How much spotting is normal at 5 weeks
Vaginal spotting or bleeding in early pregnancy
In this article
- Will my baby be safe if I have red or brown spotting or discharge?
- What causes red or brown discharge in pregnancy?
- Will I have any tests after early vaginal bleeding or brown discharge?
- What are the more serious causes of brown discharge or bleeding in pregnancy?
Light bleeding, or spotting, during pregnancy is common and usually nothing to worry about. Spotting is similar to a period but much lighter, and can vary in colour. You may notice anything from red to dark brown discharge. If you have brown discharge this just means the blood is a little older and no more a reason to worry than red spotting. Let your doctor or midwife know if you have red or brown discharge in pregnancy though even if it stops, just in case.
Will my baby be safe if I have red or brown spotting or discharge?
Your baby is likely to be fine, as spotting or light bleeding is often harmless (NHS 2015a, RCOG 2016a).
In the early weeks red or brown discharge, spotting or bleeding is very common. As many as one mum in four with a healthy pregnancy has some sort of bleeding or spotting in the first trimester (Hasan et al 2010, van Oppenraaij et al 2009).
Many pregnancies carry on, despite early bleeding problems (Norwitz and Park 2016, RCOG 2016a).
Sometimes, though, spotting can be a sign of something more serious, such as miscarriage. This is why it’s always best to tell your midwife or doctor if you have any type of vaginal bleeding, even if it stops.
If the bleeding signalled a miscarriage, you’d develop tummy cramps as well, and the bleeding would usually get heavier (Hasan et al 2010, Norwitz and Park 2016).
More often, though, spotting or light bleeding stops on its own and the pregnancy carries on as normal (Hasan et al 2010, van Oppenraaij et al 2009).
Spotting or light bleeding is likely to turn out to be no more than a worrying blip in your pregnancy (Hasan et al 2010, Norwitz and Park 2016) that you’ll soon be able to put behind you.
What causes red or brown discharge in pregnancy?
Light bleeding is likely to be caused by the developing placenta. Once you're about six weeks pregnant, there's a step-change in your pregnancy. The placenta takes over from your body the job of making pregnancy hormones (Hasan et al 2010, van Oppenraaij et al 2009) and this is thought to be associated with light bleeding.
You're most likely to have spotting or bleeding when you're between five weeks and eight weeks pregnant (Hasan et al 2010).
The bleeding is unlikely to last longer than three days (Hasan et al 2010). You may only realise you're bleeding when you go to the loo and wipe, or notice spotting in your pants.
You may have heard that light bleeding is caused by menstrual hormones breaking through around the time you would have had a period. Another theory is that bleeding happens when the embryo implants in the womb wall.
While you may get some bleeding at the time you’d expect your period, it is unlikely to be anything to do with menstrual hormones or implantation. Most normal bleeding happens about five days after implantation (Harville et al 2003).
Most normal bleeding happens about five days after implantation (Harville et al 2003).
Aside from the placenta developing, there may be other things going on inside your body that have caused some bleeding:
- Irritation to your cervix. Pregnancy hormones can change the surface of the cervix, making it more likely to bleed, such as after you have sex.
- Fibroids, which are growths in the lining of your womb. Sometimes, the placenta embeds where there is a fibroid.
- A small, harmless growth on your cervix (cervical polyp).
- A cervical or vaginal infection. (Norwitz and Park 2016)
Inherited bleeding disorders, such as Von Willebrand Disease, that make it more difficult for your blood to clot, can also cause bleeding in pregnancy (Shahbazi et al 2012).
What does the placenta do?
Our midwife explains how the placenta develops into your baby's lifelineMore pregnancy videos
Will I have any tests after early vaginal bleeding or brown discharge?
If the bleeding occurred early in your pregnancy, your midwife or doctor can refer you to your nearest early pregnancy assessment unit (EPAU) for further tests. You can also see a doctor at your local hospital (RCOG 2016a).
You can also see a doctor at your local hospital (RCOG 2016a).
Tests to check how your pregnancy is going may include:
- An ultrasound scan to check that your baby is well. Your baby will be tiny at this stage, so you may need to have a scan via your vagina to get a good image. The person doing the scan (sonographer) will ask your permission to gently insert a probe into your vagina. It's perfectly safe for you and your baby.
