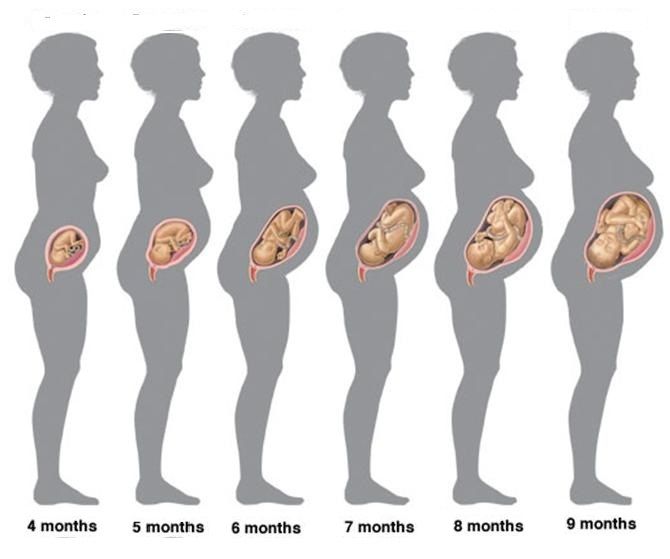
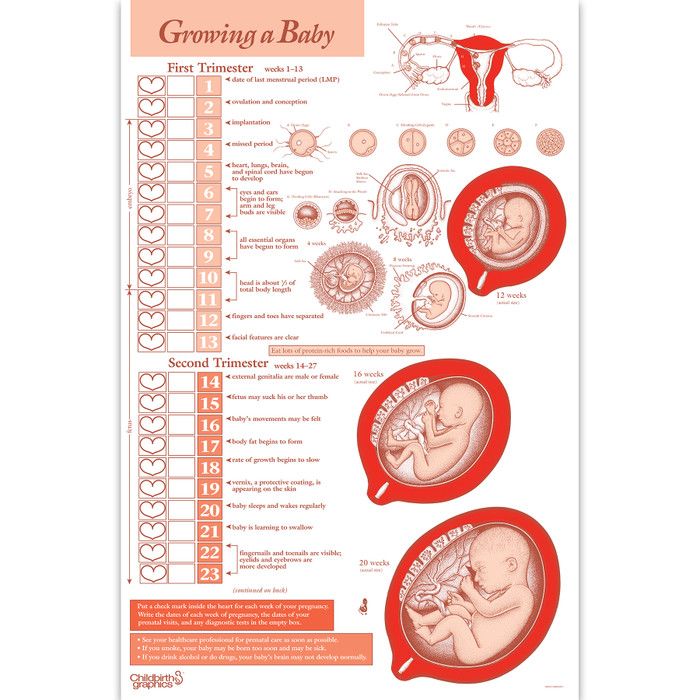
Second trimester baby growth
The Second Trimester | Johns Hopkins Medicine
What You Need to Know
- During your second trimester prenatal visits, your health care provider will continue to check on your and your baby’s health, including monitoring the fetal heartbeat.
- The second trimester is the most physically enjoyable for most women. Morning sickness usually lessens by this time, and the extreme tiredness and breast tenderness usually ease up.
- Your fetus has now developed all its organs and systems and will now begin to grow in length and weight.
- You may be able to feel the movement of the fetus for the first time at around 20 weeks. This phenomenon is called quickening.
- A fetus born at the end of 24 weeks may survive in a neonatal intensive care unit.
Prenatal Visits During the Second Trimester
During your second and third trimester prenatal visits, your health care provider may check the following, depending on your current medical condition and the health of the fetus:
-
Any current symptoms or discomforts
-
Your weight
-
Your blood pressure
-
Urine test.
This is done to find albumin, a protein that may indicate pre-eclampsia or toxemia, and glucose (which may indicate hyperglycemia).
-
Growth, size and development of the fetus
-
Size of the uterus. After approximately 12 weeks of gestation, the uterus can be felt through the abdominal wall.
-
Height of the fundus (top of the uterus), starting at 20 weeks of gestation
-
Fetal heartbeat
The Second Trimester: What to Expect
The second trimester marks a turning point for the mother and fetus. You will usually begin to feel better and start showing the pregnancy more. Your fetus has now developed all its organs and systems and will now begin growing in length and weight.
