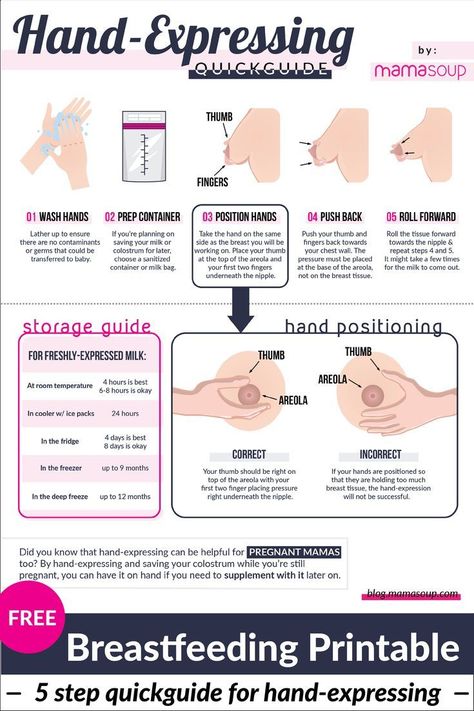
How to cure oral thrush in babies
Oral thrush (mouth thrush) - NHS
Oral thrush is usually harmless. It's common in babies and older people with dentures. It can be easily treated with medicines bought from a pharmacy.
Check if it's oral thrush
Adults
Your mouth is red inside and you have white patches.Credit:
DR P. MARAZZI/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/459245/view
When you wipe off the white patches, they leave red spots that can bleed.Credit:
DR P. MARAZZI/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/633814/view
Other symptoms in adults are:
- cracks at the corners of the mouth
- not tasting things properly
- an unpleasant taste in the mouth
- pain inside the mouth (for example, a sore tongue or sore gums)
- difficulty eating and drinking
Oral thrush in adults is not contagious.
Babies
A white coating on the tongue like cottage cheese – this cannot be rubbed off easily.Credit:
DR M.A. ANSARY/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/251590/view
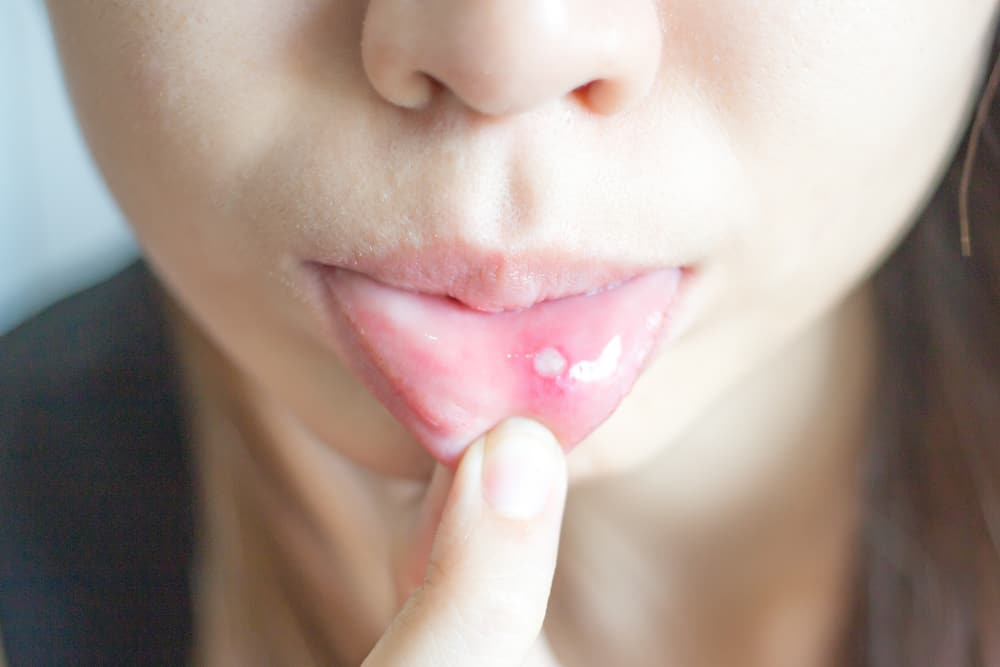
Sometimes there are white spots in their mouth.Credit:
DR P. MARAZZI / SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/252476/view
Other symptoms in babies are:
- they do not want to feed
- nappy rash
Babies can pass oral thrush on through breastfeeding. This can cause nipple thrush in mothers.
