Jaundice baby meaning
What are Jaundice and Kernicterus?
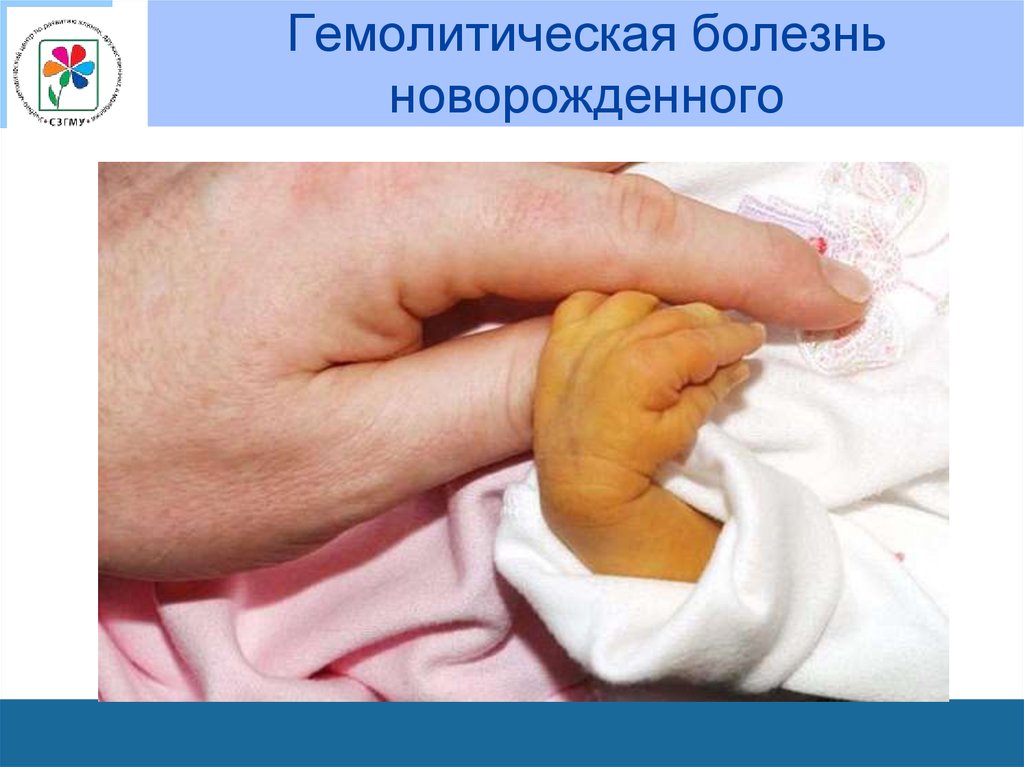
Jaundice is the yellow color seen in the skin of many newborns. Jaundice happens when a chemical called bilirubin builds up in the baby’s blood. During pregnancy, the mother’s liver removes bilirubin for the baby, but after birth the baby’s liver must remove the bilirubin. In some babies, the liver might not be developed enough to efficiently get rid of bilirubin. When too much bilirubin builds up in a new baby’s body, the skin and whites of the eyes might look yellow. This yellow coloring is called jaundice.
When severe jaundice goes untreated for too long, it can cause a condition called kernicterus. Kernicterus is a type of brain damage that can result from high levels of bilirubin in a baby’s blood. It can cause athetoid cerebral palsy and hearing loss. Kernicterus also causes problems with vision and teeth and sometimes can cause intellectual disabilities. Early detection and management of jaundice can prevent kernicterus.
Signs and Symptoms
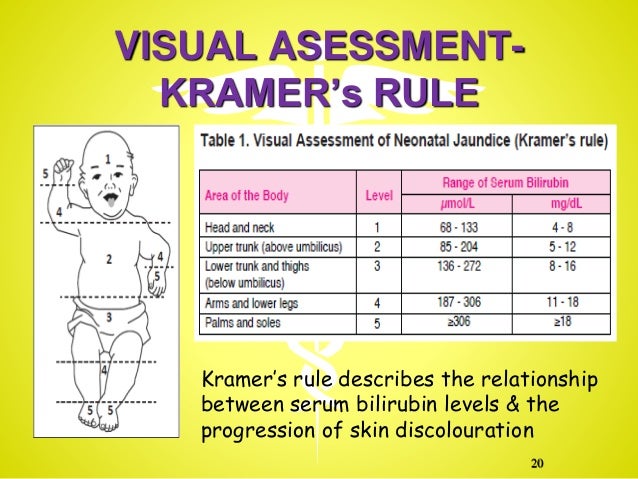
Jaundice usually appears first on the face and then moves to the chest, belly, arms, and legs as bilirubin levels get higher. The whites of the eyes can also look yellow. Jaundice can be harder to see in babies with darker skin color. The baby’s doctor or nurse can test how much bilirubin is in the baby’s blood.
See your baby’s doctor the same day if your baby:
- Is very yellow or orange (skin color changes start from the head and spread to the toes).
- Is hard to wake up or will not sleep at all.
- Is not breastfeeding or sucking from a bottle well.
- Is very fussy.
