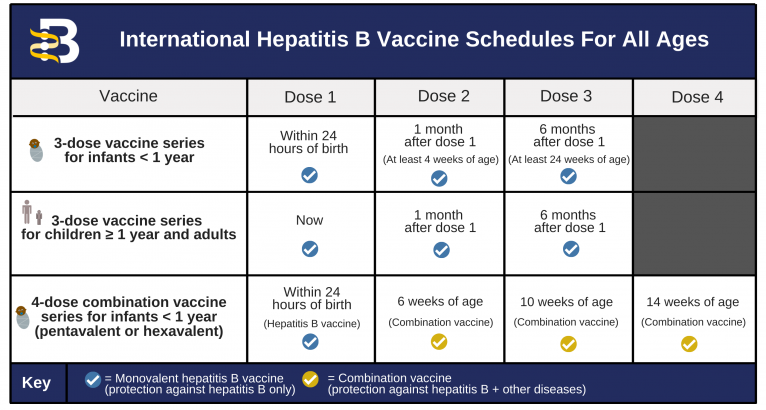
Menu for pregnant women
A Pregnant Woman's Daily Diet
Written by Elizabeth Somer, MA, RD
At no other time in life is nutrition as important as before, during, and following pregnancy. On the other hand, women can still eat foods that come in a box or a bag, eat out several times a week, or order pizza to go as long as they also follow a few simple eating-for-two dietary guidelines.
A Pregnant Woman Should Include in Their Daily Diet at Least:
- Five servings of fresh fruits and vegetables (including at least one serving of a dark orange vegetable, two servings of dark green leafy vegetables, and one serving of citrus fruit)
- Six servings of enriched, whole-grain breads and cereals. Three servings of nonfat or low-fat milk or milk products
- Two to three servings of extra-lean meats, chicken without the skin, fish, or cooked dried beans and peas
- Eight glasses of water
The guidelines for eating well for a healthy pregnancy are simple and easy to follow. When, where, and how much they eat is flexible, and often is governed by necessity. A pregnant woman in their first trimester might choose a snack for breakfast and a large evening meal if they suffer from morning sickness, but select a larger breakfast and a light evening meal in the last trimester when heartburn is more of a problem. Avoid or limit caffeine (such as coffee, tea, and colas) and avoid alcohol and tobacco. Since no safe limit has been established for alcohol, abstinence is a woman's best bet.
A Weighty Issue
If a woman does not gain enough weight, their baby also won't gain enough weight, which places the newborn at high risk for health problems. Optimal weight gains of 25 to 35 pounds in a slender woman helps ensure a healthy-sized baby. Underweight women should gain more weight, or approximately 28 to 40 pounds. Overweight women should not attempt to use pregnancy as a way to use up extra body fat, since stored body fat is not the stuff from which babies are made. A modest weight gain of between 12 to 25 pounds is recommended for these women.
A modest weight gain of between 12 to 25 pounds is recommended for these women.
Further weight gain beyond recommended amounts will not make bigger or healthier babies. It will make regaining a desirable figure more difficult after delivery. The secret is to pace the gain, with weight gain increasing from very little in the first trimester to as much as a pound a week in the last two months of pregnancy.
Folic Acid: It's a Must
Nutrition experts agree that the best place for the mother-to-be to get all the essential nutrients, including ample amounts of vitamins and minerals, is from their diet. The trick is getting enough. For example, the MRC Vitamin Study at the Medical College of St. Bartholomew's Hospital in London found that women taking folic acid supplements around conception had significantly lower risks for giving birth to babies with neural tube defects (NTD), a type of birth defect where the embryonic neural tube that forms the future brain and spinal column fails to close properly.
Luckily, in 1996 the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a regulation requiring that all enriched grain products, including breads and pasta, be supplemented with folic acid. Every woman during the childbearing years should make sure they get at least 400 micrograms of folic acid from food or supplements.
The Post-Pregnancy Diet
Whether a woman breastfeeds or not, the secret to post-pregnancy nutrition is to gradually regain a desirable figure, while maintaining or restocking nutrient stores. In addition, since some babies are planned and others are surprises, it's never too late to start nourishing the next baby by continuing to eat a diet based on fresh fruits and vegetables, nonfat milk products, whole grains, and protein-rich beans and meats.