If you're not sure it's oral thrush
Look at other causes of a white or sore tongue.
A pharmacist can help with oral thrush
Oral thrush can be easily treated with a mouth gel bought from a pharmacy. The gel is suitable for adults, children and babies over the age of 4 months.
Ask your pharmacist for advice. Always follow the instructions on the medicine packet.
If you leave oral thrush untreated, the infection can spread to other parts of the body.
Non-urgent advice: See a GP if:
- your baby is under 4 months and has signs of oral thrush
- you do not see any improvement after 1 week of treatment with a mouth gel
- you have difficulty or pain swallowing
How you can prevent oral thrush
Thrush is an infection caused by a fungus called Candida. Some things can make the fungus grow more than usual.
Some things can make the fungus grow more than usual.
You might get thrush if you're:
- taking antibiotics over a long time
- using asthma inhalers
- getting cancer treatment like chemotherapy
There are some things you can do to help prevent oral thrush:
Do
-
take care of your teeth: brush twice a day, clean your dentures, and go for regular check-ups even if you have dentures
-
brush your gums and tongue with a soft toothbrush if you do not have any teeth
-
sterilise dummies regularly
-
sterilise bottles after each use
-
rinse your mouth after eating or taking medicine
-
go to regular check-ups if you have a long-term condition like diabetes
Page last reviewed: 08 July 2020
Next review due: 08 July 2023
Thrush in newborns Information | Mount Sinai
Candidiasis - oral - newborn; Oral thrush - newborn; Fungal infection - mouth - newborn; Candida - oral - newborn
Thrush is a yeast infection of the tongue and mouth.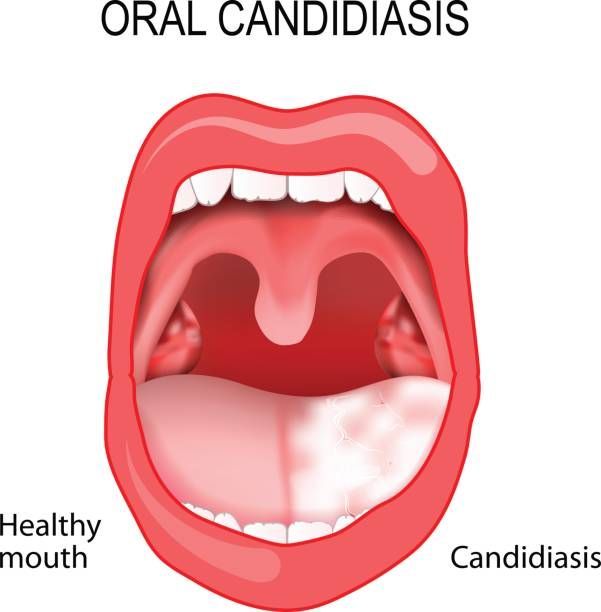 This common infection can be passed between a mother and baby during breastfeeding.
This common infection can be passed between a mother and baby during breastfeeding.
Causes
Certain germs normally live in our bodies. While most germs are harmless, some can cause infection.
While most germs are harmless, some can cause infection.
Thrush occurs when too much of a yeast called Candida albicans grows in a baby's mouth. Germs called bacteria and fungi naturally grow in our bodies. Our immune system helps keep these germs in check. But babies do not have fully-formed immune systems. That makes it easier for too much yeast (a type of fungus) to grow.
Thrush often occurs when mother or baby has taken antibiotics. Antibiotics treat infections from bacteria. They can also kill "good" bacteria, and this allows yeast to grow.
The yeast thrives in warm, moist areas. The baby's mouth and the mother's nipples are perfect places for a yeast infection.
Babies can also get a yeast infection on the diaper area at the same time. The yeast gets in the baby's stool and can cause a diaper rash.
