3Rd trimester pain in groin
Pregnancy: Pain in Groin and Inner Thigh – What Can I Do?
Pregnancy can be a beautiful time as you get ready to bring a new life into the world. However, many pregnancies also bring discomfort, pain, and other unwanted symptoms.
One example of an uncomfortable symptom during pregnancy is pain in the groin and inner thigh, particularly during the later months of pregnancy. This pelvic pain during pregnancy may be symphysis pubis dysfunction (SPD), which causes stiffness in the pelvic joints or uneven movements, such as when you walk.
What Causes SPD?
Symphysis pubis dysfunction happens when the ligaments responsible for keeping the pelvis aligned loosen up too much. When a ligament loosens beyond its normal range, the pelvic joint becomes unstable and can cause pain in the groin and inner thigh.
This loosening of ligaments is caused by a hormone called relaxin. Relaxin is an important hormone that is released from the placenta during pregnancy. It relaxes the wall of the uterus and prepares the uterus’ lining for pregnancy, and it also causes the cervix to dilate. Relaxin also prevents premature childbirth and regulates the mother’s and child’s health in a variety of ways.
However, during pregnancy, too much relaxin can be released into the system. When this happens, the excess of relaxin causes the ligaments responsible for stabilizing the pelvis to loosen up too much. This can cause pain in the inner thigh and groin area.
SPD Symptoms During Pregnancy
SPD can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Pain or difficulty walking
- Pain in the pubic or pelvic area
- Radiating pain that travels to the upper thighs
While some women experience SPD only when moving around too much, some feel it when doing normal daily activities. SPD pain is often felt when you perform any activity that requires weight-bearing or putting weight on one leg at a time. Examples include climbing stairs or even getting in and out of bed.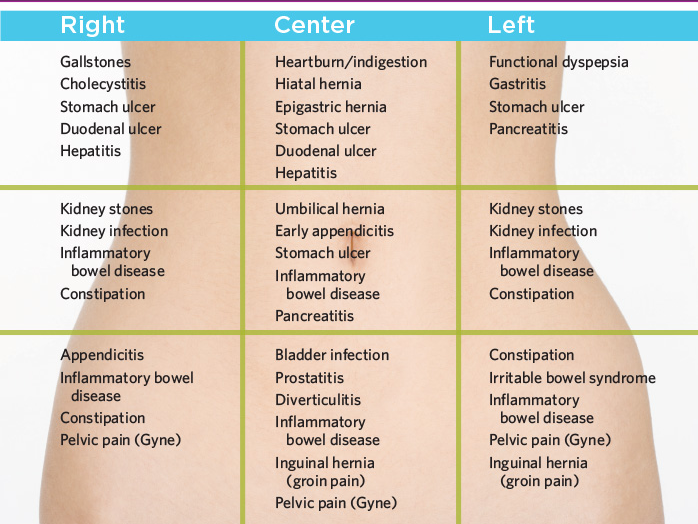
How to Deal with Pelvic Pain While Pregnant
If you experience SPD, there are a few things you can do to make your pregnancy more comfortable:
Pelvic Support Belt
Pelvic support belts help stabilize the pelvis better during pregnancy. If you experience SPD, a pelvic support belt may be able to reduce or eliminate significant SPD pain by supporting the pelvis. Talk to your OB/GYN about which pelvic support belt is right for your body.
Kegels and Pelvic Tilts
Kegels and pelvic tilts will help strengthen the pelvis’ muscles. These exercises can help stabilize the pelvis better and reduce the pain you’re feeling during your pregnancy. Talk to your OB/GYN about which types of strengthening exercises are best for you.
Rest
Sometimes, there is no better way of dealing with SPD than simply taking it easy. If you are experiencing a lot of pelvic pain, it’s time to relax.
Don’t take part in activities that will cause you pain, and make small changes to your routine to reduce the SPD pain. For example, change your clothes while sitting down instead of standing up, don’t lift heavy objects, and take the elevator or escalator instead of the stairs when possible.
For example, change your clothes while sitting down instead of standing up, don’t lift heavy objects, and take the elevator or escalator instead of the stairs when possible.
Pain Relief Medicine
Your OB/GYN may recommend pain relievers if your pain in the inner thigh and groin is severe. Talk to your doctor about your symptoms and whether pain relievers are a safe option for you and your baby.
