How much exercise does a child need each day
Physical activity guidelines for children and young people
How much physical activity should children and young people aged 5 to 18 do to keep healthy?
Children and young people need to do 2 types of physical activity each week:
- aerobic exercise
- exercises to strengthen their muscles and bones
Children and young people aged 5 to 18 should:
- aim for an average of at least 60 minutes of moderate or vigorous intensity physical activity a day across the week
- take part in a variety of types and intensities of physical activity across the week to develop movement skills, muscles and bones
- reduce the time spent sitting or lying down and break up long periods of not moving with some activity. Aim to spread activity throughout the day
What counts as moderate activity?
Moderate intensity activities will raise your heart rate, and make you breathe faster and feel warmer.
One way to tell if you're working at a moderate intensity level is if you can still talk, but not sing.
Children and young people should do a range of different activities across the week.
Examples include:
- walking to school or walking the dog
- playground activities, including jumping, running and catching
- physical education
- sports, like football or tennis
- swimming
- skipping
- dancing
- skateboarding or rollerblading
- cycling
What activities strengthen muscles and bones?
Examples include:
- gymnastics
- football
- jumping
- martial arts
- resistance exercises with exercise bands, weight machines or handheld weights
- sit-ups, press-ups and other similar exercises
Physical activity recommendation for other age groups:
- Physical activity guidelines for children under 5 years
- Physical activity guidelines for adults aged 19 to 64
- Physical activity guidelines for older adults (aged 65 and over)
GOV. UK has infographics on physical activity for children and young people
UK has infographics on physical activity for children and young people
Page last reviewed: 12 November 2021
Next review due: 12 November 2024
Physical activity guidelines for children (under 5 years)
Being physically active every day is important for the healthy growth and development of babies, toddlers and pre-schoolers.
For this age group, activity of any intensity should be encouraged, including light activity and more energetic physical activity.
Babies (under 1 year)
Babies should be encouraged to be active throughout the day, every day, in a variety of ways, including crawling.
If they're not yet crawling, encourage them to be physically active by reaching and grasping, pulling and pushing, moving their head, body and limbs during daily routines, and during supervised floor play.
Try to include at least 30 minutes of tummy time spread throughout the day when they're awake.
Once babies can move around, encourage them to be as active as possible in a safe and supervised play environment.
For more ideas, see how to keep your baby or toddler active.
Toddlers (aged 1 to 2)
Toddlers should be physically active every day for at least 180 minutes (3 hours). The more the better. This should be spread throughout the day, including playing outdoors.
The 180 minutes can include light activity such as standing up, moving around, rolling and playing, as well as more energetic activity like skipping, hopping, running and jumping.
Active play, such as using a climbing frame, riding a bike, playing in water, chasing games and ball games, is the best way for this age group to get moving.
Pre-schoolers (aged 3 to 4)
Pre-schoolers should spend at least 180 minutes (3 hours) a day doing a variety of physical activities spread throughout the day, including active and outdoor play. The more the better.
The 180 minutes should include at least 60 minutes (1 hour) of moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity.
Children under 5 should not be inactive for long periods, except when they're asleep. Watching TV, travelling by car, bus or train, or being strapped into a buggy for long periods are not good for a child's health and development.
All children under 5 who are overweight can improve their health by meeting the activity guidelines, even if their weight does not change. To achieve and maintain a healthy weight, they may need to do additional activity and make dietary changes.
Find out what you can do if your child is overweight.
Physical activity ideas for under 5s
All movement counts. The more the better.
- tummy time
- playing with blocks and other objects
- messy play
- jumping
- walking
- dancing
- swimming
- playground activities
- climbing
- skipping
- active play, like hide and seek
- throwing and catching
- scooting
- riding a bike
- outdoor activities
Physical activity guidelines for other age groups:
- children and young people (5 to 18 years old)
- adults (19 to 64 years old)
- older adults (65 and over)
GOV. UK has more information, plus physical activity infographics for every age group.
UK has more information, plus physical activity infographics for every age group.
Page last reviewed: 1 June 2022
Next review due: 1 June 2025
Physical education every day | Mamovediya
Physical exercises not only contribute to the optimal physical development of children, they also favor their mental development, memory improvement.