- A vaginal examination. Your obstetrician will ask to check the neck of your womb for any cause of bleeding. She'll insert a speculum, the same instrument that's used during a cervical screening test, to gently widen your vagina to give her a view of your cervix.
- A test for chlamydia. Chlamydia can make ectopic pregnancy more likely to happen (NHS 2015b).
- Blood tests to check your blood group, rhesus status, and perhaps also the levels of the pregnancy hormone, human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) in your blood (RCOG 2016a).

What are the more serious causes of brown discharge or bleeding in pregnancy?
Unfortunately, bleeding in early pregnancy can be a sign of a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy. In both cases, you also usually develop tummy or pelvic pain and cramps (Norwitz and Park 2016).
Early miscarriage usually happens when a baby is not developing properly, and the bleeding becomes steadily heavier (Hasan et al 2010, Norwitz and Park 2016).
Early miscarriage is a heartbreaking event, but it is common (NICE 2013, RCOG 2016a). It affects about one pregnancy in four (Tommy's 2016).
An ectopic pregnancy happens when the fertilised egg implants outside of your womb. Unfortunately, a baby can't grow if this happens. The bleeding may continue, and may look dark and watery (RCOG 2016b).
An ectopic pregnancy can make you seriously ill, so you'll need to see an obstetrician at your nearest hospital quickly (Elson et al/RCOG 2016, NHS 2016, RCOG 2016b).
You’re slightly more likely to have spotting if you conceived twins. Sadly, sometimes one twin can stop developing and eventually disappear altogether. This is called a vanishing twin (Anderson-Berry 2016), and it may trigger some bleeding (Anderson-Berry 2016, Norwitz and Park 2016).
A rare cause of bleeding is a molar pregnancy (Cancer Research UK 2016, RCOG 2010, 2011). A molar pregnancy happens when an egg is fertilised but a baby can't grow, because the wrong number of chromosomes come together. A cluster of abnormal cells grows instead of a healthy baby (NHS 2017). A molar pregnancy must be treated to remove the abnormal tissues (NHS 2017, RCOG 2010, 2011).
It is also possible for a blow to your belly, perhaps after a fall, to trigger bleeding (Norwitz and Park 2016).
You may be offered extra care if you've had vaginal bleeding. Bleeding raises the chance of complications happening later in pregnancy (Saraswat et al 2010), especially if the bleeding was heavy or carried on into the second trimester (Norwitz and Park 2016).
Complications include premature birth, and having a baby with a low birth weight (Norwitz and Park 2016). Your medical team can keep a close eye on your pregnancy and your baby's growth, with extra scans and clinic appointments.
Bleeding in late pregnancy is much rarer and more serious than early bleeding. Read more about bleeding in late pregnancy.
See these other pregnancy symptoms you should never ignore.
References
Anderson-Berry AL. 2016. Vanishing twin syndrome. MedScape. emedicine.medscape.com [Accessed January 2018]
Cancer Research UK. 2016. Gestational trophoblastic disease: risks and causes. www.cancerresearchuk.org [Accessed January 2018]
Elson CJ, Salim R, Potdar N, et al on behalf of RCOG. 2016. Diagnosis and management of ectopic pregnancy. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists / Association of Early Pregnancy Units joint guideline, Green-top guideline, 21. onlinelibrary. wiley.com [Accessed January 2018]
wiley.com [Accessed January 2018]
Elson CJ, Salim R, Potdar N, Chetty M, Ross JA, Kirk EJ on behalf of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Diagnosis and management of ectopic pregnancy. BJOG 2016;.123:e15–e55.
