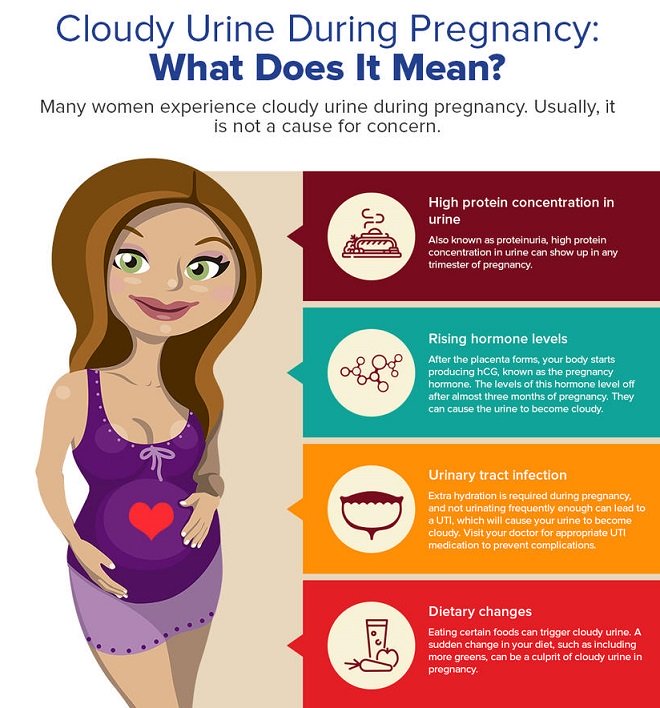
List of unsafe foods during pregnancy
Foods to avoid or limit during pregnancy
Raw meat, fish and eggs can contain harmful germs that can give you food poisoning, like salmonella infection. Cooking them fully kills the germs, which helps keep you and your baby from getting sick.
Many dairy products, like milk, eggs and cheese, are pasteurized. This means they’re heated to kill any bad germs. Look for the word “pasteurized” on labels. If the product label doesn’t say “pasteurized,” pick a different product.
Unpasteurized dairy products can give you food poisoning, like listeriosis. Listeriosis is caused by germs in foods and can cause flu-like symptoms for you or hurt your baby.
Some foods contain chemicals, like caffeine or mercury. You can pass these harmful chemicals to your baby during pregnancy.
Talk to your health care provider if you have any signs or symptoms of food poisoning or if you are worried you may have eaten a food with bacteria like listeriosis.
What foods should you limit during pregnancy?
Not every food is safe to eat during pregnancy. Some foods may be harmful to you or your baby because of the way they’re cooked or because of germs or chemicals they contain.
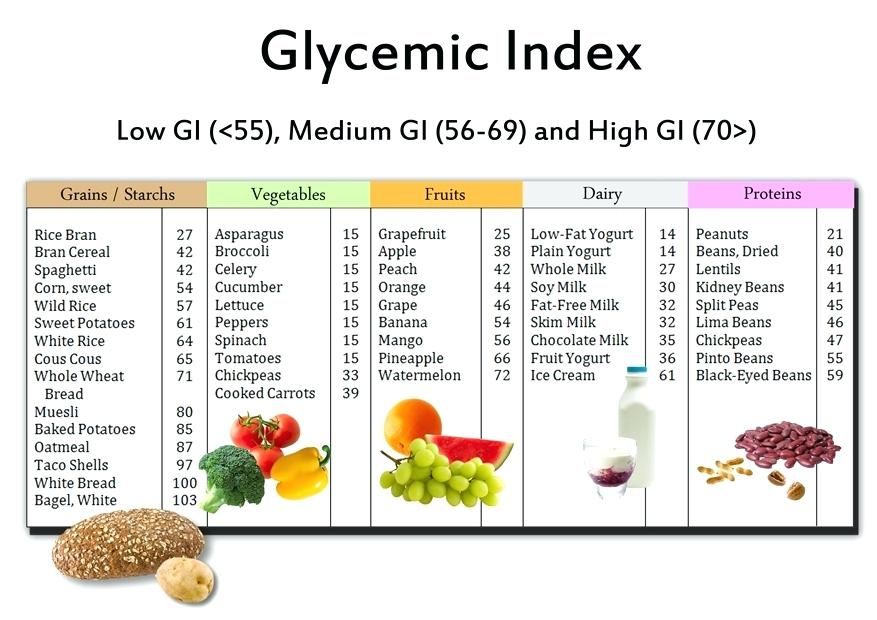
These foods are OK to eat during pregnancy in limited amounts:
- Fish that have small amounts of mercury. Mercury is a metal that can harm your baby. Fish get mercury from the water they swim in and from eating other fish that have mercury in them. By eating fish that contain mercury, you can pass the metal to your baby during pregnancy. This can cause brain damage and affect your baby’s hearing and vision. During pregnancy, eat 8 to 12 ounces a week of fish that doesn’t have a lot of mercury, including shrimp, salmon, pollock, catfish and canned light tuna. It’s also OK to eat 6 ounces a week of albacore (white) tuna. If you eat fish, cook it so that the inside temperature is 145 degrees and see if it separates into flakes.
