What is the average birth weight
Your Newborn's Growth (for Parents)
From your baby's first day, doctors will keep track of weight, length, and head size. Growth is a good indicator of general health. Babies who are growing well are generally healthy, while poor growth can be a sign of a problem.
How Big Are Newborns?
Newborns come in a range of healthy sizes. Most babies born between 37 and 40 weeks weigh somewhere between 5 pounds, 8 ounces (2,500 grams) and 8 pounds, 13 ounces (4,000 grams).
Newborns who are lighter or heavier than the average baby are usually fine. But they might get extra attention from the doctors and nurses after delivery to make sure there are no problems.
Different things can affect a baby's size at birth. The length of the pregnancy is important. Babies born around their due date or later tend to be larger than those born earlier.
Other factors include:
- Size of parents. Big and tall parents may have larger-than-average newborns; short and petite parents may have smaller-than-average newborns.
- Multiple births. If you have twins, triplets, or more, you can count on your babies being a bit small. Multiples have to share their growing space in the uterus, and they're often born early, which leads to small size at birth.
- Birth order. First babies are sometimes smaller than brothers or sisters born later.
- Gender. Girls tend to be smaller, boys larger, but the differences are slight at birth.
- Mom's health during pregnancy. Things that can lead to a lower birth weight include a mother with high blood pressure or heart problems; or one who used cigarettes, alcohol, or illegal drugs during the pregnancy. If the mother has diabetes or is obese, the baby may have a higher birth weight.
- Nutrition during pregnancy. Good nutrition is vital for a baby's growth — before and after birth. A poor diet during pregnancy can affect how much a newborn weighs and how the infant grows.
 Gaining a lot of weight can make a baby more likely to be born bigger than average.
Gaining a lot of weight can make a baby more likely to be born bigger than average. - Baby's health. Medical problems, including some birth defects and some infections during the pregnancy, can affect a child's birth weight and later growth.
p
What About Preemies?
Premature babies generally are smaller and weigh less than other newborns. A preemie's weight will largely depend on how early he or she was born. The time an infant missed being in the womb was growing time, so the baby has to do that growing after birth.
Many pre-term babies are classified as having "low birth weight" or "very low birth weight." In medical terms:
- Low birth weight means a baby weighs less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces (2,500 grams) at birth. That's the case for about 1 in every 12 babies in the United States, so it's quite common.
- Very low birth weight means a baby weighs less than 3 pounds, 5 ounces (1,500 grams).
Most babies with low birth weight or very low birth weight were born prematurely.
Premature babies get special medical attention right away after they're born. A specialist called a neonatologist may help care for them. Many preemies spend time in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) while they get medical care.
Is Bigger Better?
A baby with chubby cheeks and dimpled thighs once was many people's picture of a healthy newborn. But a baby born much larger than average may have special medical problems that need attention.
Some very large babies — especially those born to mothers with diabetes, including gestational diabetes — may have problems for a few days keeping blood sugar levels up. They might need extra feedings or even IV (given into a vein)
glucoseto keep those levels from falling too low.
Will My Baby Lose Weight?
Yes, at first. Babies are born with some extra fluid, so it's normal for them to drop a few ounces when they lose that fluid in the first few days of life.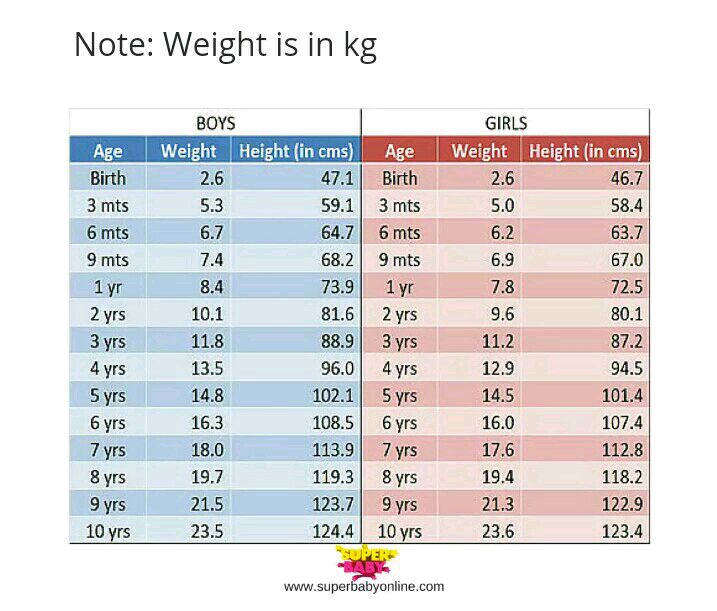 A healthy newborn is expected to lose 7% to 10% of the birth weight, but should regain that weight within the first 2 weeks or so after birth.