An Easy 7-Day Template To Follow
If you’re trying for a baby or have just fallen pregnant, it’s important to start taking care of your diet as eating healthy foods will help with your chances of conceiving and having a healthy pregnancy.
During pregnancy, daily requirements for some nutrients are higher than those for non-pregnant women and extra attention is needed to ensure you are getting enough key nutrients, including folate, iodine, calcium, iron, omega-3 fatty acids and choline.
As you're not only feeding yourself and aiming to boost your own health and wellbeing, but you are also providing all the nutrients needed for your growing baby, planning your meals can be confusing at first.
This 7-day pregnancy meal plan, curated by Accredited Dieticians, will help you meet your nutritional requirements during this wonderful time of life.
Notes About This Meal Plan
- This meal plan provides 10 eggs per week and provides at least 2 serves of fruit and 2.5 serves of dairy per day.
- Your needs may be higher or lower, therefore, for tailored advice please speak to an Accredited Practising Dietitian.
- It is important to follow the food safety recommendations during pregnancy to avoid the risk of food-borne illnesses.
 Eat leftovers within 24 hours of cooking. For advise on food safety in pregnancy visit http://www.foodstandards.gov.au/consumerinformation/pregnancyandhealthyeating/
Eat leftovers within 24 hours of cooking. For advise on food safety in pregnancy visit http://www.foodstandards.gov.au/consumerinformation/pregnancyandhealthyeating/
Want to find out more?
VIEW MORE INFORMATION ABOUT EGGS AND PREGNANCY
For easy access jump to:- Day one
- Day two
- Day three
- Day four
- Day five
- Day six
- Day seven
Day One
Breakfast
Porridge made with Rolled Oats, Milk and Mixed Seeds: + 1 serve of fruit (eg. 2 cups berries or 1 medium banana).
Lunch
Tinned tuna or salmon wrap: Small tin tuna or salmon + salad vegetables + avocado + low GI wrap.
Dinner
Lamb Stir-fry: Made with trim lamb + vegetables + brown rice + canola oil (for stir-frying).
Dessert/Supper
Chocolate Drizzled Banana: Made with half a banana and 2 teaspoons melted dark chocolate + 1 tub of yoghurt.
Snacks
Wholegrain crackers with 1 slice cheddar cheese + 1 serve of fruit (e.g. a medium apple or orange or pear).
Day Two
Breakfast
Muesli and Linseeds with Yoghurt: + 1 serve fruit (eg. 6 dried apricot halves or 2 tbsp sultanas).
Lunch
Homemade Toasted Chicken, Cheese & Avocado Sandwich: Made with multigrain bread (toasted) + chicken (ensure chicken is fresh) + cheese + avocado + margarine + a side salad served with an olive oil based dressing.
Dinner
Fried rice with sliced egg omelette (1 serve)
Dessert/Supper
Homemade smoothie: Made with milk + fruit + yogurt + chia seeds (e.g. banana or berries or mango).
Snacks
1 serve of fruit (eg. 3/4 cup grapes or 5 prunes) + 1 cup veggie sticks.
Day Three
Breakfast
Baked Beans on Multigrain Toast: + one glass of milk. + 1 serve of fruit (eg. 4 small plums or 2 cups diced watermelon).
+ 1 serve of fruit (eg. 4 small plums or 2 cups diced watermelon).
Lunch
Leftover Fried Rice with Sliced Egg Omelette from night before.
Dinner
Grilled Salmon and Vegetables: served with sweet potato mash + steamed green vegetables (e.g, broccoli and green beans).
Dessert/Supper
Fresh Fruit & Cheese Platter: Slice and serve a variety of fresh fruits in season and hard cheese.
Snacks
1 tub yoghurt + handful of mixed nuts.
Day Four
Breakfast
Wholegrain Flaky Cereal: + milk + 1 serve of fruit (eg. 1 cup homemade fruit salad or 6 dried apricot halves).
Lunch
Wild Rice, Dukkah Egg and Pomegranate (1 serve).
Dinner
Roast Vegetable, Chicken & Quinoa Salad: Made with chicken + vegetables roasted in olive oil + quinoa + mixed seeds.
