Low hcg level pregnancy
Low hCG levels in pregnancy: What does it mean?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone that is produced by cells in the placenta during pregnancy. Its job is to nurture and feed the embryo that is attached to the wall of the uterus.
Lower than normal levels of hCG may indicate a problem with the pregnancy including:
- miscarriage
- ectopic pregnancy
- fetal death
Levels of hCG can vary significantly between individuals and from one pregnancy to the next in the same person. But, typically, hCG levels follow a typical range throughout a healthy, uncomplicated pregnancy.
Share on PinterestLevels of hCG tend to decrease in the later stages of pregnancy.Levels of hCG typically increase in the first trimester of a healthy pregnancy.
Levels of hCG usually increase during the first trimester, peak by weeks 8 to 11, and then decline to a steady level in the later stages of the pregnancy.
This means that as the pregnancy develops, hCG becomes less useful as a way to monitor it. When hCG levels do not increase or decrease as they should, it may be a sign of a problem with the pregnancy.
Increasing levels of hCG usually mean that a pregnancy is healthy. However, low hCG levels are not always a sign that something is wrong.
Possible causes of low hCG levels are:
Blighted ovum
A blighted ovum occurs when a fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus, but the embryo fails to develop.
This can happen during early pregnancy, sometimes before a person even knows they are pregnant.
Miscarriage
Miscarriage is also known as spontaneous abortion and happens when the embryo dies naturally before 20 weeks of gestation.
Levels of hCG may rise initially in these situations but fail to increase or decrease as they should afterward.
Miscalculated gestational age
Share on PinterestLevels of hCG may appear low if a doctor has miscalculated the baby’s due date.
This happens when the stage of pregnancy and the estimated date of birth are wrong.
Calculating these events is based on the dates of a woman’s last menstrual period, so miscalculations can occur if someone experiences irregular periods or is not sure when they had their last period.
Low levels of hCG can indicate whether a pregnancy is in a stage where low hCG levels are normal, such as in very early pregnancy, or in a pregnancy that is post-11 weeks.
Sometimes, in cases of miscalculated gestational age, the level of hCG may be lower than expected but not abnormal for the pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy
This is an abnormal pregnancy where the embryo attaches outside of the uterus, usually inside the fallopian tube, the tube that carries the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
Symptoms can include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. An ectopic pregnancy can be a very serious, and even life-threatening, condition. Levels of hCG remain low during an ectopic pregnancy.
Low levels of hCG are not always a sign of a problem.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for situations where low hCG levels are a cause for concern.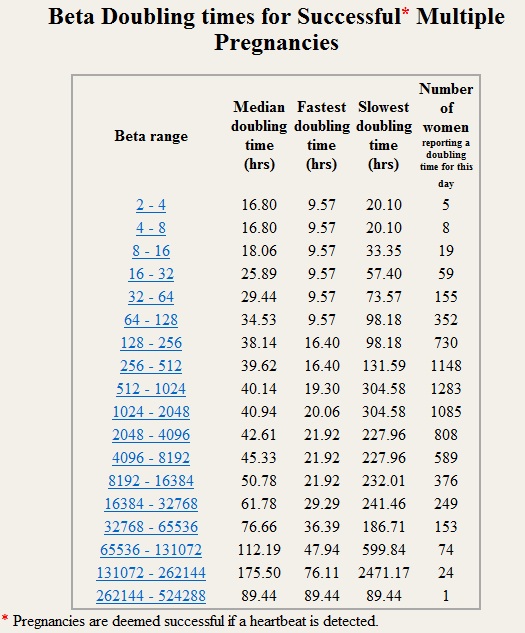
However, treatment is available for the underlying conditions that cause low hCG levels, such as a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy.
In case of a miscarriage
Treatment may involve removing any pregnancy tissue that has been left inside the uterus and might include medication or a surgical procedure.
In case of an ectopic pregnancy, the doctor may also prescribe medications or surgery to remove the affected fallopian tube and the pregnancy itself.
Low hCG levels that result from a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy are usually accompanied by abdominal pain, with or without vaginal bleeding.
There is currently no way to prevent low hCG levels or its associated complications, such as a blighted ovum, a miscarriage, or an ectopic pregnancy.
Low levels of hCG are not always a cause for concern. Levels of hCG can differ between individuals and between different pregnancies in the same person. Some people may naturally have lower levels of hCG than others.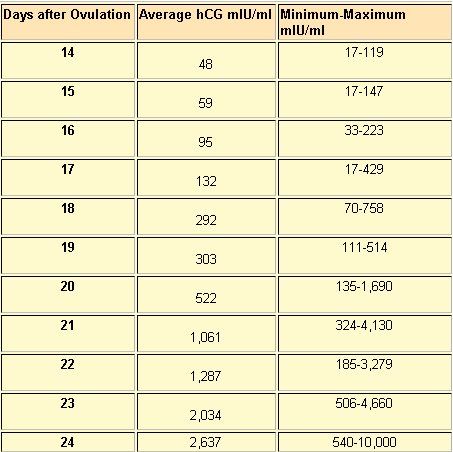
Taking measurements of levels throughout the pregnancy can indicate if the pregnancy is developing as expected.
Even if a complication associated with low hCG levels occurs, such as a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy, this does not mean that someone will be unable to get pregnant again or that their fertility is compromised. A successful pregnancy is still possible with low hCG levels.
