How much does full time child care cost
This is how much child care costs in 2022
More than half — 59% — of parents say they’re more concerned about child care costs now than in years prior. That’s just one finding of many in the Care.com 2022 Cost of Care Survey that illustrate the uphill battle parents are facing when it comes to affording and accessing quality child care.
The world has changed immeasurably over the last two years due to the pandemic and economic struggles, and families have certainly felt the shift when it comes to the cost of child care. Making matters worse: Nearly 9,000 day cares closed in 37 states between December 2019 to March 2021, according to findings from a new 2022 survey by ChildCare Aware.
“When it comes to child care, there are three critical criteria – cost, quality and availability – and based on our research findings, we’ve not only failed to make progress as a country, we’ve actually gone backwards,” said Natalie Mayslich, President, Consumer, Care.com. “Costs are growing while availability is shrinking and that’s having a profound impact on the workforce and consumer spending. We’ve all seen what happens when parents can’t work; making child care more affordable and accessible has to be a priority for all.”
New data from the ninth annual Care.com 2022 Cost of Care Survey reveals:
- The cost of child care is higher for families in 2022. 51% of parents say they spend more than 20% of their household income on child care, and 72% of parents report spending 10% or more. This is up from 70%, according to Care.com data from pre-pandemic 2019, the most recent year that mirrors parents’ options today.
- Quality child care continues to be tough for parents to find. In fact, 43% of parents say it’s much harder to find child care over the past year.
- Parents continue to struggle to pay for child care. In fact, 59% are more concerned about child care costs now than in years prior, which is driving significant changes, such as taking on a second job (31%), reducing hours at work (26%), changing jobs (25%), and leaving the workforce entirely (21%), to foot the bill.

How much does child care cost?
The cost of child care is on the rise
Based on the 2022 Cost of Care Survey, child care is not in the affordable range for most families. Of parents surveyed, 72% say they are spending 10% or more of their household income on child care, with a majority (51%) spending more than 20% or more. Yet according to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), child care is considered affordable when it costs families no more than 7% of their household income.
According to survey data, 63% report that child care is more expensive over the past year. The reasons parents say prices are skyrocketing include:
- Child care centers increased costs (46%).
- Inflation (41%).
- Child care centers taking fewer children (36%).
Interactive: Check out our Cost Calculator to figure out how much child care costs in your area.
The cost of child care can exceed that of a college education
The survey also finds that more than half of families (58%) plan to spend more than $10,000 on child care this year, which is more than the average annual cost of in-state college tuition ($9,349) per EducationData. org.
org.
Every type of child care is pricier than it was pre-pandemic
Overall, the average child care cost for one child in 2021 was $694/week for a nanny (up from $565/week in 2019), $226/week for a child care or day care center (up from $182/week) and $221/week for a family care center (up from $177/week).
Below are the 2021 national averages of weekly child care costs for each type of care, compared to costs in 2019.
National average weekly child care rates
| 2021 | 2019 | 2021 | 2019 | |
| One child | One child | Two children | Two children | |
| Nanny* | $694 | $565 | $715 | $585 |
| Child care center (toddler) | $226 | $215 | $429** | $409** |
| Family care center* | $221 | $201 | $420** | $382** |
| After-school sitter | $261 | $243 | $269 | $246 |
*Rates for infant children.

**Rates for two children calculated by adding the weekly rate for one child and the weekly rate for the second child with a national average sibling discount of 10%.
What’s the impact of rising child care costs on parents?
More than half — 59% — of parents say they’re more concerned about child care costs now than in years prior. The good news is that the majority (68%) budget for child care costs and nearly two-thirds (65%) say they will stay within or under budget.
Parents are cutting back on essentials
In turn, parents are making sacrifices to afford care and cutting back on budgets for:
- Vacations and travel (51%).
- Leisure activities (51%).
- Food, dining (45%).
- Clothing (41%).
- Extracurriculars (37%).
They’re also overhauling their work — and personal — lives
Many also plan to make the following work changes to adhere to rising care costs:
- 31% are considering taking on a second job.
- 26% are reducing hours at work.
- 25% are changing jobs.
- 21% leaving the workforce entirely.
Survey respondents are also adjusting their family plans to stay on track financially. 35% say they’re less likely to have more children with 43% listing the rising cost of child care as a major reason why.
How accessible is quality child care?
Parents say it’s harder to find child care providers than it was last year
Almost half of parents surveyed — 43% — say it’s much harder to find child care providers over the past year. According to our survey:
- 40% are having trouble finding a nanny.
- 39% are struggling to get care through a family care center.
- 37% find it challenging to book a babysitter.
- 36% are facing an uphill battle with finding a quality day care.
Child care providers are pricier to come by in some areas
Depending on where families live, the cost of hiring a nanny or paying for a day care can well exceed the national average. For example, in the District of Columbia, the cost of a nanny ($855 a week) is 23% above the national average, and the cost of day care ($419 a week) is 85% above the national average.
For example, in the District of Columbia, the cost of a nanny ($855 a week) is 23% above the national average, and the cost of day care ($419 a week) is 85% above the national average.