 Shrimp, lobster and scallops should be milky white. Clams, mussels and oysters should cook until shells open.
Shrimp, lobster and scallops should be milky white. Clams, mussels and oysters should cook until shells open. - Food and drinks that have caffeine. Limit the caffeine you get each day to less than 200 milligrams. This is about the amount in 1½ 8-ounce cups of coffee or one 12-ounce cup of coffee. Caffeine amounts in coffee vary a lot and depend on things, like the brand you drink, how it's made and the size of the cup. Not all coffee cups are the same size, even though you think of them as a cup. Check to see how many ounces your cup has, especially if you’re buying a cup of coffee or tea. Instead of drinking regular coffee, try coffee that's decaffeinated (has a small amount of caffeine). Caffeine also is found in tea, energy drinks, chocolate, soda and some over-the-counter medicine. Read labels on food, drinks and medicine to know how much caffeine you're getting.
What foods are completely off limits during pregnancy?
Don’t eat these foods during pregnancy. They can be really harmful to you and your baby.
They can be really harmful to you and your baby.
Certain meats and fish
- Raw or undercooked meat, including beef, poultry and pork. This includes hotdogs and deli meat (like ham or bologna). If you eat hotdogs or deli meat, cook them until they are steaming hot or just avoid completely.
- Raw fish, especially shellfish. Don’t eat sushi unless the fish is cooked. Also avoid ceviche, sashimi, and raw oysters.
- Fish that can be high in mercury, like shark, swordfish, king mackerel and tilefish. Always check with your local health department before you eat any fish you catch yourself.
- Refrigerated pates, meat spreads or smoked seafood. If it is cooked into a dish like casserole it is OK. Pates that are shelf-stable (they can be stored unrefrigerated) are also OK.
Certain dairy products
- Raw or lightly cooked eggs or foods made with them. This includes cake batter and raw cookie dough.
- Soft-scrambled eggs
- Products made with uncooked eggs like certain Caesar salad dressings, eggnog or certain sauces like hollandaise.
 Shelf-stable commercially made Caesar salad dressing is OK to eat because it doesn’t contain uncooked eggs.
Shelf-stable commercially made Caesar salad dressing is OK to eat because it doesn’t contain uncooked eggs. - Unpasteurized juice or milk or any foods made with them
- Unpasteurized soft cheeses, such as brie, feta, Camembert, Roquefort, queso blanco, queso fresco and Panela
Other
- Raw sprouts of any kind including mung beans, clover, radish and especially alfalfa sprouts
- Unwashed raw fruits or vegetables. Wash all your fruits and vegetables before eating them.
- Store-made salads like chicken, egg or tuna salads
- Herbal products, like pills and teas. Herbal products are made from herbs, which are plants used in cooking or medicine. We don’t know enough about herbal products to know if they’re safe to use during pregnancy. So it’s best not to use them while you’re pregnant.
- Nonfood items, like clay, starch, paraffin or coffee grounds. Tell your provider if you crave anything like this that’s not food.
