How many days fertile after ovulation
Calculating Your Monthly Fertility Window
Your fertility window is the time during your menstrual cycle when you’re most likely to get pregnant. For most people, it’s the five days leading up to ovulation, the day of ovulation and the day after ovulation. Calculating your monthly fertility window can help you target the optimal time to have sex if you’re trying to conceive. However, natural family planning is a less reliable form of contraception and does not protect against sexually transmitted infections.
Understanding Your Menstrual Cycle
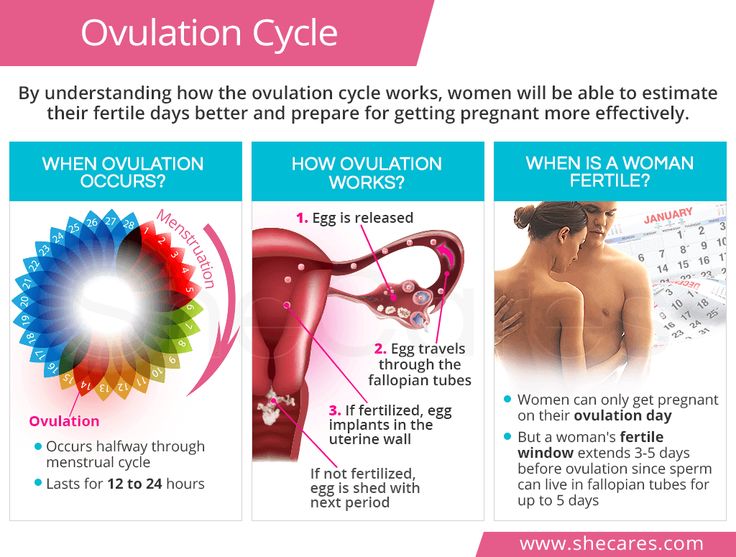
If you’re trying to get pregnant and want to track ovulation, you need to understand your menstrual cycle. Your menstrual cycle is your body’s way of preparing for pregnancy. It begins on the first day of your period and starts over when your next period begins. A typical menstrual cycle is 28 days, but cycles ranging from 21 to 35 days are considered normal.
Lots of changes happen in your body during the cycle, including hormone fluctuations. About halfway through, one of your ovaries releases a mature egg. The egg goes to one of your fallopian tubes, where it waits to be fertilized by sperm. The lining of your uterus gets thicker, too. This prepares the uterus for implantation of the fertilized egg.
If you don’t get pregnant, it could mean that the egg didn’t fertilize, or that the embryo (fertilized egg) didn’t implant into the uterus. In those cases, the uterine lining sheds and you get your period.
When am I ovulating?
Knowing when you’re ovulating is key to tracking your fertility window and determining the best time to get pregnant. There are a few different fertility awareness methods, also called rhythm methods. It’s best to use all three methods if you’re doing natural family planning.
Calendar method
Use the calendar method to track the length of your menstrual cycle. Each month, mark the first day of your period on a calendar or in a period-tracking app. The number of days between the first day of consecutive periods is the length of your menstrual cycle.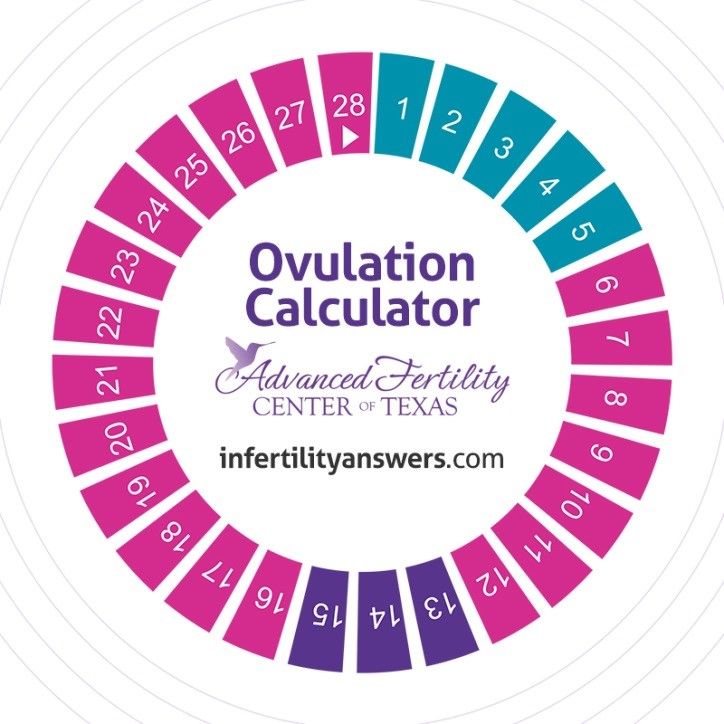 You should do this for at least six months to get good data.
You should do this for at least six months to get good data.
You ovulate about 12 to 14 days before the start of a new menstrual cycle. Your fertile window is the five days leading up to ovulation, plus the day of ovulation and the day after ovulation — so about seven days in total.
It’s important to note that if you have irregular periods and the length of your menstrual cycle varies from month to month, the calendar method won’t be accurate for you.
Cervical mucus method
Hormone fluctuations during your menstrual cycle change the amount and consistency of your vaginal mucus. You need to feel and look at your vaginal mucus each day and record the results on a chart. You’re likely ovulating (and most fertile) when the mucus is heavy, wet and slippery. It will have the consistency of raw egg whites.
You should chart your vaginal mucus for at least one menstrual cycle. It may be difficult at first to know what to look for, so talk to your provider if you want to try this method. He or she can explain how to chart and describe the mucus each day.
He or she can explain how to chart and describe the mucus each day.