Low hCG levels in pregnancy: What does it mean?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone that is produced by cells in the placenta during pregnancy. Its job is to nurture and feed the embryo that is attached to the wall of the uterus.
Lower than normal levels of hCG may indicate a problem with the pregnancy including:
- miscarriage
- ectopic pregnancy
- fetal death
Levels of hCG can vary significantly between individuals and from one pregnancy to the next in the same person. But, typically, hCG levels follow a typical range throughout a healthy, uncomplicated pregnancy.
Levels of hCG typically increase in the first trimester of a healthy pregnancy.
Levels of hCG usually increase during the first trimester, peak by weeks 8 to 11, and then decline to a steady level in the later stages of the pregnancy.
This means that as the pregnancy develops, hCG becomes less useful as a way to monitor it. When hCG levels do not increase or decrease as they should, it may be a sign of a problem with the pregnancy.
Increasing levels of hCG usually mean that a pregnancy is healthy. However, low hCG levels are not always a sign that something is wrong.
Possible causes of low hCG levels are:
Blighted ovum
A blighted ovum occurs when a fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus, but the embryo fails to develop.
This can happen during early pregnancy, sometimes before a person even knows they are pregnant.
Miscarriage
Miscarriage is also known as spontaneous abortion and happens when the embryo dies naturally before 20 weeks of gestation.
Levels of hCG may rise initially in these situations but fail to increase or decrease as they should afterward.
Miscalculated gestational age
Share on PinterestLevels of hCG may appear low if a doctor has miscalculated the baby’s due date.
This happens when the stage of pregnancy and the estimated date of birth are wrong.
Calculating these events is based on the dates of a woman’s last menstrual period, so miscalculations can occur if someone experiences irregular periods or is not sure when they had their last period.
Low levels of hCG can indicate whether a pregnancy is in a stage where low hCG levels are normal, such as in very early pregnancy, or in a pregnancy that is post-11 weeks.
Sometimes, in cases of miscalculated gestational age, the level of hCG may be lower than expected but not abnormal for the pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy
This is an abnormal pregnancy where the embryo attaches outside of the uterus, usually inside the fallopian tube, the tube that carries the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
Symptoms can include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. An ectopic pregnancy can be a very serious, and even life-threatening, condition. Levels of hCG remain low during an ectopic pregnancy.
Low levels of hCG are not always a sign of a problem.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for situations where low hCG levels are a cause for concern.
However, treatment is available for the underlying conditions that cause low hCG levels, such as a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy.
In case of a miscarriage
Treatment may involve removing any pregnancy tissue that has been left inside the uterus and might include medication or a surgical procedure.
In case of an ectopic pregnancy, the doctor may also prescribe medications or surgery to remove the affected fallopian tube and the pregnancy itself.
Low hCG levels that result from a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy are usually accompanied by abdominal pain, with or without vaginal bleeding.
There is currently no way to prevent low hCG levels or its associated complications, such as a blighted ovum, a miscarriage, or an ectopic pregnancy.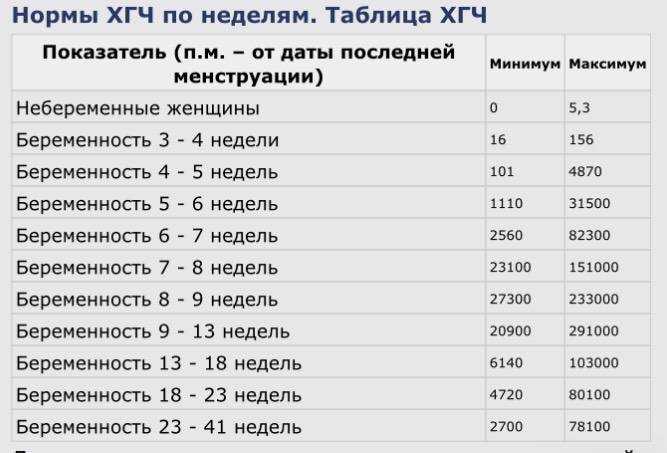
Low levels of hCG are not always a cause for concern. Levels of hCG can differ between individuals and between different pregnancies in the same person. Some people may naturally have lower levels of hCG than others.
Taking measurements of levels throughout the pregnancy can indicate if the pregnancy is developing as expected.
Even if a complication associated with low hCG levels occurs, such as a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy, this does not mean that someone will be unable to get pregnant again or that their fertility is compromised. A successful pregnancy is still possible with low hCG levels.
What low hCG indicates
During pregnancy, significant changes occur in the female body that are necessary for the normal development of the unborn child. One of the most global changes is a change in the hormonal background, which affects not only the physical, but also the emotional state of a woman. Important for the development of the fetus is a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin. It supports the functioning of the corpus luteum and provides many other functions.
It supports the functioning of the corpus luteum and provides many other functions.
What is hCG
HCG or human chorionic gonadotropin - is produced in large quantities in the female body during pregnancy. It is also synthesized in non-pregnant women and men, but in very small amounts. In this case, its increase requires an urgent consultation of a specialist, since an increase in this hormone without pregnancy indicates the development of an oncological disease. If you find an increased level of the hormone (in the absence of pregnancy or in men), you should contact your general practitioner, family doctor or oncologist to clarify the state of health.
