Weight gain pregnancy chart kg
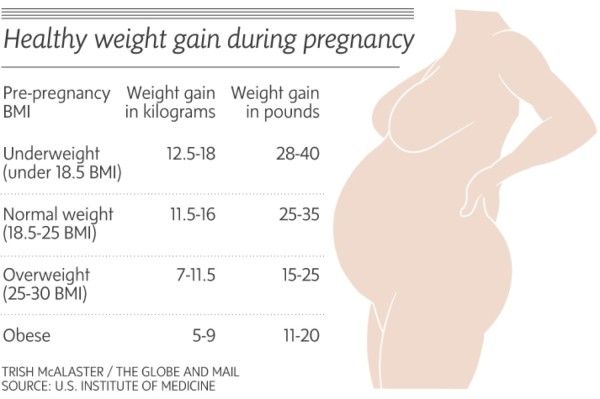
Healthy weight gain during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a time of changes within the body. It is normal to gain some weight during pregnancy due to the growth of the baby, placenta and fluid around the baby (amniotic fluid).
- However, too much extra weight during pregnancy can increase your chances of:
- high blood pressure with complications in pregnancy (pre-eclampsia)
- diabetes during pregnancy (gestational diabetes)
- needing a caesarean section
- having a large baby. This increases their risk of becoming obese in childhood and early adult life
- difficulty losing weight after your baby is born. This may increase your risk of developing diabetes, heart disease and some cancers later in life.
- Not gaining enough weight during pregnancy can increase the chances of having a premature (preterm) birth, or a small for age baby.
How much weight should I gain?
The amount of weight that you should gain during pregnancy depends on your pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI). This is your weight (measured) in kilograms divided by your height (measured) in metres squared. You can ask your health practitioner to help you with this, especially if you do not have accurate scales at home.
For example: if you are 1.68 m tall and weigh 82 kg:
Your BMI = = 29 kg/m2 = Overweight category (orange colour)
The Kidspot website has an online tool that can help you calculate your BMI.
Alternatively, you can use the chart below to help you. Find your height, then go across the chart till you are in the column headed by your weight (kg). The number in the cell is your BMI (rounded to the nearest whole number). The colour of the cell indicates which recommendations are right for you.
BMI chart
Click to enlarge.
In the first trimester (first 12 weeks), most women do not need to gain much weight (usually less than 2 kg) – which is just as well for those who have morning sickness early in pregnancy. Some women even lose a small amount of weight.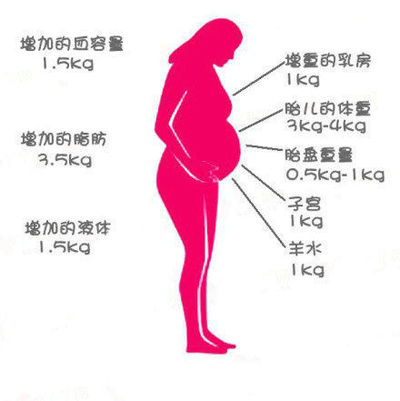 If this happens to you, you do not need to be concerned as long as you start to gain weight steadily in the second and third trimesters of your pregnancy.
If this happens to you, you do not need to be concerned as long as you start to gain weight steadily in the second and third trimesters of your pregnancy.
The table below can be used as a guide to help you work out how much weight you should gain during your pregnancy. Regardless of your BMI at the start of pregnancy, you can still have a healthy weight gain during pregnancy.
Most women do not gain much weight during the first trimester of pregnancy (between a half and 2 kilograms). The rate of weight gain can vary during the rest of your pregnancy and may not be the same every week.
Recommendations for total weight gain during pregnancy, by pre-pregnancy or early pregnancy (less than 10 weeks) BMI
| Pre-pregnancy or early pregnancy (less than 10 weeks) BMI (kg/m2) | Total weight gain range |
|---|---|
| Underweight (<18.5) | 12.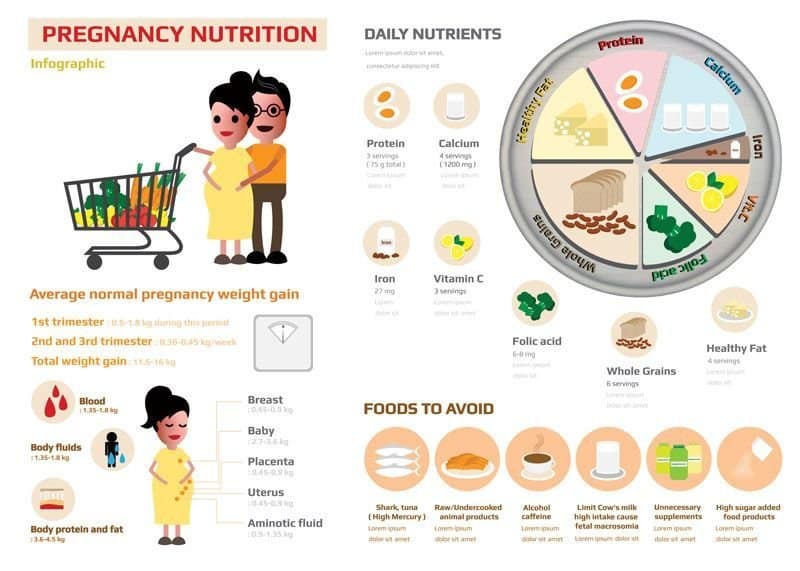 5 kg–18 kg 5 kg–18 kg |
| Healthy weight (18.5 - 24.9) | 11.5 kg–16 kg |
| Overweight (25.0 - 29.9) | 7 kg–11.5 kg |
| Obese (≥ 30.0) | 5 kg–9 kg |
Source: IOM and NRC 2009
If you’re having twins
It is especially important to gain the right amount of weight when you’re expecting twins because your weight affects the babies’ weight. And because twins are often born before the due date, a higher birth weight is important for their health. It is important you work with your health care provider to determine what’s right for you.
