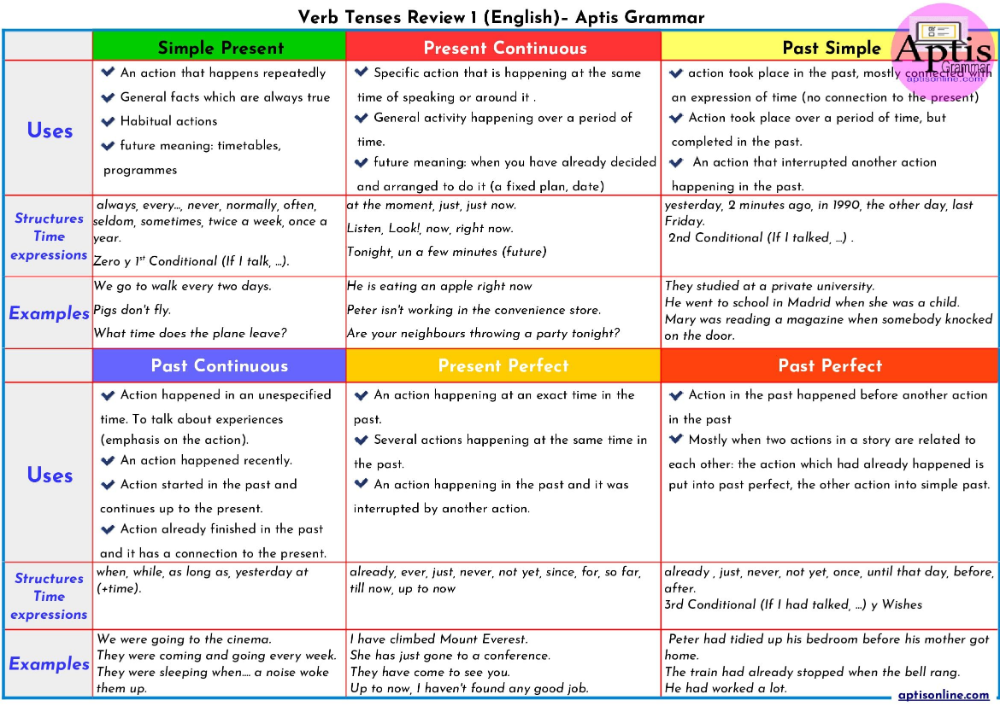
List four common discomforts of pregnancy
Common discomforts during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Common discomforts during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of contentMorning sickness
Morning sickness is a feeling of nausea or the experience of vomiting during pregnancy. Find out why some women get it and what you can do to relieve ...
Backache in pregnancy
There are several things you can do to help prevent backache from happening during your pregnancy, and to help you cope with an aching back if it does...
Bladder and bowel problems during pregnancy
During pregnancy, many women experience some rather unpleasant conditions. Maintaining a healthy diet and doing regular exercise can help make life a . ..
Changes to hair during pregnancy
Hormonal changes during pregnancy can make your hair thicker or thinner. Learn about these changes and whether you can dye hair while pregnant.
Changes to your skin during pregnancy
As your pregnancy develops, you may find that you experience changes to your skin and hair.
Dealing with fatigue during your pregnancy
Feeling tired, a bit faint and hotter than usual is quite common during pregnancy, and its all down to your hormones.
Headaches during pregnancy
Headaches are common at various stages of pregnancy. Find out what can help improve your symptoms, and when you should see your doctor.
Indigestion and heartburn in pregnancy
Indigestion (dyspepsia) and heartburn are very common during pregnancy. Find out how to recognise, treat and prevent indigestion.
Leg cramps during pregnancy
Leg cramps are a normal but sometimes uncomfortable part of your pregnancy. Find out how to treat and help prevent leg cramps.
Swelling during pregnancy
Swollen ankles and feet are very common during pregnancy. Find out how you can help relieve some of the discomfort and know whether any symptoms are s...