- Alcohol. There is no known safe amount of alcohol to drink while you’re pregnant.
More information
choosemyplate.gov
Last reviewed March, 2020
11 Foods and Beverages to Avoid During Pregnancy
The foods you should avoid while pregnant typically include undercooked or raw meat or fish and other foods that can carry a risk of infection. You may also need to minimize caffeine and certain beverages.
One of the first things people learn when they’re pregnant is what they can’t eat. It can be a real bummer if you’re a big sushi, coffee, or rare steak fan.
Thankfully, there’s more you can eat than what you can’t. You just have to learn how to navigate the waters (the low mercury waters, that is). You’ll want to pay close attention to what you eat and drink to stay healthy.
Certain foods should only be consumed rarely, while others should be avoided completely. Here are 11 foods and beverages to avoid or minimize while pregnant.
Mercury is a highly toxic element. It has no known safe level of exposure and is most commonly found in polluted water.
In higher amounts, it can be toxic to your nervous system, immune system, and kidneys. It may also cause serious developmental problems in children, with adverse effects even in lower amounts.
Since it’s found in polluted seas, large marine fish can accumulate high amounts of mercury. Therefore, it’s best to avoid high mercury fish while pregnant and breastfeeding.
High-mercury fish you want to avoid include:
- shark
- swordfish
- king mackerel
- tuna (especially bigeye tuna)
- marlin
- tilefish from the Gulf of Mexico
- orange roughy
However, it’s important to note that not all fish are high in mercury — just certain types.
Consuming low mercury fish during pregnancy is very healthy, and these fish can be eaten up to three times per week, according to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Low mercury fish are plentiful and include:
- anchovies
- cod
- flounder
- haddock
- salmon
- tilapia
- trout (freshwater)
Fatty fish like salmon and anchovies are especially good options, as they are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for your baby.
This one will be tough for you sushi fans, but it’s an important one. Raw fish, especially shellfish, can cause several infections. These can be viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections, such as norovirus, Vibrio, Salmonella, and Listeria.
Some of these infections may only affect you, causing dehydration and weakness. Other infections may be passed on to your baby with serious, or even fatal, consequences.
Pregnant women are especially susceptible to listeria infections. In fact, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), pregnant women are up to 10 times more likely to get infected by Listeria than the general population. Pregnant Hispanic women are 24 times more at risk.
Pregnant Hispanic women are 24 times more at risk.
This bacteria can be found in soil and contaminated water or plants. Raw fish can become infected during processing, including smoking or drying.
Listeria bacteria can be passed to your baby through the placenta, even if you’re not showing any signs of illness. This can lead to premature delivery, miscarriage, stillbirth, and other serious health problems, according to the CDC.
It’s definitely advised to avoid raw fish and shellfish, including many sushi dishes. But don’t worry, you’ll enjoy it that much more after baby is born and it’s safer to eat again.
Some of the same issues with raw fish affect undercooked meat, too. Eating undercooked or raw meat increases your risk of infection from several bacteria or parasites, including Toxoplasma, E. coli, Listeria, and Salmonella.
Bacteria may threaten the health of your little one, possibly leading to stillbirth or severe neurological illnesses, including intellectual disability, blindness, and epilepsy.
While most bacteria are found on the surface of whole pieces of meat, other bacteria may linger inside the muscle fibers.
Some whole cuts of meat — such as tenderloins, sirloins, or ribeye from beef, lamb and veal — may be safe to consume when not cooked all the way through. However, this only applies when the piece of meat is whole or uncut, and completely cooked on the outside.
Cut meat, including meat patties, burgers, minced meat, pork, and poultry, should never be consumed raw or undercooked. So keep those burgers on the grill well done for now.
Hot dogs, lunch meat, and deli meat are also of concern, which is sometimes surprising to pregnant people. These types of meat may become infected with various bacteria during processing or storage.
Pregnant women should not consume processed meat products unless they’ve been reheated until steaming hot.
Raw eggs can be contaminated with the Salmonella bacteria.
