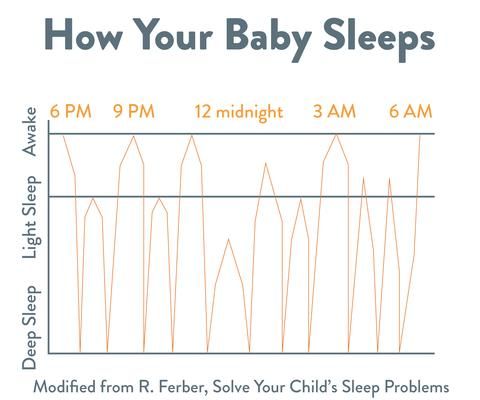
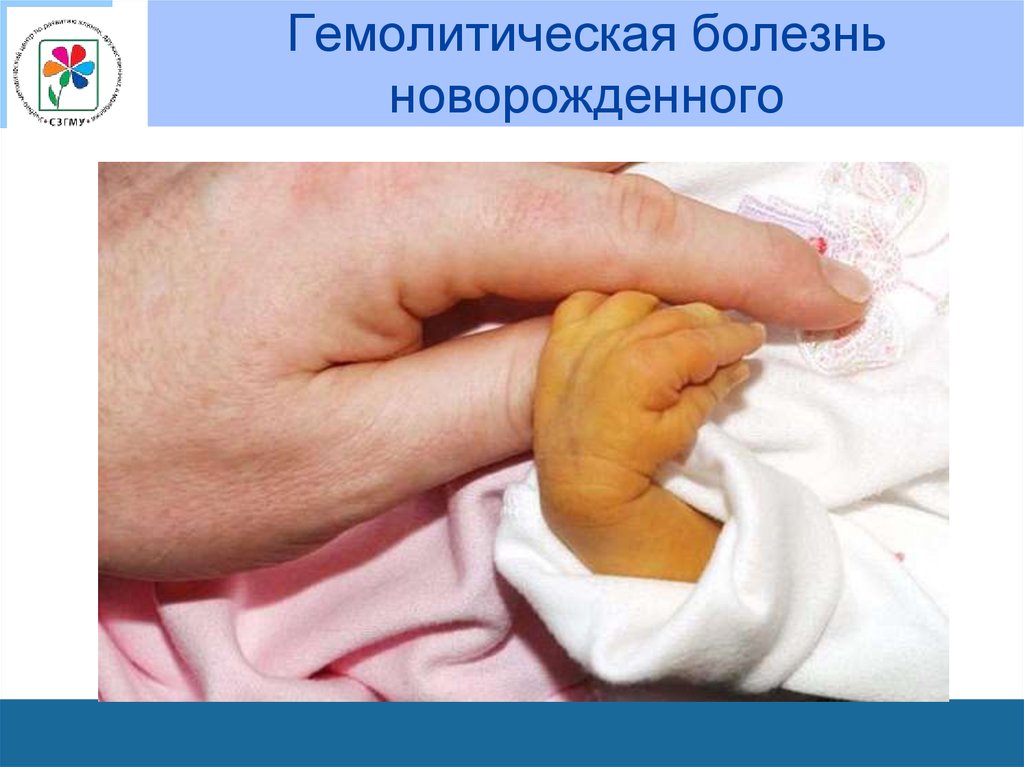
List motor skills
Fine Motor Skills: Examples, Milestones, and Problems
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- Examples of Fine Motor Skills
- Fine Motor Skills Milestones
- When to Talk With Your Child’s Doctor
Fine motor skills are activities in which you use the small muscles in your hands and wrists to make precise movements. They’re different from gross motor skills like running and jumping, which use larger muscles.
Examples of Fine Motor Skills
You need fine motor skills for self-care activities like:
- Dialing the phone
- Turning doorknobs, keys, and locks
- Putting a plug into a socket
- Buttoning and unbuttoning clothes
- Opening and closing zippers
- Fastening snaps and buckles
- Tying shoelaces
- Brushing teeth and flossing
- Bathing or showering
- Using the toilet
Fine motor skills are also necessary for cooking and eating, like:
- Picking up small foods like raisins
- Eating with a fork or spoon
- Opening and closing containers such as lunch boxes and zip-top bags
- Screwing and unscrewing lids
- Using a ladle, tongs, or a large spoon to take a serving of food
- Cutting food with a knife
- Spreading toppings like jam, mayonnaise, and butter
- Sprinkling spices
- Setting the table
- Pouring drinks and condiments like salad dressing and ketchup
- Scrubbing and peeling fruits and vegetables
- Stirring, mixing, and whisking
Fine motor skills are especially important for school activities such as:
- Turning the pages of a book
- Coloring
- Drawing and painting
- Tracing
- Writing
- Cutting with scissors
- Pasting and gluing
- Measuring with a ruler
- Typing and using a computer mousepad
- Playing musical instruments
Children use fine motor skills during play, including:
- Shaking a rattle
- Stacking blocks
- Stringing beads
- Working puzzles
- Dressing dolls
- Playing with puppets
- Sculpting with clay
- Putting together train or car tracks
- Building with Legos or other construction toys
- Playing board games (rolling dice, moving small pieces, spinning spinners)
- Playing video games (using a joystick or other controller)
Fine Motor Skills Milestones
Milestones are skills that children develop as they grow. Most of them learn fine motor skills at certain ages.
