Low body temperature in a baby
Causes, What to Do, Seeking Help
Like the temperature of an adult, a baby’s temperature can fluctuate slightly based on things like time of day, activity, and even how their temperature was taken.
A child’s temperature may be as low as 95.8°F (35.5°C) in the morning and as high as 99.9°F (37.7°C) late in the day when measured with an oral thermometer. These temperatures would still be considered in the typical range, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP).
But taking an oral temperature in a baby isn’t accurate, since they can’t hold the thermometer under their tongue. When taken with a rectal thermometer, a baby’s temperature may be anywhere from 96.8°F (36°C) in the morning to 100.3°F (37.9°C) late in the day, according to the AAP.
Taking a baby’s temperature under their arm (axillary) is another commonly used method. It’s easier to do but still less accurate than taking a rectal temperature. The axillary temperature is usually at least a degree lower than the rectal temperature.
If your baby’s rectal temperature drops below 95°F (35°C), they’re considered to have hypothermia, per the AAP.
Hypothermia is low body temperature. A low body temperature in babies can be dangerous and, though rare, may lead to death.
Read on to learn more about low body temperature in babies, including causes and next steps.
In addition to a low body temperature, other symptoms of hypothermia in babies include:
- sluggishness
- poor feeding
- weak cry
- pale, cool skin
- trouble breathing
Premature birth and low birth weight
Infants born at less than 28 weeks’ gestation have the highest risk of developing hypothermia, according to research from 2013.
Low birth weight is another risk factor. Babies who are 3.3 pounds (1.5 kilograms) or fewer are 31 to 78 percent more likely to develop hypothermia immediately after birth than babies with a higher birth weight, based on this 2013 research.
Early babies and those with low birth weight run a higher risk of hypothermia because of their large surface-area-to-volume ratio. This refers to the fact that a baby is a tiny human — especially if they’re born early or with low birth weight — which means they can’t hold as much heat inside their bodies as older children or adults.
This refers to the fact that a baby is a tiny human — especially if they’re born early or with low birth weight — which means they can’t hold as much heat inside their bodies as older children or adults.
Additional contributing factors are their:
- lack of insulating body fat
- still developing nervous system
- inability to efficiently conduct heat
Shortly after a hospital birth, if your baby is premature or has a low birth weight, they’ll be placed in specially designed bassinets that have warming lights and heated mattresses.
When you bring your baby home, use these tips to help regulate their body temperature:
- Swaddle or wrap your baby snugly in a single blanket.
- Place a hat on your baby if they’ll be out in a cold environment to help reduce heat loss.
- Limit baths. Water evaporating on skin can lower body temperature, so bathing (other than sponge bathing) isn’t recommended for babies until after their umbilical cord falls off around 2 weeks of age.

Cold birth environment
Many babies, even full-term ones, are born with a near hypothermic body temperature. Being born in a cold space can quickly cause your baby’s body temperature to drop.
In the hospital, a number of protocols may be in place to warm up your baby, including:
- immediately drying the baby after delivery to remove wet and cold amniotic fluid
- placing the baby in a bassinet with radiant heat
- using heated mattresses and blanket wraps
- encouraging skin-on-skin contact with a parent
- delaying the first bath until at least 12 hours after birth, when a baby may be a little more efficient at staying warm
If your baby is born outside of a hospital, it’s important to keep them warm using similar methods. While you may not have access to a heated mattress, you can dry baby off, use skin-to-skin contact, and swaddle or wrap them in a blanket.