- Does not have enough wet or dirty diapers (at least 4-6 thoroughly wet diapers in 24 hours and 3 to 4 stools per day by the fourth day).
Get emergency medical help if your baby:
- Is crying inconsolably or with a high pitch.
- Is arched like a bow (the head or neck and heels are bent backward and the body forward).
- Has a stiff, limp, or floppy body.
- Has strange eye movements.
Diagnosis
At a minimum, babies should be checked for jaundice every 8 to 12 hours in the first 48 hours of life.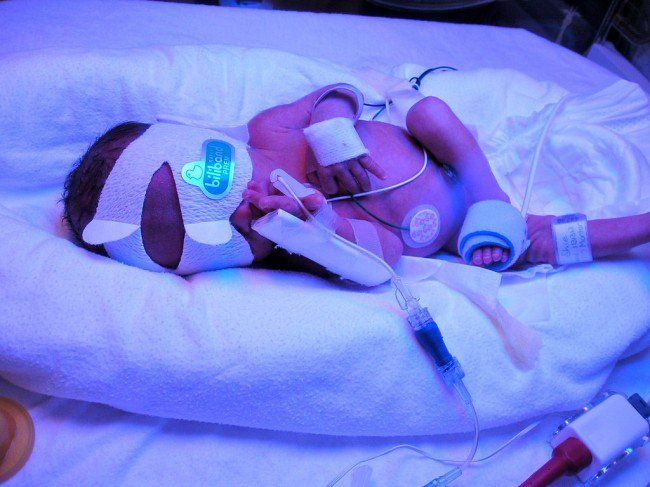 It is important for your baby to be seen by a nurse or doctor when the baby is between 3 and 5 days old, because this is usually when a baby’s bilirubin level is highest. This is why, if your baby is discharged before age 72 hours, your baby should be seen within 2 days of discharge. The timing of this visit may vary depending on your baby’s age when released from the hospital and other factors.
It is important for your baby to be seen by a nurse or doctor when the baby is between 3 and 5 days old, because this is usually when a baby’s bilirubin level is highest. This is why, if your baby is discharged before age 72 hours, your baby should be seen within 2 days of discharge. The timing of this visit may vary depending on your baby’s age when released from the hospital and other factors.
A doctor or nurse may check the baby’s bilirubin using a light meter that is placed on the baby’s head. This results in a transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) level. If it is high, a blood test will likely be ordered.
The best way to accurately measure bilirubin is with a small blood sample from the baby’s heel. This results in a total serum bilirubin (TSB) level. If the level is high, based upon the baby’s age in hours and other risk factors, treatment will likely follow. Repeat blood samples will also likely be taken to ensure that the TSB decreases with the prescribed treatment.
Treatment
No baby should develop brain damage from untreated jaundice.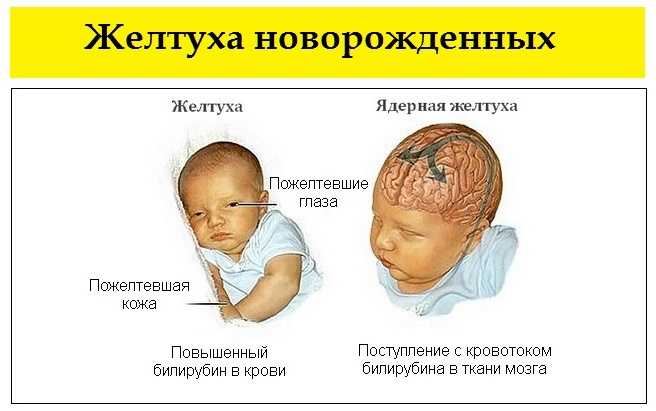
When being treated for high bilirubin levels, the baby will be undressed and put under special lights. The lights will not hurt the baby. This can be done in the hospital or even at home. The baby’s milk intake may also need to be increased. In some cases, if the baby has very high bilirubin levels, the doctor will do a blood exchange transfusion. Jaundice is generally treated before brain damage is a concern.
Putting the baby in sunlight is not recommended as a safe way of treating jaundice.
Risk Factors
About 60% of all babies have jaundice. Some babies are more likely to have severe jaundice and higher bilirubin levels than others. Babies with any of the following risk factors need close monitoring and early jaundice management:
Preterm Babies
Babies born before 37 weeks, or 8.5 months, of pregnancy might have jaundice because their liver is not fully developed. The young liver might not be able to get rid of so much bilirubin.
Babies with Darker Skin Color
Jaundice may be missed or not recognized in a baby with darker skin color. Checking the gums and inner lips may detect jaundice. If there is any doubt, a bilirubin test should be done.
Checking the gums and inner lips may detect jaundice. If there is any doubt, a bilirubin test should be done.
East Asian or Mediterranean Descent
A baby born to an East Asian or Mediterranean family is at a higher risk of becoming jaundiced. Also, some families inherit conditions (such as G6PD deficiency), and their babies are more likely to get jaundice.
Feeding Difficulties
A baby who is not eating, wetting, or stooling well in the first few days of life is more likely to get jaundice.
Sibling with Jaundice
A baby with a sister or brother that had jaundice is more likely to develop jaundice.
