How to tell if your child is mildly autistic
Signs of autism in children
Autism in young children
Signs of autism in young children include:
- not responding to their name
- avoiding eye contact
- not smiling when you smile at them
- getting very upset if they do not like a certain taste, smell or sound
- repetitive movements, such as flapping their hands, flicking their fingers or rocking their body
- not talking as much as other children
- not doing as much pretend play
- repeating the same phrases
Autism in older children
Signs of autism in older children include:
- not seeming to understand what others are thinking or feeling
- unusual speech, such as repeating phrases and talking ‘at’ others
- liking a strict daily routine and getting very upset if it changes
- having a very keen interest in certain subjects or activities
- getting very upset if you ask them to do something
- finding it hard to make friends or preferring to be on their own
- taking things very literally – for example, they may not understand phrases like "break a leg"
- finding it hard to say how they feel
Autism in girls and boys
Autism can sometimes be different in girls and boys.
Autistic girls may:
- hide some signs of autism by copying how other children behave and play
- withdraw in situations they find difficult
- appear to cope better with social situations
- show fewer signs of repetitive behaviours
This means autism can be harder to spot in girls.
The National Autistic Society has more information about autistic women and girls.
Non-urgent advice: Get advice if:
- you think your child might be autistic
You could speak to:
- a GP
- a health visitor (for children under 5)
- any other health professional your child sees, such as another doctor or therapist
- special educational needs (SENCO) staff at your child's school
Getting diagnosed can help your child get any extra support they might need.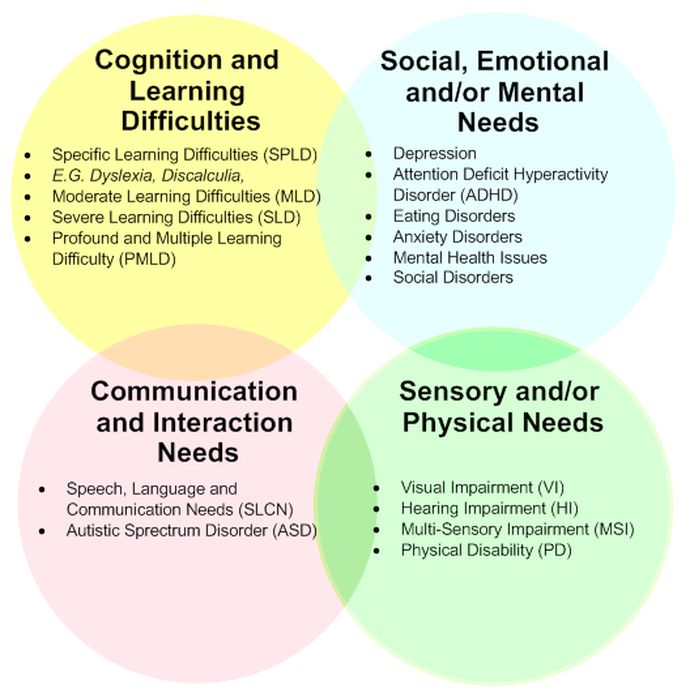
Find out how to get diagnosed
Page last reviewed: 11 November 2022
Next review due: 11 November 2025
Can a Child Be Slightly Autistic?
A child could have mild symptoms of autism, but parents and guardians should still take proactive steps to seek a diagnosis.
When a child has autism spectrum disorder (ASD), caregivers can work with professionals to develop appropriate strategies in response. These strategies help children thrive in their environment through appropriate accommodations, therapy, and parent training.
While some children with autism may rarely encounter challenges related to their disorder, others may find that negative experiences increase as they get older. This can lead to unwanted stress, potentially up to the point of a crisis event. In extreme cases, a child could lose opportunities to advance in school or other life areas.
Understanding a child’s needs is important. Individuals in their life should never brush away observations that a child might have a behavior disorder. Instead, they can educate themselves on the signs of ASD and look into the next best actions to take.
Individuals in their life should never brush away observations that a child might have a behavior disorder. Instead, they can educate themselves on the signs of ASD and look into the next best actions to take.