Ovulation predictor kits
Ovulation predictor kits are an at-home tool to help predict your ovulation. These tests may be helpful if you have regular periods, but still aren’t quite sure if you are seeing natural signs of ovulation (cervical mucus or a rise in basal body temperature). Ovulation predictor kits test your urine for levels of luteinizing hormone. When the ovulation predictor test becomes positive, ovulation will typically occur within 24 hours, indicating that you’re fertile and should have sex. These kits might not be reliable if you have irregular periods due to polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Basal body temperature method
Also called the temperature method, you take your temperature each morning as soon as you wake up (before you get out of bed). You use a basal body thermometer, which may go in your mouth or your rectum. A basal thermometer is more sensitive than a regular thermometer.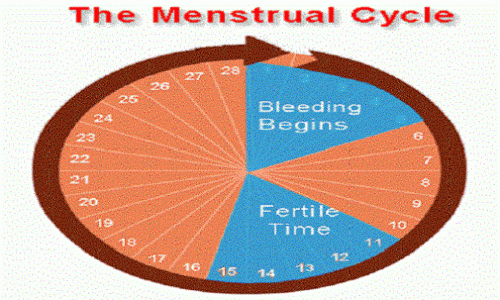 It measures body temperature to a tenth of a degree.
It measures body temperature to a tenth of a degree.
A woman’s basal body temperature rises slightly during ovulation (increases by 0.5 degrees Fahrenheit). If you track your temperatures leading up to ovulation, you should see a sustained rise in your basal body temperature after ovulation.
To help you plan, write your body temperature down each day on a tracking sheet. You should track your temperature for at least three months before using this method for family planning.
However, it’s important to note that the basal body temperature method is not good at predicting your ovulation when trying to conceive. Once you identify the rise in your temperature, you’ve already ovulated. However, this method is a good tool to monitor your pattern of ovulation.
Should I have sex before, during or after ovulation?
For the best chances of pregnancy, you should have sex every day or every other day during the:
- Five days leading up to ovulation
- Day of ovulation
- Day after ovulation
There’s a lot of information (and misinformation) about methods for having sex that could increase your chances of getting pregnant.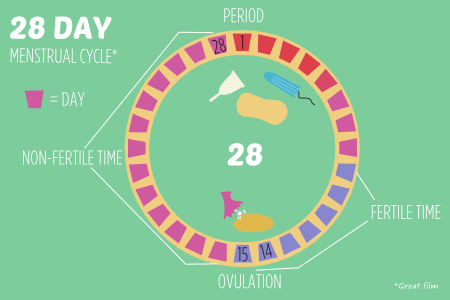 There’s no specific sex position that increases your odds of conceiving. Some lubricants may negatively affect sperm and prevent them from reaching the egg. Talk to your health care provider about which lubricants to avoid.
There’s no specific sex position that increases your odds of conceiving. Some lubricants may negatively affect sperm and prevent them from reaching the egg. Talk to your health care provider about which lubricants to avoid.
What if I have irregular periods?
If you have irregular periods, meaning that your periods are outside of the 21–35-day window or if your cycle intervals vary by more than seven days each month (30-day interval one month, 23 days the next month), you should speak with your Gyn/OB or a fertility specialist. This irregularity may be due to a hormone imbalance and could make it more challenging to get pregnant using natural family planning methods.
How else can I prepare for pregnancy?
In addition to tracking your ovulation to determine your fertile window, it’s important to schedule preconception counseling with your doctor. There are a variety of screenings and lifestyle modifications that can help increase your chances of a successful planned pregnancy.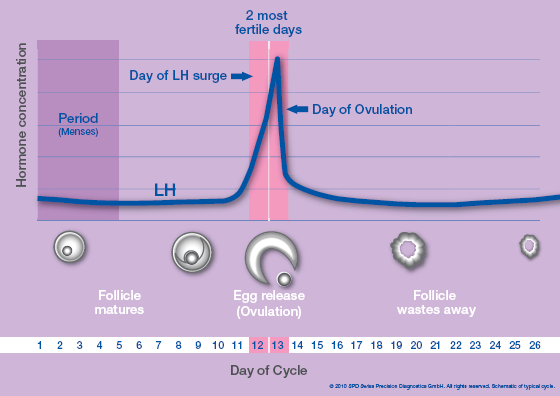
If you’re under 35 and have been trying to conceive for more than a year, or if you’re over 35 and have been trying for six months, it may be time to talk to your doctor about why you can’t get pregnant.
How many days after ovulation can you get pregnant?
It is possible to become pregnant after ovulation. When a person has sex within 12–24 hours after the release of a mature egg, there is a high chance of conceiving.
Ovulation occurs when one of the ovaries releases a mature egg. This is the time when the body is ready to receive sperm for fertilization.
If fertilization does not occur, the egg disintegrates into the uterine lining. The body will then shed the remains during a person’s monthly period.
Ovulation lasts anywhere from 12–24 hours. After the ovary releases an egg, it survives for about 24 hours before it dies, unless a sperm fertilizes it.
If a person has sex days before or during the ovulation period, there is a high chance of conceiving. This is because sperm can survive up to 5 days in the cervix. Therefore, it is important to understand the fertile window.
This is because sperm can survive up to 5 days in the cervix. Therefore, it is important to understand the fertile window.
The fertile window is the period of time during which it is possible to become pregnant from sex. This is the day of ovulation plus the amount of time that sperm can live inside the cervix before it fertilizes the egg.
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), a person can become pregnant if they have sex anywhere from 5 days before until 1 day after ovulation.
Depending on the menstrual cycle, the fertile window may vary from one person to another.
To calculate the fertility window, a person should note the first day of a period until the next period occurs. This timeframe is the menstrual cycle. On average, most people who menstruate have a 28-day cycle.
However, according to the Office on Women’s Health, for some, it may last 21–35 days.
