How much does a cvs test cost
What Is Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)?
In This Section
- Prenatal Care
- What happens at an appointment?
- What is prenatal testing?
- What’s an ultrasound?
- What’s chorionic villus sampling?
- What’s amniocentesis?
- Where can I get prenatal care?
- What pregnancy complications can happen?
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a procedure that tests a small sample of pregnancy tissue to find certain genetic abnormalities.
What is a chorionic villus sampling (CVS)?
CVS tests the tissue that holds the fetus to the walls of your uterus. It helps find chromosomal abnormalities, including Down syndrome. CVS is usually done between your 9th and 12th weeks of pregnancy.
Your doctor may suggest CVS if you:
-
are 35 years old or older
-
have a family history that increases the risk of certain birth defects
-
have had a child with a major birth defect
CVS testing is usually painless and very safe. But there is a small risk of miscarriage after CVS. About 1-3 out of 100 women who have CVS will have a miscarriage. You get to decide which, if any, genetic tests you want to have done.
How is the chorionic villus sampling procedure done?
You’ll have your CVS procedure at your doctor’s office. First they use an ultrasound to find your placenta. Then the doctor puts a very small tube through your cervix, or a thin needle through your belly into your uterus. They take a tiny piece of tissue from your placenta and send it to a lab to look for any problems.
They take a tiny piece of tissue from your placenta and send it to a lab to look for any problems.
The CVS results are usually ready in a few weeks. The test is 98 percent accurate for Down syndrome and other chromosomal defects, but it doesn’t find neural tube defects like spina bifida.
CVS usually doesn’t hurt, but you may feel cramping or have a bit of bleeding or spotting after — this usually stops in a few days. Be sure to tell your doctor if you have any discomfort or bleeding.
How much does a chorionic villus sampling cost?
The cost of a CVS procedure depends on where you get it and whether you have insurance. Many insurance plans cover at least some of the cost of CVS, but check with your insurance company to be sure.
If you don’t have insurance or your plan doesn’t cover the procedure, you’ll have to pay for it yourself. Your doctor’s office can give you more info about how much CVS costs and what type of payment plans they have.
Was this page helpful?- Yes
- No
Help us improve - how could this information be more helpful?
How did this information help you?
Please answer below.
Are you human? (Sorry, we have to ask!)
Please don't check this box if you are a human.
You’re the best! Thanks for your feedback.
Thanks for your feedback.
Back to top
We couldn't access your location, please search for a location.
Zip, City, or State
Please enter a valid 5-digit zip code or city or state.
Please fill out this field.
Service All Services Abortion Abortion Referrals Birth Control COVID-19 Vaccine HIV Services Men's Health Care Mental Health Morning-After Pill (Emergency Contraception) Pregnancy Testing & Services Primary Care STD Testing, Treatment & Vaccines Transgender Hormone Therapy Women's Health Care
Filter By All Telehealth In-person
Please enter your age and the first day of your last period for more accurate abortion options. Your information is private and anonymous.
Your information is private and anonymous.
AGE This field is required.
Or call 1-800-230-7526
Costs of Common Prenatal Tests
Prenatal tests can cost anywhere from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars.
Your health insurance usually covers tests that are recommended by a doctor. This can mean that a $268 prenatal blood test may only cost you $70, based on your plan's benefits.
For prenatal tests that are not medically necessary, you'll have to pay the entire cost yourself. This could mean paying $1,600 for a prenatal paternity test or several thousand dollars for prenatal genetic tests that are beyond what your insurance company approves.
Cost of prenatal blood test
A prenatal blood test, called an obstetric blood panel, is a routine test to check the health of the mother to identify any issues that could arise during pregnancy.
The typical cost of a prenatal blood test is $268 without insurance.
Prenatal blood tests are covered by health insurance, and how much you pay depends on your plan's level of coverage. Assuming you've already met your plan's deductible, the copayment for a prenatal blood test is typically between $20 and $78.