Dessert/Supper
Fruit Pop: Made with frozen fruits (eg. bananas or mangos) blended with Greek yoghurt and frozen.
Snacks
1 serve of fruit (eg. 1 medium apple or orange) + 1 tub yoghurt.
Day Five
Breakfast
Multigrain Bread with Peanut Butter: + 1 serve of fruit (eg. 4 small plums or 1 small mango). + 1 glass of milk.
Lunch
Grilled Chicken & Salad Wrap: made with grilled lean chicken + salad vegetables (carrot, tomato, cucumber) + avocado + shredded cheese + multigrain wrap.
Dinner
Healthy Lentil and Feta Frittata
Dessert/Supper
Fruit Salad & Yoghurt: 1 cup fresh fruit salad with 200g vanilla yoghurt.
Snacks
Wholegrain crackers with 1 slice cheddar cheese + sliced tomato + 1 hard boiled egg
Day Six
Breakfast
Muesli and Mixed Seeds with Yoghurt: + 1 serve fruit (eg. 6 dried apricot halves or 2 tbsp sultanas).
Lunch
Leftover Lentil & Feta Fritatta from night before served with salad.
Dinner
Chicken Thigh Fillets Baked in a Tomato & Vegetable Sauce: Served with rice and a side salad, including olive oil based dressing.
Dessert/Supper
Banana Souffle (1 serve): + 1 glass of milk.
Snacks
1 serve of fruit (eg. 1 medium pear or orange) + mixed nuts.
Day Seven
Breakfast
Boiled Eggs with Avocado on Sourdough Bread.
Lunch
Baked Fish: Served with vegetables and baked potato wedges + 1 serve of fruit (e.g. 2 cups diced watermelon)
Dinner
Easy Dinner: 1-2 slices multigrain toast with 1 cup baked beans + avocado.
Dessert/Supper
Homemade Smoothie: Made with milk + fruit +chia seeds (eg. a banana or berries or a mango).
Snacks
1 tub of yoghurt + handful of mixed nuts.
Choline - The Forgotten Nutrient
Choline plays a crucial role during pregnancy, helping support brain and spinal cord development – modifying development pathways into childhood and potentially adulthood. Low choline intake levels are associated with an increased risk of neural tube defects in women with adequate folate levels and a failure to provide choline during the first 1000 days post-conception could result in lifelong deficits in brain function even if adequate choline is consumed subsequently.
Latest research shows that if women consumed the equivalent of one extra egg a day, the percentage of women with adequate choline intakes would increase from 39% to 80%.
Learn More About Eggs And Nutrition
Not sure whether eggs may be beneficial in your situation? Learn more about how eggs may help serve your nutritional needs today.
Discover our super easy & delicious meal plans designed to help you achieve a healthy and balanced diet. Check out our weight loss or low cholesterol meal plan today!
Check out our weight loss or low cholesterol meal plan today!
Nutrition for pregnant women: menu TEA.RU
Nutrition for pregnant women is of particular importance. Before pregnancy, not many of us think about what is healthy and proper nutrition. From the very moment when a woman finds out about her “interesting position”, the realization comes that now you need to “eat for two”. And this does not mean at all that the menu for a pregnant woman should contain more calories and, accordingly, food. This means that proper nutrition during pregnancy leads to the correct development of the fetus in terms of anatomy and physiology.
Numerous research data have shown that malnutrition during pregnancy can not only lead to anatomical underdevelopment of the fetus, but can also affect the future cognitive abilities, memory and other developmental features of the baby.
Surprisingly, malnutrition during pregnancy is one of the underlying factors in the development of obesity. Even at the intrauterine level, the child turns on a gene that ensures the maximum absorption of all nutrients from any, even a limited, amount of food. In the future, even if the child's nutrition is sufficient, his body will still try to "accumulate" calories "with a margin."
Even at the intrauterine level, the child turns on a gene that ensures the maximum absorption of all nutrients from any, even a limited, amount of food. In the future, even if the child's nutrition is sufficient, his body will still try to "accumulate" calories "with a margin."
In addition, malnutrition of a pregnant woman can cause problems in the future:
• with the psychomotor development of the child;
• with the immune system;
• with the endocrine system;
• with metabolism;
• lead to impaired memory, attention and even behavior of the child.