Bruising
A baby with bruises at birth is more likely to get jaundice. A bruise forms when blood leaks out of a blood vessel and causes the skin to look black and blue. The healing of large bruises can cause high levels of bilirubin and your baby might get jaundice.
Blood Type
Women with an O blood type or Rh negative blood factor might have babies with higher bilirubin levels. A mother with Rh incompatibility should be given Rhogam.
A mother with Rh incompatibility should be given Rhogam.
- When severe jaundice goes untreated for too long, it can cause brain damage and a condition called kernicterus.
- Early diagnosis and treatment of jaundice can prevent kernicterus.
- If you’re concerned that your baby might have jaundice visit your baby’s doctor right away. Ask for a jaundice bilirubin test.
If You’re Concerned
If you think your baby has jaundice you should call and visit your baby’s doctor right away. Ask your baby’s doctor or nurse about a jaundice bilirubin test.
If your baby does have jaundice, it is important to take jaundice seriously and stick to the follow-up plan for appointments and recommended care.
Make sure your baby is getting enough to eat. The process of removing waste also removes bilirubin in your baby’s blood. If you are breastfeeding, you should nurse the baby at least 8 to 12 times a day for the first few days. This will help you make enough milk for the baby and will help keep the baby’s bilirubin level down.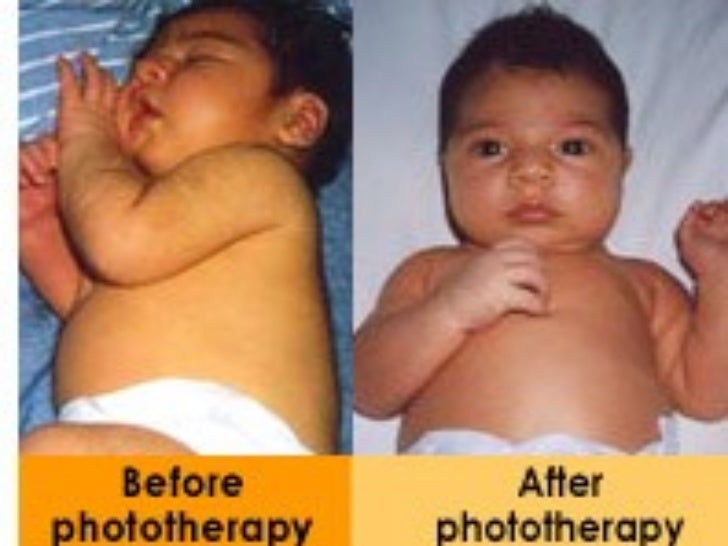 Support and advice for breastfeeding mothers may increase the chances of successful breastfeeding. If you are having trouble breastfeeding, ask your doctor, nurse, or a lactation coach for help.
Support and advice for breastfeeding mothers may increase the chances of successful breastfeeding. If you are having trouble breastfeeding, ask your doctor, nurse, or a lactation coach for help.
Infant jaundice - Symptoms and causes
Overview
Infant jaundice is yellow discoloration of a newborn baby's skin and eyes. Infant jaundice occurs because the baby's blood contains an excess of bilirubin (bil-ih-ROO-bin), a yellow pigment of red blood cells.
Infant jaundice is a common condition, particularly in babies born before 38 weeks' gestation (preterm babies) and some breast-fed babies. Infant jaundice usually occurs because a baby's liver isn't mature enough to get rid of bilirubin in the bloodstream. In some babies, an underlying disease may cause infant jaundice.
Most infants born between 35 weeks' gestation and full term need no treatment for jaundice. Rarely, an unusually high blood level of bilirubin can place a newborn at risk of brain damage, particularly in the presence of certain risk factors for severe jaundice.
Products & Services
- Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition
- Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital Edition
Symptoms
Yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes — the main sign of infant jaundice — usually appears between the second and fourth day after birth.
To check for infant jaundice, press gently on your baby's forehead or nose. If the skin looks yellow where you pressed, it's likely your baby has mild jaundice. If your baby doesn't have jaundice, the skin color should simply look slightly lighter than its normal color for a moment.
Examine your baby in good lighting conditions, preferably in natural daylight.
When to see a doctor
Most hospitals have a policy of examining babies for jaundice before discharge. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that newborns be examined for jaundice during routine medical checks and at least every eight to 12 hours while in the hospital.
Your baby should be examined for jaundice between the third and seventh day after birth, when bilirubin levels usually peak. If your baby is discharged earlier than 72 hours after birth, make a follow-up appointment to look for jaundice within two days of discharge.
If your baby is discharged earlier than 72 hours after birth, make a follow-up appointment to look for jaundice within two days of discharge.
The following signs or symptoms may indicate severe jaundice or complications from excess bilirubin. Call your doctor if:
- Your baby's skin becomes more yellow
- The skin on your baby's the abdomen, arms or legs looks yellow
- The whites of your baby's eyes look yellow
- Your baby seems listless or sick or is difficult to awaken
- Your baby isn't gaining weight or is feeding poorly
- Your baby makes high-pitched cries
- Your baby develops any other signs or symptoms that concern you
Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free, and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips and current health topics, like COVID-19, plus expertise on managing health.