Vaginal discharge during pregnancy
Almost all women have more vaginal discharge in pregnancy as it helps prevent any infections travelling up from the vagina to the womb.
Vaginal thrush during pregnancy
Changes in the levels of female hormones during pregnancy increase your chances of developing thrush and make it more likely to keep coming back.
Varicose veins
Varicose veins are a common but uncomfortable part of pregnancy and usually go away without treatment. Find out here how you can ease the discomfort.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Sign in
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.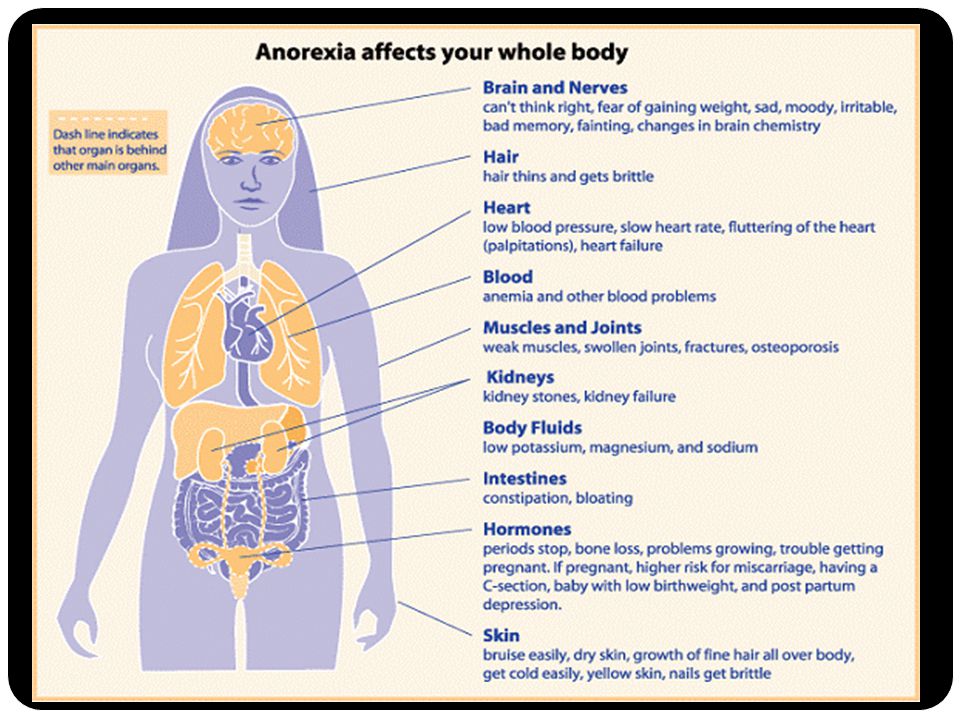
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
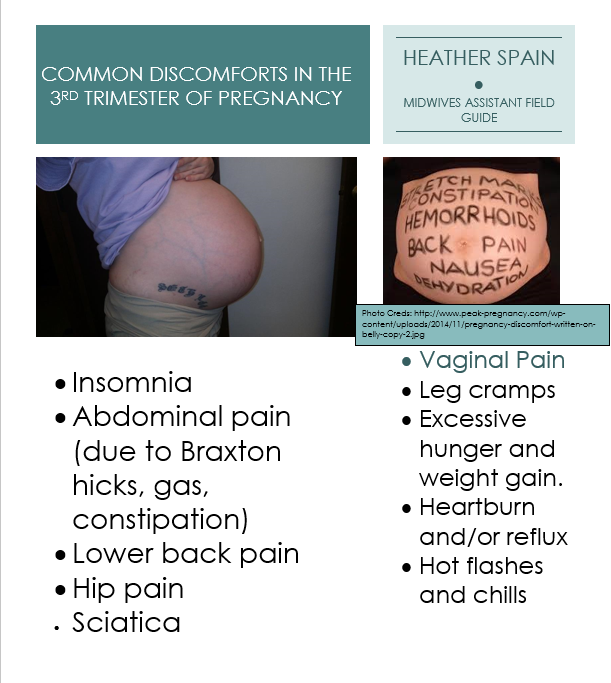
Coping With Common Discomforts of Pregnancy
Pregnancy produces many physical changes. Aside from weight and body shape, other alterations in your body chemistry and function take place. The heart works harder, your temperature registers slightly higher, body secretions increase, joints and ligaments are more flexible and hormones are altered.