HCG is produced by the chorion (upper germinal membrane) of the fetus almost immediately after it is implanted in the uterus. The presence of hCG and its rapid increase indicates the normal development of pregnancy.
HCG is a gonadotropic hormone, similar to follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, which are synthesized by the pituitary gland, but differ from them in amino acid sequence. It consists of two subunits - α and β. The α-subunit is identical to the α-subunits of follicle-stimulating, luteinizing and thyroid-stimulating hormones, and the β-subunit has a biological and immunoreactive uniqueness specifically for human chorionic gonadotropin. Therefore, the β-subunit is used as a biochemical marker in prenatal screenings. In addition, the "home" test for pregnancy in the form of a strip is based on determining the presence of the β-subunit.
It consists of two subunits - α and β. The α-subunit is identical to the α-subunits of follicle-stimulating, luteinizing and thyroid-stimulating hormones, and the β-subunit has a biological and immunoreactive uniqueness specifically for human chorionic gonadotropin. Therefore, the β-subunit is used as a biochemical marker in prenatal screenings. In addition, the "home" test for pregnancy in the form of a strip is based on determining the presence of the β-subunit.
Functions of hCG
The main task of human chorionic gonadotropin is to prolong the existence of the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone (a hormone necessary for the development of the fetus). At the same time, under the influence of hCG, the corpus luteum produces a very large amount of progesterone, which is impossible during the normal functioning of the body of a non-pregnant woman.
The corpus luteum forms at the site of a ruptured follicle after the release of an egg from it (ovulation). In a normal menstrual cycle, the corpus luteum exists for about 10-12 days, after which it dissolves.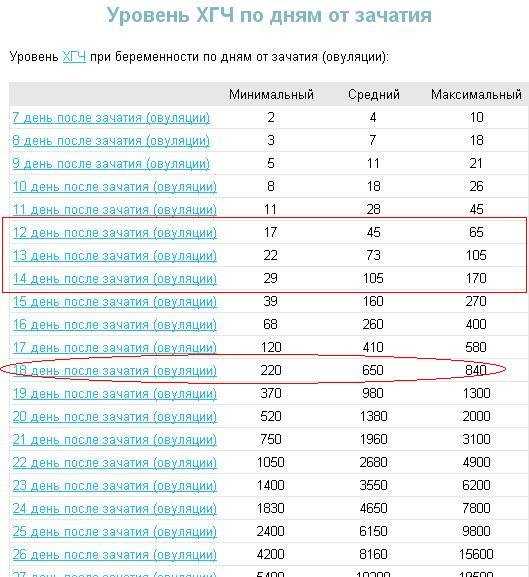 When pregnancy occurs, hCG does not allow it to disappear so that the production of progesterone does not stop. HCG will maintain the existence of the corpus luteum until the placenta of the fetus fully matures and begins to produce the required amount of progesterone on its own, i.e. by the end of the first trimester.
When pregnancy occurs, hCG does not allow it to disappear so that the production of progesterone does not stop. HCG will maintain the existence of the corpus luteum until the placenta of the fetus fully matures and begins to produce the required amount of progesterone on its own, i.e. by the end of the first trimester.
Thus, the level of the hormone begins to increase rapidly from the first days of pregnancy: starting from 0-25 mIU / ml and reaching approximately 200,000 mIU / ml by the twelfth week of pregnancy. Further, the level of hCG will gradually decrease, while still continuing to remain quite high.
In addition, human chorionic gonadotropin has an effect on the secretion of hormones in the adrenal cortex. An increase in the synthesis of glucocorticoids in pregnant women plays an important role in the mechanisms of adaptation of the female body to a stressful state, which, in essence, is pregnancy. Also, glucocorticoids provide physiological immunosuppression, which is necessary to support the development of a semi-foreign organism, i. e. fetus.
e. fetus.
Chorionic gonadotropin has a beneficial effect on the development of the placenta, improving its trophism, and helps to increase the number of chorionic villi. HCG is also used to stimulate ovulation during assisted reproductive technologies. An hCG injection is a mandatory component during IVF. HCG contributes to the normal completion of the maturation of the follicles and provokes the release of eggs to the outside.
IVF procedure in Kaliningrad is possible in the IVF Center clinic. The clinic's specialists have extensive experience in various ART methods, including IVF.
When to check the level of hCG
In order to check the presence of pregnancy, women, in most cases, firstly carry out a pregnancy test using a special strip. Such a test strip can be bought at any pharmacy or supermarket. A blood test for hCG levels is one of the first tests that a woman will take after IVF to confirm pregnancy. Usually the test is carried out after a few days of delay in menstruation. With a planned pregnancy or after IVF, it is not rational to conduct a test earlier than 2 weeks after ovulation or embryo transfer: you can get a false result.
With a planned pregnancy or after IVF, it is not rational to conduct a test earlier than 2 weeks after ovulation or embryo transfer: you can get a false result.
Despite the fact that hCG begins to be synthesized in the body immediately after the implantation of the embryo in the uterus, its level in the urine will always be several times lower than in the blood. Therefore, the most informative is a blood test for the content of hCG in it. For examination, venous blood is used, which is taken on an empty stomach.