Outdoor exercise is especially beneficial. In order for the child to reach for physical education himself, he should be interested. To do this, when conducting classes, you should try to use game exercises loved by children. Preschoolers can be allowed to hang on a tree, balance on a log, jump rope.
For kids, it is desirable to equip the apartment with a kind of home stadium. In the doorway, wooden blocks with cutouts can be nailed into which a removable crossbar is inserted. After class, they clean it up and put it in a corner.
Hanging ladder, swings, gymnastic rings, climbing rope, punching bag and other devices can be hung on the crossbar.
It is just as easy to make a gymnastic wall using an ordinary stepladder.
Ordinary furniture can also be used as exercise equipment for a child. So, two chairs can serve as parallel bars. If you put a stick on their seats, the child will be able to pull himself up on it from a prone position.
Equipment exercises attract all children. At first, they are more willing to perform those of them that turn out better.
It is not advisable to force a child to immediately master all the implements. Gradually, he himself will master both the shells and the movements that they allow you to perform.
It is not necessary to regulate the time of training on shells. The child himself will leave them as soon as he feels that the exercises are already difficult, which means he is tired.
When a child learns a new projectile, the help and appropriate encouragement of an adult is needed, and quite often a safety net.
Morning exercise helps prepare the body for daytime wakefulness. It disciplines, develops self-discipline, the ability to overcome laziness.
It disciplines, develops self-discipline, the ability to overcome laziness.
Four year old It is still difficult to perform exercises during exercise only by verbal command. Therefore, it is advisable for an adult to accompany each exercise not only with verbal instructions, but also with a demonstration and do it together with the child. Showing the movement, it is necessary to teach the child how to breathe correctly.
Complex movements, in which the load falls on many muscle groups, including the muscles of the trunk, are performed more slowly than exercises for arms or legs only.
Morning exercises are best done outdoors or with an open window. It begins with walking, which is complicated, including movement on toes, heels, the outer, and then the inner edge of the foot.
Gymnastics for children is a game. We must try to make this game fun, so as many game elements as possible should be introduced into the exercises following walking, imitating the actions of animals, hunting, traveling by transport, etc. It is useful to use various counting rhymes, short songs, simple quatrains.
It is useful to use various counting rhymes, short songs, simple quatrains.
Breathing and other exercises are diversified by imitating the flight of birds, butterflies, swimming, beating a drum, stretching, using sticks, hoops, ropes.
In addition to the previously mastered exercises (jumping, throwing the ball from the chest, from behind the head, overcoming obstacles, exercises with a stick), new ones are introduced,
such as tilting the body sideways to the left and right with sliding the arms along the body down from the side of the slope and up under the armpit on the opposite side (“pump” exercise),
bending forward (the child should touch the floor with his fingers or take an object lying on the floor with one hand),
squat and tap the floor with a stick (“the hen pecks grains”),
torso turns from a supine position with arms outstretched to the sides (one of them contains a small ball, which, when turning the torso without lifting the legs and the other hand from the floor, must be transferred to the other hand).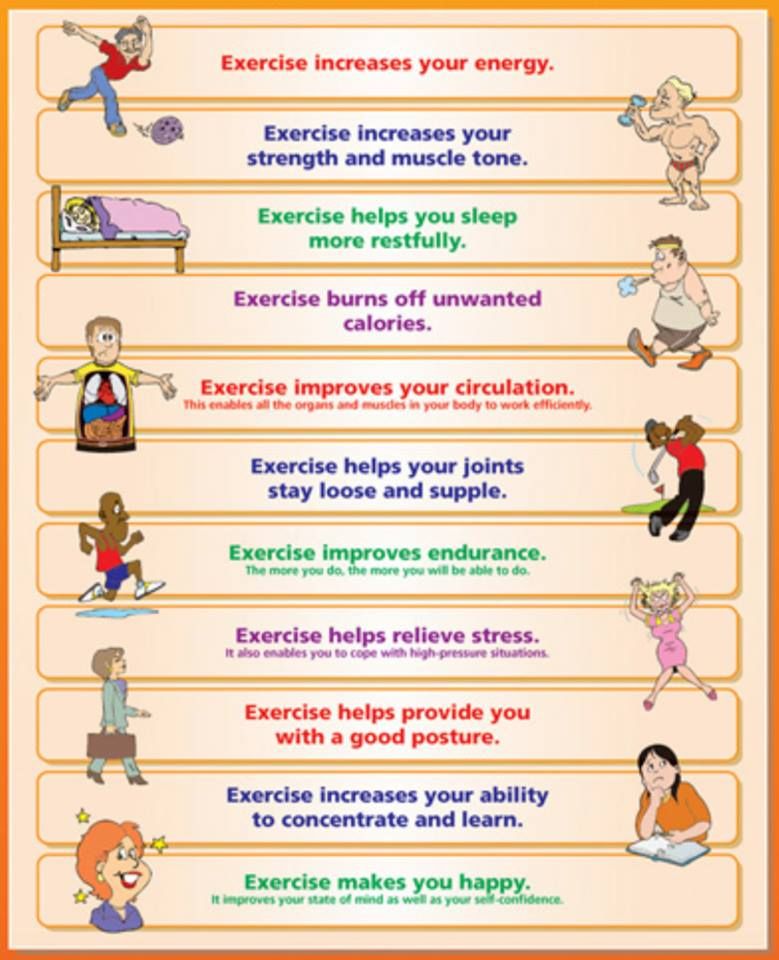
Charging usually ends with a run, followed by walking and breathing exercises.
