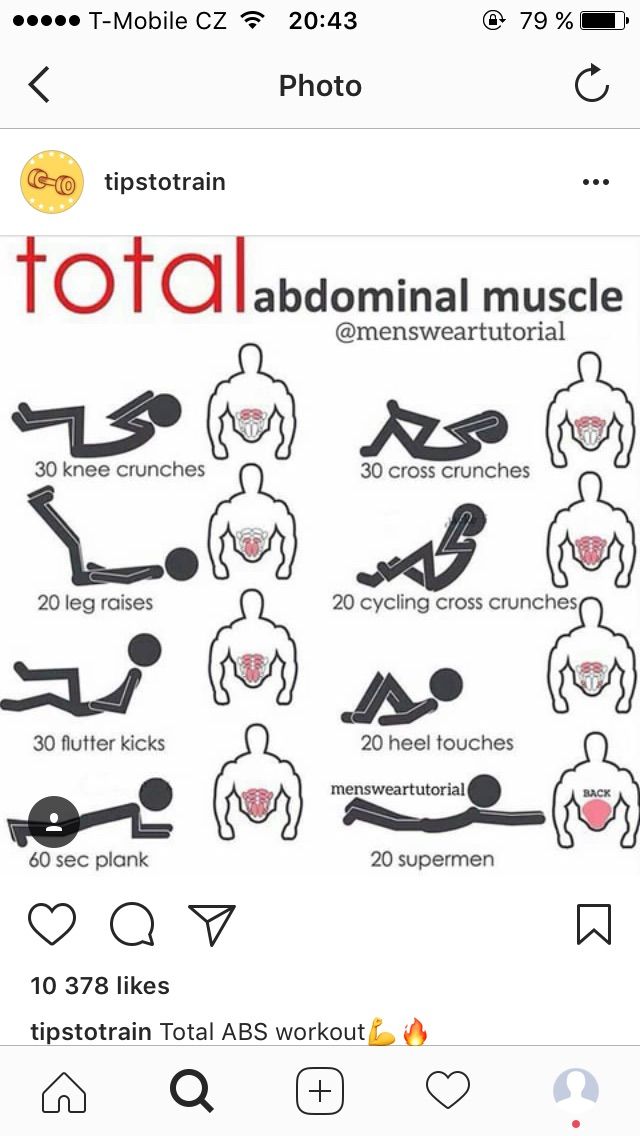
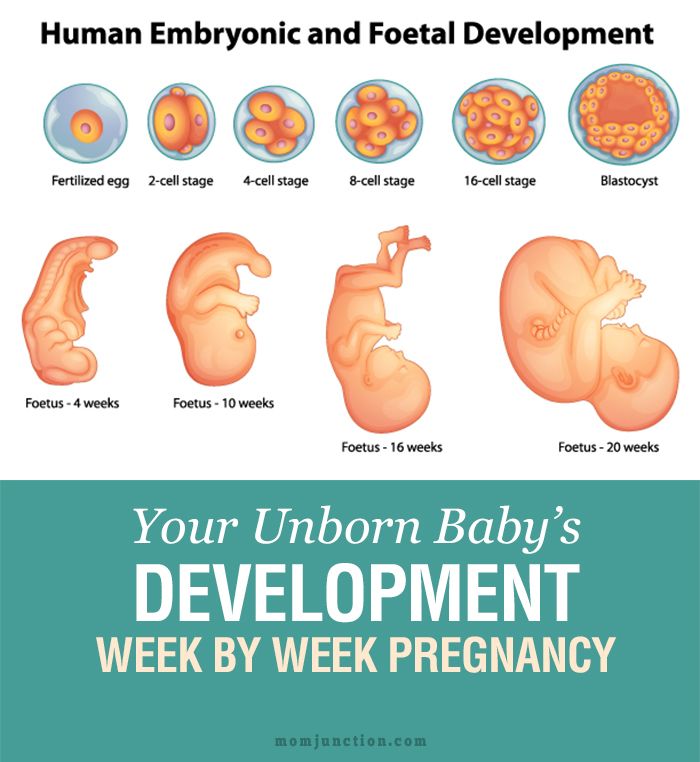
How to put your child in juvenile detention
Does Your Kid Needs Juvenile Boot Camp?
