Itchy toes during pregnancy
Why Itchy Feet Are a Thing During Pregnancy & How to Get Relief
While not the most talked-about pregnancy woe (swollen feet and back pain, anyone?) itching, also known as pruritus, is a very common complaint. Some women experience itching all over, while others feel it specifically on certain body parts such as their hands, feet, belly, or chest.
Most itching is just downright annoying, but severe itching can lead to loss of sleep or even be a sign of a very serious medical problem. We’ll talk about what could be causing your itchy feet, some treatments you can try, and when to call your doctor.
Hormonal skin changes
Your hormones are going crazy (as you’ve probably already noticed), and all that extra action from your endocrine system can cause your skin to get irritated.
Plus, your immune system works differently while you’re pregnant — it temporarily increases or suppresses certain functions so that your baby can grow in the best way possible.
The combination of hormones and immune system changes can lead to some pregnancy-specific skin conditions that may cause itchy feet.
You may notice:
- small, itchy bumps that resemble bug bites (prurigo)
- rash-like, itchy hives (PUPP)
- red, scaly, itchy patches (eczema or AEP)
The good news is that these skin conditions will not harm your baby and should go away after you deliver.
Nerve sensitivity
Again thanks to our good friends, the hormones, some pregnant women find that their nerves just seem more sensitive during pregnancy.
So seemingly “normal” things like sweating, being warm, wearing tight clothing, chafing, wearing the wrong shoes, or just lying in your bed can make your feet itchy.
Stretching
Not the kind of stretching you do in your prenatal yoga class — we’re talking about stretching of the skin. Your body goes through some amazing changes to house that rapidly growing baby, and stretching the skin, on your abdomen, thighs, buttocks, and breasts, is one of them.
Depending on your genes, hormones, and rate of weight gain you may be more or less prone to developing stretch marks (striae gravidarum). Stretch marks can be a source of itching.
Stretch marks can be a source of itching.
While your feet are unlikely to develop stretch marks, they do bear extra weight during pregnancy and the ligaments undergo some stretching of their own that can lead to an itching sensation.
Psoriasis
If you experienced psoriasis prior to pregnancy, you might get a welcome break from symptoms while you are pregnant. But, some women continue to experience painful, itchy plaques even during pregnancy, which can occur on your feet.
Cholestasis
Now for the rare, but serious, reason for itchy feet during pregnancy: intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. This is a liver condition that, if it occurs, usually shows up during the third trimester.
Normally, your liver helps send bile to your digestive tract, where it aids in breaking down dietary fat.
Hormonal and digestive changes, as well as possible genetic predisposition, can cause the liver to not work like it should, which allows bile acids to build up in your body. This buildup of bile can cause some intense itching, particularly on your hands and feet.
This buildup of bile can cause some intense itching, particularly on your hands and feet.
Cholestasis can be dangerous for your baby. It can increase the risk of premature birth, fetal distress, and even stillbirth.
Call your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms
- severe itching
- increase in itching
- itching that gets worse at night
- yellowish tinge to your skin or eyes (jaundice)
- dark urine
- pale or grey bowel movements
- right-sided upper abdominal pain
- nausea or upset stomach
For typical causes of itchy feet during pregnancy, there are several remedies you can try to get some relief and much-needed rest. These include:
- Soothing oatmeal baths. This natural and effective remedy is simple to try at home — and what pregnant mama doesn’t need a nice soak in the tub? Do check with your doctor before you add essential oils to your soak, as some are not safe for pregnancy or can further irritate your skin.

- Cold. Cool footbaths, cold washcloths, or even ice packs wrapped in towels can be applied to your feet to help soothe itchy skin. Don’t apply ice for more than 15 minutes.
- New socks. Loose-fitting socks made of natural, breathable fibers (such as cotton or even wool) can help keep feet from becoming sweaty and itchy.
- Massage. A foot massage — performed by you, your partner, or any willing pal — may help distract your nerves and decrease itchiness. Just be sure to stroke gently and avoid acupressure points on your feet and around your ankles, as some spots may stimulate uterine contractions. (Talk to your OB-GYN if you have any questions about this, especially if you’re far from your due date.)