3 months. Your infant doesn’t have a lot of control over their arms. They can probably bring their hands to their mouth. A newborn’s hands are often tightly clenched. Your baby’s hands start to relax and open up at 3 months. They may try to reach for dangling toys and might be able to swing their arm in the direction of a toy.
6 months. Most babies at this age can clasp their hands together. They can usually reach for things with both arms at the same time. At 6 months, your baby may be able to hold small objects for a short time.
9 months. Children can typically bring objects to their mouths and pass things from one hand to the other at 9 months. Their hands are relaxed and open most of the time. Many babies start using a pincer grasp. This is when they use their thumb and index finger to pick up small items.
12 months. Most children can let go of things on purpose and may be able to hand you an item if you ask for it once they are a year old. They can bang two toys together, take items in and out of a container, and point at objects.
Most children can let go of things on purpose and may be able to hand you an item if you ask for it once they are a year old. They can bang two toys together, take items in and out of a container, and point at objects.
18 months. Children at this age can often clap their hands, wave goodbye, and use a crayon to scribble without help. Your child may start drinking from a cup and eating with a spoon.
2 years. Most children will point to pictures in books and turn the pages by are 2. Your toddler may be able to stack three or four blocks into a tower.
When to Talk With Your Child’s Doctor
Children develop at different rates. Some learn to eat with a spoon earlier or later than others, and that’s OK. Talk with your child’s doctor if your child doesn’t seem to be reaching many of the milestones for their age group or if you’re concerned about their development. Your doctor can help you set up an evaluation with a specialist.
You can also call your local early intervention office for a free evaluation if your child is under 3 years old. Call your local public elementary school if your child is 3 or older. Tell them that you’re concerned about your child’s development and would like to have them evaluated for preschool special education services. Acting early can help your child get the support they need.
A List of Gross Motor Skills Examples by Age
- Share
In early childhood, children develop and learn to coordinate the large muscles of their bodies. This is known as gross motor development.
Some general examples of gross motor skills are:
- Learning to walk
- Throwing and catching a ball
- Walking backwards and forwards
- Climbing up a ladder
- Riding a tricycle
- Balancing while walking along a low wall
- Hitting a tennis ball over the net
Below is a list of gross motor skills examples by age, from babies all the way up to children in primary/elementary school.
It lists some of the typical gross motor movements you can expect kids to do at certain ages.
It is a guideline only, as children develop at their own pace and may reach some milestones earlier or later.
Children build gross motor skills naturally through play but you can also plan movement activities that give them lots of freedom to explore movement and strengthen their bodies.
Here are some of the best types of gross motor activities. They are simple and will give kids tons of practice in developing their larger muscles.
It’s also beneficial to give children access to a few, select gross motor toys – such as balls, scooters and skipping ropes.
The most important ingredient is giving children lots of time to play. Babies need lots of floor time to explore movement, and older children need lots of indoor and outdoor free play time.
Here are the examples for infants, toddlers, preschoolers and children of school-going age.
Gross Motor Skills Examples for Infants
These examples are for infants up to about 18 months:
- Controlling head and neck
- Rolling over onto tummy or back
- Sitting
- Reaching for a toy
- Crawling or shuffling
- Pulling to a standing position (by holding onto furniture)
- Standing and walking
Gross Motor Skills Examples for Toddlers
Here are some typical movements from around 18 months to 3 years:
- Walking backwards and forwards
- Running while navigating obstacles
- Sitting on a chair
- Carrying a doll or toy around
- Pushing and pulling toys
- Walking up and down stairs
- Climbing onto furniture and simple play equipment
- Throwing and kicking a large ball
- Riding a push bike or scooter
- Balancing along a low beam or wall
- Jumping with feet together
- Going down slides
Gross Motor Skills Examples for Preschoolers
Children of ages 3 to 6 years develop these skills:
- Walking and running backwards, forwards and sideways
- Playing chasing games
- Stopping and changing direction while running
- Playing movement games with simple rules
- Standing on tiptoes and walking heel-toe
- Pedalling and steering a tricycle or bicycle
- Hopping, jumping and skipping
- Galloping
- Playing ball games
- Balancing and hopping on one leg
- Carrying objects up and down stairs
- Climbing ladders, trees and playground equipment
- Swinging independently
- Walking along a balancing beam
- Sitting with knees crossed
- Aiming and hitting, throwing, bouncing, kicking or catching a ball
- Learning to swim
- Dancing rhythmically to music
- Riding a standing scooter
- Digging holes
Read all about gross motor skills for preschoolers.
Gross Motor Skills Examples for Children in Elementary/Primary School
Children in the early grades and beyond can often participate in organized sports and more complex activities and movements. Here are some examples:
- Playing movement games with complex rules
- Riding a bicycle
- Roller-skating
- Skipping with a skipping rope
- Doing somersaults
- Swimming strokes
- Doing dances with complex steps
- Movements involved in organized sports, such as tennis, cricket, netball, hockey, etc.