Symptoms
Symptoms of thrush in the baby include:
- White, velvety sores in the mouth and on the tongue
- Wiping the sores may cause bleeding
- Redness in the mouth
- Diaper rash
- Mood changes, such as being very fussy
- Refusing to nurse because of soreness
Some babies may not feel anything at all.
Symptoms of thrush in the mother include:
- Deep-pink, cracked, and sore nipples
- Tenderness and pain during and after nursing
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can often diagnose thrush by looking at your baby's mouth and tongue. The sores are easy to recognize.
Treatment
Your baby might not need any treatment. Thrush often goes away on its own in a few days.
Thrush often goes away on its own in a few days.
Your provider may prescribe antifungal medicine to treat thrush. You paint this medicine on your baby's mouth and tongue.
If you have a yeast infection on your nipples, your provider may recommend an over-the-counter or prescription antifungal cream. You put this on your nipples to treat the infection.
If both you and your baby have the infection, you both need to be treated at the same time. Otherwise, you can pass the infection back and forth.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Thrush in babies is very common and can easily be treated. Let your provider know if thrush keeps coming back. It may be a sign of another health issue.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- Your baby has symptoms of thrush
- Your baby refuses to eat
- You have symptoms of a yeast infection on your nipples
Prevention
You may not be able to prevent thrush, but these steps may help:
- If you bottle feed your baby, clean and sterilize all equipment, including nipples.

- Clean and sterilize pacifiers and other toys that go in baby's mouth.
- Change diapers often to help prevent yeast from causing diaper rash.
- Be sure to treat your nipples if you have a yeast infection.
Balest AL, Riley MM, O'Donnell B, Zarit JS. Neonatology. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 2.
Harrison GJ. Approach to infections in the fetus and newborn. In: Cherry JD, Harrison GJ, Kaplan SL, Steinbach WJ, Hotez PJ, eds. Feigin and Cherry's Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 66.
Last reviewed on: 12/12/2021
Reviewed by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Candidiasis in the mouth of a child
Contents
What kind of disease is candidiasisSymptomsCausesTreatmentMethods of therapyPreventive measures
Many parents are aware of such a common problem in children as thrush, which is characterized by the appearance of white plaque on the tissues of the oral cavity. In medicine, this pathological condition has the term "candidiasis" and refers to fungal diseases.
Most often, candidiasis develops in the mouth of a child in the first year of life. Symptoms of thrush greatly disturb the baby, but timely treatment allows you to quickly and without consequences get rid of the fungus.
What kind of disease is candidiasis
According to statistics, about 30% of infants are faced with candidiasis. The causative agent of the disease is the Candida fungus. These specific microorganisms are normally present in the body of every person, even in the absence of health problems, but only in small quantities.
These specific microorganisms are normally present in the body of every person, even in the absence of health problems, but only in small quantities.
Oral candidiasis in children is much more common, since the immune system of babies is not yet formed and is not able to withstand pathogenic microorganisms and the effects of negative external factors.
With a weakened immune system and the concomitant effect of provoking factors, the fungus begins to actively multiply, affecting the mucous membranes. Without therapeutic treatment, candidiasis is eliminated in exceptional cases. If thrush is not treated, complications arise, and the infection itself spreads throughout the body.
Symptoms
Oral candidiasis in children can have a different form of manifestation and severity of symptoms: mild, moderate and severe. As a rule, each form corresponds to the stage of development of the disease. If therapy is not carried out in a timely manner, then the signs of a fungal infection become more intense and the number of symptoms increases.
With a mild form of the disease, a red rash appears on the oral mucosa, which is covered with a white coating on top. At the next stage, the child has swelling of the tissues and the formation of localized white spots with a touch of curd consistency. Gradually, these spots merge into a large affected area. When plaque is removed, bleeding sores open. If the thrush starts, then the fungus already spreads to the entire oral cavity, including the lips, tongue and throat. All fabrics are completely covered with cheesy bloom.