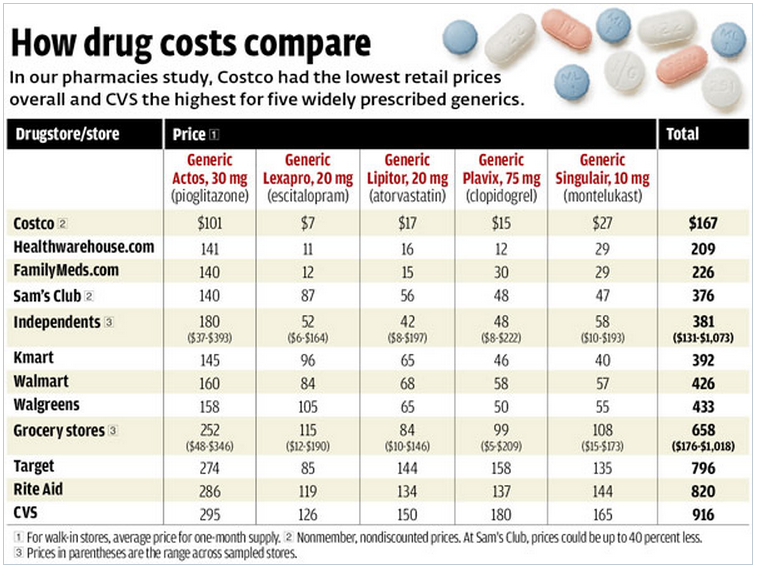
| Bronze | $78 |
| Silver | $71 |
| Gold | $56 |
| Platinum | $20 |
Generally, you'll pay less each month for a lower-tier insurance plan, such as a Bronze plan, but you'll pay more for medical care.
Having a higher-tier insurance plan would only save you about $58 on the cost of a prenatal blood test. However, the large number of medical tests and appointments that occur during pregnancy means that enrolling in a higher-tier insurance plan with better benefits is usually a good deal because of your total savings across the pregnancy.
For example, a Gold or Platinum plan could have a lower deductible, lower copays and a lower out-of-pocket maximum, as compared to a Bronze plan.
An obstetric blood panel will test for several factors about the mother's health and the compatibility between the mother and the baby using a simple blood draw.
In addition to this obstetric panel, a doctor can order screenings for sexually transmitted infections, screenings for illnesses such as rubella or tuberculosis, and blood glucose testing if there is a risk of gestational diabetes. Each of these tests is billed separately. The blood screenings are often combined with a fetal ultrasound, which costs around $639 without insurance.
Prenatal genetic test
One of the earliest prenatal genetic tests you can get, a screening that checks the health of the baby through a sample of the mother's blood, is called noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT).
A prenatal genetic test typically costs $1,345 without insurance.
The NIPT genetic test is typically covered by insurance when it's considered medically necessary by a doctor and you meet the coverage criteria set by the insurance plan. You may also find that your insurance plan covers an NIPT blood test differently from other genetic tests like amniocentesis because NIPT is an early screening that checks if you are at risk of a problem, and other procedures can more specifically diagnose problems.
When it's covered by health insurance, the cost of the NIPT prenatal genetic test is usually between $207 and $334, assuming you've already met the plan's deductible.
| Bronze | $334 |
| Silver | $240 |
| Gold | $207 |
If your insurance won't cover the test, you can ask the provider for cash pricing, which is a negotiated rate that you would pay if you don't use your insurance plan. This can bring the price down to around $340. There are also options for financial assistance if you contact the test manufacturer. For example, the Panorama-brand prenatal test can be reduced to $149 for those who qualify for a financial hardship discount.
This can bring the price down to around $340. There are also options for financial assistance if you contact the test manufacturer. For example, the Panorama-brand prenatal test can be reduced to $149 for those who qualify for a financial hardship discount.
However, any medical expenses you have for procedures that aren't covered by insurance or those you pay for in cash without using your insurance will not count toward your insurance plan's deductible or out-of-pocket maximum.
NIPT tests can identify if your baby is at risk for a chromosome disorder such as Down syndrome or potential birth defects. The genetic screening uses a sample of the mother's blood to check for different hormones and proteins. The test can be done in either the first or second trimester.
Remember that any indication of a problem will require further testing because many of these early genetic tests are unregulated by the FDA and frequently have false positive results.
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
The genetic test Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) uses a sample of the placenta to identify conditions such as Down syndrome or cystic fibrosis.
Chorionic villus sampling typically costs around $3,050.
The procedure is usually done in an outpatient facility or in a doctor's office. Costs can vary widely based on where you go for the procedure, ranging from $1,300 to $4,800.
Your itemized bill will include several individual charges including the physician fee, the procedure cost, any facility fees and the cost for the lab to process the sample.
Your health insurance may cover chorionic villus sampling if you have certain risk factors, such as being older or having a family history of certain genetic diseases. You may need to get prior authorization from the insurance company, and the amount you pay will depend on your insurance plan.
Chorionic villus sampling tests a small sample of placental tissue, which has the same genetic makeup as the fetus. This can be examined for chromosomal abnormalities but not for developmental issues such as spina bifida.