Doing the same exercises for more than 8-10 days in a row can get boring. Every week it is necessary to modify, complicate or replace one or two exercises with new ones.
For example, the “pump” exercise can be replaced by side bends with arms outstretched (“trees sway”), and forward bends can be complicated by an exercise using a small ball that the child holds in one of the raised hands and, bending over, passes to the other hand behind the legs at ankle level.
The duration of morning exercises for younger preschoolers is 5-6 minutes.
In a month and a half, the morning exercise complex is completely renewed. Some of the new exercises may seem difficult to the child at first. At first, they can be performed in a lightweight version.
In general, it must be borne in mind that the coordination of movements in younger preschoolers is still imperfect, so they cannot be required to perform exercises absolutely correctly. It is important that the basic elements of the movements are mastered.
It is important that the basic elements of the movements are mastered.
If necessary, remarks are made to the guys cheerfully, with a smile .
For children aged 5 years, a set of exercises morning exercises includes
various types of walking (for example, walking with straight or bent legs high),
jogging,
breathing exercises,
exercises for the muscles of the upper limbs (imitation of movement of the wings, throwing the ball from various positions, support and pushing off the body),
exercises for the trunk (forward bends, circular movements, wrestling),
exercises for the lower extremities (long jumps, with a rope, "spring", squat, leg raises in the prone position, "scissors", etc.).
The complex also includes exercises for attention and coordination of movements, for example, the game "Butterfly, Crane and Frog".
The child walks in a circle, at the signal “butterfly” he waves his arms up and down, at the signal “crane” he steps over with a high rise of straight legs, at the signal “frog” he crouches, touching the floor with his fingers.
When playing "Who flies?" an adult at a fast pace alternately lists flying birds, insects, and then the child waves his arms, depicting a flight, then animals that cannot fly, and the child must remain calm at the same time.
In such games, attention and composure develop. The child perceives them with great interest.
If several children participate in the morning exercises, at this age it is allowed to introduce elements of competition into games and activities, the struggle “for prizes”.
Due to the fact that part of the exercises are performed from a sitting or lying position on the floor, it is necessary to prepare a small mat (approximately 60X 150 cm).
Children love it when dance elements are included in the complex of exercises performed together with adults.
In addition to a positive emotional perception, dancing between an adult and a child brings up a sense of rhythm, synchronization of movements, the ability to finely regulate one's physical activity, and the ability to adapt to the partner's rhythm.
A complex of morning exercises for children of six years of age includes, in addition to various types of walking and running, 7-8 exercises with various gymnastic objects (balls, sticks, hoops, ropes, flags, toys). Among them, in addition to those described earlier, are such
as “taking off and putting on a hat” (the hoop raised above the head with outstretched arms is lowered, as if putting it on the head, and then again raised up),
climbing through the hoop,
sequentially raising and lowering a stick held in outstretched arms,
walking with a stick fixed behind the back with arms bent at the elbows,
tossing a ball while walking,
throwing a ball in front of oneself on the floor and then catching it,
walking between toys placed on the floor,
jumping on one foot (sometimes on the right, then on the left) in a limited space (“classics”),
climbing a ladder,
crawling under a rope,
rolling a ball along the floor in a given direction, etc.