Consider these general guidelines for pregnancy weight gain if you’re carrying twins:
| Pre-pregnancy or early pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | Recommended weight gain |
|---|---|
| Healthy weight (BMI 18.5 to 24.9) | 17 kg–25 kg |
Overweight (BMI 25 to 29. 9) 9) | 14 kg–23 kg |
| Obese (BMI 30 or more) | 11 kg–19 kg |
Source: IOM and NRC 2009
Where does the extra weight in pregnancy go?
Pregnancy is a unique time in which your body changes to meet the needs of your growing baby. Your body must store nutrients and increase the amount of blood and other fluids it makes.
Here is an example of how much each component part weighs during pregnancy if your baby’s birthweight is 3.5 kg, and you gained 12.8 kg during your pregnancy:
| Baby | 3.5 kg |
|---|---|
| Fluid around the baby (Amniotic fluid) | 0.9 kg |
| Placenta | 0.7 kg |
| Growth of your womb (uterus) | 0.9 kg |
| Growth of your breasts | 1.1 kg |
| Increased amount of blood | 1. 5 kg 5 kg |
| Increased amount of other body fluids | 1.1 kg |
| Storing of nutrients (fat and protein) | 3.1 kg |
| Total weight gain based on this example | 12.8 kg |
Is it safe to lose weight when pregnant?
Dieting to lose weight during pregnancy is not recommended.
Managing your weight gain
While it is ideal to be a healthy weight before becoming pregnant (ie, a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9), we know that this doesn’t always happen! If you are outside the healthy weight range, you can still help your baby by gaining weight within the recommended range for your BMI category.
Talk to your lead maternity carer about how you can monitor your weight, and for advice about eating and being active during your pregnancy.
Healthy weight gain tips for healthy women
Here are some tips to help you manage healthy weight gain during pregnancy.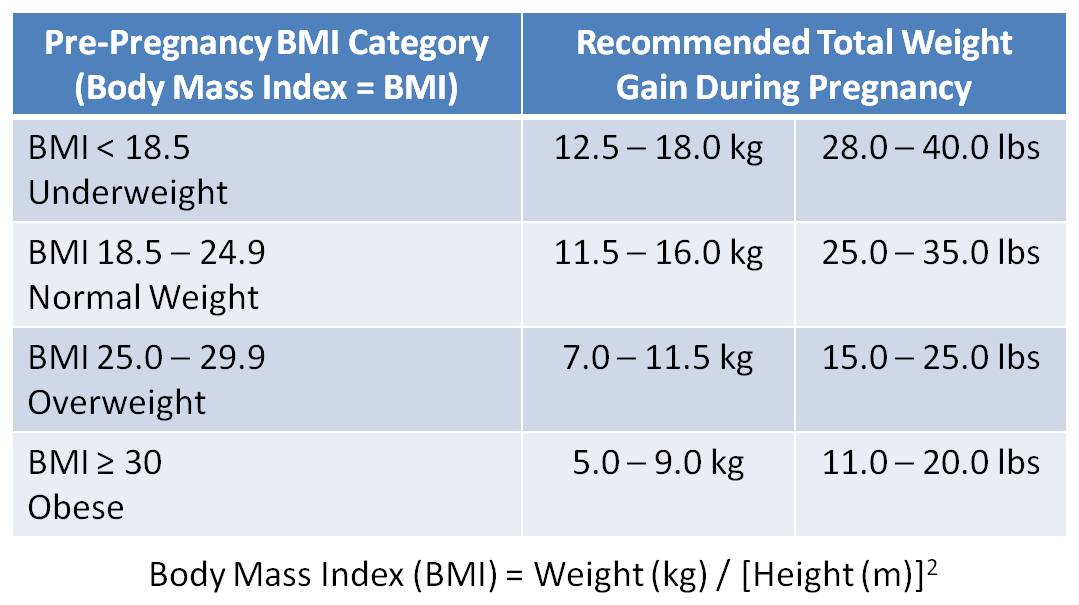
- Pregnancy is not about ‘eating for two’. In the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, you can eat the same amount as you usually would. It is important you eat healthy food.
- After the 12th week, and if you are a healthy weight, the extra food you need each day is about the same as a wholegrain cheese and tomato sandwich, or a wholegrain peanut butter sandwich and a banana. If you are overweight or obese, the extra food you need is about the same as 1 slice of wholegrain bread or 2 apples.
- Drink water rather than sweetened drinks or fizzy drinks.