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis checks a sample of amniotic fluid for specific genetic abnormalities.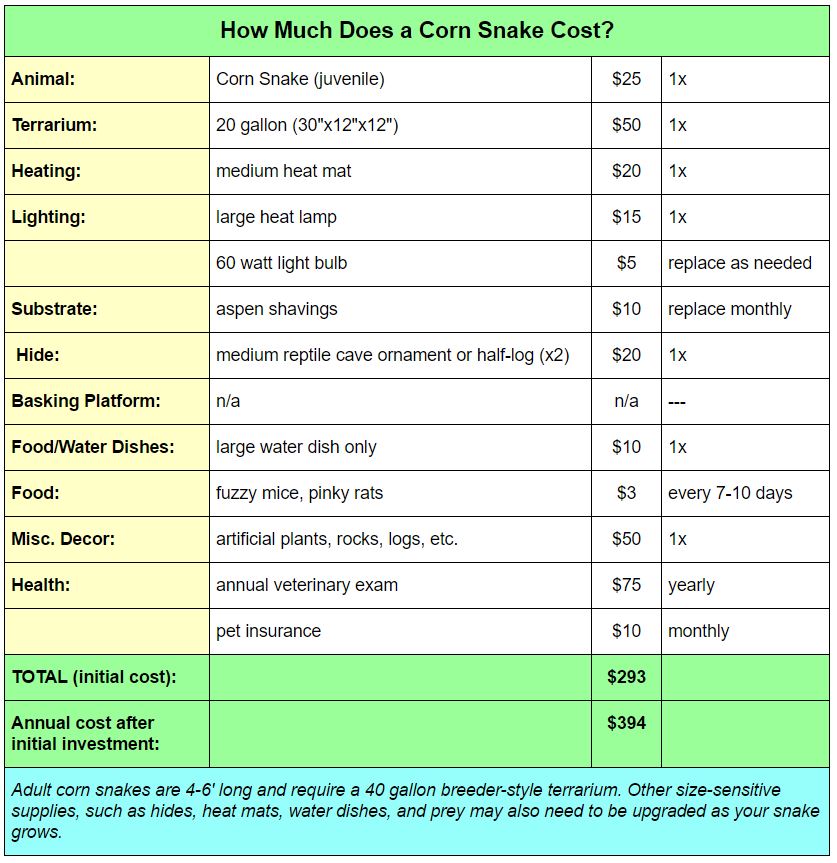
Amniocentesis typically costs $4,100 without insurance.
The cost for amniocentesis can vary based on where the procedure is done, typically ranging from $1,000 and $7,200. This includes the itemized costs from the doctor's office for physician fees and procedure fees, as well as the lab costs for processing the sample.
With a typical health insurance plan, you will pay around $1,230 for amniocentesis, or 30% of the procedure cost.
Health insurance plans usually cover amniocentesis. However, insurance plans vary in both how you qualify for coverage and what your portion of the cost is.
- Most insurers will require prior authorization. This means the insurance company will need to agree to cover the procedure before you have it done.
- Typically, your doctor must recommend the procedure as being medically necessary before an insurance company will cover it.
- An insurance company may only cover the test if there is an increased risk for chromosomal abnormalities, such as when the pregnant woman is over 35, has a family history of certain genetic diseases or had abnormal screening tests earlier in the pregnancy.
Even when health insurance covers amniocentesis, what you pay for the procedure can be high. If you start to feel worried about the high costs of prenatal care, remember that your health insurance plan's out-of-pocket maximum will cap your medical costs for the year. After you reach this spending limit, you won't pay anything for covered medical costs for the rest of the year.
Usually performed after 15 weeks of pregnancy, amniocentesis analyzes a sample of amniotic fluid to check for chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, or developmental problems with how the spine and brain form, a result of what are called open neural tube defects. The test also checks for specific genetic abnormalities, such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell disease.
Gender blood test
You can find out the sex of a baby through an at-home DNA kit that uses a small sample of blood.
An at-home gender blood test costs an average of $74 for the standard package.
These at-home tests are not covered by insurance, meaning you'll pay the full price. However, the at-home test is only one option available.
At the doctor's office, the sex of a baby can be discovered during noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT), a noninvasive prenatal paternity (NIPP) test, chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or an ultrasound. These prenatal tests won't be covered if their only purpose is to determine the sex of the baby. However, if the test is being used primarily for another purpose, it may be covered by insurance, and the test results may also tell you if your baby is a boy or a girl.
Prenatal paternity test
A prenatal paternity test is a DNA test that can confirm the father, assuming you have their DNA.
A noninvasive prenatal paternity (NIPP) test typically costs about $1,600.
A prenatal paternity test is not covered by health insurance, meaning that you must pay the entire cost yourself.