The teenage years are tough to get through for parents and teenagers alike. The natural instinct to rebel against parents is both good and bad. In some ways, the teenage years are the beginning of the time when juveniles begin to see themselves as separate adults from parents.
This is an important step in the psychology of a teenager because that separation must take place for your teenager to finally go out on his or her own and become an independent and self-sufficient adult. That “launching” of a child to become a successful adult is something all parents want to see their children achieve. The only way for that to happen is for them to navigate the stormy waters of the teenage rebellion years successfully.
The Teenage Years May Require A Parent to Take Drastic Actions
It is only somewhat comforting that all parents struggle with how to handle their teenagers successfully. But when your son or daughter show signs of becoming a troubled youth, that is when it is time to consider taking stronger action than the normal counseling and enforcement of rules that work for most parents. When a youth becomes “at-risk” or troubled, more drastic action is called for. One such action is to send your son or daughter to a juvenile boot camp.
It is tough for a parent to make that decision about whether things have gotten “bad enough” to consider sending your troubled adolescent to a teen boot camp. It helps to take advantage of the counseling that schools provide because professional psychologists who deal with teenagers will know when the dramatic environment of a juvenile boot camp is going to be the right thing to “jolt” your child back toward a more positive path through the teenage years.
Breaking the Law: When the Court Decides Your Teenagers Future
Of course, if your son or daughter has had problems with the law, the decision about whether to take advantage of a juvenile boot camp may be up to the courts rather than to mom and dad. In that case, you will do all you can to make the experience a good one for your child and comply with the orders of the court so that your troubled teenager can satisfy the judgment and get the most out of what a teen boot camp has to offer.
There are specific symptoms of psychological and behavior problems that would also be signals that something as drastic as a teen boot camp was in order.
Parent Intervention – Juvenile Boot Camps
Some signals that your young person is crossing over into that category of teen that would benefit from the intervention a teen boot camp are:
-
A hateful attitude toward parents, teachers and other authority figures.
-
A violent temper that may flare up at the least provocation.
-
Open defiance of rules of the house with an attitude of confrontation about pushing the rules as acceptable behavior.
-
Confrontations with authorities at school including skipping class, leaving campus and frequent counseling and time in detention.
-
Defiant clothing and body art.
-
Problems keeping genuine friendships resulting in association with other troubled youth.
-
Problems with drugs and other illegal activities.

-
An inability to accept responsibility or blame for wrong behavior or attitudes.
-
An unwillingness to communicate with parents or other authorities.
-
Very frequent depressions or mood swings toward anger and frustration.
Even if your teenager exhibits some or many of these characteristics, it is still smart to get some help to make the decision about whether a juvenile boot camp is the best way to correct the bad behavior. It is easy for parents to become so enraged with teenagers that you decide on a course of action that is too drastic for the teenager. Keep in mind that if you send your teenager to a juvenile boot camp, he or she may be mixing with much more troubled kids who have more extensive problems with drugs or breaking the law.
Also keep in mind that when you send a teenager to a boot camp setting, you are sending him or her a message that you are doing something dramatic to “fix’ the problem behavior.

That may feel like rejection by your teenager, which could set the tone for the entire time that he or she is in camp. Even if your teenager is successful at completing the curriculum at the juvenile boot camp, if he or she feels rejected by mom and dad, that can lead to the worst situation when the teenager gets home than before you sent the youth to camp.