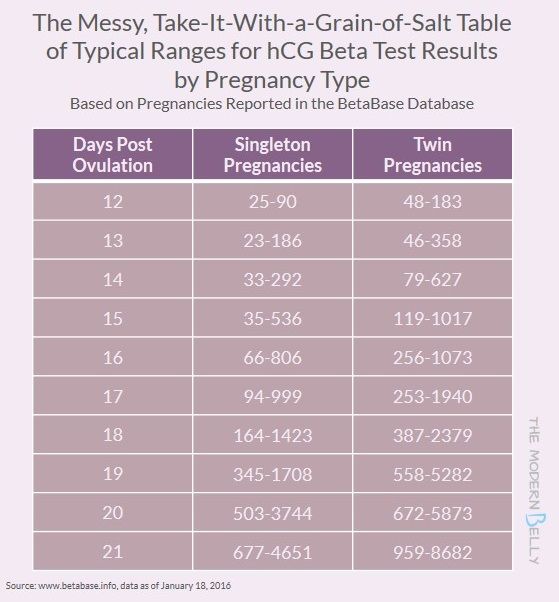
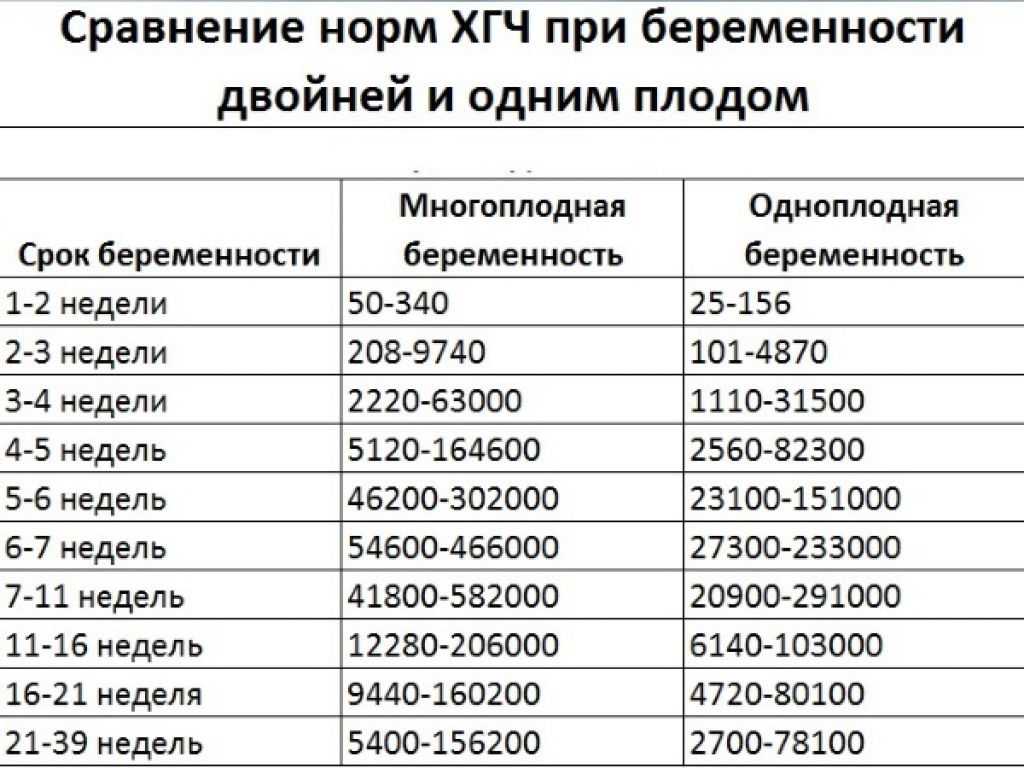
According to the level of chorionic hormone in the blood, you can determine the course of pregnancy if you monitor its performance in dynamics. The level should increase tens of thousands of times a week. With multiple pregnancies, the level will be even higher: hCG increases in proportion to the number of fetuses.
It should be noted that the same laboratory should be used to track the growth of hCG. This is due to the fact that laboratories may use different research methods: equipment and reagents may differ.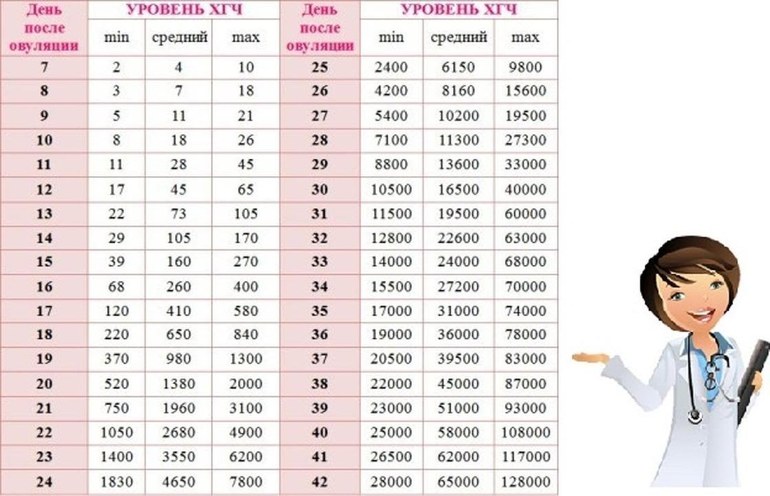 The units of measurement may also differ.