- Drink low-fat [trim (green top) or calcium-extra (yellow top)] or light blue milk instead of full-fat (blue or silver top) milk.
- Choose wholegrain bread instead of white bread.
- Eat a healthy breakfast every day, such as wheat biscuits or porridge with low-fat milk, or 2 slices of wholegrain toast.
- Have at least 4 servings of vegetables and 2 servings of fruit every day. Buy vegetables and fruits that are in season, or buy frozen vegetables to help reduce cost, wastage and preparation time. Tinned fruit in juice are also a good option.
- Examples of a vegetable or fruit serving:
- half a cup of peas, broccoli or carrots
- 1 medium-sized potato, banana, orange or apple
- 1 large kiwifruit.
- If vegetable/fruit juice or dried fruit is consumed, it contributes a maximum of only 1 serving of the total recommended number of daily servings for fruit/vegetables.
- Examples of a vegetable or fruit serving:
- Prepare and eat meals at home. Have takeaways no more than once a week.
- Choose healthy snacks such as unsweetened or low-sugar, low-fat yoghurt, fruit, cheese and crackers, home-made popcorn, a glass of trim milk, a few unsalted nuts (eg, 6 or 7 almonds) or a small wholegrain sandwich.

- Aim to do at least 30 minutes of moderate intensity activity 5 or more days a week, eg, brisk walking or swimming (or as advised by your doctor, midwife or physiotherapist). The ‘talk test’ is a simple way to estimate intensity: as a guide, you should be able to carry out a conversation but not sing while doing moderate intensity activity.
(The Ministry of Health acknowledges the work of E Jeffs and Canterbury DHB in producing these tips.)
Returning to pre-pregnancy weight
Gaining the right amount of weight during pregnancy through a mixture of good eating and activity choices will make returning to your pre-pregnancy weight easier.
If you were overweight or obese before becoming pregnant but established good eating and activity habits during pregnancy, continuing to do so after your baby is born will help support gradual weight loss. This will not adversely affect the ability to breastfeed or the quantity or quality of your breast milk.
The greatest amount of weight loss usually occurs in the first 3 months after birth and then continues at a slow and steady rate until 6 months after birth. Breastfeeding helps you return to your pre-pregnancy weight as some of the weight you gain during pregnancy is used as fuel to make breast milk.
Future pregnancies
If you are planning another pregnancy, it is a good idea to establish healthy eating and activity patterns and try to reach a healthy weight before becoming pregnant. For some, this will be a matter of returning to your pre-pregnancy weight or close to it.
Retaining excess weight over subsequent pregnancies increases your risk of developing diabetes and heart disease later in life.
Speak to your lead maternity carer for more advice.
Don’t forget to take an 800 mcg tablet of folic acid each day if you are trying to become pregnant!
Find out more from the Ministry
More detailed nutrition advice for health practitioners is available in Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Healthy Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women: A background paper.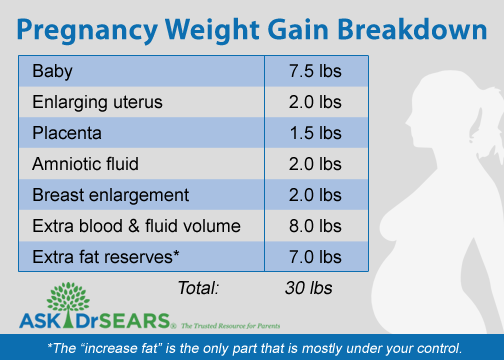
Week by Week of Pregnancy Weight Gain
Created by Łucja Zaborowska, MD, PhD candidate
Reviewed by Rijk de Wet and Aleksandra Zając, MD
Based on research by
Institute of Medicine Recommendations “Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines“ (2009)
Last updated: Oct 22, 2022
Table of contents:- How much weight should I gain?
- Eating for two: Where does all the extra weight go?
- Pregnancy weight gain breakdown by week
What's the average pregnancy weight gain week by week? Where do all the extra pounds go? Keep on reading to find all the answers!
💡 This article is a part of a bigger series, based on our pregnancy weight gain calculator.
We try our best to make our Omni Calculators as precise and reliable as possible. However, this tool can never replace a professional doctor's assessment. If any health condition bothers you, consult a physician. 2 }BMI=(height [m])2weight [kg]
2 }BMI=(height [m])2weight [kg]
Your recommended weight gain depends on your pre-pregnancy BMI:
- Underweight before pregnancy (BMI <18.5)
- Expected weight gain: 28–40 pounds (12.7–18.1 kg)
- Normal weight (BMI 18.5–24.9)
- Single pregnancy expected weight gain 25 to 35 pounds (11.3–15.9 kg)
- Twin pregnancy expected weight gain: 37–54 pounds (16.8–24.5 kg)
- Overweight (BMI between 25 and 29.9)
- Single pregnancy expected weight gain: 15–25 pounds (6.8–11.3 kg)
- Twin pregnancy expected weight gain: 14–50 pounds (16.8–22.7 kg)
- Obese (BMI over 30)
- Single pregnancy expected weight gain: 11–20 pounds (5–9 kg)
- Twin pregnancy expected weight gain: 25–42 pounds (11.3–19 kg)
First things firsts: eating for two might not be such a good idea. Your diet should increase by only 300 kcal, starting at the beginning of the second trimester, and grow up to 500 kcal when you begin breastfeeding. 🍼
🍼
As you can imagine, all the weight gain during pregnancy must serve a specific purpose. You're not wrong: all that mass goes into the birth weight of the baby, and also allows the gestation to thrive and survive. In a typical healthy pregnancy, an average woman needs to gain around 25–35 pounds (11.3–15.9 kg).