Symptoms of salmonella infections include fever, nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, and diarrhea.
However, in rare cases, the infection may cause cramps in the uterus, leading to premature birth or stillbirth.
Foods that commonly contain raw eggs include:
- lightly scrambled eggs
- poached eggs
- hollandaise sauce
- homemade mayonnaise
- some homemade salad dressings
- homemade ice cream
- homemade cake icings
Most commercial products that contain raw eggs are made with pasteurized eggs and are safe to consume. However, you should always read the label to make sure.
To be on the safe side, make sure to always cook eggs thoroughly or use pasteurized eggs. Save those super runny yolks and homemade mayo until after baby makes their debut.
Organ meat is a great source of a variety of nutrients.
These include iron, vitamin B12, vitamin A, zinc, selenium, and copper — all of which are good for you and baby. However, eating too much animal-based vitamin A (preformed vitamin A) is not recommended during pregnancy.
Consuming too much preformed vitamin A, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy, can lead to congenital malformations and miscarriage.
Although this is mostly associated with vitamin A supplements, it’s best to keep your consumption of organ meats like liver to just a few ounces once per week.
You may be one of the millions of folks who love their daily cups of coffee, tea, soft drinks, or cocoa. You’re definitely not alone when it comes to our love of caffeine.
Pregnant people are generally advised to limit their caffeine intake to less than 200 milligrams (mg) per day, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG).
Caffeine is absorbed very quickly and passes easily into the placenta. Because babies and their placentas don’t have the main enzyme needed to metabolize caffeine, high levels can build up.
High caffeine intake during pregnancy has been shown to restrict fetal growth and increase the risk of low birth weight at delivery.
Low birth weight — defined as less than 5 lbs., 8 oz. (or 2.5 kg) — is associated with an increased risk of infant death and a higher risk of chronic diseases in adulthood.
So keep an eye on your daily cup of joe or soda to make sure baby doesn’t have exposure to too much caffeine.
Your healthy salad choice may not be free from rogue ingredients, either. Raw sprouts, including alfalfa, clover, radish, and mung bean sprouts, may be contaminated with Salmonella.
The humid environment required by seeds to start sprouting is ideal for these kinds of bacteria, and they’re almost impossible to wash off.
For this reason, you’re advised to avoid raw sprouts altogether. However, sprouts are safe to consume after they have been cooked, according to the FDA.
The surface of unwashed or unpeeled fruits and vegetables may be contaminated with several bacteria and parasites.
These include Toxoplasma, E. coli, Salmonella, and Listeria, which can be acquired from the soil or through handling.
Contamination can occur at any time during production, harvest, processing, storage, transportation, or retail. One dangerous parasite that may linger on fruits and vegetables is called Toxoplasma.
The majority of people who get toxoplasmosis have no symptoms, while others may feel like they have the flu for a month or more.
Most infants who are infected with the Toxoplasma bacteria while still in the womb have no symptoms at birth. However, symptoms such as blindness or intellectual disabilities may develop later in life.
What’s more, a small percentage of infected newborns have serious eye or brain damage at birth.
While you’re pregnant, it’s very important to minimize the risk of infection by thoroughly washing with water, peeling, or cooking fruits and vegetables. Keep it up as a good habit after baby arrives, too.
Raw milk, unpasteurized cheese, and soft-ripened cheeses can contain an array of harmful bacteria, including Listeria, Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter. (These are probably sounding familiar by now.)
coli, and Campylobacter. (These are probably sounding familiar by now.)
The same goes for unpasteurized juice, which is also prone to bacterial contamination. These infections can all have life-threatening consequences for an unborn baby.
The bacteria can be naturally occurring or caused by contamination during collection or storage. Pasteurization is the most effective way to kill any harmful bacteria, without changing the nutritional value of the products.
To minimize the risk of infections, eat only pasteurized milk, cheese, and fruit juice.
It’s advised to completely avoid drinking alcohol when pregnant, as it increases the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. Even a small amount can negatively impact your baby’s brain development.
Drinking alcohol during pregnancy can also cause fetal alcohol syndrome, which involves facial deformities, heart defects and intellectual disability.
