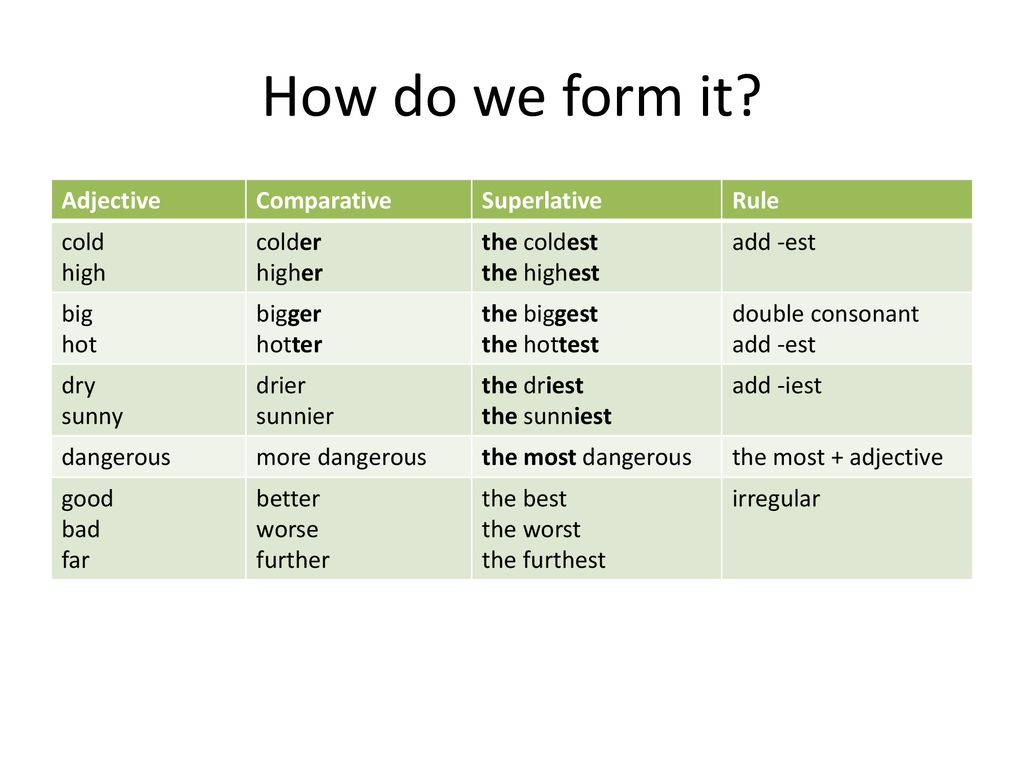
Managing pain during labor naturally
Non-medical pain relief during labour
Non-medical pain relief during labour | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content6-minute read
Listen
Key facts
- There are many non-medical methods you can use to help relieve pain and discomfort during labour and birth.
- Staying active during labour may help you manage any pain you experience and help your labour progress.
- A support person you trust can help provide practical and emotional support.
- Some techniques are not suitable for everyone and should only be administered by qualified health professionals.
- Ask your hospital or birth centre about which pain relief techniques they can provide.
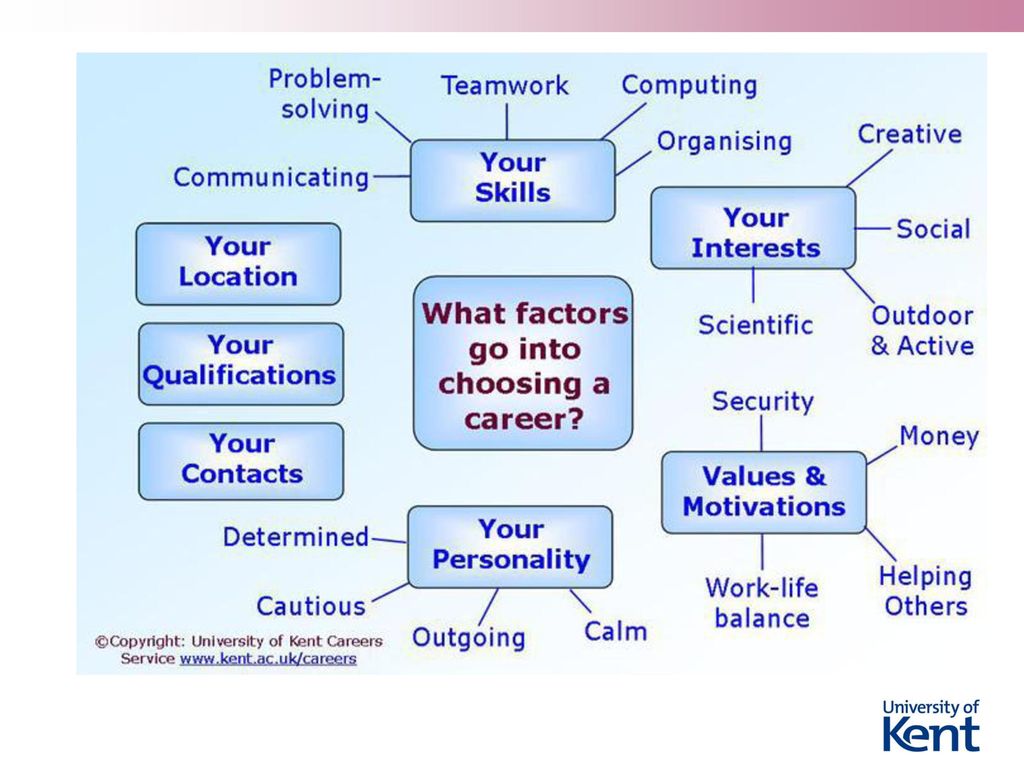
What non-medical pain relief options can I access during labour?