Being “On the Spectrum” Can Mean a Wide Variety of Experiences
Autism is described as a spectrum of disorders for a reason. Signs of autism can present differently.
Some individuals will have significant behavior and communication challenges that make the possibility of an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) diagnosis more likely.
In other cases, caregivers may notice occasional “atypical” behaviors but that don’t immediately cause them to seek a full behavioral health evaluation.
In the latter scenario, a child may never have their autism diagnosed or addressed therapeutically. It’s possible that mildly-expressed forms of ASD behavior go completely unnoticed.
But another possibility is that an undiagnosed child or their caregiver will feel frustrated by a lack of explanation for certain behavioral events. They may struggle with socialization, for instance, or they may lack commitment to extracurricular activities.
They may struggle with socialization, for instance, or they may lack commitment to extracurricular activities.
Ignoring the possibility of an autism diagnosis, especially if a child seems mostly neurotypical, can make it more difficult for them to adjust and have their needs met. For this reason, teachers and caregivers who observe subtle signs of ASD should speak with a mental health professional.
A child’s parents, teachers, and others with a direct role in their life are the best observers when it comes to picking up on a possible autism spectrum disorder diagnosis. Only a licensed mental health professional can come to a full, accurate diagnosis, but you don’t have to be a professional to suspect that an ASD diagnosis is possible.
What Are Some Possible Signs of Mild Autism?
ASD encompasses a broad range of behavioral patterns and experiences.
Inconsistency from one ASD case to the next can make it more difficult for caregivers to fully connect the dots.
Even so, there are many common behaviors that could point to a possible ASD diagnosis. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), these may include:
- Repetitive play or verbal expressiveness (echolalia)
- A fixation on certain activities, ideas, or concepts
- A reluctance to engage in new experiences or to disrupt routines
- Aversion to certain forms of interaction, especially hugging or cuddling
- Avoiding eye contact and being difficult to engage in conversation
- Missing verbal or physical cues, such as not looking at where someone is pointing
- Having difficulty understanding others’ feelings or talking about feelings in general
- Reluctance to socialize or a preference for isolation
- Trouble expressing their needs or wishes
- Unexpected reactions to certain sights, sounds, textures, or smells
- Tantrums or explosive aggression with unexpected triggers
Some children with ASD may appear to have a learning disability or other form of behavior disorder. They may also have co-occurring medical challenges, such as gastrointestinal (GI) discomfort, trouble sleeping, or seizures. Many individuals with autism may also have mental health disorders, such as anxiety, depression, or an attention deficit disorder.
They may also have co-occurring medical challenges, such as gastrointestinal (GI) discomfort, trouble sleeping, or seizures. Many individuals with autism may also have mental health disorders, such as anxiety, depression, or an attention deficit disorder.
It is also possible that any of the above behavior signs could be related to something other than autism, such as if a child has attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). This possibility should encourage those in the child’s life to seek a diagnostic assessment from a professional who can advise parents and others how best to address their needs.
Any Form of Autism Can Benefit From a Therapeutic Approach
Unnoticeable signs of autism can be detrimental to a child’s wellbeing when caregivers neglect to investigate further. People with autism can be given strategies and support that can help them work alongside their condition and be successful while still being completely and utterly themselves.
Once you begin talking with professionals about your child’s unique situation and any unexpected behaviors or occurrences, you can begin to understand him or her better. With support from clinicians and the community, you can provide conditions and strategies that encourage your child to have a less stressful, more fulfilling life.
With support from clinicians and the community, you can provide conditions and strategies that encourage your child to have a less stressful, more fulfilling life.
If you think your child or a child in your life might have autism, take the first step toward seeing if they need extra care, attention, and support from you. Seek a diagnosis and support from professionals who use an evidence-based approach to achieve goals that help children thrive.
Therapeutic Pathways offers evidence-based autism treatment, including assessments post diagnosis for treatment purposes. Contact us today with concerns or for resources to help you determine if your child has ASD and the steps to take after receiving a diagnosis.
Mild form of autism. Symptoms and signs of mild autism.