According to the ACOG, ovulation occurs around day 14 of the menstrual cycle.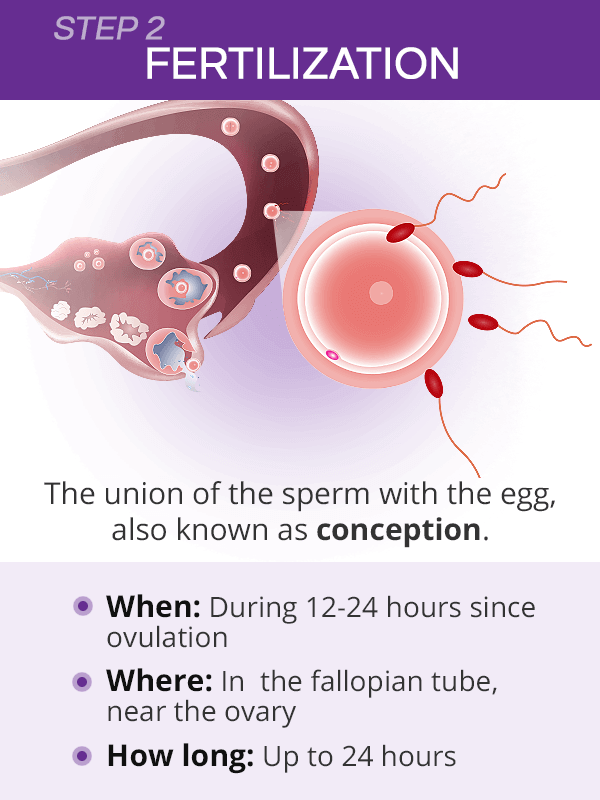
A person with a 28-day cycle, for example, will have their fertile window 5 days before the ovulation date.
Pregnancy is possible 12–24 hours after ovulation. This is because the released egg can only survive 24 hours before the sperm can no longer fertilize it.
The likelihood of getting pregnant on the days before and after ovulation varies from one person to another.
An older study from 1995 looked at the timing of sexual intercourse in relation to ovulation and the likelihood of conception.
Out of 221 healthy women, there were 192 pregnancies. Researchers concluded they could estimate the odds of becoming pregnant on each day of the fertile window as between 10–33%, depending on the day.
| 5 days before ovulation | 10% |
| 4 days before ovulation | 16% |
| 3 days before ovulation | 14% |
| 2 days before ovulation | 27% |
| 1 day before ovulation | 31% |
| Ovulation day | 33% |
The same study authors also note there could be a 12% chance of conceiving on either day 7 before ovulation and the day after ovulation.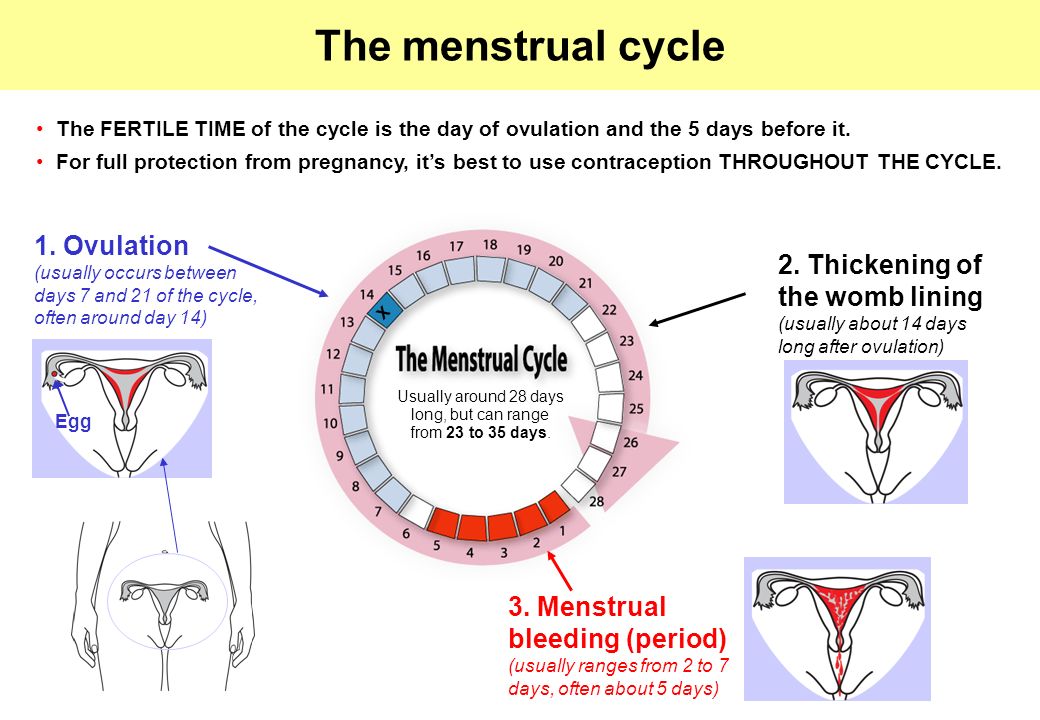
However, the chances of becoming pregnant before or after ovulation depend on several factors, including:
- age
- frequency of sexual intercourse
- menstrual cycle
For those trying to conceive, tracking ovulation is crucial to ensure they identify the most fertile days in the menstrual cycle.
Here are some of the methods a person can use to track or predict ovulation.
Basal body temperature charting
Basal body temperature (BBT) is the temperature when the body is at rest.
Charting BBT for a series of months by measuring every morning after waking up will help predict ovulation.
During or when ovulation approaches, there is a slight increase in BBT. A person can use a digital thermometer to track these small changes in temperature.
Monitoring BBT can help tell when ovulation occurs and therefore predict the days in the cycle when pregnancy is possible.