Teen Boot Camp Options for Parents
Consider how your teenager has responded to more strict forms of authority so far. When you send your younger to a juvenile boot camp, the drill instructors will impose a very forceful form of discipline on the youth in their charge. Not only will their leadership style be confrontational and loud, but the demands of the camp will also be harsh and exhausting. In other words, your teenager is going to be worked to exhaustion every day. This kind of harsh training instills a new form of discipline and self-respect in a teenager that can send the youth home to you with an entirely new outlook on life.
Think through how your teenager responds to discipline and authority and whether the level of problem you are having with him or her warrants a dramatic intervention such as is used at a juvenile boot camp. If you do decide to use this method for correcting a troubled teen, talk with the boot camp psychologists and the counselors who work with your teenager as well to come up with the best way to introduce the concept to the youth. By handling the transition both into juvenile boot camp and then back to “civilian” life carefully, you can make sure that the good your teenager will get from his or her time at the camp will yield positive fruit in the teenager’s life both now and for many years to come.
Here are additional resources you might be interested in:
What are some of the benefits of juvenile boot camps?
Do Boot Camps for Teens Really Work?
For Parents | Florida Department of Juvenile Justice
Is your child acting out or making poor choices? Find health & safety tips, helpful community resources, legal aid information, youth programs and more.
Find Help Today! The Department of Juvenile Justice's Community Resource Guide will help you locate resources available to youth and families in your local communities such as youth programs, crisis centers, and substance abuse treatments center.
Health & Safety
- Is a child or loved one struggling with addiction or mental illness? Treatment 4 Addiction provides assistance with alcoholism, drug addictions, codependency, depression, and other difficult conditions. You can get assistance directly through them, or use their treatment locator to find assistance near you.
- The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration provides hotline information for a variety of trauma and abuse services.
- Find out if your child is eligible for affordable health insurance through Florida Kid Care.
- Parents may learn about, and apply for assistance from, Medicaid.
- Visit the Social Security website for information about Supplemental Security Income (SSI), Social Security assistance, how to apply for benefits.

- The Florida Child Care Food Program, funded by the US Department of Agriculture, creates partnerships with youth care programs to provide healthy meals and snacks to children in need.
- Find dedicated medical programs that assist children with special needs. You can get medical assistance, protection, family support, and other services through Children’s Medical Services.
- Teen dating violence is more common than many people realize. Find out about this type of abuse, and discover what you can do to help.
- Help protect your child, family, friends, and community by actively preventing sexual violence.
- Find information on Florida’s sex offender laws, registration requirements, offender searches, public safety, and victim information at the Florida Department of Law Enforcement website.
- The National Child Traumatic Services Network tells you where to find help for trauma and abuse.
- Florida Gang Reduction is an initiative of the Florida Attorney General's Office to reduce and deter gang-related crime and violence throughout the state of Florida.

- Find information on the dangers of abusing alcohol, illicit drugs, prescription drugs and more at the Addiction Center website.
- Drug Rehab provides parents and families an interactive guide for treating the victims of substance abuse. This website focuses on addiction, treatment, recovery and support.
Help Your Youth & Families
- The Department of Health and Human Services provides extensive information on general family services.
- Be an active part of helping your child succeed in education. The Florida Department of Education provides assistance for every level of education from Pre-K to college, as well as other information on disciplinary actions, independent education, testing, transportation, statistics, and more. Interested in more information about public schools? Check out http://www.publicschoolreview.com
- Great Schools shows you how to help your child succeed through every step of his or her education.
- Find out if you qualify for any of the Access Florida programs that provide assistance with food, cash, and medical needs.

- The Salvation Army offers social services that provide for basic human needs. They have various programs and levels of service; some offerings include food, clothing, shelter, childcare, medical assistance, counseling, job training, substance abuse treatment, and much more.
- For a list of homeless shelters that are available in Florida, visit the Homeless Shelter Directory.
- The Florida Homeless Coalition will link you resources that assist homeless families in locating housing, medical assistance, and legal aid.
- Help keep your child away from internet predators, cyber bullying, and other internet hazards by using internet best practices for parents, and encourage them to use best practices for kids.
