Labor started and stopped
The latent phase of labour
Tommy's PregnancyHub
This part of labour can sometimes last a long time. This page explains what the latent phase of labour is and how to get through it as comfortably as possible.
This information is for mothers who are between 37–42 weeks with a low risk pregnancy. If your pregnancy is considered high risk or you are less than 37 weeks pregnant, contact your maternity unit if you think labour has started or if there is anything you’re worried about.
What is the latent phase of labour?
The start of labour is called the latent phase. This is when your cervix becomes soft and thin as it gets ready to open up (dilate) for your baby to be born.
For this to happen, you’ll start having contractions, which may be irregular and vary in frequency, strength and length. You may get lots of regular contractions and then they may slow down or stop completely.
When you have a contraction, your womb tightens and then relaxes. For some people, contractions may feel like extreme period pains. Some women say they feel pain in their back and thighs instead of, or as well as, pain in the front of their bump.
“Before the birth of my first baby, I went for a walk with my husband and moaned all morning about a lower back ache. I didn’t realise at the time my labour was starting! Looking back, I can see it was the latent phase.”
Sharon
A ‘show’
During pregnancy, your cervix is closed and plugged with mucus, to keep out infection. But when labour starts, the mucus plug may come out. This is called your show and you may notice it in your underwear or when you wipe after going to the toilet. Some women don’t have a show.
This small, sticky, jelly-like mucus may come away in one blob or in several pieces. It’s normal to lose a small amount of blood with the mucus, but contact your hospital or midwife straight away if you’re losing more blood. Bleeding at this stage of labour may be a sign that something is wrong.
Call your midwife for advice if your mucus plug comes out before you're 37 weeks pregnant.
How long does the latent phase last?
Every woman’s labour is different, so it can be difficult to say how long the latent phase will last. It can take hours or, for some women, days. The latent phase tends to be longer in a first pregnancy.
Should I contact the midwife?
Yes. You’ll probably be offered an early assessment on the phone.
Your midwife will:
- ask how you feel (any tightness, bleeding or if your waters have broken)
- ask you about your birth plans, hopes and concerns
- ask about your baby's movements, and especially about any changes (you should continue to feel your baby move right up to the time you go into labour and during labour)
- explain what you can expect in the early stage of labour, including things that might help you manage any pain
- offer you support and pain relief, if needed
- tell you who to contact next and when
- give advice and support to your birth partner if you have one.

If all is well, your midwife will recommend that you stay at home until you’re in established labour. You're more likely to have a smoother labour and fewer interventions if you stay at home until labour is stronger and your contractions are regular.
What can I do to ease the pain?
The aim during the latent phase of labour is to stay as calm and comfortable as possible. You may find it helpful to:
- try to walk or move about
- try to rest and sleep if your labour starts at night
- drink fluids, such as water. Sports (isotonic) drinks may also help keep your energy levels up
- have small, regular snacks, such as toast, biscuits or a banana (although be aware that many women don't feel very hungry and some feel, or are, sick)
- try any relaxation and breathing exercises you've learned, perhaps in antenatal classes
- have a massage – your birth partner could help by rubbing your back
- take paracetamol according to the instructions on the packet – paracetamol is safe to take in labour
- have a warm bath or shower
- gently bounce or rock on a birthing ball
- use a TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) machine, which attaches to your back with sticky pads and sends out tiny electrical impulses to block pain signals sent from your body to your brain.
 This will make you less aware of the pain.
This will make you less aware of the pain.
There is not much evidence that aromatherapy, yoga or acupressure work to relieve pain, but you can use them if you want to. Talk to your midwife during your pregnancy if you’re interested in using these therapies.
How will I know when established labour has started?
Established labour is when your cervix has dilated to more than 4cm. At this point, you’ll start having stronger, longer and regular contractions. It’s a good idea to start recording how often your contractions happen and how long they last. This will show you when they become more regular.
Contact your midwife, maternity unit or labour ward if:
- your contractions are regular and coming about 3 times in every 10 minutes
- your waters break
- your contractions are very strong, and you feel you need pain relief – if you are in severe pain during the latent phase you can ask for an epidural
- you're worried about anything.

Your baby’s movements
You should continue to feel your baby move right up to the time you go into labour and during labour. Contact your midwife or maternity unit if you have any concerns about your baby’s movements during the latent phasesof labour.
Find out more about the stages of labour
Review dates
Reviewed: 05 June 2019
Next review: 05 June 2022
This content is currently being reviewed by our team. Updated information will be coming soon.
Back to top
Prodromal Labor: Definition, Symptoms, and More
Prodromal Labor: Definition, Symptoms, and More- Health Conditions
- Featured
- Breast Cancer
- IBD
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Articles
- Acid Reflux
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Bipolar Disorder
- Cancer
- Crohn's Disease
- Chronic Pain
- Cold & Flu
- COPD
- Depression
- Fibromyalgia
- Heart Disease
- High Cholesterol
- HIV
- Hypertension
- IPF
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Skin Disorders and Care
- STDs
- Featured
- Discover
- Wellness Topics
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Skin Care
- Sexual Health
- Women's Health
- Mental Well-Being
- Sleep
- Product Reviews
- Vitamins & Supplements
- Sleep
- Mental Health
- Nutrition
- At-Home Testing
- CBD
- Men’s Health
- Original Series
- Fresh Food Fast
- Diagnosis Diaries
- You’re Not Alone
- Present Tense
- Video Series
- Youth in Focus
- Healthy Harvest
- No More Silence
- Future of Health
- Wellness Topics
- Plan
- Health Challenges
- Mindful Eating
- Sugar Savvy
- Move Your Body
- Gut Health
- Mood Foods
- Align Your Spine
- Find Care
- Primary Care
- Mental Health
- OB-GYN
- Dermatologists
- Neurologists
- Cardiologists
- Orthopedists
- Lifestyle Quizzes
- Weight Management
- Am I Depressed? A Quiz for Teens
- Are You a Workaholic?
- How Well Do You Sleep?
- Tools & Resources
- Health News
- Find a Diet
- Find Healthy Snacks
- Drugs A-Z
- Health A-Z
- Health Challenges
- Connect
- Breast Cancer
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Psoriasis
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph. D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Becky Young on August 22, 2017
D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Becky Young on August 22, 2017
What is prodromal labor?
Prodromal labor is labor that starts and stops before fully active labor begins. It’s often called “false labor,” but this is a poor description. Medical professionals recognize that the contractions are real, but they come and go and labor may not progress.
So, prodromal labor is real in terms of contraction pain and regularity. What makes these contractions different from contractions seen in active labor is that they start and stop.
Prodromal labor contractions will often come and go at the same time each day or at regular intervals. Many mothers, even experienced ones, end up calling their birth team or going to the hospital, thinking labor has begun.