Mild form of autism. Symptoms and signs of mild autism. Gimranov Rinat Fazylzhanovich
Neurologist, neurophysiologist, experience - 33 years;
Professor of Neurology, MD;
Clinic for Rehabilitation Neurology. About the author
About the author
Publication date: September 8, 2020
Updated: October 24, 2022
Mild autism is the fact that symptoms of an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are present, but not so severe as to critically impair quality of life and social connections person. Among other types of autism, it has the best prognosis.
Proper corrective work and timely treatment help an autistic person with a mild form to overcome symptoms and integrate into society. Such people get an education, make friends, arrange a personal life and find a job.
The first signs of mild autism become noticeable from the age of 1, in early childhood. At the moments when the time comes for the baby to communicate with other people or show the expected emotions. And here there are difficulties.
Article content:
- Symptoms
- 1.1 touch Disorders
- 1.2 The immunity of social signs
- 1.3 Difficulties when interacting with the company
- 1.
 4 Emotion Disorders
4 Emotion Disorders
- 2 Methods of treatment
- 2.1 of which areas are folded from which Clages are folded from which areas. used literature
Symptoms
People with mild autism are able to live in society, but the symptoms of pathology haunt them daily. Sometimes, they limit and impede social interaction.
Sometimes, interlocutors and peers try to avoid autistic people, push them away. Simply because people do not know about their diagnosis, and misinterpret the nuances of behavior, the characteristics of speech.
Or they believe the myths about autistics.
Consider in detail the leading symptoms of mild autism.
Sensory disorders
Loud noises, noise, flickering lights can cause real pain or be very distracting. It happens that even a quieter sound, in comparison with the main background, serves as a distraction. Such people will not agree to go to a music concert or to the cinema, they try to avoid shopping centers and noisy crowds, they do not like parties.
Unreceptiveness of social signs
Without special training, memorization of body language signals natural for the average person, autistic people ignore other information in conversation, except verbal.
And speech constructions are not always understood correctly.
They cannot assess the timbre of their own or someone else's voice, determine whether the phrase is said neutrally or with some kind of subtext.
Unable to feel what distance between interlocutors in a given situation is socially acceptable.
Difficulties in interacting with society
Arise due to a lack of understanding of the stereotypical behavior of other people.
An autistic person can talk for a long time on an interesting topic without noticing that the interlocutor is bored. Simply because he avoids eye contact and does not see that he is bored.
There are problems with situational facial expressions, or such people generally do without it, not expressing their attitude to what is happening with body language.
They cannot guess what other people are thinking or experiencing, so they respond inappropriately in conversation. Not able to give the expected feedback, such as sympathy, at the right time.
Emotional disorders
Lack of emotions in mild autistic people is a myth. They experience the full range of human emotions, but often show them inappropriately: excessively or imperceptibly.
Many people with this diagnosis additionally suffer from OCD - obsessive-compulsive disorders. Among “mild autists”, the frequency of depressive disorders, anxiety, and mood swings is higher. However, researchers and doctors agree that these are not so much the symptoms of the disease as the result of the specific life of an autistic person.
Existing in a world that you don't quite understand and that doesn't understand or accept you is hard psychologically. Because of this, people who do not receive the support of loved ones are constantly in an anxious state or go into severe forms of depression. This is typical not only for adults, but also for teenagers, very young children.
This is typical not only for adults, but also for teenagers, very young children.
Therefore, the support of loved ones is so important for autistic patients for successful treatment and integration into society.
Methods of treatment
If signs of a mild degree of autism appear, it is necessary to immediately carry out diagnostics, organize treatment and corrective work. Until the condition of the child worsened.
The earlier they start working with a patient, selecting adaptive methods, the higher the chances of noticeable progress by the age of elementary school.
As such, there is no treatment for mild autistic symptoms. Rather, it is about correcting behavioral reactions: the basis of the course is training and corrective work carried out by psychologists, speech therapists, and doctors.
One of the specific features of the pathologies of the ASD group is the intolerance of change. A sudden change in the schedule or environment will lead to a regression of what has been achieved.