Let's break it down pound by pound!
- The baby: An average child's birth weight is 7.7 lb (3.5 kg).
- An enlarged uterus weighs around 2 lb (0.9 kg).
- Enlarged breasts weigh around 2 lb (0.9 kg).
- The placenta adds another 1.5 lb (0.7 kg).
- Amniotic fluid is responsible for an additional 2 lb (0.9 kg).
- Your blood volume (increased by ~50%) and other bodily fluids: 6.6 lb (3 kg).
- The extra fat tissue weighs close to 7.7 lb (3.5 kg).
Pregnancy weight gain breakdown by week
Achieving a healthy weight gain during pregnancy is not that difficult! Trust your body, exercise, and eat well.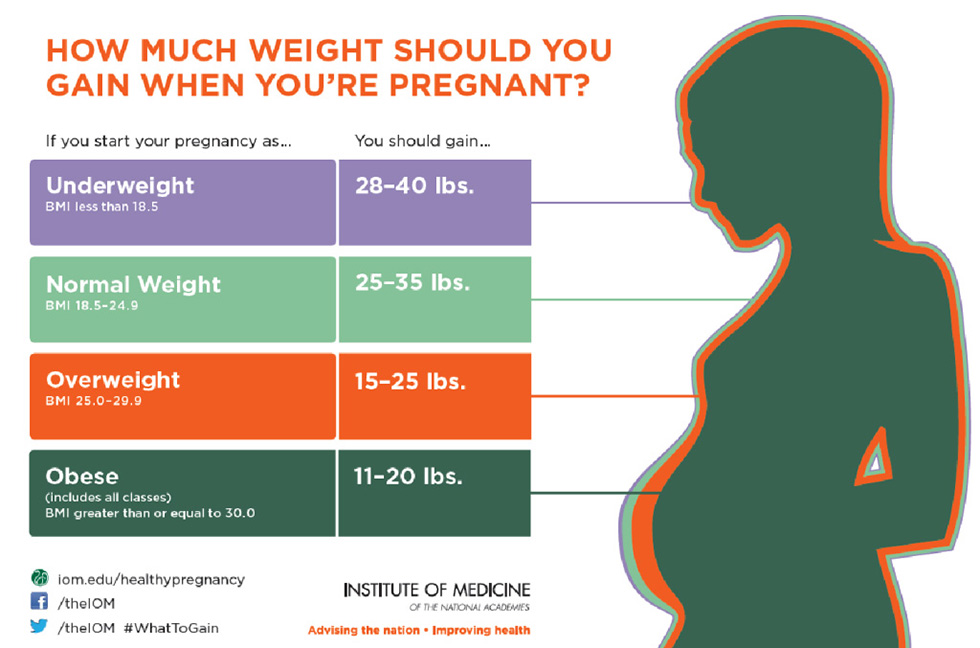 Don't get too attached to them sweets; turn to veggies and nuts instead. Keep in mind that the growth rate is different for every pregnancy. There is no single ideal way in which pregnant women gain weight - try to avoid comparing yourself to other future mums!
Don't get too attached to them sweets; turn to veggies and nuts instead. Keep in mind that the growth rate is different for every pregnancy. There is no single ideal way in which pregnant women gain weight - try to avoid comparing yourself to other future mums!
However, there's one specific thing that should catch your attention: an extremely rapid weight gain exceeding 0.5 kg (1.1 lb) per week. Track your weight, and contact your health care provider if you realize you're gaining pounds way too fast.
Here are the estimates of growth rates for the average singleton pregnancy. Remember: they do not have to fit your case entirely!
- <14 weeks — your weight during the first trimester of pregnancy should not change.
- 14–20 weeks — a steady weight gain appears for a total increase of 2.5 kg.
- 20–30 weeks — an increase of another 5 kg.
- 30–36 weeks — another 2.
 5 kg.
5 kg. - 36–40 weeks — at the end of the third trimester, you shouldn't gain weight anymore.
One available study broke it down to even finer pieces:
- 0 to 10 weeks — 0.065 kg, 2.3 oz, or 0.14 pounds per week.
- 10 to 20 weeks — 0.335 kg or 0.74 lb per week.
- 20 to 30 weeks — 0.450 kg or 1 lb per week.
- 30 to 40 weeks — 0.335 kg or 0.74 lb per week.
Visit the calculator on your left for more specific calculations!
Łucja Zaborowska, MD, PhD candidate
Before pregnancy
Height
Weight
You are...
Weight during pregnancy
Min. weight
Max. weight
Min. weight gain
Max. weight gain
Check out 32 similar fertility & pregnancy calculators 🤰
BBTBirth controlBishop score… 29 more
Weight during pregnancy. What increase is considered optimal?