Prodromal labor is really common and can start days, weeks, or even a month or more before active labor begins. Your health care provider will want you to deliver as close to 40 weeks (your due date) as possible. Prodromal labor isn’t an indication for induction or cesarean delivery.
Prodromal labor isn’t an indication for induction or cesarean delivery.
Prodromal labor vs. Braxton-Hicks
Prodromal labor is often mistaken for Braxton-Hicks contractions, but they’re not the same thing. The majority of pregnant women will experience this type of contraction at some stage during their pregnancy. Braxton-Hicks are essentially practice contractions. They’re your body’s way of preparing for labor.
Braxton-Hicks contractions can cause a very tight, uncomfortable sensation, but they’re not typically regular or intense. They rarely last a long time or grow in intensity. Prodromal labor can follow a very regular pattern. The contractions can vary and grow in intensity.
It’s sometimes possible to ease Braxton-Hicks contractions by drinking water, eating, or relaxing. These activities won’t help ease prodromal labor contractions. Your cervix can also slowly dilate or efface during prodromal labor. This doesn’t usually happen with Braxton-Hicks contractions.
Prodromal labor vs. active labor
Prodromal labor contractions usually occur less than every five minutes and may stop for long periods. Once active labor begins, your contractions will become more and more frequent and will no longer start and stop.
The closer together your contractions are, the closer you are to meeting your baby. Real labor contractions get longer, stronger, and closer together and progress to delivery without stopping or slowing. Once labor is progressing well (usually once the mother is over 4 centimeters dilated), the labor won’t stop.
What causes prodromal labor?
There are several theories as to what causes prodromal labor, but the medical community hasn’t identified a specific cause. Most researchers seem to agree that prodromal labor is the body’s way of preparing for active labor. There are several potential contributing factors:
- The position of your baby: You may be more likely to experience prodromal labor if your baby is in breech position.
 The theory is that the uterus attempts to move the baby with contractions for a period of time and then stops if it doesn’t work.
The theory is that the uterus attempts to move the baby with contractions for a period of time and then stops if it doesn’t work. - Physical factor: An uneven pelvis or uterine abnormality may lead to these contractions.
- Feeling anxious or afraid: Apprehensive emotions either about your pregnancy or other things in your life may cause prodromal labor.
- History of previous pregnancies: This may be related to the way the uterus changes or relaxes after multiple pregnancies.
Prodromal labor isn’t usually a cause for concern and doesn’t mean that your baby is in distress. But if you do have concerns, you should always contact your healthcare provider.
Does prodromal labor mean active labor is near?
Prodromal labor can occur any time within the last month of your pregnancy. However, it doesn’t necessarily mean active labor is going to happen in the next day or even week. Labor and birth are unpredictable, so there’s really no good way to predict exactly when it will begin.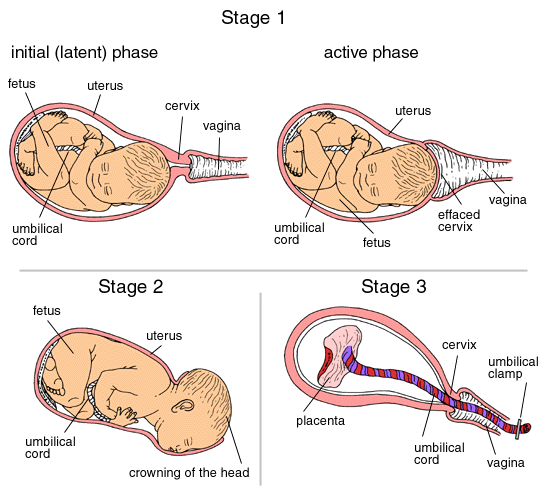 Here are some common telltale signs that may signal that baby will soon be on the way.
Here are some common telltale signs that may signal that baby will soon be on the way.
Seeking help
Whether or not you need to contact your doctor or midwife will depend on your individual situation. In general, if your pregnancy is low risk, you likely won’t need to contact your healthcare provider if you’re experiencing prodromal labor.
However, it may be difficult to tell if your contractions are a sign of active labor or prodromal labor. You should always reach out to your healthcare providers if you have concerns and to rule out other problems.
What you can do to manage this condition
If you are close to your due date, try to stay active during contractions. This could include:
- staying upright
- walking around
- using a birthing ball
- dancing
Rest during periods where contractions have ceased. Remember to stay hydrated and nourished to keep your energy levels up. Use this time to practice your coping mechanisms for getting through each contraction. Breathing and relaxation techniques can be really useful.
Breathing and relaxation techniques can be really useful.
Last medically reviewed on August 22, 2017
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- 3rd Trimester
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Angelini DJ, et al. (2013). Obstetric triage and emergency care protocols.
books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=A4f_gtPEOXcC&oi=fnd&pg=PA159&dq=prodromal+labor+pregnancy&ots=mrHcMRgTTI&sig=80ViknEOKy4VEvWp0OZr2gBaizw#v=onepage&q&f=false - Clark EAS, et al. (2015). Late preterm birth: An iatrogenic epidemic.
ajceog.us/files/ajceog0004598.pdf - True vs.
 false labor. (2016).
false labor. (2016).
my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/true-vs-false-labor
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Aug 22, 2017
Written By
Becky Young
Edited By
Nizam Khan (TechSpace)
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Rose Wilson, PhD, MSN, RN, IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Becky Young on August 22, 2017
related stories
Abnormal Labor
When to Go to the Hospital for Labor
Labor and Delivery
6 Telltale Signs of Labor
The Best Gift for New Dads Just in Time for Father's Day
Read this next
Abnormal Labor
Medically reviewed by Nicole Galan, RN
Abnormal labor is labor that slows down or stops altogether.
 Learn why abnormal labor may occur and how it’s diagnosed.
Learn why abnormal labor may occur and how it’s diagnosed.READ MORE
When to Go to the Hospital for Labor
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Is it early labor or active labor? Is it true labor or false labor? Here are the signs that will tell you when to go to the hospital for labor.
READ MORE
Labor and Delivery
Medically reviewed by Bobbie Sue Whitworth, Ph.D., MSN, RNC
Labor and delivery tends to occupy the minds of expectant parents the most. Read on if you have questions about the signs and length of labor.
READ MORE
6 Telltale Signs of Labor
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
While every pregnancy and labor is different, here are six signs that labor is on the way.
 Talk to your doctor if you experience any of the following…
Talk to your doctor if you experience any of the following…READ MORE
The Best Gift for New Dads Just in Time for Father's Day
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI
It's not usually dad who is showered with gifts when a new baby comes, but why not? He deserves appreciation too! Here are our picks of the best new…
READ MORE
11 Things to Do When You Find Out You’re Pregnant
Medically reviewed by Fernando Mariz, MD
Figuring out what to do when you find out you're pregnant can be overwhelming, but we're here to help. Here are the 11 steps to take after that…
READ MORE
What Are the Symptoms of Hyperovulation?
