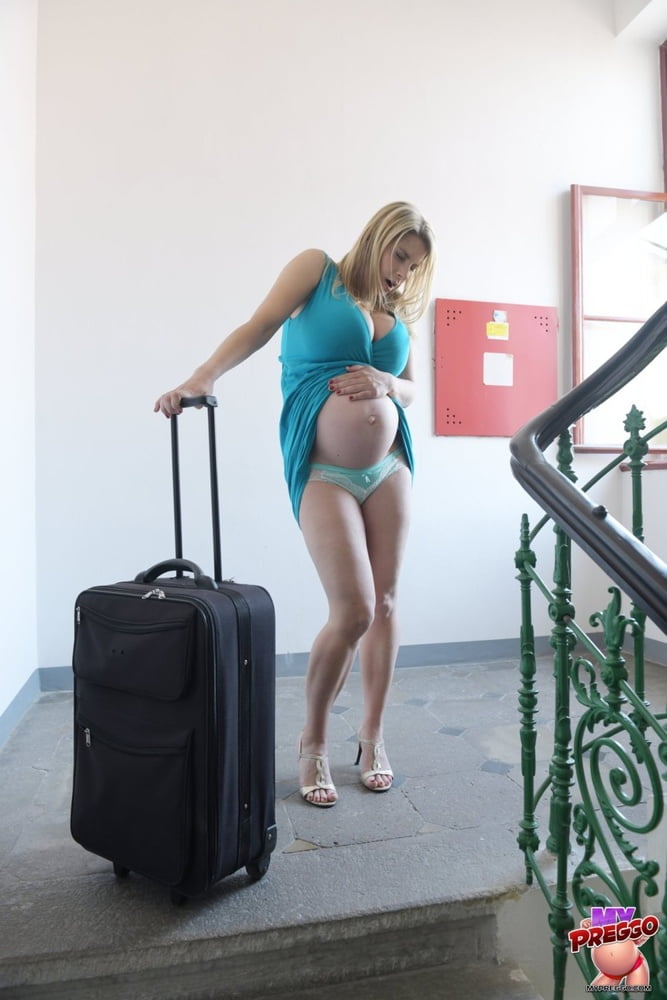
Constipation. Bowel movements that are hard to pass and infrequent may occur for many different reasons. Whatever the cause, they can be very uncomfortable! Good tactics include drinking plenty of water, prune juice, or other fruit juices, as well as eating high-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables, wholegrain bread, and bran cereal.
 Also, try walking or gentle exercises to help your digestive system. Finally, eating smaller, more frequent meals rather than a few large meals might improve your digestion.
Also, try walking or gentle exercises to help your digestive system. Finally, eating smaller, more frequent meals rather than a few large meals might improve your digestion.
34 Weeks Pregnant: Things to Consider
The arrival of a new baby can be hard for older siblings to handle because of all the changes that happen. Parents put a lot of effort into preparing for the new baby and, after the baby arrives, caring for the newborn requires much of the family’s attention. It’s not unusual for older siblings to feel some jealousy and react to the changes by acting out. However, parents can help ease the transition and prepare siblings for the new addition to the family. Talking about the pregnancy in a way that makes sense to older siblings can help. For example, you could explain where the new baby comes from in an age-appropriate way. There are children’s books that can help you with this. Plus, including kids in the preparation for the arrival of the new baby can be a great way to help them embrace the idea of your newborn joining the family.
 One way to involve your older children is to let them help you shop for items you need for your newborn. It's a good idea to talk to them about the role they can play in helping you with the new baby before he arrives, too. Be sure to spend one-on-one quality time with your older children so they understand they’re still valued and loved members of the family.
One way to involve your older children is to let them help you shop for items you need for your newborn. It's a good idea to talk to them about the role they can play in helping you with the new baby before he arrives, too. Be sure to spend one-on-one quality time with your older children so they understand they’re still valued and loved members of the family.
Calcium helps form and harden your baby’s bones and teeth, so getting enough calcium during pregnancy is a top priority, both for your baby's health and for your own. Your prenatal vitamins may contain calcium, but it’s also important to eat foods that are rich in calcium. Some great food sources other than dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt include sardines, leafy green vegetables like broccoli, and calcium-fortified juices. This means lactose-intolerant moms-to-be have great options for getting extra calcium, too! Learn more about how much calcium you need during pregnancy and ask your healthcare provider whether you’re getting enough.
 Your provider may recommend you take a calcium supplement or get more by making changes to your diet.
