How many days you bleed after miscarriage
What Does a Miscarriage Look Like? Bleeding, Duration, and More
A miscarriage is a spontaneous pregnancy loss before 20 weeks of gestation. Some 8 to 20 percent known pregnancies end in miscarriage, with the majority happening before the 12th week.
The signs and symptoms of miscarriage vary from person to person. Symptoms may also vary depending on how far along you are. For example, a fetus at 14 weeks will be much larger than a fetus at 5 weeks of gestation, so there may be more bleeding and tissue loss with a later miscarriage.
Miscarriage symptoms may include:
- spotting or bleeding from the vagina
- abdominal cramping or pain in the lower back
- passage of tissue, fluid, or other products from the vagina
Read on to learn more about identifying a miscarriage and what to do if you suspect you’re experiencing one.
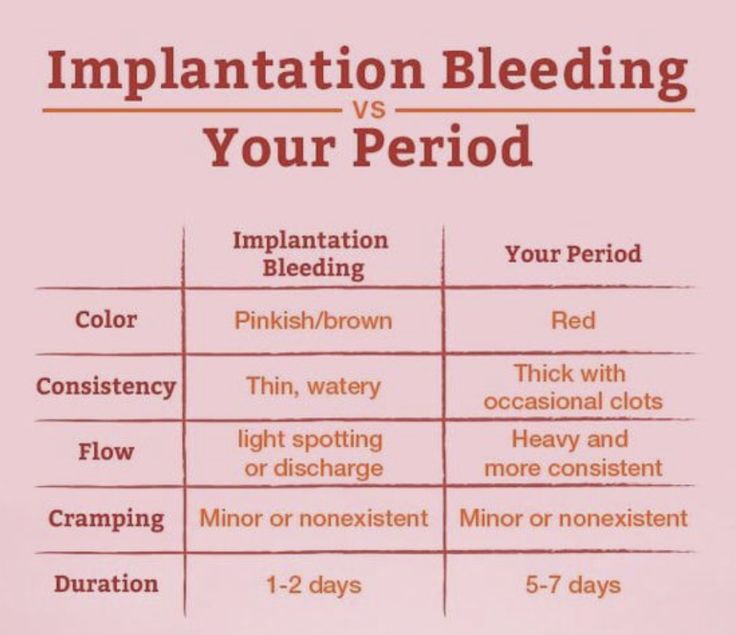
Bleeding may start as light spotting, or it could be heavier and appear as a gush of blood. As the cervix dilates to empty, the bleeding becomes heavier.
The heaviest bleeding is generally over within three to five hours from the time heavy bleeding begins. Lighter bleeding may stop and start over one to two weeks before it completely ends.
The color of the blood can range from pink to red to brown. Red blood is fresh blood that leaves the body quickly. Brown blood, on the other hand, is blood that’s been in the uterus a while. You may see discharge the color of coffee grounds, or near black, during a miscarriage.
Exactly how much bleeding you’ll experience depends on a variety of circumstances, including how far along you are and whether or not your miscarriage is progressing naturally.
While you may see a lot of blood, let your doctor know if you fill more than two sanitary pads an hour for two or more hours in a row.
What does a missed miscarriage look like?
You may not experience bleeding or other symptoms with a miscarriage, at least at first.
A missed miscarriage, also referred to as a missed abortion, happens when the fetus has died but the products of conception remain in the uterus. This type of miscarriage is usually diagnosed via ultrasound.
This type of miscarriage is usually diagnosed via ultrasound.
Just as with the amount of blood you’ll see, the duration of a miscarriage will vary from person to person and even from pregnancy to pregnancy.
In many cases, a miscarriage will take around two weeks to pass naturally. Your doctor may prescribe the medication misoprostol (Cytotec) to help a miscarriage pass more quickly. Bleeding may start within two days of beginning the medication. For others, it may take up to two weeks.
Once the miscarriage has started, the tissue and heaviest bleeding should be passed in about three to five hours. After the fetus has passed, you may still experience spotting and mild tissue loss for one to two weeks.
It may be difficult to tell a very early miscarriage from a late period. In fact, many miscarriages happen before a person even knows they’re pregnant.
In general, a miscarriage will cause more intense symptoms than a menstrual period. For example:
- Your menstrual flow may be relatively similar from month to month with heavy days and light days.
 A miscarriage can also have heavy and light days, but bleeding may be especially heavy at times and last longer than you’re used to.
A miscarriage can also have heavy and light days, but bleeding may be especially heavy at times and last longer than you’re used to. - Bleeding from a miscarriage may also contain large clots and tissue you don’t normally see during your period.
- Cramps can be a part of your normal monthly cycle, but with a miscarriage, they may be particularly painful as the cervix dilates.
- The color of blood during your period can range from pink to red to brown. If you see a color you’re not used to seeing, it may be a sign of miscarriage.
Always contact your doctor if you’re pregnant and experience bleeding. While a miscarriage can’t be stopped once it starts, you doctor can run tests to help determine if you’re experiencing the loss of your pregnancy or something else.