During the second trimester, the umbilical cord continues to thicken as it carries nourishment to the fetus. However, harmful substances also pass through the umbilical cord to the fetus, so care should be taken to avoid alcohol, tobacco and other known hazards.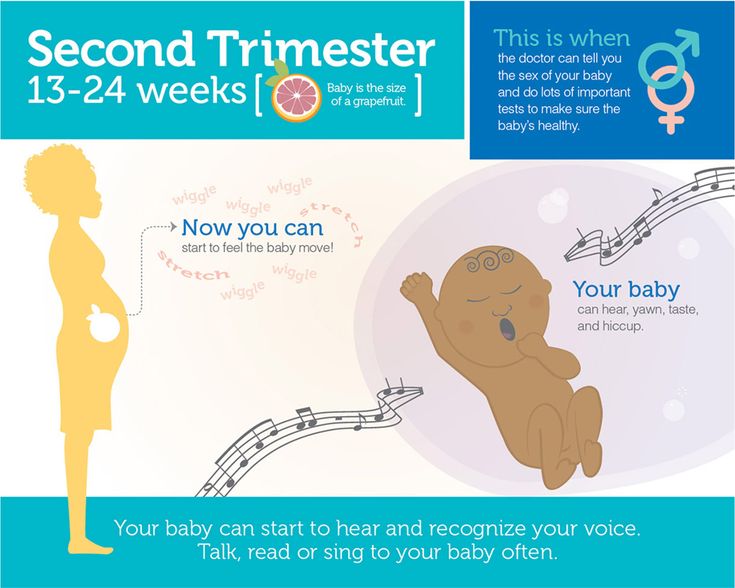
During the second trimester, both your body and the fetus continue to grow.
Johns Hopkins Hospital Designated as Baby-Friendly
The Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative, a global program launched by the World Health Organization and the United Nations Children’s Fund, has designated The Johns Hopkins Hospital as Baby-Friendly. This designation is given to hospitals and birthing centers that offer an optimal level of care for infant feeding and mother-baby bonding.
Learn more
The Second Trimester: Changes to Your Body
The second trimester is the most physically enjoyable for most women. Morning sickness usually lessens by this time, and the extreme tiredness and breast tenderness usually ease up. These changes can be attributed to a decrease in levels of human chorionic gonadotropin hormone and an adjustment to the levels of estrogen and progesterone hormones.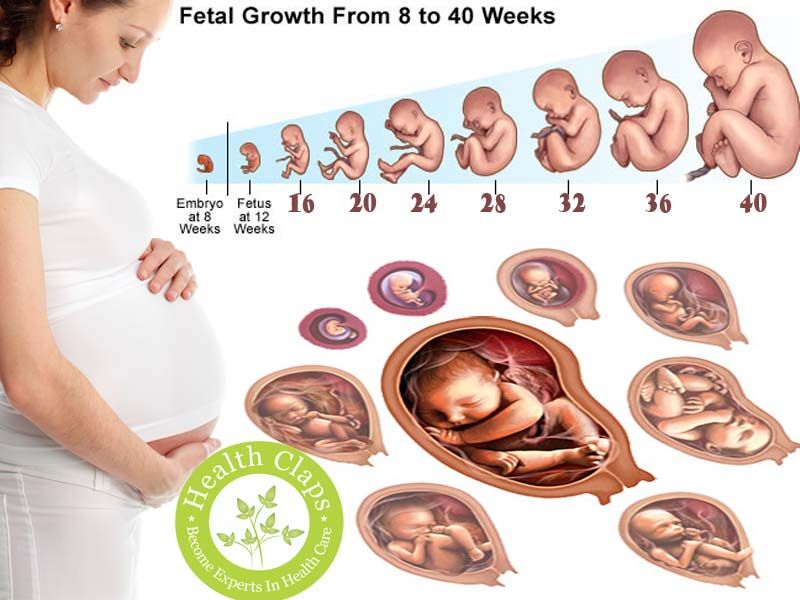
The following is a list of changes and symptoms that may happen during the second trimester:
-
Appetite may increase.
-
You may be able to feel the movement of the fetus for the first time around 20 weeks. This phenomenon is called quickening.
-
The uterus grows to the height of the bellybutton around 20 weeks, making the pregnancy visible.
-
The skin on the belly may itch as it grows, and there may be pain down the sides of the body as the uterus stretches. The lower stomach may ache as ligaments stretch to support the uterus.
-
The need to urinate often may decrease as the uterus grows out of the pelvic cavity, relieving pressure on the bladder.
-
Your nose may become congested, and you may experience nosebleeds. This is due to the increase in hormones (estrogen and progesterone) and blood flow that affect the mucous membranes and blood vessels in the nose.
-
Your gums become spongier and may bleed easily. This is due to the increase in hormones (estrogen and progesterone) that affect the mucous membranes in the mouth.
-
Varicose veins and hemorrhoids may appear.
-
You may have a white-colored vaginal discharge called leukorrhea. (A colored or bloody discharge may signal possible complications and should be examined immediately.)
-
The increasing weight gain may cause backaches.
-
Skin pigmentation may change on the face or abdomen due to the pregnancy hormones.
-
Heart burn, indigestion and constipation may continue.