- The Florida Department of Education has a number of resources for Bullying Prevention.
Hotlines & Other Help
- The Florida Department of Juvenile Justice (DJJ) wants to help. If you are concerned that your child is headed down the wrong path, call the toll-free DJJ Office of Youth and Family Advocacy Resource Helpline at 1-866-757-0634.
 Contact us before your child gets in trouble with law enforcement, and we will connect you to help available in your community.
Contact us before your child gets in trouble with law enforcement, and we will connect you to help available in your community. - Abuse and neglect are serious issues that need to be handled with care. In the event of an emergency abuse situation, ALWAYS call 911 FIRST and call the Florida Abuse Hotline second at 1-800-962-2873. In a non-emergency situation, contact the Florida Abuse Hotline via phone, fax, or web to receive assistance.
- To report a child who has run away, or if you are a runaway who needs help, contact the Florida Runaway Hotline at 1-800-621-4000 or call the National Runaway Switchboard at 1-800-RUNAWAY.
- Human trafficking is the exploitation of men and women, adults and children, foreign nationals and United States citizens for financial gain, and is criminalized under Florida, federal, and international law. Child victims of human trafficking are commonly exploited by involvement in the commercial sex trade or by participation in various abusive labor situations, such as forced domestic servitude, agricultural work, or traveling sales crews.
 Learn more about human trafficking here [insert link for DJJ HT page https://www.djj.state.fl.us/human-trafficking-intervention. To report potential trafficking of a child, call the Florida Child Abuse Hotline at 1-800-96-ABUSE (1-800-962-2873) and your local law enforcement agency. For resources related to potential trafficking of an adult, contact local law enforcement or the National Human Trafficking Resource Center Hotline at 1-888-3737-888.
Learn more about human trafficking here [insert link for DJJ HT page https://www.djj.state.fl.us/human-trafficking-intervention. To report potential trafficking of a child, call the Florida Child Abuse Hotline at 1-800-96-ABUSE (1-800-962-2873) and your local law enforcement agency. For resources related to potential trafficking of an adult, contact local law enforcement or the National Human Trafficking Resource Center Hotline at 1-888-3737-888. - The Central Communications Center (CCC) provides a complaint hotline for citizens and staff to report incidents related to a facility or program operated by the DJJ. Report a complaint/incident by calling 1-800-355-2280.
Legal Guidance
- Even if you can’t afford a lawyer, you can still receive assistance through Florida Legal Aid.
- The Florida Bar Association lawyer referral service can provide names and phone numbers of lawyers in your area who handle specific types of legal issues.
Youth Programs
- The Florida Network of Youth and Family Services, Inc.
 is a statewide association that can provide crisis counseling, parenting information, respite services, and referrals to other sources that serve homeless, runaway, and troubled youth ages ten and older.
is a statewide association that can provide crisis counseling, parenting information, respite services, and referrals to other sources that serve homeless, runaway, and troubled youth ages ten and older. - Children In Need of Services/ Families In Need of Services (CINS/ FINS) provides assistance and professional counseling services for youth, and their families, who are troubled or who just need additional support and mentoring.
- Join the national initiative to Stop Bullying! Find out about warning signs, how to get help, the risk factors, and other helpful information for families.
- Florida’s Children First assists youth in foster care through referrals to community resources and support systems that help meet their special needs and teach them valuable life skills.
- The Department of Juvenile Justice supports other delinquency prevention programs that provide tutoring, mentoring, life skills training, teen courts, temporary shelters, and other means of preventing youth from travelling down the wrong path.

experience of helping a single colony
The informal movement AUE (“The prisoner way of life is one” or “The prisoner-Urkagan unity”) promotes life “according to thieves' concepts”. It is active in social networks and is developing in a number of regions.