To diagnose a miscarriage, your doctor will likely perform an ultrasound to look for the baby’s heartbeat, if you’re far enough along to see a heartbeat. Your doctor may also order a blood test to check human chorionic gonadotropin (hcG) levels to see if they’re rising or falling.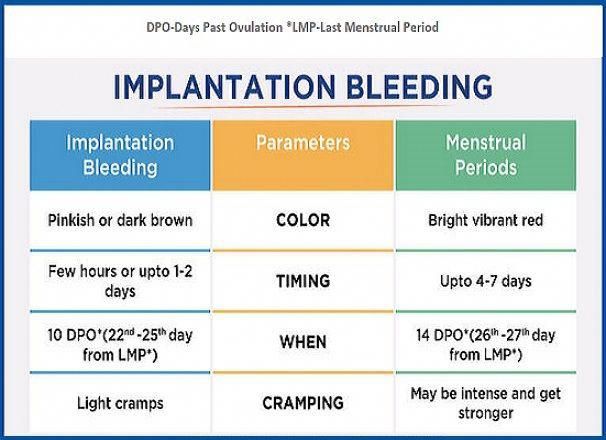
If a miscarriage is confirmed, your doctor may suggest “expectant management” or waiting for the miscarriage to pass naturally. This generally happens within two weeks.
Incomplete miscarriage
The miscarriage may be incomplete if:
- your bleeding is particularly heavy
- you have a fever
- an ultrasound reveals there’s still tissue in your uterus
If this is the case, your doctor may suggest a dilation and curettage (D and C), which is a surgical procedure done to remove remaining tissue. The procedure is done under general or regional anesthesia, and is considered safe. D and C doesn’t usually lead to long-term complications.
Threatened miscarriage
It’s important to report any bleeding or pain you experience in your pregnancy to your doctor. In some cases, you may have what’s called a threatened miscarriage, and there may be certain treatments that can help. These include:
- hormone supplements if the bleeding is caused by low progesterone
- a cerclage (stitch in the cervix) if the issue is with the cervix opening prematurely
Speak with your healthcare provider if you’re looking to get pregnant again after a miscarriage. While it may be safe to start trying after your first normal period, you may want to schedule a checkup depending on the cause or the number of miscarriages you’ve had.
While it may be safe to start trying after your first normal period, you may want to schedule a checkup depending on the cause or the number of miscarriages you’ve had.
The reason for loss isn’t always known, but around half of miscarriages are caused by issues with the baby’s chromosomes.
Other possible causes include:
- uterine issues
- hormonal imbalances
- other health conditions, such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, or polycystic ovary syndrome
After a miscarriage, you may have hcG in your blood for one to two months, which could lead to a false positive pregnancy test. In most cases, your period will return within four to six weeks, though you may start ovulating almost immediately following a miscarriage.
Speak with your doctor about birth control options if you don’t wish to become pregnant after a miscarriage.
Will I miscarry again?
Having one miscarriage doesn’t necessarily increases your chances of having another. The risk remains around 20 percent.
The risk remains around 20 percent.
Two or more miscarriages is referred to as recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL). The risk of miscarriage after two losses is 28 percent. After three consecutive losses, it increases to 43 percent.
Only 1 percent of people experience three or more miscarriages. About 65 percent of those with unexplained RPL go on to have successful pregnancies.
Activities like exercise, work, morning sickness, and sex don’t cause miscarriages. Even things like smoking or drinking alcohol or caffeine, which can lead to other complications, are also unlikely to lead to early pregnancy loss.
A miscarriage can be physically painful, and it may also cause a variety of emotions. While your body may recover in a few weeks, be sure to take time to process your feelings, grieve, and reach out for help when you need it.
Bleeding, Clots, Timing, and Other Signs
Miscarriage is fairly common in the first trimester. It happens in about 10 percent of known pregnancies.
In some cases, miscarriage can occur before you know you’re pregnant. If this happens, you might not notice anything different from your usual period.
The further along you are in a pregnancy, the less likely it is that a miscarriage will feel like a period.
Continue reading to learn more about early miscarriage, including specific symptoms to watch for, when you should see a doctor, and more.
The most common symptoms of early miscarriage are cramping and bleeding.
However, spotting or light bleeding during early pregnancy aren’t always a sign of miscarriage. If this happens, watch for any other unusual symptoms.
Other symptoms of miscarriage
- cramping in your abdomen or lower back (This could start out like period cramps, but the pain typically worsens over time.)