Why is excessive weight gain during pregnancy particularly harmful? What should be the calorie content of the diet? How to build your diet so that you can eat varied (and tasty), but at the same time not gain too much? Let's figure it out.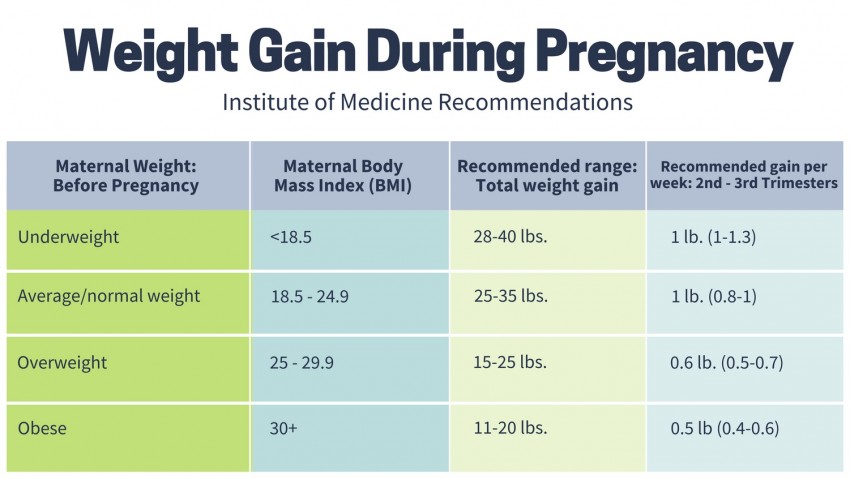
What makes up weight gain during pregnancy?
An increase in the subcutaneous fat layer during pregnancy is a normal and natural process.
While the baby is growing inside you, he needs energy and external protection. But during pregnancy, weight increases not only and not so much due to the adipose tissue of the mother: there is more fluid in the body, the uterus grows, the fetus and placenta develop, and the breasts increase in preparation for the feeding process.
Interestingly, weight loss during the period of toxicosis can later provoke its increase: the body will try to regain what was lost.
Expectant mothers especially actively gain weight in the second trimester and the beginning of the third, but closer to childbirth, a pregnant woman can even lose 1-2 kilograms. nine0004
As long as the weight increases more or less evenly and does not go beyond the upper limit of the norm, there is nothing to worry about. But if your weight is rapidly going up, you should be wary.
How to correctly calculate the weight, and what increase is considered optimal?
In Russian obstetric practice, it is generally accepted that the total increase should not exceed 12 kg. for the entire pregnancy. Of these 12 kg. 5-6 accounts for the fetus, placenta, amniotic fluid, another 1.5-2 - for an increase in the uterus and mammary glands, and only 3-3.5 - for the fat mass of a woman. nine0004
But this is a general indicator, a kind of "average temperature in the hospital." The optimal increase is calculated individually and depends on the initial weight of the pregnant woman, her age, the number of fetuses and the size of the child (children), physical activity.
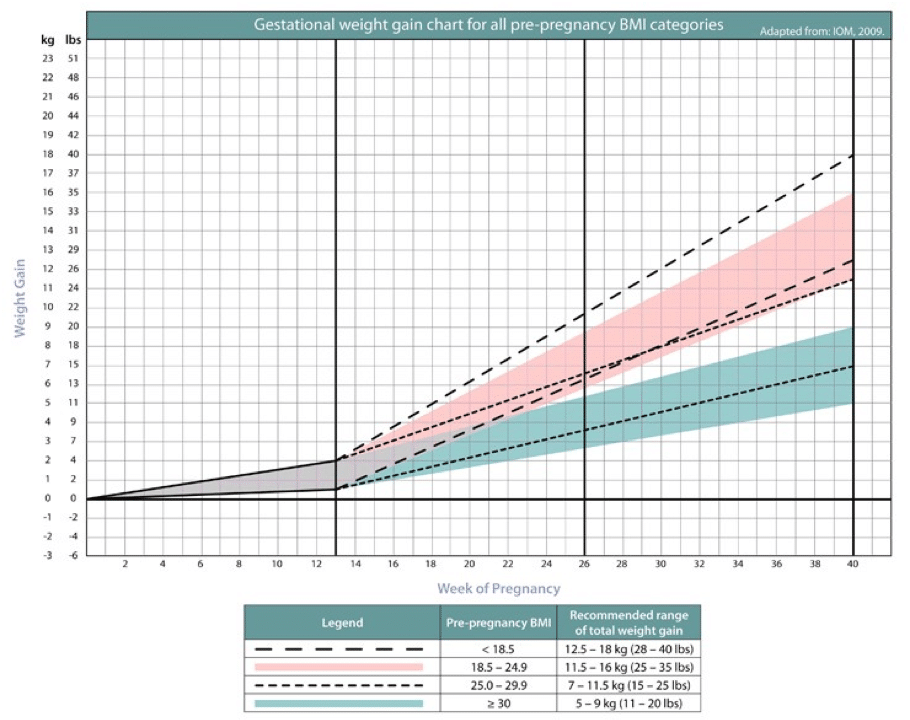
WHO recommends that optimal weight gain be calculated based on Body Mass Index (BMI).