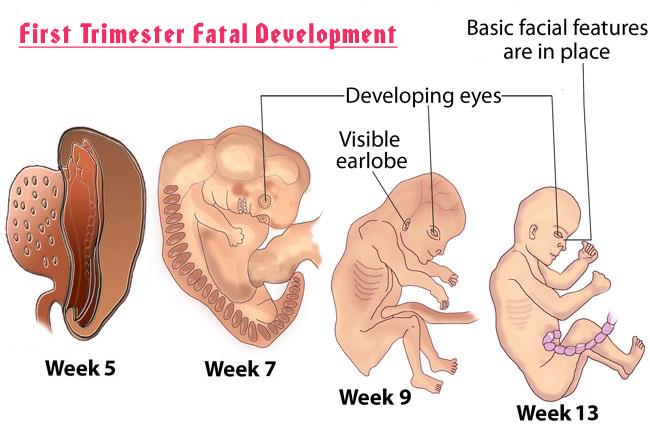
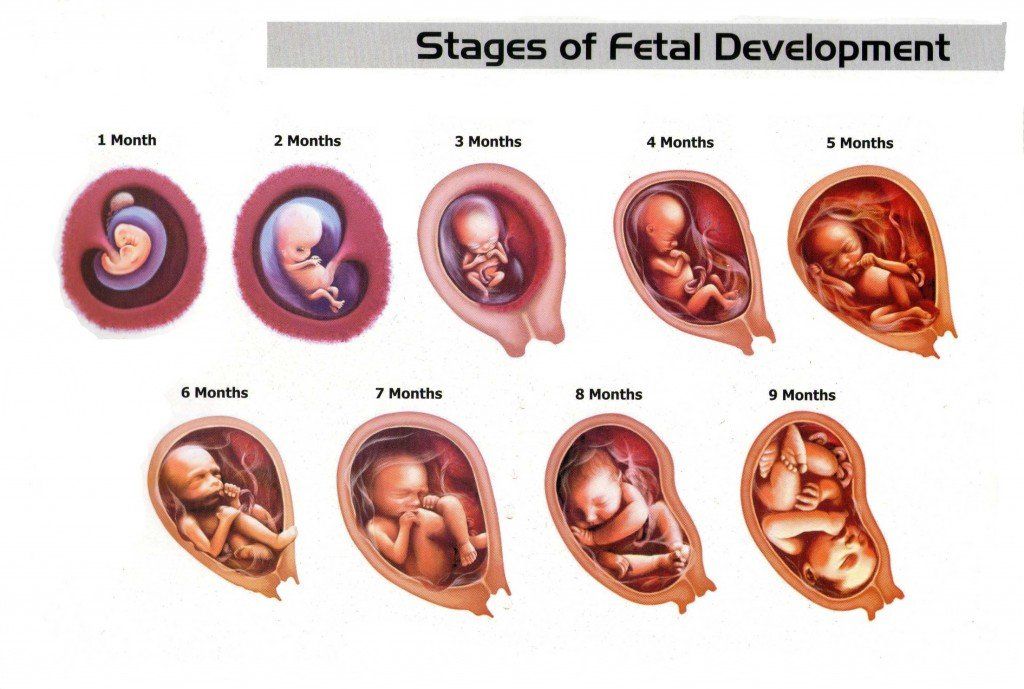
The Second Trimester: Fetal Development
Now that all the major organs and systems have formed in the fetus, the following six months will be spent growing. The weight of your fetus will multiply more than seven times over the next few months, as the fetus becomes a baby that can survive outside of the uterus.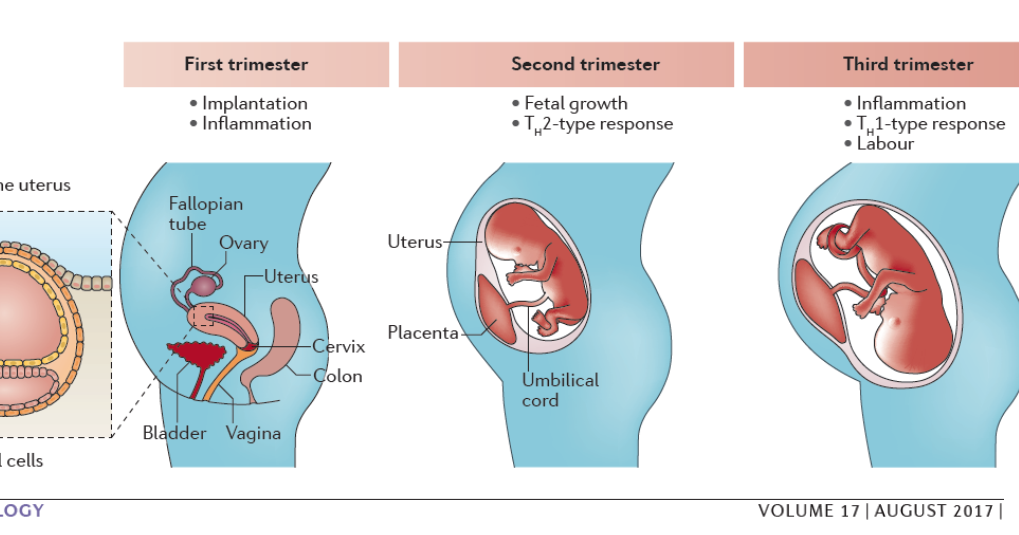
By the end of the second trimester, your fetus will be about 13 to 16 inches long and weigh about 2 to 3 pounds. Fetal development during the second trimester includes the following:
-
The fetus kicks, moves and can turn from side to side.