Active birth is when you choose to move your body in different positions during labour.
There are many non-medical pain-relief options for you to try when you are in labour. These include being active during labour, applying massage or heat packs, immersing in water, relaxation techniques, self-hypnosis, aromatherapy, acupuncture, and others. Read on to learn more.
Active birth
Staying active is one of the most helpful things you can do to manage the pain of labour and birth. Moving freely and rocking your pelvis can help you to cope with the contractions. Staying upright also allows gravity to help move your baby down into your pelvis.
Support person
Although you will have a midwife looking after you during labour, it is important to have another support person with you. This may be your partner, a close friend or family member or a paid support person such as a doula. Some people choose to have more than one support person, but it’s a good idea to limit the number of people present.
Your support person can provide practical support with the non-medical pain relief techniques described below (for example, massage). They may also help by providing emotional support and encouragement.
They may also help by providing emotional support and encouragement.
Having continuous support from someone you trust can help you cope better in labour. It also may reduce your need for medical pain relief and reduce the chance that you will need an assisted delivery.
Massage and heat
Massage and hot packs can ease your pain in labour. Massage helps distract you from the pain. Heat packs can help your body release its natural painkillers (endorphins).
Sometimes, massage during labour will feel good, but at other times, you may find it irritating. It’s a good idea to discuss this with your support person before labour.
Water immersion
Most hospitals and birthing centres will have facilities that allow you to have a bath or shower during the first stage of labour.
You may find that being in a warm bath is relaxing and helps you cope with the contractions. A shower can also help with back pain.
Having a bath or shower to ease pain during labour is not the same as having a water birth. Not all hospitals are equipped for water birth. Your midwife and doctor need to be specially trained and they need to be able to get you out quickly if there is a problem with the birth.
Not all hospitals are equipped for water birth. Your midwife and doctor need to be specially trained and they need to be able to get you out quickly if there is a problem with the birth.
Check with your hospital in advance to see if this option is available to you.
Relaxation
You can use different relaxation techniques to ease pain such as music or meditation. Relaxation techniques can help ease pain in labour.
Self-hypnosis
Practising self-hypnosis during pregnancy may help reduce fear and/or anxiety about labour and birth. There is not enough evidence to understand if self-hypnosis (also known as ‘hypnobirthing’) can reduce the need for other pain relief during labour, but you can try it and see if it helps you.
Aromatherapy
Essential oils can be used with massage or heated over a burner. There is no evidence aromatherapy provides pain relief, but some people find it pleasant. If you're thinking of using aromatherapy, check that your hospital or birth centre allows it.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture may reduce pain in labour. There are no known side effects of acupuncture for you or your baby.
Only a trained person should perform acupuncture. Not all hospitals have an acupuncture therapist on staff, so you may need to discuss arranging your own practitioner.
TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation)
A TENS machine uses two electrodes stuck to your skin. They are usually attached to your lower back. The machine sends a small electric current through your body. It is generally safe for mother and baby.
There is not a lot of evidence to show TENS reduces pain, but some people find it helpful. TENS has no known side effects for you or your baby.
A TENS machine is not suitable for everyone. People with a pacemaker should not use one, and you shouldn’t use TENS before 37 weeks gestation.
TENS can't be used in the shower or in water. Not all hospitals or birth centres have them, so if you’re interested in using TENS, it’s a good idea to check with your health team in advance.
Sterile water injections
Sterile water with no medicine in it can be injected by your midwife under the skin of your lower back to relieve lower back pain. It is not clear how they work, or whether they work very often. You may still need other pain relief.
The injections may sting but there are no known side effects for you or your baby. Not all hospitals or birthing centres will offer this service.
Resources and support
Read more on making a birth plan.