A healthy newborn is expected to lose 7% to 10% of the birth weight, but should regain that weight within the first 2 weeks or so after birth.
During their first month, most newborns gain weight at a rate of about 1 ounce (30 grams) per day. They generally grow in height about 1 to 1½ inches (2.54 to 3.81 centimeters) during the first month. Many newborns go through a period of rapid growth when they are 7 to 10 days old and again at 3 and 6 weeks.
p
Should I Be Concerned?
Newborns are so small, and it can be hard to know if your baby is gaining weight the way he or she should. You may worry that your baby has lost too much weight in the first few days or isn't taking enough breast milk or formula. If so, talk to your doctor, who may ask you about:
- How many feedings a day your baby gets. A breastfed baby may feed about 8 or more times in a 24-hour period; formula-fed babies usually eat less often, perhaps every 3 to 4 hours. A lactation (breastfeeding) counselor can make suggestions to increase comfort and improve technique, if a mom needs extra help.
- How much your baby eats at each feeding. A baby generally nurses for at least 10 minutes, should be heard to swallow after 3 or 4 sucks, and should seem satisfied when done. At this age, formula-fed babies may drink up to 3 to 4 ounces (90 to 120 milliliters) at a time.
- How often your baby pees. A breastfed baby may have only 1 or 2 wet diapers a day until the mother's milk comes in. Expect about 6 wet diapers by 3 to 5 days of age for all babies. After that, babies should have at least 6 to 8 wet diapers a day.
- How many bowel movements your baby has each day, and what they're like. Newborns may have only one poopy diaper a day at first. Poop is dark and tarry the first few days, then becomes soft or loose and greenish-yellow by about 3 to 4 days. Newborns usually have several poopy diapers a day if breastfed and fewer if formula-fed.
What Else Should I Know?
Being small or large at birth doesn't mean a baby will be small or large later in childhood or as an adult. Plenty of tall teens began life as small babies, and the biggest baby in the family can grow up to be a petite adult.
Plenty of tall teens began life as small babies, and the biggest baby in the family can grow up to be a petite adult.
By the time they're adults, kids tend to resemble their parents in size. Genetics, as well as good nutrition and your attention, will play a large part in how your baby grows in the years to come.
Whether your baby starts out large, small, or average, in the next few months you can expect your little one to keep growing fast.
Reviewed by: Madhu Desiraju, MD
Date reviewed: October 2018
Average baby weight: Chart and development
Weight is one indicator of good nutrition and physical development. It can therefore be helpful to know about babies’ average weight month by month.
First, it is worth noting that average weight is not “normal” weight. Just like adults, babies come in all shapes and sizes. If a baby’s weight is in a lower percentile, this does not necessarily signal a problem with their growth or physical development. With this in mind, using a weight chart can help a person generally track their baby’s growth.
With this in mind, using a weight chart can help a person generally track their baby’s growth.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend using the World Health Organization (WHO) weight chart for babies up to 2 years of age.
This article describes the average weight of a baby month by month from birth. It also explores what can affect a baby’s weight.