Hyperovulation has few symptoms, if any. It's typically diagnosed after an individual develops multiple pregnancies at once.

READ MORE
Pregnancy Friendly Recipe: Creamy White Chicken Chili with Greek Yogurt
This pregnancy-friendly spin on traditional chili is packed with the nutrients your body needs when you're expecting.
READ MORE
What You Should Know About Consuming Turmeric During Pregnancy
Consuming turmeric in pregnancy is a debated subject. We'll tell you if it's safe.
READ MORE
Pregnancy-Friendly Recipe: Herby Gruyère Frittata with Asparagus and Sweet Potatoes
Medically reviewed by Kathy W. Warwick, R.D., CDE
So easy and delicious. This frittata is high in protein and rich in essential nutrients your body needs to support a growing baby. Bonus: You can…
READ MORE
 What to do if there is spotting during childbirth? What to do if contractions stop during childbirth
What to do if there is spotting during childbirth? What to do if contractions stop during childbirth It is believed that the process of contractions is irreversible. If they began in childbirth, then it is not possible to stop or weaken them.
If we talk about external influences, then the contractions are really almost impossible to control. But for a variety of reasons, they can stop and weaken. In this article we will talk about why generic weakness develops and what to do if this happens.
Causes
During normal labor contractions increase in time and duration, strength and intensity. This is necessary to open the cervix so that the baby can leave the mother's womb. A situation in which the contractions are not strong enough or were regular, and then ended, is considered a complication of the birth process. If the contractions are slowed down, they talk about primary generic weakness. If the attempts stopped, they speak of a secondary weakness of the tribal forces.
Cessation of uterine contractions during childbirth is not normal. And the reason for this is hypotension of the smooth muscles of the uterus. Decreased uterine tone can be caused by:
- uterine hypoplasia;
- myoma;
- endometritis;
- uterine anomalies - saddle or bicornuate uterus;
- uterine tissue failure due to previous abortions or diagnostic curettage;
- cervical scarring in nulliparous women due to erosion treatment;
- high level of progesterone in the body of a woman, reduced level of oxytocin;
- hypothyroidism, obesity;
- the age of the mother under 20 years of age or over 36 years of age;
- preeclampsia.
Most often, this complication occurs in women who give birth to their first child, with a second or subsequent birth, the likelihood of developing weakness of the tribal forces is minimal, although not completely excluded.
According to statistics, up to 7% of all primiparas experience weakening of contractions or attempts, among multiparous this occurs in 1.5% of cases. Most often, contractions suddenly stop with premature birth or post-term pregnancy. At risk for sudden weakness of the birth forces are women who are carrying a large baby, several babies at the same time, since the walls of the uterus in this case are overstretched.
Stopping labor is a threat to women with polyhydramnios and those whose pelvises do not match the size of the fetal head. Too early outflow of amniotic fluid is also the cause of the development of weakness of contractions. In addition, factors such as placenta previa, fetal hypoxia, and malformations of the baby can also affect.
Quite often, doctors cannot determine the reasons for the sudden stop of contractions or their slowdown. With good analyzes and an ideal state of health, a woman may slow down labor activity for psychogenic reasons.

If the child is unwanted, if there is a strong fear of childbirth, if the woman was very nervous in the last days before childbirth, was at the epicenter of family conflicts, did not get enough sleep, did not eat well, the development of the so-called idiopathic weakness of childbirth is not excluded.
Sometimes the cause is too much pain medication, which the woman took on her own initiative, fearing pain in labor or administered at the maternity hospital, but the latter is the least likely.
Consequences
If nothing is done and a waiting policy is followed, the probability of negative consequences will increase every hour.
The baby can become infected because the uterus is already partly open. A long waterless period is dangerous with hypoxia, the death of a child. If weakness arose in the second half of childbirth, then heavy bleeding in the mother may begin, asphyxia and injuries in the baby are not excluded.
What to do?
The woman herself just needs to keep track of the duration and frequency of contractions in order to notice the lag in time. With pathological weak contractions, the rest intervals between uterine spasms are approximately 2 times longer than normal, and the contraction lags behind the norm in duration.
Everything else must be decided by doctors. First of all, they must understand how far behind the norm the opening of the cervix during primary contractions. Then a decision on further actions will be made. So, sometimes it is enough to insert a catheter into the bladder of a woman in labor or to puncture the fetal bladder with polyhydramnios, and labor activity resumes and then proceeds normally.
Amniotomy puncture
Medication sleep during childbirth
If a woman is very tired, she is exhausted, and the baby has no signs of trouble, hypoxia, then the woman in labor can be injected with sleeping pills so that she gets some sleep, after which labor activity can resume on its own.
If these measures fail, the woman may be induced into labor by giving intravenous oxytocin, which increases the contractility of the uterus. If the stimulation is useless, then the woman is given a caesarean section.
In favor of an emergency caesarean section initially, without labor induction, such signs as fetal hypoxia, a long anhydrous period, the appearance of blood discharge from the genital tract, indicating a possible early placental abruption, will speak.
How to prevent?
There is no prevention of weakness of ancestral forces. But doctors can do whatever is necessary if a woman goes to the maternity hospital in time for help.
More details about the primary and secondary weakness of labor can be found in the following video.
When you first became pregnant, nine months seemed like a very long time. But, as you know, no pregnancy can last forever, so your term is coming to an end. Everything is already ready for the birth of a new little man, and you are anxiously listening to your feelings - isn't it time to get ready for the maternity hospital?
Everything is already ready for the birth of a new little man, and you are anxiously listening to your feelings - isn't it time to get ready for the maternity hospital?
Date of birth
For any woman in labor, the doctor will certainly set the expected date of delivery. But, despite this, the real birthday of your baby may differ significantly from the planned date. The thing is, every pregnancy is different. A period of 37 and 42 weeks is considered normal. Moreover, such a pattern has been observed. If your menstrual cycle was short - 21 days, then most likely the pregnancy will end at 38-39 weeks. And in women with a long cycle (up to 36 days), pregnancy continues until 41-42 weeks.
Keep in mind that if your due date is approaching 40 weeks, and the baby is in no hurry to be born, you need to regularly visit a doctor who will monitor the baby's condition using cardiotocography, ultrasound and Doppler.
Harbingers of childbirth
Our organism is arranged extremely wisely. Gradually, step by step, your body will prepare itself for childbirth. It is only necessary to pay attention in time to some physical and psychological changes that are happening to you.
Gradually, step by step, your body will prepare itself for childbirth. It is only necessary to pay attention in time to some physical and psychological changes that are happening to you.