The units of measurement may also differ.
The study of hCG in dynamics also allows you to notice a decrease in its level in time, which may indicate the appearance of pregnancy developmental disorders.
In addition to the course of pregnancy, hCG analysis is part of prenatal screenings, which are carried out in the first and second trimester, to identify the risk of genetic abnormalities (Down syndrome, Edwards, etc.). During screenings, the hCG β-subunit is examined, as well as indicators of other hormones, the results of preliminary ultrasound and the incoming questionnaire data, which indicate the history of the pregnant woman. If the screening results show a high risk of pathologies, the woman is referred for invasive examinations, which will more accurately show the condition of the fetus.
Low hCG in ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a condition in which a fertilized egg is implanted elsewhere in the female reproductive system than in the uterine wall. In most cases, this site is the fallopian tubes. This condition is very dangerous for a woman's health: it can cause deformation of the reproductive organs, severe bleeding, and even death. An ectopic pregnancy is difficult to diagnose right away because its onset is very similar to a normal pregnancy. During an ectopic pregnancy, menstruation is delayed, the level of the hormone in the blood begins to rise, respectively, and the test strip will give a positive result.
In most cases, this site is the fallopian tubes. This condition is very dangerous for a woman's health: it can cause deformation of the reproductive organs, severe bleeding, and even death. An ectopic pregnancy is difficult to diagnose right away because its onset is very similar to a normal pregnancy. During an ectopic pregnancy, menstruation is delayed, the level of the hormone in the blood begins to rise, respectively, and the test strip will give a positive result.
In the early stages, an ectopic pregnancy can only be detected by ultrasound. A signal to check the localization of implantation will be low hCG. With an ectopic pregnancy, the hCG level will first rise as usual, and then it will begin to drop sharply. That is why it is useful to conduct a study of hCG in dynamics.
An ectopic pregnancy can only be treated with surgery. If an ectopic pregnancy is localized in the fallopian tube, then it must be removed to preserve the rest of the reproductive system and the health of the woman.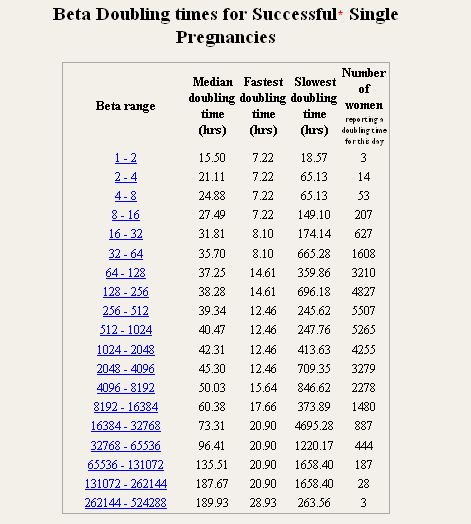
Low hCG with a threatened miscarriage
In addition to an ectopic pregnancy, low hCG can signal pregnancy problems: the appearance of a threatened miscarriage, placental insufficiency, miscarriage. In these situations, a decrease in the level of the hormone may be accompanied by the appearance of bleeding from the uterus: abundant or slight.
Bloody discharge in combination with low hCG is the basis for a serious examination of a woman and often hospitalization. The examination is necessary to find out the causes of the violation of the course of pregnancy, and in the hospital the woman will be provided with the necessary assistance to maintain the pregnancy.
Make an appointment by phone
+7 (4012) 79-55-39
or
use the appointment form:
Normal hCG during pregnancy. Table of hCG values by week. Elevated HCG. Low HCG. HCG in ectopic pregnancy. hCG during IVF (hCG after replanting, hCG at 14 dpo).
hCG or beta-hCG or total hCG - human chorionic gonadotropin - a hormone produced during pregnancy. HCG is formed by the placenta, which nourishes the fetus after fertilization and implantation (attachment to the wall of the uterus).
HCG is formed by the placenta, which nourishes the fetus after fertilization and implantation (attachment to the wall of the uterus).
- What is hCG (= beta hCG)
- When to donate blood for hCG
- HCG norm. Deciphering the analysis of hCG. HCG level during pregnancy
- Normal HCG doubling time
- HCG norms by week. HCG table
- Low hCG. What does hCG below normal mean?
- Negative hCG or hCG indicative of non-pregnancy with missed period
- hCG and biochemical pregnancy
- hCG and ectopic pregnancy
- Elevated hCG. What can hCG levels above normal mean?
- HCG and multiple pregnancy. hcg and twins.
- Blister drift
- HCG test after embryo transfer. HCG for IVF
- hCG and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- Elevated hCG levels in non-pregnant women and men
- How does hCG change after miscarriage, abortion, childbirth?
- What medications affect hCG levels?
What is hCG (= beta-hCG)
HCG or beta-hCG or total hCG - human chorionic gonadotropin - a hormone produced during pregnancy. HCG is formed by the placenta, which nourishes the fetus after fertilization and implantation (attachment to the wall of the uterus). HCG is measured in mIU/mL (mile international units per milliliter).
HCG is formed by the placenta, which nourishes the fetus after fertilization and implantation (attachment to the wall of the uterus). HCG is measured in mIU/mL (mile international units per milliliter).