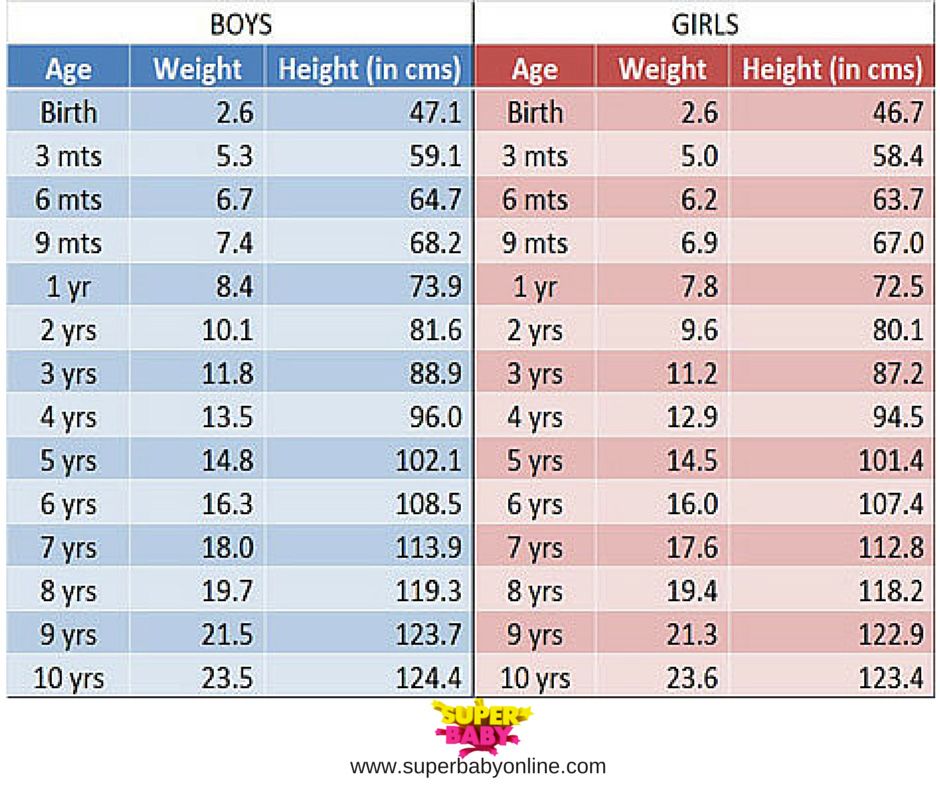
According to the WHO, the average birth weight of a full-term male baby is 7 pounds (lb) 6 ounces (oz), or 3.3 kilograms (kg). The average birth weight of a full-term female is 7 lb 2 oz, or 3.2 kg.
The average weight of a baby born at 37–40 weeks ranges from 5 lb 8 oz to 8 lb 13 oz. This is 2.5 to 4 kg.
At delivery, experts consider a low birth weight to be less than 5 lb 8 oz, or 2.5 kg.
It is common for babies to lose around 10% of their weight shortly after birth. This decrease is mostly due to fluid loss and usually nothing to worry about. Most babies gain back this weight within 1 week.
Weight charts can help a person tell what percentile their baby’s weight falls into. For example, if their weight is in the 60th percentile, it means that 40% of babies of the same age and sex weigh more, and 60% of these babies weigh less.
This does not necessarily mean that any baby weighs too much or too little. It can simply indicate where a baby’s weight falls on a spectrum.
The chart below shows baby weights in the 50th percentile. This is the average weight. Male babies tend to weigh a little more than female babies, so the chart is divided by sex.
| Baby age | Female 50th percentile weight | Male 50th percentile weight |
| Birth | 7 lb 2 oz (3.2 kg) | 7 lb 6 oz (3.3 kg) |
| 1 month | 9 lb 4 oz (4.2 kg) | 9 lb 14 oz (4.5 kg) |
| 2 months | 11 lb 5 oz (5.1 kg) | 12 lb 4 oz (5.6 kg) |
| 3 months | 12 lb 14 oz (5.8 kg) | 14 lb 1 oz (6.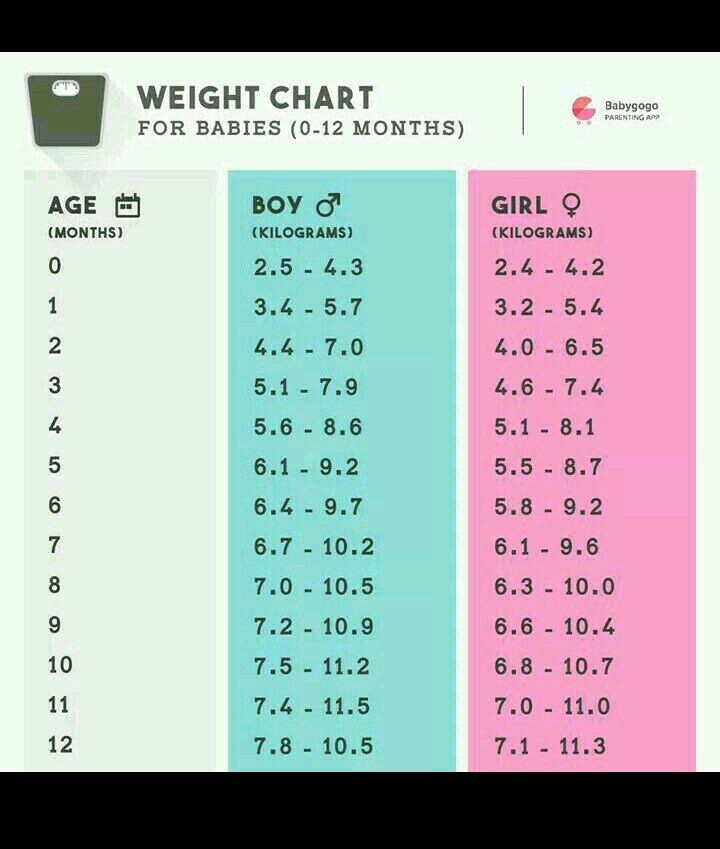 4 kg) 4 kg) |
| 4 months | 14 lb 3 oz (6.4 kg) | 15 lb 7 oz (7.0 kg) |
| 5 months | 15 lb 3 oz (6.9 kg) | 16 lb 9 oz (7.5 kg) |
| 6 months | 16 lb 1 oz (7.3 kg) | 17 lb 8 oz (7.9 kg) |
| 7 months | 16 lb 14 oz (7.6 kg) | 18 lb 5 oz (8.3 kg) |
| 8 months | 17 lb 8 oz (7.9 kg) | 18 lb 15 oz (8.6 kg) |
| 9 months | 18 lb 2 oz (8.2 kg) | 19 lb 10 oz (8.9 kg) |
| 10 months | 18 lb 11 oz (8.5 kg) | 20 lb 3 oz (9.2 kg) |
| 11 months | 19 lb 4 oz (8.7 kg) | 20 lb 12 oz (9.4 kg) |
| 12 months | 19 lb 12 oz (8.9 kg) | 21 lb 4 oz (9.6 kg) |
Babies grow and gain weight the fastest within the first 6 months of life. Although this can vary, babies tend to gain around 4–7 oz, or 113–200 grams (g), per week in the first 4–6 months.
Weight gain then slows slightly, with an average gain of around 3–5 oz (about 85–140 g) per week when the baby is 6–18 months. On average, babies triple their birth weight by their first birthday.
On average, babies triple their birth weight by their first birthday.
Growth patterns do not follow a clear schedule, however.