The cost for a prenatal paternity test is much higher than paternity tests done after the baby is born. In that case, it typically costs less than $200. The difference in cost is because the DNA test done before the baby's birth requires that the mother's blood is drawn and processed. If the paternity test is done after birth, only cheek swabs are needed for the DNA samples.
Prenatal paternity tests are never free. However, when there are child support issues, some states may pay for a paternity test after the baby is born, or they may require that the father repays any testing costs after paternity is established.
With a prenatal paternity test, a blood sample is taken from the mother who has been pregnant for at least seven weeks. This sample will include the baby's DNA. DNA is also collected through cheek swabs of the father or potential fathers.
A prenatal paternity test can usually be done by your OB-GYN. If the test is being used for legal paternity issues, there may be additional requirements such as having a witness present when the DNA is collected or blood is drawn.
Frequently asked questions
Is prenatal genetic testing covered by insurance?
Yes, major health insurance companies, such as Blue Cross Blue Shield, UnitedHealthcare and Humana, will cover genetic screening if you meet the plan's coverage criteria. This can mean that a doctor must recommend the procedure or there is a higher risk of genetic abnormalities.
How much does genetic testing cost during pregnancy?
Costs can vary based on the type of test and your insurance plan. If you have health insurance, an early genetic screening can cost $240, while amniocentesis can cost $1,230.
What's the best health insurance plan for prenatal tests and childbirth?
A higher-tier insurance plan with better medical benefits will usually save you money on the cost of childbirth and pregnancy. For example, choosing a Platinum plan versus a Bronze plan could save you more than $6,000 throughout pregnancy and delivery, after considering both the cost of a plan and the cost of medical care.
For example, choosing a Platinum plan versus a Bronze plan could save you more than $6,000 throughout pregnancy and delivery, after considering both the cost of a plan and the cost of medical care.
Sources and methodology
The cost of medical procedures is based on aggregated data from Turquoise and Healthcare Bluebook. The cost of at-home gender tests is based on the average of basic testing packages from three major providers. The cost for prenatal paternity testing is based on pricing by DDC DNA Diagnostics Center.
The average procedure cost with health insurance is based on in-network coverage from marketplace insurance plans offered in Arlington, Va., with averages across the 53 plans offered by Bright Health, Cigna, Kaiser Permanente, Innovation Health and UnitedHealthcare.
Screening tests for Down syndrome in the first 24 weeks of pregnancy
Relevance
Down syndrome (also known as Down syndrome or Trisomy 21) is an incurable genetic disorder that causes significant physical and mental health problems and disability. However, there is great variation in how Trisomy Down affects people. Some individuals have severe suffering, while others have little problems and are able to lead relatively normal lives. There is no way to predict how badly each child may be affected. nine0006
However, there is great variation in how Trisomy Down affects people. Some individuals have severe suffering, while others have little problems and are able to lead relatively normal lives. There is no way to predict how badly each child may be affected. nine0006
Parents-to-be are given the option of having a Down test during pregnancy to help them make decisions. If a pregnant woman is carrying a child with Down syndrome, then a decision must be made whether to terminate or continue the pregnancy. This information offers parents the opportunity to plan for life with a Down child.
The most accurate tests to detect Down include testing of amniotic fluid (fluid around the fetus, amniocentesis required) or placental tissue (chorionic villus biopsy (CVS)) for abnormal chromosomes associated with Down. Both tests require the insertion of a needle into the mother's abdomen and increase the risk of miscarriage. Thus, the tests are not suitable to be given to all pregnant women. Instead, screening uses tests that measure markers in the mother's blood, urine, or baby's ultrasound. These screening tests are not perfect, they can miss cases of Down and also give a "high risk" result to some women whose children do not have Down. Thus, pregnancies identified as Down's "high risk" pregnancies using these screening tests require further testing by amniocentesis or CVS to confirm a Down's diagnosis. nine0006
These screening tests are not perfect, they can miss cases of Down and also give a "high risk" result to some women whose children do not have Down. Thus, pregnancies identified as Down's "high risk" pregnancies using these screening tests require further testing by amniocentesis or CVS to confirm a Down's diagnosis. nine0006
What we did
The aim of this review was to find out which of the screening tests done during the first 24 weeks of pregnancy are most accurate in predicting the risk of Down pregnancy. We studied 7 different urinary markers that can be used alone, in ratios, or in combination, taken up to 24 weeks of gestation. This cumulatively creates 24 screening tests for Down. We found 19 studies involving 18,013 pregnant women, of which 527 were pregnancies with Down syndrome. nine0005
What we found
Evidence does not support the use of urine tests to screen for Down syndrome during the first 24 weeks of pregnancy. The amount of evidence is limited. These tests are not offered in routine clinical practice.