Therefore, it is better to study with different people first, until the child finds “his own”. This is better than changing the doctor after a month, because of the rejection of the patient.
To learn and socialize faster, a clear schedule of the day, a schedule of tasks for the day, week, month, helps. Goals discussed in detail with the child and the time to achieve them. The fewer surprises and surprises, the better.
What approaches make up the therapy
A range of methods for the treatment of mild autism in children has been developed. And each patient, depending on the specific manifestations of the disease, selects his own.
The complex of therapy consists of the following segments:
- Speech therapy, emphasis on the development of speech in all its forms. At the same time, non-verbal communication skills are being improved.
- Occupational therapy - needed for the development of fine motor skills, the development of household skills.
 The kid learns to serve himself, perform tasks of varying complexity, he develops a readable handwriting.
The kid learns to serve himself, perform tasks of varying complexity, he develops a readable handwriting. - ABA therapy (applied behavior analysis - applied behavior analysis). A technique based on behavioral technologies and teaching methods. But to count on the result, you need an experienced mentor.
- Psychotherapy - sessions help to realize oneself as a part of society. So the child feels more comfortable in public, in society.
- Group lessons - teaching social skills in groups helps to master the lines of behavior accepted in society. Instills adequate communication skills among peers.
- Family interaction therapy helps not only the child, but also the parents to come to an understanding. The baby gradually ceases to react sharply to the slightest changes. Learns to evaluate other people's points of view, broadens their horizons.
I am a text block. Click the edit button to change this text. Diverse and rich experience Constant quantitative growth and the scope of our activities require us to analyze positions.
You need to apply a set of techniques. This will help to compile a complete description of a child with autism when he goes to study at a comprehensive school.
Medications are also used, but mainly to correct severe behavioral disorders.
Treatment for autistic disorder is a long process that stretches over years and sometimes decades, even in mild cases.
References
Was this article helpful?
You can subscribe to our newsletter and learn a lot of interesting things about the treatment of the disease, scientific achievements and innovative solutions:
Your e-mail
I agree with the privacy policy and the processing of personal data
Please leave this field empty.
We're sorry!
How can this article be improved?
Please leave this field empty.
For more information, you can check with neurologists on our forum!Go to the Forum
If you have any questions, ask your doctors on our forum!
Go to forum
ADD/VIEW COMMENTS
Gimranov Rinat Fazylzhanovich
Make an appointment with a specialist
×
Autism - types of autism: mild form in children and adults
Informburo.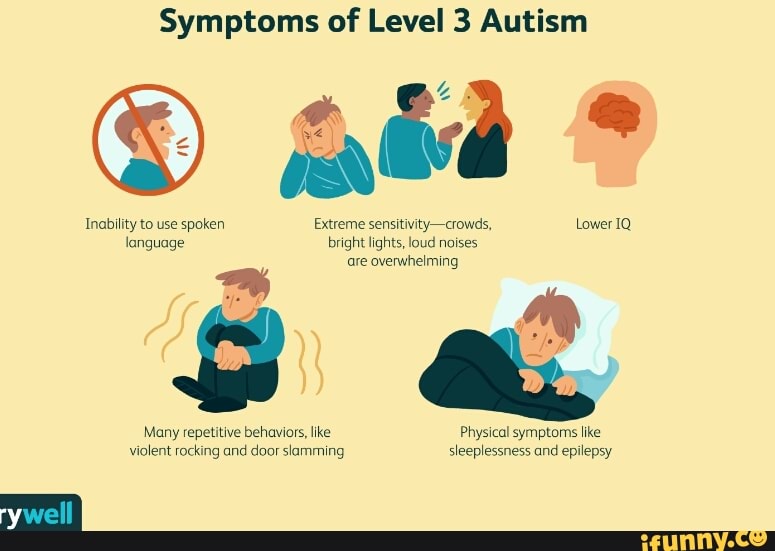 kz understands what autism is, what forms it has, and how people with autism spectrum disorders are helped in Kazakhstan. And we also spoke on condition of anonymity with a person with Asperger's syndrome (a mild form of autism), who turned to specialists only after 20 years, and as a child thought that "everything around is just smarter."
kz understands what autism is, what forms it has, and how people with autism spectrum disorders are helped in Kazakhstan. And we also spoke on condition of anonymity with a person with Asperger's syndrome (a mild form of autism), who turned to specialists only after 20 years, and as a child thought that "everything around is just smarter."