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which
information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with
other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could
include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected
health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health
information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of
privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on
the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could
include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected
health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health
information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of
privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on
the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Causes
Excess bilirubin (hyperbilirubinemia) is the main cause of jaundice. Bilirubin, which is responsible for the yellow color of jaundice, is a normal part of the pigment released from the breakdown of "used" red blood cells.
Newborns produce more bilirubin than adults do because of greater production and faster breakdown of red blood cells in the first few days of life. Normally, the liver filters bilirubin from the bloodstream and releases it into the intestinal tract. A newborn's immature liver often can't remove bilirubin quickly enough, causing an excess of bilirubin. Jaundice due to these normal newborn conditions is called physiologic jaundice, and it typically appears on the second or third day of life.
Normally, the liver filters bilirubin from the bloodstream and releases it into the intestinal tract. A newborn's immature liver often can't remove bilirubin quickly enough, causing an excess of bilirubin. Jaundice due to these normal newborn conditions is called physiologic jaundice, and it typically appears on the second or third day of life.
Other causes
An underlying disorder may cause infant jaundice. In these cases, jaundice often appears much earlier or much later than does the more common form of infant jaundice. Diseases or conditions that can cause jaundice include:
- Internal bleeding (hemorrhage)
- An infection in your baby's blood (sepsis)
- Other viral or bacterial infections
- An incompatibility between the mother's blood and the baby's blood
- A liver malfunction
- Biliary atresia, a condition in which the baby's bile ducts are blocked or scarred
- An enzyme deficiency
- An abnormality of your baby's red blood cells that causes them to break down rapidly
Risk factors
Major risk factors for jaundice, particularly severe jaundice that can cause complications, include:
- Premature birth.
 A baby born before 38 weeks of gestation may not be able to process bilirubin as quickly as full-term babies do. Premature babies also may feed less and have fewer bowel movements, resulting in less bilirubin eliminated through stool.
A baby born before 38 weeks of gestation may not be able to process bilirubin as quickly as full-term babies do. Premature babies also may feed less and have fewer bowel movements, resulting in less bilirubin eliminated through stool. - Significant bruising during birth. Newborns who become bruised during delivery gets bruises from the delivery may have higher levels of bilirubin from the breakdown of more red blood cells.
- Blood type. If the mother's blood type is different from her baby's, the baby may have received antibodies through the placenta that cause abnormally rapid breakdown of red blood cells.
- Breast-feeding. Breast-fed babies, particularly those who have difficulty nursing or getting enough nutrition from breast-feeding, are at higher risk of jaundice. Dehydration or a low caloric intake may contribute to the onset of jaundice. However, because of the benefits of breast-feeding, experts still recommend it.
 It's important to make sure your baby gets enough to eat and is adequately hydrated.
It's important to make sure your baby gets enough to eat and is adequately hydrated. - Race. Studies show that babies of East Asian ancestry have an increased risk of developing jaundice.
Complications
High levels of bilirubin that cause severe jaundice can result in serious complications if not treated.
Acute bilirubin encephalopathy
Bilirubin is toxic to cells of the brain. If a baby has severe jaundice, there's a risk of bilirubin passing into the brain, a condition called acute bilirubin encephalopathy. Prompt treatment may prevent significant lasting damage.
Signs of acute bilirubin encephalopathy in a baby with jaundice include:
- Listlessness
- Difficulty waking
- High-pitched crying
- Poor sucking or feeding
- Backward arching of the neck and body
- Fever
Kernicterus
Kernicterus is the syndrome that occurs if acute bilirubin encephalopathy causes permanent damage to the brain.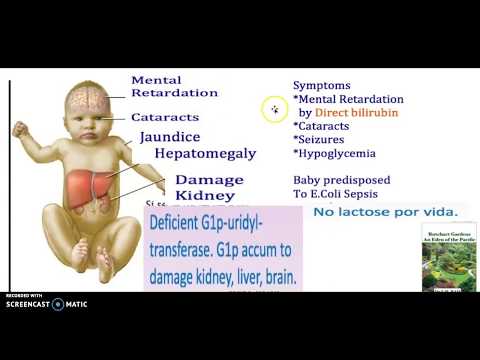 Kernicterus may result in:
Kernicterus may result in:
- Involuntary and uncontrolled movements (athetoid cerebral palsy)
- Permanent upward gaze
- Hearing loss
- Improper development of tooth enamel
Prevention
The best preventive of infant jaundice is adequate feeding. Breast-fed infants should have eight to 12 feedings a day for the first several days of life. Formula-fed infants usually should have 1 to 2 ounces (about 30 to 60 milliliters) of formula every two to three hours for the first week.
By Mayo Clinic Staff
Related
Associated Procedures
Products & Services
Treatment of jaundice in Saratov | 1DMC
Medical examination in 1 month
Additional tests In order to undergo additional types of diagnostics, you need to get a referral…
Psychiatry
Vaccination
Orthopedics
general tips for preparing for an endoscopic examination depend on. ..
..