Some babies gain weight steadily and stay in the same percentile, or close to it, for several months. Others gain weight rapidly, signalling a growth spurt, which can happen at any time. This may move a baby into a new weight percentile.
It is important not to focus on weight as the only indicator of physical development. Other measurements of this development include the baby’s length and head circumference.
Considering all three measurements gives doctors an idea about how the baby is growing, compared with other babies of the same age and sex.
Meanwhile, it is also important to keep other developmental milestones in mind. Various checklists of milestones by age are available, including one from Pathways.org, which is endorsed by organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the National Association of Pediatric Nurse Practitioners.
For anyone looking for more information about what influences the weight of a baby, several factors can be involved, including:
Sex
Male newborns tend to be bigger than female newborns, and they typically gain weight a little faster during infancy.
Nutrition
Weight gain and growth rates can also depend on whether the baby consumes breast milk or formula.
The American Academy of Pediatrics notes that breastfed babies gain weight and grow faster than formula-fed babies during the first 6 months.
However, that rate can shift during the next 6 months. Breastfed babies may gain weight and grow more slowly than formula-fed babies when they are aged 6 months to 1 year.
Medical conditions
Underlying health issues can cause a baby to gain weight more slowly. For example, babies with congenital heart irregularities may gain weight at a slower rate than babies without this condition.
Health issues that affect nutrient absorption or digestion, such as celiac disease, may also lead to slow weight gain.
Prematurity
Babies born prematurely may grow and gain weight more slowly during their first year than babies born at full term.
However, many babies born prematurely gain weight rapidly and “catch up” by about their first birthday.
The average birth weight for full-term male babies is 7 lb 6 oz, or 3.3 kg. For female babies born full-term, the average birth weight is 7 lb 2 oz, or 3.2 kg.
Baby weight charts can help a healthcare team track a baby’s physical development by comparing the baby’s weight with the weights of others of the same age and sex.
Still, a doctor usually looks for steady growth, rather than a target percentile, when assessing a baby’s physical development. And even if a baby’s weight is in a lower percentile, they will not necessarily be a small adult — just as longer babies do not necessarily become tall adults.