For more detail, here is a full list of gross motor milestones between the ages of 0 and 6.
Sources:
Pieterse, M. 2007. Language and School Readiness. Metz Press: Welgemoed.
Sheridan, M. 1997. From Birth to Five Years: Children’s Developmental Progress. Routledge: London.
Get FREE access to Printable Puzzles, Stories, Activity Packs and more!
Join Empowered Parents + and you’ll receive a downloadable set of printable puzzles, games and short stories, as well as the Learning Through Play Activity Pack which includes an entire year of activities for 3 to 6-year-olds.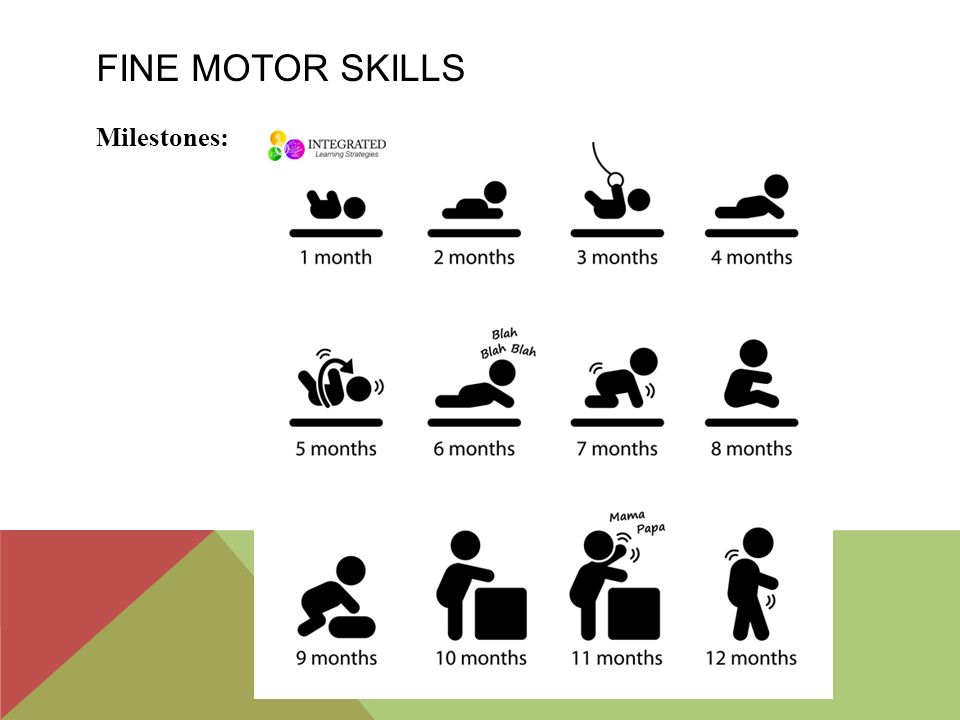
Access is free forever.
Signing up for a free Grow account is fast and easy and will allow you to bookmark articles to read later, on this website as well as many websites worldwide that use Grow.
- Share
2.2 Motor skills
In all the variety of tasks of the physical education leading is the formation systems of motor skills and abilities. Knowledge of the laws of this process provide rational content each stage of motor learning action, will help to correctly assess uneven mastery of motor action and the possibility of variation learning conditions, will allow more competently build lesson systems and leading exercises using the effect transfer of skills. nine0003
Development motor action in the process training
AT the process of learning motor action the nature of motion control changes certain parts of the body. As a result increases the level of motor skills action. Schematically, this process can be shown as follows:
As a result increases the level of motor skills action. Schematically, this process can be shown as follows:
On base of special knowledge and as a result systematic exercises students, acquiring limited opportunities to perform a motor action (motor skill), have unlimited prospects for improvement (motor skill of the highest order). Division into three levels of motor skills action is conditional, does not have stable boundaries of separation, but extremely helpful in determining educational tasks. nine0003
Motor skill
Process mastery of movement begins with the development of skills based on previously received knowledge and prior experience. Motor skill - this is ability to perform motor action (to solve a motor problem) with concentrated attention student on every movement included in studied motor action.
characteristic signs: 1.Management movements that make up the whole motor action takes place manual. As a result the student's mind is loaded with control every movement, work is done uneconomical, to a large extent fatigue. 2. Way solving a motor problem unstable: searching for the best ways her decisions. 3. Motor skill as the first level of proficiency motor action, cannot escape not a single student. True, duration this transitional level to skill varies and depends on the ability student, perfection of teaching methods, complexity of motor action, etc.