Braxton Hicks contractions
Appear from 30 weeks pregnancy. These are painless contractions of the uterus - at first rare and irregular. The stomach for 5-10 seconds, as it were, "hardens". Most often this happens in a horizontal position. Such contractions do not require any special treatment, so the uterus is simply preparing for the more serious work that lies ahead. Unpleasant sensations during such training bouts can be reduced if you take a warm bath (36-37 C) with sea salt. If the bath is not available, you can try breathing with your stomach - to control, put your hand on your stomach, while inhaling it should rise.
Hip bones and lower abdomen
Bones and ligaments are also prepared for childbirth. From 32-34 weeks, you notice how the area of the sacrum, womb, hips pulls, the gait becomes lax. Do not forget about stretching exercises (for example, the “butterfly” pose is suitable). Sitting on the floor, spread your legs, then bend them at the knees and place them so that the feet touch and the knees point in opposite directions. Place your palms on your knees and, with gentle pressure, try to press your knees to the floor, pulling your heels towards your perineum. Take your time. Feel the moment of extreme tension, after which the muscles will become a little softer and more pliable and allow you to bring your knees closer to the floor a couple of millimeters.
Do not forget about stretching exercises (for example, the “butterfly” pose is suitable). Sitting on the floor, spread your legs, then bend them at the knees and place them so that the feet touch and the knees point in opposite directions. Place your palms on your knees and, with gentle pressure, try to press your knees to the floor, pulling your heels towards your perineum. Take your time. Feel the moment of extreme tension, after which the muscles will become a little softer and more pliable and allow you to bring your knees closer to the floor a couple of millimeters.
Another well-known exercise is the “cat”. Standing on all fours, alternately round your back and bend it as low as possible. With the help of such simple exercises, as well as massage and a pool, you will help your bones and ligaments prepare for childbirth.
From the same period, you may also notice pulling pains in the lower abdomen similar to menstruation. A warm bath, stroking the abdomen, knee-elbow position for 5-10 minutes will again come to the rescue.
Belly dropped
Usually at term 36-38 weeks, the expectant mother notices that her breathing has become much easier. This baby tries on the head to the entrance to the small pelvis and really falls below. The pressure on the mother's diaphragm and stomach decreases, painful heartburn disappears. But as the pressure shifts to the pelvic organs, get ready to put more stress on the bladder. Therefore, you may experience the urge to urinate more often than before.
At this time, the hormonal background changes. As a result, mucous secretions increase. from the vagina and nasal cavities. A couple of weeks before childbirth, weight often decreases by 0.5-1 kg.
Nesting instinct
Certain changes occur in the psychological mood. For no reason at all, you suddenly want to clean the apartment to a shine, rearrange the furniture, or at least continuously ventilate the room - after all, you are preparing your “nest” for a little chick. If you consider that before that you felt tired and apathetic, the changes are very noticeable. Fighting the nesting instinct is useless, you just need to survive it. But be careful not to overdo it in preparing for the most important meeting.
Fighting the nesting instinct is useless, you just need to survive it. But be careful not to overdo it in preparing for the most important meeting.
Labor is approaching
Mucus plug
Mucus plug may come loose due to hormonal changes. It looks like a lump of mucus with a volume of one teaspoon to two tablespoons - transparent or with small streaks of blood, ichor, or even brown (all this is absolutely normal). The cork can move away at different times - from 1-2 weeks before childbirth or directly on the day "X". For some women, the cork comes out at one time, for others, the discharge continues for several days.
Contractions
As we remember, training contractions begin as early as the 30th week of pregnancy, gradually they become more frequent. How to determine how training (otherwise they are also called false) contractions differ from real, generic ones?
There are several clear indicators for this:
- Regularity. False contractions are irregular, true contractions gradually become stronger, longer and more frequent.
 However, sometimes in the evenings there are periods of regular contractions (for two or four hours), which then go away on their own. It is better to write down the time and duration of contractions in a special notebook - it will help you cope with the excitement, and it will be useful for the doctor to assess your condition.
However, sometimes in the evenings there are periods of regular contractions (for two or four hours), which then go away on their own. It is better to write down the time and duration of contractions in a special notebook - it will help you cope with the excitement, and it will be useful for the doctor to assess your condition.
- Duration. False contractions last 15-20 seconds, true contractions gradually become longer. If you managed to fall asleep peacefully between contractions, then they were false.
- Take a warm shower or bath. False contractions will disappear, true contractions will continue.
- During false contractions, there is no mucous discharge from the vagina, while true contractions are often accompanied by discharge mixed with blood.
- Well-known American pediatricians William and Martha Cerza offer this method. If you are in doubt whether you are in labor or not, follow the nature of the contractions for an hour. If within an hour you have six or more gradually increasing contractions lasting at least 30 seconds, then most likely you are going into the most real labor.
 Labor pains last an average of 10-12 hours for the first birth and 6-8 hours for repeated ones.
Labor pains last an average of 10-12 hours for the first birth and 6-8 hours for repeated ones.
Amniotic fluid discharge
Normally, amniotic fluid drains at the end of the first stage of labor, when the cervical dilatation reaches 7 cm or more. But sometimes it happens even earlier, sometimes even before the start of contractions. What is important to pay attention to if your water breaks?
- Colour. Normally, the water should be light and transparent, white flakes are also acceptable - this is a cheese-like lubricant. Dark, greenish-brown waters are an alarming sign of fetal hypoxia.
- Smell. Ordinary amniotic fluid is odorless. An unpleasant smell may indicate that the baby is passing meconium - the original feces.
- Quantity of water. They are usually about 1-1.5 liters. 500-700 ml - insufficient volume, often occurs with a post-term pregnancy. However, do not rush to diagnose yourself. Sometimes only the so-called anterior waters leave at first, while the fetal bladder itself may still remain intact.
 In this case, the amount of amniotic fluid can be quite small - about 200-300 ml.
In this case, the amount of amniotic fluid can be quite small - about 200-300 ml.
In any case, if your water has broken, labor should begin within 24 hours, so don't delay getting ready. After the waters break, the nature of the contractions changes, they become stronger and more painful.
Time to go to the hospital!
So, when is the time to go to the hospital?
- Within an hour you feel about 10 contractions with a break of 5-7 minutes.
- The duration of each contraction is 30-60 seconds.
- Your amniotic fluid broke - especially if it happened at one moment - the water rushed in a stream.
Serious symptoms for which you need to go to the hospital urgently:
- Unexpected bleeding (more than during normal menstruation)
- Sudden pain in the uterine region - not at all like pain during labor
- Constant dizziness .
Each woman in labor begins and proceeds differently. Some - as in a textbook, when contractions develop gradually, the intervals between them gradually decrease, others do it rapidly, their contractions are immediately painful, and the intervals between them are short. For the third, the first period, on the contrary, is delayed. Focus on your condition and constantly keep your doctor up to date.