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is a condition in which there’s too little glucose, or blood sugar, circulating in your body.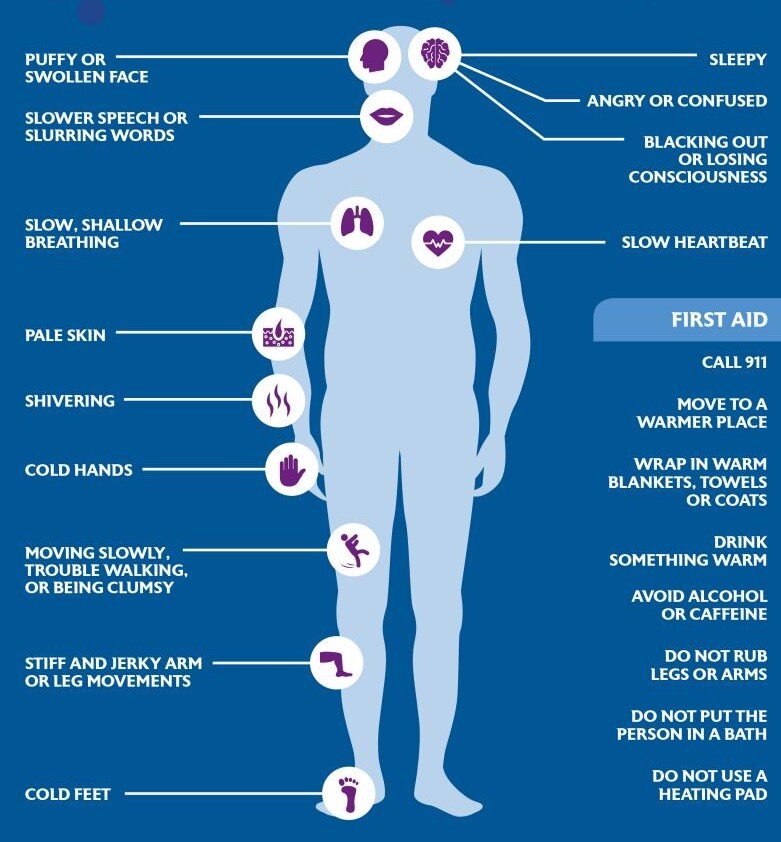 Glucose is used by your body for energy.
Glucose is used by your body for energy.
A baby can become hypoglycemic at birth or soon after because of:
- infection
- birth abnormalities
- the birthing parent’s health during pregnancy
To help prevent hypoglycemia in your baby:
- Maintain a healthy diet during pregnancy and follow your doctor’s recommendations for weight gain.
- Manage diabetes during pregnancy if you have that condition, and get tested for gestational diabetes.
- Keep your baby on a regular feeding schedule.
Infection
Some serious infections have been associated with a drop in body temperature.
Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes that surround the spinal cord. It can sometimes cause a fever in babies, but in other cases it may cause a lower-than-average body temperature.
Sepsis, a dangerous bacterial infection of the blood, commonly causes a low body temperature in infants. In some cases, it may lead to a fever instead.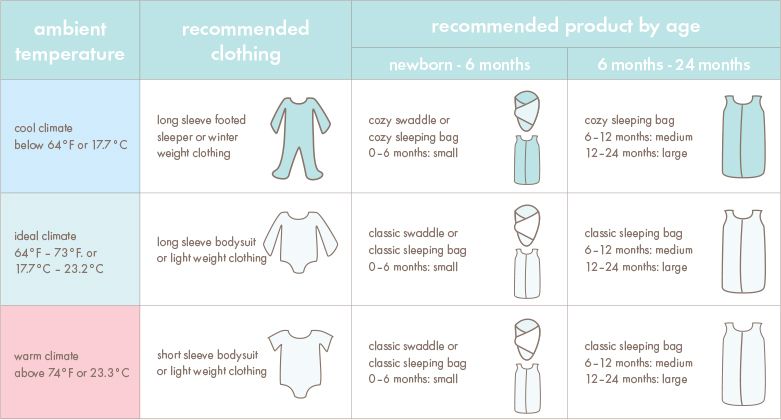
Both meningitis and sepsis are serious life threatening infections. Get immediate medical help if you notice several of these symptoms in your baby:
- pale, clammy, blotchy skin, and sometimes a rash
- poor feeding
- fast breathing
- moaning cry
- cold hands and feet
Low body temperature can be serious.
When a baby’s temperature drops below the typical range, their body uses more oxygen in an effort to create more body warmth. That increase can put a huge stress on a tiny body.
In some cases, low body temperature may even lead to death, though this is exceedingly rare in the United States.
In a 2010 study conducted in Nepal, researchers looked at newborns within the first 72 hours of birth and found that those with a body temperature below 94.1°F (34.5°C) were 4.8 times more likely to die within a week of birth than those who had higher temperatures.
If you suspect your baby has a low body temperature, the first thing you should do is take their temperature!
Rectal temperatures may be more accurate, but if you don’t have a rectal thermometer, you can use an axillary thermometer. Never use an axillary thermometer in the rectum or vice versa.
Never use an axillary thermometer in the rectum or vice versa.
If your baby’s temperature is low, try to increase it by:
- adding clothing
- using your body heat
- swaddling them in a blanket
If these steps don’t work and their temperature remains low, call their pediatrician right away.
The doctor may direct you to seek emergency medical help. If you can’t reach the doctor and your baby seems ill, go to the nearest emergency room.
Early treatment can help reduce the risk for serious complications. Always call your baby’s doctor if you suspect something is wrong. It’s better to err on the side of caution.