OB/GYN Clinic in Syracuse
A supportive and knowledgeable obstetrician can help make your pregnancy a memorable, pleasant, and safe journey. If you are searching for an excellent OB/GYN center, University OB/GYN Associates is the place for you.
Our physicians have a wealth of experience dealing with a wide range of common and uncommon obstetric and gynecological issues, so you will be in safe hands. To schedule an appointment, call us at (315) 464-5162 or request an appointment online. We look forward to taking care of you.
Filed Under: Pregnancy Tagged With: groin pain, pregnancy, pregnant pain
Groin pain in pregnancy: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
Groin pain is common during pregnancy, and it often becomes more intense as the pregnancy progresses.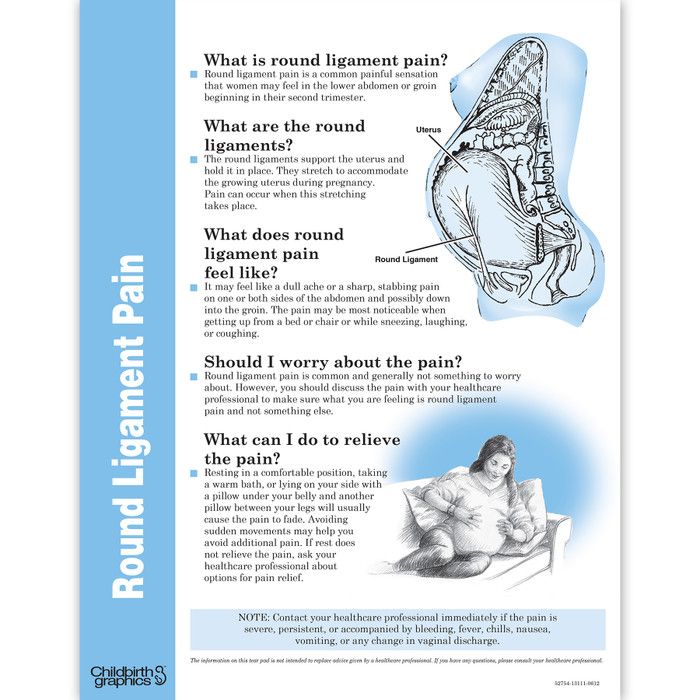 Ligament pain and vaginal issues are common causes of groin pain during pregnancy.
Ligament pain and vaginal issues are common causes of groin pain during pregnancy.
Groin pain is not an emergency, and it does not usually indicate a problem with the pregnancy. However, it is important to mention all pregnancy symptoms to a doctor or midwife.
In this article, we outline the causes of groin pain during pregnancy, along with their associated symptoms and treatments. We also provide information on when to see a doctor for this type of pain.
Share on PinterestIt is common for women to experience groin pain during pregnancy.Below are some of the most common causes of groin pain during pregnancy, alongside explanations of their associated symptoms and treatments.
Symphysis pubis dysfunction
The pubic symphysis is a joint that sits between the left and right pubic bones. During pregnancy, the ligaments and muscles that support the joint relax and stretch to accommodate the growing uterus and fetus. This relaxing and stretching causes the pubic symphysis to become unstable, resulting in symphysis pubis dysfunction (SPD).
SPD can cause the following symptoms, which tend to worsen during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy:
- clicking in the hips or pelvis
- muscle spasms or shooting pains in the pelvic area
- sharp, shooting pains in the vagina, perineum, or rectum
- electric shock-like sensations in the vagina or groin area
- pain that radiates from one part of the pelvic area to another
Many women refer to SPD as “lightning crotch” because of the strange electrical sensations they feel. The pain ranges from mild to severe and often gets worse with the following activities:
- transitioning from sitting to standing
- climbing stairs
- carrying heavy objects
Treatment
SPD is not a medical issue but a temporary pain of pregnancy. It does not indicate that there is anything wrong with the pregnant woman or the developing fetus.
For most women, the symptoms of SPD go away shortly after giving birth. In the meantime, gentle hip stretches and exercises may help alleviate the symptoms.
In the meantime, gentle hip stretches and exercises may help alleviate the symptoms.