- nausea
- diarrhea
- passing fluids, larger-than-normal blood clots, or tissue from your vagina
Timing
A miscarriage can happen any time after fertilization.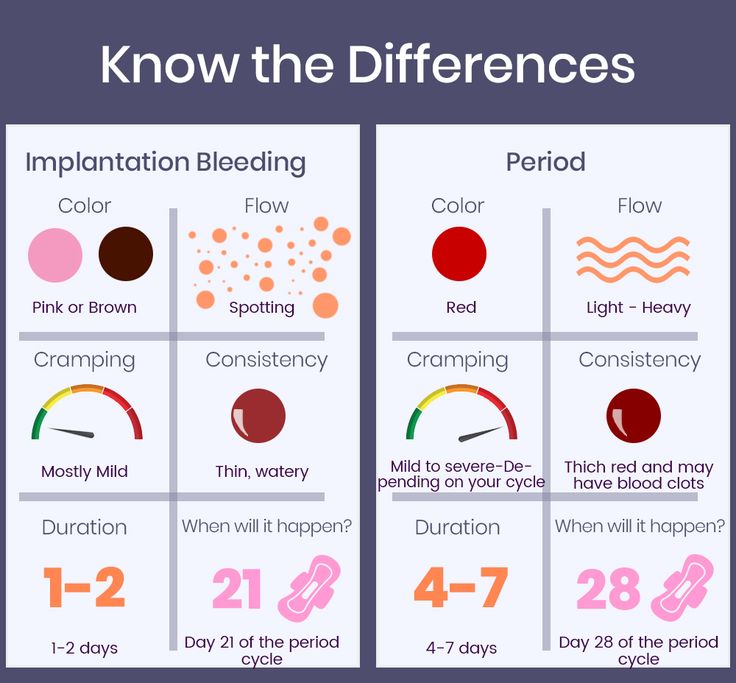 If you didn’t know you were pregnant, it would be easy to mistake it for a period.
If you didn’t know you were pregnant, it would be easy to mistake it for a period.
Both a period and a miscarriage can cause spotting to heavy bleeding.
After the first eight weeks or so, it’s less likely that you’ll mistake a miscarriage for a period.
Duration
You know how long and heavy your typical period is.
During a miscarriage, bleeding gets heavier and lasts longer than a period.
As your cervix starts to dilate, cramping may become more painful than typical period cramping.
Characteristics
Bleeding during miscarriage can appear brown and resemble coffee grounds. Or it can be pink to bright red.
It can alternate between light and heavy or even stop temporarily before starting up again.
If you miscarry before you’re eight weeks pregnant, it might look the same as a heavy period. Later, you’re more likely to notice fetal or placental tissue.
Menstruation products
Heavy bleeding, pieces of tissue, or large blood clots on your menstruation products could mean that you’re having more than a heavy period.
See a doctor if you’re soaking through a tampon or pad every hour for more than two consecutive hours.
You should call a doctor or other healthcare provider any time you experience unexpected pain or excessive bleeding.
These symptoms can result from an ectopic pregnancy. This occurs when a fertilized egg has implanted outside the uterus, possibly inside a fallopian tube. It’s a medical emergency.
You should also call a doctor if you experience bleeding alongside:
- mucus
- tissue
- blood clots
- what feels like uterine contractions
If you believe you’re having a miscarriage, ask your doctor the following:
- Should I collect a sample of blood or tissue? (This isn’t always necessary.)
- Should I go to an emergency room or make an office appointment?
- Is it fine to drive myself, or do you recommend against it?
If it appears that you’ve had a miscarriage, your doctor will want to perform a physical exam.
Be sure to discuss all your symptoms, including the amount of:
- bleeding
- clotting
- pain
- any tissue that may have been expelled
Testing may include:
- an ultrasound to check the uterus for signs of an embryo or a heartbeat
- a blood test to check for human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a substance that indicates pregnancy
There’s no way to stop a miscarriage in progress. If your doctor determines that you’ve experienced a miscarriage, they’ll want to check for:
- signs of infection
- uncontrollable bleeding
- tissue that may be left in your uterus
It can take two weeks or more to completely expel the tissue naturally. Your doctor will review with you typical bleeding patterns to expect. If you have heavy bleeding lasting several days or any signs of infection, you may need medical treatment.
If your doctor isn’t sure that all of the pregnancy tissue has been cleared from your uterus, they may order an ultrasound to confirm.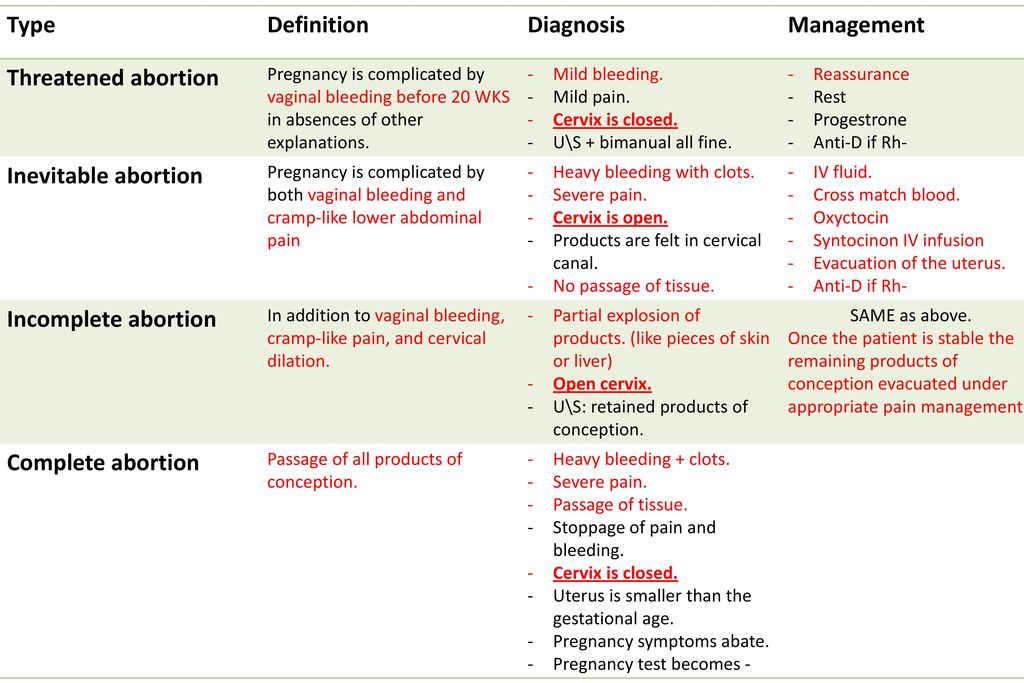
Your doctor can prescribe medication, such as misoprostol (Cytotec), to increase uterine contractions to help you expel the tissue.