Ovulation predictor kits
Using ovulation predictor kits, such as test strips and digital tests, will help measure the level of luteinizing hormone (LH), which usually rises during ovulation.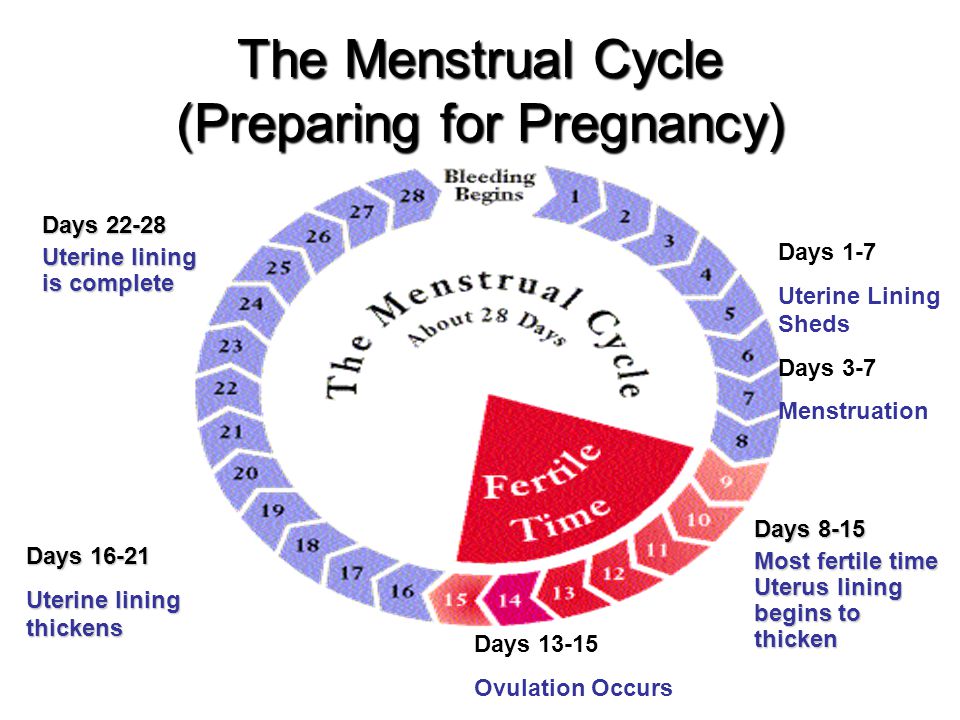
A person needs to take tests for consecutive days to detect the rise in LH.
Once they notice a consistent rise, experts recommend having sex daily for the next couple of days to increase the chances of pregnancy.
Cycle charting apps
Several cycle apps, such as the Clue period tracker and Flo period ovulation tracker, can help calculate the ovulation period and fertile window.
Charting ovulation using these apps will indicate the ovulation date and days when a person’s body is most fertile.
Fertility monitors
For people trying to conceive or wishing to avoid pregnancy, using fertility monitors to track ovulation can help people plan intercourse.
Fertility monitors work by measuring significant body changes, such as BBT, heart rate, and breathing.
By compiling this data, the fertility monitor can predict the fertile window.
Cervical mucus method
Observing cervical mucus can give an idea of when a person may be ovulating.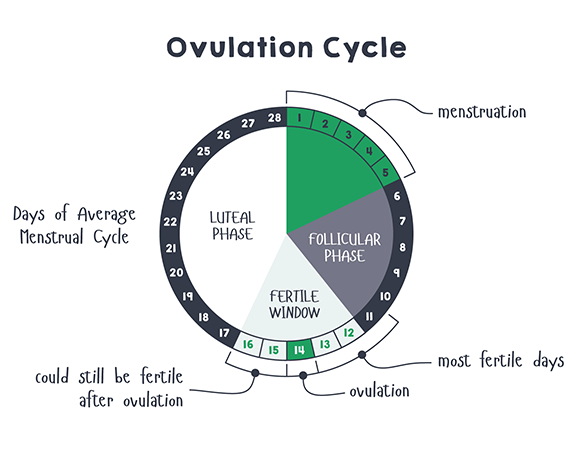
When ovulation approaches, the cervical mucus changes to a thin, clear, stringy, slippery consistency. It may look similar to raw egg whites.
The mucus allows the sperm to swim to the released egg during intercourse.
Ideally, this is the ideal time to have sex due to the high chances of becoming pregnant.
Watching ovulation signs, such as a slight increase in BBT, changes in cervical mucus, and increased sex drive, can help determine the best time to have sex to boost chances of becoming pregnant.
In addition, having sex during the fertile window increases the chances of conception. During this timeframe, the body is ready to receive sperm for fertilization.
On average, a menstrual cycle lasts between 21–35 days.
An irregular cycle or absent cycle that lasts fewer than 21 days or more than 35 days, can mean that a person is not ovulating.
A person should speak with a doctor if they do not become pregnant after 1 year of trying to conceive.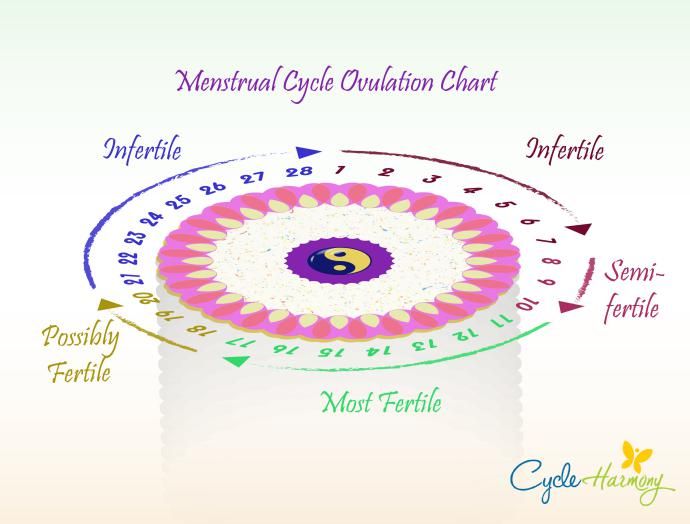
Age may also determine when to seek help. People between 35–40 years of age should speak with a doctor after 6 months of trying to get pregnant. For those above 40 years of age, a healthcare professional may run some fertility tests.