These tests are not offered in routine clinical practice.
Other important information to consider
Urine testing itself has no side effects for the woman. However, some women who have a "high-risk" screening test result and who are undergoing amniocentesis or CVS are at risk of having a non-Down's syndrome non-parous baby (healthy miscarriage). Parents will need to weigh this risk when deciding whether or not to have an amniocentesis or CVS after receiving a "high risk" screening test result. nine0006
Translation notes:
Translation: Kong Hong Han. Editing: Ziganshina Lilia Evgenievna. Project coordination for translation into Russian: Cochrane Russia - Cochrane Russia (branch of the Northern Cochrane Center on the basis of Kazan Federal University). For questions related to this transfer, please contact us at: [email protected]
VLSI - an ecosystem for business: accounting, management and communications
VK_37992622
finance, automate purchases and warehouse, move the customer through the funnel in CRM. nine0006
nine0006
Select personnel, calculate salaries, keep personnel records, motivate through KPIs, badges and ratings. Here you can also hold meetings and webinars, communicate with colleagues and partners.
From the dry corporate structure, VLSI forms a live social network with chats, groups, news.
Reporting to the Federal Tax Service, Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund
Electronic contracts
Labeling of medicines
Financial analysis
Search for tenders
Checks for utilities and services
Catalog of master-dane
Restaurant
Military accounting
Product store
Reporting in the Federal Tax Service, PF, FSS
Electronic Treats
9000Master data catalog
Restaurant
Tax analysis and optimization
Perfume labeling
Restaurant chain management
Reporting to FSRAR
Organization of purchases and tenders
KKT Park
Price and approval of prices
Beauty Salon
Accounting for personnel
Corporate certificate 9000,
Analysis and optimization of taxes
Marking of Spiries
Restaurants
Reports on FSRAR
Purchasing and bidding
KKT fleet management
Prices and price negotiation
Beauty salon
Reporting in the Federal Security Service
Electronic labor books
Automation of shopping centers
Tire marking
Tender Department
Output employees 9000
Automation of delivery
Data on API Reporting to the Federal Migration Service
Electronic employment records
Automation of shopping centers
Tire marking
Tender department
Office Outbound employees
Automation of delivery
Data on API
reconciliation of VAT
Electronic factoring
Information on contractors
Sales control
Personnel Marking
Control 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 reconciliation of calculations
CRM and customer accounting
Video conferences and meetings
VAT reconciliation
Electronic factoring
Information about contractors
Control of sales department
Marking beer
Statement of personnel
Control of travel officers
Electronic reconciliation of calculations
Reporting in Rosprirodnadzor 9000,
Molding of sales points 9000 9000 9000 9000 Payroll
Work and vacation schedules
Settlements with accountable persons
Corporate telephone network
Working with EGAIS and FSRAR
Canteen
Reporting in Rosprirodnadzor
Monitoring of sales points
Personnel training
Pharmacy
Calculation of salary
Calculations with accountable persons
Corphaments
Audit and consolidation of reporting
Electronic invoices
Partner verification
Sales and assortment analysis
Social network of the company
Personnel Management
Electronic passage
Accounting
EDO without roaming
Milk marking
Audit and reports Consolidation of 9000
Electronic invoices
9000 company networkHuman resources management
Electronic checkpoint
Accounting
Reconciliation of settlements with the budget
Documents transfer to state bodies
Retail store
Employees Motivation
Financial planning
Commission Trade
All for "Remanding"
Webinars
Tobacco 9000
Electronic signature documents to government agencies
Retail store
Employee motivation
Financial planning
Commission Trade
All for "Remanding"
Webinars
Work with Mercury and VSD
Documents transfer to courts
Management network
Fastfood
Service center
Electronic archive of documents
EP on your site
Designer of commercial proposals, contracts, invoices
Procurement organization
Competitive intelligence
Work with Mercury and VVD
Submission of documents to courts
Retail network management
Fastfood
Service center
Electronic archive of documents
EP on your site
Designer of the CP, contracts, accounts
Shoe marking
Warehouse accounting 9000
9000 9000
Accounting
Corporate portal
Cloud telephony
EDI and logistics
Hardware store
Electronic sick leave
Fiscal data operator
Shoe marking
Warehouse accounting
The cost of the company
Accounting for working time
Corporate portal
,0002 cloud telephony
EDI and Logistics
Construction store 9000
More business sizes and directions -
from individual entrepreneurs to transnational corporations, from Sakhalin to Kaliningrad, from churches to casinos, from kindergartens to ministries.