You’ll experience cramping and bleeding as you pass tissue and blood.
Most people pass the tissue within 24 hours after taking the drug. For others, it can take a few days to complete. Either way, it doesn’t require a hospital stay.
Your doctor may be able to prescribe pain medication to help ease your symptoms.
If your blood type is Rh negative, you’ll need an injection of Rh immunoglobulin. This may help prevent complications in a future pregnancy.
There are also a few surgical options to remove tissue from the uterus. This includes:
- Vacuum aspiration. Your doctor inserts a thin tube that contains a suction device into your uterus. This can be done with local anesthesia in your doctor’s office.
- Dilation and curettage (D&C). Your doctor dilates your cervix, and then uses an instrument called a curette to scrape your uterine lining.
 This can be done at a surgical center or operating room on an outpatient basis. Regional or general anesthesia can be used.
This can be done at a surgical center or operating room on an outpatient basis. Regional or general anesthesia can be used.
Both of these treatments have been well-studied and are considered safe. They each carry a very small risk of serious complications.
If you’ve experienced a miscarriage, it’s important to understand that it isn’t your fault.
In many cases, doctors are unable determine the cause. Here are some things that can contribute to miscarriage:
During the first trimester
As many as 80 percent of miscarriages occur in the first trimester.
When a miscarriage occurs in the first five weeks after fertilization, it’s called a “chemical pregnancy.” It’s so early that you might not have known you were pregnant.
Although your period may seem heavier than usual, there might not be any other noticeable sign of miscarriage.
Miscarriages in the first trimester often have to do with chromosome abnormalities that interfere with normal development. Missing or extra chromosomes are linked to 50 percent of all miscarriages.
Missing or extra chromosomes are linked to 50 percent of all miscarriages.
Sometimes, a fertilized egg simply doesn’t develop into an embryo (blighted ovum).
It may help to know that having sex, exercising, morning sickness, and previous use of oral contraceptives don’t cause miscarriage. Even an accidental fall doesn’t necessarily cause it.
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), smoking and alcohol consumption in the first trimester may result in a slightly higher risk of miscarriage. But the research on this is mixed.
It’s also worth noting that drinking less than 200 milligrams of caffeine per day doesn’t appear to increase the risk of miscarriage.
Some things that may increase the risk of early miscarriage are:
- fibroids or other abnormalities of the uterus
- hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism
- uncontrolled diabetes
- use of cocaine or similar drugs
During the second trimester
About 2 to 3 percent of miscarriages occur during the second trimester.
Some things that may increase the risk are:
- conditions that can cause blood clots
- early preeclampsia or eclampsia
- fetal abnormalities
- fibroids or other abnormalities of the uterus
- infection of the uterus
- lupus
- prior surgery of the cervix
- trauma
- uncontrolled diabetes
- hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism
- high blood pressure
- use of cocaine or similar drugs
During the third trimester
Losing a pregnancy starting from the 20th week of pregnancy and into the third trimester is considered stillbirth, not miscarriage.
In general, the risk of stillbirth increases with maternal age.
If you’ve experienced a miscarriage, it doesn’t mean you’ll have another, and it doesn’t mean you can’t have children.
Most people who experience a miscarriage can go on to have a successful pregnancy.
Miscarriage shouldn’t affect your ability to get pregnant. You can ovulate and become pregnant within two weeks of an early miscarriage.
You can ovulate and become pregnant within two weeks of an early miscarriage.
If you don’t want to become pregnant again, you should use birth control right away.
About 1 percent of people have multiple miscarriages. If you’ve experienced several miscarriages, your doctor might recommend special testing.
Even if you’ve had three miscarriages in a row, there’s a 70 percent chance your next pregnancy will be successful.
Your doctor will probably advise you to avoid sex, tampons, and douches for two weeks. This will help prevent infection.
They may also want you to take a pregnancy test after about two weeks. This can help them determine whether your hormone levels are back to normal.