For this and other reasons, a balanced diet is a very important component, along with the psycho-emotional state. The diet of pregnant women should be carefully thought out and conscious so that the child from the moment of conception to the very birth develops as harmoniously and correctly as possible.
Pregnancy menu: what will be useful?
The dietary menu for pregnant women should include a full range of vitamins, nutrients and minerals. In addition, such a menu should include immunonutrients and micronutrients. What is it and what is the significance of these substances in the formation of the fetus?
In addition, such a menu should include immunonutrients and micronutrients. What is it and what is the significance of these substances in the formation of the fetus?
The main task of micronutrients is the direct protection of the fetus from any adverse external influences. These impacts include both environmental factors and exposure to various chemicals that are abundant in the environment. Micronutrients are involved in almost all biochemical processes in the body of the mother and fetus.
Immunonutrients are chemicals that have a direct impact on the formation of a child's immunity, the ability of his body to resist various bacterial, viral and other attacks of pathogens. These substances include amino acids, probiotics, nucleotides, fatty acids and some other elements.
Not only the lack of such elements in the future mother's diet is dangerous, but also their excess. For example, vitamin A is useful for the formation of the organs of vision in the fetus, but in large doses this vitamin can be toxic and lead to the development of intrauterine pathologies. For this reason, it is better to choose a menu for every day during pregnancy, taking into account the recommendations of a specialist leading your pregnancy. Any "amateur", in this case, it is better to exclude.
For this reason, it is better to choose a menu for every day during pregnancy, taking into account the recommendations of a specialist leading your pregnancy. Any "amateur", in this case, it is better to exclude.
Early pregnancy nutrition
In the early stages of pregnancy, experts say, the energy needs of a woman practically do not change. It is not necessary at this time to drastically change your lifestyle and diet. If your diet was balanced, then you can stick to it throughout the first trimester.
Attention should be paid to ensure that the diet includes:
• fresh seasonal vegetables and fruits;
• greens;
• berries;
• horse crops.
Numerous studies have found that early pregnancy menus often exclude this particular food group. These products are recommended to be consumed raw or with minimal heat treatment. When choosing a diet, it is worth considering the history in terms of the presence of allergies in the mother and a predisposition to the development of diabetes.
The norm of sugar consumption per day in the menu for pregnant women is no more than 60 gr. If you cannot do without sweets, and you also need to avoid foods that cause allergic reactions, it is recommended to include foods such as:
• jams and jams without sugar;
• chocolate without sugar;
• dark chocolate with a cocoa content of at least 70%;
• peanut butter without sugar, etc.
Contrary to popular belief, such products have not only beneficial properties for the body, but also excellent organoleptic characteristics. Foods that are low in sugar or do not contain sugar at all have a taste and aroma that are in no way inferior to similar products with sugar.
Otherwise, the menu for pregnant women in the 1st trimester should not differ from the usual. For the formation of the fetus in the early stages, "building materials" in high doses are not needed. Thus, all the calories that a woman receives are spent at the same rate as usual. Increasing the amount of food and its calorie content can lead to overweight and will not benefit the child at all.
Increasing the amount of food and its calorie content can lead to overweight and will not benefit the child at all.
So, what should pregnant women eat in the early stages? The same as usual, including a large amount of fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs and berries. Vegetables and fruits should be typical for your region, you should not give preference to exotic and new products for you. Dishes for pregnant women should be as simple and familiar as possible, there is no need to invent something new. Eat what you want most, but don't overeat.
Proper nutrition for pregnant women in the 2nd trimester
In the second half of pregnancy, there is an active growth of the fetus, as well as various changes in the organs of the woman's reproductive system themselves. It is during this period that the need for nutrients and microelements for the normal physiological development of the fetus may increase.
A sample menu during pregnancy should be such that the pregnant woman receives all groups of the following foods:
• Dairy products, including whole milk and lactic acid products. The approximate volume of this product group should be 500 ml.
The approximate volume of this product group should be 500 ml.
• Meat and poultry. The total amount of meat products should not be less than 170 gr. In the second trimester of pregnancy, 250 grams of any, but better - dietary, meat - this is the norm.
• Fish and seafood. It is enough to eat 70 grams daily.