- Moisturizers. A simple, unscented moisturizer such as cocoa butter, shea butter, or colloidal oatmeal can help soothe itchy feet. Check with your doctor before using any kind of topical medications, such as calamine lotion or lotion with diphenhydramine (Benadryl), as some may not be safe during pregnancy.

- Medications. If your itchy feet are caused by eczema or psoriasis, check with your doctor before using medications, even if they are over the counter. Many of these meds are not safe to use during pregnancy, and your doctor can help find safer alternatives. One preferred treatment for psoriasis during pregnancy is ultraviolet B phototherapy. If your itchy feet are keeping you from sleeping, in spite of trying at-home remedies, your doctor may be able to recommend a mild sleep aid to help you rest in spite of the discomfort.
If you think you have any symptoms of cholestasis, call your doctor right away. They may want to do blood tests to check your liver function, as well as an ultrasound called a biophysical profile to check on your baby’s movement, breathing, heartbeat, blood flow, and fluid levels.
If you do have cholestasis, your doctor will monitor you and your baby more frequently. Some possible treatments and tests include:
- nonstress test and biophysical profile
- blood work to check your liver function
- soaking itchy areas in cool or lukewarm water
- medication, such as ursodiol, to help decrease bile accumulation
- early delivery of your baby
While it may sound scary to deliver your baby earlier than you expected, your doctor will carefully weigh the risks of both early delivery and continuing your pregnancy with cholestasis.
The risks of cholestasis can be high, so it is often safer to deliver your baby, especially if you are at least 37 weeks pregnant. Babies delivered at this time typically do amazingly well, and you get to snuggle your bundle a little sooner!
Pregnancy is a wonderful, bumpy (pun intended) ride. In addition to all of the excitement and anticipation, there may be some less-than-glamorous side effects along the way. One of these may be itchy feet.
Itchy feet can be caused by a variety of hormonal and immunological changes that are normal during pregnancy. There are options to relieve your discomfort at home, such as oatmeal baths, cold packs, and moisturizers. If these aren’t effective, your doctor may be able to help.
In rare cases, itchy feet can be a sign of a serious medical problem. It’s important to call a doctor if you’re concerned about any of your symptoms so that they can help keep you and your baby safe. They will be able to monitor your baby, as well as recommend medication or delivery if needed.
Itching and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
Itching is common in pregnancy. Usually it's thought to be caused by raised levels of certain chemicals in the blood, such as hormones.
Later, as your bump grows, the skin of your tummy (abdomen) is stretched and this may also feel itchy.
However, itching can be a symptom of a liver condition called intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP), also known as obstetric cholestasis (OC).
ICP needs medical attention. It affects 1 in 140 pregnant women in the UK.
Symptoms of ICP
The main symptom is itching, usually without a rash. For many women with ICP, the itching is often:
- more noticeable on the hands and feet, but can be all over the body
- worse at night
Other symptoms can include:
- dark urine
- pale poo
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), but this is less common
Symptoms of ICP typically start from around 30 weeks of pregnancy, but it's possible to develop the condition as early as 8 weeks.
Non-urgent advice: Call your midwife or GP if you have itching that's:
- mild or distressing, possibly worse at night
- anywhere on your body, but may be worse on the palms of your hands and soles of your feet
Feeling itchy like this can be a sign of ICP and needs to be checked.
Mild itching
Wearing loose clothes may help prevent itching, as your clothes are less likely to rub against your skin and cause irritation.
You may also want to avoid synthetic materials and opt for natural ones, such as cotton, instead. These are "breathable" and allow the air to circulate close to your skin.
You may find having a cool bath or applying lotion or moisturiser can help soothe the itching.
Some women find that products with strong perfumes can irritate their skin, so you could try using unperfumed lotion or soap.
Mild itching is not usually harmful to you or your baby, but it can sometimes be a sign of a more serious condition, particularly if you notice it more in the evenings or at night.
Let your midwife or doctor know if you are experiencing itching so they can decide whether you need to have any further investigations.
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) is a potentially serious liver disorder that can develop in pregnancy.
Normally, bile acids flow from your liver to your gut to help you digest food.