A doctor may also test for possible signs of infertility or if a person has ever had repeated miscarriages, pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, prior cancer treatment, or a history of irregular periods.
A person can get pregnant 12–24 hours after ovulation, as a released egg can survive up to 24 hours within the cervix.
For those trying to conceive, it is crucial to understand the menstrual cycle.
Beyond this, a person can use methods, such as BBT charting, cycle charting apps, fertility monitors, changes in cervical mucus, and ovulation predictor kits to boost the chances of pregnancy.
How to recognize fertile days and ovulation?
In Brief Determining fertile days allows a woman to consciously plan her pregnancy and increase her chances of getting pregnant.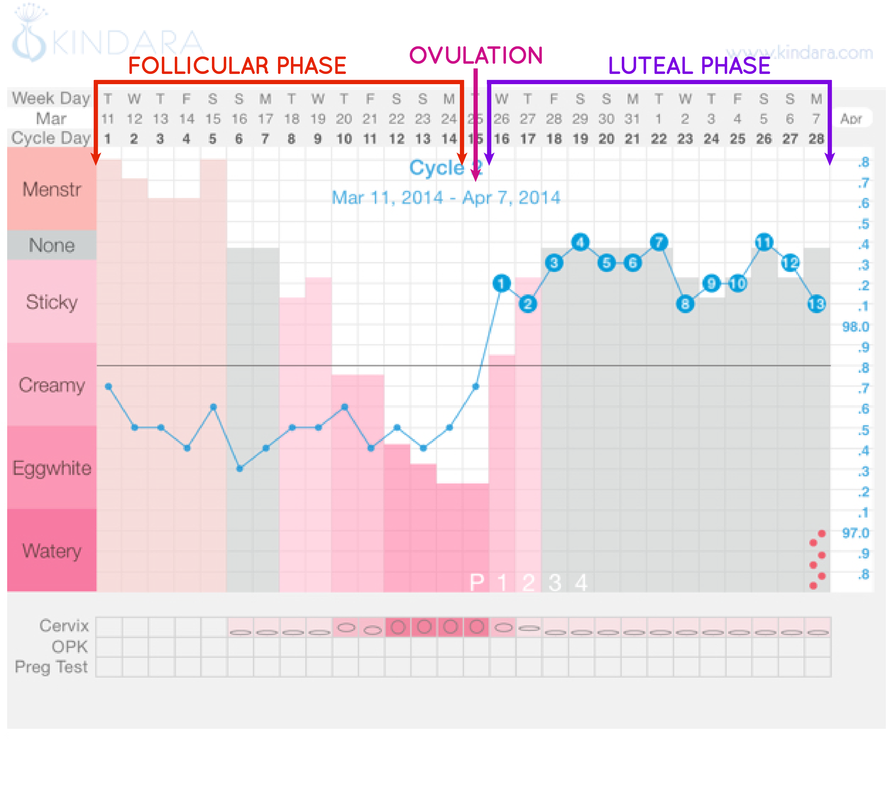 There are several ways to determine fertile days. They differ in both accuracy and method.
There are several ways to determine fertile days. They differ in both accuracy and method.
How to recognize fertile or fertile days?
The beginning of a woman's menstrual cycle is considered the first day of menstruation (bleeding) and the day before the next menstruation (until the next bleeding). One menstrual cycle has an average of 5 to 7 fertile days. The number of these days is related to both ovulation and the length of time that sperm cells survive in a woman's body.
Ovulation lasts about 24 hours and occurs 14 days before menstruation, but spermatozoa can survive in a woman's genitals for 5-7 days, waiting for their chance to fertilize an egg. Thus, sexual intercourse a few days before ovulation can lead to pregnancy. Often women wonder which method to choose to determine the day of ovulation? Are basal temperature measurements enough to determine ovulation? How many days is vaginal mucus favorable for sperm activity? How does vaginal mucus change after ovulation? When to start ovulation monitoring? How to make a calendar favorable for conception? Should I use ovulation tests? What body signals can indicate ovulation? We will try to answer these questions below.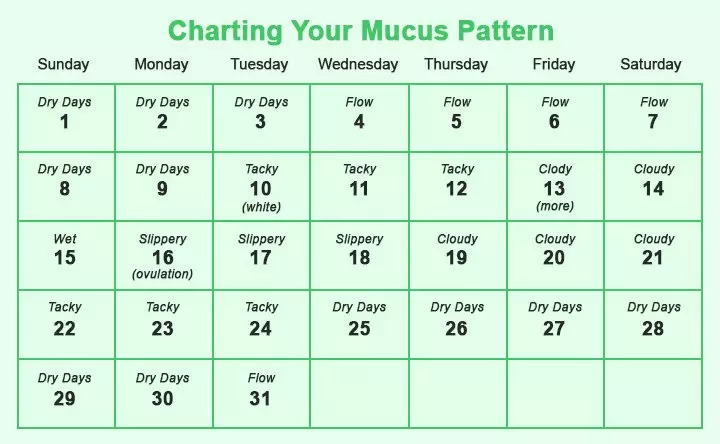
Do you have any questions? Contact us!
Ovulation monitoring
The most accurate monitoring of the menstrual cycle is carried out by a gynecologist using ultrasound. This is a painless examination carried out on certain days. Usually, 3-4 ultrasound examinations are performed during one cycle. Its purpose is to determine the course of the menstrual cycle, the growth of follicles, as well as their quantity, quality, rupture, while simultaneously monitoring the state of the endometrium. Ultrasound examinations allow you to accurately determine the day of ovulation and, thus, fertile days.
The first examination is usually carried out by a doctor on the fifth day of the cycle, after which the following are observed:
- follicle growth,
- endometrial thickness,
- cervical mucus quality.