• Cereals and bakery products in limited quantities. This group of products is simply necessary to prevent such problems in the gastrointestinal tract as constipation and bloating, which women often suffer from during the period of bearing a child.
• Vegetables, fruits and berries, as well as juices. Total quantity - up to 1000
• Sugar and confectionery. Preference should be given to marmalade, marshmallows, marshmallows and jams on a natural basis, as well as products with low or no sugar content.
• Fats. Dishes for expectant mothers are best cooked in butter. The amount of vegetable fats should not exceed 15 g per day.
In the second trimester, a large load falls on the liver and kidneys. The menu for pregnant women in the 2nd trimester should exclude a large number of any salty foods, smoked meats and excess fluids. You need to focus on the fact that a woman should normally gain no more than 300 grams per week, and for the entire pregnancy - no more than 10-12 kg. If you are gaining more, then the diet should be reconsidered.
The menu for pregnant women in the 2nd trimester should exclude a large number of any salty foods, smoked meats and excess fluids. You need to focus on the fact that a woman should normally gain no more than 300 grams per week, and for the entire pregnancy - no more than 10-12 kg. If you are gaining more, then the diet should be reconsidered.
Nutrition during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester: menus and recommendations
The diet for pregnant women in the third trimester also has its own characteristics. The menu for the 3rd trimester should include products that stimulate lactation. First of all, these are dairy and lactic acid products, such as kefir, milk, fermented baked milk, cheese and cottage cheese.
Breakfast for pregnant women should be 30-40% of the total diet. You can have oatmeal, a few slices of cheese, yogurt and tea for breakfast. It is good to use herbal teas, which not only have high taste, but also have the following properties:
• anti-inflammatory;
• immunostimulating;
• normalizing metabolism;
• restoring the optimal water-salt balance and other useful properties.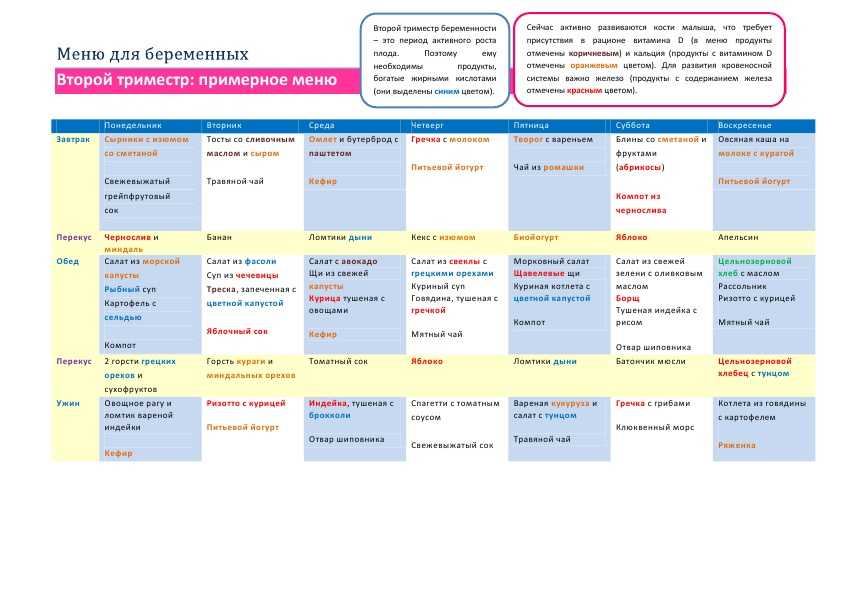
Herbal tea may contain chamomile, rose hips, berries or fruits, calendula, string, twigs and leaves of useful plants. For a woman during childbearing, in general, green and herbal teas are much more beneficial than black teas and their blends.
Late pregnancy diets should be high in protein and avoid heavily spiced foods, including salt. These foods retain water in the body and can cause swelling and other complications.
A sample menu for proper nutrition for pregnant women might look like this:
This is an approximate table of nutrition during the period of bearing a child. You can adjust it according to the season and the availability of seasonal fruits and vegetables, as well as your personal preferences. Recipes for pregnant women, menus for days or weeks today can be easily found in the public domain. Using these recommendations, you can create your own diet that will satisfy both the needs of the body and your own preferences.