These are the priciest places to live if you’re hiring a nanny or sending kids to day care:
| State | Weekly Rate | $ Above National Avg | % Above National Avg |
| 1. District of Columbia | $855 | $161 | 23% |
| 2. Washington | $840 | $146 | 21% |
| 3. Massachusetts | $834 | $140 | 20% |
| 4. California | $829 | $135 | 19% |
| 5. Colorado | $763 | $69 | 10% |
| 6. Oregon | $741 | $47 | 7% |
| 7. New York | $736 | $42 | 6% |
| 8. Connecticut | $734 | $40 | 6% |
9. New Jersey New Jersey | $715 | $21 | 3% |
| 10. Vermont | $706 | $12 | 2% |
| State | Weekly Rate | $ Above National Avg | % Above National Avg |
| 1. District of Columbia | $419 | $193 | 85% |
| 2. Massachusetts | $324 | $98 | 44% |
| 3. Washington | $304 | $78 | 34% |
| 4. California | $286 | $60 | 26% |
| 5. Connecticut | $258 | $33 | 14% |
| 6. New York | $258 | $32 | 14% |
| 7. Arkansas | $255 | $29 | 13% |
| 8. Maryland | $254 | $28 | 12% |
| 9. Colorado | $254 | $28 | 12% |
| 10. Oregon | $249 | $23 | 10% |
How can you save money on child care?
As the cost of child care continues to rise, consider these steps to make the expense more affordable.
Find the best care for your budget
Once you’re clear on what you can afford, you can steer toward the child care option that’s the best fit for your family. The first step: Research current rates in your area. Care.com has free interactive tools you can use to identify the average costs of full-time child care, nanny and babysitter rates and nanny taxes in your region.
Discuss care benefits with your employer
Whether you’re hoping to find backup child or adult care or utilize paid family leave, it can pay to investigate whether or not your employer offers family care benefits. And if they don’t, ask for them.
It’s quite possible that they’ll be open to the idea now more than ever. Due to the pandemic, 57% of employers are prioritizing child care benefits more this year, and 63% said they plan to increase their company’s already existing child care benefits, according to Care.com’s 2021 Future of Benefits Report.
Set aside pre-tax dollars to pay for care
Talk to your workplace Human Resources department to see if a Dependent Care Account (a type of flexible spending account, or FSA) is available to you and how you can get started. With this account, you can put aside up to $5,000 in pre-tax dollars in your Dependent Care Account to pay for dependent care expenses. (Generally, only one spouse can enroll.)
With this account, you can put aside up to $5,000 in pre-tax dollars in your Dependent Care Account to pay for dependent care expenses. (Generally, only one spouse can enroll.)
The savings you will ultimately see varies depending on what your marginal tax rate is. A good approximation is around $2,000 in tax savings, assuming the family uses the full $5,000.
Make the most of tax breaks and credits
By paying your caregiver on the books, you can take advantage of tax breaks and credits. For example, by itemizing care-related expenses on your federal income return, you could receive a Child and Dependent Care Tax Credit on up to $600 of care-related expenses if you have one child, or $1,200 of care-related expenses if you have two or more children.
This year’s Cost of Care survey concluded that just over 1/3 of parents (34%) did not claim the expanded child care tax credit on their 2021 taxes, and 43% say that’s because they were unaware of it.
In addition, parents can save $2,000 per child using the Child Tax Credit.
Research child care subsidies and programs
Depending on your income, employee benefits and other factors, your family might qualify for a variety of cost-cutting child care subsidies. We’ve rounded up various programs, resources and other options that could reduce how much you’re paying for quality care.
__________________________
2022 Cost of Care Survey methodology
This scientific sample of 3,003 US adults (18 years or older) who are all parents paying for professional child care was surveyed between March 24, 2022, and March 30, 2022. All respondents are parents of children 14 years or younger and currently pay for professional child care, confirmed by both consumer-matched data and self-confirmation. DKC Analytics conducted and analyzed this survey with a sample procured using the Pollfish survey delivery platform, which delivers online surveys globally through mobile apps and the mobile web along with the desktop web. No post-stratification has been applied to the results.
- The Care.com Cost of Child Care Survey: 2021 Report
- The Care.com Cost of Child Care and COVID-19 Child Care Surveys: 2020 Report
- The Care.com Cost of Child Care Survey: 2019 Report
- The Care.com Cost of Child Care Survey: 2018 Report
- The Care.com Cost of Child Care Survey: 2017 Report
- The Care.com Cost of Child Care Survey: 2016 Report
- The Care.com Cost of Child Care Survey: 2015 Report
- The Care.com Cost of Child Care Survey: 2014 Report
Average Cost of Child Care
Many new parents realize they should start saving for college as soon as possible. But there’s an expense that can cost as much as college and starts much sooner: child care.
Shocking but true: In the U.S, the cost of child care at a day care center, full-time, is about as much as annual tuition and fees at a public college in the same state.
The day care costs range from a state average of $5,547 for an infant in Alabama to $16,549 for one in Massachusetts. A full-time nanny can cost as much as or more than tuition and fees at an Ivy League institution. Yet unlike college, for which almost all students can get subsidies and loans, child care is usually paid out of parents’ pockets.
A full-time nanny can cost as much as or more than tuition and fees at an Ivy League institution. Yet unlike college, for which almost all students can get subsidies and loans, child care is usually paid out of parents’ pockets.