Common symptoms of candidiasis in children include:
-
burning sensation and itching in the mouth;
-
discomfort and pain when eating;
-
frequent spitting up in babies;
-
the formation of cracks in the corners of the lips;
-
temperature rise.
Children of the first two years of life report their condition with refusal to eat, constant whims and causeless crying. It is not difficult to see signs of candidiasis, so if a child has a sharp rise in temperature or refuses to eat, pediatricians and dentists recommend checking the oral cavity for white plaque. If you suspect thrush, it is undesirable to delay a visit to a specialist, since the fungal infection progresses rapidly.
It is not difficult to see signs of candidiasis, so if a child has a sharp rise in temperature or refuses to eat, pediatricians and dentists recommend checking the oral cavity for white plaque. If you suspect thrush, it is undesirable to delay a visit to a specialist, since the fungal infection progresses rapidly.
Reasons
The main reason for the development of candidiasis of the oral mucosa in children is a weakened immune system. If a child is born prematurely, then the likelihood of having thrush is very high. Children who are breastfed or have congenital pathologies are also often exposed to fungal infection.
Provoking factors include:
-
the presence of vaginal candidiasis in the mother during pregnancy - the child can become infected when passing through the birth canal;
-
insufficient hygiene of the female breast during breastfeeding - the fungus is often localized precisely on the nipples because of the favorable environment for it;
-
poor processing of the child's initial things - bottles, nipples, and so on;
-
the habit of parents to lick the nipples - even if the adult does not have signs of thrush, a fungus may be present in the mouth, which will be transmitted to the child;
-
long-term use of drugs of the "antibiotics" group - drugs help to reduce one's own immunity;
-
frequent regurgitation in infants - after regurgitation, an increased acidic environment, favorable for the fungus, remains inside the oral cavity;
-
excessive and frequent dry mouth - the absence of saliva, as a protective agent against the activity of pathological microorganisms.

Infection with Candida fungus in children older than 2 years can occur as a result of unwashed foods, raw milk or running water. If a child over 3 years of age has suddenly developed signs of thrush, one should be examined not only for a fungal infection, but also for other possible diseases that may be accompanied by a “fading” of the immune system.
Treatment
Children's fungal diseases can be dealt with by a pediatrician, infectious disease specialist or dermatologist. If we are talking about the treatment of thrush of the oral cavity, then the dentist can also carry out therapy.
The diagnosis of "candidiasis" is determined in most cases on the basis of a specialist examination of the oral cavity. If there is any doubt, the doctor directs the patient for additional examinations. To confirm the disease, a laboratory method is used to study a smear taken from the mouth for the presence of a fungus.
Treatment of thrush in children involves an integrated approach. If the disease is not advanced, then local therapy is carried out in combination with the adoption of measures to strengthen the immune system. In severe form, oral candidiasis in children is treated with systemic drugs, local remedies and compliance with preventive recommendations.
If the disease is not advanced, then local therapy is carried out in combination with the adoption of measures to strengthen the immune system. In severe form, oral candidiasis in children is treated with systemic drugs, local remedies and compliance with preventive recommendations.
Methods of therapy
Treatment of candidiasis begins with the treatment of the oral cavity. The first procedure is already performed at the reception. Antiseptic agents are used to remove plaque. The doctor may then apply an antifungal agent.
The parent should carefully monitor the actions of the dentist, as in the future they will have to independently process the oral cavity at home. The necessary drugs will be prescribed by a specialist. Local antifungal agents are dangerous in case of overdose, especially for the child's body, so you must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations.
In advanced cases, medications are prescribed in the form of solutions, drops or tablets. There are only a few drugs for the treatment of candidiasis in children. Replacing them with adult counterparts is dangerous. The dosage must be strictly observed.
There are only a few drugs for the treatment of candidiasis in children. Replacing them with adult counterparts is dangerous. The dosage must be strictly observed.
A mandatory addition to the main therapy is hygiene, good sleep, proper nutrition and taking measures to strengthen immunity (eating healthy foods, if necessary, pharmacy vitamins, walking.
Preventive measures
In order to prevent and even shorten the course of therapy, it is recommended to rinse the mouth (if the child is older than 3-4 years), or use antiseptic sprays several times a day.