Some - as in a textbook, when contractions develop gradually, the intervals between them gradually decrease, others do it rapidly, their contractions are immediately painful, and the intervals between them are short. For the third, the first period, on the contrary, is delayed. Focus on your condition and constantly keep your doctor up to date.
What sensations indicate the approach of childbirth
C grip before childbirth - periodic spasms of the muscles of the uterus, characterized by increasing dynamics and intensity. Understanding the mechanism of this process and its purpose will help overcome fear and act consciously during childbirth.
In the modern practice of obstetrics, childbirth begins precisely with the appearance of rhythmic uterine contractions of increasing intensity. It is important to know the difference between true contractions in order to be in the hospital in a timely manner.
As obstetricians note, the behavior and mood of the woman in labor has a noticeable effect on the course of childbirth. The right attitude gives a woman an understanding of the processes taking place in her body. Contractions are indeed one of the most difficult periods in childbirth, but they are the force that contributes to the birth of a child. Therefore, they should be taken as a natural state.
The right attitude gives a woman an understanding of the processes taking place in her body. Contractions are indeed one of the most difficult periods in childbirth, but they are the force that contributes to the birth of a child. Therefore, they should be taken as a natural state.
Training, prenatal or prenatal contractions
From the fifth month of pregnancy, expectant mothers may feel occasional tension in the abdomen. The uterus contracts for 1-2 minutes and relaxes. If at this moment you put your hand on your stomach, you can feel that it has become hard. Pregnant women often describe this condition as a "petrification" of the uterus (stone belly). These are training contractions or Braxton Hicks contractions: they can occur constantly until the end of pregnancy. Their characteristic features are irregularity, short duration, painlessness.
The nature of their appearance is associated with the process of gradual preparation of the body for childbirth, but the exact causes of occurrence have not yet been clarified. In addition, there is an opinion that “training” is provoked by increased physical and emotional activity, stress, fatigue, and they can also be a response of the muscles of the uterus to fetal movements or sexual intercourse. The frequency is individual - from once every few days to several times per hour. Some women do not feel them at all.
In addition, there is an opinion that “training” is provoked by increased physical and emotional activity, stress, fatigue, and they can also be a response of the muscles of the uterus to fetal movements or sexual intercourse. The frequency is individual - from once every few days to several times per hour. Some women do not feel them at all.
The inconvenience caused by false contractions is easily eliminated. You need to lie down or change your position. Braxton Hicks contractions do not open the cervix and do not cause any harm to the fetus, so they should be considered only as one of the natural moments of pregnancy.
Approximately from the 38th week of pregnancy, the period of precursors begins. Along with the omission of the bottom of the uterus, weight loss, an increase in the amount of discharge and other processes noticeable for a pregnant woman, it is distinguished by the appearance of precursor or false contractions.
Just like training ones, they do not open the uterus and do not threaten pregnancy, although they are more vivid in terms of the strength of sensations and may well inspire excitement in primiparous women. Precursor contractions have intervals that do not decrease over time, and the strength of the spasms that compress the uterus does not increase. A warm bath, sleep, or snack can help relieve these contractions.
Precursor contractions have intervals that do not decrease over time, and the strength of the spasms that compress the uterus does not increase. A warm bath, sleep, or snack can help relieve these contractions.
Real or labor contractions cannot be stopped by rest or change of posture. Contractions appear involuntarily, under the influence of complex hormonal processes in the body, and are not amenable to any control by the woman in labor. Their frequency and intensity is increasing. In the initial phase of labor, contractions are short, lasting about 20 seconds, and repeating every 15-20 minutes. By the time of perfect opening of the neck, the interval decreases to 2-3 minutes, and the duration of contractions increases to 60 seconds.
| Characteristic | Braxton Hicks contractions | Anticipatory contractions | True contractions |
|---|---|---|---|
| When you start to feel | From 20 weeks | From 37-39 weeks | With the onset of labor |
| Frequency | Single abbreviations. Occur sporadically. Occur sporadically. | Approximately every 20-30 minutes. The interval is not shortened. They subside over time. | Approximately once every 15-20 minutes in the first phase and once every 1-2 minutes at the end of labor. |
| Duration of contractions | Up to 1 minute | No change | 20 to 60 seconds depending on the phase of labour. |
| Soreness | Painless | Moderate, depends on individual sensitivity threshold. | Increases with the course of childbirth. The severity of pain depends on the individual threshold of sensitivity. |
| Localization of pain (feelings) | Anterior wall of uterus | Lower abdomen, ligament area. | Loin. Girdle pain in the abdomen. |
In order to make sure that real contractions start, you should correctly calculate the interval between them. As a rule, false contractions are chaotic, the interval between the first and second can be 40 minutes, between the second and third - 30 minutes, etc. While in the process of real contractions, the interval becomes stable, and the length of contractions increases.
While in the process of real contractions, the interval becomes stable, and the length of contractions increases.
Description and function of contractions
Contraction is a wave-like movement of the muscles of the uterus in the direction from the bottom to the pharynx. With each spasm, the neck softens, stretches, becomes less convex, and, thinning, gradually opens. Having reached a disclosure of 10-12 cm, it is completely smoothed out, forming a birth canal that is one with the walls of the vagina.
Visualization of the process of labor pains can help to cope with pain and uncontrollable emotions.
In each stage of childbirth, the spastic movements of the organ are aimed at achieving a certain physiological result.
- In the first period, contractions provide opening.
- In the second - along with attempts, the function of contractions is to expel the fetus from the uterine cavity and move it along the birth canal.
- In the early postpartum period, the pulsation of the uterine muscles promotes separation of the placenta and prevents bleeding.

- In the late postpartum period, spasms of the muscles of the uterus return the organ to its previous size.
After there are attempts - active contraction of the muscles of the press and diaphragm (duration 10-15 sec.). Arising reflexively, attempts contribute to the advancement of the child through the birth canal.
Phases and duration of contractions before childbirth
There are several types: latent, active and deceleration phase. Each of them differs in the duration of the period, intervals and the contractions themselves.
| Characteristic | Hidden phase | active phase | Deceleration phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase duration | 7-8 hours | 3-5 hours | 0.5-1.5 hours |
| Frequency | 15-20 minutes | Up to 2-4 minutes | 2-3 minutes |
| Contraction duration | 20 seconds | Up to 40 seconds | 60 seconds |
| Opening degree | Up to 3 cm | Up to 7 cm | 10-12 cm |
The above parameters can be considered average and applicable to the normal course of labor. The real time of contractions strongly depends on whether the woman is giving birth for the first time or is it a repeated birth, her physical and psychological readiness, the anatomical features of the body and other factors.
The real time of contractions strongly depends on whether the woman is giving birth for the first time or is it a repeated birth, her physical and psychological readiness, the anatomical features of the body and other factors.