- Average cost of child care
- How much families pay for child care
Average cost of child care
Child care costs can vary widely by type and by geographic location. And families may need different amounts depending on parents’ work schedules and other factors such as the child’s age and time spent in school. When parents can’t care for their children themselves, most patch together a variety of solutions from among the following:
| Extended family members or friends | $0 and up |
| Care in a day care center | 9,991 |
| Care in a home-based day care center | 7,431 |
| Nanny | 38,813 |
| Babysitters | 30,493 |
| Au pair | 18,000 |
| Baby nurse (helps with newborns, especially overnight) | $11 to $30 per hour (not typically employed on an annual basis) |
For families who must pay someone to watch their little ones at least some of the time, the annual average cost of child care in the U. S. is $3,863 for a middle-income, two-parent family with an infant. This figure includes a broad array of child care arrangements, from occasional babysitting to nanny care. Single parents with lower incomes pay about $1,948 on average, while high-earning couples pay about $11,000 per year on average. Unsurprisingly, families with more than one child pay higher costs for their care.
S. is $3,863 for a middle-income, two-parent family with an infant. This figure includes a broad array of child care arrangements, from occasional babysitting to nanny care. Single parents with lower incomes pay about $1,948 on average, while high-earning couples pay about $11,000 per year on average. Unsurprisingly, families with more than one child pay higher costs for their care.
Why is child care so expensive? In a word: labor. While technology has helped workers in other industries to be more productive in recent years, it hasn’t changed child care much. We still need human hands to pick up, feed and diaper babies; and human eyes to keep toddlers from eating sand or wandering off.
Child care workers in the U.S. earn relatively low salaries. In 2012, the typical child care worker earned $9.38 per hour, or $19,510 per year. While the cost of child care is typically borne in full by the parents who need the care, low-income families are eligible for child care subsidies in many states.
How much does day care cost?
The average cost across all states in the U.S. for an infant in full-time child care is $9,991 annually.
Most states require child care providers to meet certain standards, like specific staff-to-child ratios. For example, Maryland day care centers must have one staffer for every three infants, while in Georgia that ratio is 1:6. As much as 80% of a day care center’s expenses cover employee salaries and payroll-related expenditures, like taxes and benefits.
Day care providers might also have to pay for space, equipment, utilities, facilities maintenance, food, insurance, training and background checks for staff and other general safety and administrative costs.
About 35% of children under the age of five who need child care go to a day care center. An additional 8% of young children go to a home-based day care. In these, caretakers tend to earn less, and may not have benefits like health care or retirement savings plans. They often have lower expenses for things like rent or mortgage, and so cost less for parents.
The average annual cost for an infant in full-time care in a home-based day care center is $7,431.
How much does a nanny cost?
An in-home babysitter, or nanny, may be a better solution for some families, especially those with multiple children. About 5% of young children with a child care arrangement are cared for in their home by a babysitter or nanny.
The nanny market is competitive, with more experienced workers demanding higher pay. Families also try to woo nannies with good benefits, like health insurance, paid vacation and guaranteed pay on days or weeks when he or she isn’t needed, like when the family goes on vacation or a grandparent is visiting.
The average salary for a nanny is $19.14 per hour (that’s $39,811 annually for 40-hour weeks), according to a 2017 survey of mostly U.S.-based nannies done by the International Nanny Association. It ranges from an average of $14.08 per hour for a nanny with less than one year of experience to $21.98 per hour, on average, for those with 20-25 years of experience.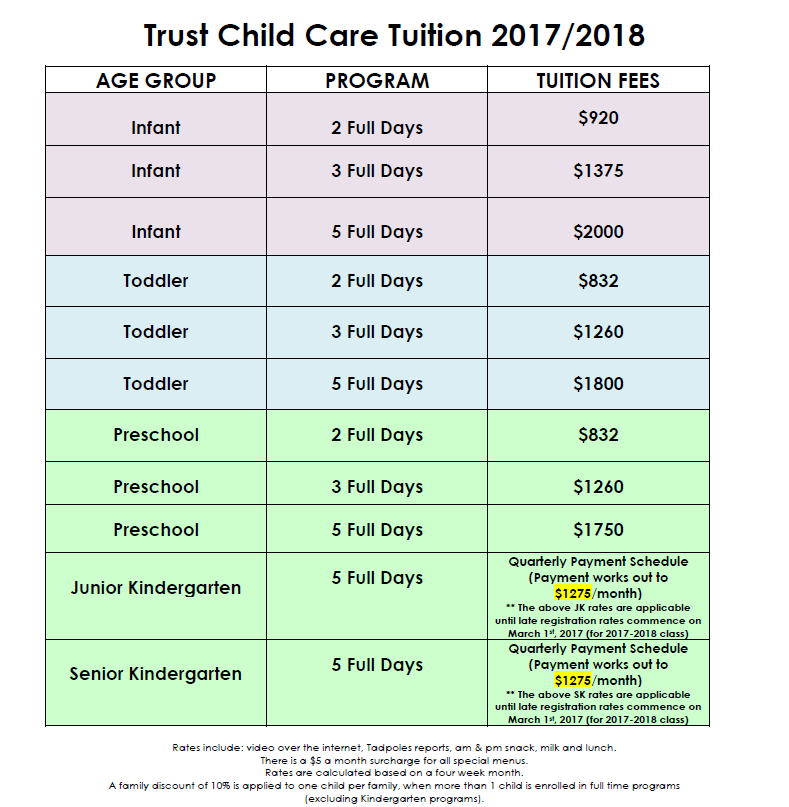
About 62% of nannies are compensated for overtime at time and a half, and 60% receive an annual bonus from their employer. More than 70% also get paid vacation and paid holidays. Only 17% of nannies get their health insurance costs paid either fully or partially.
