How much does canada pay per child
What is the Canada Child Benefit?
December 2021 – 15 min read
Key takeaways
What’s in this article?
- An intro to the Canada Child Benefit (CCB)
- Who can claim the CCB?
- CCB payments explained
- How to apply for the CCB
- What's next?
An intro to the Canada Child Benefit (CCB)
The CCB is a government benefitOpens in a new window that helps families in Canada with the costs of raising children.
Administered by the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA), it was introduced in July 2016 to replace the Universal Child Care Benefit (UCCB). The CCB provides eligible parents with children under the age of 18 a monthly, tax-free payment. The CCB could include the Child Disability Benefit (CDB)Opens in a new window and is payable on top of any other child benefits that might be offered at provincial or municipal level.
Who can claim the CCB?
You could be eligible to receive the CCB if you meet all the following criteria:
- You’re a resident of Canada for tax purposes
- You live with a child under 18 years of age
- You have primary responsibility for the child’s care and upbringing
You could be eligible to receive the CCB if you or your spouse or common-law is:
- A Canadian citizen or permanent resident
- A temporary resident who has lived in Canada for the previous 18 months
- A protected person
- An indigenous person
About primary responsibility
You should apply for the CCB if you’re considered “primarily responsible” for raising your child. That means being responsible for things such as:
- Supervising the child's everyday activities
- Taking care of their daily needs
- Taking care of any medical needs
- Arranging childcareOpens in a new window
Only 1 parent can apply for the CCB, and which parent does so will depend on your own family situation.
CCB payments explained
Based on CCB payments in 2021, you could receive a maximum of:
- $6,833 per year ($569.41 per month) for each eligible child under the age of 6
- $5,765 per year ($480.41 per month) for each eligible child aged 6 to 17
However, the amount you actually receive will depend on several factors, such as whether your child lives with you full or part time, your net family income, and the number of eligible children you have. You can use the government’s CCB calculatorOpens a new website in a new window - Opens in a new window to get an idea of what your payments might be.
Payments are recalculated every July. This is to account for inflation, as well as your family net income from the year before. For example, if there was a change in your income in 2021, this will be reflected in your payments starting in July 2022. If your total benefit amount for the year is less than $240, you’ll receive this as 1 lump sum payment in July instead of receiving it monthly.
This is to account for inflation, as well as your family net income from the year before. For example, if there was a change in your income in 2021, this will be reflected in your payments starting in July 2022. If your total benefit amount for the year is less than $240, you’ll receive this as 1 lump sum payment in July instead of receiving it monthly.
How to apply for the CCB
You should apply for the CCB as soon as any of these events happen:
- Your baby is born
- Your child starts to live with you after a period of living elsewhere
- Your custody arrangements change, or you are granted custody of a child
- You or your spouse or partner start to meet the criteria and become eligible
You can apply at the same time you register the birth of your baby with the province or territory, or afterwards using your CRA online account. You can also download and complete Form RC66, Canada Child Benefits ApplicationOpens a new website in a new window - Opens in a new window, and return this via mail along with any additional documents and forms required.
Your payments will start within 8 weeks of the government receiving your online application, or within 11 weeks of sending a paper application through the mail. The payments will stop when your child turns 18, or when your net family income exceeds the threshold of $120,000.
What’s next?
This material is for information purposes only and shouldn’t be construed as providing legal or tax advice. Every effort has been made to ensure its accuracy, but errors and omissions are possible. All comments related to taxation are general in nature and are based on current Canadian tax legislation and interpretations for Canadian residents, which are subject to change. For individual circumstances, consult with your tax, legal or accounting professionals. This information is provided by The Canada Life Assurance Company and is current as of date of publication.
Related articles
How do RESP contributions work?
What is an ETF?
How are RESPs taxed?
What is the Canada Child Benefit?
Raising kids can be expensive, but qualifying families can receive tax-free monthly payments from the government to help with some of the costs.
Known as the Canada Child Benefit, the amount your family gets will depend on factors like household income, family size, and province or territory of residence. Fortunately, the process of applying for this assistance is straightforward and quick.
What is the Canada Child Benefit?
In 2016, the Canada Child Benefit, or CCB, replaced the Canada Child Tax Benefit, or CCTB. The government made this change to make more money available to parents with lower incomes.