As a result the student's mind is loaded with control every movement, work is done uneconomical, to a large extent fatigue. 2. Way solving a motor problem unstable: searching for the best ways her decisions. 3. Motor skill as the first level of proficiency motor action, cannot escape not a single student. True, duration this transitional level to skill varies and depends on the ability student, perfection of teaching methods, complexity of motor action, etc.
basis motor skill is creative search, comparison, evaluation of ways performing movements, connecting them in holistic motor action, and this carries great educational opportunities. Motor skill is the level of motor skills action that is common to all leading exercises. If they will stabilized, there may be complications in the formation of motor skill of the studied motor action (it is known that studied in isolation part that is part of the whole motor action, undergoes some changes). nine0003
Motor skill
Multiple systematic manifestation of motor skills at relatively constant learning environment leads to skill turns into motor skill.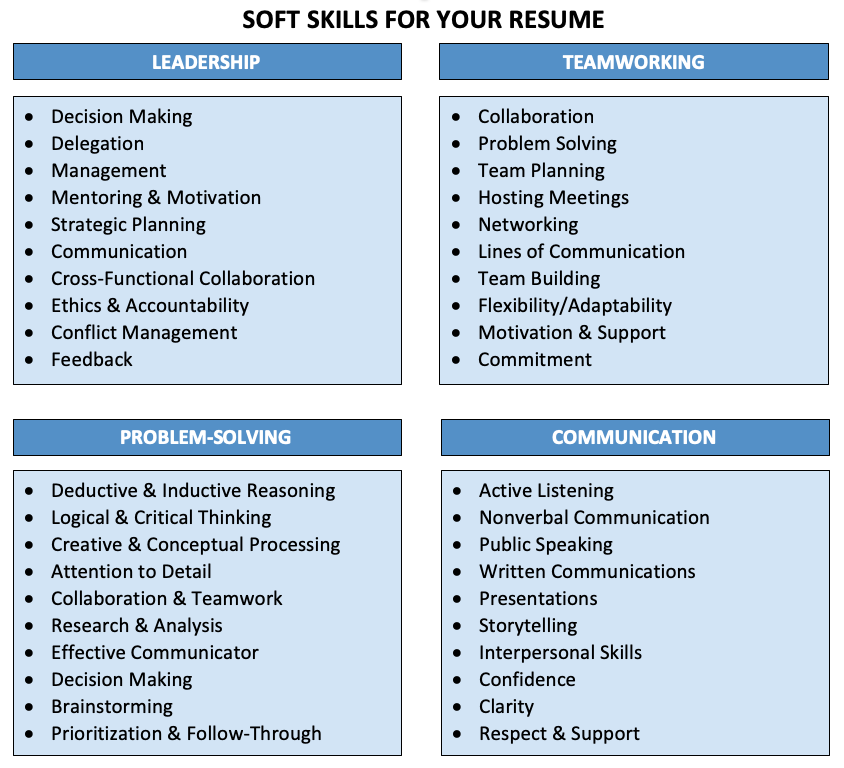 motor skill - this is ability to perform motor action to emphasize focus on conditions and results actions, not on individual movements, included in it.
motor skill - this is ability to perform motor action to emphasize focus on conditions and results actions, not on individual movements, included in it.
characteristic signs: 1. Fulfillment individual movements included in the motor action, no focus on them attention student. This is achieved through coming process automation performing movements.
2. Automated execution of movements is acquired as a result learning or life practice.
3. Automation does not take the lead consciousness during the execution of motor actions. During the formation of motor skills are not automated content, not the meaning of actions, but the process of execution some movements, some elements their structures (for example, coordination relationship of neuromuscular processes, relationship between motor and autonomic components). Therefore, it is impossible oppose conscious automated. Conscious and automated in motor skills appears in the dialectical unity. nine0003
nine0003
four. The consciousness of the student is directed mainly on the nodal components of the action, on the accounting changes in environment and creativity solving a motor problem.
By necessary, the trainee takes under control over the execution of each movement, making the necessary adjustments to the implementation or switching to another actions (for example, when losing balance headstand and handstand student groups up and rolls forward).
five. Motor skills are highly sustainability. It means that movement can be performed with less potential for disruption other conditions (in a different gym, on other projectiles, etc.), under the action on students of unusual stimuli (spectators, loud noise, increased temperature, etc.). nine0003
6. For a motor skill, it is characteristic a certain system in movements. This is expressed by combining individual movements into a holistic motor action with the elimination of unnecessary movements, delays. Increased accuracy of movement their rhythm improves, shortens duration of action in general. This is achieved due to the fact that proprioceptive signals about the end of each previous parts of the action become automatic starting impulse for each subsequent parts.
Increased accuracy of movement their rhythm improves, shortens duration of action in general. This is achieved due to the fact that proprioceptive signals about the end of each previous parts of the action become automatic starting impulse for each subsequent parts.
7. Formation of a motor skill accompanied by redistribution analyzer functions. The role is rising motor analyzer, because muscle feeling becomes dominant importance in the control of movements and in in this sense partly replaces the functions visual analyzer. Visual analyzer switches to control environment and performance activities. nine0003
Perfect mastering the skill leads to a kind of complex feeling, which is the result of subtle differentiation and synthesis of indications all analyzers. Athlete swimmer this sensation is called the feeling of water, soccer player - feeling ball, etc.