Healthy nutrition during pregnancy
Category: Healthy food.
Happiness, agonizing expectation, anticipation and even fear - all these feelings inevitably accompany pregnant women. And it is very important during this period not to surrender to emotions, but to remember the responsibility that is an integral part of this time. It is during this period that it is important to follow the basics of a healthy lifestyle, taking into account the requirements of pregnancy. Proper nutrition during pregnancy is the most relevant, since what a woman eats largely determines how her child will develop. For example, whether a pregnant woman receives enough protein depends on whether the child will have enough building material.
It makes sense to take into account one important feature: proper nutrition in early pregnancy will be somewhat different from the diet of a pregnant woman in the last weeks.
Not everyone understands where such differences come from, but understanding the topic will be quite simple. Judge for yourself, important systems of the body are laid in the early stages, but the size of the fetus increases slightly. Therefore, in the early stages, a healthy diet for pregnant women is based on sufficient intake of minerals, vitamins, and the like.
Therefore, in the early stages, a healthy diet for pregnant women is based on sufficient intake of minerals, vitamins, and the like.
In the second trimester of pregnancy, nutrition should focus on increased protein intake, since it is now that the active growth of the child and its internal organs begins. All this requires a building material, that is, protein.
Nutrition in the third trimester of pregnancy is, first of all, vitamins and minerals that are necessary for the development of the internal systems of the child's body, especially calcium for bone growth and the development of the nervous system.
When planning a pregnancy, proper nutrition is also very important. The more healthy, hardy, strong the woman's body is at the time of conception, the greater the chances of successfully fixing the fetal egg in the uterus. And a certain set of vitamins in the body contributes to the proper development of the embryo.
As you can see, the difference in recommendations for proper nutrition of pregnant women by months, and sometimes even by weeks, is quite justified. However, there are, of course, general rules for proper nutrition during pregnancy, which will be discussed further.
However, there are, of course, general rules for proper nutrition during pregnancy, which will be discussed further.
General principles of proper nutrition during pregnancy
First of all, it is worth remembering one simple thing: it is better to get up from the table slightly hungry than with heaviness in the stomach from overeating. In this regard, it is better to adhere to the principles of fractional nutrition at all: eat less, but more often. The ideal option would be to eat 5-6 times a day. The last meal should be 3 hours before bedtime. If the feeling of hunger is unbearable, you can drink a glass of milk or yogurt, eat an apple or a pear. It is this diet for pregnant women that will be most optimal.
Proper nutrition during pregnancy, like, in fact, any proper nutrition, involves the exclusion or maximum restriction of fried foods, pickled foods and smoked meats. Steamed, boiled, stewed or baked food will be much more useful. Food for pregnant women should be as fresh and natural as possible, should not contain preservatives, excess salt, and the like.
Food for pregnant women should be as fresh and natural as possible, should not contain preservatives, excess salt, and the like.
Obviously, canned foods, various sausages and other long-term storage products, if not banned, then require strict control of their use.
Of course, it is recommended to give up fast food. However, it is worth noting that if the choice arises - to remain hungry or eat something not very healthy, it is better to choose the latter. A pregnant woman should not starve. Another thing is, if you get suspiciously often before such a choice, then you should think about carrying fruit or sandwiches with you.
Of great importance is the balance between such important components of nutrition as proteins, fats, carbohydrates, as well as vitamins and minerals. Of course, a balanced diet for pregnant women at different times implies a different balance of these components, the fact itself remains unchanged.
Weekly meals
1-3 weeks pregnant
Gynecologists count pregnancy not from the day of conception, since it is almost impossible to calculate it, but from the first day of the last menstruation. Therefore, the first 2 weeks of the obstetric gestation period falls on the time before conception.
Therefore, the first 2 weeks of the obstetric gestation period falls on the time before conception.
Pregnancy planning is an extremely important period, on which, whatever one may say, both the health of the unborn child and the absence of any complications during pregnancy depend. So it turns out that proper nutrition before pregnancy is of paramount importance. At this stage, it is very important to increase the amount of folic acid. Doctors often recommend drinking it in the form of capsules, but it is much better to get all the vitamins from normal food. Folic acid is found in green leafy vegetables (spinach, lettuce, cabbage, etc.), asparagus, beans and legumes, seeds and nuts, citrus fruits.