Knowing about average weights by month can help people gauge their babies’ physical development, but doctors also look for other important indicators, such as length and head circumference.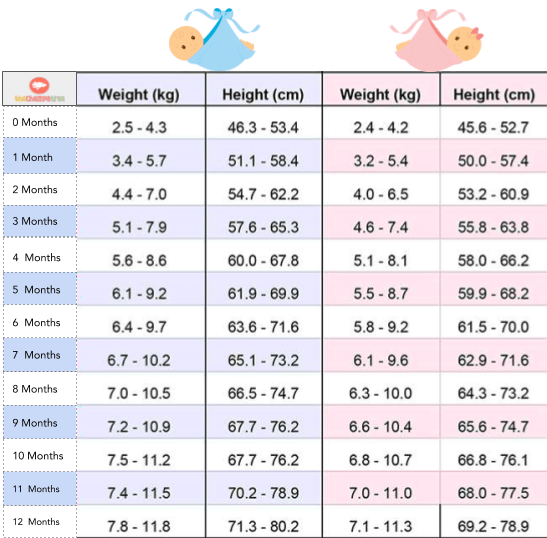
Healthcare professionals also take into account whether a baby is generally hitting other milestones on time. And by taking a detailed medical history, they can rule out any medical conditions or nutritional considerations that may be preventing a baby from gaining weight appropriately.
Weight gain in newborns by months: norms and deviations
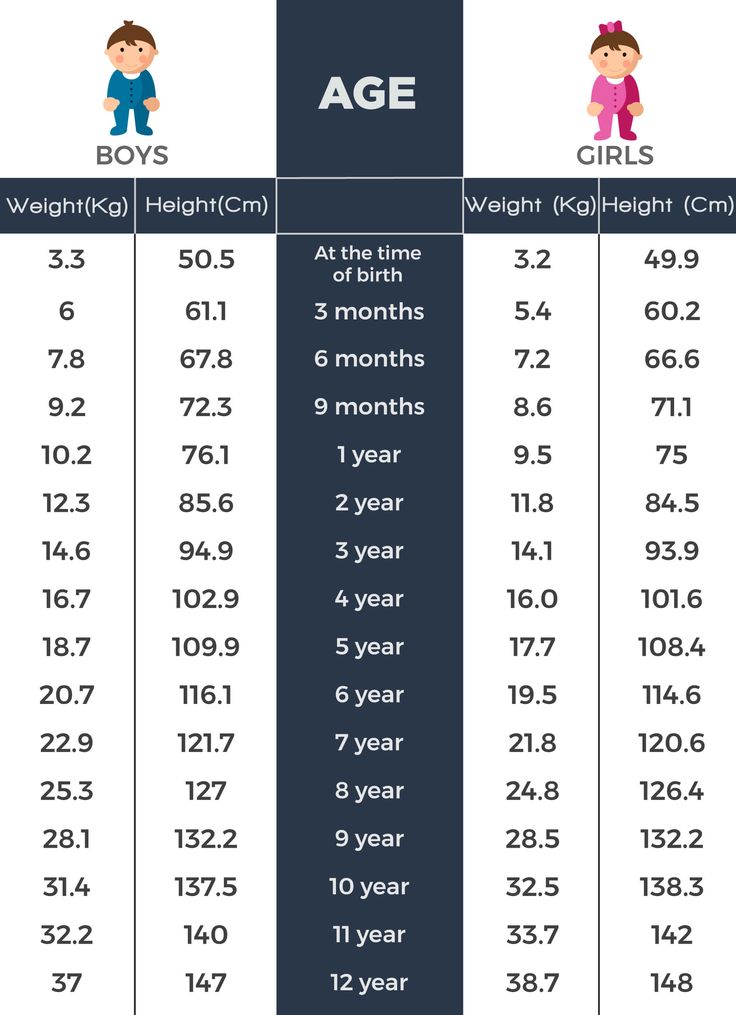
Height and weight are the main parameters by which the pediatrician evaluates the physical development of the child. The normal weight of a full-term newborn can be from 2600 to 4500 kg. Weight gain rates for breastfed and formula-fed babies differ. Statistically, formula-fed babies gain weight faster than their breastfed peers. The standards for boys and girls set by WHO also differ.