Main the content of educational tasks physical education is formation of a system of motor skills. Physical education programs students provide training those systems of motor actions, which are created in combination with other factors readiness for life, work, military and sports activities. Moreover, the expansion of the volume of formed motor skills increase success in all types of physical activity. The field of human consciousness is not unlimited, so bringing to automatism performing a series of movements does work less tiring, does not constrain consciousness the need to control everyone the element of movement, on the contrary, releases consciousness for creative activity. nine0003
Physical education programs students provide training those systems of motor actions, which are created in combination with other factors readiness for life, work, military and sports activities. Moreover, the expansion of the volume of formed motor skills increase success in all types of physical activity. The field of human consciousness is not unlimited, so bringing to automatism performing a series of movements does work less tiring, does not constrain consciousness the need to control everyone the element of movement, on the contrary, releases consciousness for creative activity. nine0003
works THEM. Sechenov and I.P. Pavlova was installed basic physiological mechanism formation of voluntary movements. It consists in the formation of temporary connections that govern performance of a motor act by muscles. They may be based on education. conditioned reflexes of the first order, higher order, manipulative reflexes, etc. The most important belongs to the last reflexes, so How are they related to the emergence non-inherited types of responses. nine0003
nine0003
Process motor skill formation conditionally divided into three physiological phases. (We are talking only about physiological phases associated with direct repetition of movement. Therefore, it will not be considered here. creation of a motivational setting, prior to practical implementation motor action.)
1st phase is characterized by the formation conditioned reflex connections with a wide irradiation of excitatory processes in the central nervous system. Externally this is expressed by recreating only the general movement pictures, accompanied by inaccurate and often unnecessary movements. nine0003
2nd phase is different in that it is redundant irradiation of excitation is limited development of inhibitory processes clarification of central nervous processes in time and space. This corresponds to a more correct execution motor action, elimination extra movements. However, in connection with insufficiently perfect interactions excitatory and inhibitory processes there is excessive stiffness in movements.
3rd phase is characterized by completion formation of motor dynamic stereotype that determines the correct better performance of motor actions. The skill acquires all those traits mentioned above. nine0003
Consequently, motor skill formation culminates in the development of motor dynamic stereotype, that is well-coordinated balanced system nervous processes formed by mechanism of conditioned reflexes.
Dynamic stereotype is physiological the basis of consistency in movements with standard activities (for example, running along the track) when all its components movements are stereotypically repeated in the same sequence. If the action takes place in less stereotypical conditions (for example, running cross-country) or in unexpected changes (for example, running on a wet track), then the efficiency action provided by variations the main stereotype (the theory of "emergency stereotypes" involves the formation backup stereotypes to the main as motor experience is accumulated). nine0003
nine0003
However dynamic stereotype is not the only form of adaptation organism to the environment (I.P. Pavlov). With constantly changing business environment (for example, sports) one of the forms of emergency adaptation is the ability nerve centers to extrapolation, then there is a rapid formation of motor and autonomic functions in accordance with the operating conditions. The effect of extrapolation depends on the level possession of a motor action and from the number of formed in humans motor skills. The richer motor experience of the student, the wider extrapolation range. For example, the goalkeeper is able to effectively an unusual throw for the ball only in that if owns the school of all goalkeeper tricks. nine0003
Dynamic stereotype and extrapolation matter in every type of movement, but the degree of their expression and interaction different. This should always be considered when learning.
Physiological phases of motor skill formation not to be confused with learning stages motor actions. Physiological phases - this is biological processes that take place in the body under the influence of motor actions. And the stages of learning - this is pedagogical process of mutual activities of teachers and students learning the latest motor actions. Knowing biological laws, you can choose such tools and methods learning that will speed up and facilitate skill formation. nine0003
Physiological phases - this is biological processes that take place in the body under the influence of motor actions. And the stages of learning - this is pedagogical process of mutual activities of teachers and students learning the latest motor actions. Knowing biological laws, you can choose such tools and methods learning that will speed up and facilitate skill formation. nine0003
Should remember that in physiology the process mastery of movement considered only as a process motor skill formation without allocation of such levels of ownership motor action, as a motor skill and motor skill of higher order. Identification of similar levels makes it easier to specify pedagogical tasks in accordance with learning stages. 1st phase of formation motor skill is characterized signs that are inherent in motor skill, and the 3rd phase - motor skill of a higher order (see "Motor skill of the highest order). nine0003
AT 3rd phase is the so-called movement automation. Without knowing her laws can not be correctly drafted learning process. More I.P. Pavlov found that as stabilization conditioned reflexes, they can be carried out areas of the cerebral cortex that currently have a reduced excitability (a certain degree retardation). Areas of the cortex with optimal excitability at the same time freed up for creativity activities. If functioning creative departments of the cortex is accompanied phenomena of consciousness, then the work of departments with reduced excitability is what what do we call automated activity. nine0003
Without knowing her laws can not be correctly drafted learning process. More I.P. Pavlov found that as stabilization conditioned reflexes, they can be carried out areas of the cerebral cortex that currently have a reduced excitability (a certain degree retardation). Areas of the cortex with optimal excitability at the same time freed up for creativity activities. If functioning creative departments of the cortex is accompanied phenomena of consciousness, then the work of departments with reduced excitability is what what do we call automated activity. nine0003
According to latest data, motion automation associated with the appearance in certain areas of the cerebral cortex called brake shafts, that is a kind of functional isolation, that surrounds automated temporary connections, protecting them from knocking down external influences and allowing nervous processes to proceed with high efficiency. In that case when established stereotype of nervous processes do not respond to the changed conditions, functional isolation is removed (disinhibition occurs) and these processes are included in the overall system functional connections in the central nervous system. In other words, there is a change in the old stereotype or the formation of a new one. nine0003
In other words, there is a change in the old stereotype or the formation of a new one. nine0003
patterns automation of movements can enter contrary to some pedagogical methods of implementing the principle consciousness. It has been established that at coming automation attempts the student to realize in the course of implementation actions each element of movement can lead to deautomatization of the skill. At the following apply rules: first, if the attention of the student refers to external characteristics movements (direction, amplitude, pace movements), then the deautomatization of the skill does not come, if attention focuses on internal structure of movements (coordination contractions of individual muscle groups), then she comes; secondly, if the student taught to control each characterization of the movement from the first steps motor skill formation awareness of all moments of movement and in 3rd phase will not lead to deautomatization; Thirdly, the student's attention should be focused on every element movements during retraining, with the need to destroy the old habit. nine0003
nine0003
AT physiology is conventionally distinguished three components of motor skill: afferent, central (programming) and efferent.