Your provider may recommend you take a calcium supplement or get more by making changes to your diet.
The last thing you want to worry about when you go into labor is deciding what to throw into your bag to take to the hospital. That’s why we've compiled a comprehensive hospital bag packing checklist to make sure you don’t leave out those must-haves and nice-to-haves you might want to take with you on the big day. We list the things you, your partner, and your newborn baby will need.
If you have time this week, consider stocking up your pantry and pre-cooking batches of food that you can freeze for after your baby’s arrival. Getting these things ready in advance can ensure you have one less thing to worry about when you’re busy tending to your newborn. You might also like to set up online grocery deliveries now so that they’re ready to go, or ask friends and family members to pitch in with delivering some home-cooked meals during those first few weeks postpartum.
If you haven’t already, start thinking about what comfort measures you might like during labor, and ask your healthcare provider what options may be available to you. Your options may include medical pain relief options like an epidural as well as non-medical pain relief like massage or focused breathing.
34 Weeks Pregnant: Ask Your Doctor
What position is your baby in?
If your baby is breech, what are the chances he’ll move into a head-down position?
If your baby is breech closer to the due date, what would you recommend?
What exercises or stretches can you do to help relieve the pressure on your lower back?
Is there an infant CPR training course you recommend?
34 Weeks Pregnant: Your Checklist
Make sure you have the essential gear for your newborn.

If you haven’t already chosen a proper baby car seat, now is a good time to take a look at your options.
Think about whether you want visitors at the hospital after your baby is born. You might be OK with a few friends and members of your closest family stopping by during hospital visiting hours, but having too many could be stressful. Some parents prefer to organize a sip and see party as opposed to have lots of separate visits.
Start finalizing your baby name choice, or at least start consolidating your shortlist of favorite names. Our Baby Name Generator can help you find the perfect name.
If you’d like to have a newborn photoshoot, find and book a photographer in your area whose work you like and who you will feel comfortable with. To make your choice, you might like to see some examples of past work, or ask other moms in your area for their recommendations. If the photographer is experienced in newborn shoots, ask him or her for tips on the best time of day to schedule the shoot, where the shoot will take place, and how long the shoot usually takes.
 You should also talk about whether the shoot will have a theme, and who is responsible for bringing any items like blankets, headbands, and props.
You should also talk about whether the shoot will have a theme, and who is responsible for bringing any items like blankets, headbands, and props.
There’s so much baby gear out there, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed by the choice. We asked Pampers Parents to vote and review the best products in categories ranging from the best stroller to the best breast pump… and everything else in between…to help make your choice a little easier. If you have some spare time this week, check out the best baby products as voted by thousands of Pampers Parents.
Sign up for even more weekly pregnancy tips:
Recognizing Premature Labor | Patient Education
What is Premature Labor?
A term pregnancy takes about 40 weeks to complete. Babies born before 37 weeks may have problems breathing, eating and keeping warm. Premature labor occurs between the 20th and 37th week of pregnancy, when uterine contractions cause the cervix, the mouth of the uterus or womb, to open earlier than normal. This can result in premature birth.
This can result in premature birth.
Certain factors may increase a woman's chances of having premature labor, such as carrying twins. However, the specific cause or causes of premature labor are not known. Sometimes a woman may have premature labor for no apparent reason.
Warning Signs of Premature Labor
It may be possible to prevent a premature birth by knowing the warning signs of premature labor and by seeking care early if these signs occur. Warning signs and symptoms for premature labor include:
- Uterine contractions that happen six or more times in an hour, with or without any other warning signs.
- Menstrual-like cramps felt in the lower abdomen that may come and go or be constant.
- Low dull backache felt below the waistline that may come and go or be constant.
- Pelvic pressure that feels like your baby is pushing down. This pressure comes and goes.
- Abdominal cramping with or without diarrhea.
- Increase or change in vaginal discharge such as change into a mucousy, watery or bloody discharge.

Continue reading
Uterine Contractions: How to Tell What's Normal
It is normal to have some uterine contractions throughout the day. They often occur when you change positions, such as from sitting to lying down. It is not normal to have frequent uterine contractions, such as six or more in one hour. Frequent uterine contractions or tightenings may cause your cervix to begin to open.
Since the onset of premature labor is very subtle and often hard to recognize, it is important to know how to feel your abdomen for uterine contractions. You can feel for contractions in this way:
- While lying down, place your fingertips on the top of your uterus
- A contraction is a periodic tightening or hardening of your uterus. If your uterus is contracting, you will actually feel your abdomen get tight or hard, and then feel it relax or soften when the contraction is over.