After the day of ovulation, the doctor checks whether ovulation has actually taken place. This is evidenced by “traces” of follicle rupture or the presence of a corpus luteum in the ovary.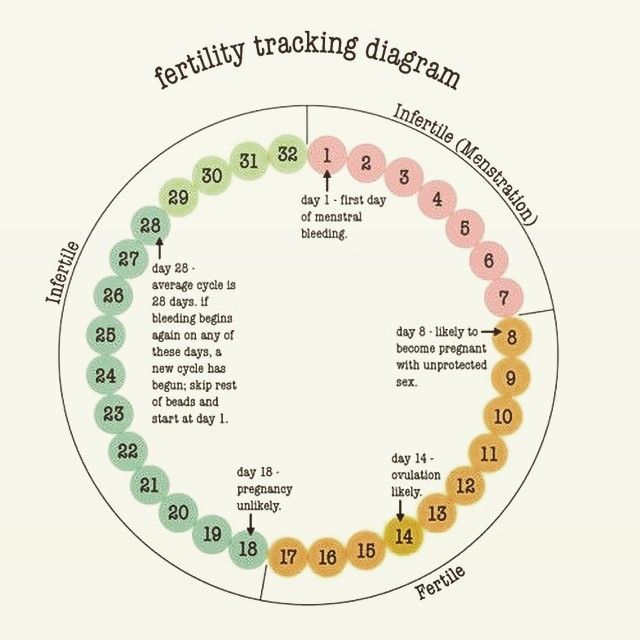 Ovulation monitoring also makes it possible to identify possible causes, difficulties in pregnancy. An accurate diagnosis of ovulation monitoring is provided by the Fertility Clinic.
Ovulation monitoring also makes it possible to identify possible causes, difficulties in pregnancy. An accurate diagnosis of ovulation monitoring is provided by the Fertility Clinic.
Fertile days calendar
In turn, the easiest way to determine the date of ovulation is a method based on the calculation of the average length of the menstrual cycle based on the length of the cycle for several months. Based on this, you can roughly determine the date of the next menstruation. To calculate the day of ovulation, subtract 12 from the length of the menstrual cycle, and then 4 days.
For example, in the case of a 28-day cycle, it looks like this: 28-12 = 16, and in the next step 16-4 = 12. This means that ovulation can occur between 12 and 16 days of the cycle. The method is simple, but unfortunately there is a very high error rate.
A woman's menstrual cycle is variable and influenced by many factors, such as:
- Diet
- Stress
- Colds
- Climate
This method does not work for irregular cycles.
How many days is mucus favorable for conception?
Expected ovulation can also be determined by monitoring vaginal mucus. Often women ask how many days mucus favorable for conception can be observed. It is worth remembering that this is due to fertile days of about 5-7 days. On fertile days, the mucus is clear, slippery, sticky, and elastic, reminiscent of fresh egg white. Such mucus has a favorable pH for spermatozoa and facilitates their survival and movement. After ovulation, the amount of vaginal mucus decreases, it turns white, thickens and loses viscosity. This is how it stays until menstruation. Immediately after menstruation, the secretion of mucus is reduced until the secretion of mucus favorable for conception begins. The mucus monitoring method does not confirm ovulation, it is only a sign that ovulation is approaching. Also, be aware that some medications can interfere with mucus production, so this will not indicate ovulation is near.
Temperature increase after ovulation
Changes in body temperature can also be used to determine ovulation.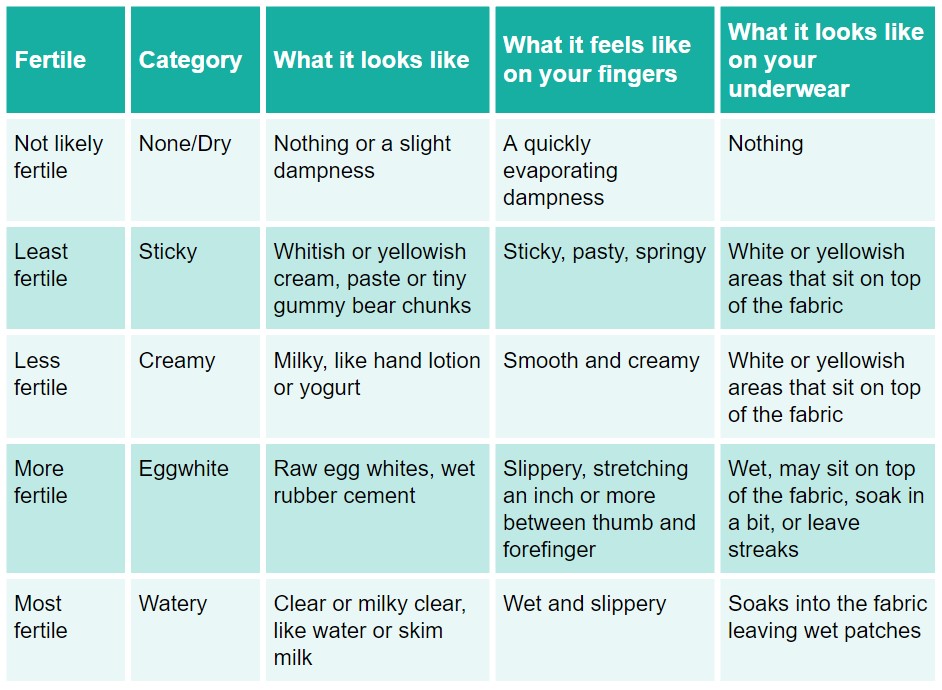 After ovulation, a corpus luteum forms in the ovary, which secretes progesterone, and this, in turn, causes an increase in temperature by about 0.2 - 0.6 degrees Celsius. The temperature rises about 24 hours after the egg is released from the ovary, so measuring it can only serve to confirm ovulation, and this information can be used to determine the optimal time for conception in the next cycle. With regular menstruation, if the temperature rises, for example, systematically on the 16th day of the cycle, then ovulation occurs 1-2 days earlier, i.e. fertile days fall on the 13th, 14th and 15th days of the cycle.