It is determined by the formula: body weight (kg) / height squared (m).
| BMI | Recommended weight gain |
|---|---|
19. 8-26 (normal body weight) 8-26 (normal body weight) | 12.5-15 kg |
| 26.1-29 (overweight) | 11.5 - 14 kg |
| over 29 (obese) | 7-9 kg |
How to calculate the optimal weight gain?
To do this, use the following chart:
- Calculate your BMI: divide your initial weight in kg. for height in meters squared. nine0072
For example, your "pre-pregnancy" weight was 60 kg with a height of 170 cm.
BMI = 60: (170 x 170) = 20.76.
- A BMI of less than 18.5 indicates underweight. Indicators from 18.5 to 25 are within the norm, from 25 to 30 are above the norm, and a figure greater than 30 indicates obesity.
- Now that you know your BMI, find the optimal weekly increase in the table and compare it with yours.
| Week of pregnancy | nine0033 Underweight before pregnancy (BMI less than 18.Normal pre-pregnancy weight (BMI 18.5 to 24.9) | Overweight before pregnancy (BMI over 30) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0-0.9 kg | 0-0.7 kg | 0-0.5 kg |
| 6 | 0-1.4 kg | 0-1 kg | 0-0.6 kg |
| 8 | 0-1.6 kg | 0-1.2 kg | 0-0.7 kg |
| 10 | 0-1.8 kg | 0-1.3 kg | 0-0.8 kg |
| 12 | 0-2 kg | 0-1.5 kg | 0-1 kg |
| 14 | 0.5-2.7 kg | 0.5-2 kg | 0.5-1.2 kg |
| 16 | up to 3.6 kg | up to 3 kg | up to 1.4 kg |
| 18 | up to 4.6 kg | up to 4 kg | up to 2.3 kg | nine0039
| 20 | up to 6 kg | up to 5.9 kg | up to 2.9 kg |
| 22 | up to 7.2 kg | up to 7 kg | up to 3. 4 kg 4 kg |
| 24 | up to 8.6 kg | up to 8.5 kg | up to 3.9 kg |
| 26 | up to 10 kg | up to 10 kg | up to 5 kg |
| 28 | up to 13 kg | up to 11 kg | up to 5.4 kg |
| 30 | up to 14 kg | up to 12 kg | up to 5.9 kg |
| 32 | up to 15 kg | up to 13 kg | up to 6.4 kg |
| 34 | up to 16 kg | up to 14 kg | up to 7.3 kg |
| 36 | up to 17 kg | up to 15 kg | up to 7.9 kg |
| 38 | up to 18 kg | up to 16 kg | up to 8.6 kg |
| 40 | up to 18 kg | up to 16 kg | up to 9.1 kg |
Recently, doctors are increasingly talking about an individual approach and urge not to panic if the increase is slightly beyond the normal range. When assessing the health status of a pregnant woman, the doctor focuses not only on weight, but also takes into account the results of tests and examinations and other important indicators.
When assessing the health status of a pregnant woman, the doctor focuses not only on weight, but also takes into account the results of tests and examinations and other important indicators.
Why is excessive weight gain dangerous?
Gaining extra pounds can lead to gestational diabetes, hypertension, preeclampsia, or cause a caesarean section.
In addition, excessive weight gain during pregnancy may increase the risk of obesity and associated cardiovascular disease.
What can I do to keep my weight within normal limits during pregnancy?
First of all, consult a nutritionist. If there is no such doctor in the antenatal clinic, it makes sense to contact a specialist on a commercial basis. He will develop an individual diet, which will contain all the useful elements, and will offer to keep a food diary. It will also tell you how to eat right and weigh yourself. nine0003 To prevent excessive weight gain during pregnancy, it is enough to follow simple rules of a healthy diet:
- Eat often and in small portions;
- Always keep a “healthy snack” on hand: fresh apple wedges, unsweetened crackers, dried fruit, or sugar-free yogurt;
- Refuse soda, chips, sausages and sausages;
- Minimize sweets;
- Avoid fast food;
- Limit the use of condiments, especially salt, which retains water in the body; nine0072
- Choose steamed dishes;
- Eat more fiber-rich foods such as whole grain bread, bran, vegetables;
The diet of a pregnant woman should be varied. Include grains, vegetables, fruits, dairy products, meat and fish, legumes, or nuts.
Include grains, vegetables, fruits, dairy products, meat and fish, legumes, or nuts.
It must be remembered that expectant mothers should never starve and adhere to extreme diets.
How many calories per day do you need during pregnancy? nine0006
It is difficult to calculate the energy value per day on your own, and then strictly adhere to a certain number of calories, and it is not necessary, unless it is recommended by a nutritionist or endocrinologist. On average, you can aim for 2000-2500 calories per day, but it is important to understand that the need for calories depends on many factors: age, initial weight, health status and level of physical activity.
When should I be on the alert?