It is not difficult to prevent oral candidiasis in children. The responsible approach of parents to the health of the child from the moment of planning conception and pregnancy will help to avoid fungal infections in babies.
Thrush in a child in the mouth in the language of causes - symptoms and treatment of candidiasis
Candidiasis or thrush is an infectious disease caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida albicans. In infants, it manifests itself mainly in the form of candidal stomatitis. If a child shows signs of illness, it is necessary to visit a pediatrician. In a complicated form of the disease, a consultation with a dermatologist, ENT, urologist or gynecologist will be required.
In infants, it manifests itself mainly in the form of candidal stomatitis. If a child shows signs of illness, it is necessary to visit a pediatrician. In a complicated form of the disease, a consultation with a dermatologist, ENT, urologist or gynecologist will be required.
Causes of thrush in children
Fungi of the genus Candida belong to the opportunistic microflora of the oral cavity and small intestine. Uncontrolled reproduction of microorganisms begins with the weakening of the protective functions of the body. Pathogens damage the mucous membrane and nearby tissues.
Internal factors for the development of thrush:
- prematurity;
- artificial feeding;
- surgical interventions;
- beriberi;
- alimentary dystrophies;
- anemia;
- rickets;
- imbalance of intestinal microflora;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- SARS, HIV, chronic viral pathologies;
- violation of protein, carbohydrate, fat metabolism;
- vomiting and frequent regurgitation.

Internal factors include prematurity, formula feeding, surgery, hypo- and avitaminosis, alimentary dystrophy, anemia, rickets, disruption of normal intestinal microflora, SARS, chronic viral diseases (including HIV), protein and fat metabolism disorders and carbohydrates, endocrine pathologies (including diabetes mellitus), malignant neoplasms, frequent regurgitation and vomiting.
The external factors of thrush include:
- frequent damage to the mucous membranes;
- teething in a child;
- long-term use of antibacterial, hormonal or immunosuppressive drugs, cytostatics;
- non-compliance with the rules of oral care.
Candidal vulvovaginitis in the mother, contact with a carrier of pathogenic strains of the fungus, and mechanical ventilation can provoke the development of thrush in a child.
Symptoms of thrush in children
Incubation period - 2-60 days, on average - 3-6 days. Clinical manifestations depend on the severity of candidal stomatitis. The main symptom is a white coating on the tongue.
The main symptom is a white coating on the tongue.
Forms and characteristic signs of thrush in children:
- Mild form - most often diagnosed in children. In the oral cavity, areas appear covered with a white coating of a curdled consistency. Localization - the inner surface of the cheeks, the upper surface of the tongue, sometimes - the soft and hard palate. Plaque is easily removed by scraping. The general well-being of the child is within the normal range, there is no specific sour smell from the mouth.
- Moderate form - a child has a dense curd coating on the tongue or in the form of a film. Nearby tissues are red and swollen. The plaque is hardly separated from the mucous membranes, after removal, the affected areas bleed. With this form of candidiasis in the mouth, the mood, sleep and appetite of the child worsens.
- Severe form - all mucous membranes of the oral cavity, gums, lips, posterior pharyngeal wall are affected in a child. The plaque is dense, it is practically not removed when scraped off, a light film remains under it.
 With this form of candidiasis, a pronounced sour smell from the mouth appears. The child is naughty, refuses breast or food, does not sleep well.
With this form of candidiasis, a pronounced sour smell from the mouth appears. The child is naughty, refuses breast or food, does not sleep well.
Complications in infants
In infants, thrush develops rapidly, the pathological process spreads to other parts of the body. Signs of candidiasis appear in the perineum, between the buttocks, symptoms of an intestinal fungal infection are observed. A severe form of thrush can cause sepsis.
Without proper treatment, candidiasis becomes chronic. Frequent exacerbations negatively affect the immune system and the general condition of the infant. The risk of developing allergic and atopic diseases increases. In children with chronic candidiasis, bronchial asthma is often detected.