Some women also find relief using the following treatments:
- acupuncture
- chiropractic massage
- application of heat or ice to the pubic region
Round ligament pain
Round ligaments are tough, fibrous bands of connective tissue in the pelvis that attach to and support the uterus. The growth of the uterus throughout pregnancy causes these ligaments to stretch. This stretching can trigger the following symptoms:
- pain that radiates from the groin to the hips or upper legs
- dull aches in the groin or on either side of the stomach
- spasm-like muscle pain on one or both sides of the stomach
- sharp, sudden, intensely painful aches that last for just a second
Many women notice that the pain is worse during sudden movements, such as changing positions in bed or going from standing to sitting or vice versa.
Treatment
Round ligament pain does not indicate an issue with the pregnancy, and it usually goes away shortly after a woman gives birth. In the meantime, some strategies that may help alleviate the pain include:
In the meantime, some strategies that may help alleviate the pain include:
- bending or flexing the hips before doing anything that tends to cause round ligament pain
- supporting the uterus with the hand before standing, sitting, or coughing
- changing position slowly
- applying a heat pad to the painful area
Vaginal infections
The vagina contains a delicate balance of certain yeasts and bacteria. Vaginal yeast infections occur when there is an overgrowth of yeast inside the vagina. In most cases, there is an overgrowth of a yeast called Candida albicans.
Many factors can cause an overgrowth of yeast in the vagina, including pregnancy. The hormone changes that occur during pregnancy can disrupt the normal pH levels of the vagina, causing yeasts to multiply out of control.
Women who develop a vaginal yeast infection may experience the following symptoms:
- itching and burning in the vagina and vulva
- itching and burning of the perineum or anus
- thick, white vaginal discharge that is usually odorless and resembles cottage cheese
- pain when urinating
- pain when having sex
Treatment
Antifungal medications are the usual treatment for vaginal yeast infections. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take oral antifungal medications. However, it is safe for pregnant women to apply a topical antifungal cream or insert an antifungal suppository into the vagina.
Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take oral antifungal medications. However, it is safe for pregnant women to apply a topical antifungal cream or insert an antifungal suppository into the vagina.
Women who experience the symptoms above during pregnancy should make an appointment with their doctor or midwife. Certain conditions can cause symptoms that mimic those of a vaginal yeast infection. These conditions will require different treatment.
Vaginal dryness
Some women report experiencing vaginal dryness during pregnancy. Vaginal dryness can cause the following symptoms:
- soreness, itchiness, and general discomfort in and around the vagina
- pain or discomfort during sex
- the need to urinate more often than usual
- recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Treatment
Vaginal moisturizers can help alleviate vaginal dryness. These are topical medications that a woman can apply to the inside of the vagina.
Water-based sexual lubricants should help alleviate vaginal dryness during sexual activity. However, a woman should not use estrogen-based lubricants during pregnancy.
If vaginal dryness does not get better with home treatment, a woman should talk to her doctor or midwife for further advice.
Pregnant women should discuss any and all aches and pains with their doctor or midwife.
Groin pain is a common symptom during pregnancy, and it often has a relatively benign and treatable cause. Nonetheless, a woman should see a doctor to rule out more serious underlying medical conditions. A doctor can also provide treatment to help manage the pain and any associated symptoms.
Anyone who experiences any of the following symptoms during pregnancy should see a doctor as soon as possible:
- severe pain
- worsening pain
- other aches and pains, such as pain in the upper abdomen
If the following symptoms occur during pregnancy, it is important to call a doctor immediately or go to the nearest emergency room:
- painful contractions before the 37th week of pregnancy
- bleeding from the vagina
- fever or chills
- chest pain
Groin pain during pregnancy is common. It is usually the result of normal hormonal and other bodily changes that occur throughout the pregnancy. Nonetheless, a woman should report any aches and pains to her doctor or midwife. It is important to receive the correct diagnosis and any necessary treatment.
It is usually the result of normal hormonal and other bodily changes that occur throughout the pregnancy. Nonetheless, a woman should report any aches and pains to her doctor or midwife. It is important to receive the correct diagnosis and any necessary treatment.
Vaginal yeast infections are highly treatable, and a woman can expect to make a full recovery following appropriate treatment. Vaginal dryness should also improve with home treatment. However, if either of these conditions persists, a woman should go back to her doctor for further advice.
For most women with SPD or round ligament pain, groin pain goes away shortly after giving birth. However, about 1 in 10 women with SPD experience ongoing pain that requires continued treatment. If the pain persists, a doctor may order diagnostic tests to rule out other underlying health issues, such as hip problems or hypermobility syndrome.