Strictly speaking, it is better for a pregnant woman not to worry and entrust her condition to a doctor who will control the development of pregnancy, analyzes and monitor weight. It is important to take tests to determine the level of fasting blood glucose once a trimester.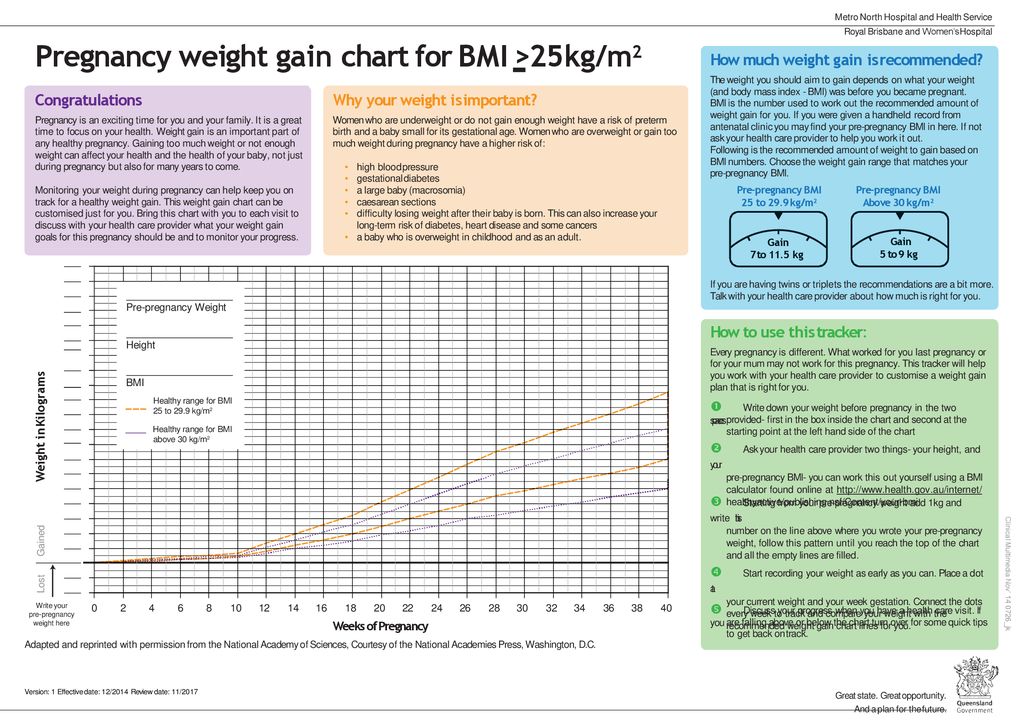 The appearance of glucosuria, an increase in fasting blood glucose (more than 5.5 mmol / l) or an hour after a meal (more than 7.7 mmol / l) indicate the possible development of "diabetes in pregnancy", in connection with which the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment . In addition, a sharp increase in body weight can cause preeclampsia. nine0004
The appearance of glucosuria, an increase in fasting blood glucose (more than 5.5 mmol / l) or an hour after a meal (more than 7.7 mmol / l) indicate the possible development of "diabetes in pregnancy", in connection with which the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment . In addition, a sharp increase in body weight can cause preeclampsia. nine0004
These and other diseases can be dangerous, which is why you need to carefully monitor the body weight during the gestation period, but remember that pregnancy is not the time for strict diets.
When using any materials from the site nutriclub.ru, a link to the site is required.
© Nutriclub, 2020
You will also be interested
- Nutriclub - healthy nutrition and child development nine0072
- Pregnancy
- Mom's health and well-being
- weight during pregnancy.
 What increase is considered optimal? - Nutriclub
What increase is considered optimal? - Nutriclub
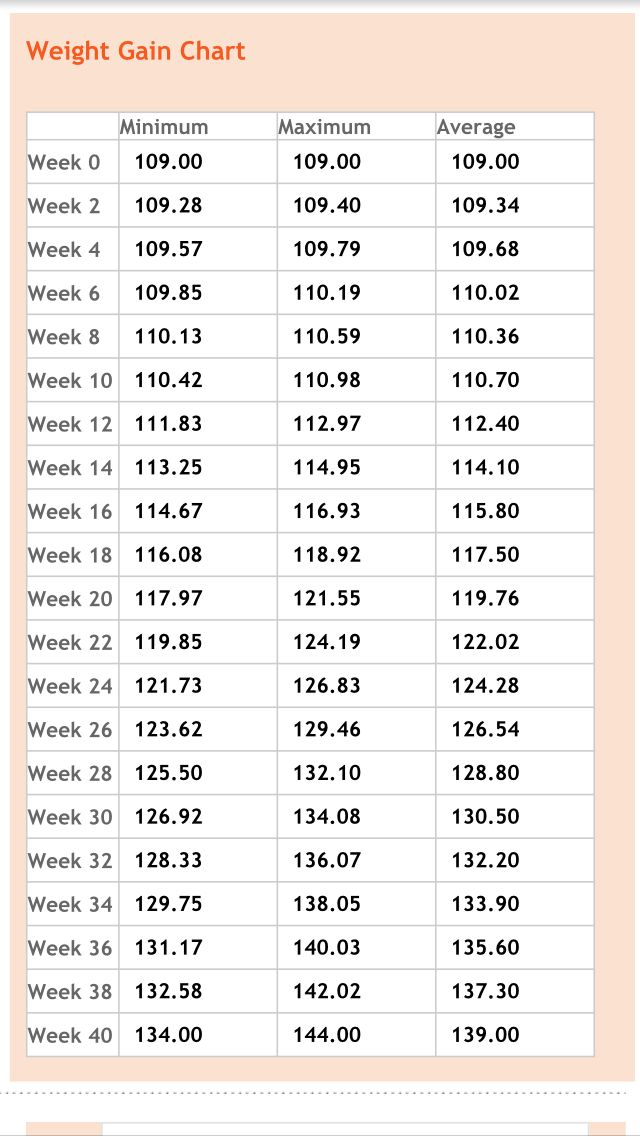
Weekly pregnancy weight calculator
The weight of the expectant mother is very important for the development of the fetus. It is desirable to have a normal body weight before pregnancy. Lack of weight is a serious risk factor, as a result of which a child may be born too small. nine0004
Being overweight increases the likelihood of having an oversized baby. In such situations, only a timely caesarean section made by obstetricians can help.