Neurology
If you find any abnormalities, do not panic. However, put off going to a pediatric neurologist…
Massage
X-ray
Hematology
Stuttering: causes and forms
Stuttering in children is a speech disorder characterized by frequent repetition or stretching…
0 General speech underdevelopment
0 underdevelopment of speech (OHP) - disorders related to the formation of speech in children. This speech underdevelopment ...
Voice disorders
Voice disorders are a group of speech disorders manifested in complete or partial absence of phonation,…
Speech therapy
A speech therapist for children is a specialist who corrects speech disorders caused by both physical and…
Alalia
Alalia in children - a speech disorder, which is characterized by a lack of development of speech skills (or . ..
..
Bradilalia
Bradilalia is a pathology of speech, manifested in the form of a violation of the tempo and rhythm of speech. A person with such speech ...
Dysarthria
Dysarthria is a pathology of speech in which there is an incorrect (distorted or difficult) pronunciation ...
Dyslalia
Dyslalia - a violation of sound pronunciation in children with normal hearing and preserved innervation of articulation ...
Speech development delay 0 (ZRR) - speech pathology, expressed in a slower pace of development ...
Rhinolalia
Rhinolalia - a speech disorder, manifested by severe distortion of speech and incorrect pronunciation of individual ...
Laser treatment of skin pathologies
Your child's health should be entrusted to professionals. If you experience the first symptoms, contact…
If you experience the first symptoms, contact…
Comprehensive examination of multifactorial diseases
Multifactorial diseases are diseases caused by different factors that require consultation…
Children’s cosmetology
Halotherapy
traditional therapeutic…
Issue of certificates and conclusions
In various situations, children need to issue medical certificates. First Children's Medical…
Pulmonology
Obstructive syndrome in children You need to understand that without qualified and proper treatment of bronchitis ...
Therapeutic exercise
Physical activity is one of the important conditions for human life and development. It is a biological irritant…
Surgery
Pediatric Surgeon Choice The choice of a qualified doctor is important in pediatric surgery.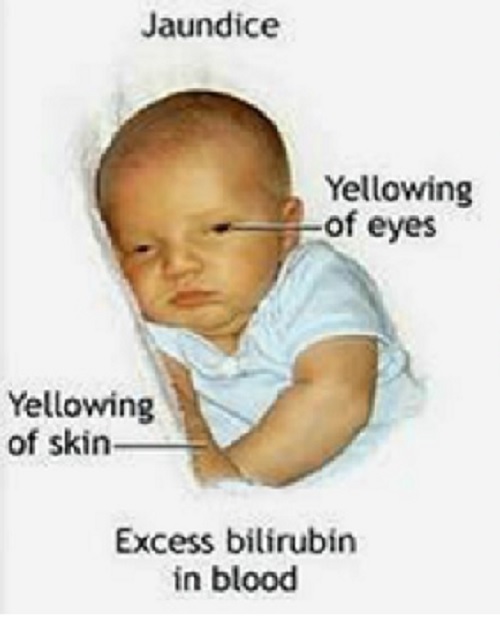 Medical…
Medical…
Laboratory
We offer a full range of traditional methods of general clinical and biochemical analysis. Laboratory…
Day hospital
On a day hospital basis in our Center we provide all types of infusion therapy, complex…
Annual follow-up program
Children's health - parents' peace of mind! Indeed, when children grow up healthy and strong, in a family…
Functional diagnostics
All equipment in the functional diagnostics room of our Center is digital (that is, working…
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is administered in courses. The duration of the course of treatment is 5-7 for some diseases, ... The development of many eye diseases can be prevented and stopped...
Otorhinolaryngology
Treatment of ENT diseases ENT of the First Children's Medical Center deals with diagnostics and treatment…
Nephrology
Dermatology
Treatment of skin diseases The skin is the most visible organ of the human body.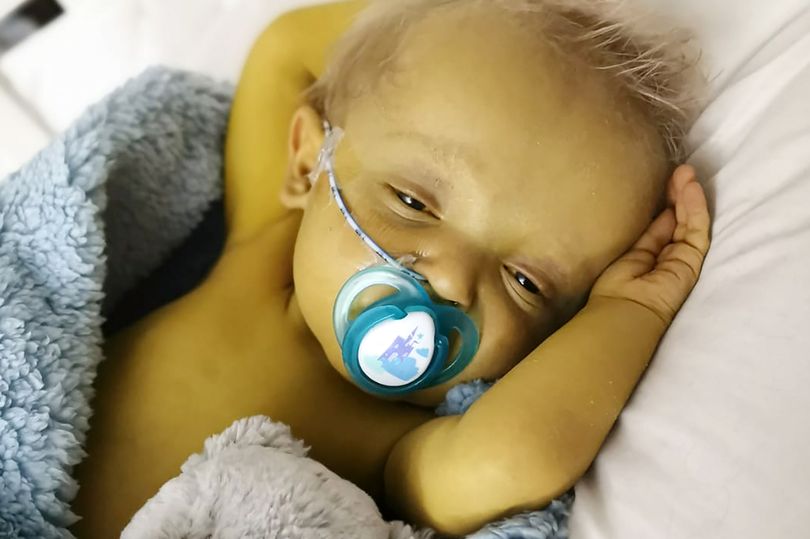 Experienced and attentive…
Experienced and attentive…
Gynecology
It is important to help patients and their parents in a timely manner to identify and adequately deal with female problems…
Anesthesiology
Pediatric anesthesiologist in Saratov A pediatric anesthesiologist talks to the parents, as well as to the child himself…
Endocrinology
All this allows for timely and adequate treatment. If the child complies with the necessary ...