-
The eyes have been gradually moving to the front of the face, and the ears have moved from the neck to the sides of the head. The fetus can hear your voice.
-
A creamy white substance (called vernix caseosa, or simply vernix) begins to appear on the fetus and helps to protect the thin fetal skin. Vernix is gradually absorbed by the skin, but some may be seen on babies even after birth.
-
The fetus is developing reflexes, like swallowing and sucking.
-
The fetus can respond to certain stimuli.
-
The placenta is fully developed.
-
The brain will undergo its most important period of growth from the fifth month on.

-
Fingernails have grown on the tips of the fingers and toes, and the fingers and toes are fully separated.
-
The fetus goes through cycles of sleep and wakefulness.
-
Skin is wrinkly and red, covered with soft, downy hair (called lanugo).
-
Hair is growing on the head of the fetus.
-
Fat begins to accumulate in the fetus.
-
Eyelids are beginning to open, and the eyebrows and eyelashes are visible.
-
Fingerprints and toeprints have formed.
-
Rapid growth is continuing in fetal size and weight.
-
The 20th week marks the halfway point of the pregnancy.
A fetus born at the end of 24 weeks may survive in a neonatal intensive care unit.
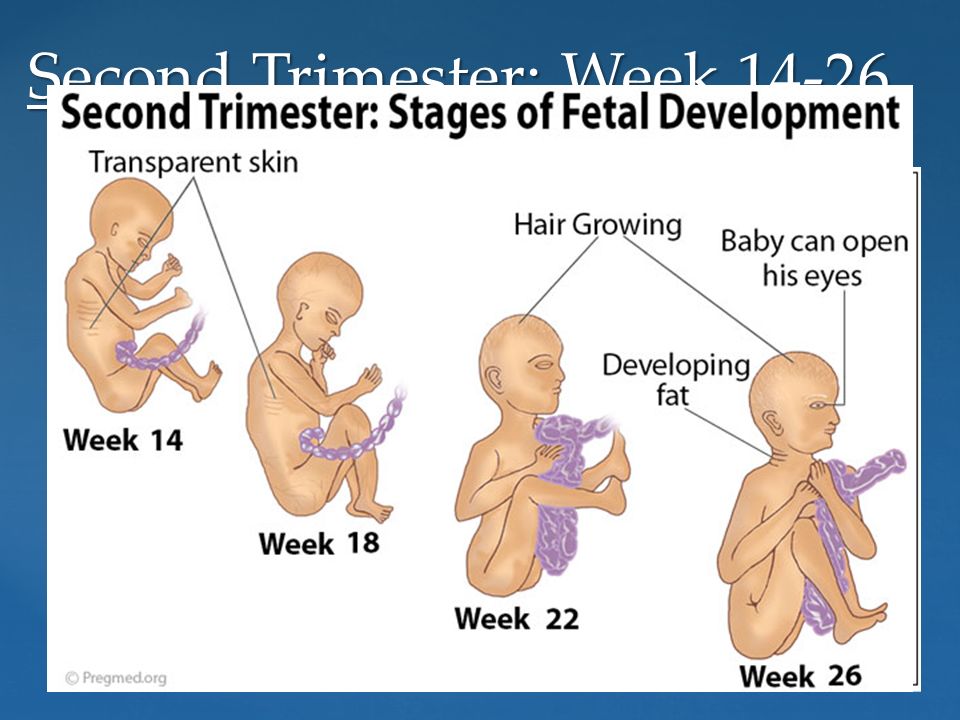
Stages of Fetal Development - Second Trimester
Stages of Fetal Development - Second TrimesterStages of Fetal Development - Second Trimester
14 - 23 Weeks
| WEEK 14
| |
| WEEK 16
| |
| WEEK 18
| |
| WEEK 20
| |
| WEEK 22
| |
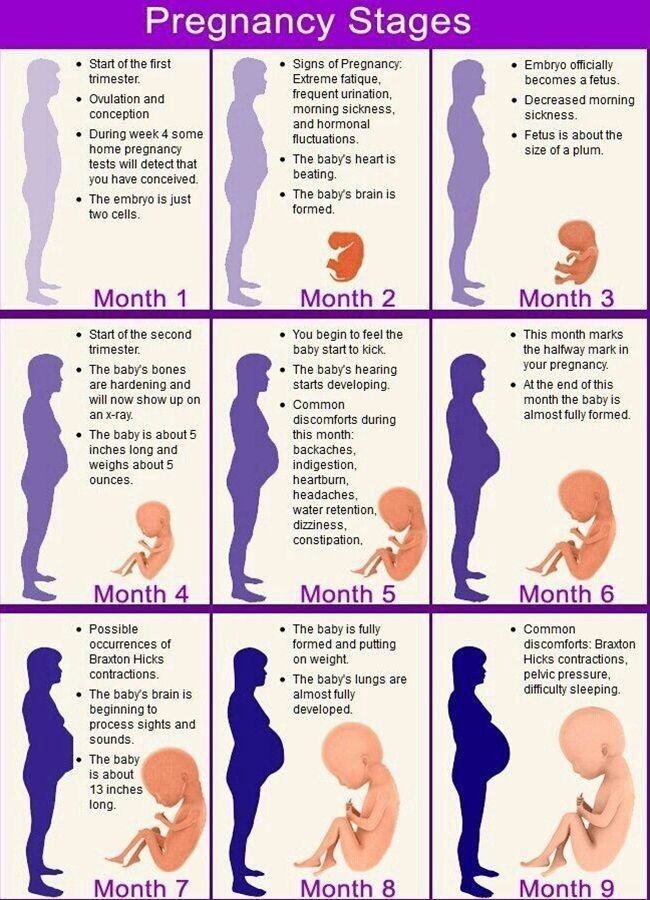
Second trimester of pregnancy: 4, 5, 6 months
Second trimester of pregnancy