Harville EW, Wilcox AJ, Baird DD, et al. 2003. Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy. Hum Reprod 18(9):1944-7
Hasan R, Baird DD, Herring AH, et al. 2010. Patterns and predictors of vaginal bleeding in the first trimester of pregnancy. Ann Epidemiol 20(7):524-31. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov [Accessed January 2018]
NHS. 2015a. Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy. NHS Choices, Health A-Z. www.nhs.uk [Accessed January 2018]
NHS. 2015b. Chlamydia. NHS Choices, Health A-Z. www.nhs.uk [Accessed January 2018]
NHS. 2016. Ectopic pregnancy. NHS Choices, Health A-Z. www.nhs.uk [Accessed January 2018]
NHS. 2017. Molar pregnancy. NHS Choices, Health A-Z. www.nhs.uk [Accessed January 2018]
NICE. 2013. Miscarriage. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, Clinical Knowledge Summaries. cks.nice.org.uk [Accessed January 2018]
Miscarriage. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, Clinical Knowledge Summaries. cks.nice.org.uk [Accessed January 2018]
Norwitz ER, Park JS. 2016. Overview of the etiology and evaluation of vaginal bleeding in pregnant women. UpToDate 08 Nov
RCOG. 2010. The management of gestational trophoblastic disease. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, Green-top guideline, 38. www.rcog.org.uk [Accessed January 2018]
RCOG. 2011. Information for you: gestational trophoblastic disease. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. www.rcog.org.uk [Accessed January 2018]
RCOG. 2016a.Information for you: bleeding and/or pain in early pregnancy. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. www.rcog.org.uk [Accessed January 2018]
RCOG. 2016b.Information for you: Ectopic pregnancy. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. www.rcog.org.uk [Accessed January 2018]
Saraswat L, Bhattacharya S, Maheshwari A, et al. 2010. Maternal and perinatal outcome in women with threatened miscarriage in the first trimester: a systematic review. BJOG 117(3):245-57
2010. Maternal and perinatal outcome in women with threatened miscarriage in the first trimester: a systematic review. BJOG 117(3):245-57
Shahbazi S, Moghaddam-Banaem L, Ekhtesari F, et al. 2012. Impact of inherited bleeding disorders on pregnancy and postpartum hemorrhage. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 23(7):603-7
Tommy's. 2016. Miscarriage information and support. www.tommys.org [Accessed January 2018]
van Oppenraaij RHF, Jauniaux E, Christiansen OB, et al, on behalf of the ESHRE Special Interest Group for Early Pregnancy (SIGEP). 2009. Predicting adverse obstetric outcome after early pregnancy events and complications: a review. Hum Reprod Update 15(4):409-21. academic.oup.com [Accessed January 2018]
Show references Hide references
How Much Bleeding Is Normal In Early Pregnancy?
Light amounts of vaginal bleeding early in your pregnancy can occur. In most cases, it’s not serious. It can happen in the first 20 weeks for different reasons. It can be the result of something serious or non-serious. Continued bleeding throughout the pregnancy is not common. Call your doctor immediately if you are bleeding heavily. Go to the emergency room if you have severe pain.
It can be the result of something serious or non-serious. Continued bleeding throughout the pregnancy is not common. Call your doctor immediately if you are bleeding heavily. Go to the emergency room if you have severe pain.
Path to improved health
Vaginal bleeding can happen from conception to delivery. Spotting is a type of light bleeding. You may see just a few drops of blood in your underwear. Heavy bleeding is more noticeable. It will require a sanitary pad to protect your clothing.
Call your doctor whenever you experience bleeding of any kind. Call your doctor if you have vaginal bleeding or spotting. This is important even if an ultrasound test confirms your pregnancy is normal. An ultrasound is where a technician moves a wand around your stomach to see an image of the baby.
Non-serious reasons for bleeding early in your pregnancy can include:
- Implantation (as the egg settles into your uterus the first 6-12 days)
- Sex
- Infection
- Hormones.

More serious causes of vaginal bleeding during the early part of pregnancy can include:
- An ectopic pregnancy (a pregnancy that starts outside the uterus and will not survive but can be life threatening).
- A miscarriage (losing the baby early in a pregnancy).
- A molar pregnancy (a fertilized egg that implants in the uterus that does not live).
In later pregnancy, the following serious medical conditions can cause vaginal bleeding:
- Placental abruption (the placenta detaches from the wall of the uterus before birth).
- Placenta previa (the placenta is lying too low in the uterus and nearly covers the cervix).
- Placenta accreta (when the placenta invades the uterus and doesn’t separate from the uterine wall).
- Preterm labor (labor that starts before completing 37 of 40 weeks of pregnancy).
Bleeding may be just one sign of preterm labor. Preterm labor also can include vaginal discharge, pressure in your pelvis or abdomen (lower stomach), a dull backache, cramps, contractions, and your water breaking.