Aside from weight and body shape, other alterations in your body chemistry and function take place. The heart works harder, your temperature registers slightly higher, body secretions increase, joints and ligaments are more flexible and hormones are altered.
Mood changes are common, resulting from a combination of hormonal changes and greater fatigue, as well as normal anxiety over body image, sexuality, finances, marriage roles and impending parenthood.
The following is a list of the most common discomforts of pregnancy and some guidelines for coping with them.
Nausea and Vomiting
- Eat small frequent meals. Going too long without eating during pregnancy can cause nausea or make it worse. If you experience continuous nausea, eat every one to two hours.
- Avoid greasy, high-fat foods. They are more difficult to digest.
- Consume dry starch foods, such as crackers, toast or cereal, in the morning before you get out of bed. Also, it helps if you stay in bed for 20 minutes or so after eating and get up slowly from the bed for a sudden change of position can aggravate nausea.

- Drinking carbonated beverages as well as peppermint, spearmint and chamomile teas may help.
- Eat plenty of carbohydrate-rich foods such as cereal, fruit, bread and rice. They are easy to digest and provide energy.
- Take prenatal vitamins only as directed. If they cause stomach upset, ask your practitioner if you can delay taking them for a few weeks.
- Some foods, such as milk or tea, that are soothing to one woman may be upsetting to another. However, most women find cold foods and beverages easier to tolerate than hot ones.
- Eat a high-protein snack before bed to stabilize blood sugar.
- Limit your consumption of coffee. It stimulates acid secretion, which can make the nausea worse.
- Consume liquids separately from meals, waiting about 20 to 30 minutes.
- Wear sea sickness wrist bands. These can be found at most pharmacies.
- Increase the amount of fiber in your diet, eating foods high in fiber such as fruits, raw vegetables, whole grain products, nuts and dried fruits.
 Choose a breakfast cereal that has at least 5 grams of fiber per serving. These foods help soften the stool and promote natural bowel activity.
Choose a breakfast cereal that has at least 5 grams of fiber per serving. These foods help soften the stool and promote natural bowel activity. - Drink a lot of fluids.
- Exercise, even walking, will help relieve constipation.
- Eat prunes or figs, or drink prune juice. These fruits contain a natural laxative.
- Avoid laxatives. If the problem is not resolved with the above suggestions, let your health care practitioner know. Stool softeners that are safe during pregnancy can be prescribed.
- Iron supplements can aggravate constipation — the prescription for iron can be adjusted if it becomes a problem.
Continue reading
- To help avoid hemorrhoids, prevent constipation by maintaining a diet that is high in fluids and fiber.
- Witch hazel or Tucks pads can be applied to the hemorrhoid area to relieve symptoms.
- Avoid over-the-counter laxatives. If hard stools are aggravating hemorrhoids, stool softeners can be used, but first consult your practitioner for specific suggestions.

Fatigue
This is very common during the first trimester. Get as much sleep or rest as you can — even short naps will help. Your energy level will pick up after the first three months. However, fatigue and insomnia tend to recur in the last months of pregnancy. A warm bath, massage or hot drink before bed often helps you relax and get ready to sleep.
Breast Tenderness
Breast tenderness is most pronounced during the first three months. The breasts enlarge in size and can be quite tender. Wearing a good support bra may help you feel more comfortable.
Frequent Urination
Frequent urination is another pregnancy symptom that is most pronounced during the first trimester as well as the end of pregnancy. Do not restrict fluid intake in an effort to decrease the frequency of urination. As long as you do not experience burning or pain with urination, increased frequency is normal and will go away with time.