The second trimester of pregnancy lasts from 12 to 27 weeks. During this period, you will continue to be monitored by a specialist doctor with visits once every 3 weeks, pass a number of necessary tests, in particular, a complete blood count, a biochemical blood test, blood for a coagulogram, a glucose tolerance test, a general urinalysis and bacteriological culture of urine for sterility 1-3 . At a period of 18-21 weeks, an ultrasound of the fetus will be performed with an assessment of its condition.
During this period, you will continue to be monitored by a specialist doctor with visits once every 3 weeks, pass a number of necessary tests, in particular, a complete blood count, a biochemical blood test, blood for a coagulogram, a glucose tolerance test, a general urinalysis and bacteriological culture of urine for sterility 1-3 . At a period of 18-21 weeks, an ultrasound of the fetus will be performed with an assessment of its condition.
Second trimester abdomen
The circumference of your abdomen increases markedly, by the end of the second trimester of pregnancy, the increase in the abdomen is more noticeable, and the bottom of the uterus is located at the level of the navel. Wear comfortable clothes, avoid tight belts, elastic bands around the abdomen 1-3 .
Second trimester of pregnancy and pain
In case of sudden pains of a different nature (cramping sharp or monotonous pulling pains) of the abdomen, you should immediately consult a doctor.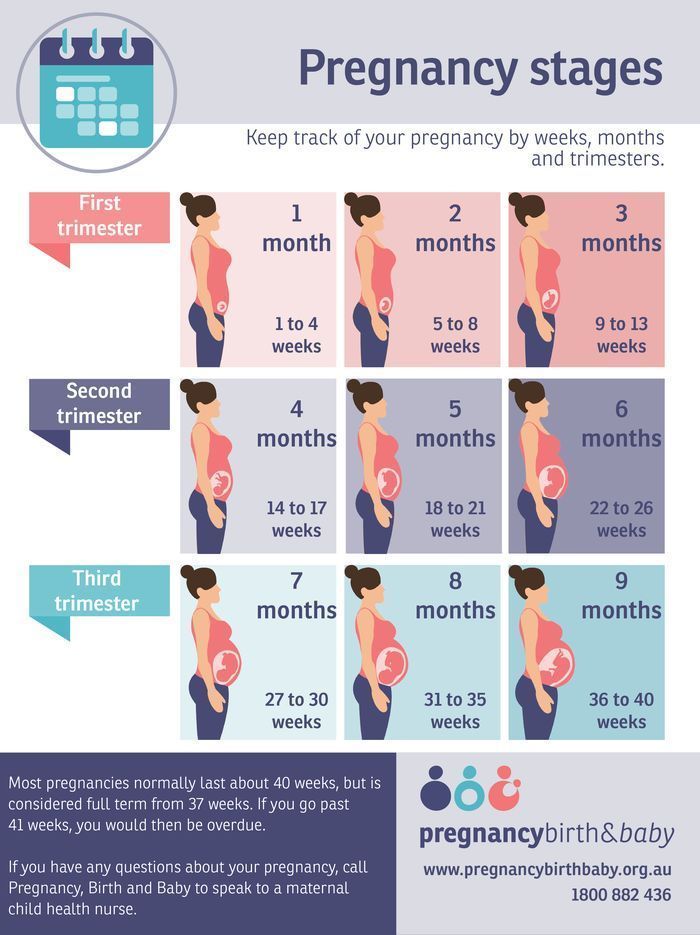 Pain in the abdomen may be associated with the threat of abortion and other complications. If the 2nd trimester is coming to an end and you have pain in the lumbar region, this may be due to compression of the ureters by the enlarged uterus. It is necessary to pass a urine test and do an ultrasound of the kidneys 1-3 .