A rectal temperature lower than 95°F (35°C) puts a baby at increased risk for:
- infections
- respiratory problems
- blood clotting disorders
- death
Babies lose heat more quickly than adults. If you notice any of the symptoms of hypothermia in babies — such as rapid or difficult breathing, pale skin, lethargy or a lack of interest in eating — try to increase your baby’s temperature with extra clothing and warm liquids, and seek medical help right away.
Be especially attentive if your baby was born early or at a low birth weight, as these children are more likely to experience a low body temperature than full-term babies.
Baby temperature is low: Causes, treatments, and prevention
When a healthy baby has a low temperature, it may not signal a problem. However, very low temperatures may indicate or cause a serious health problem.
The average healthy body temperature is 98.6°F. Shifts in a baby’s activity level or environment can affect their temperature, while different methods of taking a temperature can give slightly different readings.
Newborns and babies are less able to regulate their body temperature. Because of this, when a baby has a low temperature, it is important to address the cause quickly.
Share on PinterestA baby’s temperature may be low following a prolonged period in water.A variety of factors can cause a low temperature in a baby. They include:
- cold weather
- prolonged periods in water
- not drying a baby after birth
The most common reason for low body temperature is that babies, especially newborns, cannot regulate their body temperature as well as older children and adults. So exposure to even slightly low temperatures is more likely to cause a low body temperature in a newborn.
So exposure to even slightly low temperatures is more likely to cause a low body temperature in a newborn.
It is also important to note that taking temperatures incorrectly or using inaccurate equipment may give incorrect readings. Using a variety of methods or thermometers may address inaccuracies.
A low body temperature poses more dangers to newborns, especially those born prematurely or at a low birth weight.
A baby who has a low body temperature may:
- develop blue lips or fingers
- feel very cold
- act lethargic or sick
The risks of a prolonged low body temperature include:
- problems with the baby’s metabolism
- breathing issues
- an increased risk of dying, even when low body temperature is not the direct cause of death
Share on PinterestA rectum temperature reading usually provides the most accurate information.
The ideal baby temperature depends on the method a person uses to take the temperature. In babies younger than 2 years old, rectum temperature readings offer the most accurate information, provided the parent or caregiver takes the measurement correctly, using working equipment.
In babies younger than 2 years old, rectum temperature readings offer the most accurate information, provided the parent or caregiver takes the measurement correctly, using working equipment.
Healthy temperature readings are as follows:
- Rectal: 97.9 to 100.4°F
- Mouth: 95.9 to 99.5°F
- Armpit: 97.8 to 99.5°F
- Ear: 96.4 to 100.4°F
Temperatures below these ranges may signal hypothermia, which is a dangerously low body temperature. Temperatures above these ranges could be a sign of a fever. A fever may mean the baby has an infection or is too hot.
Each baby is different. Sometimes a falling temperature indicates a problem even if the baby’s temperature is within the normal range. So ask a healthcare provider about the ideal temperature for the baby.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommend measuring a very unwell baby’s temperature as frequently as hourly. In a very small baby, taking the temperature two to four times daily can help with detecting unhealthy temperature swings. The WHO advise taking daily temperature readings in an infant whose condition is improving.
The WHO advise taking daily temperature readings in an infant whose condition is improving.
The correct treatment depends on why the baby’s temperature is low. Babies are vulnerable both to cold and to overheating. Because of this, parents or caregivers should not overdress babies, put them in front of hot radiators, or otherwise expose them to intense heat in an attempt to warm them.
It is important to see a healthcare provider if a baby has a low temperature that does not rise after using strategies such as dressing the baby more warmly or increasing the temperature of the house.
When a newborn has trouble regulating their body temperature, some strategies can help. They include:
- drying the baby to prevent heat loss
- holding the baby skin-to-skin against the warm body of a parent or caregiver
- covering the baby with a blanket, especially during skin-to-skin contact
- breastfeeding
If these strategies fail, a healthcare provider may recommend:
- warming devices, such as an over-the-bed warmer or heat lamp
- placing the baby in an open bed with a radiant warmer
- putting the baby in an incubator
Dressing a baby in seasonally appropriate clothing—without overdressing or overheating the baby—can prevent them from getting too cold. Skin-to-skin contact with a parent or caregiver is also helpful because their warm body may help regulate the baby’s body temperature.
Skin-to-skin contact with a parent or caregiver is also helpful because their warm body may help regulate the baby’s body temperature.
However, it is not possible to prevent all cases of hypothermia or low body temperature. Sometimes, a low body temperature indicates that the baby’s brain is not sending the right signals to regulate its body temperature or that the baby’s body cannot do certain things that would generally raise body temperature.