Afferent motor skill component perceives stimuli that require response motor acts. When the stimulus is complex (for example, in sports games such a complex stimulus this or that situation of the game appears), afferent synthesis is difficult. AT afferent synthesis essential belongs to feedback. At slow reverse movements connections allow you to correct this movement or its phase in the course of execution. With rapidly occurring repeated movements (for example, when running) deficit no time to make adjustments into the current movement and correction carried out only at each subsequent movement. Finally, for short one-act movements (for example, when projectile throws) correct them only possible with repeated attempts. nine0003
Central the skill component provides processing received information and programming upcoming movements. Implementation this process is difficult lack of time, when the performer have to make a decision very quickly.
Implementation this process is difficult lack of time, when the performer have to make a decision very quickly.
efferent component provides execution programmed movements. Effect implementation will depend on compliance developed program in cash functionality of the body. The discrepancy between the program and by actually doing the movements more often only observed when the student is tired, with negative emotions. nine0003
Formation and further improvement motor skill at its full bioenergy supply of the most proceeds efficiently with optimal level of emotional arousal. If the level of arousal exceeds conditional boundary of the threshold, then drops sharply skill reproduction efficiency. Therefore, technically trained a footballer sometimes misses empty gate with 3-5 m., and basketball player fails to take free kicks throws.
Stabilization and skill plasticity
After how the motor skill was formed, its development never ends. If rational repetition continues, then there is further improvement. skill. At the same time, there is a contradiction between ongoing stabilization skill and desire to make a skill more flexible, reproducible in changing conditions (see "Motor skill of the highest order). Vital justified would be such a motor skill, which, on the one hand, has great resistance to various interference (to the effect on the student of increased temperature, noise, etc.), on the other hand, enough flexibility to reproduce it in changed conditions (when performing gymnastic exercises on other projectiles, with jumping over a ditch, etc.). Permission This contradiction is based on such properties of higher nervous activity, as stability and plasticity. I.P. Pavlov already reflected this in the very the name of the physiological basis consistency in movements – dynamic stereotype. nine0003
If rational repetition continues, then there is further improvement. skill. At the same time, there is a contradiction between ongoing stabilization skill and desire to make a skill more flexible, reproducible in changing conditions (see "Motor skill of the highest order). Vital justified would be such a motor skill, which, on the one hand, has great resistance to various interference (to the effect on the student of increased temperature, noise, etc.), on the other hand, enough flexibility to reproduce it in changed conditions (when performing gymnastic exercises on other projectiles, with jumping over a ditch, etc.). Permission This contradiction is based on such properties of higher nervous activity, as stability and plasticity. I.P. Pavlov already reflected this in the very the name of the physiological basis consistency in movements – dynamic stereotype. nine0003
AT pedagogical process is a contradiction overcome by the optimal ratio simple repetition of the studied motor action with variable (See "Structure of learning"). Definition the duration of both repetitions and the measure of diversity of options is the main task of any teaching method.
Definition the duration of both repetitions and the measure of diversity of options is the main task of any teaching method.
Progression and uneven skill formation
gradualism motor skill formation reflected in its phase: the skill appears through a series of partial transformations, for relatively long period time. The uneven formation skill is expressed in different ways qualitative growth in individual moments of its development. She may have four varieties:
1. Formation of habit with "negative acceleration." This means that at first stages of learning occurs relatively rapid mastery of motor action, and then a qualitative increase in skill slows down. This type of skill building characteristic of learning relatively light motor actions the student quickly grasps the basis of the action and takes a long time to master its details.