Pain in the abdomen may be associated with the threat of abortion and other complications. If the 2nd trimester is coming to an end and you have pain in the lumbar region, this may be due to compression of the ureters by the enlarged uterus. It is necessary to pass a urine test and do an ultrasound of the kidneys 1-3 .
Constipation can also cause pain in the abdomen, along the final section of the large intestine (sigmoid colon). Pain during bowel movements, that is, during bowel movements, may be associated with an increase in hemorrhoids, the appearance of anal fissures. To ensure regular bowel movements, follow the drinking regimen and diet 1-3 .
The 2nd trimester of pregnancy may be accompanied by headaches (cephalgia). One of the causes of cephalalgia during pregnancy can be an increase in blood pressure. When a headache occurs, control the level of blood pressure (you need to measure at rest, on both hands at least one measurement on each).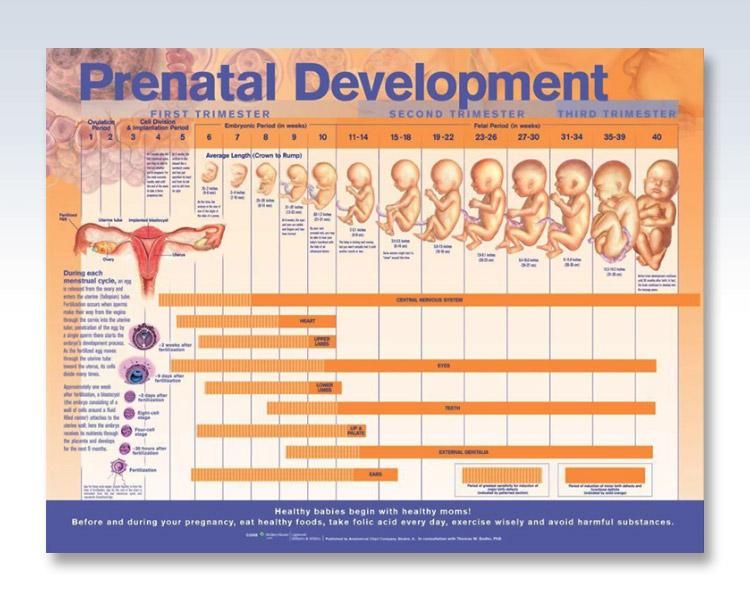 Remember that headaches and high blood pressure require urgent medical attention 1-3 .
Remember that headaches and high blood pressure require urgent medical attention 1-3 .
Fourth month of pregnancy and fetal development
1-3- All your baby's organs are already formed, his height is about 10 cm, and his weight is about 70 grams, he makes active movements in the joints.
- By the end of 4 months, the fetus actively increases in size, its height is about 13 cm, weight is about 140 grams.
- The development of teeth, sweat, salivary glands occurs, the liver begins to produce bile, and the pancreas - insulin.
- The baby begins to move his eyes, blink, and hear sounds well, because the bones of the inner ear are already formed.
- By the end of the fourth month, the woman begins to feel the movements of her baby.
- The liver and spleen form blood cells.
Fifth month of pregnancy and fetal development
1-3- The fetus is actively moving, on ultrasound you can see how the baby sucks his fingers.
 Weight about 240 grams, height about 15 cm.
Weight about 240 grams, height about 15 cm. - At 5 months, the fetal intestine is formed and individual nutrients can be absorbed, meconium accumulates.
- The immune system is fully formed and blood cells begin to produce bone marrow. The 5th month is coming to an end, and the baby's weight is about 400 grams.
- Your belly at 5 months of pregnancy no longer allows you to wear ordinary trousers and jeans, but dresses from an ordinary wardrobe can still fit, the uterus is just below the level of the navel.
- The breast at the 5th month of pregnancy also increases, usually by 1 size, the areolas of the nipples become more pigmented.