Ask your doctor or midwife about non-medical pain relief during labour, or visit one of the following orgnsiations:
- Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists & Faculty of Pain Medicine
- Royal Australian and new Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
- South Australian Women’s and Children’s Hospital
- The Women’s — The Royal Women’s Hospital, Victoria
Sources:
RANZCOG (Pain Relief in Labour and Childbirth), Cochrane (Pain management for women in labour - an overview), King Edward Memorial Hospital Obstetrics & Gynaecology (Clinical practice guideline, Pain management), Royal Women's Hospital (Managing pain in labour), The Royal Women's Hospital (Active birth), The Royal Women's Hospital (Water birth at the women's), Cochrane Library (Perceptions and experiences of labour companionship), Cochrane Review (Continuous support for women during childbirth), British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (Self-hypnosis for intrapartum pain management in pregnant nulliparous women: a randomised controlled trial of clinical effectiveness), Cochrane Library (Acupuncture or acupressure for pain management during labour (Review)), NSW Government (Fact Sheet Active Birth)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: July 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Epidural
- TENS (Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation)
- Gas (Entonox)
- Pain relief during labour
- Making a birth plan
- Giving birth - stages of labour
Need more information?
Pain relief during labour
Learn what options are available to you to relieve pain during labour pain, and how your birth support partner can help you.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pain Relief in Labour and Childbirth
Read more on RANZCOG - Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists website
Pain relief during labour | Raising Children Network
Pain relief in labour includes natural options like massage, as well as medical options. It’s best to discuss options with a midwife or doctor in pregnancy.
It’s best to discuss options with a midwife or doctor in pregnancy.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Giving birth - second stage of labour
The second stage of labour is when you give birth to your baby.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
ANZCA | Pain relief and having a baby
Labour is among the most painful human experiences.
Read more on ANZCA – Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists website
Childbirth - pain relief options - Better Health Channel
Understanding your pain relief options can help you cope better with the pain of childbirth.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Gas (Entonox)
Gas or Entonox is nitrous oxide mixed with oxygen. Gas can help with pain relief, and it is safe for you and your baby.
Gas can help with pain relief, and it is safe for you and your baby.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
TENS (Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation)
TENS machine delivers a small electrical current to the body through electrodes attached to the skin. TENS, is a form of pain relief without medicine.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Epidurals for childbirth
An epidural can be used to relieve pain during child birth and is very safe. Your anaesthetist will discuss pain relief options with you as part of your antenatal care.
Read more on WA Health website
Caesarean Section - Birth Trauma
Being abdominal surgery, pain in the early months is very common after a caesarean section (C-section) and needs to be managed with rest, pain relief, and
Read more on Australasian Birth Trauma Association website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Natural Pain Management Techniques for Childbirth
We have all heard the stories about how incredibly painful it is to give birth, but that hasn’t stopped a large number of women in recent years from deciding on a more holistic approach to the process.
At Dedicated to Women ObGyn, we fully support a patient’s decision to do what is right for their body. We also want to provide as much education and information about these methods, and when they may no longer be a safe option to pursue. No matter what you decide, our OBGYN providers are here to help educate all expecting mothers about their options when it comes to pain management during childbirth.
Natural Labor Pain Relief Techniques
For women looking to achieve a completely natural labor and delivery, there are several options when it comes to effective pain relief. These techniques are best for those who are able to safely complete a natural birth without a high risk for potential health complications of mom and/or baby.
Stay Active
Many moms can find it difficult to lie in a hospital bed as soon as their labor starts all the way until their child is born. Getting up to walk around the room can help to not only distract from painful contractions, but can also assist during the delivery by letting gravity take its natural effect on the baby and pull it gently downward. Utilization of a birthing ball, rocking chair, or other strategic positioning can also be encouraging for the birthing process.
Breathing Exercises
This particular tip may seem rather minor, but it can have a huge impact on the relaxation of the body during delivery. Deep breathing techniques help to not only focus the mind, but also to cause a bodily response to loosen tension within the patient’s muscles.
Deep breathing techniques help to not only focus the mind, but also to cause a bodily response to loosen tension within the patient’s muscles.
Massage and Reflexology
Massage may also be used to help a woman relax her muscles during childbirth. There is often a significant degree of variation between the massage methods used and how beneficial they are for the individual using them, so be sure to try out a few to find which is best for you.
Reflexology is a particular process used to strategically apply pressure to specific areas of the body. The primary focus of reflexology is the individual’s feet and how the nerve endings located in the feet can be manipulated to relieve tension and reduce pain.
TENS Device
Another common solution to naturally relieve labor pains is to implement the use of a Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) unit toward the beginning of the delivery. This device is meant to inhibit pain signals as they travel toward the brain. Stimulations from the TENS unit can be increased along with the woman’s pain level so that it remains consistent in its ability to relieve discomfort from her contractions.
Stimulations from the TENS unit can be increased along with the woman’s pain level so that it remains consistent in its ability to relieve discomfort from her contractions.