U.S. families who pay a nanny (or any other domestic help) more than $2,300 per year are responsible for paying social security and Medicare taxes of 15.3% of the cash wages, according to the IRS. This amount can be split between the employer and the employee.
If your child’s caregiver earns more than $1,000 from you in any one quarter, you must also pay federal unemployment tax of 6% on the first $7,000 of their earnings. And depending on your state, you might also have to pay state unemployment taxes, workers’ compensation insurance and disability benefits.
How much does a babysitter cost?
Parents who don’t work full time, or who have nontraditional schedules, can sometimes provide more child care themselves and use babysitters to fill in the gaps. Parents in U.S. cities generally pay babysitters between $15 and $23 per hour, averaging $17.50 per hour (or $36,400 for one year of full-time care), according to SitterCity. The rate is highest in expensive cities like San Francisco.
Parents in U.S. cities generally pay babysitters between $15 and $23 per hour, averaging $17.50 per hour (or $36,400 for one year of full-time care), according to SitterCity. The rate is highest in expensive cities like San Francisco.
Families with more children typically pay more per hour. And nannies or sitters with special qualifications, like a second language, many years of experience, CPR or First Aid certification, or who do some housework, such as laundry, might also charge more for their services. Most families provide food for the caregiver when he or she is in the home or offer a ride or taxi fare for travel to or from the home late at night.
Babysitter wages are also subject to the tax laws for domestic employees, as outlined above.
How much does a baby nurse cost?
New parents without access to maternity or paternity leave benefits might have to go back to work when their newborn is still waking up every three hours. Others, with cash to spare, might also appreciate the assistance of an experienced newborn caregiver. Enter the baby nurse, who can come to your home for 12-hour shifts or even round-the-clock help during those early weeks of your baby’s life. Some stay for just a week or two, while others for up to six weeks or longer.
Enter the baby nurse, who can come to your home for 12-hour shifts or even round-the-clock help during those early weeks of your baby’s life. Some stay for just a week or two, while others for up to six weeks or longer.
New mothers report paying a baby nurse, or night nurse, rates that start at about $11 per hour in lower-cost-of-living parts of the U.S. Baby nurses hired through agencies tend to cost more. In some expensive cities, families pay up to $30 per hour.
How much does an au pair cost?
If you have a spare room in your home for a live-in caregiver for your child, you might consider hosting an au pair. Several agencies can help you connect with a young person from another country as well as coordinate their visa, travel, insurance and orientation. Several of these agencies include Cultural Care Au Pair and Au Pair in America, to name a few.
The average cost for an au pair for a full year is about $18,000, plus room and board. In return for this expense, you get about 45 hours of child care per week. It breaks down to less than $8 per hour, alongside your extra costs for groceries and other family activities, like going out to restaurants or traveling for a ski trips or summer vacation, since au pairs are generally treated as members of the family.
It breaks down to less than $8 per hour, alongside your extra costs for groceries and other family activities, like going out to restaurants or traveling for a ski trips or summer vacation, since au pairs are generally treated as members of the family.
How much families pay for child care
The percentage of income paid for child care by a family with a working mother has ranged between 6% and 8% in the U.S. since 1985. In 2011, such families, including many who only require part-time or even occasional paid child care, paid an average of 7.2% of their income.
Those who require full-time child care tend to pay a much larger share of their income for the service. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services considers child care to be affordable when it is 10% or less of a family’s income. However, in 38 states, the average annual cost of full-time care for an infant at a day care center is above this threshold.
The cost of full-time child care can be a huge burden for low income and single parent families, as well as those who live in high-cost-of-living parts of the country.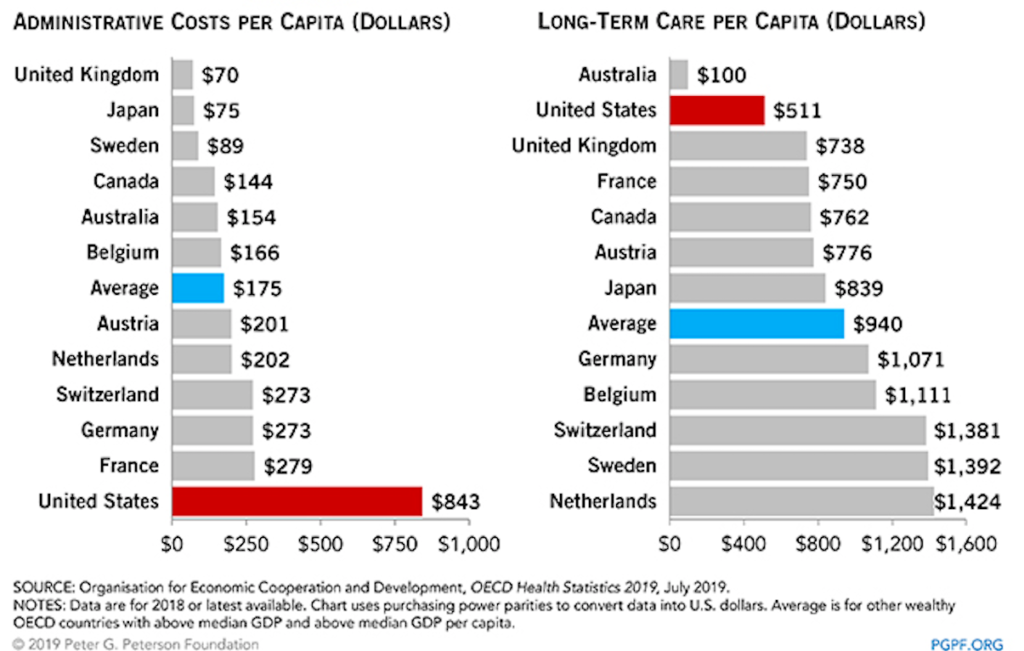
Throughout the country, the cost of full-time care at a day care center eats up 40% of the state median income for single mothers. And in New York State, where child care is least affordable as a percentage of income, the typical married couple must pay 16% of their income (on average, $14,500) for full-time care of an infant at a day care center.