Table of weight gain in newborns by months
| Child's age, months | Boy, weight, g. | Boy, height, see | Girl, weight, g. | Girl, height, see |
| Newborn | 3600 | fifty | 3400 | 49.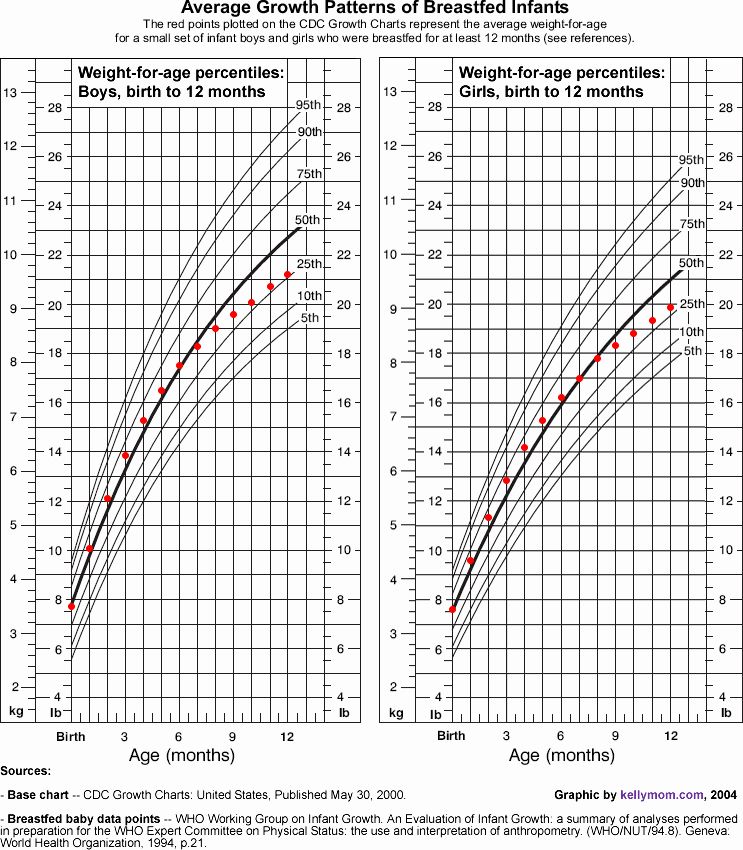 5 5 |
| 1 month | 4 450 | 54.5 | 4 150 | 53.5 |
| 2 month | 5 250 | 58 | 4 900 | 56.8 |
| 3 month | 6050 | 61 | 5 500 | 59.3 |
| 4 month | 6 700 | 63 | 6 150 | 61.5 |
| 5 month | 7 300 | 65 | 6 650 | 63.4 |
| 6 month | 7 900 | 67 | 7 200 | 65.3 |
| 7 month | 8 400 | 68.7 | 7 700 | 66.9 |
| 8 month | 8 850 | 70.3 | 8 100 | 68.4 |
| 9 month | 9 250 | 71.7 | 8 500 | 70 |
| 10 month | 9 650 | 73 | 8 850 | 71.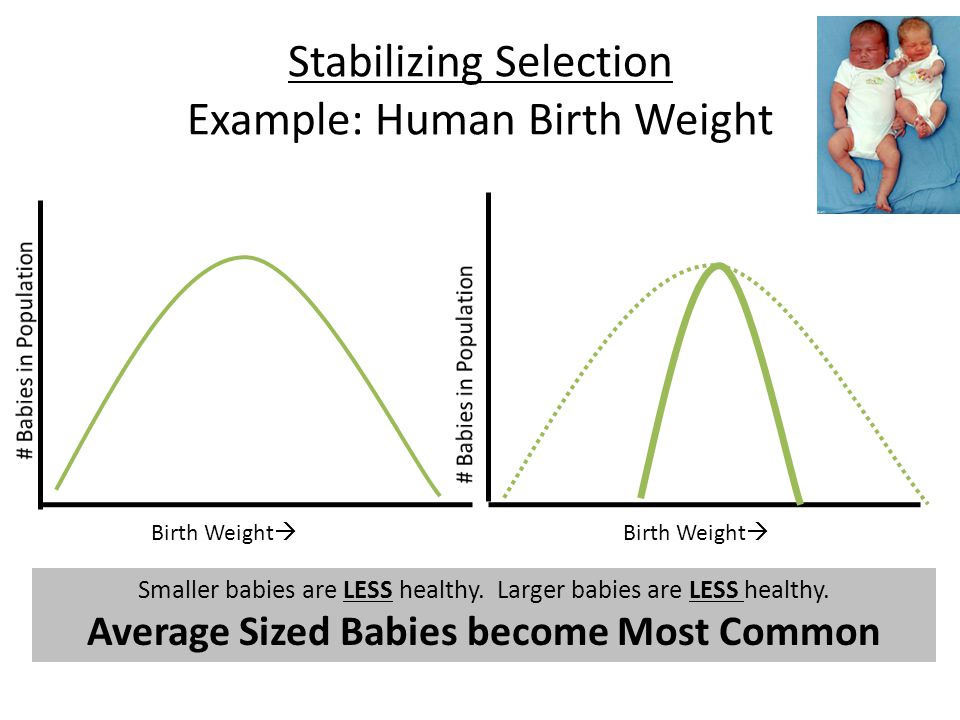 3 3 |
| 11 month | 10,000 | 74.3 | 9 200 | 72.6 |
| 12 month | 10 300 | 75.5 | 9 500 | 73.8 |
Minor discrepancies should not worry parents, however, significant deviations from the norm of height and weight signal the presence of problems in the body. The reasons for the deviation from the norm of weight and height are:
- energy imbalance: the child receives more or less calories than he needs;
- diseases associated with hormonal levels.