Other Natural Pain Management Methods
There are of course several other approaches that individuals can take when trying to manage their pain during labor and delivery. In addition to those mentioned above, the following are other common pain relief practices that may be used during childbirth:
- Bathing or remaining partially submerged in water
- Acupuncture
- Music therapy
- Having your partner as a birthing coach (the Bradley Method)
- Aromatherapy
Knowing the Risks of Natural Childbirth
While natural births have certainly grown in popularity, they are still not a suitable option for every single expectant mother. Obstetric anesthetics are often used to relieve pain during delivery, along with other modern medicines and techniques to keep both mom and baby safe throughout the birthing process.
Women involved in a high-risk pregnancy are often not encouraged to attempt a natural birth. Pregnancies are typically categorized as being high-risk if the mother has a known medical condition that may interfere with the development or birth of the fetus, such as diabetes, a thyroid disorder, uterine fibroids, and more. Dedicated to Women ObGyn will be able to diagnose and routinely monitor these types of existing conditions all throughout the length of a woman’s pregnancy to help avoid any severe outcomes.
There are also a number of complications that can arise while a woman is in labor, making it critical for her to receive additional medical treatment and care in order to safely deliver her baby. These common labor complications include:
- Malposition
- Fetal distress
- Uterine rupture
- Perinatal asphyxia
- Excessive bleeding
- Failure to progress
- Shoulder dystocia
- Placenta previa
- Cephalopelvic disproportion
To learn more about the safety of your pregnancy and the potential of a natural delivery, please contact Dedicated to Women ObGyn to schedule a consultation with one of our specialists today!
As always if you have any further questions, please call Dedicated to Women ObGyn at (302) 674-0223 today!
Methods of natural pain relief in childbirth | State Budgetary Institution RO “OCSOS and R”
Every woman who is waiting for the birth of her baby, along with bright, joyful experiences, experiences fear. Fear of the unknown, fear of pain during childbirth. How strong will this pain be, how long will it last, is it possible to endure it. And she is also possessed by approximately such thoughts: how I will look and how I will behave, whether I will fall into hysterics, whether I will swear at the medical staff. nine0003
Fear of the unknown, fear of pain during childbirth. How strong will this pain be, how long will it last, is it possible to endure it. And she is also possessed by approximately such thoughts: how I will look and how I will behave, whether I will fall into hysterics, whether I will swear at the medical staff. nine0003
In response to these fears and worries, very effective methods of pain relief have emerged in obstetric practice in recent years. The most popular of these is epidural anesthesia , which completely relieves pain during the first stage of labor (the period when the cervix opens, often long and painful). And at the same time, there are many doctors and women in labor who believe that the process of childbirth should proceed as naturally as possible, and pain, since it is conceived by nature, has the right to exist. nine0003
To sort out these conflicting views, let's look at the scientific research on what pain is and what influences pain tolerance.
Today, there are a number of studies in medical science on pain and how people experience pain in different circumstances, what affects pain tolerance and how this can be used in medical practice.
To investigate this issue, scientists turned to the experience of people who not only do not avoid pain in their lives, but, on the contrary, deliberately seek it. These were people involved in oriental martial arts, representatives of some religious movements, people striving for an ascetic lifestyle. nine0003
By investigating extraordinary cases of pain immunity in these people, scientists have deduced some patterns of pain management.
Thus, the intensity of pain depends on the following factors:
The purpose for which pain is experienced.
Pain is much easier to experience if the goal is self-improvement or the religious idea of saving the soul. Scientists believe that labor pain also has a great positive force, since its purpose is the birth of a child, unlike, for example, the pain experienced by a seriously ill person. Thus, it is very important what the thoughts of a person experiencing severe pain are directed to - whether he expects, as a result of personal spiritual growth, the birth of a new life, or, on the contrary, his own death. nine0005 Based on this, it can be assumed that experiencing labor pain is much more difficult for those women who experience fear of their own death or loss of a child during childbirth.
Thus, it is very important what the thoughts of a person experiencing severe pain are directed to - whether he expects, as a result of personal spiritual growth, the birth of a new life, or, on the contrary, his own death. nine0005 Based on this, it can be assumed that experiencing labor pain is much more difficult for those women who experience fear of their own death or loss of a child during childbirth.
The intensity of pain is affected by the environment.
For example, if it is pain that a person forces himself to for the sake of religious beliefs, it is much easier for him to experience this pain in the presence of other believers who empathize with him and believe that this pain is necessary for the implementation of a high goal. So and during the birth of a child, surrounded by close people, it is much easier for a woman in labor to experience pain, because close people empathize with her and share her condition.
In Africa and Brazil, the ‘sledgehammer phenomenon’ is widely known: when the time comes for a woman to give birth, a man goes to bed, screams and complains. Ethnologists have found that this relieves a significant part of the mental and even physical stress of the woman in labor, and childbirth is easier.