After ovulation, a corpus luteum forms in the ovary, which secretes progesterone, and this, in turn, causes an increase in temperature by about 0.2 - 0.6 degrees Celsius. The temperature rises about 24 hours after the egg is released from the ovary, so measuring it can only serve to confirm ovulation, and this information can be used to determine the optimal time for conception in the next cycle. With regular menstruation, if the temperature rises, for example, systematically on the 16th day of the cycle, then ovulation occurs 1-2 days earlier, i.e. fertile days fall on the 13th, 14th and 15th days of the cycle.
However, in order for measurements of ovulation temperature to be reliable, it is necessary:
- do this every morning
- at a certain time, immediately after waking up
- take the temperature in the vagina or in the mouth.
With this method, a very high percentage of error is possible, since many other factors related to general health can influence the temperature increase without hormonal fluctuations.
Ovulation Tests
Available ovulation tests detect increases in luteinizing hormone levels. This hormone ensures the rupture of the walls of the follicle and the release of the egg. For regular cycles, such as 28-30 day cycles, tests should be performed around day 10-11 of the menstrual cycle. They are carried out in a similar way to a pregnancy test with morning urine. A positive test means that you will ovulate in about 24-36 hours.
How to recognize ovulation? - blood tests
When assessing the course of ovulation, a progesterone test is also used, which is carried out on the basis of a blood test. This test allows you to confirm the presence of ovulation in the corresponding cycle. With a 28-day cycle, it is carried out on the 21st day. If menstruation is irregular, the examination should be carried out 7-8 days after a positive ovulation test.
Body Signals
Many women experience no symptoms during their fertile days, but some experience improved mood and increased libido. Ovulation can also be accompanied by pain, which is experienced by about half of women. Characteristic of this is pain in the lower abdomen and burning in one of the ovaries. In the middle of the cycle, breast tenderness and soiling may be observed. Skillful recognition of body signals will help determine the best date for a chance to get pregnant.
Ovulation can also be accompanied by pain, which is experienced by about half of women. Characteristic of this is pain in the lower abdomen and burning in one of the ovaries. In the middle of the cycle, breast tenderness and soiling may be observed. Skillful recognition of body signals will help determine the best date for a chance to get pregnant.
When is a woman most fertile?
If you are a woman taking precautions to prevent pregnancy, or if you are thinking about pregnancy in some way in the future, the issue of fertility usually remains in the background.
The question of when a woman is most fertile has two aspects.
First, is the menstrual monthly cycle and the period when a woman is most fertile.
To figure out the arithmetic, a fertility calendar or an ovulation calculator will help. The second aspect of the question concerns biological age and the stage of life at which women are most fertile. In our article, we will look at the monthly cycle, the days that are the most fertile during this cycle, and various means of monitoring and predicting ovulation.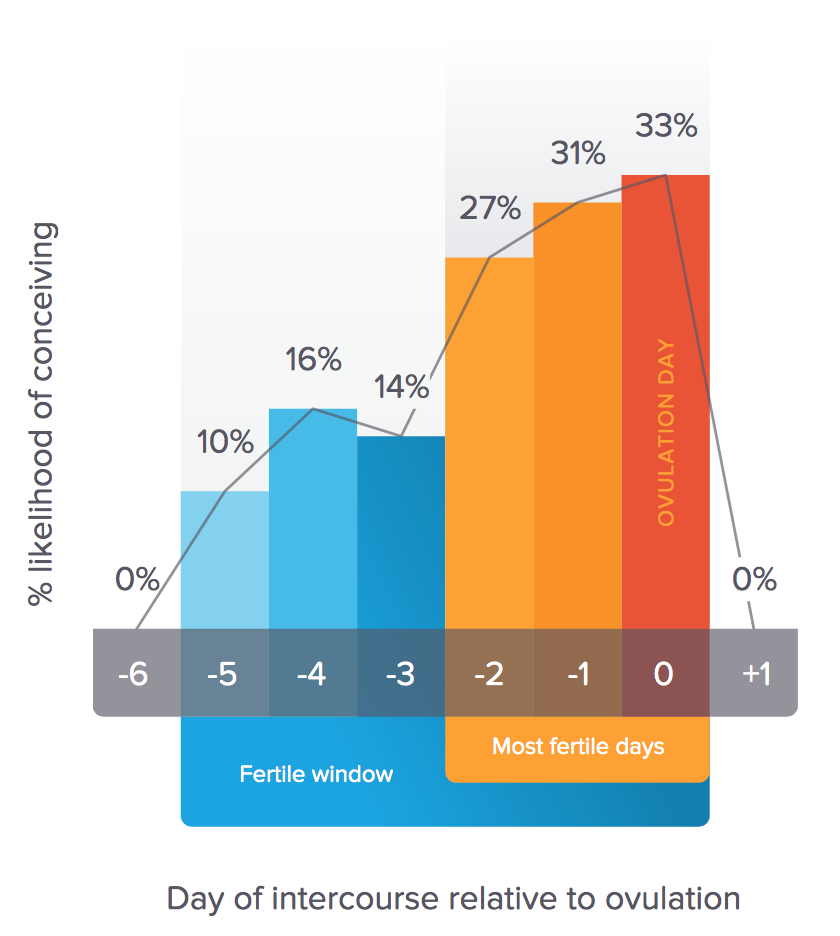 This makes it possible to predict the time of maximum fertility with some accuracy.
This makes it possible to predict the time of maximum fertility with some accuracy.
Second, , we look at the stages of fertility at various times in a woman's life and their impact on her ability to conceive.