Seeking prompt medical care when a baby has a body temperature more than a degree below normal can help prevent serious complications.
Share on PinterestParents and caregivers should talk to a doctor if their baby has an abnormal temperature.
Infections are more dangerous in young infants. Babies and newborns are also less able to regulate their body temperature.
Parents or caregivers should err on the side of caution when a baby has an abnormal temperature, especially if the baby was born prematurely or is younger than 3 months old. Call a doctor anytime a baby’s temperature falls outside the normal range.
Call a doctor anytime a baby’s temperature falls outside the normal range.
Seek emergency care if a baby seems lethargic or their temperature continues falling despite efforts to warm them.
Parents of low birth weight and premature babies should ask a healthcare provider when to seek emergency care for a low temperature.
It is important to take changes in temperature seriously, particularly if the baby has other health risk factors, such as an infection, a history of breathing problems, or they were born prematurely.
However, a low body temperature is not a reason to panic, especially if the temperature is just a few tenths of a point outside the normal range.
A pediatrician or other healthcare provider can help parents or caregivers decide if the low temperature is normal and healthy, or a sign of a problem. Seek treatment as soon as possible, since a healthcare provider can offer peace of mind and ensure the baby gets the right treatment.
Low body temperature in a child
Content of the article:
- 1 What should I do if my child has a low temperature?
- 2 What is low body temperature in a child?
- 3 How dangerous is a very low temperature in a child?
- 4 Causes of low body temperature in children
- 4.
 1 Causes that do not require parents to worry.
1 Causes that do not require parents to worry. - 4.2 Reasons that require special attention from parents.
- 4.
- 5 What should I do if my child has a low temperature?
What should I do if my child has a low temperature?
The vital functions of the body of children require a certain temperature at which chemical and biochemical processes proceed correctly. Therefore, low temperature in a child , below the normal value, can lead to various risks for his health and indicate the presence of certain pathologies.
But a low body temperature in a child does not always indicate some disease. For example, the temperature of the extremities is always lower than the temperature of the main body. The temperature, as a rule, decreases somewhat during sleep or prolonged rest.
What is low body temperature in a child?
It is widely believed that the normal body temperature of a healthy child is 36.6. In fact, it depends on a lot of factors: the gender and age of the child, the degree of his physical activity, the composition and amount of food and drink consumed, methods of measurement, time of day (morning, afternoon, evening), etc.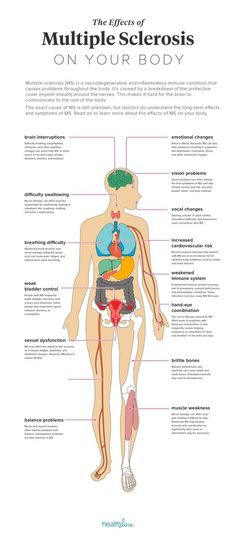 On average, it is believed that in healthy children, the temperature is normally in the range of 36.5-37.5 degrees. But pediatricians are more guided by the upper permissible temperature limits, which depend on age. Namely, if the measurement is carried out in the armpit (the most common method), then the limits are: newborns - 36.8, from 6 months to 3 years - 37.7 and over 6 years - 37.0.
On average, it is believed that in healthy children, the temperature is normally in the range of 36.5-37.5 degrees. But pediatricians are more guided by the upper permissible temperature limits, which depend on age. Namely, if the measurement is carried out in the armpit (the most common method), then the limits are: newborns - 36.8, from 6 months to 3 years - 37.7 and over 6 years - 37.0.
Then what is a low temperature in a child? Permissible is the temperature in the range of 36.0-36.5 degrees. But the child's body temperature should not be below 36 degrees, and the interval from 35.4-35.6 for children is unacceptable. If, for example, a child has a low temperature of 36, then they usually talk about a low temperature. If there is a very low body temperature in a child (about or below 35 degrees), then they talk about hypothermia. Sometimes the term hypothermia combines the state of actually low temperature in a child and very low.
It is also important how long the temperature has been lowered. A short-term decrease in temperature can be caused by simple hypothermia. And it is a completely different matter if a child has a low temperature for a long time, which may be associated with hidden diseases. Constant very low body temperature in a child is extremely rare, but low body temperature in an infant is not uncommon.
A short-term decrease in temperature can be caused by simple hypothermia. And it is a completely different matter if a child has a low temperature for a long time, which may be associated with hidden diseases. Constant very low body temperature in a child is extremely rare, but low body temperature in an infant is not uncommon.