Since no level of alcohol has been proven to be safe during pregnancy, it’s recommended to avoid it altogether.
There’s no better time than pregnancy to start eating nutrient-dense foods to help both you and your growing little one. You’ll need increased amounts of many essential nutrients, including protein, folate, choline, and iron.
It’s also a myth that you’re “eating for two.” You can eat as you normally do during the first semester, then increase by about 350 calories per day in your second trimester, and about 450 calories per day in your third trimester.
An optimal pregnancy eating plan should mainly consist of whole foods, with plenty of nutrients to fulfill yours and baby’s needs. Processed junk food is generally low in nutrients and high in calories, sugar, and added fats.
While some weight gain is necessary during pregnancy, excess weight gain has been linked to many complications and diseases. These include an increased risk of gestational diabetes, as well as pregnancy or birth complications.
Stick to meals and snacks that focus on protein, vegetables and fruits, healthy fats, and fiber-rich carbohydrates like whole grains, beans, and starchy vegetables. Don’t worry, there are lots of ways to sneak veggies into your meals without sacrificing taste.
Don’t worry, there are lots of ways to sneak veggies into your meals without sacrificing taste.
When you’re pregnant, it’s essential to avoid foods and beverages that may put you and your baby at risk.
Although most foods and beverages are perfectly safe to enjoy, some, like raw fish, unpasteurized dairy, alcohol, and high mercury fish, should be avoided.
Plus, some foods and beverages like coffee and foods high in added sugar, should be limited in order to promote a healthy pregnancy.
If you want to learn more about what foods you should eat during pregnancy, check out this article: Healthy Eating During Pregnancy.
Quick tips for foods to avoid when pregnant
- Avoid high-mercury fish including shark, swordfish, tuna, and marlin.
- Raw fish and shellfish can be contaminated with bacteria and parasites. Some of these can cause adverse health effects and harm both you and baby.
- Raw or undercooked meat may contain harmful bacteria.
As a general rule, meat should be cooked all the way through.
- Raw eggs may be contaminated with Salmonella, and may put you and your baby at risk. Be sure to thoroughly cook eggs before eating.
- Organ meat is a great source of iron, vitamin B12, vitamin A, and copper. To prevent consuming too much vitamin A limit your intake of organ meat to a few ounces once a week.
- Limit caffeine intake to under 200 mg per day, which is about 2 to 3 cups of coffee. High caffeine intake during pregnancy may limit baby’s growth and cause low birth weight.
- Raw sprouts may be contaminated with bacteria. Only eat them thoroughly cooked.
- Fruits and vegetables may be contaminated with harmful bacteria, including Toxoplasma. It’s important to thoroughly wash all fruits and vegetables with plenty of clean water.
- Don’t consume unpasteurized milk, cheese, or fruit juice, as these foods increase the risk of bacterial infections.
- Avoid all alcohol.
Drinking alcohol can increase the risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, and fetal alcohol syndrome.
- Eating processed foods during pregnancy can increase your risk of excess weight gain, gestational diabetes, and complications. This can have long-term health implications for you and your child.
8 foods that pregnant women should not eat
June 15, 2019 Likbez Health
Even scrambled eggs and healthy fish oil can do harm.
If you are pregnant, you should reduce the amount of coffee and avoid alcohol altogether. Everyone knows this.
But there are far more insidious foods. At first glance, they seem innocent and even useful. But in fact, they can harm mom or an unborn baby more than a couple of cups of double espresso three times a day.
Here is a list of popular foods to avoid during pregnancy. Or at least think twice before you eat.
