How to detect adhd in your child
ADHD (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
What Is ADHD?
ADHD stands for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. It is a medical condition. A person with ADHD has differences in brain development and brain activity that affect attention, the ability to sit still, and self-control. ADHD can affect a child at school, at home, and in friendships.
What Are the Signs of ADHD?
All kids struggle at times to pay attention, listen and follow directions, sit still, or wait their turn. But for kids with ADHD, the struggles are harder and happen more often.
Kids with ADHD can show signs in any or all these areas:
- Inattentive. Kids who are inattentive (easily distracted) have trouble focusing their attention, concentrating, and staying on task. They may not listen well to directions, may miss important details, and may not finish what they start. They may daydream or dawdle too much. They may seem absent-minded or forgetful, and lose track of their things.
- Hyperactive. Kids who are hyperactive are fidgety, restless, and easily bored. They may have trouble sitting still, or staying quiet when needed. They may rush through things and make careless mistakes. They may climb, jump, or roughhouse when they shouldn't. Without meaning to, they may act in ways that disrupt others.
- Impulsive. Kids who are impulsive act too quickly before thinking. They often interrupt, might push or grab, and find it hard to wait. They may do things without asking for permission, take things that aren't theirs, or act in ways that are risky. They may have emotional reactions that seem too intense for the situation.
Sometimes parents and teachers notice signs of ADHD when a child is very young. But it's normal for little kids to be distracted, restless, impatient, or impulsive — these things don't always mean that a child has ADHD.
Attention, activity, and self-control develop little by little, as children grow. Kids learn these skills with help from parents and teachers. But some kids don't get much better at paying attention, settling down, listening, or waiting. When these things continue and begin to cause problems at school, home, and with friends, it may be ADHD.
Kids learn these skills with help from parents and teachers. But some kids don't get much better at paying attention, settling down, listening, or waiting. When these things continue and begin to cause problems at school, home, and with friends, it may be ADHD.
What Causes ADHD?
It's not clear what causes the brain differences of ADHD. There’s strong evidence that ADHD is mostly inherited. Many kids who have ADHD have a parent or relative with it. Kids also can be more at risk for it if they were born early, are exposed to environmental toxins, or their mothers used drugs during pregnancy.
ADHD is not caused by too much screen time, poor parenting, or eating too much sugar.
How Is ADHD Diagnosed?
If you think your child has ADHD, make an appointment with your child's doctor. They will do a checkup, including a vision and hearing check, to be sure something else isn't causing the symptoms.
To diagnose ADHD, doctors start by asking about a child's health, behavior, and activity. They talk with parents and kids about the things they have noticed. Your doctor might ask you to complete checklists about your child's behavior, and might ask you to give your child's teacher a checklist too.
They talk with parents and kids about the things they have noticed. Your doctor might ask you to complete checklists about your child's behavior, and might ask you to give your child's teacher a checklist too.
After gettng this information, doctors diagnose ADHD if it's clear that:
- A child's trouble with paying attention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity go beyond what's usual for their age.
- The behaviors have been going on since the child was young.
- The behaviors affect the child at school and at home.
- A health check shows that another health or learning issue isn't causing the problems.
Many kids with ADHD also have learning problems, oppositional and defiant behaviors, or mood and anxiety problems. Doctors usually treat these along with the ADHD.
The doctor can refer you to a child psychologist or psychiatrist, if needed.
How Is ADHD Treated?
Treatment for ADHD usually includes:
- Medicine.
 This activates the brain's ability to pay attention, slow down, and use more self-control.
This activates the brain's ability to pay attention, slow down, and use more self-control. - Behavior therapy. Therapists can help kids develop the social, emotional, and planning skills that are lagging with ADHD.
- Parent coaching. Through coaching, parents learn the best ways to respond to behavior problems that are part of ADHD.
- School support. Teachers can help kids with ADHD do well and enjoy school more.
The right treatment helps ADHD improve. Parents and teachers can teach younger kids to get better at managing their attention, behavior, and emotions. As they grow older, kids should learn to improve their own attention and self-control.
When ADHD is not treated, it can be hard for kids to succeed. This may lead to low self-esteem, depression, oppositional behavior, school failure, risk-taking behavior, or family conflict.
How Can Parents Help?
If your child is diagnosed with ADHD:
- Be involved.
 Learn all you can about ADHD. Follow the treatment your child's health care provider recommends. Go to all recommended therapy visits.