When artificial feeding, it is important to follow the instructions for preparing the formula and the feeding regimen. Some mothers try to feed their baby more satisfying formula, not suspecting that they are making a mistake. Yes, the child gains more weight, but his physical development slows down - the baby begins to walk later, his immunity weakens and allergic reactions appear. Insufficient weight gain is also unfavorable - a lack of body weight can become a symptom of pathologies. To avoid problems associated with physical development disorders, pediatricians advise parents to create comfortable conditions so that the child can independently hear the signals of hunger and satiety. Parents need to monitor the balance of the diet and follow the feeding regime, controlling the dynamics of growth and weight. The most practical solution for monitoring these indicators is the use of AGU smart scales for children (with a height meter), which automatically, using a convenient application, calculates whether all indicators are normal.
Insufficient weight gain is also unfavorable - a lack of body weight can become a symptom of pathologies. To avoid problems associated with physical development disorders, pediatricians advise parents to create comfortable conditions so that the child can independently hear the signals of hunger and satiety. Parents need to monitor the balance of the diet and follow the feeding regime, controlling the dynamics of growth and weight. The most practical solution for monitoring these indicators is the use of AGU smart scales for children (with a height meter), which automatically, using a convenient application, calculates whether all indicators are normal.
How much should a newborn weigh? Problems of heroes and thumbs | Healthy life | Zdorovye
consultant-professor of the department for premature babies of the SCCH RAMS, Honored Worker of Science of the Russian Federation, Academician of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences Galina Yatsyk talks about large and small babies .
Living crumbs
Let's see what it means - small. A baby weighing more than 2.5 kg at birth is normal weight. Infants of 2.5–2.7 kg are not considered small by pediatricians. A full-term newborn with such a weight does not need any special enhanced nutrition, no wrapping, or a hotly heated room. Sometimes parents want to feed a miniature baby, quickly see how chubby cheeks have become, folds have appeared on thick legs ... They begin to give the baby a little more food than necessary. The result is spitting up. Do not overfeed mini-babies. Yes, he eats a little less milk or infant formula by volume than a large baby, but he has enough. It's just a different constitution. In parents, grandmothers, grandfathers and great-grandfathers, who are also probably fragile. He will eat his norm, but develop normally, catch up with his peers in all respects, and after a year he can weigh no less than them.
But babies who were born weighing less than 2.5 kg already require more attention from doctors and special care. Pediatricians call such crumbs small.
Pediatricians call such crumbs small.
Causes of very small babies:
- prematurity,
- malnutrition,
- multiple pregnancy.
Prematurity is not a sentence
The main problem of premature babies is not low weight at all, but the immaturity of some body systems - respiratory, thermoregulatory ... They are naturally designed to live while in their mother's tummy, develop further, and their weight for intrauterine life is quite normal. And then suddenly bad luck: something made prematurely born.