Leg Cramps
Cramps in your calf or thigh occur most frequently at night. One remedy may be to increase your intake of calcium. Ask your provider about a calcium supplement. While in bed, stretch with your heels pointed, not your toes. This will help relieve a cramp.
One remedy may be to increase your intake of calcium. Ask your provider about a calcium supplement. While in bed, stretch with your heels pointed, not your toes. This will help relieve a cramp.
Heartburn
- Try eating smaller but more frequent meals.
- Avoid highly seasoned, rich and fatty foods.
- Do not lie down flat after eating. If you must lie down, elevate your head and shoulders with pillows.
- Carbonated beverages and milk often can help alleviate heartburn.
- Certain antacids are not recommended during pregnancy. Check with your health care provider before using over-the-counter antacid preparations.
Backache
Lower back pain is common during pregnancy. It is caused by the shift in posture necessitated by carrying extra weight in front.
- Try not to stand in one position for too long.
- An exercise called the pelvic rock will help alleviate back pain and strengthen the lower back muscles that experience the most stress.

- Elevating the feet onto a stool while sitting will help.
Dizziness
Dizziness or lightheadedness can be caused by low blood sugar or a sudden change of position. To help avoid this feeling:
- Move slowly when getting up from a sitting or lying position.
- Eat well and frequently. Women who are prone to low blood sugar should carry snacks at all times. Juices and fruit are particularly good choices.
Swelling of the Hands and Feet
Slight swelling of the hands and feet are common in the later stages of pregnancy. Adequate fluid intake is always important. Improve the circulation in your legs and feet by elevating them as often as possible. Lie on a bed or floor and raise your legs up on the wall keeping your knees bent. If you are wearing elastic hose, drain your legs this way before putting them on.
UCSF Health medical specialists have reviewed this information. It is for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace the advice of your doctor or other health care provider. We encourage you to discuss any questions or concerns you may have with your provider.
We encourage you to discuss any questions or concerns you may have with your provider.
Awards & recognition
Recommended reading
Anemia and Pregnancy
During the last half of pregnancy, your body makes more red blood cells which can cause Anemia. Learn more about causes and prevention here.
Domestic Violence and Pregnancy
Domestic violence is the most common health problem among women during pregnancy. It greatly threatens both the mother's and baby's health. Learn more here.
Eating Right Before and During Pregnancy
It is important to get the nutrients you need both before getting pregnant and during your pregnancy. Find more nutrition information including macros here.
Exercise During Pregnancy
Most women can, and should, engage in moderate exercise during pregnancy. Exercise can help you stay in shape and prepare your body for labor and delivery
FAQ: Prenatal Tests
Commonly asked questions regarding Prenatal Tests including, types available, positive screenings, diagnostic testing, health insurance coverage, and more.
HIV and Pregnancy
If you are pregnant, we recommend you be tested for the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) even if you do not think you are at risk. Learn more here.
Recognizing Premature Labor
Premature labor occurs between the 20th and 37th week of pregnancy, when uterine contractions cause the cervix to open earlier than normal. Learn more.
Sex During Pregnancy
The pregnancy may alter how a woman and her partner feel about making love, and differences in sexual need may arise. Learn more here.
Substance Use During Pregnancy
While pregnant, it is best to eat well, stay healthy and avoid ingesting anything that might be harmful to the mother's or baby's health. Learn more.
The Circumcision Decision
If you give birth to a boy, you will be asked if you'd like him circumcised. This is a matter to be considered carefully before the baby is born. Learn more.
Related clinics
Center for Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery
1500 Owens St. , Suite 380
, Suite 380
San Francisco, CA 94158
(415) 885-7788
M-F, 8 a.m. - 5 p.m.
Obstetrics & Gynecology at Mount Zion
2356 Sutter St.
San Francisco, CA 94143
(415) 885-7788
M-F, 8 a.m. - 5 p.m.