Learn all you can about ADHD. Follow the treatment your child's health care provider recommends. Go to all recommended therapy visits. - Give medicines safely. If your child is taking ADHD medicine, always give it at the recommended time and dose. Keep medicines in a safe place.
- Work with your child's school. Ask teachers if your child should have an IEP or 504 plan. Meet often with teachers to find out how your child is doing. Work together to help your child do well
- Parent with purpose and warmth. Learn what parenting approaches are best for a child with ADHD — and which can make ADHD worse. Talk openly and supportively about ADHD with your child. Focus on your child's strengths and positive qualities.
- Connect with others for support and awareness. Join a support group like CHADD for ADHD to get updates on treatment and other information.
ADHD can improve when kids get treatment, eat healthy food, get enough sleep and exercise, and have supportive parents who know how to respond to ADHD.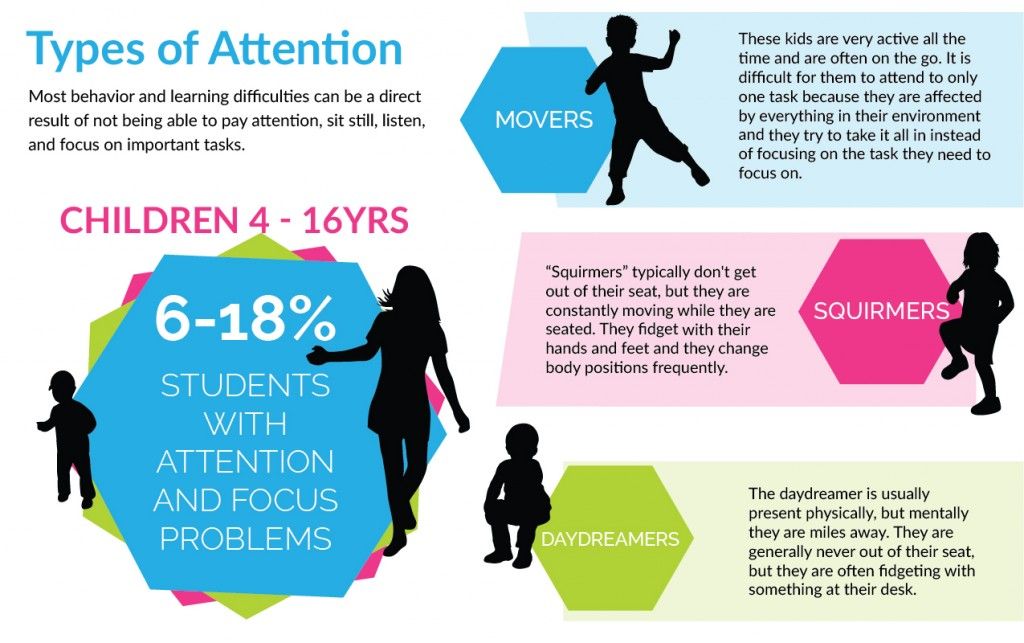
Symptoms, Types and Tests for ADD in Children
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
Children with ADHD show signs of inattention, hyperactivity, and/or impulsivity in specific ways. These children:
- Are in constant motion
- Squirm and fidget
- Do not seem to listen
- Have trouble playing quietly
- Often talk excessively
- Interrupt or intrude on others
- Are easily distracted
- Do not finish tasks
How Is ADHD Diagnosed?
Though your child may have some symptoms that seem like ADHD, it might be something else. That's why you need a doctor to check it out.
There is no specific or definitive test for ADHD. Instead, diagnosing is a process that takes several steps and involves gathering a lot of information from multiple sources. You, your child, your child's school, and other caregivers should be involved in assessing your child's behavior. A doctor will also ask what symptoms your child has, how long ago those symptoms started, and how the behavior affects your child and the rest of your family. Doctors diagnose ADHD in children after a child has shown six or more specific symptoms of inattention or hyperactivity on a regular basis for more than 6 months in at least two settings. The doctor will consider how a child's behavior compares with that of other children the same age.
Doctors diagnose ADHD in children after a child has shown six or more specific symptoms of inattention or hyperactivity on a regular basis for more than 6 months in at least two settings. The doctor will consider how a child's behavior compares with that of other children the same age.
A doctor will give your child a physical exam, take a medical history, and may even give them a noninvasive brain scan.