What is autism and why is it wrong to say "disease"?
Autism is a pervasive (that is, general, extensive) name for a mental state with a reduced or distorted ability to interact with the social environment. A person with this type of psyche (most often it is called disorder or deviation from the norm ) cannot learn through the social environment and receive from it a lot of information important for "normal" development.
See also: "It is very important to accept the baby as he is." Why autism is not a disease
Doctors most often recognize children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) as developmentally retarded - such children start talking late, do not look into the eyes, withdraw into themselves. Kindergarten teachers and teachers in schools cannot afford to give them special attention and deal with them individually, so parents are advised to send them to a remedial kindergarten or special school.
Kindergarten teachers and teachers in schools cannot afford to give them special attention and deal with them individually, so parents are advised to send them to a remedial kindergarten or special school.
"There are difficulties in recognizing a lie or some kind of hint. For others, some signals may be obvious, but it can be difficult for me. For example, once they told me that they were flirting with me, but I didn’t understand. It’s a shame sometimes very much,” says Ilyas (the name was changed at the request of the hero). “A phrase like “You understand what I mean” is damned at all. No, I don’t understand.”
It is not clear which influences the occurrence of autism spectrum disorders more: the interaction of many genes or rare mutations. Symptoms of ASD include:
-
Stereotypical behavior. A person is absorbed in monotonous actions, as he tries with all his might to avoid any changes in the way of life;
-
Lack of learning.
 Nearly 100% of children with Kanner's syndrome (a nuclear form of childhood autism) have an IQ level below 100. At the same time, learning problems are not only in severe ASD: the intelligence of people with Asperger's syndrome is usually average or even above average, but the learning problem is not disappears;
Nearly 100% of children with Kanner's syndrome (a nuclear form of childhood autism) have an IQ level below 100. At the same time, learning problems are not only in severe ASD: the intelligence of people with Asperger's syndrome is usually average or even above average, but the learning problem is not disappears; -
Seizures. A quarter of people with severe forms of ASD and about 5% of autistic people with a mild disorder and a normal level of intelligence development suffer from seizures;
-
Hyperexcitability and motor activity, disorder of concentration. Most often, hyperactivity manifests itself with tasks and actions imposed from outside, it is easier for a person to concentrate on independently chosen tasks;
-
Outbursts of anger , caused by the fact that a person cannot explain his needs or that someone interferes with his rituals and routine;
-
Increased sensory perception and increased attention.
 There is no firm evidence that sensory symptoms may be a feature that distinguishes autism from other developmental disorders.
There is no firm evidence that sensory symptoms may be a feature that distinguishes autism from other developmental disorders.
Of course, there are a number of traits that can lead to a diagnosis of autism in a person (for example, any distortion of verbal communication), but if you look at the details, then no two people with an autism spectrum disorder are the same. Different habits, different fears and manners, different principles and methods of interaction with the surrounding reality. Other methods. Not the kind people are used to, whose condition is closer to the norm accepted in society. Hence the main marker by which these people can be "identified" is stigmatization. Children and adults with an autism spectrum disorder are immediately recognized as mentally ill, and some relatives, parents, or even doctors try to treat autism. Sometimes in rather strange ways.
So, on one of the information sites, under an article about autism spectrum disorders, a woman seriously writes that the wording "another type of psyche" was invented by the Americans, whose goal, of course, is to destroy our people (the site is Russian, and the people mean Russian), and, in order to resist, this must be "uprooted". For example, eliminating dairy products from the child's diet. How and in what way this will help - the commentator does not specify.
For example, eliminating dairy products from the child's diet. How and in what way this will help - the commentator does not specify.
Is autism a disease?