1. Raw eggs
As well as products containing them: eggnog, homemade mayonnaise, raw dough, poached eggs, fried eggs with raw yolk, tiramisu.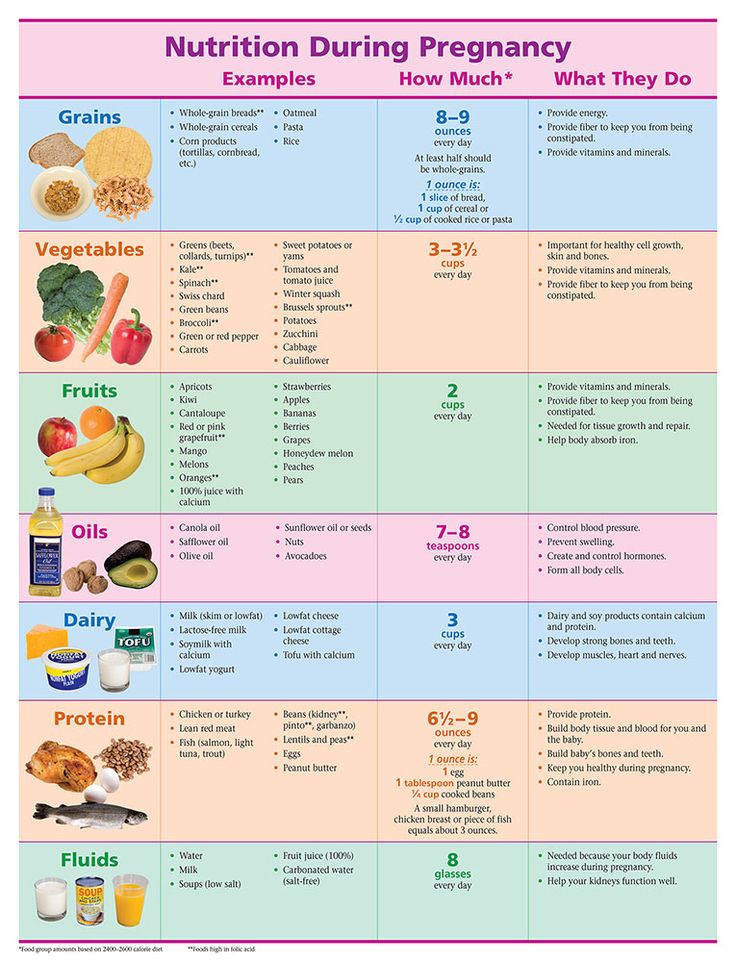
What is the danger
One word is enough: salmonellosis. This acute intestinal infection is fortunately not fatal, but is accompanied by severe diarrhea and vomiting that can cause dehydration. But this is already bad: the normal blood supply to the fetus and the level of amniotic fluid in the uterus depend on the amount of moisture. Water deficiency can result in violations in the development of the unborn baby, as well as an increased risk of miscarriage.
What to do
If you have no strength to give up eggs, make sure that they are thoroughly washed and heat-treated. Hard boiled eggs, scrambled eggs, baked goods are safe.
2. Raw meat
As well as rare fried steaks (“with blood”), raw smoked and cured sausages, poorly fried minced meat, for example, in fast food.
What is the danger
Raw meat can be infected with parasites. For example, Toxoplasma. They are able to penetrate the placental barrier and cause serious disturbances in the development of the unborn baby.
What to do
Removing parasites from meat is easy - heat it properly. If we are talking about dried or smoked products, freezing them for four days will help reduce the risk.
3. Raw fish
Be especially careful with river and wild ocean fish, shellfish (oysters, mussels), dried, smoked fish of all kinds and sushi.
What is the danger
The range of troubles that you can get by eating a roll or dried perch is wide:0003
- like meat, fish can be infested with parasites;
- in the pulp there are also pathogenic bacteria - for example, listeria or botulinum bacteria, which cause deadly (for mothers as well) botulism;
- river fish can be caught in chemically polluted reservoirs - and all toxic substances will go to both mother and baby;
- oceanic fish accumulate mercury. Shark, swordfish, king mackerel and tilefish are especially dangerous in this regard. Mercury poisoning affects the health of both the mother and the unborn baby - this element can cause brain damage and developmental delays.

What to do
Eat only properly cooked fish. You can take a chance with canned food: just keep an eye on the expiration date and in no case use the product from swollen cans.
4. Liver
As well as liver pate and sausage, cod liver oil.