Contractions before the first and subsequent births
However, a common factor affecting the duration of labor is the experience of the previous birth. This refers to a kind of "memory" of the body, which determines the differences in the course of certain processes. In the second and subsequent births, the birth canal opens on average 4 hours faster than in the first. This is due to the fact that in women giving birth to a second or third child, the internal and external os open at the same time. At the first birth, the opening occurs sequentially - from the inside to the outside, which increases the time of contractions.
The nature of contractions before repeated births may also differ: women in labor note their intensity and more active dynamics.
The factor smoothing out the differences between the first and subsequent births is the time interval separating them. The probability of long-term disclosure is higher if more than 8-10 years have passed since the birth of the first child.
In the articles devoted to the topics of motherhood and pregnancy, there is information that contractions before the second birth often come not before, but after the water breaks, and this happens not at 40, but at 38 weeks. Such options are not excluded, but there is no scientifically confirmed data indicating a direct connection between the serial number of childbirth and the nature of their onset.
It must be understood that the described scenarios are only options, and by no means an axiom. Each birth is very individual, and their course is a multifactorial process.
Feelings during contractions
In order to determine the onset of contractions, you should pay attention to the nature of the pain: before childbirth, they are similar to menstrual pain. Pulls the lower abdomen and lower back. There may be pressure, a feeling of fullness, heaviness. Here it is more appropriate to talk about discomfort, not pain. Soreness occurs later, with an increase in contractions. It causes the tension of the uterine ligaments and the opening of the neck.
Pulls the lower abdomen and lower back. There may be pressure, a feeling of fullness, heaviness. Here it is more appropriate to talk about discomfort, not pain. Soreness occurs later, with an increase in contractions. It causes the tension of the uterine ligaments and the opening of the neck.
The localization of sensations is quite subjective: in some women in labor, the spasm has a girdle character, its spread can be clearly associated with a wave that rolls from the bottom of the uterus or from one of the sides and covers the entire abdomen, in others the pain originates in the lumbar region, in others - directly in the uterus.
However, in the vast majority of cases, women experience the peak of spasm as a contraction, a strong contraction, a “grasp”, which follows from the very name of the contraction.
Is it possible not to notice contractions?
Not all women in labor cause unbearable pain due to tension in the muscles of the uterus. How a woman tolerates it depends on the threshold of sensitivity, emotional maturity and special preparation for childbirth. Someone endures contractions, for someone they are too painful to hold back a cry. But it is impossible not to feel contractions. If they are not, then there is no labor activity, which is an essential condition for physiological childbirth.
Someone endures contractions, for someone they are too painful to hold back a cry. But it is impossible not to feel contractions. If they are not, then there is no labor activity, which is an essential condition for physiological childbirth.
Some uncertainty in the expectations of expectant mothers can be introduced by the stories of women who have already given birth, in whom childbirth began not with contractions, but with a break in the water. It must be understood that such a scenario in obstetrics is considered a deviation. Normally, at the peak of one of the contractions, intrauterine pressure pulls and breaks the membrane of the fetal bladder, the amniotic fluid is poured out.
Spontaneous discharge of water is called premature. This situation requires the immediate intervention of a doctor; it is unacceptable to wait for contractions at home.
Mechanism of action at the onset of labor
It is important to understand what to do at home in case of onset of labor and impending labor. A few recommendations:
A few recommendations:
- First, don't panic. Lack of concentration and unconstructive emotions interfere with concentration, lead to unreasonable actions.
- Feeling the onset of contractions, you need to determine their type: are they really contractions before childbirth or harbingers. To do this, you need to use a stopwatch or special applications on your mobile phone to record the time and calculate the duration of intervals and contractions. If the frequency and duration do not increase, then there is nothing to worry about. Harbingers usually subside completely within two hours.
- If spasms become regular, the time of pauses between them is clearly defined, you can start going to the maternity hospital. Departure should be planned in such a way as to be examined by a doctor by the time when the frequency of contractions reaches 10 minutes. In the normal course of childbirth, this will happen approximately no earlier than after 7 hours. Therefore, if the contractions began at night, you should try to get at least a little rest.

- You can take a shower, do hygiene procedures.
- In case of repeated births, you should go to the hospital immediately after the contractions become regular, without waiting for the contraction of their interval.
3 Sep 1 2121
Natalia Kachanova, expert in integrative psychology (co-author Natalia Solokhina, obstetrician, perinatal psychologist):
What should I do if there is a pause or an unexpected delay in the labor itself - right during the contractions (about attempts - in the following posts)? This knowledge will save you from unnecessary medical intervention and personal panic. I hope you represent the phases of labor. As you know, when you know the route, it is easier to get to your destination. You remember the harbingers of childbirth and will be able to distinguish most of them. You understand the essence of contractions and attempts, you are familiar (at least theoretically) with the difference between them.
However, some women have a question: what to do if something goes wrong during childbirth? I can assure you that the attempts will definitely not change places with contractions. And the child will not jump out of you without warning of the harbingers. Those. the order of the process does not change.
But as you remember, is a delicate process , and it is quite easy to bring it down in modern conditions (and in ordinary maternity hospitals, everything contributes to this). It all started and suddenly ... stopped!!!
Therefore, the anxiety of the woman in labor is somewhat justified. And in order to save you from it, we will tell you how to start the process if it has stopped (for some external or internal reasons). And run it can NATURALLY, without resorting to medicines and medical interventions. (We are talking about healthy women with favorable pregnancies, not pathology - it definitely needs to be dealt with by doctors).
Start of labor. Let's say your cork has come off, or water is leaking, or contractions have begun (irhythmic or regular, it doesn't matter). Or all these signs knocked on your door in a friendly company. Meet them as dear guests of and - rejoice!
Let's say your cork has come off, or water is leaking, or contractions have begun (irhythmic or regular, it doesn't matter). Or all these signs knocked on your door in a friendly company. Meet them as dear guests of and - rejoice!
Why? Because joy helps release oxytocin (and many other hormones that make up a natural pain-killing natural cocktail). But fear reliably closes the door for them (and for a woman - the cervix).
It is very useful to know the reasons why contractions stop:
1 THE REASON for stopping contractions is MENTAL CONTROL
Our brain produces a hormonal cocktail for successful childbirth. But not the whole BRAIN, namely its ancient (primitive) part. Along with it, there is a new - neokora - the dignity of a highly developed modern man. The Secret of Successful Births is simple: the more active the ancient part of the brain, the easier everything will go.
You can become a little primitive, plunge into the depths of unconscious bodily impulses, open up to the animal nature - give birth like a cat (easily and painlessly), and if you are lucky, you will also experience a couple of revelations or just experience a powerful orgasm.