HCG partially crosses the placental barrier. The level of hCG in newborns is approximately 1/400 of the level in maternal blood. And it is approximately 10-50 mIU / ml at birth. The half-life is 2-3 days. Thus, at 3 months of life, the level in newborns corresponds to the norm of hCG for an adult.
When to donate blood for hCG
An increase in hCG in the blood can be detected a few days before the expected menstruation. The optimal time for a blood test to determine hCG is after a missed period.
A single determination of hCG cannot be used to diagnose miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
HCG norm. Deciphering the analysis of hCG. HCG level during pregnancy
An hCG level of less than 5 mIU / ml indicates the absence of pregnancy or that the test was taken too early. The level of hCG is above 25 mIU / ml - about the presence of pregnancy.
The level of hCG is above 25 mIU / ml - about the presence of pregnancy.
On average, a doubling of hCG levels occurs every 36-72 hours. The level of hCG reaches its peak at 9-11 weeks of gestation (from the date of the last menstrual period) and then decreases until the 15th week of pregnancy, remaining unchanged during the remainder of the pregnancy. In 85% of cases, the level of hCG in the early stages doubles every 48-72 hours. As pregnancy progresses, the doubling time for hCG levels increases to 96 hours.
Normal HCG doubling time
HCG level Doubling time
1200 mIU/ml 48-72 hours
1200 – 6000 mIU/ml 72-96 hours
More than 6000 mIU/ml More than 96 hours
hcg calculator
At what hCG value do ultrasound?
After reaching an hCG level of 1000 - 2000 mIU / ml, a fetal egg can be visualized by ultrasound. Since the level of hCG has a large variability, and the date of conception can be erroneous, the gestational age is determined by ultrasound or IVF data, but not by hCG.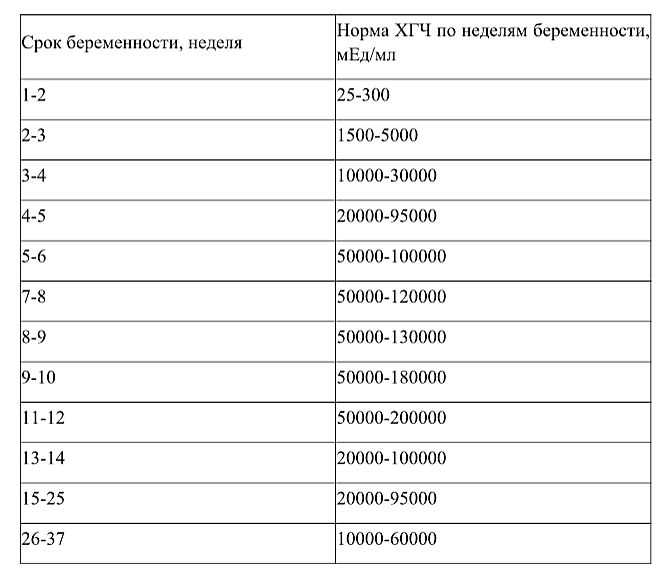
A single determination of hCG is not enough, since it is important to evaluate the growth dynamics of the hormone every 48-72 hours.
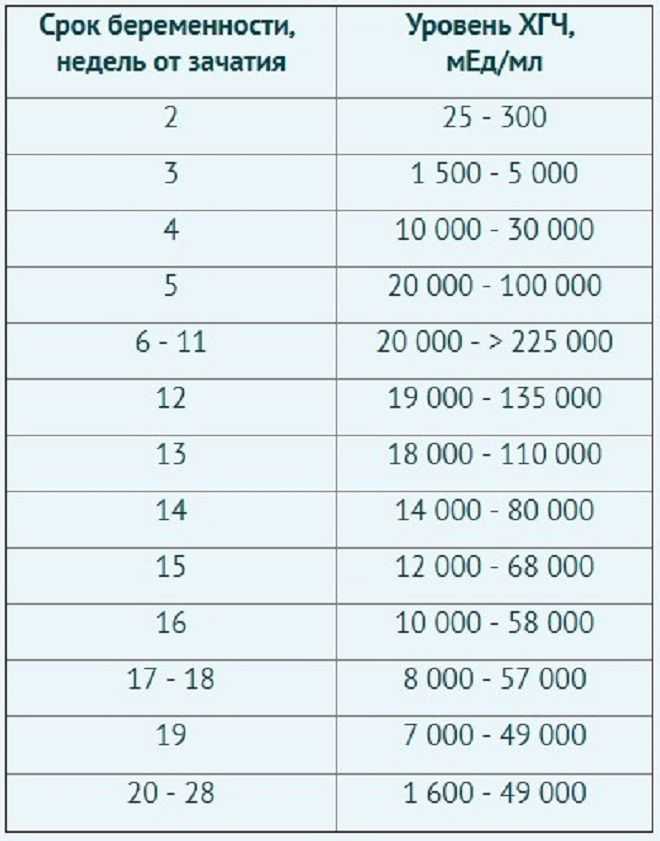
HCG norms by week. HCG table
| Indicator (p.m. - from the date of the last menstruation) | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|
| Non-pregnant women | 0 | 5.3 |
| Pregnancy 3 - 4 weeks | 16 | 156 |
| Pregnancy 4 - 5 weeks | 101 | 4870 |
| Pregnancy 5 - 6 weeks | 1110 | 31500 |
| Pregnancy 6 - 7 weeks | 2560 | 82300 |
| Pregnancy 7 - 8 weeks | 23100 | 151000 |
| Pregnancy 8 - 9 weeks | 27300 | 233000 |
| Pregnancy 9 - 13 weeks | 20900 | 291000 |
| Pregnancy 13 - 18 weeks | 6140 | 103000 |
| Pregnancy 18 - 23 weeks | 4720 | 80100 |
| Pregnancy 23 - 41 weeks | 2700 | 78100 |
These ranges are provided as a guide and should not be used to interpret a particular hCG assay.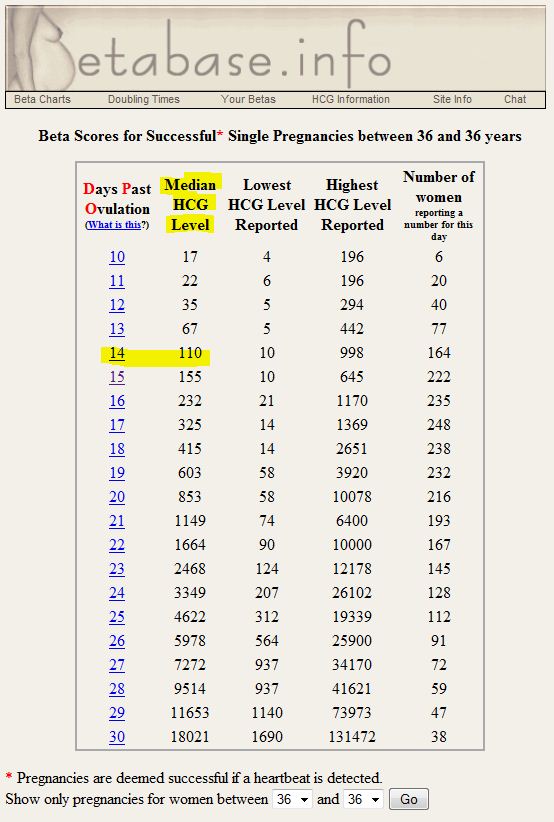
Low hCG. What does hCG below normal mean?
- Not pregnant
- Error in calculating the gestational age
- Pregnancy arrest or miscarriage, biochemical pregnancy
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Threat of spontaneous abortion