2. Formation of a habit with a "positive acceleration. " This means that at first stages of training qualitative increase skill is negligible. Then he abruptly increases. This type of formation skill characteristic for learning relatively complex motor actions when external imperceptible quality savings only with over time, they may show themselves in the form of an increase in the level of proficiency motor action. nine0003
" This means that at first stages of training qualitative increase skill is negligible. Then he abruptly increases. This type of formation skill characteristic for learning relatively complex motor actions when external imperceptible quality savings only with over time, they may show themselves in the form of an increase in the level of proficiency motor action. nine0003
3. Slowdown in skill development. going on this is for both types of accelerations, when skill reaches a certain perfection. Therefore, than the more perfect the skill, the more it takes efforts and pedagogical skills, to further improve it.
four. Delay in skill development (“plateau”). There are two possible reasons for the delay: internal, due to leakage subtle adaptive changes in the body, which only over time time are transformed into noticeable qualitative skill improvement; external, caused improper teaching methods or underdevelopment motor qualities. If the reason defined correctly, then to overcome delay will be required or just time (first reason), or significant changing the means and methods of teaching (The second reason). Delay duration may be the most varied. nine0003
Delay duration may be the most varied. nine0003
Skill Destruction
Motor skill, like any conditioned reflex, if there is no reinforcement, is destroyed. Destruction is like skill formation takes place gradually, but in reverse order.
AT the beginning of the regression of the skill is not undergoes qualitative changes but students begin to experience self-doubt, so sometimes disruptions occur motor action. Then is lost ability to accurately differentiate movements, complex coordination relationships between movements disappearance of individuality in technology execution, on which in the past it was a lot of time and work has been spent. Externally this is reflected in the quality deterioration motor action: the student shows worst result in projectile throwing, makes errors in execution gymnastic exercises, etc. When further lack of exercise these phenomena become more tangible. Finally, the student can completely lose ability to perform some complex motor actions. nine0003
nine0003
Consequently, qualitative differences in skill (quickly run, jump high, etc.) systematic studies worsen quickly. However, motor skills does not completely disappear, its basis persists for a relatively long time, and repetitions, he recovers quickly. For example, if there is no exercise a person loses the ability to swim quickly, economically, beautifully, but he never will not lose the ability to swim at all. That the same can be said about cycling, about skiing. In a special The study found that even in such a complex coordination exercise, like skating, people who have become on ice after 10-12 year old break, in one lesson restored previous ability to move. nine0003
Motor skills can deteriorate not only due to lack of repetition, but and when the level drops motor qualities, functional body's capabilities. For example, sports success of runners-stayers will become smaller if due to age changes will decrease the level of maximum oxygen consumption. Further an athlete can completely lose ability to perform those motor skills in which he once achieved great skill. Yes, old gymnasts quite easily perform swing exercises of average technical difficulties on the crossbar and uneven bars, but no longer able to cope with ring exercises. nine0003
Further an athlete can completely lose ability to perform those motor skills in which he once achieved great skill. Yes, old gymnasts quite easily perform swing exercises of average technical difficulties on the crossbar and uneven bars, but no longer able to cope with ring exercises. nine0003
Motor transfer skills
One from the educational tasks of the physical education is the task of creating certain motor systems skills. As a result, several motor skills, forming simultaneously or sequentially influence each other. FROM physiological point of view interaction skills is a process of interaction simultaneously or sequentially formed coordination structures actions (when teaching several motor actions in about one and the same time, for example: in a series of lessons, in one lesson or after completion learning one action teach to another). nine0003
Distinguish several types of interaction skills. positive transfer This interaction of skills is called in which the previously formed skill facilitates the formation process subsequent skill. For example, skill throwing a small ball will help to master throwing a grenade. The formation of each subsequent motor skill builds on previously acquired the result of life experience and learning. At the same time, those structural elements of already formed skills, which are similar to the corresponding elements of a new skill. nine0003
For example, skill throwing a small ball will help to master throwing a grenade. The formation of each subsequent motor skill builds on previously acquired the result of life experience and learning. At the same time, those structural elements of already formed skills, which are similar to the corresponding elements of a new skill. nine0003
negative transfer (interference) is called This interaction of skills which previously formed skill complicates the process of formation subsequent skill. For example, skill lifting the curtain on the crossbar can slow down the ascent.
Character interaction skills needed be taken into account when classifying physical exercises, program development physical education, planning educational process, selection of systems leading exercises. At the same time, it should make the most of the possible the effect of positive transfer and prevent negative impact. However, if two is negative interacting skills already formed, then their combination in one lesson can be used as a guide technique for improving motor skills actions. For example, basic skills jump, bending your legs, and in a dismount at close range, sitting on a horse, act on the principle negative transfer. But if both motor actions are learned (skills formed), then for the purpose of their further improvement, to develop skills change from one character movements on the other they can be repeated in one lesson in turn: then a jump, then a jump at close range. nine0003
For example, basic skills jump, bending your legs, and in a dismount at close range, sitting on a horse, act on the principle negative transfer. But if both motor actions are learned (skills formed), then for the purpose of their further improvement, to develop skills change from one character movements on the other they can be repeated in one lesson in turn: then a jump, then a jump at close range. nine0003
Motor higher order skill
Process improvement of the formed motor skill is infinite. His the main task - teach student to be fluent in skills in any conditions – production, household, military, sports. Only in In this case, the skill will receive its practical value. If a student, for example, confidently overcomes height when jumping in the gym but cannot use this skill when overcoming the natural obstacles, the practical value such a skill is reduced to zero. nine0003
Motor superior skill - this is ability to apply learned motor skills actions in real life.