Sixth month of pregnancy and fetal development
1-3- The most intensive growth of the fetus begins, which will continue for only 3 trimesters.
- At the beginning of this period, the weight of the fetus is about 500-600 grams, and by the end of 6 months, the weight of the baby already reaches 900 grams.
- The 6th month of pregnancy is characterized by the formation of the surfactant system and the maturation of your baby's lungs.
- The breast at 6 months of pregnancy continues to increase due to the growth of glandular tissue, the size and pigmentation of the areola increases, the mammary glands prepare for lactation under the influence of estrogens.
2nd trimester of pregnancy:
macro- and micronutrient supplement
Pregnancy and iodine:
- To prevent iodine deficiency, all pregnant and lactating women are advised to take 200 micrograms of potassium iodide daily.
- Optimal absorption of iodides is observed in the morning hours. 4-8
Talk to your doctor about taking potassium iodide.
Pregnancy and calcium:
- The need for calcium increases to 1200-1500 mg per day, calcium salts are most often found in the form of carbonate and citrate, they have good bioavailability.

- Calcium is well absorbed in the evening. 9-11
Discuss the need to take calcium salts with your doctor.
Pregnancy and iron:
- Iron preparations are not recommended for all women, but iron deficiency anemia often accompanies the 2nd trimester of pregnancy 4 .
- If the level of ferritin (an accessible and reliable indicator of iron sufficiency) decreases, iron supplements should be taken at an average dose of 30-60 mg per day 4 .
The decision to prescribe iron supplements is made by your doctor or hematologist.
Pregnancy and vitamin D:
- The requirement for vitamin D throughout pregnancy and lactation is 2000 IU per day 9-11 .
Ask your doctor if you need to take vitamin D.
Second trimester pregnancy and complications
When the above symptoms appear, either alone or in combination, i.e. several symptoms at once, you need to urgently consult a doctor, since the lack of specialized medical care may be associated with a risk to your life and the life of the child.
2nd trimester and gestational diabetes mellitus
12-13 :- The list of mandatory examinations now includes a standard glucose tolerance test. Based on the results of this test, the state of carbohydrate metabolism is judged.
- In the presence of deviations from the norm, you will first of all be advised to follow a diet with a sharp restriction of fast carbohydrates and physical activity in accordance with the general state of health and the characteristics of the course of pregnancy.
- It will be necessary to consult an endocrinologist, nutritionist, physiotherapist.
2nd trimester and preeclampsia
14 :- An increase in blood pressure (may be asymptomatic!), the appearance of protein in the urine and edema are manifestations of preeclampsia.
- It is important to have your blood pressure checked regularly, have a urinalysis, and monitor weight gain.
2nd trimester and pyelonephritis
1-3 :- With an increase in the duration of pregnancy, the risk of developing pyelonephritis increases, this is due to a violation of the outflow of urine due to compression of the ureters by the growing uterus.
- Sitting and supine position contribute to urinary obstruction.
- Motor activity, knee-elbow position make urine outflow optimal.
- 1. National guidance. Gynecology. 2nd edition, revised and enlarged. M., 2017. 446 p.
- 2. Guidelines for outpatient care in obstetrics and gynecology. Edited by V.N. Serov, G.T. Sukhikh, V.N. Prilepskaya, V.E. Radzinsky. 3rd edition, revised and expanded. M., 2017. S. 545-550.
- 3. Obstetrics and gynecology. Clinical guidelines. — 3rd ed., rev. and additional / G.M. Savelyeva, V.N. Serov, G.T. Dry. — M.: GEOTARMEDIA. 2013. - 880 p.
- 4. WHO antenatal care guidelines for a positive pregnancy experience. 2017.196 s. ISBN 978-92-4-454991-9
- 5. Dedov I.I., Gerasimov G.A., Sviridenko N.Yu. Iodine deficiency diseases in the Russian Federation (epidemiology, diagnosis, prevention). Toolkit. — M.; 1999.
- 6. Iodine deficiency: current state of the problem. N.M.
 Platonov. Clinical and experimental thyroidology. 2015. Volume 11, No. 1. S. 12-21.
Platonov. Clinical and experimental thyroidology. 2015. Volume 11, No. 1. S. 12-21. - 7. Melnichenko G.A., Troshina E.A., Platonova N.M. Iodine deficiency diseases of the thyroid gland in the Russian Federation: the current state of the problem. Analytical review of publications and official state statistics (Rosstat). Consilium Medicum. 2019; 21(4):14–20. DOI: 10.26442/20751753.2019.4.19033
- 8. Clinical guidelines: diagnosis and treatment of (multiple) nodular goiter in adults. 2016. 9 p.
- 9. National program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation (4th edition, revised and supplemented) / Union of Pediatricians of Russia [et al.]. — M.: Pediatr, 2019. — 206 p.