Obstetrics, Gynecology & Perinatal Specialties at Mission Bay – Fourth Street
Ron Conway Family Gateway Medical Building
1825 Fourth St., Third Floor
San Francisco, CA 94158
(415) 885-7788
M-F, 8 a.m. - 5 p.m.
Great Expectations Pregnancy Classes
Get ready for the baby! Choose from a variety of classes that prepare moms and partners for pregnancy, birth, baby care, breastfeeding and parenting.
Patient Resource
Lactation Consultant Support
Get support for all your breastfeeding needs. Troubleshoot with a lactation consultant, find equipment and supplies, join a support group and more.
Patient Resource
Women's Health Resource Center
Access free health resources here, from classes and webinars to support groups and medical referrals, plus pregnancy, birth and breastfeeding services.
Physiological changes in the body during pregnancy
From the very first days of pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes profound transformations. These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body. During pregnancy, many internal organs undergo significant restructuring. These changes are adaptive in nature, and, in most cases, are short-lived and completely disappear after childbirth. Consider the changes in the basic systems of the vital activity of a woman's body during pregnancy.
The respiratory system during pregnancy works hard. The respiratory rate increases. This is due to an increase in the need of the mother and fetus for oxygen, as well as in the limitation of the respiratory movements of the diaphragm due to an increase in the size of the uterus, which occupies a significant space of the abdominal cavity.
The mother's circulatory system during pregnancy has to pump more blood to ensure an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. In this regard, during pregnancy, the thickness and strength of the heart muscles increase, the pulse and the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute increase. In addition, the volume of circulating blood increases. In some cases, blood pressure increases. The tone of blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for increased supply of tissues with nutrients and oxygen. During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply. On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure.
In this regard, during pregnancy, the thickness and strength of the heart muscles increase, the pulse and the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute increase. In addition, the volume of circulating blood increases. In some cases, blood pressure increases. The tone of blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for increased supply of tissues with nutrients and oxygen. During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply. On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure.
And changes in the blood system. During pregnancy, blood formation increases, the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, plasma and bcc increases. BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%. Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period.
BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%. Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period.
Kidneys work hard during pregnancy. They secrete decay products of substances from the body of the mother and fetus (the waste products of the fetus pass through the placenta into the mother's blood).
Changes in the digestive system are represented by increased appetite (in most cases), cravings for salty and sour foods. In some cases, there is an aversion to certain foods or dishes that were well tolerated before the onset of pregnancy. Due to the increased tone of the vagus nerve, constipation may occur.
The most significant changes, however, occur in the genitals of pregnant women. These changes prepare the woman's reproductive system for childbirth and breastfeeding.
The uterus of a pregnant woman increases significantly in size. Its mass increases from 50 g - at the beginning of pregnancy to 1200 g - at the end of pregnancy. The volume of the uterine cavity by the end of pregnancy increases by more than 500 times! The blood supply to the uterus is greatly increased. In the walls of the uterus, the number of muscle fibers increases. The cervix is filled with thick mucus that clogs the cavity of the cervical canal. The fallopian tubes and ovaries also increase in size. In one of the ovaries, there is a "corpus luteum of pregnancy" - a place for the synthesis of hormones that support pregnancy. Walls vaginas will loosen and become more elastic. External genitalia (labia minor and major), also increase in size and become more elastic. The tissues of the perineum are loosened. In addition, there is an increase in mobility in the joints of the pelvis and a divergence of the pubic bones. The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth.
Skin in the genital area and in the midline of the abdomen usually becomes darker in color. Sometimes "stretch marks" form on the skin of the lateral parts of the abdomen, which turn into whitish stripes after childbirth.
Mammary glands increase in size, become more elastic, tense. When pressing on the nipple, colostrum (first milk) is released.