If you are bleeding early in your pregnancy, your doctor will want to know how long and how much. If you have cramps and pain early in the pregnancy, he or she will order tests. This may include an ultrasound, blood, and urine tests.
If continued bleeding is not serious, your doctor may treat it by recommending that you rest, relax, stay off your feet, and not have sex. Keep your body healthy. Take a prenatal vitamin with folic acid daily while pregnant. Take it earlier if you plan to get pregnant. Avoid smoking, drinking alcohol, and taking illegal drugs. Talk to your doctor before taking prescription medicine. When you are pregnant, you should never douche (use vaginal cleansing products) or use tampons. Serious bleeding may need to be treated with a long-term bed rest, hospitalization, or surgery.
You cannot prevent a miscarriage after it has started. The exact cause is usually unknown. It’s rarely something the mother did wrong. Most women can have healthy pregnancies in the future. If you have lost more than 3 pregnancies, talk to your doctor.
If you have lost more than 3 pregnancies, talk to your doctor.
Things to consider
If you experience bleeding or spotting at any time during your pregnancy, your doctor will want to collect as much information as possible. That will include:
- How far along is your pregnancy?
- Have you had bleeding at any other time during your pregnancy?
- When did the bleeding start?
- Is the bleeding heavy or spotting?
- Does it start and stop?
- How much blood is there?
- What color is the blood (bright red or dark brown)?
- Does the blood have an odor?
- Do you have cramps or pain?
- Do you feel weak, tired, faint, or dizzy?
- Have you experienced vomiting, nausea, or diarrhea?
- Do you have a fever?
- Were you recently injured (such as a fall or car accident)?
- Have you engaged in any physical activity?
- Are you under extra stress?
- When did you last have sex? Did you bleed afterward?
- Do you have a bleeding disorder? Women with bleeding disorders are at risk of complications during and after pregnancy.
 This includes iron-deficiency anemia, bleeding during pregnancy, and serious bleeding after delivery (postpartum hemorrhage). Talk to your doctor before getting pregnant if you have a bleeding disorder. Also, bleeding disorders are genetic.
This includes iron-deficiency anemia, bleeding during pregnancy, and serious bleeding after delivery (postpartum hemorrhage). Talk to your doctor before getting pregnant if you have a bleeding disorder. Also, bleeding disorders are genetic. - What is your blood type? If your blood type is Rh negative, you will need treatment with a medicine called Rho(D) immune globulin. This prevents complications with future pregnancies.
Vaginal bleeding is usually blood without clots or tissue. If you see something other than blood, call your doctor immediately. Try to collect the discharge in a container and bring it with you when you see your doctor. It may mean you have miscarried. If that is the case, your doctor will provide additional care. If not all the tissue from the miscarriage has passed, your doctor may need to perform a procedure. This procedure is called a dilation and curettage (D and C). It involves opening (dilating) the cervix. Your doctor will gently suction out the remaining tissue from the miscarriage.
Questions to ask your doctor
- Can certain foods (such as spicy foods) cause bleeding?
- Is it best to avoid having sex throughout your entire pregnancy?
- Is spotting during later pregnancy normal?
- Is my life at risk?
- I feel sad. Is there someone I could talk to about my feelings? Is there a support group?
Resources
U.S. National Library of Medicine, Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy
March of Dimes, Bleeding and Spotting From the Vagina During Pregnancy
Copyright © American Academy of Family Physicians
This information provides a general overview and may not apply to everyone. Talk to your family doctor to find out if this information applies to you and to get more information on this subject.
Pregnancy discharge | What are the discharge during pregnancy? | Blog
In the absence of menstruation, girls usually suspect that conception has occurred. However, during pregnancy, the female body may continue to secrete a secret of a different color and character. We recommend that you keep a close eye on everything that happens so as not to miss the development of adverse events. We will talk about how to recognize problem situations during pregnancy in the article.
We recommend that you keep a close eye on everything that happens so as not to miss the development of adverse events. We will talk about how to recognize problem situations during pregnancy in the article.
What discharge can occur during conception
Many women note that immediately after the delay and in the later stages, the nature of the secretion changes. It can be:
- With or without scent.
- Depending on the color - transparent, white, cream, yellow, greenish, bloody.