The Russian Children's Fund has been drawing attention to the problems of child and juvenile delinquency for more than 20 years, proving that prohibitive measures without rehabilitation work and socialization of prisoners are ineffective. To change the correctional system for children, the Children's Eyes Behind Bars program was created. Officially, the year 2000 is considered the start of its operation in the regions, when the chairman of the Russian Children's Fund, Albert Likhanov, together with the wife of the President of Russia, Lyudmila Putina, and the Deputy Prime Minister of the Russian Federation, Valentina Matvienko, visited the orphanage of the Mozhaisk women's colony. But the work of the Russian Children's Fund with juvenile delinquents began long before that. nine0003
nine0003
By 2017, the experiment had virtually ceased in many regions. But in a single Kamyshin colony in the Volgograd region, largely thanks to the support of its leadership and local authorities, it was possible to create a precedent - to radically transform the existing system. How, why and at the expense of what this happens - in the material of the correspondent of the Agency for Social Information.
punishment cell for misconduct
— In 1996, we went to the Kamyshin correctional colony together with Galina Karman, a journalist from the Gorodskie Vesti newspaper, she almost lost consciousness when she saw the children who were in the punishment cell for misconduct, they were terribly thin, exhausted , were kept literally on water and bread, - recalls the chairman of the Volgograd branch of the Russian Children's Fund Raisa Skrynnikova . We raised a cry: let these children out immediately! They quickly found a doctor who could help them. After checking the menu, it turned out that the inmates of the colony had not eaten meat for a long time, the diet lacked bread, milk and sugar.
This was the situation in the mid-90s in most correctional institutions in the region: in the absence of their own production, orders and earnings, only the budget remained, which did not allow for normal conditions for prisoners. At that moment, more than 400 teenagers were kept in the Kamyshinskaya educational colony. nine0003
Raisa Skrynnikova appeared on local television and asked concerned citizens to help the inmates of the colony. Several small businesses have responded to her call. Juvenile prisoners were taken food, furniture, bed linen, one of the firms of the Krasnoarmeysky district sent a dump truck of meat to the colony.
Speeches in the media took place regularly, with the help of journalists, social activists attracted volunteers who were ready to help prisoners and their needy relatives. nine0003
— Until now, before my eyes, thin Vanya from Volzhsky (name changed. - Note ed. ), - says Raisa Skrynnikova. - Now he has already served in the army, works at a pipe factory, is married and has a child. He was given two years in prison, in fact, because there was nothing to feed his bedridden mother and younger sister. Late in the evening, he went to the nearest kiosk and asked the seller for bread, explaining the situation, the woman refused. He cried and persuaded, but when he realized that everything was useless, he threatened the seller with a folding button knife. The knife opened and hit the heart, the woman did not die, but the boy was given a term. nine0003
- Now he has already served in the army, works at a pipe factory, is married and has a child. He was given two years in prison, in fact, because there was nothing to feed his bedridden mother and younger sister. Late in the evening, he went to the nearest kiosk and asked the seller for bread, explaining the situation, the woman refused. He cried and persuaded, but when he realized that everything was useless, he threatened the seller with a folding button knife. The knife opened and hit the heart, the woman did not die, but the boy was given a term. nine0003
In a face-to-face conversation with employees of the children's fund, the teenager asked to find his mother and sister and buy them milk and bread, promising to return all the money when he was free. Volunteers of the children's fund took care of the woman, helped to identify the girl in kindergarten and agreed with the neighbors so that they could take and pick her up.
Subsistence farm and rock opera "The Little Prince"
Since 2000, the program "Children's Eyes Behind Bars" has received support from the executive branch. The governor of the Volgograd region, Nikolai Maksyuta, established a board of trustees at the colony, the work of which was coordinated by the deputy head of the region. A vocational school was opened in the colony, equipment for the production of pasta appeared, a sewing workshop was opened, they began to plant grain, planted melons, and started breeding cows, pigs and poultry. nine0003 Photo: official website of the Federal Penitentiary Service for the Volgograd Region
The governor of the Volgograd region, Nikolai Maksyuta, established a board of trustees at the colony, the work of which was coordinated by the deputy head of the region. A vocational school was opened in the colony, equipment for the production of pasta appeared, a sewing workshop was opened, they began to plant grain, planted melons, and started breeding cows, pigs and poultry. nine0003 Photo: official website of the Federal Penitentiary Service for the Volgograd Region
When the living conditions and nutrition of adolescents improved, the need to maintain a large subsidiary farm disappeared. Today, in the greenhouses and gardens of the colony, vegetables and fruits are grown for the table of the wards and for sale. From the production there was a workshop for sewing bed linen for the institutions of the Federal Penitentiary Service.