Changes in the bone skeleton and muscular system . An increase in the concentration of the hormones relaxin and progesterone in the blood contributes to the leaching of calcium from the skeletal system. This helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the bones of the pelvis and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Also, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus.
This helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the bones of the pelvis and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Also, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus.
It should be noted that calcium compounds are washed out of all bones of the maternal skeleton (including the bones of the foot and spine). As shown earlier, a woman's weight increases during pregnancy by 10 -12 kg. This additional load against the background of a decrease in bone stiffness can cause foot deformity and the development of flat feet. A shift in the center of gravity of the body of a pregnant woman due to an increase in the weight of the uterus can lead to a change in the curvature of the spine and the appearance of pain in the back and pelvic bones. Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women).
Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women).
Changes in the nervous system . In the first months of pregnancy and at the end of it, there is a decrease in the excitability of the cerebral cortex, which reaches its greatest degree by the time of the onset of childbirth. By the same period, the excitability of the receptors of the pregnant uterus increases. At the beginning of pregnancy, there is an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve, in connection with which various phenomena often occur: changes in taste and smell, nausea, increased salivation, etc.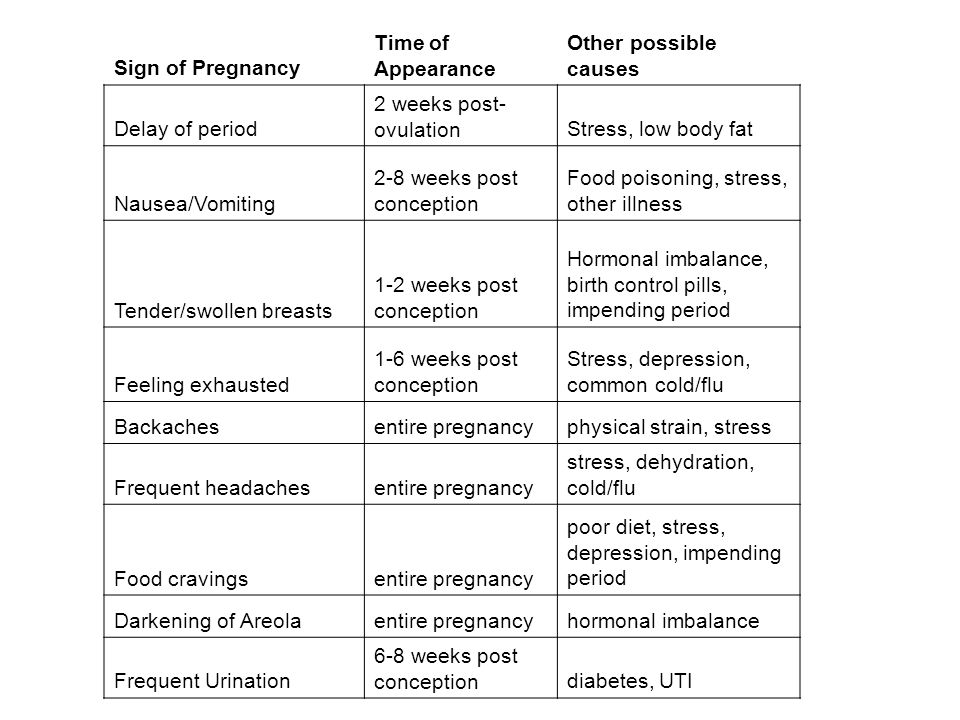
Active endocrine glands there are significant changes that contribute to the proper course of pregnancy and childbirth. Changes in body weight. By the end of pregnancy, a woman's weight increases by about 10-12 kg. This value is distributed as follows: fetus, placenta, membranes and amniotic fluid - approximately 4.0 - 4.5 kg, uterus and mammary glands -1.0 kg, blood - 1.5 kg, intercellular (tissue) fluid - 1 kg , an increase in the mass of adipose tissue of the mother's body - 4 kg.