In the meantime, call your doctor if you:
- are bleeding heavier than expected or notice that the blood stays bright red
- are soaking through more than two maxi pads an hour for more than two hours
- notice a foul-smelling discharge
- experience abdominal tenderness or severe pain
- have persistent cramping
- develop a fever or chills
For the first few days, you may notice blood clots and tissue passing, but this should taper off after about a week.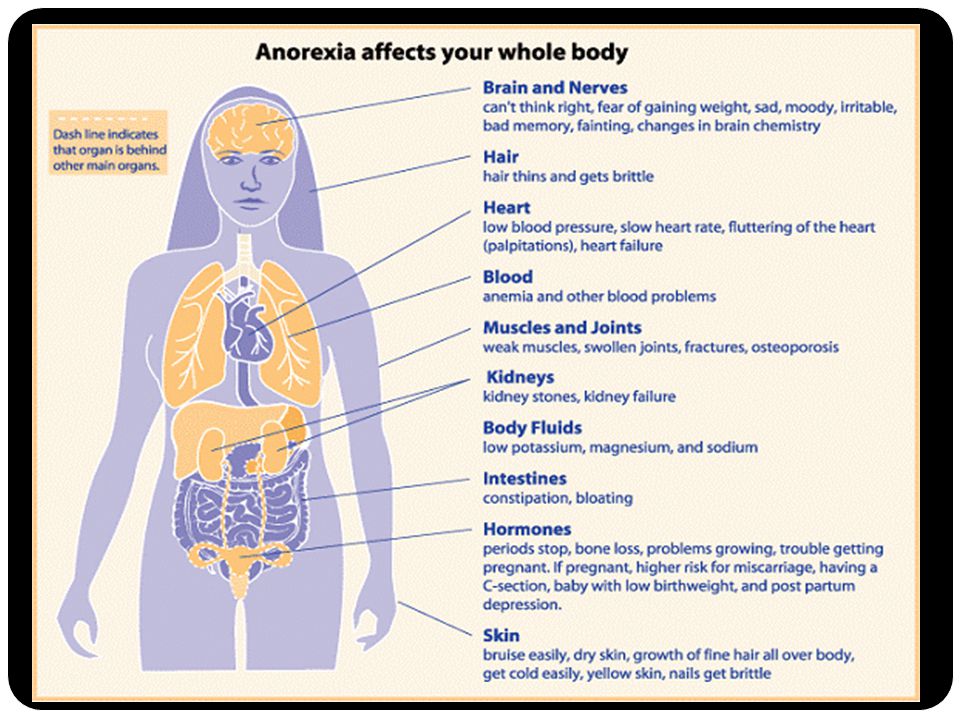 It will take about four to eight weeks for your regular period to return.
It will take about four to eight weeks for your regular period to return.
Mild exercise following an early miscarriage is usually fine, but check with your doctor. It may depend on how far along you were, as well as your overall health.
There are many emotions a person might have following a miscarriage. Some feel anger, sadness, or profound loss. Others might feel relieved.
These feelings may have to do with whether you knew you were pregnant or if you were trying to have a baby.
Pregnancy and miscarriage also cause hormone fluctuations, which can affect your emotions.
Everyone is different, so there’s no correct way to feel about experiencing a miscarriage. It may take some time for you to process everything.
You may find it helpful to talk to your partner, family, or friends about what you’re going through.
You may also consider looking into support groups for people who have experienced miscarriage. Sometimes it helps to talk to others who have been through the same thing.
Here are a few places to seek support:
- your doctor’s office or local hospital for referrals to support services
- clergy
- Compassionate Friends, which has a searchable database of local chapters
- March of Dimes Loss and Grief Forum
- Share Pregnancy & Infant Loss Support which offers online support and information on how to find local groups
If grief continues to worsen after a few weeks, talk to a doctor about your options for treatment. You may benefit from grief counseling or treatment for depression.
Miscarriage isn’t your fault.
Physical recovery generally takes a few weeks. Everyone has their own timetable for emotional recovery.
There’s no need to rush yourself or to pretend to “get over it” for anyone else’s sake.
And if you need it, reaching out for support is a reasonable thing to do. You aren’t alone in this.
Complications of abortion
Any abortion, as a serious medical intervention, inevitably carries the risk of complications. Some negative consequences and complications after an abortion may be characteristic of a certain method of abortion. For example, with medical abortion, mild pain in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, headaches, dizziness, chills, fever, uterine contractions. In 2.5% of cases with medical abortion, the pregnancy is not interrupted, up to 5% of cases an incomplete abortion occurs, in this case, curettage is additionally done.
Some negative consequences and complications after an abortion may be characteristic of a certain method of abortion. For example, with medical abortion, mild pain in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, headaches, dizziness, chills, fever, uterine contractions. In 2.5% of cases with medical abortion, the pregnancy is not interrupted, up to 5% of cases an incomplete abortion occurs, in this case, curettage is additionally done.
The most dangerous type of abortion is curettage (surgical abortion). it is the most traumatic. During surgical abortion, damage to the uterus by surgical instruments is possible. The risk of complications is markedly reduced if the method of abortion is chosen taking into account its duration.
Complications arising after an abortion are divided into two groups: early and late.