Weight in the first trimester
In addition to body weight before conception, weight during pregnancy by weeks and its constant control play an important role. In the first couple of months, it increases slowly, the baby and mother only adapt to each other. During this period, there are frequent cases of toxicosis, which additionally reduces weight. During the first trimester of pregnancy, a woman gains about 1.5 kg. nine0004
Weight in the second half of pregnancy
Intensive weight gain occurs in the second half of the term.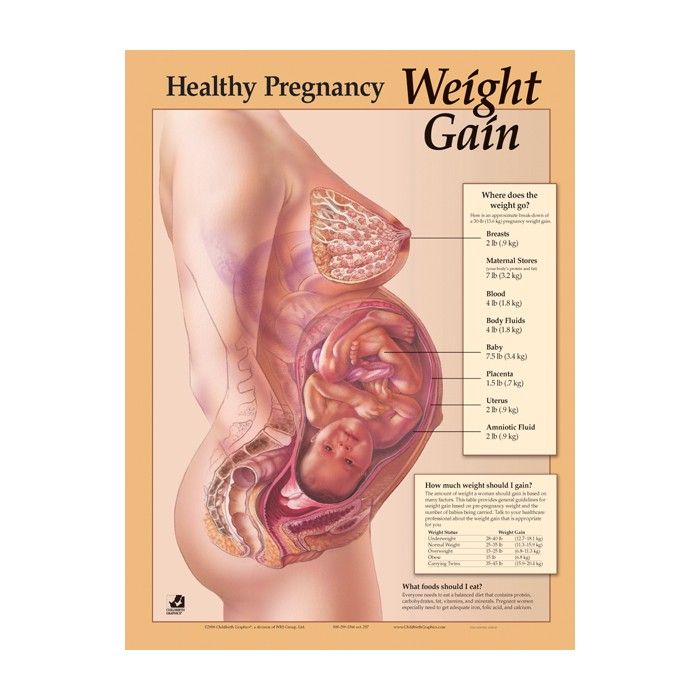 Most women gain only 40% in the first 4 months, and the remaining 60% in the second half. However, it also happens the other way around - in some women, weight during pregnancy is gained week by week faster in the first months, there is no pathology in this.
Most women gain only 40% in the first 4 months, and the remaining 60% in the second half. However, it also happens the other way around - in some women, weight during pregnancy is gained week by week faster in the first months, there is no pathology in this.
The increase is distributed as follows:
| Fat | 28% |
| Water | 13% |
| Fruit | 27% |
| Blood | 10% |
| Uterus | 8% |
| Amniotic fluid | 6% |
| Placenta | 5% |
| Breast | 3% |
Permissible weight gain
If we take the allowable value of weight gain in women, then it is 350 g per week (50 g per day), with a maximum of 500 g per week. Using the weight calculator during pregnancy, you can find out what it should be at different times. To exceed this norm, it is desirable to lead an active life and monitor nutrition. Although an extra increase is undesirable, in no case should you exhaust yourself with hunger strikes. And there is nothing good in the abuse of flour products in an attempt to get to the norm either. You need to eat something that will benefit not only you, but also the child. nine0004
To obtain an accurate calculation, enter the following digital data into the pregnancy weight calculator:
- initial weight;
- growth;
- approximate gestational age in weeks.
What causes the difference in weight in different women at the same time?
The difference can be due to several reasons. One of them is age; with increasing age, the tendency to be overweight also increases. More weight is gained by women with a lack of mass before pregnancy and who have undergone early toxicosis. The body thereby tries to compensate for the losses. nine0004
The body thereby tries to compensate for the losses. nine0004
An important factor is the peculiarity of the constitution, the difference with the readings of the weight calculator during pregnancy by weeks may be due to a tendency to thinness or fullness. It also depends on the size of the baby: the larger it is, the larger the placenta will be. Sometimes a sharp increase in the appetite of the expectant mother leads to intensive weight gain, it is quite difficult to deal with it.
How is the weight gained distributed?
The normal weekly weight gain during pregnancy is as follows:
- the uterus accounts for 0.9 kg;
- adipose tissue of the order of 2.2 kg;
- children weigh about 3.3 kg;
- tissue fluid - 2.7 kg;
- amniotic fluid approximately 1.2 kg;
- mammary glands increase by 0.5 kg
- circulating blood - per 1.2 kg.
Approximately 12.1 kg. In case of multiple pregnancy, at least 2-4 kg must be added to the figures obtained.
 5)
5)