Is it possible to treat teeth during pregnancy
Pregnant women also need dental treatment and dental check-ups. Statistics show that many expectant mothers avoid going to the dentist's office due to common myths. But this approach leads to the development of gum disease, neglected caries and other problems.
There are three reasons why a woman should take care of her teeth during pregnancy:
- Hormonal changes take place in the body. This is the cause of many diseases of the oral cavity, gums, mucous membranes, changes in microflora.

- Decreased calcium levels. This is especially pronounced in the second and third trimester. Dental health is under serious threat, enamel deteriorates, and the risk of caries increases.
- The composition and properties of saliva are changing. The ability to naturally disinfect the oral cavity is weakened. The result is an increase in the number of microbes, bad breath, and enamel destruction.
When can I see a dentist?
If you have a toothache or there are signs of other problems, the timing does not matter. In other cases, the second trimester is best. The fetus by this time is well protected from external threats.
Between weeks 14 and 20, anesthetics and x-rays can be used. The main thing is to ensure proper protection and monitor the composition of the drug, the percentage of adrenaline in it should be minimal.
We do not recommend seeing a doctor unless absolutely necessary during the first and third trimesters. In the first, anesthesia cannot be used, and in the third, visiting the dentist is difficult from a physical point of view, and stress is contraindicated for the expectant mother.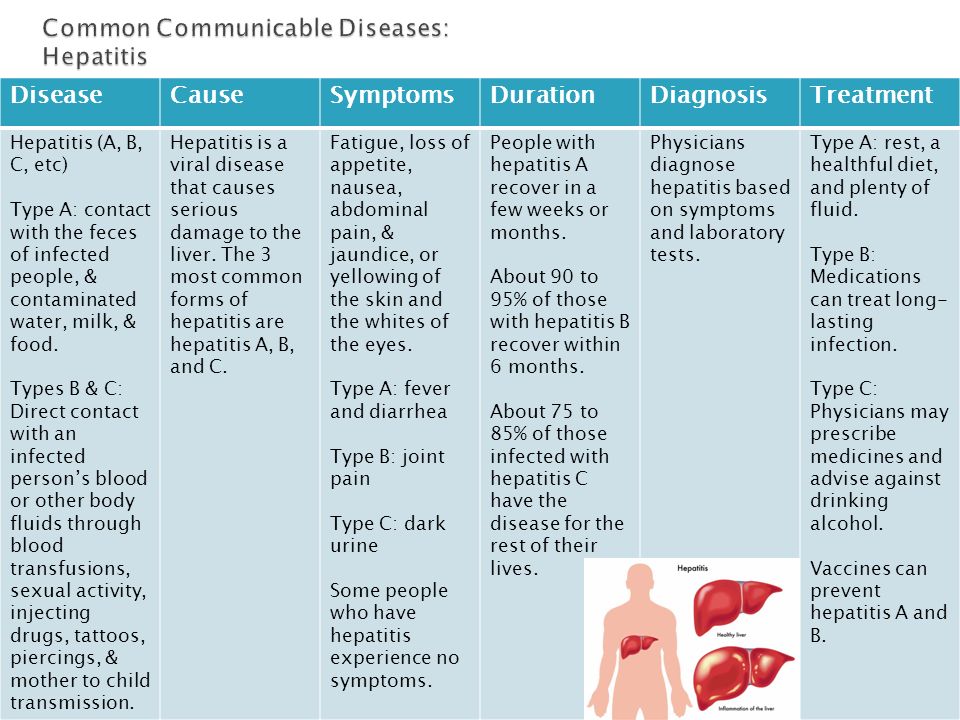
What diseases should pregnant women fight?
When you visit a dentist, tell him about your complaints, accompanying symptoms and accurately state the duration of pregnancy. In the list of the most common diseases:
- Caries. At an early stage, it is characterized by the destruction of enamel, then the tooth tissue, pulp, and nerve are affected. Arsenic should not be used during pregnancy. Many are wary of fillings, but modern formulations are completely harmless to the female body.