Cardiology
After collecting an anamnesis and carrying out diagnostic measures, the pediatric cardiologist of the Center will draw up an individual…
Urology
If a child develops pulling pains in the lower abdomen, there is no need to self-medicate, let alone hope that…
Children Gastroenterology
less protected from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract than adults. Unbalanced…
Unbalanced… Pediatrics
Fast trace icon translate If your child often gets sick with acute respiratory…
Allergology-immunology
Fast trace icon translate The main task of specialists in allergology and immunology is…
types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment in children and adults
Jaundice is a syndrome in which the skin, mucous membranes and whites of the eyes turn yellow. This is not an independent disease, but only a manifestation of some kind of pathology. The reasons for the development of jaundice can be completely different. nine0173
What causes jaundice?
Jaundice occurs when there is too much bilirubin in the blood. It can be increased due to many factors: disorders in the liver, disorders of the outflow of bile (bile itself contains bilirubin) from the gallbladder and bile ducts, disorders of the blood, in which too many red blood cells containing bilirubin break down.
Bilirubin is a yellow substance formed during the breakdown of red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body. When red blood cells die, the liver filters their breakdown products from the bloodstream. But with pathologies (diseases of the liver itself and biliary tract, increased destruction of red blood cells), the liver may not keep up with this process, bilirubin accumulates, and the skin, sclera of the eyes and mucous membranes become yellow. nine0173
Get tested for bilirubin at CITILAB
- Total bilirubin
- Bilirubin direct (conjugated)
Types of jaundice
There are several types of jaundice, and depending on this, the mechanism of damage differs.
There are three types of jaundice:
- Prehepatic (hemolytic) jaundice. Appears when too many red blood cells break down. This process is called hemolysis. When too many red blood cells break down at once, a large amount of bilirubin is released that the liver cannot handle.
 This happens, for example, with hereditary types of anemia, when a person's erythrocytes (red blood cells) have a special shape and are prone to more rapid destruction. nine0186
This happens, for example, with hereditary types of anemia, when a person's erythrocytes (red blood cells) have a special shape and are prone to more rapid destruction. nine0186 - Hepatic (parenchymal) jaundice. This type is associated with damage to the liver, from which the filtering ability of the organ suffers, and too much bilirubin enters the bloodstream. This is possible with liver infections, hepatitis, cirrhosis.
- Subhepatic (mechanical) jaundice. This type of jaundice occurs due to blockage of the bile ducts that connect the liver, gallbladder, and intestines.
The bile ducts are a series of tubes that look like blood vessels but are responsible for transporting bile from the liver to the gallbladder. If the obstruction does not allow the liver to remove excess bilirubin, serious malfunctions occur in its work, which in turn provoke jaundice. This happens due to gallstones, enlarged lymph nodes or tumors. nine0003
Symptoms of jaundice
From the name of the syndrome it is clear what constitutes the main symptom. With jaundice, the whites of the eyes, skin and other tissues of the human body turn yellow. Interestingly, the shade of yellow can suggest the type of jaundice. With hemolytic jaundice, the skin becomes pale and acquires a light yellow, lemon tint. With hepatic - orange. With mechanical jaundice, the skin darkens, becomes earthy, greenish in color.
With jaundice, the whites of the eyes, skin and other tissues of the human body turn yellow. Interestingly, the shade of yellow can suggest the type of jaundice. With hemolytic jaundice, the skin becomes pale and acquires a light yellow, lemon tint. With hepatic - orange. With mechanical jaundice, the skin darkens, becomes earthy, greenish in color.
Acute jaundice usually accompanied by fever, chills, abdominal pain, flu-like symptoms, dark urine, and light-colored stools. nine0003
If jaundice develops as a result of a chronic pathology, there may be symptoms such as weight loss or pruritus. Jaundice caused by cancer of the pancreas or biliary tract may be accompanied by abdominal pain.