There are no autism spectrum disorders in the classification of mental disorders and diseases in Kazakhstan according to ICD-10 (Tenth Revision of the International Classification of Diseases). According to specialists from the Bulat Utemuratov Foundation, autism as a mental illness is included in the classification of diseases, but there is no concept of "autism spectrum disorder", which does not apply to diseases.
Autism is not a disease / Photo by the Bulat Utemuratov Foundation
The classification of mental disorders adopted in Russia includes several diagnoses related to ASD - childhood autism, atypical autism, Asperger's syndrome (F-84.0, F-84.01 and F-84.5 according to the ICD-10 classification, respectively). It is important that during the life of one person these diagnoses can change, and doctors can confuse one with the other. The problem has not been sufficiently studied, and society knows very little about it at all. What do you imagine when you hear "autism" other than Dustin Hoffman in "Rain Man"?
In the public domain there are special tests for diagnosing autism spectrum disorders. It is important to understand that after going through them, you will not be able to make a diagnosis for yourself, but they will help you navigate and understand whether you need to go to a specialist. You can take such a test here or here (the latter is more complicated, it is just designed for self-diagnosis of Asperger's syndrome; tests for children can also be found on the same site).
"The disorder manifests itself in the fact that, for example, you may be annoyed by too bright lights or loud sounds. I'm not sure that this can be understood correctly the first time. I'll try to explain. You don't feel discomfort or some other unpleasant feelings, but horror "Stranger company - panic attack, no clear, predictable structure and topic of conversation - panic attack. Help, although it may sound funny, repetitive actions, it calms the nerves, and sometimes alcohol."
There are statistics only for children: according to the PMPK (Psychological-Medical-Pedagogical Commission) for 2018, the number of children with autism in Kazakhstan is 3820. However, according to an expert assessment by Professor Eric Fombonne (University of Oregon, USA), who studied the prevalence of the disorder in Kazakhstan – We have 59 thousand children with ASD. Unfortunately, it is impossible to name the exact number of people who are born, live and try to overcome sometimes insurmountable barriers in interaction with the social environment in Kazakhstan.
In the United States, for example, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, autism is diagnosed in 1 in 68 children.
Autism is an umbrella term for many different conditions. The root difference between people with ASD lies in the disorder of empathy (a person's ability to perceive other people's emotions and respond to them), due to genes. About 70% of cases are associated with mutations in genes. Also, the cause of autistic disorder may be late pregnancy, late age of parents at the time of conception, illness of the mother during pregnancy. Modern methods of genetic examination can detect autism in only 25% of patients.
About 70% of cases are associated with mutations in genes. Also, the cause of autistic disorder may be late pregnancy, late age of parents at the time of conception, illness of the mother during pregnancy. Modern methods of genetic examination can detect autism in only 25% of patients.
How is autism treated?
Autism, specialists of the Bulat Utemuratov Foundation are sure, is not a disease, but a special state of development of a child with impairments in three areas: communication, social interaction, patterns of repetitive actions. Therefore, autism is not treated, but helps to improve skills in these areas in order to improve the quality of life of the child. Yes, a person with ASD needs special treatment, and this does not make him different from everyone else, but society is not ready to recognize ASD as a variant of the norm.
Asperger's Syndrome (named after the Austrian pediatrician and psychiatrist Hans Asperger) is a high-functioning autism disorder that retains basic cognitive skills but has severe socialization problems.
Asperger's is often characterized by marked clumsiness. The term was introduced in the 80s, and diagnostic standards were developed in the 90s.
Say the word "autistic" and then describe what comes to mind. This is a child. Most likely a boy. He sits in a corner, hugging his knees, and sways from side to side. He hardly talks, only mumbles something under his breath, does not look into his eyes and plays with only one toy. Plus, he's probably a genius. So? Type "autism" in a search engine and you will get two dozen articles mentioning Newton, Einstein, Mozart, Marie Curie. In the minds of the majority, this "disease" works on the principle of conservation of energy: if you cannot integrate into social society, you will be a great mathematician. This is not true.