Ethnologists have found that this relieves a significant part of the mental and even physical stress of the woman in labor, and childbirth is easier.
The degree of pain sensation depends on the state of consciousness of the person. nine0003
Pain is much easier to bear when a person is not completely immersed in it, but is in a state of trance, meditation or prayer. It is known that women who are able to pray during childbirth experience them more easily.
Another factor influencing the experience of pain is the psychological readiness for its onset.
In other words, unexpected pain is always experienced as more intense. Some people - for example, martial artists - are able to change their physiological state before exposure to pain factors - their blood pressure rises in advance and their pulse quickens, and at the moment of a strong blow to the pain point, the pressure increased by this moment begins to decrease, and not jump sharply , as happens in case of an unexpected blow. nine0003
nine0003
Women who prepare themselves for pain in advance and study various methods of pain relief on special crucibles are also in an advantageous position during labor pain. And even if they do not have to put their knowledge into practice, the very confidence that they are ready and know how to behave during childbirth greatly relieves the pain. And vice versa, the most painful, painful memories of childbirth remain with women who turned out to be completely unprepared for them.
There are countries, and these are by no means third world countries, where women give birth in conditions close to natural, for example, Holland, where childbirth is fundamentally not anesthetized, and epidural anesthesia is used only in case of caesarean section. And this does not mean at all that a woman is forced to suffer - no, they simply create certain conditions for her: the atmosphere of the birth is close to home, the presence of close people of the woman in labor is encouraged, the midwife who observed the woman during childbirth can be present and take part in them. pregnancy, which means that a woman trusts. In addition, the woman in labor is encouraged to use natural methods of anesthesia (breathing and voice techniques, relaxation method), water is widely used for the same purposes (showers, baths, pools). nine0003
pregnancy, which means that a woman trusts. In addition, the woman in labor is encouraged to use natural methods of anesthesia (breathing and voice techniques, relaxation method), water is widely used for the same purposes (showers, baths, pools). nine0003
As for Russia (including Novosibirsk), today a different approach to anesthesia is very common: for a certain amount, a woman in labor can receive epidural anesthesia in any maternity hospital.
If a woman wants to give birth naturally, she needs to take care in advance, during pregnancy, sign up for courses where she (and her husband) will be taught natural methods of pain relief. Unfortunately, now it is not necessary to expect that a midwife or a doctor in the maternity hospital will give a woman an anesthetic massage or breathe with her during labor, so the presence of a husband or other close person (mother, sister or close friend) at the birth is becoming more and more relevant. The fact is that even the most prepared woman in a stressful situation can forget everything that she studied during pregnancy, and in this case, a loved one who was preparing for childbirth with her will help her remember what she needed. nine0003
nine0003
What methods of natural (non-drug) pain relief are offered to a woman in labor today?
Relaxation.
This method was proposed back in the thirties of the last century by the famous English obstetrician Grantley Dick-Read. G. Dick-Read's wife, Jessica, helped bring the idea of painless, natural childbirth to life by organizing prenatal classes where expectant mothers could prepare for childbirth in small groups. One of the main skills taught in these courses was the relaxation technique, because, according to Dick-Read, relaxation is the key to calmness in childbirth. nine0003
Relaxation is a state of the body when the muscle tone of the whole body is reduced to a minimum. The ability of a woman to relax during contractions renders her an invaluable service, because the pain always increases with tension and decreases significantly with a decrease in muscle tone.
There are many different ways to relax, which you can learn about in courses or in specialist literature. A description of the method used by Dick-Read himself is in his book Childbirth Without Fear. nine0003
A description of the method used by Dick-Read himself is in his book Childbirth Without Fear. nine0003
Respiratory methods of anesthesia.
In principle, all breathing practices used in childbirth lead to the same decrease in muscle tone, to relaxation.
The first method of pain relief offers to train the ability to breathe slowly. So, if a person normally takes 16 breaths and exhalations per minute, women are invited to learn how to do only 8 breaths and exhalations, and the breaths should be small and the exhalations should be long. During childbirth, a woman will breathe like this only during the contraction, after it ends - normal breathing. nine0003
The second method of anesthesia suggests the following: imagine that you have a feather in front of your lips, and you need to make a series of short exhalations with such force that the feather does not fly away. After exhaling, you take a small breath and repeat the series again (it can be 4, 6 or 8 exhalations). This breathing also helps to stay relaxed during the fight and not focus on the pain.
This breathing also helps to stay relaxed during the fight and not focus on the pain.
The third method of pain relief is suitable for well-trained women - it suggests not breathing at all during the contraction, and after it is over, go to normal breathing. nine0003
Voice practices.