- By consistency - thick, liquid, cheesy.
- As a symptom for assessing the state of health - threatening, safe.
During ovulation, the egg is released from the ovary, its membrane is deflated, a small amount of fluid is released - so it becomes ready for fertilization. At this time, the thick mucus that fills the cervical canal of the cervix becomes less viscous. This makes it easier for the spermatozoa to penetrate and move further into the tubes for fertilization. At this time, you may notice an abundance of clear mucous secretions. nine0003
At this time, you may notice an abundance of clear mucous secretions. nine0003
After the fusion of the egg with the spermatozoon, movement into the uterus begins, which should end with implantation in the inner layer. During penetration, its slight detachment may occur - this causes damage to the blood vessels that abundantly penetrate the muscular layer of the uterus. You may see light brown discharge, which is common during pregnancy. The color is due to the fact that the blood has time to clot.
Sometimes the discharge is brightly colored and some women mistake it for a period that has started too early. But in this case, a short duration is characteristic, a different shade (dark or scarlet), a slight mark on the linen. nine0003
With some features of the structure of the female genital organs (for example, with a bicornuate uterus), after implantation of the embryo in one part, rejection of the endometrium may begin in the other, as usually occurs during menstruation. This rarely happens.
This rarely happens.
Characteristics of discharge in the event of a threatened miscarriage
Spontaneous abortion is the rejection of an embryo in the early stages after conception. If at the first signs of pregnancy, you notice spotting, there is a high probability that a miscarriage begins. nine0003
Also, miscarriage symptoms include:
- pulling or pressing on the lower abdomen, sacrum, lower back;
- the muscles of the uterus are tense.
The woman may feel cramps. This continues all the time or intermittently. From the vagina there are scarlet or brown discharge during pregnancy, which was previously confirmed. Sometimes the period may be still small, and the first signs did not have time to appear.
After 22 weeks, this phenomenon is called preterm labor. The child in this case is still weak, the organs are not sufficiently developed, and there is little chance of survival. nine0003
The following factors increase the risk of miscarriage:
- various diseases;
- progesterone deficiency;
- nervous and physical overexertion;
- pathologies in the genitals;
- fetal developmental defects.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound scan. If it shows that the fetal heart rate is disturbed, the tone of the uterus is increased, its size differs from normal for this period, hospitalization will be recommended to maintain pregnancy. nine0003
What discharge during pregnancy is considered normal
This secretion does not pose a threat to health:
- transparent;
- whitish;
- yellowish;
- odor free;
- mucous;
- without itching, burning, redness of the genitals.
Clear fluid on underwear is a symptom of ovulation. During pregnancy, the activity of ongoing processes in the body increases, so the amount of secretion secreted may increase. However, a violation of the norm is the leakage of amniotic fluid. You can determine the problem with the help of special diagnostic tests that the doctor will prescribe if he has suspicions. nine0003
White color, small amount, homogeneous structure should also not cause concern. The increased volume of fluid in this case is associated with increased hormonal activity.
The increased volume of fluid in this case is associated with increased hormonal activity.
One of the variants of the norm is mucous discharge, which smells of slight sourness. If there is no pain, discomfort, there is nothing to worry about.
Yellow discharge, there are signs of pregnancy, there is no unpleasant odor - you are all right. Some women had this color before conception, only they did not pay attention. Now there are more of them, therefore more noticeable. nine0003
Sometimes a woman observes that the laundry gets wet and there is a smell of urine. This may indicate incontinence due to the constant pressure of the growing uterus. In this case, it is recommended to go to the toilet more often, change underpants twice a day.
What discharge during pregnancy is considered a sign of infection?
White discharge during pregnancy with a cheesy texture is a symptom of thrush (candidiasis). In pregnant women, it is diagnosed quite often - the reason is a change in hormonal levels. The disease is accompanied by itching, redness of the vulva, a strong sour smell. Sometimes external manifestations are not detected, then treatment is not carried out. nine0003
The disease is accompanied by itching, redness of the vulva, a strong sour smell. Sometimes external manifestations are not detected, then treatment is not carried out. nine0003
Infection is indicated by pain, pain, skin irritation, ulcers, smell of rot or fish, gray or green color, frothy discharge, increased nervousness, large inguinal lymph nodes. The reason may lie in sexually transmitted infections. This includes syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and others. They are dangerous because they cause premature birth and fetal developmental defects.