- 10. National program Vitamin D deficiency in children and adolescents of the Russian Federation: modern approaches to correction / Union of Pediatricians of Russia [et al.]. — M.: Pediatr, 2018. — 96 s.
- 11. Pigarova E.A., Rozhinskaya L.
 Ya, Belaya Zh.E., et al. Clinical guidelines of the Russian Association of Endocrinologists for the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of vitamin D deficiency in adults // Problems of Endocrinology. - 2016. - T.62. — No. 4. — P. 60-84.
Ya, Belaya Zh.E., et al. Clinical guidelines of the Russian Association of Endocrinologists for the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of vitamin D deficiency in adults // Problems of Endocrinology. - 2016. - T.62. — No. 4. — P. 60-84. - 12. Russian national consensus "Gestational diabetes mellitus: diagnosis, treatment, postpartum care" / Dedov I.I., Krasnopolsky V.I., Sukhikh G.T. On behalf of the working group//Diabetes mellitus. —2012. -No4. —S.4-10.
- 13. Clinical guidelines. Algorithms of specialized medical care for patients with diabetes mellitus. 9th edition (updated). 2019. 216 p.
- 14. Adamyan L.V., Artymuk N.V., Bashmakova N.V., Belokrinitskaya T.E., Belomestnov S.R., Bratishchev I.V., Vuchenovich Yu.D., Krasnopolsky V.I. , Kulikov A.V., Levit A.L., Nikitina N.A., Petrukhin V.A., Pyregov A.V., Serov V.N., Sidorova I.S., Filippov O.S., Khodzhaeva Z.S., Kholin A.M., Sheshko E.L., Shifman E.M., Shmakov R.G. Hypertensive disorders during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period.
 Preeclampsia. Eclampsia. Clinical guidelines (treatment protocol). M.: Ministry of Health of Russia; 2016.
Preeclampsia. Eclampsia. Clinical guidelines (treatment protocol). M.: Ministry of Health of Russia; 2016.
Second trimester of pregnancy (13 to 28 weeks)
The beginning of the second trimester is traditionally considered one of the calmest. Walk more. Walking is very helpful. Sit down to rest only when you are tired. Movement in the fresh air improves the supply of oxygen to the fetus, which is very necessary for its normal development.
Nausea disappears, appetite improves. Do not eat a lot of salty, refuse marinades, smoked meats, if you have not done this before. The increased need of the child's body for proteins and vitamins begins. The daily diet should include meat or fish (boiled or stewed), dairy products, especially cottage cheese, eggs. Do not forget about vegetables, fruits, greens. An excellent source of vitamin C is sauerkraut (rather than salted) cabbage. Salads from carrots, cabbage, beets, apples, green radish should be on your table every day.
At 17-20 weeks you will feel your baby's first kicks. From them you can determine how comfortable the baby feels. Intense tremors are a signal of lack of oxygen. Maybe you haven’t walked for a long time or, on the contrary, you are engaged in hard physical labor. Get out into the fresh air or lie down to rest and you will immediately feel how the child has calmed down.
But the lack of movement is an alarm. See a doctor immediately!
The need for calcium in the fetus increases sharply - an intensive growth of the skeleton has begun. If you don't have enough free calcium in your body right now, you could lose your teeth. To prevent this from happening, start taking calcium supplements in consultation with your doctor.
At this time, toxicosis of the second half of pregnancy may occur, the child suffers greatly from it. Therefore, if the doctor suggests hospitalization, do not refuse. Toxicosis can, if not be avoided, then at least reduce its manifestations. Be sure to follow your diet. Completely exclude salty, smoked, fried, spicy, canned food, chocolate. Do not eat a lot of grapes and drink fresh milk. Limit flour and rich products. As before, your diet should include boiled meat and fish, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge, vegetables and fruits
Be sure to follow your diet. Completely exclude salty, smoked, fried, spicy, canned food, chocolate. Do not eat a lot of grapes and drink fresh milk. Limit flour and rich products. As before, your diet should include boiled meat and fish, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge, vegetables and fruits
Periodically, once a week, check for fluid retention. It is allowed to release liquid 200-300 ml less than what was drunk. If little urine is released, this is a signal of latent edema and the onset of toxicosis.
It is very good if you can measure your blood pressure at home. Show the results of measurements at the next visit to the doctor. Both high and too low pressure should alert. With low pressure, blood sluggishly crosses the placenta, and the baby does not receive enough nutrients.
Do not neglect blood tests - it is important not to miss the development of anemia. In this case, you will be prescribed iron supplements and multivitamins. The diet should include beef liver, tomato juice, buckwheat porridge, apples, preferably Antonovskie (they contain more iron than other varieties).