Early consequences of abortion
Early complications develop during abortion or immediately after it. Discharge after abortion. Bloody discharge that appears after an abortion usually lasts up to a week and is somewhat more abundant than normal periods. In some cases, light bleeding lasts up to a month. It is necessary to pay attention to the presence of impurities in the discharge after an abortion, their color and smell. This will make it possible to suspect a developing complication in time and take action. It is also important to control the amount of blood loss. If, after an abortion, the discharge is too abundant (two “maxi” pads are consumed per hour), you should immediately see a doctor, because. this may indicate an incomplete abortion. The appearance of an odor may indicate an infection. The first day of the abortion is considered the first day of the cycle. Normally, menstruation begins 3 weeks after the abortion; for several months, some shift in the cycle (up to 10 days) is acceptable. Perforation of the uterus is one of the most serious complications of abortion.
In some cases, light bleeding lasts up to a month. It is necessary to pay attention to the presence of impurities in the discharge after an abortion, their color and smell. This will make it possible to suspect a developing complication in time and take action. It is also important to control the amount of blood loss. If, after an abortion, the discharge is too abundant (two “maxi” pads are consumed per hour), you should immediately see a doctor, because. this may indicate an incomplete abortion. The appearance of an odor may indicate an infection. The first day of the abortion is considered the first day of the cycle. Normally, menstruation begins 3 weeks after the abortion; for several months, some shift in the cycle (up to 10 days) is acceptable. Perforation of the uterus is one of the most serious complications of abortion.
During the operation, the uterine wall is ruptured by the inserted instruments. The risk of this complication increases with the length of pregnancy.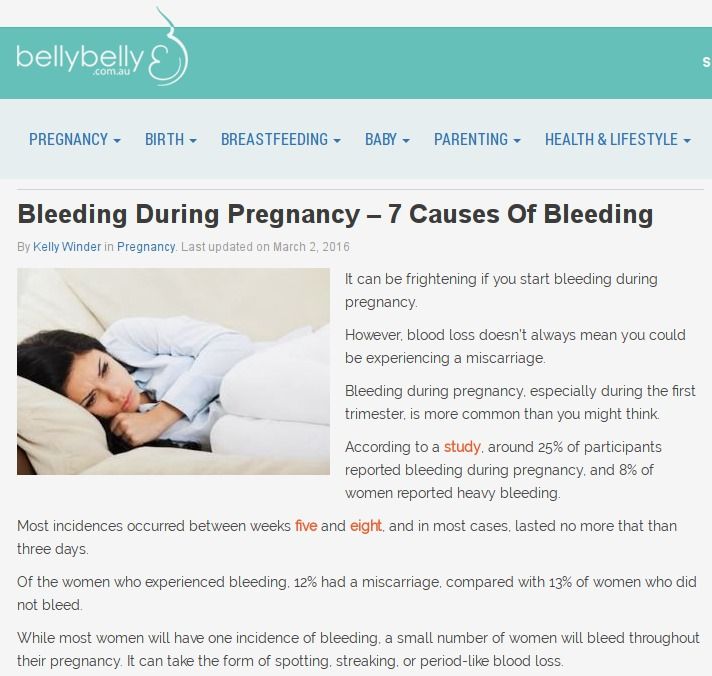 Perforation of the uterus requires immediate surgical treatment, and in especially severe cases, surgical removal of the uterus is necessary. In addition, when the uterine wall is perforated, the intestines, bladder, or large vessels can be damaged. Sometimes a rupture or incision of the cervix occurs. These consequences can significantly reduce the likelihood of pregnancy after an abortion, or even lead to infertility. In subsequent pregnancies, bearing is difficult, there is a high risk of uterine rupture during childbirth. Severe bleeding occurs when large vessels are damaged, with uterine myoma or after numerous births. Requires urgent therapy, in severe cases, a blood transfusion is done. If it is impossible to stop bleeding, the uterus is removed, because. prolonged blood loss can lead to the death of a woman.
Perforation of the uterus requires immediate surgical treatment, and in especially severe cases, surgical removal of the uterus is necessary. In addition, when the uterine wall is perforated, the intestines, bladder, or large vessels can be damaged. Sometimes a rupture or incision of the cervix occurs. These consequences can significantly reduce the likelihood of pregnancy after an abortion, or even lead to infertility. In subsequent pregnancies, bearing is difficult, there is a high risk of uterine rupture during childbirth. Severe bleeding occurs when large vessels are damaged, with uterine myoma or after numerous births. Requires urgent therapy, in severe cases, a blood transfusion is done. If it is impossible to stop bleeding, the uterus is removed, because. prolonged blood loss can lead to the death of a woman.
Incomplete abortion - sometimes during an abortion, the ovum is not completely removed. In this case, bleeding develops, abdominal pain appears, and chronic inflammation of the uterus, endometritis, may develop. With this complication, a second abortion is performed, the remnants of the fetal egg are removed.
With this complication, a second abortion is performed, the remnants of the fetal egg are removed.
Penetration of the infection into the uterine cavity during surgery can cause inflammatory processes and exacerbation of diseases of the pelvic organs - endometritis (inflammation of the uterus), parametritis (inflammation of the periuterine tissue), salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes). In especially severe cases, sepsis can develop - blood poisoning. This condition is very life-threatening and requires urgent antibiotic treatment.