What is the danger
Too much vitamin A. Its excess can lead to the development of birth defects in the fetus.
What to do
Do not abuse liver products. Especially if for some reason you are taking vitamin A supplements. Yes, and in no case should you prescribe vitamins and supplements for yourself - only your doctor can do this.
5. Soft cheeses
Special attention:
- soft cheeses with white mold - brie and camembert;
- blue cheeses - gorgonzola, roquefort, danish blue.
What is the danger
Due to the high humidity and mold, such cheeses are an ideal environment for the development of all kinds of bacteria, including those dangerous to the fetus. The same listeria, once in the body of a future baby, can provoke severe developmental disorders, miscarriage or stillbirth.
The same listeria, once in the body of a future baby, can provoke severe developmental disorders, miscarriage or stillbirth.
What to do
The ideal option is to switch to hard cheese (cheddar, parmesan, stilton and others): it is safe. Soft cheeses can also be consumed, but only if they are made from pasteurized milk. These are mozzarella, feta, ricotta, cream cheeses, halloumi, processed cheeses.
6. Unpasteurized milk
As well as yogurt and ice cream prepared from it.
What is the danger
All in the same high risk of bacteria content. Unpasteurized milk is a product that has not undergone heat treatment. Therefore, the same listeria, which is deadly for the unborn child, can be found in it.
What to do
Try to drink only pasteurized milk. If for some reason only raw is available, be sure to boil it before drinking.
7. Caffeinated products
Not only coffee, but also green tea, chocolate, cola, energy drinks, and some cold and flu medications.
What is the danger
An excess of this substance can cause the baby to have a low birth weight - and this increases the risk of health problems in the future. Sometimes the abuse of caffeine products provokes a miscarriage.
What to do
You don't have to cut out caffeine completely, you just need to go no more than 200 mg per day. In order not to cross the line, be guided by approximate values:
- 1 cup of instant coffee - 100 mg of caffeine;
- 1 cup espresso - 140 mg;
- 1 cup tea - 75 mg;
- 1 can cola (330 ml) - 40 mg;
- 1 Energy Drink (250 ml) - 80 mg;
- 50 g dark chocolate - up to 25 mg;
- 50 g milk chocolate - up to 10 mg.
Once again we emphasize: these are approximate figures. But they can be used for calculation. For example, if you drank a cup of espresso in the morning and a can of cola in the middle of the day, you received almost 200 mg of caffeine.
8.
 Poorly washed vegetables and fruits
Poorly washed vegetables and fruits As well as berries that grow close to the soil - the same strawberries or currants on the lower branches of the bush. Freshly squeezed juices are also questionable if you do not know how thoroughly you washed the ingredients before cooking.
What is the danger
The bacteria that cause toxoplasmosis and botulism also live in the soil. There is a risk that an apple picked up from the ground or a poorly washed carrot carries them on itself.
What to do
Avoid vegetables and fruits during pregnancy as part of a healthy, balanced diet. But keeping them clean is a must. Not only the health of the mother herself depends on this, but, possibly, the life of the unborn baby.
Read also 🤰👶👩⚕️
- What to do if your stomach hurts during pregnancy
- What rights a pregnant woman has at work
- Which signs of pregnancy can be trusted and which not
- Why toxicosis occurs during pregnancy and how to treat it
- What is the danger of ectopic pregnancy and how to recognize it in time
What foods should not be eaten by pregnant women: a gynecologist compiled a forbidden list
- Health
- Lifestyle
Although pregnancy is a physiological condition, during the period of bearing a baby, the expectant mother should pay special attention to her health and nutrition. Not all foods will be useful at this time.
Not all foods will be useful at this time.
September 5, 2022
- Source:
- iStockphoto
During pregnancy, women naturally gain weight, but this happens unevenly throughout the trimesters. In the first weeks, toxicosis is possible, when the weight can even decrease. But in the future, the baby is actively growing, the volume of amniotic fluid increases, the uterus increases. Additionally, the amount of blood in the mother’s vessels, fluid in the tissues increases, and the amount of fat also grows, which will be needed in the future in order to maintain strength during childbirth and lactation.