Your child's primary care doctor can determine whether your child has ADHD using standard guidelines developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics, which says the condition may be diagnosed in children ages 4 to 18. Symptoms, though, must begin by age 12.
It is very difficult to diagnose ADHD in children younger than 5. That's because many preschool children have some of the symptoms seen in ADHD in various situations. Also, children change very rapidly during the preschool years.
In some cases, behavior that looks like ADHD might be caused instead by:
- A sudden life change (such as divorce, a death in the family, or moving)
- Undetected seizures
- Medical disorders affecting brain function
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Bipolar disorder
3 Types of ADHD in Children
Doctors may classify symptoms as the following types of ADHD:
- Hyperactive/impulsive type.
 Children show both hyperactive and impulsive behavior, but for the most part, they are able to pay attention.
Children show both hyperactive and impulsive behavior, but for the most part, they are able to pay attention. - Inattentive type. Formerly called attention deficit disorder (ADD). These children are not overly active. They do not disrupt the classroom or other activities, so their symptoms might not be noticed.
- Combined type (inattentive and hyperactive/impulsive). Children with this type of ADHD show both categories of symptoms. This is the most common form of ADHD.
ADHD Treatment Overview
Treatment plans may include special education programs, psychological intervention, and drug treatment. Learn as much as you can about the options and talk them over with your child's health care provider so you can make the best plan for your child.
Studies show that long-term treatment with a combination of medications and behavioral therapy is much better than just medication treatment, or no specific treatments in managing hyperactivity, impulsivity, inattention, and symptoms of anxiety and depression. Those kids treated with both ADHD drugs and therapy also had better social skills.
Those kids treated with both ADHD drugs and therapy also had better social skills.
Drugs for Childhood ADHD
A class of drugs called psychostimulants (or sometimes just stimulants) is a highly effective treatment for childhood ADHD. These medicines, including Adderall, Adzenys XR-ODT, Concerta, Focalin, Daytrana, Quillivant XR, Ritalin, and Vyvanse,, help children focus their thoughts and ignore distractions.
Another treatment used to treat ADHD in kids is non-stimulant medication. These medications include Intuniv, Kapvay, Qelbree, and Strattera.
ADHD medicines are available in short-acting (immediate-release), intermediate-acting, and long-acting forms. It may take some time for a doctor to find the best medication, dosage, and schedule for someone with ADHD. ADHD drugs sometimes have side effects, but these tend to happen early in treatment. Usually, side effects are mild and don't last long.
Behavioral Treatments for Children With ADHD
Behavioral treatment for children with ADHD includes creating more structure, encouraging routines, and clearly stating expectations of the child.
Other forms of ADHD treatment that may benefit your child include:
- Social skills training. This can help a child with ADHD learn behaviors that will help them develop and maintain social relationships.
- Support groups and parenting skills training. This includes support for the parents and helping them learn more about ADHD and how to parent a child who has ADHD.
What Treatment Is Best for My Child?
No single treatment is the answer for every child with ADHD. Each child's needs and personal history must be carefully considered.
For example, a child may have undesirable side effects to a medication, making a particular treatment unacceptable. If a child with ADHD also has anxiety or depression, a treatment combining medication and behavioral therapy might be best.
It's important to work with a doctor to find the best solution for your child.
The ADHD Coach
Coaching is a relatively new field in the treatment of ADHD in children. ADHD coaches are meant to help children achieve better results in different areas of their lives by setting goals and helping the child find ways to reach them. A child, however, must be mature and motivated enough to work with a coach.
ADHD coaches are meant to help children achieve better results in different areas of their lives by setting goals and helping the child find ways to reach them. A child, however, must be mature and motivated enough to work with a coach.
How to recognize ADHD in a child and help him
November 23, 2019 Likbez Adviсe
This disorder is often confused with ordinary bad manners. Nevertheless, we are talking about a serious diagnosis.
What is ADHD
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurological behavioral disorder that the affected person cannot control (this is important). It has three key manifestations. Or, in some cases, their combination:
- Carelessness. It is difficult for a child to concentrate on a task. He lacks the persistence to continue what he started for more than a couple of minutes. And these problems are not related to the fact that he "does not obey" or does not understand the question.
- Hyperactivity. The child cannot sit still, including in situations where calm and silence are required. He jumps, twists, taps his foot, asks a million questions, scratches, giggles, or is just plain nervous.