But then a woman begins to be clever, speak, manage, control - the activity of the neocortex increases, and the impulses of the primitive brain decrease. And already looming on the horizon are long, protracted labors, oxytocin stimulation, then epidural anesthesia, forceps, and even a caesarean at the exit! … Dear ones! I am one of the smart and educated women, I have enough regalia to maintain my status, but during childbirth I am just a giving birth female who periodically falls into divine ecstasy, buzzes, sings, makes unusual sounds, takes strange postures and “does not taking a steam bath”, how it looks from the outside… (Natalya Kachanova)
Therefore, and you relax! Get out of your head the multiplication table, reasoning about quantum physics and an attempt to remember notes with the stages of childbirth.
There is nothing, there is only your body and what happens to it - new unusual sensations into which you plunge headlong. Experienced midwives rejoice at this state of the woman in labor and do not try to bring her back to consciousness. Believe me, you are here and now, you don’t talk about it from the outside, and live every moment 100%.
Believe me, you are here and now, you don’t talk about it from the outside, and live every moment 100%.
Yes, if you rush to the maternity hospital at the very first contractions, then after answering the questions in the questionnaire during the paperwork, the contractions may subside. They make you remember everything (from the beginning of your period to the birth of your grandmother) - i.e. turn on logical connections and turn off the primitive brain!
Here is an excerpt from the mother's letter:
“I arrived happy. I am finally giving birth! Regular contractions, already sensitive. To arrange me for my sister. And she just filled up with questions: something about the birth of my mother, grandmother. How do I know? A bunch of unnecessary details. I collected brains in a heap - answered. And as the "interrogation" ended, the contractions stopped. It is clear that they provoked the whole process, from which the memories are terrible ... "
It is good if the midwife or assistant who accompanies you can answer these questions. But if the registry torture is still a success (or they could have scared at the same time), then you should not be upset. Ways to activate contractions ahead (read the next post).
But if the registry torture is still a success (or they could have scared at the same time), then you should not be upset. Ways to activate contractions ahead (read the next post).
GOOD ADVICE: when registering at the maternity hospital, be a “fool”, say that you don’t understand anything. And let the husband take care of all the formalities. You have ahead - childbirth and MEETING WITH THE BABY.
So let it be a naturally intensive process with a happy outcome and pleasant memories!
2 THE REASON for stopping contractions is FEAR
Suppose you are prepared for childbirth and are not afraid. But the appearance of fear can be provoked from outside.
- For example, when my contractions during my first birth were in full swing (not yet peaking, but increasing), and my husband and I were laughing, I laughed at any object in the room, and he laughed at me, our midwife asked me about my feelings and recommended look at the cervix.
I got scared. How was she to know that since my youth I have been tense with gynecological examinations! I spread my legs, and the vagina tensed to stone. So they didn't examine me. And… the contractions subsided. Of course, movements, water, breathing - all this “launched” the further process, but I learned the lesson. It was an IMPORTANT EXPERIENCE for me: no one dares to interfere with my process when it is in full swing. I can ask for help if I feel something is wrong. But until then, let it be as it is.
The process of childbirth is individual, unpredictable, and requires SUPER efforts from the Mother. Therefore, is worth preparing to him not only the body, but also the mind.
With setting you have the possibility to:
- fix on the subconscious level the POSITIVE course of childbirth,
- dissolve your fears,
- tune in to a successful outcome,
- “live through” the stages of the birth process in advance and know how to behave in each of them
Remember the MOST IMPORTANT thing: if the birth process has begun, your body is ready to give birth, your child is ready to be born, it remains to stop the mental fuss and join the process.

3rd REASON for stopping contractions - LACK OF SLEEP
Lack of sleep disturbs the balance in the cells that make up muscle fibers. In the process of muscle contraction, potassium, sodium, calcium are involved. This is not a reason to run for vitamins! Let's not load ourselves with chemistry. I explain in a simple way (primitive for a biochemist, but understandable for a pregnant woman): childbirth begins, oxytocin is released. The uterus is shrinking. And the uterus is a muscle that spends a lot of calcium during intensive work.
In a normal state, it is enough, but if you didn’t get enough sleep, for example, the contractions started in the evening, you have to work all day, then you will feel an imbalance of sodium, potassium and calcium in the muscle tissue very soon. As a result, the uterus ceases to be sensitive to oxytocin.
If you are in a maternity hospital, the doctors state a weak labor activity and inject additional oxytocin. This leads to painful contractions with no natural breaks in between. It hurts and it's useless! And what you need? Just send you sleep for 2-3 hours. Or whatever you need. They measured that everything is in order with the baby, the heart is beating - and good luck. By the way, it's easier to do it at home. I went and slept.
This leads to painful contractions with no natural breaks in between. It hurts and it's useless! And what you need? Just send you sleep for 2-3 hours. Or whatever you need. They measured that everything is in order with the baby, the heart is beating - and good luck. By the way, it's easier to do it at home. I went and slept.
The secret is that the cellular balance of potassium, sodium and calcium is restored during sleep. And when you have rested (and the contractions are weak at this moment, they don’t bother you much), labor activity resumes. But not at the beginning, but from the level at which it ended. And now you are cheerfully ready to give birth to your wonderful baby!
false or real / “Waiting for a baby”
February
Shortly before the birth, the expectant mother may be disturbed by training contractions, rhythmic contractions of the uterus, which quickly pass and appear occasionally. How to distinguish them from real contractions, and why they are needed, we will try to find out.
How to distinguish them from real contractions, and why they are needed, we will try to find out.
For the first time, the phenomenon of temporary contractions was described by the English doctor John Braxton Hicks. That is why they are called - Braxton Hicks contractions or false, training contractions, precursor contractions. In his scientific work of 1872, he argued that these contractions are short-term (from half a minute to 2 minutes) contractions of the muscles of the uterus, which are felt by a pregnant woman as an increase in the tone of the uterus. They appear after the 20th week of pregnancy. And during the day they happen often, but the expectant mother in the daytime may not even notice them. However, as time goes on, they intensify, becoming more and more obvious.
WHAT DO YOU NEED FALSE BROUGHT
The uterus is a muscular organ. And like any muscle that has to perform the work allotted to it in the body, it needs training. After all, if she hangs for all forty weeks like a bag, she will not cope with the load in childbirth. Thus, the purpose of training or false contractions is to prepare the uterus and cervix for childbirth. That is why one of the names of training bouts is contractions harbingers - harbingers of an approaching birth.
Thus, the purpose of training or false contractions is to prepare the uterus and cervix for childbirth. That is why one of the names of training bouts is contractions harbingers - harbingers of an approaching birth.
ARE FALSE PARTS PAINFUL?