Pain in the pubic region during pregnancy
Subscribe to our Instagram! Useful information about pregnancy and childbirth from leading obstetricians and gynecologists in Moscow and foreign experts: https://www.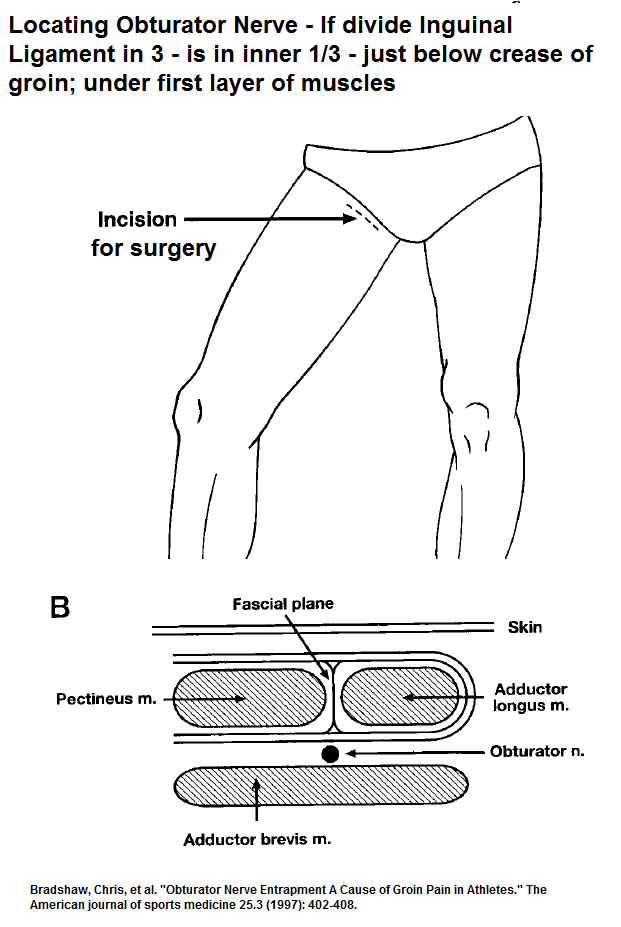 instagram.com/roddompravda/
instagram.com/roddompravda/
Tips and opinions from leading child professionals: https://www.instagram.com/emc.child/
The pubic bone is one of the three bones that make up the pelvic bone. Two pubic bones, forming the pubic articulation (symphysis), form the anterior wall of the pelvis. The pubic bone in women with a regular physique has the form of a roller about the thickness of the thumb, which is curved and forms a pubic eminence. This bone hangs in a kind of arch over the entrance to the vagina. nine0005
The main cause of pain in the pubic bone is the divergence and increased mobility of the pubic symphysis. To refer to pathological changes in the pubic symphysis of the pelvis during pregnancy and after childbirth, the following terms are used: symphysiopathy, symphysitis, arthropathy of pregnant women, divergence and rupture of the pubic symphysis, dysfunction of the pubic symphysis. The most commonly used terms are "symphysitis" or "symphysiopathy".
So, symphysiopathy is a disease associated with a pronounced softening of the pubic joint under the influence of the hormone relaxin, which is produced during pregnancy. The process of softening the interosseous joints is natural, it helps the child to pass more easily through the bone pelvis during childbirth. The diagnosis of "symphysiopathy" is made when severe pain appears, the pubic joint swells, greatly stretches, becomes mobile, and the pubic bones diverge excessively. One of the striking, characteristic symptoms of this pathology is that it is impossible to raise the leg in the prone position. In addition to acute pain in the pubis, there are difficulties when walking up the stairs, it becomes difficult to turn from side to side on the bed and get up from the sofa, and the gait changes and becomes like a "duck". According to most doctors, the cause of symphysiopathy is a lack of calcium, an increased concentration of the hormone relaxin, and increased physical activity on the bones of the pelvic region. In addition, the development of symphysiopathy can be provoked by a serious sports injury or a fracture of the pelvic bones. nine0005
In addition, the development of symphysiopathy can be provoked by a serious sports injury or a fracture of the pelvic bones. nine0005
At what stage of pregnancy do they occur?