Late effects
Late complications after an abortion can occur months or even years after the operation. These are chronic inflammatory diseases, adhesive processes, hormonal disorders and dysfunctions of the organs of the reproductive system. During pregnancy, large-scale hormonal and physiological changes occur in a woman's body, which ensure gestation, prepare the body for birth, and feeding. Abortion is a severe stress for the body, in which the hormonal system suffers first of all.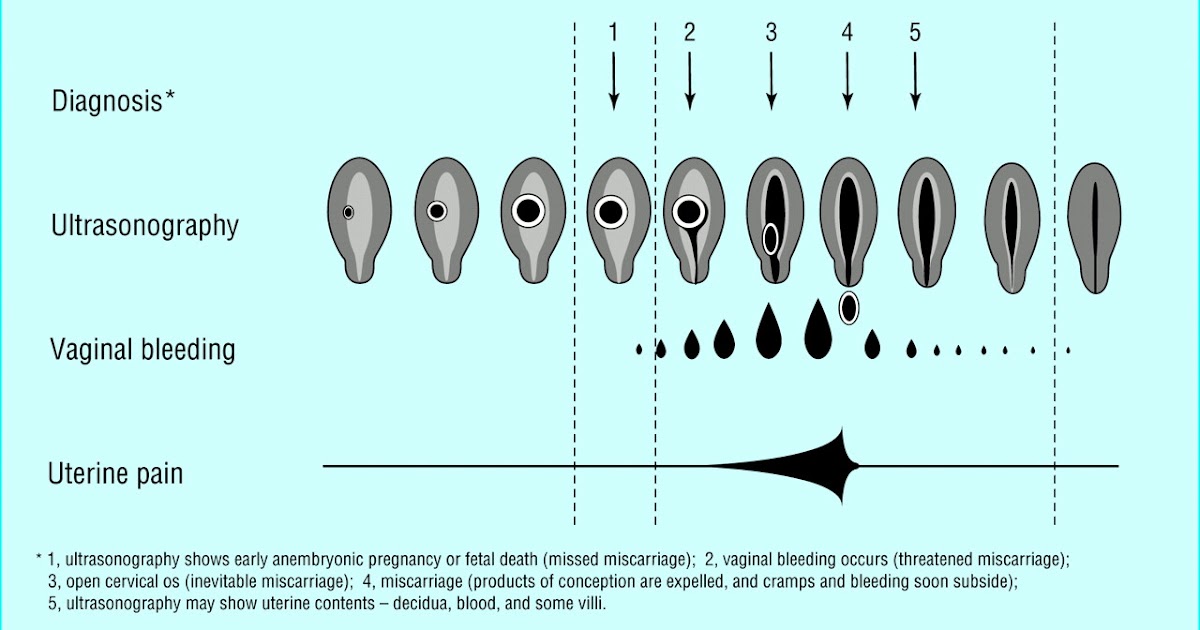
Menstrual disorders
- when menstruation becomes irregular after an abortion, with frequent delays - a very common problem, it occurs in more than 12% of patients. surface of the uterus (endometrium). In this case, deeper layers are often damaged, which leads to the formation of adhesions and scars. Subsequently, the growth of the endometrium occurs unevenly. Because of this, menstruation after an abortion becomes very scarce, or vice versa, abundant and painful. Unlike surgical curettage, after medical abortion, periods usually return immediately, because. mechanical damage to the endometrium does not occur. Secondly, a strong hormonal failure leads to disruption of the ovaries. Dysfunction develops, which contributes to the occurrence of other complications. Here are some of them:
- uterine fibroids,
- endometriosis (growing of the uterine mucosa into the muscle layer),
- pathological growth of the endometrium (hyperplasia),
- endometrial polyps,
- intrauterine adhesions (synechial)
- polycystic ovaries,
- adenomyosis (modification of endometrial tissue due to inflammation of the uterine glands), etc.

Serious hormonal disorders can lead to the formation of benign and malignant tumors.
Endocrine disorders
- caused by hormonal failure, include disorders of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands, termination of pregnancy significantly increases the risk of breast cancer.
Inflammatory diseases
Directly affect the possibility of carrying a pregnancy after an abortion, can cause pain during sex, as a result, sexual desire decreases, a woman experiences less orgasm. Inflammatory diseases, which very often accompany abortions, can negatively affect the blood supply to the fetus - his food and breath. The risk of pregnancy fading, stillbirth, fetal growth retardation, neonatal diseases increases. With severe complications, the likelihood of infertility is high.
Ectopic pregnancy
More common among women who have had an abortion, because adhesions that form in the fallopian tubes make it very difficult to pass them.
Impact of abortion on subsequent pregnancies
Abortion has a clear negative effect on reproductive function. Forced expansion of the cervix during an abortion leads to its weakening, which can later provoke a miscarriage. The risk of miscarriage during a subsequent pregnancy after one abortion is 26%, after two abortions - 32%, and after three or more - increases to 41%. Adhesions and damage to the uterus prevent the fetus from fixing in the uterus, its incorrect location, and perforation can provoke its rupture during childbirth.