The CCB is a tax-free monthly payment made directly to families with children under 18 years old. It’s handled by the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA), but you don’t need to include it on your income tax return — you just need to file your income taxes every year.
If you’re eligible, the CCB payments you receive may include additional benefits for your children, including a child disability benefit and provincial and territorial benefits.
» MORE: What Canadian employees should know about T4 slips
How much is the Canada child benefit?
Monthly CCB payments are based on:
- The number of children in your care.
- The age of the children.
- Your marital status.
- Your adjusted family net income (AFNI) from the previous year’s tax return.
If your AFNI is less than $32,028, you can receive up to the following amounts per child:
- Under six years of age: $6,833 per year ($569.41 per month)
- Six to 17 years of age: $5,765 per year ($480.41 per month)
Since the CCB is meant to deliver assistance to lower-income families, payments start to decrease if your AFNI exceeds $32,028. Additionally, if you’re over this income threshold, the CCB is reduced for each additional child you have.
Admittedly, CCB calculations and adjustments can be a bit complicated. However, the Government of Canada has an online CCB calculator that can help you estimate exactly how much CCB you’ll receive each month.
Payments are recalculated every July based on the previous year’s tax return. The government also adjusts the maximum payout for the CCB every year to account for inflation.
There’s also a young child supplement that’s paid out four times a year to families with children under the age of six. To get this benefit, you must file your income taxes.
» MORE: What is a kids bank account?
Canada child benefit eligibility
To qualify for the CCB, you, your spouse, or your common-law partner must be a Canadian citizen, permanent resident, protected person, or an Indigenous person as defined under the Indian Act. You may also qualify as a temporary resident in Canada for the past 18 months who has a valid permit with resident status for the following month.
You must also meet the following conditions:
- You live with at least one child under the age of 18.
- You’re the person primarily responsible for the child’s care.
- You’re a Canadian resident for tax purposes.
If you have a foster child or care for a child under a kinship or close relationship program, you would only get the CCB if you’re not receiving funds from the Children’s Special Allowances, or CSA, program.
Only one person — the individual primarily responsible for the child’s care — should apply for the CCB. To determine who fills that role in a household with two parents or guardians, ask yourself the following:
- Who takes care of the child’s daily activities and needs?
- Who makes sure the child’s medical needs are met?
- Who arranges child care when needed?
If two individuals share the responsibilities equally and one of them is female, the CRA assumes she is primarily responsible for the child’s care. Therefore, the female parent should apply for the CCB. The female parent can sign a letter stating that the other parent is primarily responsible, however, in which case, the other parent would apply for the CCB.
In the case of same-sex parents, one parent should apply for the CCB for all the children.
If you’re in a joint custody situation, the CRA will calculate how much each parent qualifies for based on your custody arrangement.
» MORE: How does Canada’s Registered Disability Savings Plan (RDSP) work?
How to claim the Canada Child Benefit
You can apply for the CCB as soon as a child is born or starts to live with you, or you begin to meet the eligibility requirements.
For example, you can apply for the CCB when you register the birth of your newborn child, usually at the hospital or birthing centre. As long as you provide your consent and social insurance number (SIN), the CRA will get your information.
If you didn’t apply when the child was born, you can apply online via My Account (your personal CRA account) or by mail.
CCB payments are made monthly via direct deposit or cheque. As long as you file your taxes every year and continue to meet the eligibility requirements, you’ll continue to get the CCB.
Canada Child Benefit
Canadian Child Benefit Features
A unique program created with the assistance of the
Canadian Federal Government,
and the Provincial and Territory Governments.
National Childhood Insurance Program.
Canada Child Tax Benefit.
Canadians often refer to their social security system as the “social security system”. Assistance programs are designed for all sectors of society, especially for minors, the unemployed and the elderly. Child allowance introduced from January 1993 years old It is paid to low- and middle-income families with children under the age of 18. The amount of the benefit depends on the total annual income of the family, as follows:
In Canada, the minimum tax-free family income is $20,435 Canadian dollars per year and qualifies for National Child Benefit (NCB) assistance from the state.
Families with annual incomes below $20,435 are eligible for government assistance of:
1) $266.67 per month ($3,200 per year) for first child;
2) $247.92 per month ($2.975 per year) for second child;
3) $248.33 per month ($2,980 per year) for the third and each child up to the 7th in the family.