The IRS allows families a tax credit for up to 35% of qualifying expenses up to $3,000 for one child under the age of 13, and up to $6,000 for two or more children. This translates to a maximum of $1,050 in tax savings for one child (i.e., 35% of $3,000) or $2,100 for two children. The actual credit depends on your adjusted gross income (AGI) and decreases to 20% of allowable expenses for parents with an AGI of more than $43,000 per year.
The cost of child care may be as challenging to many families as sleep deprivation is during their child’s early years. Fortunately, it’s necessary for a limited time, until the children go to school and become more self-sufficient.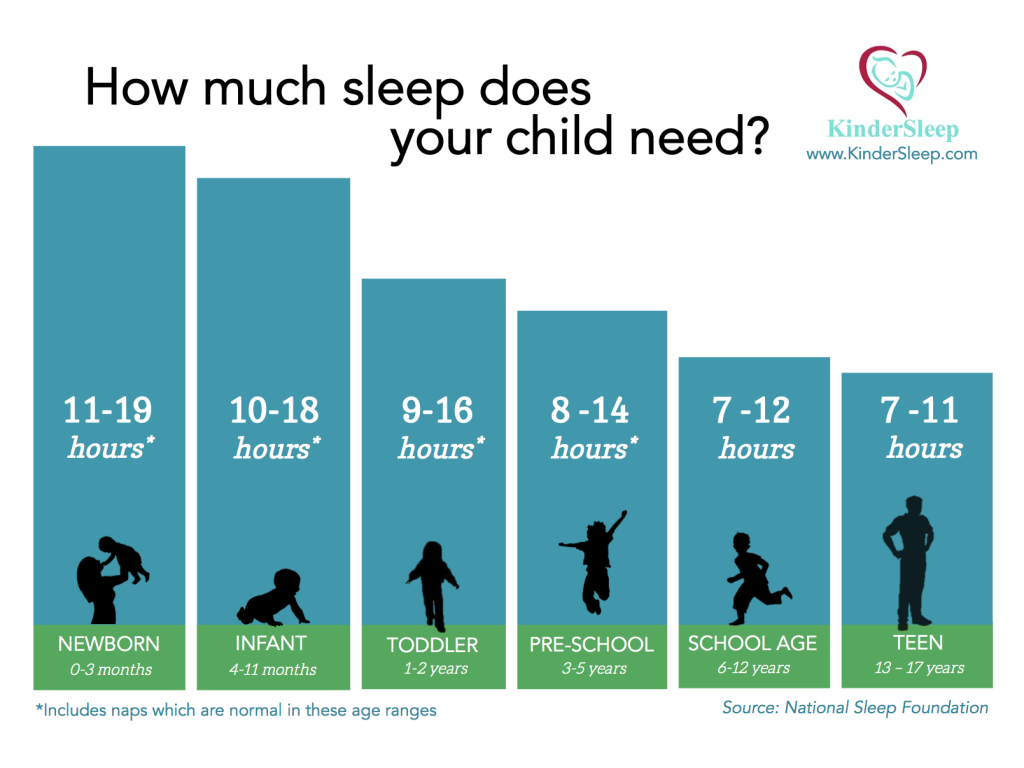 If it allows both parents to work, they can reap benefits both in terms of salary and experience, which might pay off in higher wages down the line.
If it allows both parents to work, they can reap benefits both in terms of salary and experience, which might pay off in higher wages down the line.
Methodology and sources
To find the average cost of childcare, we analyzed data provided by Childcare Aware of America, a nonprofit that provides childcare resources to parents. We also consulted other sources, including SitterCity and the IRS.
Child Care Aware® of America, Parents and the High Cost of Child Care
Caring for a newborn baby - a note to mom
During the first year of life, a child makes a giant leap in his physical and emotional development (just imagine that his brain grows 1.5 times!). But parents also learn a lot, especially if the baby is the first. “How to care for the ears, nose, eyes is, of course, very important, and we will definitely talk about it. But it is equally important to learn to feel your child, ”according to Yulia Viktorovna Andronnikova, pediatrician of the highest category, head of the pediatric department of the Center for Traditional Obstetrics and Family Medicine, this feeling of security and love will accompany the child all his life.
All children are different, their needs are different, and mom and dad will have to find their own way, relying on the opinions of specialists and their own intuition.
The only thing that can be said for sure is that extreme is always bad. And in the upbringing of children in the first place.