Jaundice in children
A common occurrence is neonatal jaundice. As in adults, childhood jaundice is associated with elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood, but in the vast majority of cases it does not pose a serious threat to life or health.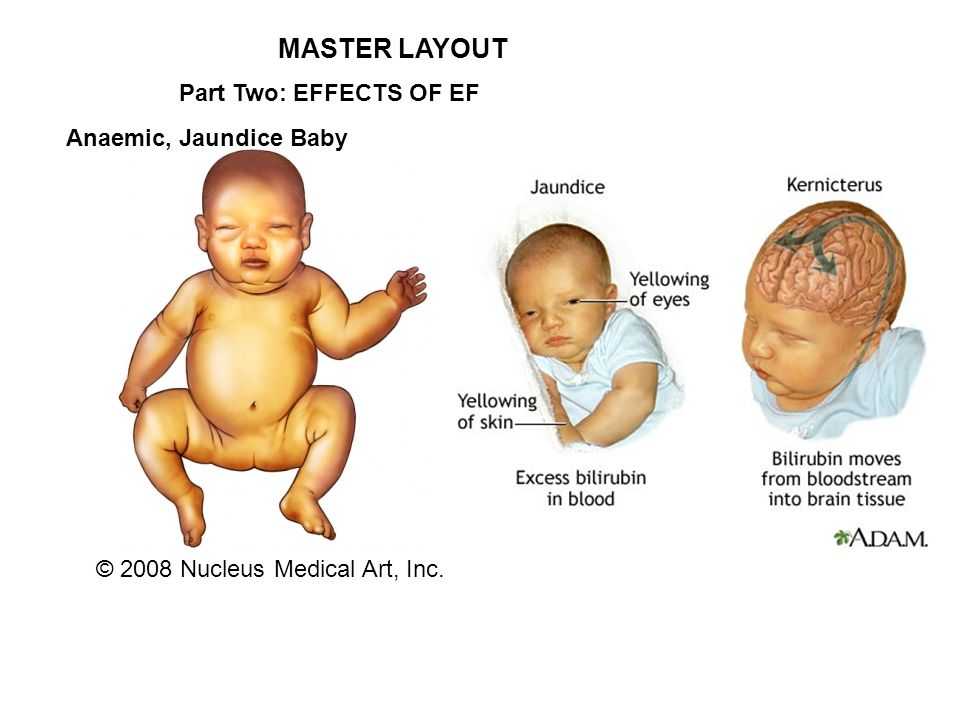 nine0003
nine0003
Jaundice is one of the most common syndromes faced by newborns. According to statistics, almost 60% of full-term children and 80% of those born prematurely (before the 37th week of pregnancy) have jaundice of varying degrees at birth. At the same time, 60-70% of this number are faced with a physiological, and not a pathological, form of jaundice. And only one in 20 babies has bilirubin in the blood so high that it needs treatment.
Neonatal jaundice usually develops 2 to 3 days after birth and resolves without treatment by 2 weeks. Most hospitals screen children for jaundice before discharge. Despite the fact that jaundice in newborns usually goes away without medical attention, at the first symptoms it is necessary to show the baby to the doctor so that the specialist can determine the cause of the yellow sclera or yellow skin and give individual recommendations. nine0003
Jaundice is common in newborns because infants' red blood cells break down faster. In addition, a newborn's liver is not fully developed, so it does not remove bilirubin from the blood as efficiently as it does in an adult. Plus - the low content of bacteria in the intestines of newborns also affects the exchange of bilirubin, increasing its content in the blood. Usually, by the end of the second week of a baby's life, his liver begins to cope with the amount of bilirubin, and the indicator returns to normal. nine0003
Plus - the low content of bacteria in the intestines of newborns also affects the exchange of bilirubin, increasing its content in the blood. Usually, by the end of the second week of a baby's life, his liver begins to cope with the amount of bilirubin, and the indicator returns to normal. nine0003
Treatment is usually only recommended if tests show a very high level of bilirubin in the child's blood. In especially high amounts, bilirubin has a neurotoxic effect - that is, it can harm the baby's brain. The extent of the damage depends on the duration of the jaundice and the degree to which the bilirubin is elevated.
Phototherapy is often used to lower the baby's bilirubin levels. Light from a special lamp falls on the skin and converts bilirubin into a form that is more easily broken down by the liver. In rare and severe cases, exchange transfusion is used: the baby's blood is removed using a catheter and replaced with blood from a suitable donor. Most babies respond well to treatment and are discharged from the hospital within a few days.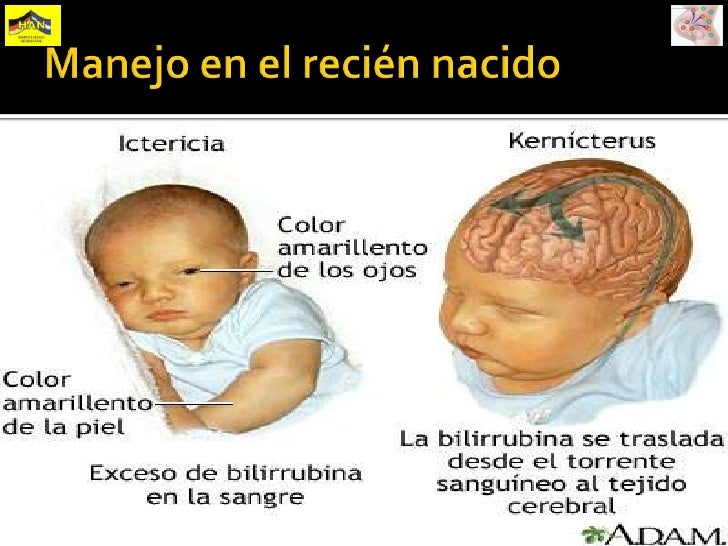 nine0003
nine0003
Jaundice in adults
Jaundice in adults is less common than in children and can occur for many reasons, including:
- Hepatitis. This is an inflammatory disease of the liver, often caused by a virus. Hepatitis can be acute (completely curable) or chronic. Other causes of hepatitis: drugs, drugs, alcohol, autoimmune diseases. Such damage to the liver eventually leads to jaundice.