- Impulsivity. This means that children do what they want, instantly, without thinking about the consequences. For example, another child takes their car in the sandbox - they beat the offender. It is necessary to the carousel - they run towards it, pushing the rest with their shoulders. I wonder what the appearance of others is connected with - they directly and loudly ask: “Why is this old aunt so fat?”
Most often, ADHD is associated only with hyperactivity. But this is a mistake. The child can be reserved and balanced phlegmatic. Just extremely careless.
For a doctor to make a diagnosis, it is enough that one or two of the manifestations of the disease indicated above are observed. In this case, ADHD is divided into types: predominantly inattentive and predominantly hyperactive-impulsive. But in most children, all three problems are present in a complex - this type of ADHD is called combined.
But in most children, all three problems are present in a complex - this type of ADHD is called combined.
How to recognize ADHD
If you think that almost all children exhibit this behavior from time to time, you don't. Almost everyone at some point in their lives may behave like someone with ADHD. That is why there is an opinion that this disorder does not exist - they say, these are inventions designed to hide poor upbringing or, let's say, a low level of intelligence.
But despite the controversy, ADHD is quite an official medical diagnosis. The International Classification of Diseases ICD-11 refers it to neurodevelopmental disorders - diseases in which the psyche fails and produces a pathological reaction to sensory information coming from outside.
And there are quite clear diagnostic criteria that help recognize ADHD.
1. Age
Symptoms of ADHD most often first appear between the ages of 3 and 6, but most cases are diagnosed between 6 and 12 years of age.
If you suspect ADHD in a teenager, but you are not sure if he had the same problems in preschool age, most likely it is some other disorder. Or just behavior problems that don't have neurological implications.
2. Symptoms that last at least 6 months
Diagnosis requires long-term observation of the child's behavior, at least six months. And not only in the family or familiar environment, but also in kindergarten or school.
A pediatrician, neurologist, psychologist, psychiatrist should talk in detail with the parents and the child himself. And also, ideally, interview other people working with him - educators or teachers. Only this allows you to put together a whole picture.
3. Symptoms that recur both at home and in kindergarten or school
A child with ADHD cannot control their behavior. Therefore, the symptoms will be the same - in the familiar environment, in the kindergarten or school.
If your child seems to be unable to sit still even for a second, blows up the house and exhausts you with endless questions, but behaves normally in kindergarten, this is not about attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
4. Symptoms that reduce the quality of life
You can be diagnosed if you notice at least a few of the following symptoms every day.
In case of inattentive ADHD, the child:
- Not able to keep attention on one thing for a long time (at least 5 minutes).
- Easily distracted, instantly forgetting what he was doing just now.
- He regularly makes elementary mistakes: in the example “1 + 2”, he can forget that the first digit was a unit, and output the answer 4. Or, when reading, skip a line and not even notice it.
- Often, being distracted, he cannot perform a simple task that other children can easily cope with.
- Regularly does not hear the speech of a parent, educator or teacher addressed to him, because his thoughts are somewhere far away.
- Cannot keep things in order, even when this is specially emphasized to his attention.
- Loses things endlessly - mittens, pencils, books, wallets, keys.
- When going somewhere, he “digs” all the time – he cannot quickly put together the necessary accessories, even if there are very few of them.

With hyperactive-impulsive ADHD child:
- Cannot sit still for more than a few minutes. In the literal sense: fidgeting, wriggling, twisting with brushes and knocking with his feet.
- Often forgets and jumps out of place in situations where it is impossible to do this, for example, in a lesson.
- Shows aimless motor activity: jumping, waving his arms, climbing or running somewhere.
- Does not know how to play quietly and thoughtfully, for example, to assemble a construction set on his own.
- Cannot wait in line. So, the teacher's question can be answered by interrupting the classmate to whom this question was addressed.
- He can be very talkative and often quite tactless.
- Seems to lack a sense of danger that could threaten his life.