- Gingivitis. In pregnant women, diseases occur due to an increase in the number of microbes in the oral cavity and hormonal failure. With gingivitis, the gums swell greatly, increasing the risk of inflammation. You will need a course of treatment compiled by a doctor and correction of oral hygiene methods.
- Stomatitis. It manifests itself against the background of a weakened immune system. Small ulcers will appear in the mouth. They cause pain, swelling, so you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
 There are many drugs that can be used during pregnancy - they give quick results.
There are many drugs that can be used during pregnancy - they give quick results. - Pulpitis and periodontitis. Both of these diseases are associated with inflammatory processes. With pulpitis, inflammation is localized in the nerve, and with periodontitis - in the root tissues. Both ailments often develop if caries is not cured in time. The patient complains of severe pain, swelling of the gums and cheeks may appear. The dentist cleans and seals the canals. The problem may arise due to restrictions on the use of anesthesia and x-rays, therefore we advise you to consult a doctor at the stage of pregnancy planning or make an appointment in the second trimester, to eliminate deep caries.
- Tartar. Against the background of changes in the microflora of the mouth in a woman during pregnancy, plaque accumulates faster. Deposits become harder, tartar occurs. It leads to the appearance of an unpleasant odor, bleeding gums. The removal procedure does not require anesthesia, I simply act on the tooth with ultrasound, and then polish and grind the enamel to remove all remnants.

Pregnancy and Anesthesia
Anesthetics should be used very carefully during pregnancy. But this does not mean that expectant mothers will have to treat their teeth without anesthesia. This is a myth that dentists have been unsuccessfully trying to fight for years.
Safe preparations based on melivacaine and articaine are used. They do not constrict blood vessels, they act locally. Getting them to the fetus is excluded.
Therefore, if you have a toothache, do not listen to anyone and go to treat it. The suffering of the mother will bring much more harm to the child.
Is it possible to do x-rays for pregnant women
The procedure is allowed, but only 12-13 weeks after conception. It should be done only in emergency cases. We use digital radiography - it allows you to reduce the radiation dose by 80% compared to standard methods.
Additional methods of protecting the expectant mother are also used:
- Lead blanket.
 It covers the neck and chest, reducing the impact on unused areas of your body.
It covers the neck and chest, reducing the impact on unused areas of your body. - Use of special grade "E" film and clear definition of safe exposure.
- Maximum time reduction. It is necessary to try to keep within one procedure without repeated shots.
Treatments contraindicated for the expectant mother
There are a few manipulations that should be abandoned. These include:
- Implantation. It is associated with the healing process of the steel base under the implant. It takes a lot of body strength, possibly inflammation and rejection. Reducing the disinfecting properties of saliva also does not improve the situation.
- Deletion. This is especially true for wisdom teeth. After removal, the temperature may rise, an inflammatory process may occur. Therefore, any surgical intervention is recommended to be postponed for the period after pregnancy.
- Whitening. Studies show that some components of the drugs used can have a toxic effect on the fetus - they easily penetrate the placenta to it, overcome protective barriers.
 It does not benefit the body of the expectant mother and the effect on enamel - a decrease in the amount of calcium leads to undesirable consequences.
It does not benefit the body of the expectant mother and the effect on enamel - a decrease in the amount of calcium leads to undesirable consequences.
Why not refuse treatment?
Delaying a dental appointment can be dangerous for a child for several reasons:
- Injury to the female body. Pain can affect the child and should be carefully avoided.
- Infectious lesion. This is especially dangerous with numerous inflammatory diseases, such as pulpitis.
- Inflammation and intoxication. Accompanied by high temperature, lead to indigestion. The result is fetal hypoxia and preeclampsia.
Don't put off preventive visits
If you are expecting a baby, but you are sure about the health of your teeth, visit the dentist at least once for preventive maintenance.
In conclusion, let's give some important additional tips:
- When you are just planning a pregnancy, contact a specialist and treat caries and other concomitant diseases.