It is equally useful to consume yellow fruits and vegetables. But it is better to refuse fatty and sweet foods. This will avoid problems with obesity, as well as reduce the risk of early toxicosis.
Approximately on the 10-14th day of the cycle, fertilization occurs and the movement of the fetal egg begins towards the uterus. From this time on, we can talk about the onset of pregnancy.
From this time on, we can talk about the onset of pregnancy.
3 week
Nutrition at the beginning of pregnancy is a very complicated topic, since literally every week new organs and systems appear in the fetus, which means that the need for vitamins and nutrients is constantly changing.
In the third week of pregnancy, the egg is implanted and the placenta begins to develop, as well as the fetal membrane. For their full development, calcium is needed, which is found in dairy products, nuts, fish, legumes, fruit juices and cereals; and manganese, it can be obtained from nuts, spinach, beets, mushrooms, animal liver.
4 week
For 4 weeks, the nutrition remains the same as for 3, but at this time it is especially important to give up coffee. However, drinking this certainly tasty, but not very healthy drink during pregnancy should be done with extreme caution. Especially coffee is contraindicated in the evening. As you can see, proper nutrition in the first month of pregnancy is not too difficult. Further it will be a little more difficult.
As you can see, proper nutrition in the first month of pregnancy is not too difficult. Further it will be a little more difficult.
5 week
As a rule, toxicosis of pregnant women begins around this time. To alleviate this condition, you can slightly change your daily menu. So, meat and eggs, as well as other animal proteins, can be replaced with nuts, soy and other legumes. Instead of milk, you can eat yogurt and cheese. It will not be superfluous to introduce carrots, mangoes, apricots into the diet.
6 week
Toxicosis is in full swing, so the morning should start with crackers or unsweetened crackers. It is better to eat them immediately after waking up, without getting out of bed. At this stage, it is better to drink plenty of fluids, at least 8 glasses a day (for example: water with lemon juice or tea with lemon). At night, you can eat a handful of raisins.
7 week
At this time, problems with the intestines may arise. Therefore, you should avoid foods that promote gas formation, including cabbage. It will not be superfluous to refuse those products that strengthen. It is better to introduce prunes, fresh kefir and the like into the diet.
Therefore, you should avoid foods that promote gas formation, including cabbage. It will not be superfluous to refuse those products that strengthen. It is better to introduce prunes, fresh kefir and the like into the diet.
8 week
Ginger tea will help to cope with toxicosis, and do not forget about nuts.
9-10 weeks
Give preference to whole grain cereals and whole grain bread. Brown rice is better than white. In general, the body of a pregnant woman at this stage needs quite a lot of fiber.
11-12 weeks
The first trimester of pregnancy is coming to an end, and nutrition at this time should be special. This is the most difficult time, and it is very important to listen to yourself, to your body. If you want to eat a particular dish, then it is precisely those substances that are contained in it that your baby lacks. Of course, you shouldn't go to extremes.
13-16 weeks
Nutrition in the 2nd trimester during pregnancy is characterized, as already mentioned, by abundant protein intake. In addition, it is necessary to increase the total daily caloric intake of food. If in the first trimester it will be enough to eat 2400-2700 kcal, then from this time it is necessary to eat 2700-2900 kcal.
In addition, it is necessary to increase the total daily caloric intake of food. If in the first trimester it will be enough to eat 2400-2700 kcal, then from this time it is necessary to eat 2700-2900 kcal.
16-24 weeks
Nutrition at 6 months of pregnancy should contribute to the development of the child's vision and hearing. That is, you need vitamin A and beta-carotene. It is better to eat cabbage, yellow peppers, carrots at this time. Keep in mind that vitamin A is absorbed only with fats.
24-28 weeks
It is at this time that fractional nutrition becomes especially relevant. The uterus is actively growing, taking up more and more space in the abdominal cavity, and begins to put pressure on the stomach. Accordingly, the stomach becomes smaller, and it is difficult for it to contain a large amount of food. Even when eating small meals, a pregnant woman may be bothered by heartburn. It is better to give up carbonated drinks and coffee, they also provoke heartburn. In general, the nutrition of a pregnant woman in the third trimester should be as diverse as possible, as the needs of the baby grow.