Families with annual incomes between $20,435 and $36,378 and more than 3 children receive an allowance for the 3rd and each subsequent child (up to the 7th).
Families with more than 4 children raise the minimum annual income cap to $36,378.
Families with one and two children with annual incomes between $36,378 and $99,128 are also eligible for indexed child support.
Larger families are eligible for indexed child support even if the income is $99,128.
Do you know the law, rules, procedures and policies of immigration?
How does the National Child Benefit (NCB) system work?
The NCB program is a combination of 2 elements: a monthly federal allowance for each child in low-income families and additional provincial benefits and payments (health insurance, transportation benefits, social benefits and numerous budgetary grants for sports sections for children and etc.).
Achievement of the Welfare Social Benefit level, the so-called “Welfare Wall”.
The National Childhood Insurance system is closely linked to the taxation system, if the family income exceeds the allowable tax-free minimum, then this affects the amount of the child allowance issued and may threaten with the deprivation of some social benefits, such as compulsory health insurance, benefits for receiving free dental services, free medicines, etc. Thus, it turns out that families in which parents work in low-paid jobs may be lower or at the same material level as families receiving Welfare. To avoid this phenomenon, the Canadian government split the payment between NCB and Welfare. Now only working parents will have child benefits.
Federal Government Supplements to the National Childhood Insurance Program.
According to these additions, the Federal Government has the right to revise the amount of the monthly allowance for children in the direction of indexation, i.e. increase taking into account economic changes in the country. The increase in the amount of the allowance for children has been observed since 1998 .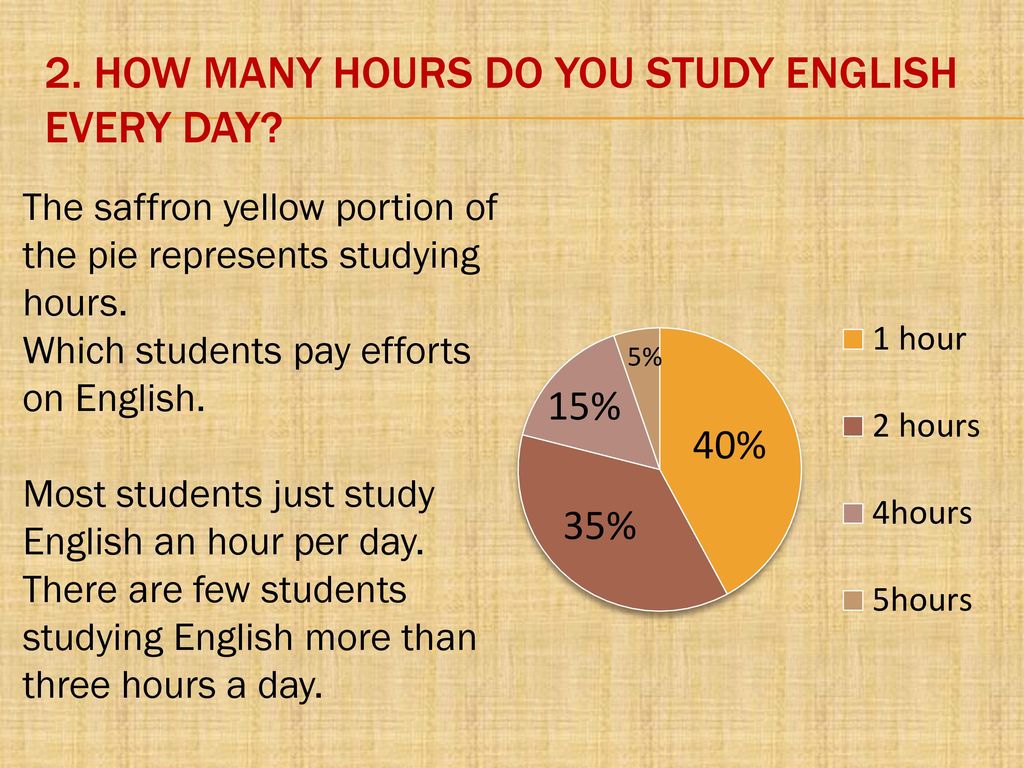
In 2003-2004, 82% of Canadian families with children received an NCB. The amount of additional funds allocated to the Childhood Insurance Scheme increased by $3.4 billion Canadian dollars.