In ICP, the bile acids do not flow properly and build up in your body instead. There's no cure for ICP, but it should go once you've had your baby.
ICP seems to run in families, but it can happen even if there is no family history. It is more common in women of south Asian origin, affecting around 1 in 70 to 80 pregnancies.
It is more common in women of south Asian origin, affecting around 1 in 70 to 80 pregnancies.
If you have had ICP in a previous pregnancy, you have a high chance of developing it again in another pregnancy.
Some studies have found that babies whose mothers have ICP have a higher chance of being born prematurely or stillborn.
Because of the link with stillbirth, you may be offered induction of labour. This could be any time from 35 weeks, depending on the level of bile acids in your blood.
If you have ICP, you will probably be advised to give birth in hospital under a consultant-led maternity team.
Diagnosis and treatment of ICPICP is diagnosed by excluding other causes of the itch. Your doctor will probably talk to you about your medical and family history and order a variety of blood tests.
These will include tests to check your liver function (LFT) and measure your bile acid levels (BA).
If you are diagnosed with ICP, you will have regular liver function tests so your doctor can monitor your condition.
There is no agreed guideline on how often these tests should happen, but the Royal College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RCOG) and the British Liver Trust advise weekly tests.
ICP Support, the UK's largest research group investigating ICP, also recommends weekly bile acid measurements. These readings help doctors recommend when your baby should be born.
If your LFTs and bile acids are normal and you continue to have severe itching, the blood tests should be repeated every week or 2, to keep an eye on them.
Creams and medicines for ICPCreams, such as aqueous cream with menthol, are safe to use in pregnancy and can provide some relief from itching.
There are some medicines, such as ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), that help reduce bile acids and ease itching.
UDCA is considered safe to take in pregnancy, although it is prescribed on what is known as an "informed consent" basis as it has not been properly tested in pregnancy.
You may also be offered a vitamin K supplement. This is because ICP can affect your absorption of vitamin K, which is important for healthy blood clotting.
Most experts on ICP only prescribe vitamin K if the mother-to-be reports pale stools, has a known blood clotting problem, or has very severe ICP from early in pregnancy.
If you are diagnosed with ICP, your midwife and doctor will discuss your health and your options with you.
Further information
The Royal College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RCOG) has more information about obstetric cholestasis, including what it means for you and your baby, and the treatment that's available. You can also get information about ICP from the British Liver Trust.
You can also get information about ICP from the British Liver Trust.
The charity ICP Support provides information about ICP. You can also watch their video about ICP featuring mums and clinical experts.
Community content from HealthUnlockedWhy does the skin itch during pregnancy?
Skin itching during pregnancy is not a very common phenomenon. Most often, the skin begins to itch unbearably (as after mosquito bites) in the evening, closer to night, which can provoke insomnia and generally worsen a woman’s mood. Usually itching does not harm the baby and goes away after childbirth. However, it is still worth consulting with a gynecologist and dermatologist.
What does it come from? nine0005
The cause of itching during pregnancy in most cases is a violation of the liver: the production and outflow of bile, a general increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood. This is due to a hormonal failure in the body of the future mother - a violation of the synthesis of estrogens, as well as due to fetal pressure on the bile ducts. The fatty acids produced in large quantities enter the woman's skin with the bloodstream and irritate the nerve endings, causing excruciating itching. Similar phenomena associated with stagnation of bile in the body can make themselves felt in the third trimester of pregnancy. Sometimes itching is accompanied by such dangerous diseases as diabetes mellitus. nine0003
The fatty acids produced in large quantities enter the woman's skin with the bloodstream and irritate the nerve endings, causing excruciating itching. Similar phenomena associated with stagnation of bile in the body can make themselves felt in the third trimester of pregnancy. Sometimes itching is accompanied by such dangerous diseases as diabetes mellitus. nine0003
Who is predisposed?
Itching during pregnancy is usually observed in women with chronic diseases of the biliary tract and with high levels of cholesterol in the blood. Such future mothers need to regularly (at least once a month) do a biochemical blood test to exclude toxic effects on liver cells.
How to fight?