What To Do If You Think You May Have Symptoms of Premature Labor
If you think you are having uterine contractions or any other signs and symptoms of premature labor:
- Lie down tilted towards your side.
 Place a pillow at your back for support.
Place a pillow at your back for support.
- Sometimes lying down for an hour may slow down or stop the signs and symptoms.
- Do not lie flat on your back, because lying flat may cause the contractions to occur more often.
- Do not turn completely on your side, because you may not be able to feel the contractions.
- Hydrate yourself by drinking several large glasses of water. Sometimes being dehydrated can cause contractions.
- To tell how often contractions are occurring, check the minutes that elapse from the beginning of one contraction to the beginning of the next.
- You have six or more uterine contractions in one hour
- You have any of the other signs and symptoms for one hour
- You have any spotting or leaking of fluid from your vagina
With acknowledgement to Dr. Robert K. Creasy for his assistance and to the March of Dimes Birth Defects Foundation for their support.
Robert K. Creasy for his assistance and to the March of Dimes Birth Defects Foundation for their support.
what is happening, the development of pregnancy and fetus
Week by week
33 - 36 weeks of pregnancy
Elena Gevorkova
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Moscow
33rd week
BABY
At the 33rd week, the weight of the fetus is 1800-1900 g, and the body length is 43-44 cm. The amount of subcutaneous fat increases, due to which the folds and wrinkles on the baby's body are smoothed out, the skin turns pink. The fluffy hairs that cover the body of the fetus, which are called lanugo, become smaller, and the hair on the head darkens and thickens. The baby's skin is covered with a thin layer of cheese-like lubricant, its largest amount accumulates in the folds - axillary, cervical, inguinal - as well as on the back of the body and face. Grease is a viscous mass of white color, it is a secret of the sebaceous glands, mixed with skin scales. Its function is to protect the baby's skin from damage and facilitate its passage through the birth canal.
Its function is to protect the baby's skin from damage and facilitate its passage through the birth canal.
By this time, the movements of the fetus gradually change their habitual character - they become more and more limited and less pronounced in amplitude due to insufficient space. However, the strength of the movements increases, since by this time the muscular system of the fetus is already sufficiently strengthened. Sharp and strong tremors of the fetus can be sensitive to the internal organs of a pregnant woman. Depending on the position of the baby, the liver, stomach, bladder, ribs, etc. may “suffer”. By 33 weeks, the movements of the fetus are already quite coordinated.
FUTURE MOTHER
The height of the fundus of the uterus from the level of the pubis at this time is 34 cm. The volume of the abdomen is increased due to the weight of the baby, placenta, amniotic fluid. The increase in uterine pressure and strong tremors of the fetus can cause some discomfort in the pregnant woman.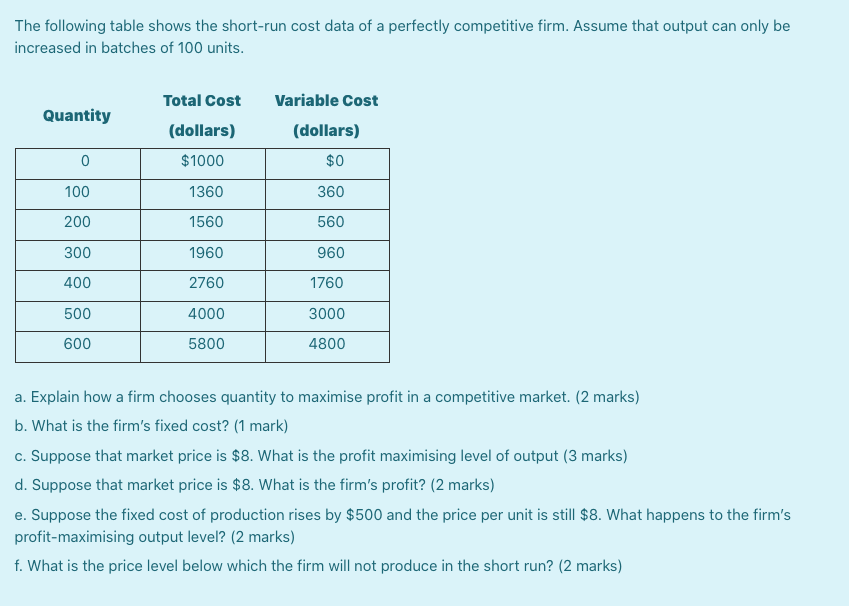 Many movements previously available to the expectant mother, such as squats, become limited. Moderate physical activity - walking, fitness, etc. - Requires frequent respite.