How dangerous is a very low temperature in a child?
Low body temperature in a child, if it is long enough, can be a symptom of dangerous diseases. If it even outwardly leads to poor general well-being, you should immediately consult a pediatrician.
A very low temperature in a child, if it lasts for a long time, significantly slows down metabolic processes and, in general, inhibits the functioning of all organs and systems. And when falling to 32 degrees. the child may lose consciousness. But for the same reasons, the method of artificially lowering the temperature is used in medicine, for example, in organ transplants or in neurosurgical operations.
Causes of low body temperature in children
The causes of low fever in children can be very diverse. The cause of a short-term low body temperature in a child may be hypothermia of the body when exposed to low ambient temperature. Ultimately, it can lead to cold injuries, various frostbites, and even freezing of the child. But the causes of prolonged or relatively prolonged low temperature in children may be associated with completely different factors.
Reasons that do not require special worries of parents
.- A period of rapid development and growth . A slight, but noticeable, decrease in temperature can occur in adolescence, with the rapid and uneven development of all body systems. A decrease can also occur in children in the first 2 months of life (low body temperature in an infant or in an infant, low temperature due to an imperfect thermoregulation system) or in the first hours of a child's life (the so-called transient decrease in temperature).

- After or during infectious diseases . If during infectious diseases that are accompanied by too high a temperature, the doctor recommends the use of an antipyretic, then an artificial temperature failure can lead to a decrease below its usual normal level. Therefore, it is not surprising that, for example, a child has diarrhea and a low temperature at the same time. The same thing can happen immediately after recovery (it is usually said that the child has a “failure”). But this is usually compensated by a relatively quick reaction of the body, and the temperature returns to its proper range.
Reasons that require special attention of parents.
- Vitamin and mineral deficiency . They are essential for all body systems, and a lack of intake can lead to their deficiency and the appearance of a prolonged low temperature. Sometimes this is observed in children with iron deficiency anemia or in adolescents who are fond of diets for weight loss, leading to depletion of the body up to cachexia (a sharp slowdown in physiological processes).

- Immune system failure conditions . These can be pathologies of the immune system, or a strong weakening of the general state of the immune system after serious illness, or any effect on the immune system. For the same reasons, a low temperature is sometimes observed in a child after vaccination.
- Some specific intoxications . Usually poisoning (intoxication) leads to an increase in temperature, but in some cases the opposite happens - the temperature decreases. This is due to the specific reaction of the child's body to this particular toxin and is usually accompanied by severe chills and trembling (tremor) of the hands. A typical case is tetraethyl lead poisoning.
- Stress, chronic fatigue syndrome . Constant stressful situations, excessive psychological stress, age-related experiences, especially characteristic of adolescence, can provoke a prolonged drop in temperature.
 These factors should not be underestimated, since in their effect on the body they can be equivalent to a severe internal disease with violations of all physiological systems.
These factors should not be underestimated, since in their effect on the body they can be equivalent to a severe internal disease with violations of all physiological systems. - Other pathologies and diseases . These include allergic reactions in children (for example, to house dust or animal hair), reduced hemoglobin levels, endocrine pathologies, and some hidden brain diseases.
What should I do if my child has a low temperature?
If parents record a short-term low temperature, then this is not a cause for great concern. But if it is observed for more than one or two days, then it is necessary to pay attention to this and show the child to a pediatrician (pediatrician).
Pediatrician . He will assess the general condition of the child, prescribe primary examinations (ECG, general and biochemical blood tests). If the cause of low body temperature in a child is a decrease in immunity, overwork, the consequences of common diseases, then the doctor will adjust the diet and diet, general daily routine, physical activity. But if the pediatrician has suspicions of hidden diseases, he will refer you to specialist pediatricians for examination.
But if the pediatrician has suspicions of hidden diseases, he will refer you to specialist pediatricians for examination.
Medical Specialists . First of all - a pediatric neurologist, pediatric endocrinologist, functional diagnostics doctor, gastroenterologist, oncologist. Additional tests may be required, such as a blood test for hormones, and instrumental studies (ultrasound).