But this does not mean that pregnant women can eat everything in unlimited quantities. Some foods can even harm the baby. "Doctor Peter" found out from Tatyana Lekareva, a gynecologist, endocrinologist, candidate of medical sciences, which products expectant mothers should refuse and why.
Exclusion of certain products in the diet of the expectant mother is necessary only in case of allergies or individual intolerance. This is important so as not to provoke serious reactions, up to Quincke's edema or anaphylactic shock.
This is important so as not to provoke serious reactions, up to Quincke's edema or anaphylactic shock.
But besides allergens, there are certain groups of foods or drinks that have a potentially negative impact on the baby or mother's health. Therefore, gynecologists strongly recommend either completely eliminating them from the diet, or reducing consumption to a minimum.
See also
1. Alcohol - damages fetal tissues
There is no "safe" amount of alcohol during pregnancy, no matter how long. Alcohol crosses the placenta and can cause a range of fetal developmental disorders. That dose, which for the woman herself is considered relatively small, can cause irreparable harm to the child. Alcohol consumption also increases the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth.
2. Vitamin A in supplements and foods
Vitamin A refers to fat-soluble vitamins that come with a variety of foods - these can be fruits, vegetables, especially yellow and orange. If there is too much vitamin intake, its excess accumulates in the body. An increased content of this substance can lead to the formation of congenital malformations of the fetus. Therefore, vitamin A supplementation, especially in the form of high retinol supplements, is not recommended during pregnancy.
If there is too much vitamin intake, its excess accumulates in the body. An increased content of this substance can lead to the formation of congenital malformations of the fetus. Therefore, vitamin A supplementation, especially in the form of high retinol supplements, is not recommended during pregnancy.
See also
3. Ocean fish
Although fish is very healthy because it contains a lot of complete and easily digestible protein, you need to be very careful with it during pregnancy. Unfortunately, the world's oceans are polluted with heavy metal compounds, including mercury. Therefore, large breeds of oceanic fish, primarily tuna, may contain mercury compounds, which are extremely toxic elements, especially for an actively growing and developing fetus.
Small river fish or seafood are generally safe in this respect. However, they must be thoroughly cooked before consumption to ensure they are fully cooked. The use of half-baked fish is dangerous in terms of infection with parasites. For the same reason, it is worth giving up sushi or sashimi with raw fish for a while.
For the same reason, it is worth giving up sushi or sashimi with raw fish for a while.
4. Very spicy or caustic foods
Edible vinegar, cayenne pepper, wasabi and many other very spicy, caustic and spicy foods should be included in this group. If you eat them often and in large quantities, they can lead to contraction of the muscles of the uterus, causing a threat of miscarriage. Therefore, adding them to food while you are pregnant should be done with great care.
And it is best to avoid such products until the end of lactation, as they can also change the taste of breast milk. The baby may not like such milk, and he will refuse the breast.
See also
5. Spices and aromatic herbs
Some plants that we traditionally eat fresh or dried can cause contraction of the uterine muscles. Because of this, the risk of miscarriage or premature birth increases.
First of all, such herbs include parsley, as well as basil, fennel and some other types of greens - even mint. By the way, such popular spices as cloves and anise are also banned
By the way, such popular spices as cloves and anise are also banned
6. Soft, unpasteurized cheeses
Cheeses made from unpasteurized milk—most often soft cheeses, products with noble molds—may contain pathogenic bacteria. Often, listeria or toxoplasma are found in them, which adversely affect the course of pregnancy and can cause premature birth. An organism that is not burdened by bearing a child will cope with the threat without problems, but the expectant mother should take care.
7. Products with E additives
The list of permitted additives varies depending on the country in which the food is produced. Some additives can have a toxic effect on fetal tissues, so you need to carefully read the composition of the products. It is better to add jam to natural yogurt than to eat yogurt with "natural identical flavors". The same is true for many other products.
See also
8. Meat products and eggs without proper processing
Raw meat, smoked sausages, soft-boiled eggs may also contain Listeria, Toxoplasma or Salmonella.