Many movements previously available to the expectant mother, such as squats, become limited. Moderate physical activity - walking, fitness, etc. - Requires frequent respite.
A change in the center of gravity increases the load on the spine, which can manifest itself as pain in the lower back, sacrum, and pelvic region. The pressure of the uterus on the stomach can cause or increase nausea, heartburn, and a feeling of heaviness. An increase of almost 1 liter of the volume of circulating blood in the body of a pregnant woman increases the load on the kidneys, and the growing uterus puts pressure on the bladder. All this can be manifested by frequent urination.
These ailments are usually associated with the mechanical pressure of the uterus on the surrounding organs; they are not symptoms of the disease and are temporary. And to relieve nausea, heartburn and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, frequent meals in small portions are recommended.
34th week
BABY
By this time, the weight of the fetus is approximately 2100 g, and the height is 45 cm. From this period, the cheeks are very pronounced, because, developing a sucking reflex, the fetus often sucks its thumb. This leads to the fact that the baby strengthens the facial muscles, in particular the buccal. The total muscle mass of the fetus increases, the bones become denser.
From this period, the cheeks are very pronounced, because, developing a sucking reflex, the fetus often sucks its thumb. This leads to the fact that the baby strengthens the facial muscles, in particular the buccal. The total muscle mass of the fetus increases, the bones become denser.
There is an intensive functioning of the baby's internal organs. During the day, he repeatedly swallows portions of amniotic fluid. Passing through the gastrointestinal tract, the amniotic fluid stimulates the work of the muscular wall. The dense part of the amniotic fluid, which is a suspension of skin flakes, lubricant, vellus hair, is processed by the enzymes of the liver and pancreas, and the liquid part is intensively excreted by the kidneys of the fetus.
Approximately 500 ml of amniotic fluid is treated in this way per day. The production of bile continues, which accumulates in the gallbladder and, as the stomach fills with a suspension of amniotic water, enters the lumen of the small intestine. The functional development of the liver and pancreas during the prenatal period does not play a significant role, since the fetus does not have digestion; processes for the production of bile and enzymes: lipase, which breaks down fats; trypsin, which breaks down proteins; amylase, which breaks down carbohydrates, etc. - are preparatory in nature.
The functional development of the liver and pancreas during the prenatal period does not play a significant role, since the fetus does not have digestion; processes for the production of bile and enzymes: lipase, which breaks down fats; trypsin, which breaks down proteins; amylase, which breaks down carbohydrates, etc. - are preparatory in nature.
FUTURE MOTHER
Most pregnant women begin to feel rather intense false contractions at this time. Strictly speaking, false or training contractions, which are also called Braxton-Hicks contractions, can occur after the 20th week of pregnancy: the longer the period, the more frequent and pronounced the contractions. They are episodic contractions of the muscles of the uterus, lasting from a few seconds to 3-5 minutes. Braxton-Hicks contractions are not pathological - this is a completely normal process of preparing the muscles of the uterus for the difficult process of childbirth. This phenomenon with varying degrees of intensity is observed in almost all pregnant women.
This phenomenon with varying degrees of intensity is observed in almost all pregnant women.
Many primiparas are concerned about the difference between preparatory contractions and labor.
Here are some differences:
- Frequency of contractions. Training bouts do not become more frequent, the intervals between them may be different. Labor pains are regular, the interval between them is reduced.
- Duration of contractions. Training bouts have different durations, from a few seconds to minutes, their duration does not increase over time. Labor pains tend to lengthen.
- Soreness. Preparatory contractions may not be accompanied by pain at all, or they may be quite noticeable, up to a feeling of sharp pain. However, their intensity weakens over time and the pain disappears. Labor pains are painful and constantly intensify.
- Localization. Braxton-Hicks contractions can be felt in various places - in the lower part of the uterus, in the region of its bottom, along the side walls, covering the entire abdomen.
 Labor pains begin with a contraction of the lower abdomen, spreading to the front. Often in childbirth, pain in the lower back is felt, while the nature of the pain resembles menstrual pain.
Labor pains begin with a contraction of the lower abdomen, spreading to the front. Often in childbirth, pain in the lower back is felt, while the nature of the pain resembles menstrual pain. - Relationship with body position. Preparatory contractions may disappear after walking or, on the contrary, rest. A change in body position can relieve the tension in some muscles, which also causes a decrease in the appearance of training contractions. Labor pains may be somewhat relieved in a certain position - when leaning forward, in the knee-elbow position, etc. - but their frequency and duration will still increase.