Premature babies are also divided into those who are very low - less than 1.5 kg, and those who are extremely low - less than 1 kg. Of course, such crumbs are not born often, they are 0.4% and 0.2% of all premature babies. Previously, it seemed that if a child was born weighing only 1 kg, this is a disaster! How to get it out? Now, according to the WHO classification, a fetus that was born alive after 22 weeks of intrauterine development and weighing more than 500 g (!), Is considered a child who can and should be nursed.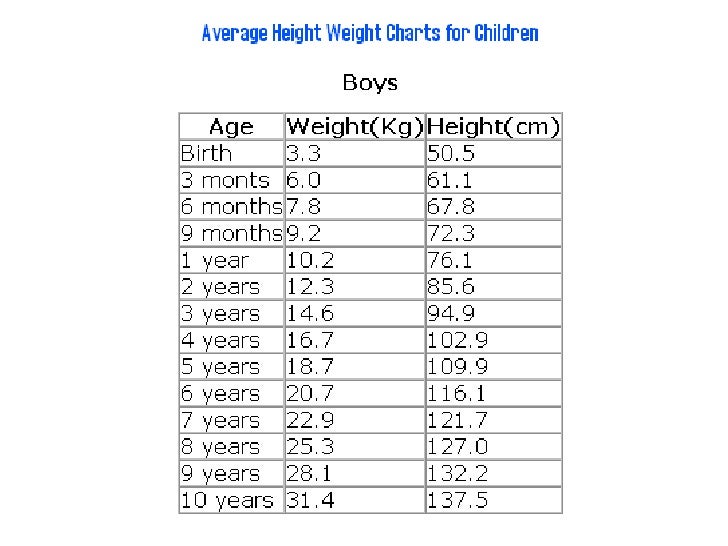 Now both society and doctors are psychologically differently tuned, they believe that a healthy child can be raised from a newborn weighing 1–1.2 kg and mentally he will be full-fledged.
Now both society and doctors are psychologically differently tuned, they believe that a healthy child can be raised from a newborn weighing 1–1.2 kg and mentally he will be full-fledged.
Premature babies require special care at first, they are placed in special hospitals, but if the baby is already discharged home, it means that he can live under normal conditions, like all babies, he can breathe, drink and eat, and he must be fed as usual baby.
The fact that prematurity is not a verdict and among famous people there were prematurity, probably everyone has already heard. Goethe and Napoleon were premature ... Low birth weight did not become an obstacle to longevity, talent, or happiness.
Sometimes babies are born at term, and their height is quite normal for newborns, and their weight is very small - 1.3–1.5 kg. This is hypotrophy. It is caused by the mother's illness. Such children appear in women with cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, with diseases of the endocrine system . .. Thin, long, they continue to gain weight poorly, although nutritionists have created special foods for them enriched with proteins, fats, vitamins. For the rest of their lives, they can remain little ones, but they will develop well at the same time.
.. Thin, long, they continue to gain weight poorly, although nutritionists have created special foods for them enriched with proteins, fats, vitamins. For the rest of their lives, they can remain little ones, but they will develop well at the same time.
Bad habits of the mother can also cause hypotrophy in an infant. If a woman smokes during pregnancy, the fetus is constantly poisoned, the child is born small.
And still small children are born from multiple pregnancy, and they are born earlier, because they are cramped in the mother's womb. They are cared for in the same way as premature babies. And quite healthy twins and triplets grow out of them.
The problems of giants
But for large children, those who weigh more than 4 kg at birth, doctors are not very happy.
They are harder to give birth to, that's understandable. They more often get birth injuries: fractures of the collarbone, hematomas, paralysis ... Therefore, when doctors, doing an ultrasound scan on a pregnant woman, see a large fetus, they often offer her a caesarean section.
But the most important thing is that large children are born to sick mothers. It happens, of course, that a baby is big simply because his father is under two meters, and his mother is not small. But such a cause of high weight is rare. But the hero of a mother with diabetes, including a mother who does not yet know about her illness, is the rule. And each subsequent child of this mother will be bigger and bigger. And there is a great danger that these children will also get diabetes.
So families where there are people suffering from this disease should definitely consult a pregnant woman with an endocrinologist. She will receive special treatment so that the baby is not born too large and does not suffer during fetal development.
Big babies take longer to adjust after birth. Usually, in the first three days, five days at most, the cardiovascular system begins to function rhythmically in a newborn, the pulse evens out, breathing is established - without shortness of breath, without signs of apnea, the gastrointestinal tract enters its rhythm . .. But in large ones, adaptation can stretch over two weeks.
.. But in large ones, adaptation can stretch over two weeks.
But then the hero came home from the maternity hospital. How to feed him now? He should eat the same volume of food as the average child. But at the same time, a hero can gain more weight than an average child.
And such a baby must be shown to an endocrinologist. We have well-equipped children's centers where a baby can be checked for any endocrine pathology.
Important
► On average, larger babies are born in Scandinavia, smaller ones in Africa.
► The average weight of boys (3200–3500 g) is slightly larger than that of girls (3000–3250 g).
► Firstborns are usually born smaller than the second and third children in a family. Although if parents and children are healthy, the differences in grams and centimeters can be barely noticeable.
► Accelerations already at birth are larger in weight and height of children of the generation that was not affected by acceleration.