With combined ADHD, the symptoms may be combined. And in any type, they obviously interfere with the child. For example, due to restlessness or lack of concentration, he cannot learn a lesson or complete an assignment.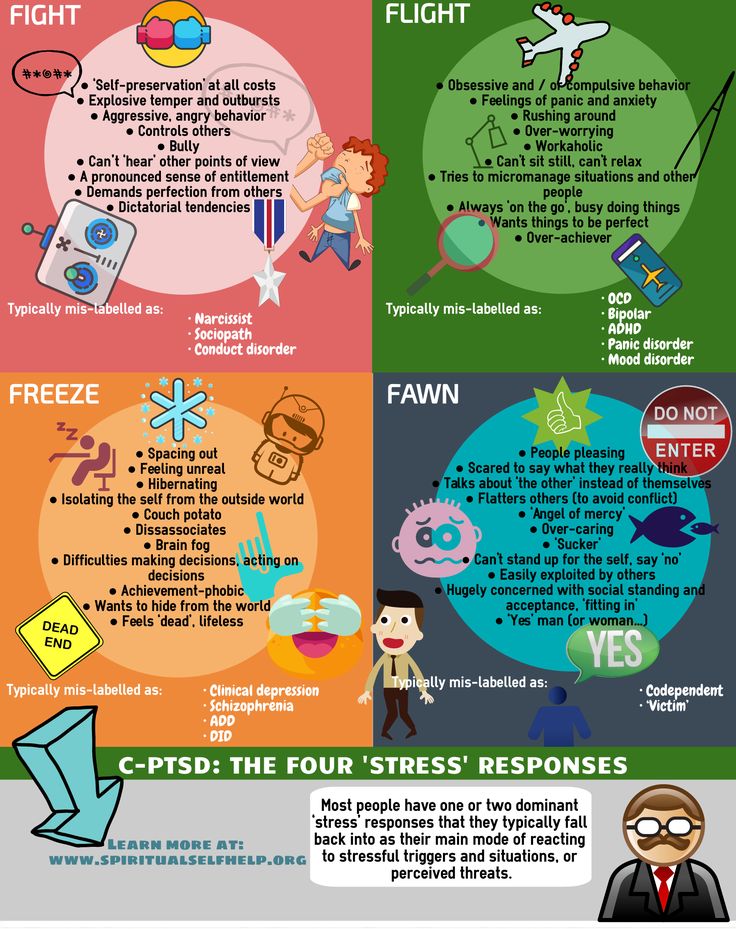 And because of tactlessness or slowness, it causes irritation in others.
And because of tactlessness or slowness, it causes irritation in others.
Why ADHD is dangerous
Inattention, hyperactivity and impulsivity can persist into adulthood. This often leads to serious psychosocial problems:
- poor academic performance and, as a result, the inability to get a good education;
- lack of friends and support;
- ridicule and related mental trauma;
- low self-esteem;
- inability to make and keep plans;
- optional, which has a bad effect on career and relationships within the team;
- frequent mood swings;
- vehemence, inclination to commit rash acts;
- persistently high levels of stress, which can lead to the development of other mental disorders such as anxiety or depression;
- inability to build long-term relationships, including family ones;
- alcohol and drug abuse;
- problems with paying debts and the law.
Conclusion: if the diagnosis of ADHD is made, the disease must be corrected.
How to treat ADHD
Good news first.
Between 30% and 70% of children diagnosed with the syndrome "outgrow" it with age.
In other children, the disorder remains for life. It is not always possible to cure it completely. However, there are quite effective methods of correction that can reduce symptoms.
1. Psychotherapy
In particular, we are talking about behavioral therapy. A qualified psychotherapist will help the child cope with emotions and disappointments, teach social skills in a playful way, for example, wait in line and share, and will not let self-esteem sink.
2. Work in the family
Family relationships are a key part of successful correction. It is extremely important for parents to do everything so as not to increase the already high level of stress in the child.