- Blocked bile ducts. These thin tubes carry bile from the liver and gallbladder to the small intestine. Gallstones and tumors can block the ducts. nine0186
- Pancreatic cancer: This is the 10th most common cancer in men and 9th in women.
- Blood disorders that cause rapid breakdown of red blood cells.
Gilbert's syndrome
Separately, it is worth highlighting Gilbert's syndrome, a common hereditary disease, also known as constitutional liver dysfunction and familial non-hemolytic jaundice.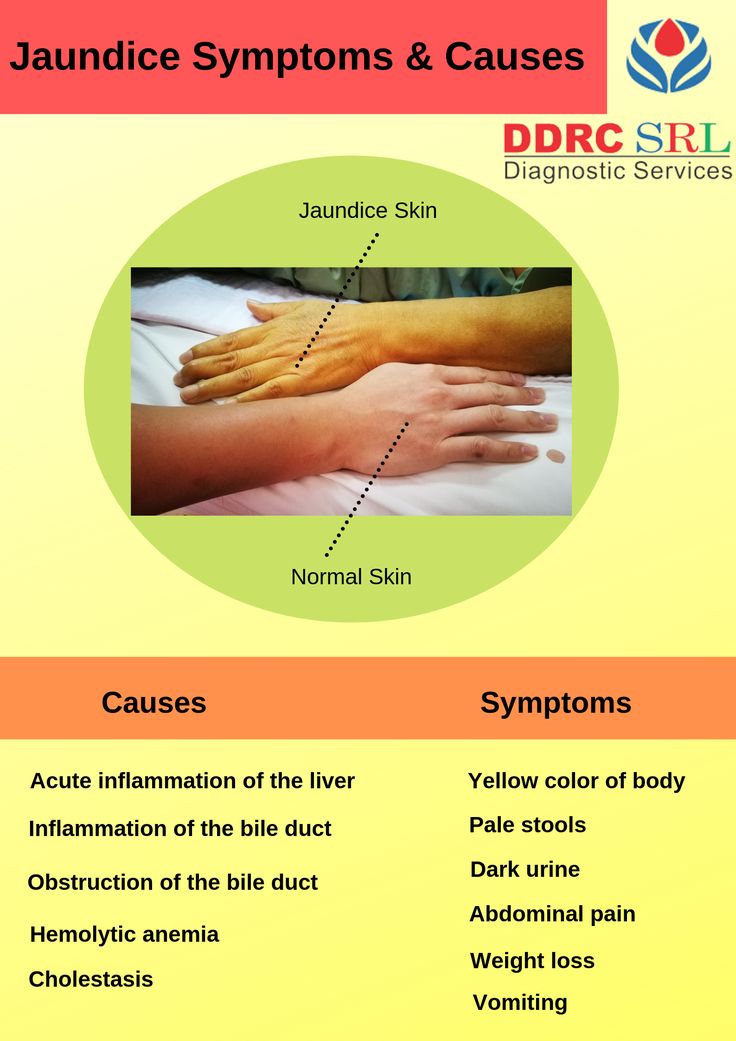 It does not require treatment, and many doctors do not consider it a disease and consider it as a variant of the norm and an individual feature. Gilbert's syndrome occurs in 1-5% of the population, depending on the region. It is associated with a defect in the gene that is responsible for the production of a liver enzyme. This enzyme binds indirect bilirubin. nine0003
It does not require treatment, and many doctors do not consider it a disease and consider it as a variant of the norm and an individual feature. Gilbert's syndrome occurs in 1-5% of the population, depending on the region. It is associated with a defect in the gene that is responsible for the production of a liver enzyme. This enzyme binds indirect bilirubin. nine0003
In a third of carriers of Gilbert's syndrome, the pathology does not manifest itself throughout life. It is often asymptomatic and is only detected by a blood test for bilirubin. However, more pronounced symptoms are also possible: pain in the right hypochondrium, metallic taste in the mouth, flatulence, vomiting, general weakness and fatigue, loss of appetite, insomnia. The symptoms are varied, and often patients with Gilbert's syndrome experience low mood, irritability, and anxiety. nine0003
There is usually no specific treatment for Gilbert's syndrome. The patient needs to limit the amount of fatty foods in the diet, adhere to a healthy lifestyle and visit a gastroenterologist - he is the one who diagnoses and treats this disease.
Diagnosis and treatment of jaundice
A preliminary diagnosis can be made already by skin color, but we repeat that jaundice is not a disease, but a syndrome. Therefore, all further diagnostics after the initial examination will be aimed at identifying the cause of the symptoms. nine0003
In case of yellowing of the skin or sclera, the following tests are required:
- complete blood count;
- urinalysis;
- biochemical blood test, including a blood test for total bilirubin and direct bilirubin;
- urinalysis for total bilirubin and direct bilirubin;
- blood for antibodies to viral hepatitis.
The next step is hardware diagnostics. Ultrasound of the liver and biliary tract is often required. An MRI or tomography may also be ordered by a doctor. nine0003
Treatment is selected individually, depending on the causes of jaundice, the condition of the internal organs and the results of the studies.