A pregnant woman should tell her gynecologist about the discomfort associated with skin itching. In some cases, itching can be a sign of the development of such a dangerous disease as hepatitis. The doctor will conduct appropriate examinations. If, according to an objective examination, itching does not pose any danger, it is often possible to get rid of discomfort simply by following a diet aimed at lowering cholesterol levels, limiting the intake of fatty, spicy and salty foods that prevent the liver from coping with the function of bile secretion, as well as drinking plenty of water - it is necessary to eliminate dry skin. If the diet does not help, the doctor may prescribe choleretic drugs suitable for pregnant women. nine0003
If the diet does not help, the doctor may prescribe choleretic drugs suitable for pregnant women. nine0003
It is important to find the cause of the bothersome itching, eliminating a whole group of skin diseases that can occur during pregnancy.
Itching in the abdomen and chest
This itch is worth mentioning separately. As a rule, the skin on the abdomen or chest itches in the second and third trimesters due to its stretching, because it is these parts of the body that increase in volume during pregnancy. In this case, it is very important not to scratch the skin - this will lead to the appearance of stretch marks, which, unlike itching, will not go away after childbirth. Regularly use moisturizing creams, special products for stretch marks, do a light massage of the chest and abdomen with circular movements of your fingers and do not take hot showers. nine0003
You can get answers to any questions about pregnancy and childbirth from leading EMC experts in the classes of the School of Moms.
Subscribe to our Instagram. You will find useful information about pregnancy and childbirth from leading EMC obstetricians and gynecologists.
Itchy skin during pregnancy: causes and remedies
Itching of the skin during pregnancy can be psychogenic. In this case, itching is a consequence of stress, an early symptom of multiple sclerosis. nine0003
In the early stages, itching occurs due to loss of skin elasticity caused by hormonal changes and excessive dryness of the skin. In the second and third trimester, the reasons may be the rapid weight gain of the expectant mother, the developing stretching of the skin of the abdomen as it increases.
Some expectant mothers experience intimate itching. It is provoked by genital infections, urological and proctological diseases.
The causes of skin itching also include dermatoses of pregnant women (atopic dermatitis, cholestasis of pregnancy). They are provoked by hereditary predisposition, decreased immunity, physiological changes (stretching of the skin with damage to the connective tissue).
Atopic dermatitis is the most common cause of itching during pregnancy. A specific condition is caused by hormonal immune restructuring of the whole organism. In 80% of cases, the disease manifests itself exclusively during pregnancy, and all signs disappear after childbirth without specific treatment. nine0003
Atopic dermatitis is more common in nulliparous women in the early stages and in the second trimester. Itching is caused by papular and exametic rashes localized on the face, neck, limbs, elbows, palms.
Atopic dermatitis is the most benign form of dermatosis of pregnancy and usually does not adversely affect the fetus. However, children born to mothers who suffered from this disease at the stage of gestation are also prone to allergic skin diseases. nine0003
Itching of the skin, as a symptom of cholestasis, is provoked by intrahepatic stagnation of bile as a reaction to increased estrogen production. The disease occurs at the end of the second - beginning of the third trimester, closer to the date of birth. A pregnant woman experiences severe itching in the abdomen, back, palms, legs.
A pregnant woman experiences severe itching in the abdomen, back, palms, legs.
Cholestasis is dangerous for the health of the mother and unborn child in severe cases of the disease. There is a risk of fetal hypoxia, delayed development and even premature birth. nine0003
Symptoms
The main sign of pathological changes is the appearance of irritating-itchy sensations in different parts of the body. Locally, a woman may also feel a tingling and burning sensation.
Other symptoms include:
- blistering or eruption of blistering character;
- peeling, irritation and redness of the skin;
- formation of scaly spots;
- sores and sores caused by scratching; nine0057
- deterioration in general condition caused by sleep disorders and emotional depression.