Negative hCG or hCG indicative of non-pregnancy with missed period
It is necessary to repeat the analysis for hCG in 1-2 days, perhaps the pregnancy came later than expected. If the level of hCG does not rise, it is necessary to look for other reasons for the delay in menstruation.
hCG and biochemical pregnancy
The so-called "biochemical pregnancy" is a condition in which an increase in hCG above normal was detected, but the pregnancy did not continue to develop. The level of hCG in this case rises slightly, and then in a short time decreases to zero values.
HCG and ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy in which the fertilized egg is outside the uterine cavity. With an ectopic pregnancy, there may be pain in the lower abdomen, spotting. The level of hCG during an ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy may not increase as quickly and not as significantly as with a normally developing uterine pregnancy. However, the low level of hCG does not allow such a conclusion to be made unambiguously. Starting with an hCG level of 1000 mIU / ml, a fetal egg can be detected in the uterine cavity. With an hCG level of 2000 mIU / ml and the absence of a fetal egg in the uterine cavity during ultrasound, the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy is significant.
With an ectopic pregnancy, there may be pain in the lower abdomen, spotting. The level of hCG during an ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy may not increase as quickly and not as significantly as with a normally developing uterine pregnancy. However, the low level of hCG does not allow such a conclusion to be made unambiguously. Starting with an hCG level of 1000 mIU / ml, a fetal egg can be detected in the uterine cavity. With an hCG level of 2000 mIU / ml and the absence of a fetal egg in the uterine cavity during ultrasound, the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy is significant.
Increased hCG. What can hCG levels above normal mean?
- Error in calculating the gestational age
- Blister drift
- Multiple pregnancy
- Complications of pregnancy (preeclampsia)
- Maternal diabetes mellitus
- Taking synthetic progestogens
- Risk of fetal malformations
HCG and multiple pregnancy. hcg and twins.
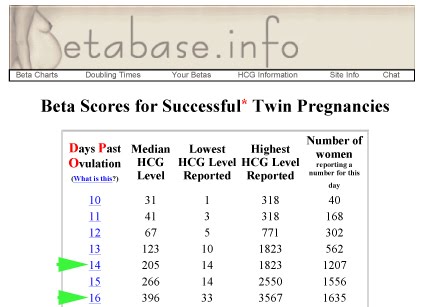
The level of hCG in a multiple pregnancy is higher than in a single pregnancy, but the rate of increase in hCG is the same in both cases.
Blister
Vesicular drift is a rare complication of pregnancy in which the level of hCG will be significantly increased, on average 2 times higher than the average value for a given period. For example, the possible level of hCG with cystic mole for 36 days from the first day of the last menstruation can reach 200,000 mIU / ml, while with a normally developing pregnancy, hCG will be from 1,200 to 36,000 mIU / ml.
HCG test after embryo transfer. HCG in IVF
An hCG test is performed approximately 2 weeks after embryo transfer (12-14 days after transfer (dpp)). Usually the level of hCG at 14 dpo is more than 100 mIU / ml.