The National Childhood Insurance Program is administered by the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA). NCB applications must be filed each year in July to be eligible for Child Benefit for the next 12 months.
For more information, visit: http://www.nationalchildbenefit.ca/index.html
Immigrant Benefits in Canada
Canada is very loyal to immigrants. All those who legally enter the country become full members of Canadian society. Therefore, finding themselves in a difficult life situation, immigrants can count on the help of the state and the regional government.
The Government of Canada is doing everything possible to ensure that the people of the country do not fall below the poverty line. Whether it is job loss, illness, the birth of a child or the death of a loved one - a resident of the country can count on the comprehensive support of social services.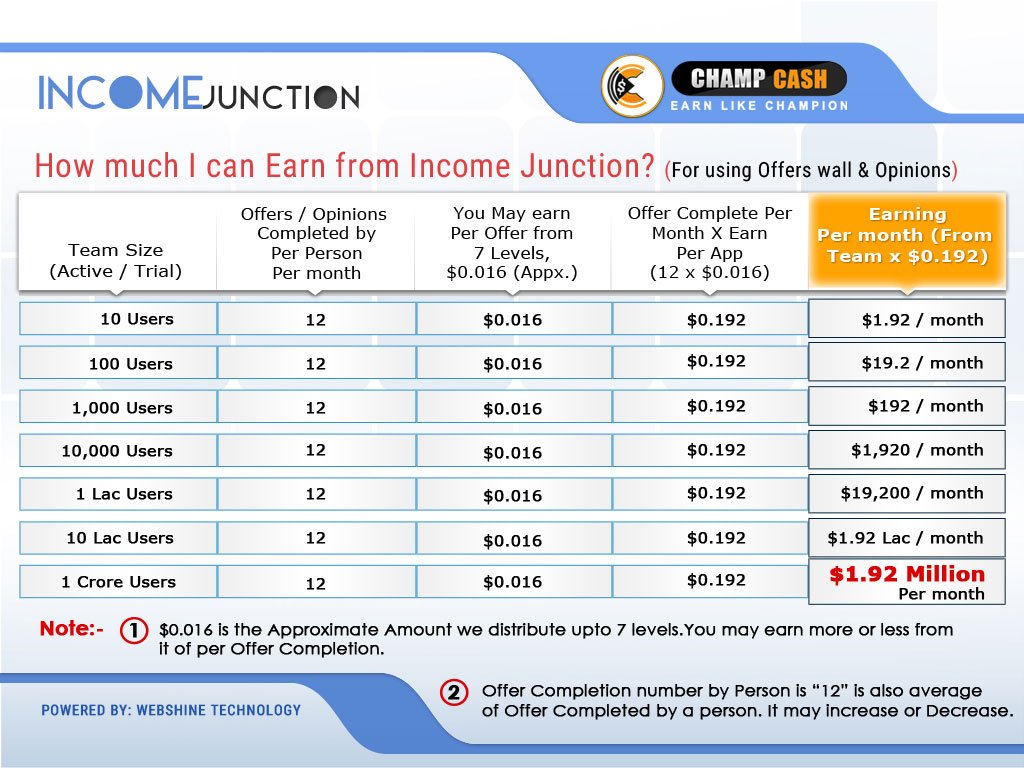
Immigrant benefits in Canada: Welfare
Welfare - benefits are provided to those , who want, but are temporarily unable to find a job (for example, you need to pass qualifying exams to get a job).
Any person legally residing in the country and whose income is below the subsistence level can receive benefits.
Many newly arrived immigrants go through the walfare process. It takes several days and consists of an interview and the provision of documents (purchase receipts, customs declaration, etc.). The applicant must show:
- how much money was brought into the country
- what this amount was spent on
- explain the reasons why employment is currently not possible.
At the same time, a person who is “below the poverty line” can own one car, one piece of real estate and insignificant savings.
If all the information provided is correct, a benefit is paid, the amount of which depends on the province and personal circumstances.
Unemployment benefit
Taxable unemployment benefit is subject to a number of conditions, namely:
- people lost their jobs through no fault of their own (eg downsizing). In the event that an employee is dismissed for unsuitability or violation of labor discipline, the allowance is denied.