In most cases, itching of the skin during pregnancy does not pose a real danger to the intrauterine development of the fetus, but significantly worsens the quality of life of the expectant mother, acts depressingly on the state of her nervous system and general well-being.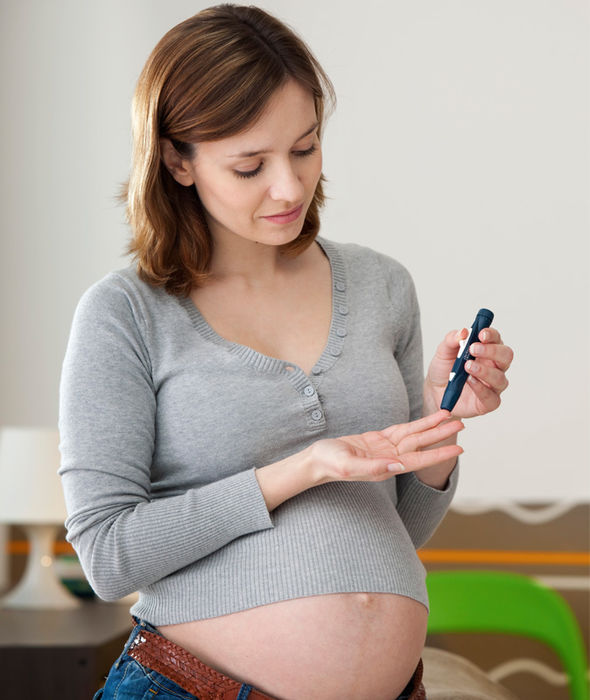
Diagnostics
In order to successfully deal with itching, it is necessary to establish the cause that causes it. The choice of diagnostic methods is determined based on the degree of intensity and localization of itching, the presence of concomitant symptoms and chronic diseases, the duration of pregnancy, and the individual characteristics of the health of the expectant mother. nine0003
Treatment is prescribed only after the exact cause of the itching is established.
At the initial examination, the doctor listens to the patient's complaints, examines the condition of the skin, paying attention to the appearance of rashes or spots. This allows you to draw a preliminary conclusion and determine what laboratory tests and instrumental studies will be needed.
The main diagnostic measures for itchy skin in pregnant women include: nine0003
- general urine and blood tests;
- biochemical blood test;
- studies of hormone levels - if endocrine pathologies are suspected;
- analysis of vaginal smear for microflora;
- skin scraping examination;
- allergy testing;
- Ultrasound of the digestive tract, liver and kidneys;
- histological examination;
- analysis of feces for the detection of helminth eggs.
 nine0057
nine0057
The choice of research methods is determined individually. In some cases, a pregnant woman is shown a consultation with an endocrinologist, urologist, gastroenterologist, venereologist.
Identification of atopic dermatitis is usually not difficult. In addition to the general examination, such types of diagnostics as dermatoscopy and examination under the Voodoo lamp are carried out.
If itching in a pregnant woman is allergic in nature, a mandatory diagnostic measure is the determination of the allergen (pathogen). nine0003
Treatment of itching
Although itching during pregnancy is not dangerous in many cases, it should not be tolerated either. You need to tell the gynecologist about unpleasant sensations, who will determine the diagnostic methods and, if necessary, give a referral to other specialists. Treatment of itching during pregnancy is carried out by the attending gynecologist together with a dermatologist.
You can not self-medicate and use medicines without the approval of a doctor. Many of them have contraindications and can cause severe side effects. A pregnant woman should remember the prohibition of scratching itchy places. This leads to a violation of the integrity of the skin, the appearance of wounds and abrasions, which will become sites of infection. nine0003
Many of them have contraindications and can cause severe side effects. A pregnant woman should remember the prohibition of scratching itchy places. This leads to a violation of the integrity of the skin, the appearance of wounds and abrasions, which will become sites of infection. nine0003
The treatment regimen depends on the disease that causes itching. When choosing drug therapy, the risks of negative effects on the fetus are taken into account. This is especially true in the case of the appointment of antibiotics, hormonal and antifungal drugs. Self-medication is unacceptable!