Female infertility
- the impossibility of fertilization and bearing, may occur as a result of a violation of the function of the genital organs, if they are damaged or removed. According to doctors, up to 50% of all cases of female infertility are due to previous abortions.
Remember that there is no safe abortion. Abortion is a serious blow to a woman's health and a price to pay for a careless attitude towards contraception and the prevention of unwanted pregnancies.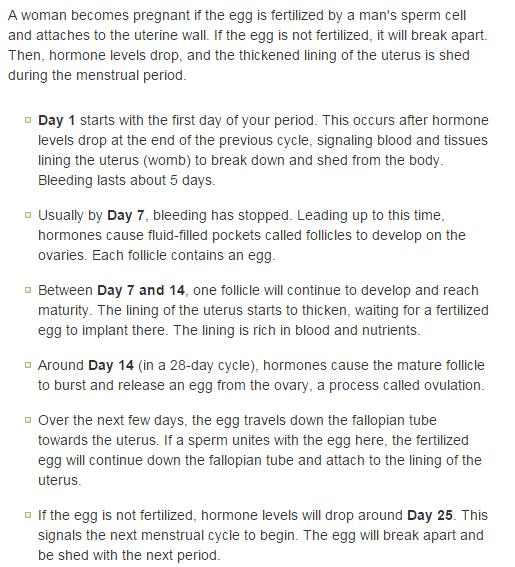
normal or cause for panic
- Main page
- Useful articles
- Bleeding after abortion: the norm or cause for panic
Bleeding after abortion: the norm or cause for panic
Uterine bleeding after termination of pregnancy is a common phenomenon in obstetric practice that occurs on the first day after the operation. The intensity and duration of blood loss are individual and depend not only on the characteristics of the female body, but also on the type of abortion.
Features of bleeding after abortion
Bleeding may be completely absent during the first two days after surgical termination of pregnancy, but later increases to menstrual bleeding and continues in some clinical pictures up to 6 weeks. This pathology indicates a hormonal imbalance, that is, there is insufficient "support" of endometrial tissues, which supports the development of pregnancy. As a result of this bleeding after termination of pregnancy can only intensify, and continue intermittently for several weeks. It is important to understand that here we are talking about pathology.
It is important to understand that here we are talking about pathology.
Most women of reproductive age are concerned about the main question, how long will bleeding after an abortion last? The question is individual, but if it does not pass more than two weeks after getting rid of the fetus, it is important to urgently contact the local gynecologist. The duration of the hemorrhage also depends on the gestational age: the earlier an abortion is performed, the more likely it is to solve such a piquant problem in a gentle “mode” and without serious consequences.
Cause of abnormal bleeding after an abortion
The occurrence of bleeding after an abortion should not confuse the patient, but its duration should be a cause for concern. Among the pathological causes of this symptom, the following should be singled out:
- Perforation of the uterus;
- Injury of the cervix;
- Presence of residual fetal tissue;
- bleeding disorder;
- The reaction of the female body to individual anesthetics.
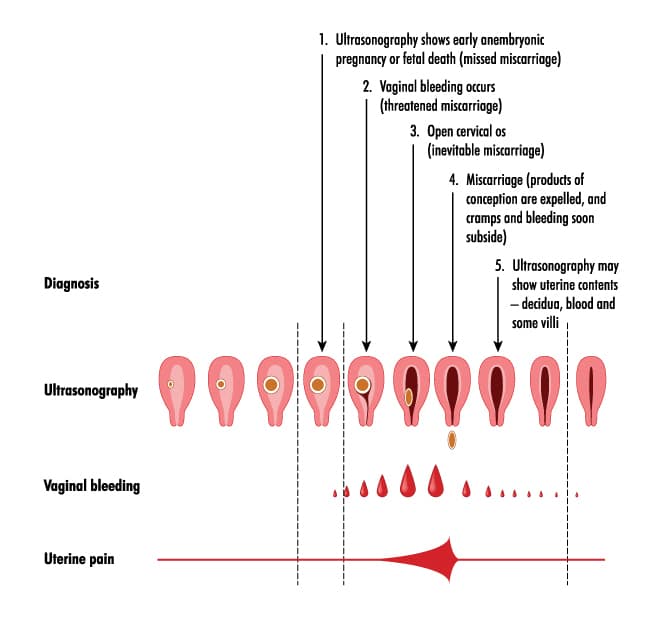
With such diagnoses, along with hemorrhage, there is an obvious violation of the temperature regime, convulsions, general weakness, fainting, hypotension, increased heart rate. It is important not to ignore such signs of shock, but to visit a medical center and a qualified specialist in a timely manner.
How to deal with bleeding after a miscarriage
It is important to understand that to stop prolonged bleeding after a miscarriage at home is impossible, only a competent gynecologist can determine an accurate and effective treatment regimen. Delay in this matter can cost the patient her life.
If the appeal to the doctor is timely, then the first thing the patient is referred for is an ultrasound scan. This accurate clinical examination allows to determine the etiology of the pathological process and the future treatment regimen. If it became known that there is residual fetal tissue in the uterus, additional surgical intervention is necessary to properly clean its cavity.