In case of prolonged low temperature in a child, only a comprehensive examination can establish the causes of this and allow, based on the diagnosis, to prescribe the correct and timely treatment.
description of the disease, causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Hypothermia is a violation of heat transfer, which is manifested by a significant decrease in body temperature (less than 35.5 ° C). Occurs with prolonged exposure to low ambient temperatures or a decrease in heat production and an increase in its return. Hypothermia often becomes a sign of certain diseases.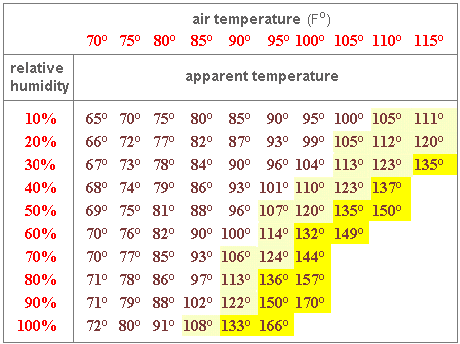
Mechanism of heat production
Mandatory heat production is the heat that is produced in the course of the body's metabolic processes. It is enough to maintain normal body temperature, but only if the ambient temperature is comfortable. For an adult, the range from 18 to 23 ° C is considered comfortable, but with minimal physical activity and light clothing. When the body is hypothermic, muscle tone increases, so muscle tremors appear.
However, there is the concept of additional heat production. It becomes active if the air temperature becomes too low. Additional heat production includes contractile thermogenesis, which is based on involuntary muscle contraction, as well as non-contractile thermogenesis, carried out by splitting brown fat. It is practically absent in adults, since it regresses with growing up. Brown adipose tissue is located in the area of the kidneys, shoulder blades, on the neck. Young children have more of it, and it is metabolically very active, because it protects them from severe hypothermia.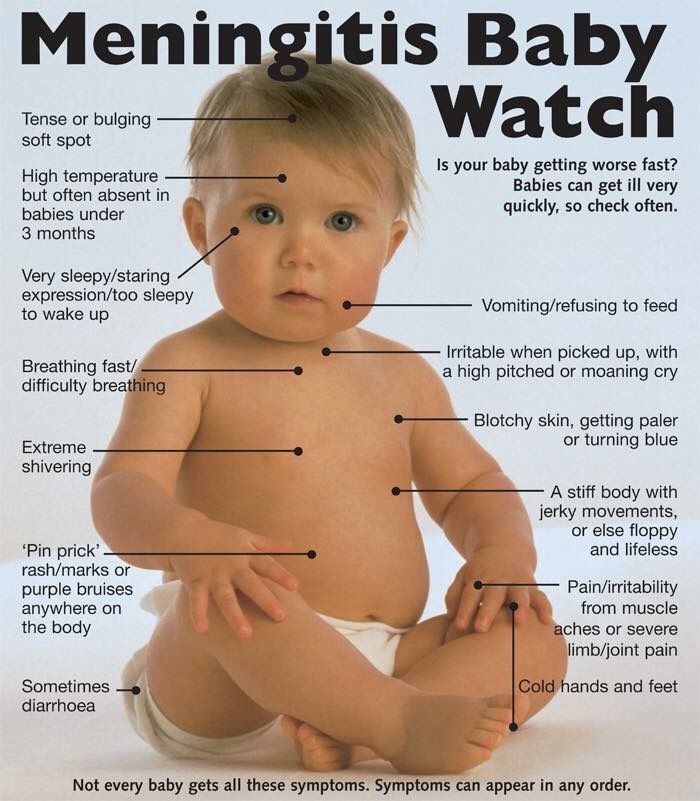
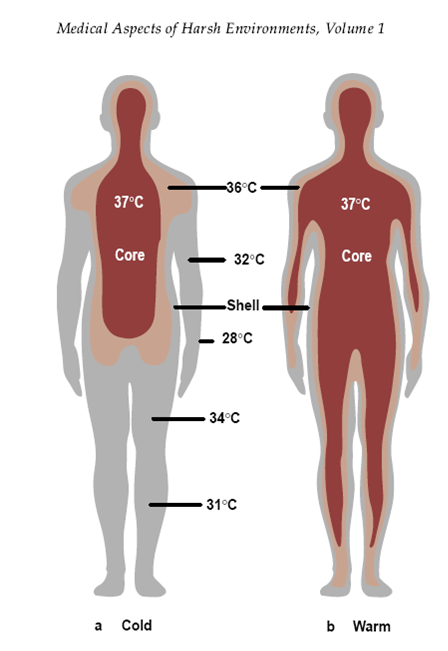
The metabolic rate is influenced by thyroid and adrenal hormones. The thermoregulatory center is located in the hypothalamus. The central body temperature is measured in the oral cavity, rectum, ear canal, and in a medical institution - in the bladder, nasopharynx and esophagus. In the central vessels and most internal organs, it is maintained at a level of 36–38°C.
Peripheral body temperature is measured in the armpits or on the forehead. Normally, it is slightly below the center.