These practices are usually taught in pregnancy courses. If we try to describe this method in words, then we can say that a woman is invited to sing her pain, sending a sound to the place of its greatest concentration. The sound should be long, on the exhale, while singing, you do not need to inhale often. I would like to note that singing pain has nothing to do with cries for help.
Pain relief massage.
Acupressure or general massage of the sacrum, buttocks and thighs often relieves pain. nine0003
Anesthesia with warm water.
It is very good if during the contractions a woman will have the opportunity to spend some time in a warm bath, or at least stand or sit under the shower, directing a jet of warm water to the sacrum during the contraction. The necessary conditions for this have already been created in many Russian maternity hospitals.
The necessary conditions for this have already been created in many Russian maternity hospitals.
Trance techniques.
A number of experts believe that a woman does not need to relax or breathe in a special way, but during a contraction she needs to concentrate on certain images that contribute to the connection between her and her child in a single birth process. For example, a woman is invited to imagine the cervix as a thousand-petalled bud and during each contraction, open this flower one petal at a time. Another trance technique invites a woman in labor to imagine herself emerging from a very deep lake with a baby in her arms during a fight. Specialists who prepare women for such childbirth note significant pain relief. nine0003
In conclusion, I would like to wish every woman who is about to give birth to a child to make her choice regarding labor pain in advance. But even if before childbirth you decided to give birth naturally, and during them you encountered unbearable pain, use medical methods, and vice versa, if you have definitely decided that you will give birth under epidural anesthesia, give yourself at least a little experience of the sensations that you have prepared for you nature.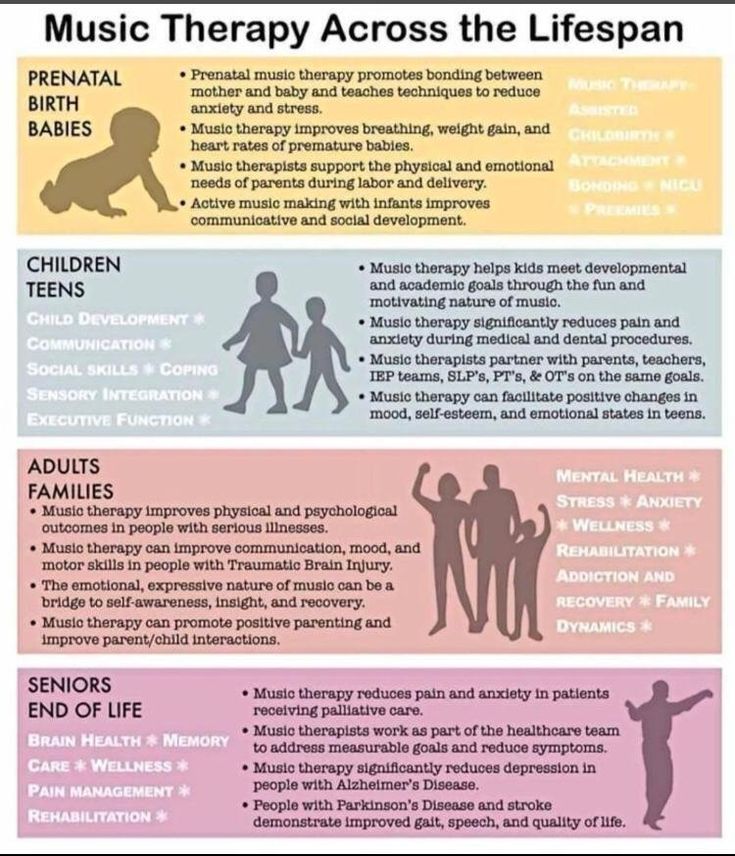 In any case, I wish you and your baby a happy birth! nine0003
In any case, I wish you and your baby a happy birth! nine0003
Popular methods of pain relief during childbirth
Many pregnant women are very anxious about the upcoming birth and fear the pain associated with it. Of course, you ask yourself: “Will I be able to cope with this pain and will I be able to give birth without anesthesia?” I won't lie to you, childbirth is painful. But there are a number of reliable methods to relieve pain, both natural and medicinal.
Nature has endowed women with a special analgesic hormone - endorphin, which is synthesized during childbirth and relieves pain. If you are thinking about whether to use anesthesia in childbirth or not, then you should know that it suppresses the secretion of endorphins. Yes, the anesthetic effectively relieves pain, but at the same time blocks the production of hormones. Also, remember that we are all unique and our reactions to pain are different. Some women perceive their childbirth as a unique experience, as something special. Other women reach the limit of their strength during childbirth and then try to erase this event from memory as quickly as possible. nine0003
Other women reach the limit of their strength during childbirth and then try to erase this event from memory as quickly as possible. nine0003
It is very difficult to determine in advance which method is best for you, as each pregnancy is unique and the assessment of the current situation can only be made during labour. But getting as much information as possible about the methods of anesthesia of labor pain will not be superfluous.