The disease begins gradually or suddenly during pregnancy, childbirth or after childbirth. Most often, women begin to feel pain in the area of the pubic joint in the third trimester of pregnancy. This is due to the fact that the places of adhesions of the pubic bones, their ligaments and cartilage, soften under the influence of the hormone relaxin. This hormone of pregnancy naturally softens the bony joints, which is necessary to facilitate the passage of the child's bone pelvis and birth canal at the time of childbirth. nine0005
Some women begin to complain of pain in the pelvic bones some time after giving birth. This may be the result of traumatic childbirth (imposition of obstetrical forceps, shoulder dystocia, excessive separation of the hips during childbirth, etc.) or physical exertion (lifting a heavy baby stroller up the stairs, prolonged motion sickness in the arms of a well-fed baby, etc. ). It is recommended to limit physical activity, wear an orthopedic bandage, consult a traumatologist. Complaints usually recur after the next pregnancy. In a small proportion of patients, pain persists for a long time. nine0005
). It is recommended to limit physical activity, wear an orthopedic bandage, consult a traumatologist. Complaints usually recur after the next pregnancy. In a small proportion of patients, pain persists for a long time. nine0005
When can this be considered the norm, and when not?
Obstetricians-gynecologists do not consider a slight soreness of the pubic joint to be a pathology, but if the pain is acute, restricting the movements of the pregnant woman, accompanied by edema, then we can talk about pathology. Pain can be quite strong and especially manifest itself while walking, turning the body to the right and left in a sitting position and even lying down. In this case, you need to urgently consult a doctor and undergo an ultrasound diagnosis (ultrasound) to determine the size of the divergence of the pubic bones. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is also used, which allows assessing the state of the symphysis, the state of the bone tissue, as well as soft tissues. nine0005
nine0005
With ultrasound, the degree of divergence (diastasis) of the pubic bones is determined. The severity of the clinical picture largely depends on the degree of divergence of the pubic bones, and therefore there are three degrees of divergence of the pubic branches: in the first degree - by 6-9 mm, in the second - by 10-20 mm, in the third - more than 20 mm. The severity of the symptoms of the disease varies from mild discomfort to unbearable pain.
How can pain be relieved? nine0017
There are some recommendations that will help reduce bone pain during pregnancy, if the cause of its occurrence is the divergence of the pubic bones. Be sure to wear a bandage, especially in later pregnancy. The bandage takes on most of the load, thereby releasing pressure from the pubic joint. Limitation of heavy physical exertion is indicated for any manifestations of pain, lying down more often, walking less and being in a sitting position for no longer than 30-40 minutes. In severe cases, before and sometimes after childbirth, a woman may be shown strict bed rest. Moreover, the bed should not be hard and flat. nine0005
In severe cases, before and sometimes after childbirth, a woman may be shown strict bed rest. Moreover, the bed should not be hard and flat. nine0005
Since the appearance of symphysiopathy is associated not only with a large production of the hormone relaxin, but also with a lack of calcium in the body, the expectant mother is prescribed calcium preparations and complex vitamins for pregnant women, which contain all the necessary vitamins and trace elements in the right amount and proportions. There is evidence that pain is reduced during acupuncture and physiotherapy.
In especially severe cases of symphysiopathy, the pregnant woman is hospitalized. nine0005
What is the danger of this condition?
The occurrence of symphysiopathy is due to several reasons. This is a lack of calcium in the body of the future mother, and an excess amount of the hormone relaxin, and the individual structural features of the woman's body, and possible hereditary or acquired problems of the musculoskeletal system.
With an unexpressed clinical picture of the disease, with an expansion of the pubic fissure up to 10 mm, normal pelvic sizes, a small fetus, childbirth can be carried out through the birth canal, avoiding the use of physical force, such as the Christeller maneuver. With a pronounced stretching of the pubic symphysis, pain syndrome, especially with anatomical narrowing of the pelvis, a large fetus, there is a danger of rupture of the pubic symphysis, and the method of choice in this case is caesarean section. This is due to the fact that during natural delivery, the bones can disperse even more and the woman subsequently will not be able to walk at all. nine0005
Prevention
The body of a healthy woman is able to independently cope with all the difficulties of the pregnancy period. First of all, the expectant mother should include enough foods containing calcium in her diet, as well as take vitamins for pregnant women.