See also: Learning to speak with JASPER: how to help people with autism
"The hardest part, to be honest, was when I was a child. I don't know how it is for others, because Asperger's is the mildest form of autism, but it's a shame when you're doing homework with your mom and you tell her that you can’t understand something, you don’t understand and you can’t do anything about it, and the answer is: “You can do everything, don’t be lazy!” Of course, it’s important to say that mom is not to blame for this, such disorders have only recently been diagnosed, but this gives rise to fears in you, a feeling of inferiority, a feeling that they are here - normal people who understand that you are, and you are somewhere outside.
People with ASD do develop asynchronously: some cognitive skills improve faster, some may not show progress at all, but the philistine idea of their genius is exaggerated - there are as many gifted among them as among "normal" people. "Genial madman" (or "scientific idiot") is a very different disorder - savantism (outstanding abilities in one or more areas of knowledge, in contrast to the general narrowness of the personality) - which does not occur only in autistic people.
The latest Danish study - the largest to date - looked at 6,517 cases of autism from a sample of 650,000 children followed over 10 years. No association with the MMR (measles-mumps-rubella) vaccine could be found.
The otherness of people with ASD is due to their characteristics: a person can be obsessed with mechanical objects and echolocation (uncontrolled repetition of other people's words) or reversal of pronouns (you ask: “What is your name?”, the child answers: “Your name is Ilyas”), fixated on what -something repetitive action, may have difficulty with when to say, why to say and what to say in a given situation. Most often, people with ASD cannot assess social risks, because they do not understand the generally accepted rules and unspoken signals (the most difficult is with the unspoken rules of behavior, for example, the same flirting). In addition, people with ASD are more prone to stress and phobias.
Most often, people with ASD cannot assess social risks, because they do not understand the generally accepted rules and unspoken signals (the most difficult is with the unspoken rules of behavior, for example, the same flirting). In addition, people with ASD are more prone to stress and phobias.
"At the same time, I'm not stupid, I understand that my fears have no rational basis. No one is watching me, no one is laughing at me, and normal people have problems with speech," says Ilyas. I have a daughter, I am the same as you. My morning differs from yours only in daytime tranquilizers and an auto-training program at the mirror. I have a job, friends, although they are few, but, for example, I do not need to take drugs to please serotonin pit. I don't get out of it most of my life."
Due to the fact that there are problems with fitting into social norms, a person with an autism spectrum disorder tends to streamline: this is how a world that was not created for him becomes more or less comfortable.
I must say that children with autism are well trained, but this, in contrast to working with ordinary children, is a much more complex process, subject to a slightly different logic. By helping a child with ASD learn from an early age, professionals can transform the child. In Kazakhstan, both non-profit and commercial organizations work with children with ASD. They provide a variety of services, including behavioral intervention services, sports activities, tutoring services, inclusion in general education programs, and more.
"Learning is very difficult. Information is hard to assimilate, it's hard for you to understand what you read or what they tell you, but even if you understand, but don't know why it is necessary, how to use this information, it is assimilated even worse. At the same time, you see, that others already bounce off their teeth and think that you are just stupid. Why do you need to behave this way at school and not otherwise? This question tormented me all my childhood. But you can adapt. Doing it like this is great, good, I will Imitation turned out to be the best option for me: you choose an object for yourself and just behave in the same way," says Ilyas.
But you can adapt. Doing it like this is great, good, I will Imitation turned out to be the best option for me: you choose an object for yourself and just behave in the same way," says Ilyas.
Corrective therapy, or so-called behavioral intervention, is used to work with people with ASD. The goal is to eliminate unwanted behaviors and develop useful skills for the person. (Thus, they work not only with autism, but also with phobias and, for example, drug addiction).
"There are statistics on children who are registered and receive services at the Asyl Miras Autism Centers," says Zhanyl Mukashova, program director of the Bulat Utemuratov Foundation, "including the diagnostic service, intervention programs, the program of work with parents. Currently, 6783 are registered in our centers children aged 0-15 years, of which 82% of children, according to the results of the work of the diagnostic service, revealed the autism spectrum.
There are at least two types of interventional therapy: Early Intensive Behavioral Intervention (EBE) and problem-based outpatient or counseling services.