Fungal tonsillitis is a common complication of oral candidiasis. A characteristic symptom is the appearance of a white cheesy plaque on the tonsils, burning, sore throat.
When a fungus affects the digestive tract, a child develops colic, and the process of food digestion slows down. Disturbed by constipation, pain in the lower abdomen. Mycosis of the respiratory organs is accompanied by frequent bronchitis, prolonged SARS, pneumonia.
Disturbed by constipation, pain in the lower abdomen. Mycosis of the respiratory organs is accompanied by frequent bronchitis, prolonged SARS, pneumonia.
Girls with chronic oral thrush often develop vulvovaginal candidiasis. Signs - redness and swelling of the external genital organs, due to the dryness of the mucous membranes, erosions form. In infancy, due to the anatomical features of the structure of tissues, pathology can lead to fusion of the labia and vaginal walls. In such cases, long-term medical treatment and surgery will be required.
Fungal infection of the genital organs in boys is accompanied by redness of the head of the penis, a secret similar to sour cream is secreted from the urethra. Against the background of thrush, urethritis and cystitis often develop.
Diagnosis of thrush
Thrush has characteristic symptoms. Therefore, there are no diagnostic problems. When collecting an anamnesis, the doctor determines the time of the onset of the disease. Assesses the general condition of the child, finds out the presence of fungal infections in the mother during pregnancy and childbirth.
Assesses the general condition of the child, finds out the presence of fungal infections in the mother during pregnancy and childbirth.
During the physical examination of the child, the doctor performs a number of necessary procedures:
- examines the condition of the oral mucosa;
- detects the presence of specific plaque in the mouth;
- determines the severity of the pathological process.
Be sure to examine other parts of the body that may have been infected with a fungus.
Laboratory methods for the diagnosis of thrush:
- Microscopy. A scraping is made from the affected area, the resulting biomaterial is studied under an electron or light microscope. The analysis reveals yeast-like cells and mycelial filaments.
- Culture method. Carried out to determine the type of pathogen, its sensitivity to antimycotic drugs.
- Serological research methods are used in the absence of clear clinical manifestations, lack of information of other diagnostic methods.

For fungal angina, sputum is analyzed to identify the type of pathogen. With candidiasis of the genital organs, it is necessary to pass a smear on the microflora. If mycosis of the internal organs is suspected, an analysis of feces, blood and urine is prescribed.
Be sure to carry out differential diagnosis to exclude diphtheria, acute herpetic stomatitis, acute tonsillitis.
Treatment of thrush
The choice of drugs for the treatment of thrush depends on the severity of the pathological process.
Peculiarities of therapy:
- In case of mild form, the oral cavity is irrigated with antifungal solutions with clotrimazole, nystatin. Soda or boric solution removes plaque well. Apply local disinfectants and antiseptics - methylene blue, Lugol's solution, Miramistin. When breastfeeding, the mother must treat the breast with a solution of soda, a decoction of calendula or oak bark before each feeding. The average duration of treatment is 2 weeks.

- For moderate to severe disease, oral or parenteral antifungals are prescribed. Additionally, symptomatic treatment of concomitant diseases is carried out.
Older children are given a diet. From the diet it is necessary to exclude sweet and salty dishes, flour. These products create favorable conditions for the reproduction of fungi. Additionally, it is necessary to take folic and ascorbic acid to restore the balance of microflora, drugs to strengthen the immune system.
With timely treatment, you can completely get rid of thrush in your mouth. Recovery occurs within 7-10 days. Severe forms of the disease and complications occur only in the complete absence of antifungal therapy.
Prevention of thrush in infants
Prevention of candidiasis in children is either specific or non-specific.
Non-specific methods of prevention:
- correct and regular care of the child's skin and mucous membranes;
- proper and rational nutrition of the mother during breastfeeding;
- with artificial feeding, choose high-quality mixtures with probiotics and vitamins;
- rational use of antibiotics during pregnancy;
- timely treatment of fungal infections during childbearing;
- do not give sweets to a child under one year, older children - sugar and sweets in limited quantities;
- strengthen immunity - hardening, exercise, long walks in the fresh air, adherence to the daily routine.