Natural methods
Support for a loved one
Many women feel that you can help by simply holding her hand. A husband, friend or personal midwife can support you during childbirth. Sometimes just a word of encouragement or help with breathing is enough to get you through the tough times. The accompanying person should encourage you and constantly tell you about how the birth process is going. The feeling of security reduces tension and, accordingly, reduces pain. The idea of calling someone close to the people is good because you know for sure that there is someone to support you, this thought alone already gives you strength. nine0003
nine0003
Gradually, our maternity hospitals are getting acquainted with such a phenomenon as “dula”. A doula is an experienced woman who supports the mother emotionally and physically. She also acts as an intermediary between the woman in labor and the medical staff. Even during pregnancy, the doula learns about the needs and fears of the expectant mother. This is not a midwife suddenly hired during childbirth, but a friend, a person who is completely trusted by a woman in childbirth. A doula accompanies the mother during the entire birth process. At the same time, she does not need to work as a midwife, she just needs to undergo special training, have relevant experience and be able to establish a warm and cordial relationship with the patient. In our conditions, the function of a doula is best performed by midwives, although this is a fairly new direction in general. In European countries, doulas have been known for a long time and are considered a necessary part of the birth process. Women who are accompanied by doulas feel better after childbirth, and the process of childbirth itself is less traumatic compared to traditional childbirth. nine0003
Women who are accompanied by doulas feel better after childbirth, and the process of childbirth itself is less traumatic compared to traditional childbirth. nine0003
Water
Warm water relaxes. You can both take a shower and lie down in the bath. Of course, it all depends on the equipment in your hospital. A relaxing shower should last 15-25 minutes. While showering, point the jet of water at the stomach or lower back, this will relieve pain and increase blood flow to the muscles. After that, the muscles will be easier to stretch. While taking a bath, you will feel how tension and fatigue disappear, and you will feel a strong surge of energy.
Remember! The water should be either warm or slightly warm. Never use hot water. Remember that if you are not in the mood to take a shower or bath, no one can force you. nine0003
Massage
During childbirth, massage of the lumbosacral region can provide significant relief. Lie down or sit comfortably and ask the person accompanying you to massage your lower back. Your partner should make circular movements in the painful area with the entire surface of the palm, first in one direction, then in the other. You can also apply pressure to painful points using the base of your palm or fists.
Your partner should make circular movements in the painful area with the entire surface of the palm, first in one direction, then in the other. You can also apply pressure to painful points using the base of your palm or fists.
You may not want to be massaged at all, or you may prefer having a midwife massage rather than your husband. Remember that you can always talk about how you feel and what exactly you need. If you do not want the accompanying person to touch you, ask the obstetrician for help. Do not be afraid that in this way you will offend your partner. He should not be offended, thinking that he is a bad helper and that he is not needed. He must understand and respect the rights of the woman who gives birth. nine0003
Compresses
Compresses are very helpful in relieving pain. A cold or warm compress applied to the sacrum or lower abdomen will definitely give you some relief.
Breathing
Breathing is very important during childbirth. When you start to panic, your breathing becomes rapid, and this, in turn, can lead to hyperventilation. So try to focus on your breathing. This will greatly ease the pain.
So try to focus on your breathing. This will greatly ease the pain.
Breathing in is important to your baby because your body is supplying oxygen to your baby, and breathing out is important to you because it helps you relax. Breathe deeply. Exhale the air completely, imagine that you are exhaling all the tension and pain. Synchronize the rhythm of your breathing with the rhythm of contractions. nine0003
Scream
During contractions you may scream, moan or even sing. This is quite natural. Do not suppress your emotions, otherwise you will overstrain the muscles involved in childbirth, and this will only increase the pain.
If you make any sounds as you exhale, you will not only relieve the pain, but also relax the muscles of the birth canal.
But everything is good in moderation. Remember that loud screaming can make you tired, and fatigue slows down the birth process. If you scream instead of pushing in the second stage of labor, the pushing will be ineffective and the baby will not move through the birth canal. Therefore, moaning and screaming to relieve pain is possible only at the moment of weakening of the contraction. nine0003
Therefore, moaning and screaming to relieve pain is possible only at the moment of weakening of the contraction. nine0003
Acupressure
For severe sacral pain, try acupressure. This is a technique from Chinese medicine. Your partner should press hard on the base of the big toe. This method does not require much effort on either your part or your partner's, so it's worth a try.
Movement
Change positions during childbirth. Movement reduces pain. Depending on what stage of labor you are in, completely different positions can alleviate your condition. Using this or that position, you can both speed up and slow down the process of childbirth. Your body itself will tell you exactly what to do in order to relieve the pain during contractions as much as possible. Any posture is good - you can sit, walk, squat or get on all fours. Have a partner help you, or use the furniture and equipment in the antenatal room to help you. nine0003
TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation)
A special device produces the hormone endorphin, which is needed to relieve pain. With TENS, four electrodes are attached to the skin in the lumbar region, through which current is supplied. Electrical impulses block the transmission of pain along the nerves, and as a result, contractions are easier to bear. This method has no effect on the child, but is not recommended for women with a pacemaker.