It is well known that fertility peaks at age 20 and begins to decline after age 30; after 35 years, natural conception rates begin to drop sharply. However, in today's society, many women, for understandable financial and social reasons, choose to delay childbearing until the age of thirty. Thus, we are faced with the paradoxical situation where many women, who have long sought to prevent pregnancy in their younger years, find themselves in a situation where they begin to look for ways to increase their chances of conceiving.
When is a woman most fertile? What does the menstrual cycle show?
In a woman, the ability to conceive is maximum a day or two before and after ovulation. This is when the egg is released from the ovaries.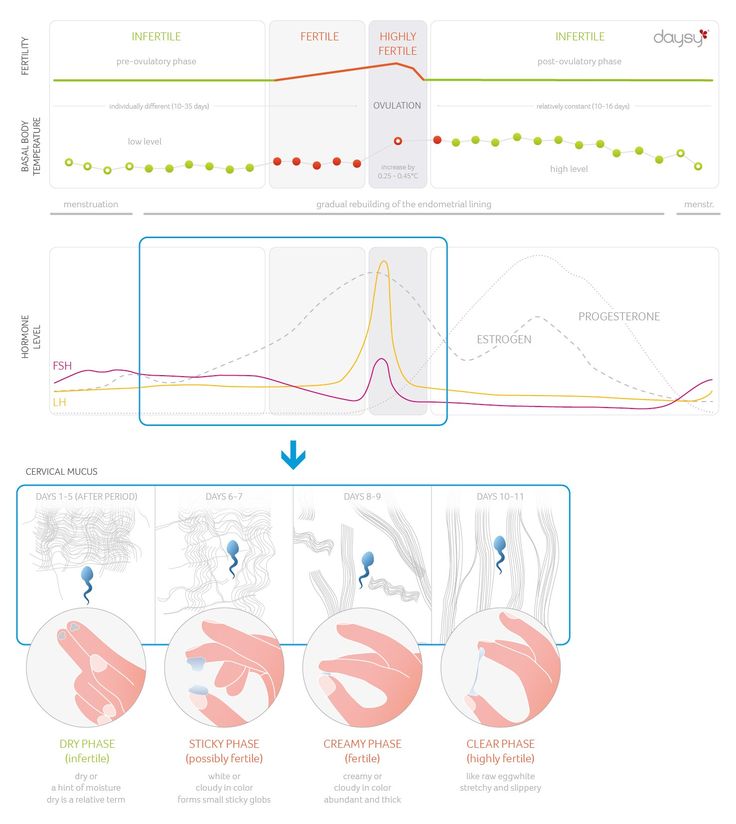 You can calculate with a reasonable degree of accuracy when ovulation will occur, especially if your cycle is regular, anywhere between 24 and 35 days. Consider the start of your period (bright spotting) as the first day of your cycle, and the day before the next as the end of your cycle. Ovulation usually occurs 12-16 days before the start of the next cycle. Thus, if you have a regular 28-day cycle, then the indicator remains the same: ovulation occurs on the 12th-16th day. However, fertile time is not limited to these few days. Remember that you can get pregnant if you have unprotected sex at any time during the week before ovulation, as sperm can live in a woman's genital tract for up to seven days.
You can calculate with a reasonable degree of accuracy when ovulation will occur, especially if your cycle is regular, anywhere between 24 and 35 days. Consider the start of your period (bright spotting) as the first day of your cycle, and the day before the next as the end of your cycle. Ovulation usually occurs 12-16 days before the start of the next cycle. Thus, if you have a regular 28-day cycle, then the indicator remains the same: ovulation occurs on the 12th-16th day. However, fertile time is not limited to these few days. Remember that you can get pregnant if you have unprotected sex at any time during the week before ovulation, as sperm can live in a woman's genital tract for up to seven days.
Fertility specialists generally advise that if you are hoping to get pregnant, it is advisable to specifically schedule contacts around this time, as it can be difficult to calculate the exact day of ovulation, and trying to have sex on a schedule can cause unnecessary stress and anxiety.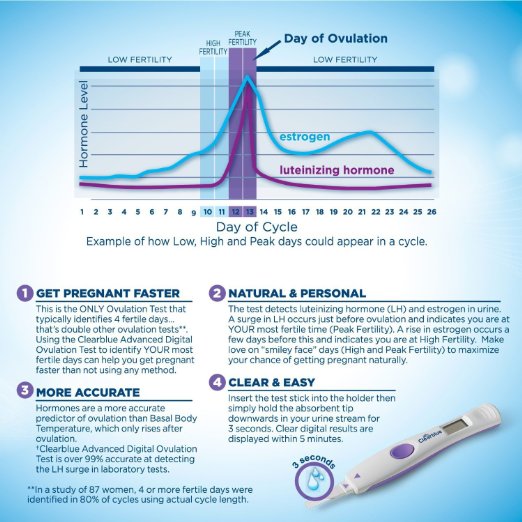 For the best chance of getting pregnant as long as there are no underlying fertility problems, it is recommended to have intercourse every 2-3 days during your cycle. In addition, fertility calendars, an ovulation test, and self-monitoring for signs of ovulation can help predict the ideal time to conceive.
For the best chance of getting pregnant as long as there are no underlying fertility problems, it is recommended to have intercourse every 2-3 days during your cycle. In addition, fertility calendars, an ovulation test, and self-monitoring for signs of ovulation can help predict the ideal time to conceive.
Menstrual calendar
It could be an old-fashioned pen and paper, a spreadsheet, or one of the many online calendars available. They are also known as ovulation calendars or ovulation calculators. They all do the same thing: keep track of your menstrual cycle dates and use the 12-16 day calculation outlined above to determine the days on which you are most likely to conceive.
Ovulation Tests
These are test kits that measure the level of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your urine. The essence of the measurement is to capture the surge in LH levels that occurs during your cycle a couple of days before ovulation. There are also tests that measure the same hormone pulsation but use a saliva sample.