What kind of discharge during pregnancy should I pay special attention to and should I consult a doctor? nine0005
The following indicates that pregnancy is at risk:
- Severe pain in the perineum, bleeding, difficulty defecation, convulsions - these may be injuries to the vaginal mucosa.
- Nausea, profuse vomiting, edema, headaches, cough, hypertension, bright red secretion are symptoms of hydatidiform mole (abnormal development of the embryo).

- A drop in blood pressure, pallor, weakness, sweating, pulling sensations, bleeding during pregnancy against the background of a lack of growth of hCG in the blood - this is how ectopic attachment manifests itself. nine0010
- Isolation of clots, sharp pain, vomiting, diarrhea may indicate a frozen fetus.
If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
It is also necessary to go to the clinic if you have been physically abused, had rough sex, had an accident, fell, hit. The likelihood that the situation will be resolved successfully is much higher if you do not delay the visit, listen to the symptoms and take good care of your health. nine0003
Remember, despite the fact that pregnancy is a normal state of health of the female body, the diagnosis and treatment tactics are still different, due to the many restrictions on manipulations and medications during pregnancy. That is why diagnosis and treatment during pregnancy should take place only under the supervision of a doctor. By ignoring the symptoms or self-medicating, a pregnant woman risks not only her health, but also the health of her child.
By ignoring the symptoms or self-medicating, a pregnant woman risks not only her health, but also the health of her child.
Doctors of the Leleka maternity hospital manage pregnancies of any complexity, including those aggravated by infections, pathologies, and the threat of miscarriage. Our own diagnostic laboratory allows us to accurately and in the shortest possible time to obtain the results of the tests. Thanks to constant medical supervision throughout the entire period, the chances of a successful birth are greatly increased. nine0003
Trust the life and health of your child to Leleka doctors, and we will make sure that you are satisfied.
articles of the Oxford Medical clinic Kyiv
Contents:
-
What discharge during pregnancy is considered normal?
-
When should you see a doctor for discharge?
-
Discharge in early pregnancy
-
Discharge in late pregnancy
-
Characteristics of discharge during pregnancy by color
-
Bloody discharge during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes a number of physiological changes - her body changes, adapts to bearing a baby and future childbirth. Changes can also occur with vaginal discharge. After conception, their number or color may become different, which often makes a woman worry. In order not to worry for no reason, but also not to miss a possible reason to see a doctor, you need to know which discharges are normal and which are not. nine0003
Changes can also occur with vaginal discharge. After conception, their number or color may become different, which often makes a woman worry. In order not to worry for no reason, but also not to miss a possible reason to see a doctor, you need to know which discharges are normal and which are not. nine0003
What is normal discharge during pregnancy?
The nature of the discharge at different stages of pregnancy may vary slightly.
-
transparent or white discharge;
-
odor free;
-
not exceeding the usual volume;
-
not accompanied by itching, burning or other painful symptoms.
At the same time, in the first 2-4 weeks, the daily discharge may increase slightly and become thicker.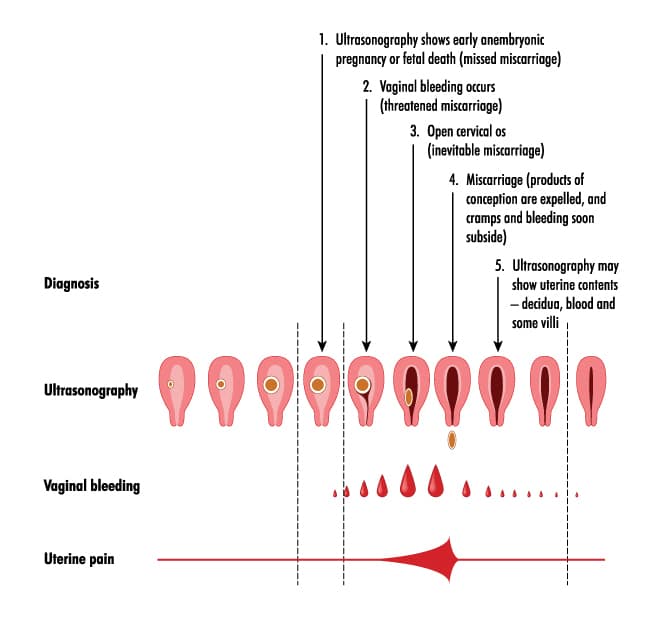 It is also possible the appearance of light spotting within a few hours or a day, which occurs as a result of the implantation of the embryo to the uterine wall. nine0003
It is also possible the appearance of light spotting within a few hours or a day, which occurs as a result of the implantation of the embryo to the uterine wall. nine0003
When should you see a doctor for discharge?