- is temporarily unable to work for health reasons.
- before losing his job, he worked from 420 to 700 hours.
- the employer made contributions to the appropriate fund.
Documents for cash payment can be processed online.
Benefits start to be paid 28 days after application is submitted. The maximum payment period is 52 weeks. If the benefit is paid due to temporary incapacity for work, then the period of payments is no more than 15 weeks.
Various factors are taken into account when calculating the amount of benefits. But usually it is 55% of the average salary, up to $524 per week.
Unemployment benefits can be higher - up to 80% of earnings if:
- the family is classified as low-income, that is, the total annual income of the family is $ 25,921 or less
- has several children
- and receives the Child Tax Benefit.

The benefit amount is reviewed annually.
It must be remembered that the social service can check at any time whether their ward is looking for work or not.
Immigrant benefits in Canada: for employers
Entrepreneurs can also receive unemployment benefits if they are registered with the Canadian Employment Insurance Commission and have made contributions to the Employment Insurance Fund for at least 12 months. In 2016, the maximum annual payment to the Fund was $955.04.
In addition, the following conditions must be met:
- decrease in business income by more than 40% due to: a child was born or adopted, a seriously ill family member requires care, an employee is sick or injured.
- for the previous year, earnings amounted to the minimum amount for entrepreneurs. In 2015, for example, it is $6820.
Entrepreneur can expect to receive $537 per week. This is the maximum amount for 2016.
Child benefits, system of payments and benefits for families with children
Even during pregnancy, a woman can count on assistance from the social services.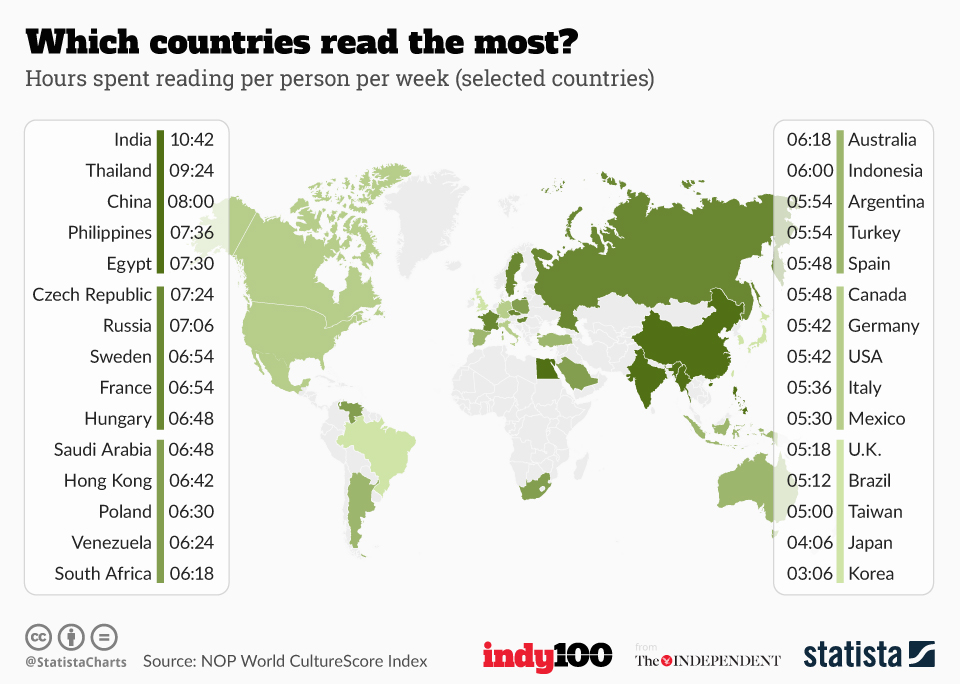 Expectant mothers and women who have just given birth and are in a difficult life situation receive support from the state in the form of coupons for food and vitamins. Support programs and their content in each province are different.
Expectant mothers and women who have just given birth and are in a difficult life situation receive support from the state in the form of coupons for food and vitamins. Support programs and their content in each province are different.
Maternity benefits
After a child is born and a woman takes maternity leave, she can count on Child Care Benefit, also known as Employment Insurance. You can fill out the form for benefits online and this should be done no later than four weeks after you go on maternity leave.