The duration of morning exercises at this age increases to 8-10 minutes.
When organizing physical education classes for girls, one should try to include more flexibility exercises, dance-like movements and limit the lifting and carrying of weights. Excessive loads of this kind can contribute to the displacement of the pelvic organs and further cause a number of gynecological diseases or obstetric pathologies.
If a child is ill , do not stop classes altogether. Movement is just as necessary for the sick as it is for the healthy. Even with bed rest, you can and should carry out breathing exercises.
If the patient's routine is simply at home, it is advisable to carry out a light complex of morning gymnastic exercises with him from a sitting position.
From the complex it is necessary to temporarily exclude the most difficult exercises that require a large expenditure of muscle strength, reduce the total number of exercises, reduce the number of their repetitions and the duration of classes.
Between individual exercises it is reasonable to take small pauses for the patient to rest.
Morning exercise is the most effective way to prepare a child's body for active daily activities. And those parents are wrong who, regretting waking up the baby, let him sleep for an extra 10-15 minutes and thereby deprive him of such a powerful charge of vivacity.
If circumstances still do not allow you to exercise with your child in the morning immediately after sleep, you can transfer it to the daytime and do it 1.5-2 hours after breakfast or after daytime sleep.
In general, with preschool children it is good to do physical exercises several times a day. They are carried out in the form of games with imitation movements. Only gymnastics at night is not recommended, as it excites the child and he does not fall asleep well.
Gymnastics that a mother can do with her baby on her own
In this article we will try to describe those exercises that a mother can independently carry out for her child at home without much difficulty and “risk to life”. Also, these exercises can be carried out between courses of professional massage.
Also, these exercises can be carried out between courses of professional massage.
Before carrying out any professional or independent massage, gymnastics, it would be optimal if the child is examined by a pediatrician, neurologist and orthopedist. Specialists will confirm the absence of contraindications, as well as suggest which areas should be emphasized when performing a massage.
Nevertheless, it should be understood that self-study with the baby, despite the undoubted benefits, will not replace professional massage courses for the child.
Gymnastic exercises for children of the first year of life are best done together with massage, and finish with aqua gymnastics.
Conditions, contraindications
During massage and gymnastics, educational toys can be used to attract the child's attention, but there should not be too many of them.
All gymnastic exercises are divided into active and passive. Active exercises are those that a person performs on his own, passive, in other words, when they wave your arm and leg, and you lie down, bored. In children's wellness massage and gymnastics, both types of exercises are used.
In children's wellness massage and gymnastics, both types of exercises are used.
Gymnastics for children from 0 to 3 months
The optimal age at which it is recommended to start a course of massage and gymnastics is discussed in the article "general principles of massage". Massage and gymnastics in children of the first year of life
Breathing exercises
Breathing exercises are very important for babies of this age. They contribute to the development of the respiratory muscles, the physiological abilities of the respiratory system, its reserve capabilities, and serve as a prevention of respiratory diseases.
Starting position: child in mother's arms, facing her. Produce rhythmic pressure with the palm on the back of the child, moving the palm from the neck to the waist.
Starting position: the child lies on his back. Alternate abduction of the handles to the side and up, starting from three months, this exercise can be performed simultaneously with two handles.
Reflex exercises
Babies have a certain physiological feature of the nervous system - the presence of unconditioned reflexes that appear and disappear at a certain time.
Thus, in infants, a special group of exercises can be distinguished. These are reflex exercises. They are based on the special evoking of certain unconditioned reflexes.
Naturally, no one will cause the Moro reflex as a charge (a loud blow on the surface on which the child lies, while he makes a “hugging” movement).
But some of them, such as the Babinski reflex (special stroking of the foot) or the support reflex, are very useful as developmental exercises.
The number of repetitions of reflex exercises during the lesson 1-2 times.
The exercise is based on the Babinski reflex.
Starting position: the child lies on the tummy.