During pregnancy, a woman is advised to visit a gynecologist regularly for examinations and tests. First, consultations are prescribed once a month, and then once every 2 weeks. This allows you to carefully monitor the health of the pregnant woman and the development of the fetus. But, if discomfort appears, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
One of the alarming symptoms is the appearance of atypical discharge:
-
yellow, green, brown;
-
bloody;
-
thick;
-
too abundant;
-
slimy;
-
malodorous;
-
accompanied by itching, burning and other symptoms.
Such a change in the nature of the discharge may be associated with the development of an inflammatory or infectious disease, as well as pregnancy complications. To find out the exact cause, you need to do tests, conduct an ultrasound and, if necessary, other studies. nine0003
Discharge during early pregnancy
When conception occurs, changes begin in the body. First of all, the synthesis of the hormone progesterone increases and blood flow to the pelvic organs increases. These processes are often accompanied by profuse vaginal discharge. They can be translucent, white or with a slight yellowish tint. There should be no unpleasant odor or skin irritation.
Shortly thereafter, progesterone levels decrease and estrogen levels rise. At this time, a mucous plug is formed that covers the cervix. Its formation can also cause increased secretion, but gradually it should decrease and become more liquid and transparent. nine0003
nine0003
In addition, in the first weeks, the ovum attaches to the wall of the uterus, which can cause light brown discharge. As a rule, they are scarce and quickly stop - within a few hours or a day. If heavy bleeding has begun, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Approximately from 5 to 20 weeks, the discharge should be the same - transparent or whitish, in small volume, odorless.
Late pregnancy discharge
From the 20th to 40th week of pregnancy, the discharge is normally white, free from impurities and an unpleasant odor. nine0003
In the last week before delivery, the discharge may become thinner. If they are very abundant, leakage or discharge of amniotic fluid is possible, which requires a visit to a doctor.
Characterization of pregnancy discharge by color
Normal discharge should be colorless or white. A change in color and consistency may indicate the development of a disease or complications of pregnancy.
Bright or dark yellow discharge most often occurs when inflammation develops. Grey-green and green may result from infection. Thick white discharge speaks about it - as a rule, candidiasis manifests itself. Brown discharge may be due to slight bleeding. nine0003
Oxford Medical experts say that it is important to consider not only the color of the discharge, but also its smell, volume and consistency. A sharp and unpleasant odor appears only with bacterial or fungal diseases, so it should by no means be ignored. Also, an alarming signal is a strong increase in the volume of secretions, a change in structure, foaminess and other deviations from the norm.
There can be many reasons for abnormal discharge. To find them out, you need to conduct examinations, and then, if necessary, treatment. nine0003
Bloody discharge during pregnancy
The appearance of bloody discharge at any stage of pregnancy is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
The exception is small spotting in the first weeks (usually the same as the date of the expected menstruation), which indicates the implantation of the embryo. At this point, capillaries and small vessels can be injured, which causes light bleeding. Normally, it is very weak, not accompanied by pain or other unpleasant symptoms. nine0003
Blood-streaked discharge may also occur on the eve of childbirth as a result of cervical dilatation. This is normal, but a doctor's consultation is required.
In other cases, both in the first and last trimester, any discharge from pale pink and brown to red is a dangerous symptom. The violation may be minor, but it is necessary to conduct an examination.
Bleeding can be caused by:
-
hormonal disorders; nine0003
-
cervical erosion;
-
cysts;
-
fibroids;
-
inflammatory and infectious diseases;
-
ectopic pregnancy;
-
miscarriage;
-
placental abruption;
-
threatened miscarriage or premature birth.