Do not scold him for inattention, slowness or restlessness: children with ADHD are objectively unable to cope with this.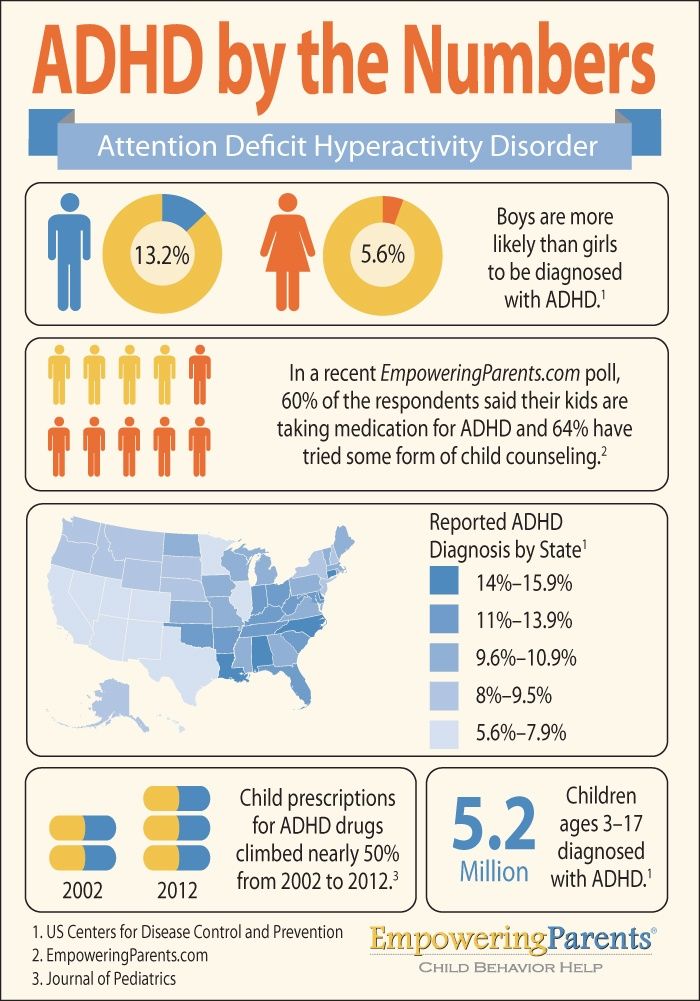 Your task is to be supportive, to show the child that he is loved no matter what. You may also need psychotherapy, which will teach you to control your own emotions and tell you where to draw the psychological resource necessary for communication.
Your task is to be supportive, to show the child that he is loved no matter what. You may also need psychotherapy, which will teach you to control your own emotions and tell you where to draw the psychological resource necessary for communication.
Here's what mom and dad can do:
- Organize your child's home life. Try to follow a strict daily regimen with clearly defined times for getting up, having breakfast, getting ready for the garden or school, bathing, going to bed. It is also worth making a schedule that will remind the child what he should do during the day. Be sure to place your schedule sheet somewhere visible, such as a magnet on the refrigerator door.
- Adjust diet. Diet research has yielded mixed results. But still, there is reason to believe that certain foods can help the brain cope with the disorder. Add high protein foods to your daily diet - meat, eggs, beans, nuts. Try to replace fast carbohydrates like sweets and cakes with slow ones like fruits, whole grain bread.
 An important nuance: before changing the diet, you should consult on this topic with the pediatrician observing the child.
An important nuance: before changing the diet, you should consult on this topic with the pediatrician observing the child. - Limit time for watching TV and playing with gadgets. No more than 2 hours a day!
- Be consistent in your actions. Children with ADHD need clear and predictable rules to follow.
3. Drug therapy
The most commonly used in the correction of ADHD are nootropics (substances that improve brain function) and psychostimulants (help control behavior). Which drug is needed in your case, only the doctor can decide.
One must be prepared for the fact that the chosen medicine may not be effective, and then a change in the drug will be required.
In addition, any side effects that occur, including loss of appetite or trouble sleeping, should be reported to the physician. This is also an indication for looking for another remedy.
Where ADHD comes from
The exact cause of the development of the disorder has not been established. But it is known that an excess of sugar or excessive TV viewing does not cause attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. An unbalanced diet or obsession with gadgets can make ADHD difficult to manage. But they are not able to provoke its development.
But it is known that an excess of sugar or excessive TV viewing does not cause attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. An unbalanced diet or obsession with gadgets can make ADHD difficult to manage. But they are not able to provoke its development.
Scientists have only been able to identify a number of factors that seem to play a role in causing ADHD.
1. Heredity
The syndrome runs in families, which makes it possible to link it with genetics. It has been found that if one parent had ADHD, the child has a 50% chance of inheriting the disorder. If the family already has an older brother or sister with the syndrome, the risks of the younger one are 30%.
2. Preterm birth
ADHD is often diagnosed in babies born prematurely or with low birth weight (less than 2,500 g).
3. Bad habits of the mother during pregnancy
The risk of ADHD in a child increases if the mother smoked, consumed alcohol or drugs while carrying the fetus.
4. Damage to the frontal lobe of the brain
For example, during falls. The frontal lobe is responsible for controlling emotions and behavior.
5. Exposure to toxins in infancy
Talking about lead or pesticides. The poisoning caused by them can also provoke the development of ADHD.