Breastfeeding
An important aspect of infant care is proper breastfeeding. This is “the core on which the whole care of the baby is wound. Breast sucking is the main interest of the baby in the first months of life, and in the future and for quite a long time - a priority interest. Breastfeeding helps to build the rhythm of life, help the baby in time, calm down, feed," says Lilia Valentinovna Kazakova, pediatrician of the Territory of Health and SM, AKEV breastfeeding consultant. Sucking activates the bowels. This will help to accustom to "planting" from early childhood. Just in case, let's make a reservation - breastfeeding is certainly good, but it is not a panacea and does not guarantee either good health or deeper affection. With other mother's efforts, "artificials" can easily catch up, or even overtake "babies" in all respects.
With other mother's efforts, "artificials" can easily catch up, or even overtake "babies" in all respects.
Bathing, caring for the umbilical wound and skin
Baby's skin is thin and vulnerable, sweating and diaper rash quickly appear on it. Therefore, it is necessary to arrange air baths for the child (the optimum temperature in the room is 20-22 C, humidity is 55-60%). You can bathe daily - the first month for 2-3 minutes (water - about 37 C). Then gradually increasing the time (up to 10 minutes) and lowering the temperature (by 1-2 C). It is better to use baby soap / foam less often - once a week, not more often.
"Never bathe your baby on an empty stomach." This is not a swimmer's training, but a relaxing and hygienic procedure. The kid should be calm and contented with life," reminds L. V. Kazakova. When taking it out of the water, wrap it in a large towel and immediately breastfeed (eat). He sucks, dries, calms down, and after 10-15 minutes you will calmly do everything you need. Use only sterile water to treat the remaining umbilical cord (other solutions may interfere with the natural healing process). After rinsing, dry thoroughly with a clean towel (not cotton! To avoid leaving fibers on the navel).
Use only sterile water to treat the remaining umbilical cord (other solutions may interfere with the natural healing process). After rinsing, dry thoroughly with a clean towel (not cotton! To avoid leaving fibers on the navel).
Hygiene for girls and boys
“The first and most important thing for a newborn girl is not to injure her genitals by mechanically removing the lubricant (she will go away on her own over time). Rinse with warm water (use soap once every 3-4 days), and then be sure to moisturize (distribute 1 drop of oil over the entire washed surface),” Galina Vladimirovna Ovsyannikova, an obstetrician-gynecologist of the Health Territory, advises washing from front to back (for this it is more convenient keep your daughter upside down). For signs of inflammation, take chamomile baths, and for more severe redness, treat with Miramistin. Another important - exclusively "female" - nuance of hygiene: "Immediately after birth, a neonatologist-pediatrician should look at the genital gap. Mom needs to be constantly monitored until 5-6 years old so that she does not overgrow (once every 3-4 days).
Mom needs to be constantly monitored until 5-6 years old so that she does not overgrow (once every 3-4 days).
For boys, pediatricians recommend washing the genitals only from the outside (up to adolescence): during the day, if necessary, wipe with wet baby wipes, and in the evening, while bathing, wash with warm water from the outside and do not climb anywhere else (closing foreskin and smegma are the best natural defense against bacteria)! As for phimosis, up to 3 years is the norm, and a variant of the norm almost until adolescence.
Eye Care
The eyes of a newborn do not require special care. Everything that accumulates on the surface of the baby's eye is removed on its own when the baby blinks. In the morning, in the corners of the eyes, you can see the mucus accumulated during the night - this is also the norm. Rinse the eyelashes / eyelids of the baby with boiled water, wiping with a cotton swab from the outer corner to the inner.
The cause of profuse discharge from the eyes of a newborn may be dacryocystitis, blockage of the nasolacrimal canal. "Proper massage allows you to cope with this disease by the age of 2 months." Massage is simple, but it will be better if a specialist shows it. Also, ophthalmologist Anastasia Borisovna Petukhova recalls that the first examination by an ophthalmologist is immediately after birth, while still in the maternity hospital, and the second is at the age of 1 month: “It is a mistake to think that nothing can be done if the child is still very small. For example, a congenital cataract is operated on at the age of 2-3 months, while later surgical treatment may not be as effective.”
"Proper massage allows you to cope with this disease by the age of 2 months." Massage is simple, but it will be better if a specialist shows it. Also, ophthalmologist Anastasia Borisovna Petukhova recalls that the first examination by an ophthalmologist is immediately after birth, while still in the maternity hospital, and the second is at the age of 1 month: “It is a mistake to think that nothing can be done if the child is still very small. For example, a congenital cataract is operated on at the age of 2-3 months, while later surgical treatment may not be as effective.”
Nose and ear care
Yes, they can and should be cleaned. But the main thing is not to overdo it, warns the otolaryngologist, homeopath and mother of three children Ekaterina Vladislavovna Polinskaya: “You only need to clean the auricle (by no means the ear canal!) After bathing the child.” A small child still does not know how to blow his nose himself (he will learn this by the age of 2-3), so you can instill drops in him in the morning and in the evening based on isotonic sodium chloride solution. Children under one year of age do not need to use sprays - the auditory tube is still short and wide, this can provoke a rapid reflux of infection from the nasal cavity. The same applies to instillation of breast milk into the nose. “This is physiologically unreasonable and blocks the mucociliary clearance of the nasal cavity. Yes, milk contains proteins, fats and carbohydrates, as well as protective antibodies that are necessary for the baby. But they must still act through the oral cavity, ”explains the doctor.