Temperature readings are individual for each person and differ depending on the part of the body. There is a certain norm, which changes slightly during the day.
Causes of hypothermia
Possible causes of decreased body temperature include:
- CNS pathology;
- low muscle mass;
- alcohol or other types of intoxication;
- prolonged physical activity;
- decreased metabolic rate;
- period of pregnancy;
- drug exposure;
- recovery period after a long illness.
Hypothermia is also caused by prolonged exposure to ice-cold water, wet clothes, and low ambient temperatures. These factors often lead to disruption of thermal exchange and heat loss.
Types of low temperature
Hypothermia is endogenous, when pathologies of internal organs are observed, or exogenous, when body temperature depends on external factors.
Medical hypothermia is also classified as exogenous. It is used when a temporary slowdown in blood circulation is required. That is, its task is to reduce metabolism and activity in organs and tissues. This is necessary to increase resistance to lack of oxygen. Medical hypothermia is indicated during open surgical interventions on the heart and blood vessels, with injuries of the brain and spinal cord, ischemic stroke, neonatal hypoxia.
The following types of low temperature are noted:
- Mild degree - observed at body temperature from 32.2 to 35 ° C, characterized by drowsiness, chills, increased heart rate and respiration.
- Medium degree - noted at a temperature of 27 to 32.1 ° C, it is characterized by a decrease in reflexes, bradycardia and slow breathing.
- Severe degree - observed at temperatures below 27 ° C, when a person is in a depressed state, and he has no reflexes at all.
The degree of severity is assessed by the doctor not only by the level of decrease in the central temperature, but also by some clinical signs.
Pathologies causing hypothermia
The most rare causes include:
- spinal cord injury;
- terminal liver failure;
- septic condition;
- uremia;
- some types of diabetes.
Common causes of hypothermia include heart attack and stroke, Addison's disease, hypothyroidism, anemia, hypoglycemia, as well as VSD and depression.
Body temperature may decrease during shock conditions, with a sharp expansion of blood vessels. Heat transfer increases many times, and the body temperature drops by 4-5 ° C below the accepted norm. If this is combined with chest pain and low blood pressure, then myocardial infarction is possible.
If this is combined with chest pain and low blood pressure, then myocardial infarction is possible.
Occasionally, hypothermia is caused by ischemic stroke. The patient feels drowsiness, some stupor, a short-term loss of consciousness is possible. As a rule, neurological symptoms and temperature decrease increase gradually.
A decrease in temperature below 32°C is noted with hemorrhages or inflammatory processes in the hypothalamus. When the posterior hypothalamus is affected, temperature fluctuations associated with the environment (poikilothermia) are observed. In cold conditions, a hypothermic coma is possible with irreversible consequences for some parts of the brain.
Addison's disease is also often the cause of a decrease in temperature. Corticosteroids, which are synthesized by the adrenal glands, maintain the metabolism at the proper level, including the temperature. However, with their insufficient production, a number of disorders appear, against their background, the body temperature drops.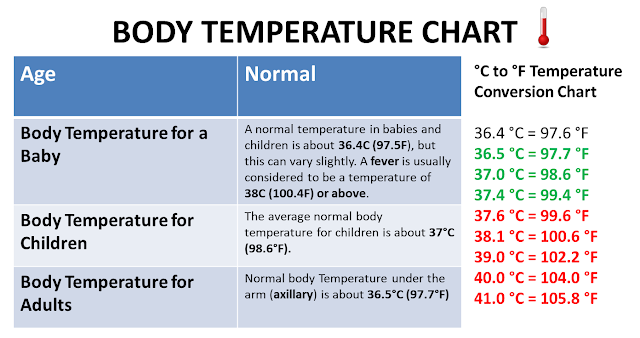 A sudden decrease in blood pressure, muscle weakness, loss of consciousness, combined with a temperature below 33 ° C, indicate an Addisonian crisis.
A sudden decrease in blood pressure, muscle weakness, loss of consciousness, combined with a temperature below 33 ° C, indicate an Addisonian crisis.
Hypothyroidism slows down metabolism, and the brain center responsible for proper thermoregulation reduces its activity. Such conditions negatively affect the skin: pallor, waxiness are the main signs. Due to microcirculation disorders, hair can fall out. The patient complains of loss of strength, constant drowsiness.
Initially, with hypoglycemia, there is a slight decrease in temperature, but if the causes are not eliminated, the condition rapidly worsens, and the temperature continues to decrease. Deep syncope is possible, because with hypoglycemia, energy starvation of the brain occurs.