Apply pressure on the sole at the base of the fingers - the child reflexively bends the fingers, then draw along the inner edge of the foot to the heel and the outer edge to the little finger - the sole is unbent.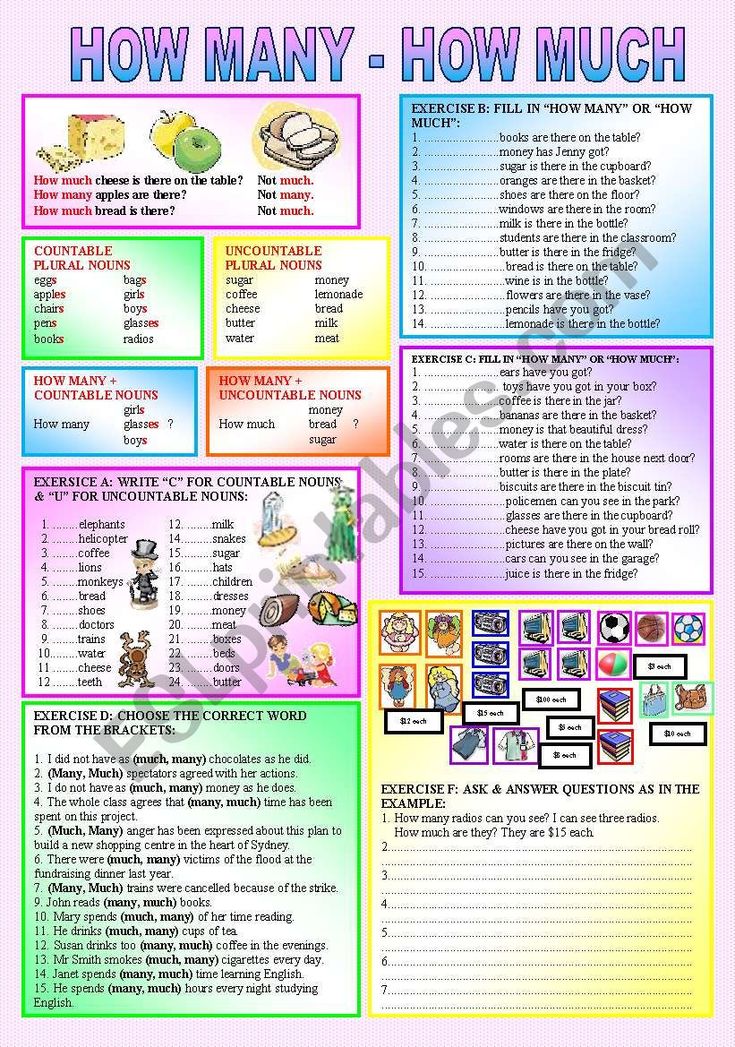 The movement is performed by the thumb of an adult. Repeat 1-2 times. Important! When performing the exercise, the child's leg is always fixed at the ankle joint (not at the fingers).
The movement is performed by the thumb of an adult. Repeat 1-2 times. Important! When performing the exercise, the child's leg is always fixed at the ankle joint (not at the fingers).
Of the reflex exercises at this age, reflex crawling, reflex support and reflex walking are also performed. These exercises are usually carried out at the end of the lesson.
Reflex crawling
This exercise is based on the Bauer crawling reflex.
Starting position: on the stomach. The palm of an adult is placed under the stacks of the child, so that the child can rest against it with slightly bent legs. The child pushes and straightens, moving forward. Repeat 1-2 times. Important! Do not forget to leave a free place where the baby will make this movement (so as not to hit his head).
Reflex support and walking
Starting position: the child is in a vertical position, the adult's hands are in the armpits of the child. The child should be allowed to fully rest their feet on the surface of the table. Slightly tilt the child's torso forward, and he will reflexively take a few steps.
Slightly tilt the child's torso forward, and he will reflexively take a few steps.
Laying on the stomach is useful, this is also an exercise for the child, based on a protective reflex (the baby raises and turns his head to the side). In the “on the stomach” position, the muscle tone of the extensor muscles is stimulated, the muscles of the abdomen are toned, the work of the intestines is stimulated - the removal of “gaziks” is facilitated, and is the prevention of constipation.
Laying on the stomach is recommended daily, starting from 30 seconds and up to 15-20 minutes in the first months of life.
Passive exercises
Sliding steps - "stomp"
Starting position: on the back. The leg is bent at the knee and hip joints, the foot rests on the table, the foot is glided along the table surface.
Skating in the fetal position.