Similar skill arises on the basis of the formed motor skills and relatively high level of specialized knowledge. By in essence, it is skills of a higher order and are the ultimate goal of learning.
characteristic signs: 1. Skill higher order is characterized by increased the role of the starting function of consciousness. Only an objective analysis of the current situation, and most often with a shortage of time, allows you to reproduce that motor skill that will lead to the most effect. 2. Movements, components of movement can be done automatically but can also fall under the control of consciousness, if correction is required for unusual conditions. 3. Skill higher order is always manifested in holistic motor activity. nine0003
fixture formed skill to changing conditions - process creative, intensive intellectual realm of the student. Formation of higher order skills is an expression of applied value physical education, reserve improving sportsmanship.
Varieties higher order skills
Character requirements for motor skills, allows us to distinguish three varieties of higher order skills.
1. Ability to use effectively acquired skills in parallel or in various sequences in accordance with the requirements of the environment environment. For example, the ability to implement running skill, overcoming natural obstacles.
2. Ability to use two or a few acquired skills. For example, throwing while running.
3. Ability to use effectively two or more consecutive formed skills. For example, after somersaults to perform an exercise in balance. nine0003
Listed species are closely related to each other and can expressed in various combinations. For example, the skills of the last two types in the first form. Moreover, the first type of skills is the most difficult, but the most significant in terms of applicability.
patterns formation and improvement motor skills are manifested in each case of motor training action. However, the duration of the formation improvement or fading very variable and dependent on ability student, the characteristics of the skill itself, excellence in teaching methods and personality of the teacher who preceded motor experience, etc.
Movement qualities - Movement is life
| Physical (motor) qualities are called individual quality aspects motor abilities of the child motor abilities. They show up in concrete actions - the main movements (walking, running, jumping, climbing, throwing), gaming, sports activities. One and the same quality can determine success in performing various actions. For example, the ability to move quickly allows you to run, swim, ride fast on a bike. And short-term power tensions are needed in jumping, climbing, when throwing objects. Physical qualities in children are manifested through motor skills and abilities, and they, in turn, are sufficient level of development. These two sides of motor function closely interrelated and interdependent. If the formation of motor skills in children is fixed at a low level development of motor qualities, then in this may further lead to reinforcing wrong skills performing the movement. For performing a series of movements for preschool children age needs a certain level of development of speed, dexterity, strength, endurance. Without this, the movements of children, despite their diversity, not enough economy, expediency, cannot fully display the existing body's reserves. nine0003 Level physical fitness in many ways reflects the possibilities of functional body systems. Top performance physical qualities (for example, speed) marked with good functional state of the body, with favorable emotional background. Objectivity assessment of physical fitness during largely determined by knowledge of age features and patterns motor development in preschoolers, including physical qualities. Most The most important of these features are their conditioning by incompleteness formation of physiological structures organism and the presence in the dynamics of the physical development of a child sensitive to external influences of the periods. Characteristic for preschoolers are considered also a large variability of proportions body and uneven development functional systems of the body. Everybody this dictates the need to implement strictly corresponding to the possibilities children teaching methods and diagnostics development of motor skills and physical qualities. To number of basic physical qualities refer flexibility, various types of endurance, strength quality (muscle strength), speed quality (speed), their combination (speed-strength qualities), agility, as well as coordination abilities .[9] Flexibility defines the degree of mobility of the musculoskeletal apparatus and is of particular importance for health. Ability to turn and circular movements in the joints of the body indicates a good physical human condition. Flexibility indicator serves as the greatest range of motion. nine0003 Fast – a person's ability to do motor actions to the maximum a short period of time. She belongs to the number of conservative, i.e., it is difficult developed, human qualities. Development speed largely depends on natural data often passed down from generation to generation. Endurance is one of the most important physical qualities person, characterizing his physical condition. Distinguish two type of endurance : total and special . General endurance – ability to perform physical work involving most muscle groups. Special endurance – ability to perform physical work aimed at a particular motor activity involving certain muscle group. nine0075 Strength – interaction of psychophysiological processes in the human body that overcome external resistance account of muscle effort. Power quality is expressed through a set of forces abilities. Distinguish self-powered abilities ( static strength ), which manifests itself in static work (muscles do not change their length), and speed-power abilities . |
 nine0003
nine0003  In turn, at accumulation of fatigue in the body or with negative emotions noticeable the frequency of movements and their speed decrease, motor response slows down the number of inaccurate movements increases, especially difficult to coordinate. nine0003
In turn, at accumulation of fatigue in the body or with negative emotions noticeable the frequency of movements and their speed decrease, motor response slows down the number of inaccurate movements increases, especially difficult to coordinate. nine0003  nine0003
nine0003  It is closely related to the level development of the cardio-respiratory system body and overall performance. This quality ensures durability performance of work without reducing it intensity and efficiency. nine0003
It is closely related to the level development of the cardio-respiratory system body and overall performance. This quality ensures durability performance of work without reducing it intensity and efficiency. nine0003