Hypothermia in anemia is caused by low levels of red blood cells and hemoglobin. Among the clinical signs are headache, darkening in the eyes, fatigue. The condition of nails, hair, skin worsens.
In VVD, hypothermia is caused by impaired blood circulation and autonomic regulation. Such conditions are characterized by weakness, dizziness, trembling in the limbs. Such attacks occur periodically, they are provoked by prolonged stress, physical activity, prolonged stay in a stuffy room.
Such conditions are characterized by weakness, dizziness, trembling in the limbs. Such attacks occur periodically, they are provoked by prolonged stress, physical activity, prolonged stay in a stuffy room.
It is not uncommon to have a low body temperature after a viral infection. This is due to the sluggish activity of the immune system and the depletion of the body. Among the symptoms of asthenia are fatigue, weakness, drowsiness. The condition persists for 2-3 weeks.
In some cases, hypothermia is noted in depression, as associations change and the limbic system is disturbed, which causes malfunctions in the thermoregulatory center. However, temperatures are rarely set below 34.5°C, although hypothermia in depressive disorders is prolonged. Along with a low temperature, patients experience depression, sleep problems, they have cold extremities with a marbled pattern on the skin.
Hypothermia is possible with various intoxications of the body. Toxins, accumulating in the blood, penetrate into the parts of the brain, disrupting the transmission of impulses.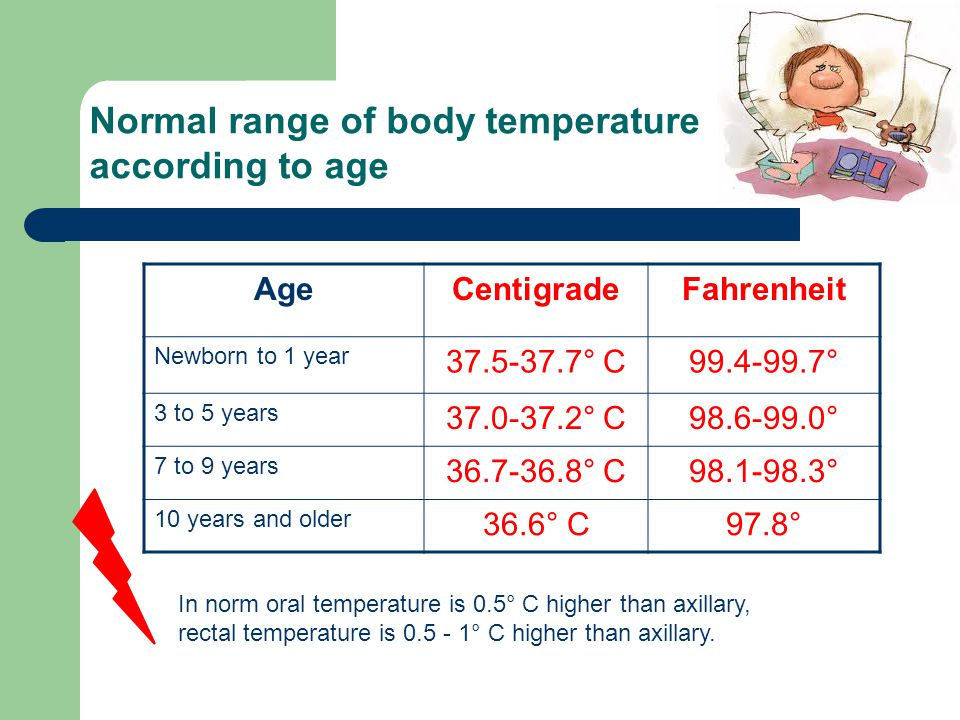 Under the influence of toxic compounds, the body temperature decreases, the general condition of the body worsens.
Under the influence of toxic compounds, the body temperature decreases, the general condition of the body worsens.
Which doctor should I contact if my body temperature drops?
If a slight decrease in temperature, which is not associated with hypothermia, persists for a long time, then it is necessary to consult a therapist, neurologist, endocrinologist.
In case of a sharp drop in temperature, which is accompanied by other life-threatening symptoms, severe hypothermia, an ambulance will be required.
Diagnosis of hypothermia
The volume of diagnostic measures depends on the degree of temperature decrease and the general condition of the body. At indicators below 32 ° C, instrumental studies of the body are necessary, as well as advanced laboratory tests. The most informative are:
- biochemical blood test to determine the level of nitrogen and urea;
- hormonal test for the content of thyroxine and free T3, pituitary hormones;
- CT scan of the brain;
- thyroid scintigraphy;
- electrographic methods - ECG, EEG to assess brain activity, in the clinic - electromyography and electroneurography.