For the prevention of symphysiopathy, the use of a prenatal bandage is recommended, which supports the abdomen and prevents excessive stretching of the ligaments and muscles. Prophylactic antenatal bandage is usually recommended from 25 weeks of gestation, when the abdomen begins to actively grow. nine0005
Prophylactic antenatal bandage is usually recommended from 25 weeks of gestation, when the abdomen begins to actively grow. nine0005
In order to ensure the plasticity of the ligaments and muscles, as well as the flexibility of the joints, special exercises must be done even during the planning of pregnancy. Yoga gives good results.
Groin pain during pregnancy
General
The groin or groin area is the part of the lower edge of the abdominal region adjacent to the thigh. Here is the inguinal canal through which the large blood vessels of the thigh and the round ligament of the uterus pass, loops of the intestines can also descend here and form a hernia. nine0005
Causes of groin pain during pregnancy
Hernia
If you have groin pain during pregnancy on either side, always think of hernia first. A hernia can occur when local supporting tissues weaken and allow bowel loops to slip out of the abdomen and into the groin. Hernia becomes noticeable as a swelling in the groin, especially when you stand. But you can feel pain without a visible bulge.
Hernia can cause unpleasant complications. If the opening is relatively small and the intestinal loop is relatively large, then the latter may be trapped or strangulated in it. When this happens, it is called a "strangulated hernia." A strangulated hernia requires immediate surgery, as the blood supply to the strangulated intestine is disrupted, which leads to its destruction. nine0005
Infection in the pelvic region
• infections in the pelvic region:
• adnexitis;
• endometritis;
• proctitis;
• parametritis
Infections can cause swelling and tenderness of the lymph nodes in the groin.
With tumors of lymph nodes in the groin, there is a possibility of cancer or benign tumors . It may also be a manifestation of an early (primary stage) syphilis.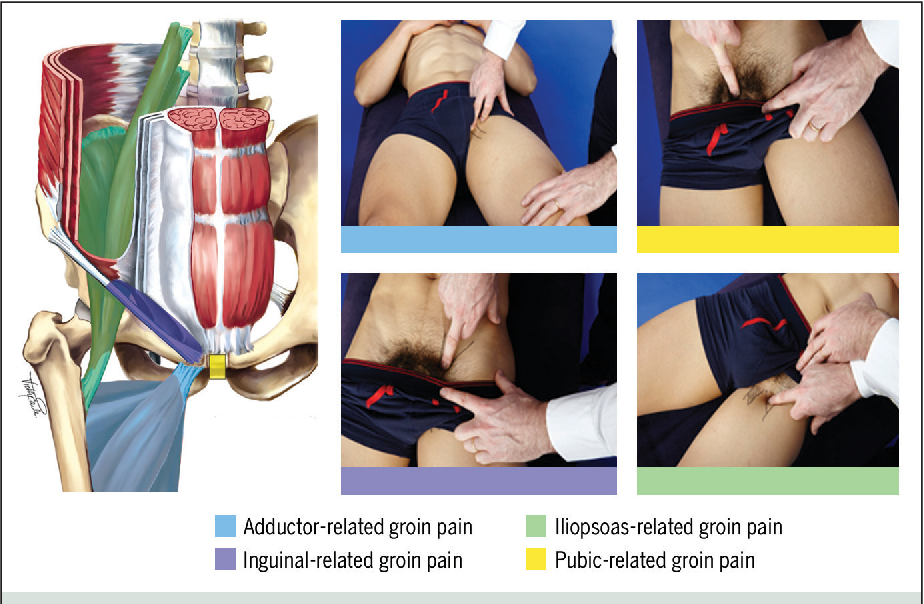
Kidney stones
A low-lying kidney stone, ureteral stone will also cause pain in the groin. An attack of renal colic occurs suddenly, can last several minutes, hours or even days. It is characterized by the following symptoms: acute pain in the lower back or hypochondrium with irradiation along the ureter to the inguinal region, bladder, external genitalia. Frequent urination and blood in the urine will help in determining the correct diagnosis. nine0005
If the pain in your groin is not associated with enlarged lymph nodes or kidney stones, then it may be due to the fact that the spinal disc is compressing the nerves that go to this area. The reason for this may be osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine.
Infections and injuries
Pain in the groin during pregnancy may indicate genitourinary infections and inflammation, which lead to enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes in the groin.