In the treatment of itching during pregnancy, the following types of drugs can be prescribed:
- antihistamines - to eliminate itching caused by dermatitis, urticaria; nine0057
- glucocorticoids - used to treat dermatitis;
- emollients - have a moisturizing and regenerating effect in case of excessive dryness and dehydration of the skin;
- adsorbents and hepatoprotectors - to normalize the liver;
- choleretic preparations - for the correction of the state of the digestive tract;
- sedatives - to normalize the state of the nervous system, if a pregnant woman has signs of increased anxiety and sleep disturbances.
 nine0057
nine0057
With moderate itching, a pregnant woman is shown taking baths with a decoction of a string or oatmeal. An oatmeal bath is effective for itching caused by stretch marks, eczema, or psoriasis. To prepare it, crushed oatmeal is mixed with baking soda and a little milk is added, the mixture is poured into a warm bath.
Lotions on herbal decoctions can be applied to itchy areas of the skin. Chamomile, succession or St. John's wort is poured with boiling water and insisted. After a few hours, the decoction for lotions is ready for use. nine0003
To eliminate itching of the genital organs, medicinal suppositories with local action are prescribed. Of great benefit are sitz baths of decoctions of sage or chamomile.
Itching in the abdomen, caused by skin tension, can cause stretch marks. To prevent aesthetic imperfections, it is necessary to moisturize the skin with special means.
To reduce itching, a pregnant woman should only wear clothes made from natural fabrics, preferably cotton. Natural fabrics allow the skin to breathe freely. It is useful for future mothers to take a cool shower without the use of soaps or bathing gels. The skin needs to be effectively protected from external aggressive factors: sun, frost and wind. nine0003
Natural fabrics allow the skin to breathe freely. It is useful for future mothers to take a cool shower without the use of soaps or bathing gels. The skin needs to be effectively protected from external aggressive factors: sun, frost and wind. nine0003
When itching of the skin appears, it is better to refuse the use of perfumes, take the choice of cosmetics very responsibly.
Prophylaxis
Itching during pregnancy can be prevented if you follow the doctor's recommendations and preventive measures. Tips for expectant mothers:
- carefully observe body hygiene, take regular showers or baths without the use of fragrances;
- refuse underwear and clothes made of synthetic fabrics; nine0057
- after taking a shower or bath, moisturize the skin of the body with special products, with a neutral pH level, creams, lotions, emulsions are suitable for this;
- use phosphate-free laundry detergents;
- wear loose clothing that does not restrict movement;
- avoid stuffy rooms or open places under the scorching summer sun;
- exclude intense physical activity that provokes increased sweating; nine0057
- provide the expectant mother with a plentiful drinking regimen that prevents dehydration of the body;
- avoid stressful situations, get positive impressions.

Proper nutrition plays an important role in the prevention of itching of the skin. This is especially important if itching is provoked by various foods. The woman is recommended a hypoallergenic diet, with the exception of fast food, smoked, salty and pickled foods, as well as foods with preservatives, emulsifiers and artificial flavors. The diet of the future mother should be rich in vitamins, minerals, fatty acids, antioxidants. To do this, the menu includes sour-milk products, meat and fish of low-fat varieties, vegetable dishes, fruits. nine0003
Itching during pregnancy when following medical recommendations has a favorable prognosis and is not an obstacle to natural childbirth.
If a woman had signs of atopic dermatitis during her first pregnancy, the likelihood of a recurrence of the disease during subsequent pregnancies is high. At the stage of planning a child, it is necessary to visit a dermatologist.
Itching
A series of products "Emolium" effectively eliminates the symptoms of skin diseases, including itching, peeling, irritability. They are prescribed to moisturize the skin, eliminate dryness and tightness in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, and allergies. Means of the Emolium series are used in the complex treatment of these and other diseases that provoke itching. nine0003
They are prescribed to moisturize the skin, eliminate dryness and tightness in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, and allergies. Means of the Emolium series are used in the complex treatment of these and other diseases that provoke itching. nine0003
The main advantages of the series:
- have a mild anti-inflammatory effect;
- ensure the normal functioning of the skin;
- restore skin structure;
- retain moisture in cells and intercellular space;
- restore the water-lipid layer;
- relieve irritation and itching.
The delicate and delicate consistency of the products makes it easy to apply and distribute them over the entire surface of the affected areas. nine0003
With severe itching of pregnant women, a triactive series is recommended, taking care of atopic and damaged skin. Triactive cream enriched with rapeseed oil and sodium hyaluronate has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and antipruritic effects.