During the years of active development of the program from 2000 to 2005, employees of the children's fund organized regular consultations with psychologists and lawyers for the pupils, visited them on holidays with gifts, brought stationery and sweets. Children's and youth groups from Kamyshin and Volgograd performed with concerts, creative circles were opened for pupils. nine0003 Photo: Russian Children's Fund
Children's and youth groups from Kamyshin and Volgograd performed with concerts, creative circles were opened for pupils. nine0003 Photo: Russian Children's Fund
For the final of the "Teacher of the Year" competition, which was held among the schools of Russian educational colonies, the children staged the rock opera "The Little Prince," recalls Colonel of the Internal Service Igor Burov, who headed the Kamyshinskaya educational colony until the recent release on retire. - And when the representatives of 11 participating regions at the end of the performance said: "Are you showing us artists here?" Family". nine0003
With the assistance of the regional branch of the Russian Children's Fund and the mayor of Volzhsky Igor Voronin, a chapel in honor of the faithful Tsarevich Dimitry of Uglich, to whom mothers pray for their children, appeared on the territory of the colony.
Photo: official website of the Federal Penitentiary Service for the Volgograd RegionA chance for a different life
According to the children's fund, the Children's Eyes Behind Bars program helped prevent 70-80% of the inmates of the Kamyshinskaya colony from returning to places of deprivation of liberty.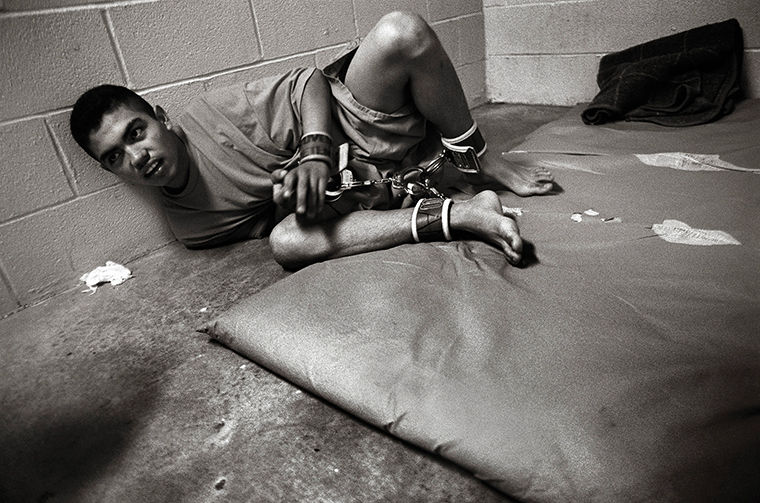 The correctional facility believes that this is a rather conditional indicator - it is almost impossible to track the fate of the wards in adulthood if they themselves do not get in touch after their release. And most often those who managed to successfully settle down in life strive to remind themselves of themselves, says Igor Burov:
The correctional facility believes that this is a rather conditional indicator - it is almost impossible to track the fate of the wards in adulthood if they themselves do not get in touch after their release. And most often those who managed to successfully settle down in life strive to remind themselves of themselves, says Igor Burov:
- One of the former prisoners - a guy from Volzhsky - served six years, after his release his father helped him open his own business, now he has two jewelry departments in Volgograd. After his release, he received an economic education, firmly stood on his feet, recently visited me to share his plans - he is going to open an agricultural company together with a Saratov entrepreneur - to trade in greenery.