Read also 🤱🧒👶
- Allergy in a child: everything parents should know about diagnosis and treatment
- What to do if a child has diabetes
- How to raise an independent child: the method of a lazy mother
- What to do if the child is overweight
- 5 mistakes of parents, due to which the child's eyesight deteriorates
causes, symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adults
Symptoms of ADHD in children
Causes of pathology
Diagnosis
Treatment methods for ADHD
Prevention 9003
Today, more and more children are being diagnosed with ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder). As a rule, it is diagnosed in children aged 6-8 years, when the child goes to school. It is at this time that it becomes obvious that the child has pronounced problems with behavior and perception of information.
As a rule, it is diagnosed in children aged 6-8 years, when the child goes to school. It is at this time that it becomes obvious that the child has pronounced problems with behavior and perception of information.
ADHD is a neurological-behavioral developmental disorder. Pathology makes itself felt in childhood, but in the absence of timely therapy, it can persist into adulthood. According to statistics, ADHD is most common in boys, but can also occur in girls. If the pathology is not diagnosed and treated in a timely manner, this is fraught with poor school performance, the child may develop serious social problems, which increases the risk of substance abuse in the future.
Symptoms of ADHD in children
Consider some of the signs that may signal ADHD in children:
- The child is constantly distracted, inattentive, when communicating with him there is a feeling that he is not listening to you.
- It is difficult for him to keep his attention on the teacher's words for a long time, because of which the understanding of information also suffers.
- Increased activity is observed - the child literally cannot sit in one place. Even during school hours, he can get up and walk around the classroom.
- The child is impatient, cannot wait for his turn, constantly interrupts, answers questions without waiting for them to end.
- Children with ADHD are characterized by emotional instability, which can be manifested by frequent mood swings: a child can suddenly become irritable, tearful, and restless for no reason.
- Lack of concentration is characteristic - children with this diagnosis often lose their belongings (for example, school supplies, money, keys).
- Problems with sleep and appetite, with daily routine.
Additionally, some neurological abnormalities may be observed. For example, a child with ADHD may have poor motor coordination, resulting in some clumsiness. Also, in some cases, twitching of the facial muscles and trembling of the limbs are observed.
The first signs of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder are observed at the age of 2-3 years, but at this age it is difficult to determine whether they are a manifestation of pathology or normal age-related features.
However, if by the age of 6-8 years the child has not become more attentive and collected, this is an alarming sign that makes it possible to assume ADHD with a high degree of probability. That is why, if you have the above symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor and start treatment.
Causes of pathology
There is no single reason for the development of ADHD. Many experts agree that the most common cause may be genetic mutations that lead to a disruption in the production of dopamine and the work of dopamine receptors.
Also, the causes of the development of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder may be the following factors:
- Severe pregnancy, complicated delivery, including prolonged or rapid.
- Use by the expectant mother during pregnancy of potent drugs, alcoholic beverages, toxic substances.

- Serious pathologies suffered by a child at an early age, including craniocerebral trauma.
- Psychological trauma in a child.
- Fetal asphyxia.
It is also worth noting that this pathology has a hereditary predisposition. It was found that the presence of ADHD in parents significantly increases the likelihood of developing this syndrome in a child.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of ADHD is not established only on the basis of existing complaints. To accurately confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct some examinations. First of all, you need to visit a neurologist, psychiatrist and psychologist.
During the consultation, the doctor collects an anamnesis, conducts various tests, conversations, and diagnostic surveys.
In order to identify the cause of the development of ADHD, consultations with other specialists may also be required, as well as instrumental and laboratory examination methods, such as: EEG, MRI of the brain, general and biochemical blood tests.
ADHD treatments
It should be noted that attention deficit hyperactivity disorder most often has a favorable prognosis (provided that therapy is started in a timely manner). It is possible to significantly improve the behavior and learning of the child.
Depending on the severity of the pathological process and the causes of its occurrence, the doctor may prescribe such types of treatment as:
- Drug treatment: the patient may be prescribed sedatives, antidepressants, neurostimulants.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy.
- A clear daily routine: a balanced diet, good sleep.
- Family therapy: if there are conflicts in the family, ADHD often develops against this background.
- Biofeedback therapy: this method of treatment is aimed at training the child's ability to self-regulate their states with the help of computer game tasks.
- Physiotherapy techniques, eg massage, exercise, kinesiotherapy.
Additionally, other methods of treatment can be used.
Prophylaxis
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to prevent the development of ADHD. However, there are some factors that significantly reduce the risk of developing pathology. For example, the expectant mother should follow a healthy lifestyle, eat a balanced diet, give up bad habits. Before conception, it is desirable to undergo a complete examination, if necessary, to pre-treat existing pathologies.