Children under one year of age do not need to use sprays - the auditory tube is still short and wide, this can provoke a rapid reflux of infection from the nasal cavity. The same applies to instillation of breast milk into the nose. “This is physiologically unreasonable and blocks the mucociliary clearance of the nasal cavity. Yes, milk contains proteins, fats and carbohydrates, as well as protective antibodies that are necessary for the baby. But they must still act through the oral cavity, ”explains the doctor.
Fundamentals of Fundamentals
Not all advances that make life easier for older people benefit the younger generation. Due to the constant use of diapers, pediatrician Yulia Viktorovna Andronnikova warns, the child may have difficulties with the formation of toilet skills, in the "diaper" he does not feel "bottom", does not realize that he is pissing - he does not have the necessary feeling of discomfort for this. Instead of disposable diapers, pay attention to "reusable" cloth diapers - they help to form the necessary skills much faster and are more physiological. The next important task for parents of babies up to a year, according to Yulia Viktorovna, is to teach them to chew and swallow correctly! “Our children drink and eat everything puree until almost 3-4 years old! This has a bad effect on chewing skills, diet. Does not "teach" the stomach to work normally. And finally, you need to organize a sleep schedule. “Unfortunately, modern children often live in a mode that is convenient for their parents: late bedtime, late rising. Whereas all the hormones necessary for the growth and proper formation of internal organs work precisely in sleep, moreover, from nine in the evening. Hug, kiss and rejoice... Together!
The next important task for parents of babies up to a year, according to Yulia Viktorovna, is to teach them to chew and swallow correctly! “Our children drink and eat everything puree until almost 3-4 years old! This has a bad effect on chewing skills, diet. Does not "teach" the stomach to work normally. And finally, you need to organize a sleep schedule. “Unfortunately, modern children often live in a mode that is convenient for their parents: late bedtime, late rising. Whereas all the hormones necessary for the growth and proper formation of internal organs work precisely in sleep, moreover, from nine in the evening. Hug, kiss and rejoice... Together!
And finally, the most important thing. The mental development of the baby, the development of different parts of the brain, and, therefore, different sensory organs, depend on the external impressions that he receives in the first year of life. “Without the proper experience of one-on-one communication with a caring adult, the orbito-frontal cortex is unlikely to be sufficiently developed. It has been found that the baby's heart rate synchronizes with the parent's, so if the parent is relaxed and calm, so will the baby. The mother's nervous system essentially communicates with the baby's nervous system, calming it down through touch." (Sue Gerhardt "How Love Shapes the Baby's Brain").
It has been found that the baby's heart rate synchronizes with the parent's, so if the parent is relaxed and calm, so will the baby. The mother's nervous system essentially communicates with the baby's nervous system, calming it down through touch." (Sue Gerhardt "How Love Shapes the Baby's Brain").
By hugging our baby, we, in fact, develop and strengthen it. But we don’t spoil at all and we teach it to be handled, as other grandmothers assure us. Nod to these grandmothers and hug your little (yet small) happiness even more tenderly: this will only make it stronger!
Monthly allowance for child care for persons not subject to compulsory social insurance
The applicant has the right to file a complaint against the decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, its officials in the provision of public services (complaint), including in the pre-trial (out of court) procedure in the following cases:
- violation of the application registration deadline;
- violation of the term for the provision of public services;
- requirement from the applicant of documents, information or actions not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation for the provision of public services;
- refusal to provide a public service, if the grounds for refusal are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them;
- refusal to accept documents, the submission of which is provided for by regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation for the provision of public services;
- requesting from the applicant, when providing a public service, a fee not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation;
- refusal of the authorized body, its officials to correct the misprints and errors made by them in the documents issued as a result of the provision of public services or violation of the deadline for such corrections;
- violation of the term or procedure for issuing documents based on the results of the provision of public services;
- suspension of the provision of public services, if the grounds for suspension are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them, laws and other regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipal legal acts.

Subject of complaint
The subject of the complaint is a violation of the rights and legitimate interests of the applicant, unlawful decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, its officials in the provision of public services, violation of the provisions of the administrative regulations and other regulatory legal acts that establish requirements for the provision of public services.
A citizen has the right to file a complaint in writing on paper by mail or in person to any PFR Client Service, as well as in electronic form:
- on the official website pfr.gov.ru;
- portal vashkontrol.ru;
- portal do.gosuslugi.ru.
The reason for the appeal may be dissatisfaction with the quality of the provision of public services by the PFR, violation of the terms for the provision of services, violation of the terms for registering a request for a service, refusal to correct errors or typos, refusal to provide a public service, refusal to accept documents, demand for an additional fee.
Procedure for filing and reviewing a complaint
The complaint must contain:
- name of the authorized body, last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of its officials providing public services and (or) their leaders, decisions and actions (inaction) of which are being appealed;
- last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the applicant, information about the place of residence, as well as contact phone number(s), e-mail address(es) (if any) and postal address to which the answer should be sent to the applicant;
- information about the appealed decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, an official of the authorized body, its head;
- arguments on the basis of which the applicant does not agree with the decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, an official of the authorized body, its head.
The applicant shall submit documents (if any) confirming his arguments or copies thereof.