The amount of the payment depends on the average income. In most cases, this is at least 55% of the average earnings. For example, as of January 1, 2016, the maximum annual benefit payment was $50,800.
Benefit duration varies from 14 weeks to 45 weeks depending on the region.
Types of Child Benefit
Canada Child Benefit is a tax-free monthly payment of $160 for each child under 6 and $60 for each child aged 6 to 17.
Canada Child Tax Benefit is a tax-free monthly benefit for children under 18 years of age. The amount depends on the total family income.
The amount depends on the total family income.
Provincial Benefits depend on local law and are paid until the child reaches 18 years of age. The amount of payments also depends on the total family income.
Child Disability Benefit is approximately $224.58 per month for each child.
To apply for child support immediately upon arrival in Canada, you must have documents on the total family income for the previous year in the country where the immigrants came from.
The amount of the allowance is calculated based on the family's income and the child's age.
Canada Immigrant Benefits: Family Benefits
Compassionate care benefits is a benefit for caring for a family member who is seriously ill. Subject to tax, the percentage of which depends on the total income and the region of residence.
In order to receive this allowance, you must prove to the social service that due to the need to care for the sick, your income has decreased by 40%, you have worked at least 600 hours in the last year, and you must provide all the necessary medical documents.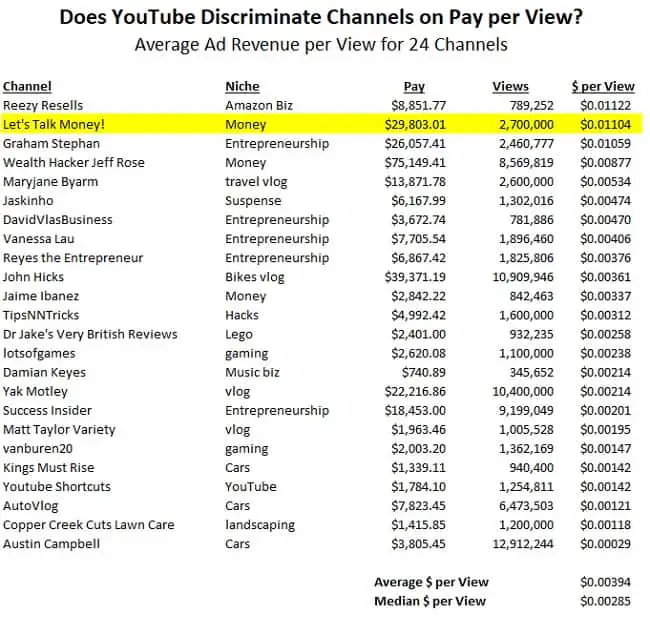
The maximum benefit period is 26 weeks. In 2016, the weekly payout amounted to $537.
Severely Ill Child Care Allowance
Benefit Conditions: Income reduced by more than 40% due to needing to care for a seriously ill child, worked at least 600 hours in the last 52 weeks, child no 18 years old. The maximum benefit in this situation is $537 per week.
Federal Assistance for Parents of Murdered or Missing Children
This taxable benefit is paid in the amount of $350 for 35 weeks after the incident. The tax is calculated individually, depending on the total income and place of residence.
Pension after the death of a spouse
In the event of the death of a spouse, financial assistance is provided for the funeral, a monthly pension and a one-time payment to the heir of the Pension Fund contributor. The amount of assistance is equal to six times the pension of the deceased, but does not exceed $2,500. This allowance is available to immigrants from the day they officially start working. After all, the employer deducts money for this program. The amount of benefits and payments depends on the age of the spouse and the amount of pension contributions.
This allowance is available to immigrants from the day they officially start working. After all, the employer deducts money for this program. The amount of benefits and payments depends on the age of the spouse and the amount of pension contributions.
Canada Immigrant Benefits: Students
Low Income Student Benefit is $250 per month, depending on the region where the family lives.
Mid-income student benefit is $100 per month.
The amount of average and minimum income that determines whether a student is eligible for these payments is different in each region.
Allowance for full-time students with children under 12 years of age.
The allowance is $200 per month for each child. This amount does not cancel the benefits for a student from a low-income family.
Financial assistance for disabled students.
If a student has the required medical records to qualify for financial aid, the student may receive up to $8,000 per academic year.