In general, the nutrition of a pregnant woman in the third trimester should be as diverse as possible, as the needs of the baby grow.
29-34 weeks
At the 8th month, bones are actively growing and teeth are being laid, therefore, it is very important to eat as many calcium-containing foods as possible. For brain development, fatty acids are simply necessary, and they contribute to the absorption of calcium. Iron deficiency at this time can lead to the development of anemia, both in the mother and in the child. Fatty fish, nuts, red meat, dark green vegetables and seeds are the foods to eat during this period of pregnancy.
35-40 weeks
Nutrition at the 9th, last month of pregnancy, should contribute to the overall strengthening of the mother's body. After all, she has a very difficult and time-consuming job ahead of her - childbirth. The main source of energy in the body is carbohydrates, and it is their consumption that should become the basis of the nutrition of a pregnant woman before childbirth. Cereals and vegetables are the foods that you should eat during this period.
Cereals and vegetables are the foods that you should eat during this period.
That's all that can be said about trimester nutrition. An example of a menu for pregnant women by trimesters may also be useful. Based on these menus and explanations for them, you can create a menu for yourself.
Sample menu for pregnant women for the 1st trimester
1. Breakfast: muesli with yogurt and freshly squeezed pear juice.
2. First snack: salmon sandwich.
3. Lunch: mushroom soup, cabbage salad, herbal tea.
4. Second snack: whole grain bread with cheese.
5. Dinner: carrot salad and vegetable risotto. You can drink everything with kefir.
In the first trimester, it is very important that a woman receives a large amount of folate and vitamin B6 from food.
An example of a menu for pregnant women for the 2nd trimester
In the second trimester for pregnant women, the presence of omega-3 acid, calcium, vitamin D and iron in the diet is important.
1. Breakfast: oatmeal in milk with apple and cinnamon, chamomile tea.
2. First snack: almonds with prunes.
3. Lunch: lentil soup, seaweed salad, cranberry juice.
4. Second snack: sandwich with herring.
5. Dinner: omelet with mushrooms and yogurt.
An example of a menu for pregnant women for the 3rd trimester
Carbohydrates and vitamin K play a special role here.
1. Breakfast: pancakes with cream cheese and curdled milk.
2. First snack: whole grain cheese sandwich.
3. Lunch: fish hodgepodge, tuna and green salad, rosehip broth.
4. Second snack: cheesecake.
5. Dinner: fish with rice and fermented baked milk.
Special nutrition for pregnant women
But this is not all the nutritional features of pregnant women. In some cases, women develop pathologies during pregnancy that require special nutrition. So, with anemia in pregnant women, special nutrition is simply necessary. A woman who has experienced pregnancy anemia should consult a doctor not only about drug treatment, but also about an appropriate diet. With such a disease, it is very important to increase the intake of foods containing iron. Iron can be obtained from animal products (lean red meat, fish, poultry) and vegetable (nuts, dried porcini mushrooms, spinach, buckwheat, legumes, etc.) origin. In addition, it is important not only to know which foods to use, but also in what combinations, as this affects the absorption of iron in the human body. Vitamin C increases the absorption of iron in the body, that is, the combination of products containing iron and vitamin C is favorable. Foods containing calcium (dairy products) and tannin (tea, coffee) prevent the absorption of iron in the intestine. Therefore, their use should be separated.
So, with anemia in pregnant women, special nutrition is simply necessary. A woman who has experienced pregnancy anemia should consult a doctor not only about drug treatment, but also about an appropriate diet. With such a disease, it is very important to increase the intake of foods containing iron. Iron can be obtained from animal products (lean red meat, fish, poultry) and vegetable (nuts, dried porcini mushrooms, spinach, buckwheat, legumes, etc.) origin. In addition, it is important not only to know which foods to use, but also in what combinations, as this affects the absorption of iron in the human body. Vitamin C increases the absorption of iron in the body, that is, the combination of products containing iron and vitamin C is favorable. Foods containing calcium (dairy products) and tannin (tea, coffee) prevent the absorption of iron in the intestine. Therefore, their use should be separated.
With obesity that has developed during pregnancy, there may be a need for dietary nutrition for pregnant women.