When filing a complaint in electronic form, the documents specified in paragraph 106 of the administrative regulations may be submitted in the form of an electronic document signed with an electronic signature, the form of which is provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation. In this case, an identity document of the applicant is not required.
In the authorized body, officials authorized to consider complaints are determined, who ensure:
- receiving and handling complaints;
- sending complaints to the body authorized to consider them.
Complaints against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of an official of the authorized body are considered by the head of the authorized body or an official of the authorized body authorized to consider complaints. Complaints against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the head of the authorized body are considered by an official of the executive authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation authorized to consider complaints.
If the complaint is filed by the applicant with a body whose competence does not include making a decision on the complaint, within 3 working days from the date of its registration, the said body sends the complaint to the body authorized to consider it and informs the complainant in writing about the redirection of the complaint.
The authorized body ensures:
- equipment for receiving complaints;
- informing applicants about the procedure for appealing against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, officials of the authorized body by posting information on information boards in places where public services are provided, on the website of the authorized body, on the Single portal, service portal;
- advising applicants on the procedure for appealing against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, officials of the authorized body in person, by phone, using the website of the authorized body;
- conclusion of agreements on interaction between the multifunctional center and the authorized body in terms of the implementation by the multifunctional center of receiving complaints and issuing the results of consideration of complaints to the applicant;
- formation and quarterly submission to the Federal Service for Labor and Employment of reports on received and considered complaints (including the number of satisfied and unsatisfied complaints).

Deadlines for considering a complaint
A complaint received by the authorized body shall be subject to registration no later than the working day following the day of its receipt.
The complaint is subject to consideration within 15 working days from the date of its registration, and in the event of an appeal against the refusal of the authorized body to accept documents from the applicant or to correct misprints and errors, or in the event of an appeal against a violation of the established deadline for such corrections - within 5 working days from the date of its registration.
Result of consideration of the complaint
The result of the consideration of the complaint is the adoption of one of the following decisions:
- satisfy the complaint, including in the form of cancellation of the decision made by the authorized body, correction of typos and errors in documents issued as a result of the provision of public services, return to the applicant of funds, the collection of which is not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, regulatory legal acts of the subjects Russian Federation, municipal legal acts;
- refuse to satisfy the complaint.
When satisfying the complaint, the authorized body takes comprehensive measures to eliminate the identified violations, including the issuance of the result of the public service to the applicant no later than 5 working days from the date of the relevant decision, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
A complaint may be denied in the following cases:
- availability of a court decision that has entered into legal force on a complaint about the same subject and on the same grounds;
- filing a complaint by a person whose powers have not been confirmed in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- the presence of a decision on a complaint made earlier in accordance with the requirements of the Rules for filing and considering complaints against decisions and actions (inaction) of federal executive bodies and their officials, federal civil servants, officials of state non-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation, state corporations endowed with in accordance with federal laws, the powers to provide public services in the established field of activity, and their officials, organizations provided for by Part 1.
 1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services and their employees, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 840 dated August 16, 2012, in respect of the same applicant and on the same subject of the complaint.
1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services and their employees, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 840 dated August 16, 2012, in respect of the same applicant and on the same subject of the complaint.
A complaint may be left unanswered in the following cases:
- presence in the complaint of obscene or offensive language, threats to life, health and property of an official of the authorized body, as well as members of his family;
- the inability to read any part of the text of the complaint, the last name, first name, patronymic (if any) and (or) the postal address of the applicant indicated in the complaint.
In response to the results of the consideration of the complaint, the following shall be indicated:
- name of the public service provider that considered the complaint, position, last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the official who made the decision on the complaint;
- number, date, place of the decision, including information about the official of the authorized body, the decision and (or) action (omission) of which is being appealed;
- surname, name, patronymic (if any) of the applicant;
- grounds for making a decision on the complaint;
- decision made on the complaint;
- if the complaint is found to be justified, the terms for eliminating the identified violations, including the term for providing the result of the public service;
- information on the procedure for appealing the decision taken on the complaint.

In the event that, during or as a result of consideration of a complaint, signs of an administrative offense or crime are established, an official of the authorized body authorized to consider complaints shall send the available materials to the prosecutor's office.
Procedure for informing the applicant about the results of the consideration of the complaint
A reasoned response based on the results of the consideration of the complaint is signed by the official authorized to consider the complaint and sent to the applicant in writing or, at the request of the applicant, in the form of an electronic document signed by the electronic signature of the official authorized to consider the complaint, the type of which is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, no later than the day following the day the decision is made on the results of the consideration of the complaint.
Procedure for appealing a decision on a complaint
The applicant has the right to appeal the decision taken on the complaint by sending it to the Federal Service for Labor and Employment.
If the applicant is not satisfied with the decision made during the consideration of the complaint or the absence of a decision on it, then he has the right to appeal the decision in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The applicant's right to receive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the complaint
The applicant has the right to receive comprehensive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the complaint.
Ways to inform complainants about the procedure for filing and considering a complaint
Information on the procedure for filing and considering a complaint is posted on information boards in places where public services are provided, on the website of the authorized body, on the Single Portal, Services Portal, and can also be communicated to the applicant orally and (or) in writing.
List of normative legal acts regulating the procedure for pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal against decisions and actions (inaction) of the authorized body, as well as its officials
The procedure for pre-trial (out-of-court) appeals against decisions and actions (inaction) of the body providing the public service, as well as its officials, is regulated by Federal Law No.