- Reaction to medication. The use of antispasmodic drugs - NO-ShPY, BUSCOPAN, PAPAVERIN, etc. - approved by the attending physician, can weaken or completely stop false contractions. The effect of antispasmodics on labor pains is minimal.
Any pain or discomfort should be reported to the gynecologist: this will help the expectant mother to resolve doubts and cope with anxiety. Feeling safe is the best companion of pregnancy.
Feeling safe is the best companion of pregnancy.
35th week
BABY
The length of the body of the fetus is 46--47 cm, weight - 2200-2300 g. These figures in the last weeks of pregnancy can vary greatly. The growth and weight of the fetus largely depend on heredity, individual parameters. Starting from 35 weeks, the baby will gain 200-250 g weekly. The fetus occupies almost the entire uterine cavity, its back is rounded, arms and legs are bent, brought to the body. The layer of subcutaneous fat increases significantly, which significantly “rounds” the body of the fetus. The closing of the eyelids and the contraction of facial muscles change the baby's facial expression quite often. The skin of the body becomes pink, smooth, the amount of cheese-like lubricant begins to decrease. Vellus hair covers separate small areas of the body - shoulders, back. The nails protrude beyond the tips of the fingers.
FUTURE MOTHER
The fundus of the uterus is 35 cm higher from the pubis and 15 cm higher from the navel. particularly light. The growing uterus does not allow the lungs to expand, respiratory movements are limited, which is manifested by shortness of breath. Almost all pregnant women to one degree or another experience a feeling of shortness of breath - a feeling of lack of air, frequent and shallow breathing, a desire to take a deep breath. As a rule, these sensations occur for a period of 28 weeks and reach their peak at the 35-36th week. After 37 weeks of pregnancy, the abdomen droops, which greatly facilitates breathing.
particularly light. The growing uterus does not allow the lungs to expand, respiratory movements are limited, which is manifested by shortness of breath. Almost all pregnant women to one degree or another experience a feeling of shortness of breath - a feeling of lack of air, frequent and shallow breathing, a desire to take a deep breath. As a rule, these sensations occur for a period of 28 weeks and reach their peak at the 35-36th week. After 37 weeks of pregnancy, the abdomen droops, which greatly facilitates breathing.
Shortness of breath during pregnancy is associated not only with the mechanical pressure of the uterus on the diaphragm, but also with the relaxing effect of hormones on the muscles of the bronchi and lungs. Most often, it is provoked by physical activity - climbing stairs, a long walk, etc. However, it is not uncommon for shortness of breath to occur at rest, especially when lying down. Both prolonged lying in a horizontal position and excessive exercise can contribute to increased shortness of breath. To alleviate her condition, the expectant mother needs to be rational about the daily routine - it is reasonable to alternate rest and physical activity. It is important to monitor your posture, as slouching exacerbates shortness of breath, reducing the already insufficient lung capacity. If shortness of breath is accompanied by blue lips or nails, sensations of pain behind the sternum, darkening before the eyes, nausea or vomiting, fainting, then an urgent need to consult a doctor.
To alleviate her condition, the expectant mother needs to be rational about the daily routine - it is reasonable to alternate rest and physical activity. It is important to monitor your posture, as slouching exacerbates shortness of breath, reducing the already insufficient lung capacity. If shortness of breath is accompanied by blue lips or nails, sensations of pain behind the sternum, darkening before the eyes, nausea or vomiting, fainting, then an urgent need to consult a doctor.
36th week
BABY
The growth of the fetus by this term is about 47--48 cm, and the weight is about 2300-2500 g. The fetus enters a period of intensive preparation for childbirth. Each of the organs is already functionally mature enough to ensure the viability of the fetus. 36 weeks is the beginning of the preparatory journey, and the upcoming weeks of pregnancy are designed to finally form the baby's readiness for extrauterine life.
By 36 weeks, the fetus is in its final position in the uterus. As a rule, this is a longitudinal position, occipital presentation - in this case, the fetus is located head down, facing the mother's back. This is the most comfortable position that ensures the greatest safety of the baby during childbirth. More rarely, breech presentation is a condition in which the buttocks and legs of the fetus are located at the bottom of the uterus. This is a relative indication for operative delivery. The final decision on caesarean section or independent childbirth is made by doctors in each case individually.