With TENS, four electrodes are attached to the skin in the lumbar region, through which current is supplied. Electrical impulses block the transmission of pain along the nerves, and as a result, contractions are easier to bear. This method has no effect on the child, but is not recommended for women with a pacemaker.
Music
You can listen to your favorite music during childbirth. To do this, simply download your favorite playlists to your phone before heading to the hospital. nine0003
As long as you listen to your favorite tunes, you will not think about pain, and this will bring you relief in difficult moments.
Pharmacological methods
Epidural analgesia
This is probably the most popular and most effective method for pain relief during childbirth.
An anesthetic needle is inserted between two lumbar vertebrae. You will not feel pain below the belt, but you will be conscious, able to move and push. However, remember that this method has certain drawbacks. Such anesthesia weakens contractions, which leads to a significant slowdown in the birth process. In general, the anesthetic does not affect the child, but sometimes, unfortunately, the baby's heartbeat can slow down for a while, which will be seen from the CTG records. This does not happen often, but before you ask for such anesthesia, you must weigh the pros and cons. It is also necessary to know that anesthetics administered through an epidural catheter are derivatives of cocaine, although they are administered in low and authorized doses. nine0003
Such anesthesia weakens contractions, which leads to a significant slowdown in the birth process. In general, the anesthetic does not affect the child, but sometimes, unfortunately, the baby's heartbeat can slow down for a while, which will be seen from the CTG records. This does not happen often, but before you ask for such anesthesia, you must weigh the pros and cons. It is also necessary to know that anesthetics administered through an epidural catheter are derivatives of cocaine, although they are administered in low and authorized doses. nine0003
Dolargan / Pethidine
It is an antispasmodic drug derived from morphine. It is recommended in the presence of contraindications to epidural anesthesia. It is administered either intramuscularly or intravenously. However, this remedy is not recommended for use, because it penetrates the child's body and can cause depression of the respiratory system of the newborn. You may also feel drowsy after the injection, and you may experience nausea or vomiting.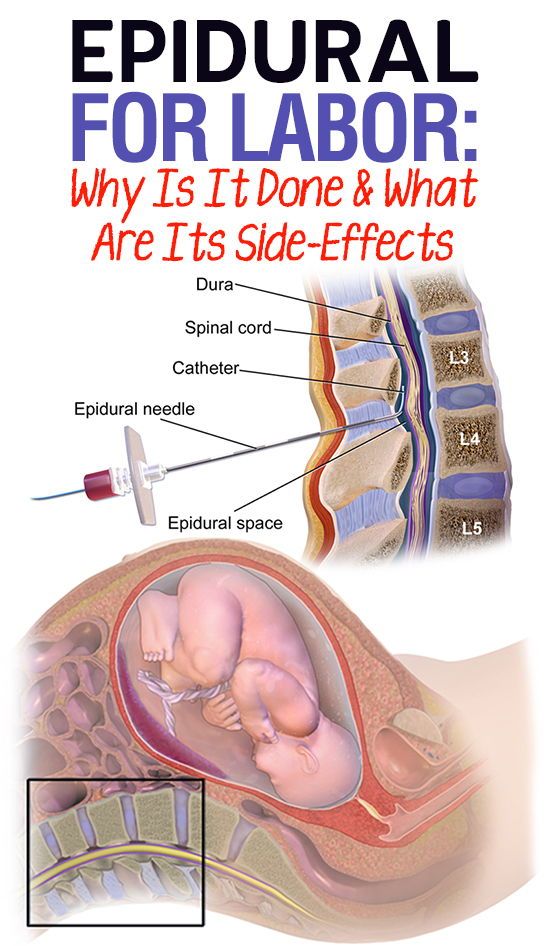
Nitrous oxide
When using this type of anesthesia, you inhale the gas mixture through a special mouthpiece or using a face mask. This is a rather mild type of anesthesia that has a slightly relaxing and pain-reducing effect. This method is effective when you inhale gas before a contraction. In this case, the maximum level of gas in the blood is reached during the contraction itself. nine0003
Nitrous oxide is now rarely used, and maternity hospitals are phasing out this type of anesthesia.
Pudendal Anesthesia
In this type of pain relief, an anesthetic is injected into a nerve in the perineum on both sides of the pelvis. Anesthesia of this type is also used extremely rarely.
As for me, I perceive childbirth as an exceptional and very difficult experience. From the very beginning I knew that I did not want to use any pharmacological agents. I was very scared, but at the same time I believed that everything would end well. And so it happened.