If the hCG level is less than 25 mIU / ml, pregnancy has not occurred. If the hCG level is more than 25, the test is repeated after 2 days, with the development of pregnancy, its level should increase.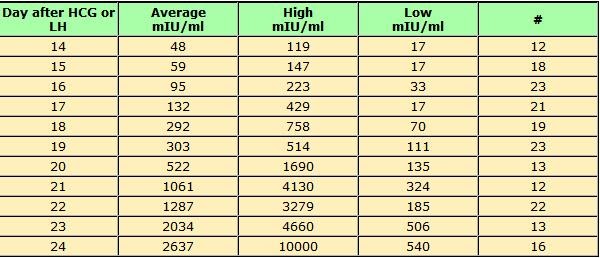 The hCG level will double approximately every 48 hours until 21 days after infusion.
The hCG level will double approximately every 48 hours until 21 days after infusion.
Higher hCG values (300-400 mIU / ml) are more likely to indicate multiple pregnancy.
hCG and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
In patients with ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, hCG levels should be interpreted with caution. These patients may develop edema, which leads to thickening of the blood, which can lead to a false increase in the level of hCG, and when the blood composition is normal, to a false absence of an increase in the level of hCG.
HCG in later pregnancy
The test for hCG is also included in the prenatal screening of the second trimester - an analysis that allows you to assess the risk of developing fetal defects.
Elevated hCG levels in non-pregnant women and men
Outside of pregnancy, hCG can be produced by the cells of some tumors (seminoma, testicular teratoma, neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract (including pancreas, liver, colorectal cancer and stomach cancer).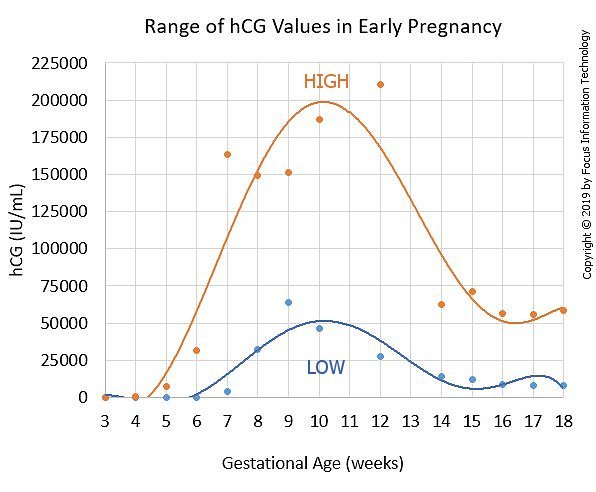
With successful treatment of an hCG-producing tumor, the hCG level should decrease to normal.
How does hCG change after miscarriage, abortion, childbirth?
In most cases, the level of hCG decreases. The half-life of hCG is 24-36 hours. The speed of reaching zero hCG values depends on what exactly happened: spontaneous miscarriage, abortion, childbirth, curettage) and how high the hCG level was at the time of pregnancy loss. Doctors recommend continuing to assess hCG levels until levels are below 5 mIU/mL. If the hCG level remains high, you should consult a doctor.
What medications affect hCG levels?
The level of hCG is affected by drugs that contain hCG (Pregnil, Horagon).
-
ToRCH infections and pregnancy
What are ToRCH infections, what are the dangers of these infections during pregnancy, how and when is the examination performed, how to interpret the results. Perinatal infections account for approximately 2-3% of all congenital fetal anomalies.
-
Pregnancy Tests in the CIR Laboratories
In our laboratory you can undergo a complete examination at the onset of pregnancy, take tests at any time, and in our clinics you can conclude an agreement on pregnancy management.
-
Online hCG calculator during pregnancy
The hCG calculator is used to calculate the increase in hCG (the difference between two tests taken at different times).
The increase in hCG is important for assessing the development of pregnancy. Normally, in the early stages of pregnancy, hCG increases by about 2 times every two days. As the hormone levels increase, the rate of increase decreases.
-
False positive pregnancy test or why hCG is positive but not pregnant?
When can a pregnancy test be positive?
-
The norm of a complete blood count during pregnancy. Hemoglobin, platelets, hematocrit, erythrocytes and leukocytes during pregnancy. Clinical blood test during pregnancy.
 Hematological changes during pregnancy.
Hematological changes during pregnancy. Translation of materials from UpTodate.com
A normal pregnancy is characterized by significant changes in almost all organs and systems to adapt to the requirements of the fetoplacental complex, including changes in blood tests during pregnancy. -
Risk assessment of pregnancy complications using prenatal screening
Prenatal screening data allow assessing not only the risks of congenital pathology, but also the risk of other pregnancy complications: intrauterine fetal death, late toxicosis, intrauterine hypoxia, etc.
-
Parvovirus B19 and parvovirus infection: what you need to know when planning and getting pregnant.
What is a parvovirus infection, how is the virus transmitted, who can get sick, what is the danger of the virus during pregnancy, what tests are taken for diagnosis.
-
Pregnancy planning
Obstetrics differs from other specialties in that during the physiological course of pregnancy and childbirth, in principle, it is not part of medicine (the science of treating diseases), but is part of hygiene (the science of maintaining health).