Starting position: the child lies on his back. The legs are bent, brought to the tummy, the head is also bent, the chin is brought to the chest. The baby is “rolled” in this position on the back. As a rule, children really like this exercise.
The baby is “rolled” in this position on the back. As a rule, children really like this exercise.
Active exercises
Various bright, sounding toys are used, which are shown to the child at a distance of 25-30 cm, thus stimulating eye tracking of the object, auditory concentration, and an attempt to grab the object.
Gymnastics for children 3-4 months old
In order to avoid repetition, we will add descriptions of new elements of gymnastics to the above exercises.
Breathing exercises
Starting position: on the back. Simultaneous movement of the hands up and down, circular movements of the handles are added.
Boxing exercise
Starting position: on the back. Arms bent at the elbows alternately straighten them. The movements are like boxing. Important! The handles are fixed at the wrist joints to prevent sprains.
Half-turns and turns from back to stomach and back
Starting position: on the back. With one hand, the shins of the child are clasped from below, the index finger of the other hand of the adult is put into the palm of the baby, the remaining fingers cover his hand. Then, slightly straightening the child's legs, you should turn his pelvis, after which the child turns his head and shoulder girdle. Similarly, make turns in both directions.
With one hand, the shins of the child are clasped from below, the index finger of the other hand of the adult is put into the palm of the baby, the remaining fingers cover his hand. Then, slightly straightening the child's legs, you should turn his pelvis, after which the child turns his head and shoulder girdle. Similarly, make turns in both directions.
Exercises on the ball
Starting from 3 months, you can introduce a new type of activity - exercises on the ball. For these exercises, you will need a ball with a diameter of 50-60 cm, slightly deflated.
Swinging on the ball promotes the development of coordination, the vestibular apparatus, promotes toning of the abdominal muscles, back, legs.
The baby is placed on the ball in different ways: on the back, on the tummy, in turn on the sides.
Swings are carried out with support on the legs, with the legs raised.
It is important not to forget to securely fix the child on the ball.
Gymnastics for children 4-6 months
Unconditioned reflexes gradually fade away, so the proportion of passive-active exercises increases. It also increases the number of repetitions of the same exercise.
Passive exercises are carried out - flexion and extension in large joints.
Circular movements in the hip joints, with obligatory fixation of the child's knees with your own hands.
Simultaneous flexion - extension of the legs.
Starting position: on the back. Grab the child's legs at the bottom of the lower leg from behind, holding the feet. Bend the legs in all joints, slightly pressing them to the stomach (the child's knees should be spread apart), then straighten the baby's legs.
Connection of opposite and similar knee-elbow.
The range of exercises on the ball is expanding.
At this age, many children sway on the ball with interest, lifting the toy from the surface.
On the ball in the position on the back, you can rock the baby with a slight “sit down” when the legs reach the support.
From 5 months you can rock the baby on its side with repulsion from the support surface.
Gymnastics for children 6-9 months old
The following exercises are added to the exercises already described:
Breathing exercises are done on the back, on the side, begin to do them while sitting.
Simultaneous and alternate abduction of the arms to the sides, upwards, clasping movements of the arms.
All leg exercises are performed: “stomping”, sliding steps, circular movements of the legs, alternate flexion-extension.
A new exercise is introduced: bicycle.
Starting position: on the back. With the child's legs bent at the hip and knee joints, circular movements are performed, reminiscent of the movement of the legs while riding a bicycle.
In the sitting position (in the tailor's position, when the feet are connected or in Turkish), the child is swayed, using a toy, sipping is stimulated.
Try to encourage your baby to actively turn from back to stomach and vice versa.
Useful exercise aimed at developing crawling skills. During this period of time, you can help the child by substituting your palm as a support.
Exercises for the development of walking are performed: stepping from foot to foot is stimulated, while the adult first supports the child's armpits, and, subsequently, by the hands of both hands.
In exercises on the ball: you can use the swing on it in a sitting position.
Gymnastics for children 9-12 months
Exercises are performed in a variety of positions: lying, sitting, standing.
At this age, they try to encourage them to perform certain exercises with the words: "sit down, lie down, take the toy from the front, from behind."
Exercises with objects are used: squatting with a stick, exercises for hands with rings.
While exercising on the ball, you can also jump on it: on the buttocks, on the legs.
At this fertile age for exercise with a child, the more imagination, the better.