Photo: official website of the Federal Penitentiary Service for the Volgograd Region Another pupil, whose fate subsequently turned out well, ended up in a colony from another region. After his release, he remained in Kamyshin, the curators of the Children's Eyes Behind Bars program helped him get a room in a hostel. The young man was fond of playing the guitar, created his own group and worked in a local house of culture. Then he took up a career as an official, first became an adviser, and now he holds a position in the district administration. Today he actively helps the colony, comes with concerts on holidays. The management is modestly silent about the fact that the distinguished guest in the past was a pupil of a correctional institution. nine0003
The young man was fond of playing the guitar, created his own group and worked in a local house of culture. Then he took up a career as an official, first became an adviser, and now he holds a position in the district administration. Today he actively helps the colony, comes with concerts on holidays. The management is modestly silent about the fact that the distinguished guest in the past was a pupil of a correctional institution. nine0003
Another former prisoner of the Kamyshinsk educational colony runs a construction company in Lipetsk and is considering moving to the Altai Territory, where he can get a large order for the construction of hotels.
Breaking out of the criminal environment
One of the biggest problems in the release of pupils in the late 90s was the control by senior representatives of the criminal community - they guarded the next "graduates" at the checkpoint in cars. Then, at the request of the children's fund, the committee for youth affairs of the regional administration introduced the staff of a specialist who supervised teenagers leaving the colony. He had to know the expiration date of each pupil, help with employment or continuation of studies, registration with the commission on juvenile affairs. nine0003 Photo: official website of the Federal Penitentiary Service for the Trans-Baikal Territory
He had to know the expiration date of each pupil, help with employment or continuation of studies, registration with the commission on juvenile affairs. nine0003 Photo: official website of the Federal Penitentiary Service for the Trans-Baikal Territory
Children were often personally picked up from the colony and brought home by administration officials. But even such guardianship did not guarantee that the teenagers would not go to jail again. As in the case of two brothers who were released ahead of schedule, whose escort was taken over by one of the local officials. The administration worker took care of the basic necessities for teenagers - he bought them sneakers, sports suits, phones. A week later, one of the brothers committed a serious crime and again sat down for several years. The second, having the specialty of a plasterer-tiler, received at a vocational school at the colony, began to earn money with repairs, and a few years later he opened his own construction and finishing company. nine0003
nine0003
Trustees - who?
The effectiveness of the program "Children's Eyes Behind Bars" has always directly depended on the activity of the head of the board of trustees, whose duties until recently were assigned to the deputy head of the region.
— During the period when the program was created, the Board of Trustees was headed by Vice Governor Galina Khorosheva, she had a lot of experience working with children, — recalls Igor Burov. - Together with Raisa Skrynnikova, it was an excellent tandem, which provided assistance in matters of spiritual education and financial support. Regular meetings were held with the participation of the heads of large enterprises who were ready to donate funds for specific needs. nine0003
Today, the chairman of the board of trustees is the head of the Volgograd regional branch of the Russian Charity and Health Foundation Irina Rokotyanskaya, also includes: the commissioner for children's rights in the Volgograd region and the head of the regional branch of the Russian Children's Fund, the chief director of the Kamyshin Drama Theater, representatives of the city center "Family" and job center.