Also, as a prevention of ADHD, the following recommendations should be observed:
- The child should be active, walk outdoors more often.
- The regimen of the day and meals must be clear.
- Monitor the child's behavior, immediately stop unacceptable behavior on his part.
- It is very important to build a trusting relationship between parents and children.
- Family conflicts should be avoided.
At the first signs of ADHD, it is recommended to contact specialists who will help minimize the risk of developing more serious pathologies in the future.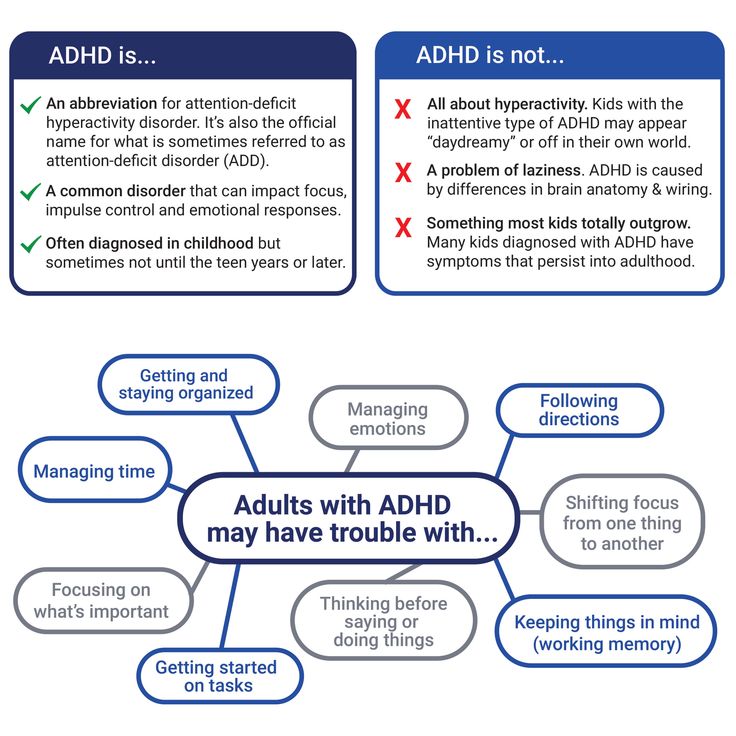
You can learn more about the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder at a face-to-face appointment with a doctor. Be healthy!
Author of the article:
Markelov Gleb Vladimirovich
neurologist, online consultations
work experience 4 years
reviews Leave a review
Clinic
m. Sukharevskaya
Reviews
Services
- Title
- Appointment, consultation of a neurologist primary
- Repeated appointment, consultation with a neurologist
Health articles
All articlesAllergistGastroenterologistHematologistGynecologistDermatologistImmunologistInfectionistCardiologistCosmetologistENT doctor (otolaryngologist)MammologistNeurologistNephrologistOncologistOphthalmologistProctologistPsychotherapistPulmonologistRheumatologistTraumatologist-orthopedistTrichologistUrologistPhlebologistSurgeonEndocrinologist 905 years. Red Gates. AvtozavodskayaPharmacy. Glades. Sukharevskaya. st. Academician Yangelam. Frunzenskaya Zelenograd
Red Gates. AvtozavodskayaPharmacy. Glades. Sukharevskaya. st. Academician Yangelam. Frunzenskaya Zelenograd Dmitrieva Olga Nikolaevna
Chief physician of "Polyclinika.ru" on Frunzenskaya, neurologist, ENMG specialist
reviews
Clinic
m. Frunzenskaya
Sumina Evgenia Yurievna
Head doctor "Polyanka.ru" on Polyanka, neurologist
reviews
Clinic
m. Polyanka
Demina Evgenia Sergeevna
neurologist, reflexologist, ENMG specialist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Sukharevskaya
Kuzmina Irina Vladimirovna
neurologist, reflexologist, hirudotherapist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Street 1905 Goda
Street 1905 Goda
Shcherbenkova Alina Lvovna
neurologist, specialist in ENMG, KMN
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Frunzenskaya
Agayeva Takhmina Khanovna
neurologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Polyanka
Aleksandrova Tatyana Sergeevna
neurologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Sukharevskaya
Apevalova Anastasia Romanovna
neurologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m.