As a rule, false contractions are painless, but with increasing duration they become more noticeable and bring more discomfort. However, in all women, they manifest themselves in different ways, someone does not feel them at all, and someone does not sleep at night, tossing and turning and trying to find a comfortable position for sleeping. It all depends on the pain threshold. The main thing in this situation is to stop being nervous about this and calm yourself with the thought that such training is necessary for the most important upcoming event - the birth of your crumbs. And to calm down a little and sleep better, ask your doctor to prescribe a sedative for you and get a special pillow for expectant and nursing mothers. With her, falling asleep and experiencing the discomfort of the last weeks of pregnancy will be much easier!
With her, falling asleep and experiencing the discomfort of the last weeks of pregnancy will be much easier!
HOW TO LIVE WITH FREQUENT PARTS
Some expectant mothers complain that their Braxton Hicks contractions are frequent and cause significant discomfort, even when they are doing housework or other light physical activity. In such a situation, obstetricians are advised to lie down or vice versa, take an easy walk, in any case, change the type of activity. If training contractions bother you a lot, it is recommended to drink a glass of water, juice or herbal tea, calm down and get some rest. Ask someone close to give you a massage. Lie in silence. And to also benefit from training fights, try doing breathing exercises: practice breathing techniques in childbirth in practice.
HOW TO DIFFERENTIATE TRAINING FROM LIVING
The most important thing to understand is that real contractions are much more painful than Braxton Hicks contractions. You will understand it right away. In addition, the contractions that bring you closer to childbirth are more regular. The contractions begin in the lower back, spread to the front of the abdomen, and occur every 10 minutes (or more than 5 contractions per hour). Then they occur with an interval of about 30-70 seconds and over time the intervals between them are reduced. Some women describe the sensations of labor pains as severe menstrual cramps, or sensations during diarrhea, when the pain rolls in waves in the abdomen. These contractions, unlike false ones, continue even after a change in position and when walking, constantly intensifying. As soon as you feel all these symptoms, call your ob-gyn - hour X has arrived. If in doubt, also do not be afraid to disturb the doctor. The doctor will ask you a few questions that will help him determine the type of contractions and eliminate all your doubts and worries. After all, it is always better to consult a doctor and trust his professional experience.
You will understand it right away. In addition, the contractions that bring you closer to childbirth are more regular. The contractions begin in the lower back, spread to the front of the abdomen, and occur every 10 minutes (or more than 5 contractions per hour). Then they occur with an interval of about 30-70 seconds and over time the intervals between them are reduced. Some women describe the sensations of labor pains as severe menstrual cramps, or sensations during diarrhea, when the pain rolls in waves in the abdomen. These contractions, unlike false ones, continue even after a change in position and when walking, constantly intensifying. As soon as you feel all these symptoms, call your ob-gyn - hour X has arrived. If in doubt, also do not be afraid to disturb the doctor. The doctor will ask you a few questions that will help him determine the type of contractions and eliminate all your doubts and worries. After all, it is always better to consult a doctor and trust his professional experience.
You should seek help if:
• you have more than four contractions an hour and they happen regularly
• contractions are accompanied by pain in the lower spine
• contractions are accompanied by watery or bloody vaginal discharge
• the contractions are so strong that it is very difficult for you to endure them
• there is a marked change in the child's movement, or less than 10 movements every 2 hours
• you think your waters have started to break
Alla Misyutina, Consultant Physician, Independent Laboratory INVITRO
Dear women, during labor, the body needs a lot of oxygen, so proper breathing is very important. A large influx of oxygen into the blood of mother and baby alleviates the condition of the crumbs, which during childbirth experiences oxygen starvation. Special breathing techniques help to properly open the birth canal and make contractions and attempts as effective as possible.
Different types of breathing should be used at different stages of labor.
• During "false" contractions, breathing should be deep and slow. During the period when the contractions become more intense, it is necessary to use "pain-relieving breathing". This breathing is slow, deep, the inhalation is done through the nose, it should be longer than the exhalation through the mouth. More details: inhale is done at the expense of 1-2-3-4, and exhale - at the expense of 1-2-3-4-5-6. With the help of such breathing: mom relaxes, distracts from pain, focuses on the score; the baby receives as much as possible, so he needs oxygen.
• In breaks from contractions, you need to rest and breathe evenly without any effort, so that you can then easily follow the doctor's recommendations.
• During attempts, you need to exhale all the air from the lungs, then take a deep breath and push for up to 6-9 seconds. Quickly exhale all the air, quickly take a deep breath and again hold your breath for 6-9 seconds, and so on - about three times per attempt.
• In breaks from attempts to rest and breathe deeply, evenly and relaxed.
• It is very important to only push on the perineum and never push on the head. In this case, all efforts are wasted and will appear in the form of burst vessels in the eyes and on the face.
• In the period after the birth of the head, it is necessary to stop pushing and breathing shallowly, some call this breathing “dog-like”, deep breathing can harm both mom and baby. Then everything goes on as usual, the main thing is to obey the doctor.
• After the baby was born, within half an hour the last stage of labor begins - the birth of the placenta. Special breathing is no longer required, at the doctor's command, push a little into the perineum and EVERYTHING! Dear women, pain during childbirth is good, it means that your baby will be born soon. There is no need to resist the pain, this is a mistake that brings a woman and a child nothing but fatigue. On the contrary, it is necessary to concentrate and help in every possible way to give birth to a healthy baby.
BIRTH AGAIN
So, you have decided that this is no longer a “teaching”, but the beginning of childbirth. In addition to contractions, the onset of labor can be indicated by the outflow of amniotic fluid and the passage of a mucous plug that closes the lumen of the cervix. The mucous plug can also come off 2-3 days before delivery. However, her departure does not always mean that it is time to go to the hospital. During pregnancy, the cervix is tightly closed. With the onset of labor pains, its opening begins: the cervix of the uterus gradually expands to 10-12 cm in diameter (full disclosure). The birth canal is preparing to "release" the child from the womb. Intrauterine pressure increases during contractions as the uterus shrinks. And in the end, this leads to rupture of the fetal bladder and the outflow of part of the amniotic fluid.
The first, preparatory, period of labor for women giving birth for the first time takes an average of 12 hours, and 2-4 hours less for those who have second births. At the beginning of the second stage of labor, contractions join the contractions - contractions of the muscles of the abdominal wall and diaphragm. In addition to the fact that different muscle groups are involved in contractions and attempts, they have one more important difference: contractions are an involuntary and uncontrollable phenomenon, neither their strength nor frequency depend on the woman in labor, while attempts to a certain extent obey her will , it can delay or strengthen them. Therefore, at this stage of childbirth, a lot depends on the expectant mother and her ability to quickly and correctly follow the commands of the obstetrician taking delivery. And most importantly - to tune in correctly and not allow panic and thoughts about something bad. Obstetricians and gynecologists recommend that mothers perceive childbirth as a holiday, a baby's birthday. Then it will be easier to concentrate on the fact that now your main task is to help the baby be born. If, during childbirth, the expectant mother panics, the concentration of adrenaline in her blood will increase significantly.