A change in the position of the fetus in the uterus is possible, but this happens infrequently, since at this time the fetus occupies almost all the free space in the uterus, which significantly limits its motor activity. As a rule, if a change in the position of the fetus occurs, then only from the pelvic to the head. The reverse cases - the transition of the baby from the head position to the pelvic position - are practically impossible, since the head of the fetus is heavier than the buttocks and occupies the longitudinal position completely, by analogy with a float in water, the heavy part of which always outweighs.
FUTURE MOTHER
The height of the uterus is 36 cm, the volume of the abdomen is maximally increased, the bottom reaches the costal arches. At this time, the pregnant woman's body also begins its journey of preparing for the upcoming birth. Changes begin with hormonal changes: the level of special hormones, oxytocin and prostaglandins, increases slightly in a woman. These active substances play a crucial role in the process of preparing for childbirth and directly during them. A slight increase in their level from the period of 36-37 weeks of pregnancy leads to an increase in Braxton-Hicks training contractions, an increase in urination and defecation, and the appearance of more abundant mucous discharge from the vagina.
How can you tell real contractions from training contractions?
Shemyakina Natalya Nikolaevna, head of the obstetric department of the Leleka maternity hospital , will help you figure it out.
Training contractions, or as they are also called, fake, or Braxton-Hicks contractions, are irregular contractions that do not have increasing intensity. The uterus may tone up, but normally, it should pass quickly.
For example, the tone appeared once in half an hour and the uterus relaxed rather quickly. Then the tone reappeared only after two hours and again passed. These are training contractions, they do not increase in intensity and do not become more frequent.
Training bouts are physiologically provided by our body. So the uterus is preparing to do the hard work in the process of childbirth. Normally, training contractions appear in terms of pregnancy close to childbirth - from the 37th week of pregnancy.
The appearance of training contractions in the early stages of pregnancy is not the norm
The uterus can tone up with an active lifestyle, physical activity, with a change in body position, but this tone should quickly pass. Normally, the uterus should not often come into tone. And even more so, contractions, as such, should not be until the 37th week of pregnancy.
And even more so, contractions, as such, should not be until the 37th week of pregnancy.
Braxton-Hicks contractions in the early stages are a threat of preterm labor. If a woman has contractions periodically during the day: after an hour, after 2, then again after an hour, (even if they are not regular), for periods up to 37 weeks, such a tone should alert the expectant mother.
Because this is not the norm, but the threat of premature birth. This is an occasion to contact a specialist and change your rhythm of life, put on a bandage. The causes of premature birth are most often internal, caused by hormonal disorders and a violation of the physical health of a woman. But significant physical activity and stress can also cause premature birth.
Labor pains
Unlike training pains, labor pains are regular. The uterus comes to tone first once every 15 minutes, and after a while - once every 7-10 minutes. Contractions gradually become more frequent, longer and stronger. And already occur every 5 minutes, then 3 and finally every 2 minutes.
And already occur every 5 minutes, then 3 and finally every 2 minutes.
True labor pains are contractions every 2 minutes, 40 seconds. If within an hour or two the contractions intensify - pains that begin in the lower abdomen or in the lower back and spread to the stomach - most likely, these are real labor pains.
Training contractions are NOT so much painful as unusual for a woman. When the expectant mother sees how the stomach comes into tone, its shape changes and it becomes dense, like an inflated ball. This might scare you a little. But a woman must understand that in real, labor pains, there must be a clear periodicity, intensification and acceleration over a certain period of time. Real fights never stop, but practice fights do. The uterus then comes to tone, then relaxes.
Women often confuse contractions with tone, which is caused by other physiological processes in the body. For example, increased intestinal peristalsis, intestinal infections, colic, etc.
What else should alert a woman?! If within an hour or two the uterus periodically comes into tone and mucous, bloody (streaked with blood or brown) discharge appears, then most likely there are structural changes in the cervix - it opens. Also an important sign to seek help is the discharge of the mucous plug long before childbirth. Her departure in terms of childbirth, a week or two before childbirth is normal.
Tracking labor pains
There are several methods for determining the types of contractions. A woman can do this herself, writing down the frequency and duration of contractions on paper or tracking them using special programs for a computer and phone. Or you can contact a doctor at antenatal clinic or at the maternity hospital, where a specialist will conduct fetal monitoring (fetal CTG). With the help of 2 sensors, the fetal heartbeat, uterine contractions are monitored and it is determined whether these are training contractions or labor.