What is happening today
Throughout all the years, the Children's Eyes Behind Bars program has acted as a charity, without receiving support from the federal and local budgets. In recent years, the circle of people interested in the rehabilitation of adolescents behind bars in the Volgograd region has noticeably narrowed, and the requirements for sponsorship have become more stringent. Volunteers of the Children's Fund and the Office of the Ombudsman for Children go to teenagers on average once a quarter, bring psychologists, legal consultants, and arrange meetings with parents. Today, the program is based mainly on the activity of the board of trustees and personal contacts of the colony's leadership, developed in previous years. nine0003 Photo: official website of the Federal Penitentiary Service for the Volgograd Region
The Kamyshin educational colony ranks third in the all-Russian rating. After the recent reform of the FSIN system, as a result of which the number of educational colonies for minors was reduced from 62 to 23, the quality of the conditions of detention of inmates has noticeably improved. 70 teenagers are currently serving sentences in Kamyshin. How safely they will be able to return to society after release depends not only on the level of material support and organization of leisure in the colony. nine0003
After the recent reform of the FSIN system, as a result of which the number of educational colonies for minors was reduced from 62 to 23, the quality of the conditions of detention of inmates has noticeably improved. 70 teenagers are currently serving sentences in Kamyshin. How safely they will be able to return to society after release depends not only on the level of material support and organization of leisure in the colony. nine0003
“The most valuable thing is attention to the spiritual state of children,” says Igor Burov. “The interest of those who personally faced a similar problem is especially visible. In the colony, in turn, they are always happy to cooperate with specialists, teachers who know the psychology of adolescents and the characteristics of deviant behavior. Well, if we solve the problem systematically at the state level, then we need to seriously analyze where it all comes from and prevent negative trends even at the school level. nine0003
You can be sent to prison from the age of 12
Now in Russia you can be sent to a colony for serious crimes from the age of 14. The number of crimes for which it is supposed to judge from the age of 12 will include murder, kidnapping, hostage-taking, rape, writes "RG".
The number of crimes for which it is supposed to judge from the age of 12 will include murder, kidnapping, hostage-taking, rape, writes "RG".
In the Novgorod village of Lychkovo, a boy, who was given the nickname Dwarf, kept adults and children in fear for several years. At first he hung dogs. Then he killed a five-year-old child, Vanya Volkov, who was trying to protect his puppy. The juvenile murderer could not be judged. And briefly sent to a local hospital. Returning home, the Dwarf raped his 7-year-old niece. Then he kicked a fallen rural alcoholic. Then he locked the women sellers in the shop and set it on fire. They were saved by chance. nine0003
More than 300,000 juvenile crimes are recorded in Russia every year. A third is committed by children under 14
This is a wild, but not the only fact. Official statistics say that juvenile delinquency is falling. But the cruelty of their crimes grows proportionately. In Russia, more than 300,000 crimes committed by teenagers are recorded every year. A third are committed by children under 14 years of age. Child cruelty is dangerous for others and for the teenage environment itself. nine0003
A third are committed by children under 14 years of age. Child cruelty is dangerous for others and for the teenage environment itself. nine0003
From the age of 12, the Investigative Committee and the Ministry of Internal Affairs advocate for prosecution. Against - Commissioner for Children's Rights Pavel Astakhov. He says that we need to look for the origins of the cruelty of children.
In the West, this issue has been resolved in principle long ago.
The most stringent "child" legislation in India, Ireland and Singapore. In these countries, people are imprisoned from the age of seven. In the United States, Australia, Great Britain and Switzerland, criminal liability begins at the age of ten. So, in the state of Pennsylvania, the court gave life to an 11-year-old who shot a pregnant woman. nine0003
Psychologists say that in a family where cruelty is a part of everyday life, a kind person is unlikely to grow up. The situation in the family gives rise to an evil attitude towards the world in the child, and cruelty is a way to avenge insults and humiliations.
You don't have to be an expert to see that the number of stories about violence on television, in movies and in the press is constantly growing. It is not easy for an adult to cope with such a flow of negative information, not to mention a child.
The draft law on bringing to criminal liability children from 12 years of age for committing certain types of grave and especially grave crimes was developed two years ago. State Duma in 2009rejected it for a year.
We have already lowered the age of responsibility to 12 years. There was a resolution of the Central Executive Committee and the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR of April 7, 1935. It stated that minors, starting from the age of 12, convicted of theft, violence, bodily injury, mutilation, murder, should be brought to justice. On December 10, 1940, the list of these crimes was supplemented with actions that could cause a train crash.
In 1941, the age of criminal responsibility for all other crimes was set at 14.