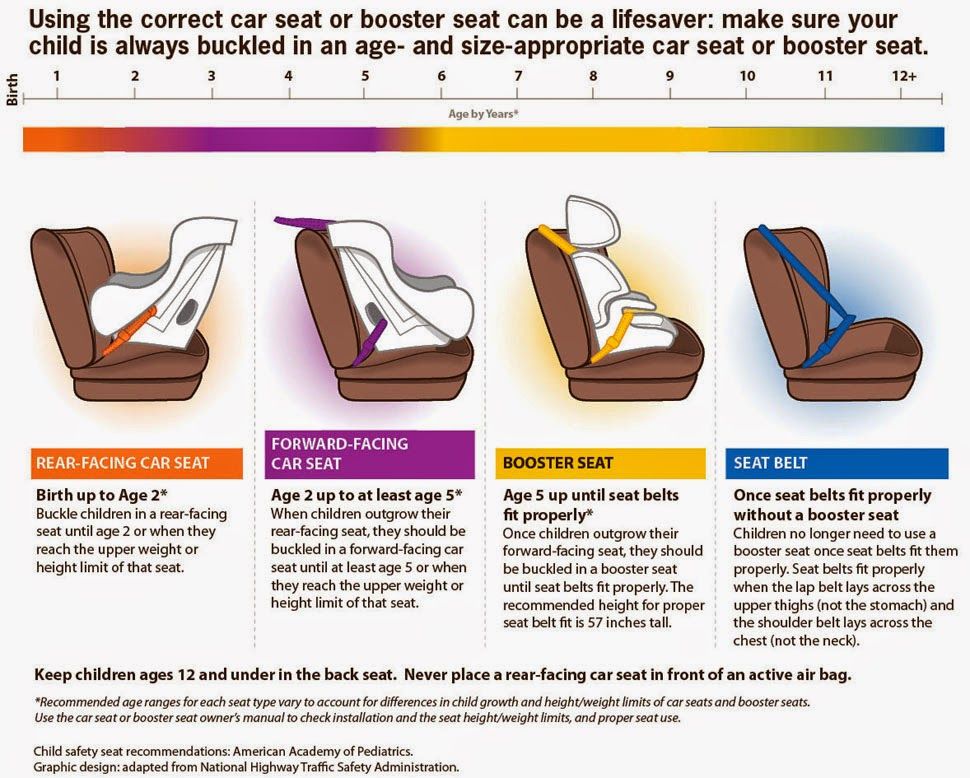
How long should child use car seat
Car Seats: Information for Families
One of the most important jobs you have as a parent is keeping your child safe when your child is riding in a vehicle.
Each year, thousands of young children are killed or injured in car crashes. Proper use of car safety seats helps keep children safe. But, because so many different seats are on the market, many parents find this overwhelming. If you are expectant parents, consider working with a certified passenger safety technician (CPST or CPS technician), before your baby is born, to ensure a safe ride home from the hospital.
The type of seat your child needs depends on several things, including your child's age, size, and developmental needs. Here is more information from the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) about choosing the most appropriate car safety seat for your child.
Visit here for a listing of car seats & car seat manufacturers.
Types of car seats at a glance:
This chart is a quick guide on where to start your search. It's important to continue your research to learn about each seat you use.
Age-group | Type of Seat | General Guidelines | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Infants and toddlers | All infants and toddlers should ride in a rear-facing seat until they reach the highest weight or height allowed by their car safety seat manufacturer. Most convertible seats have limits that will allow children to ride rear facing for 2 years or more. | |||
Toddlers and preschoolers | Children who have outgrown the rear-facing weight or height limit for their convertible seat should use a forward-facing seat with a harness for as long as possible, up to the highest weight or height allowed by their car safety seat manufacturer. | |||
School-aged children |
| All children whose weight or height exceeds the forward-facing limit for their car safety seat should use a belt-positioning booster seat until the vehicle seat belt fits properly, typically when they have reached 4 feet 9 inches in height and are 8 to 12 years of age. All children younger than 13 years should ride in the back seat. | ||
Older children |
| When children are old enough and large enough for the vehicle seat belt to fit them correctly, they should always use lap and shoulder seat belts for the best protection. All children younger than 13 years should ride in the back seat. | ||
Car safety seats may be installed with either the vehicle's seat belt or its LATCH (lower anchors and tethers for children) system. LATCH is an attachment system for car safety seats. Lower anchors can be used instead of the seat belt to install the seat, and many parents find them easier to use in some cars. The top tether should always be used with a forward-facing seat, whether you use the seat belt or lower anchors to secure it. The seat belt and LATCH systems are equally safe, so caregivers should use one or the other, whichever works best for them, for their car safety seat, and their vehicle. In general, caregivers should only use 1 of the 2 options unless the car safety seat and vehicle manufacturers say it is OK to use 2 systems at the same time.
LATCH is an attachment system for car safety seats. Lower anchors can be used instead of the seat belt to install the seat, and many parents find them easier to use in some cars. The top tether should always be used with a forward-facing seat, whether you use the seat belt or lower anchors to secure it. The seat belt and LATCH systems are equally safe, so caregivers should use one or the other, whichever works best for them, for their car safety seat, and their vehicle. In general, caregivers should only use 1 of the 2 options unless the car safety seat and vehicle manufacturers say it is OK to use 2 systems at the same time.
Vehicles with the LATCH system have lower anchors located in the back seat, where the seat cushions meet. Tether anchors are located behind the seat, either on the panel behind the seat (in sedans) or on the back of the seat, ceiling, or floor (in most minivans, SUVs, hatchbacks, and pickup trucks). All forward-facing car safety seats have tethers or tether connectors that fasten to these anchors.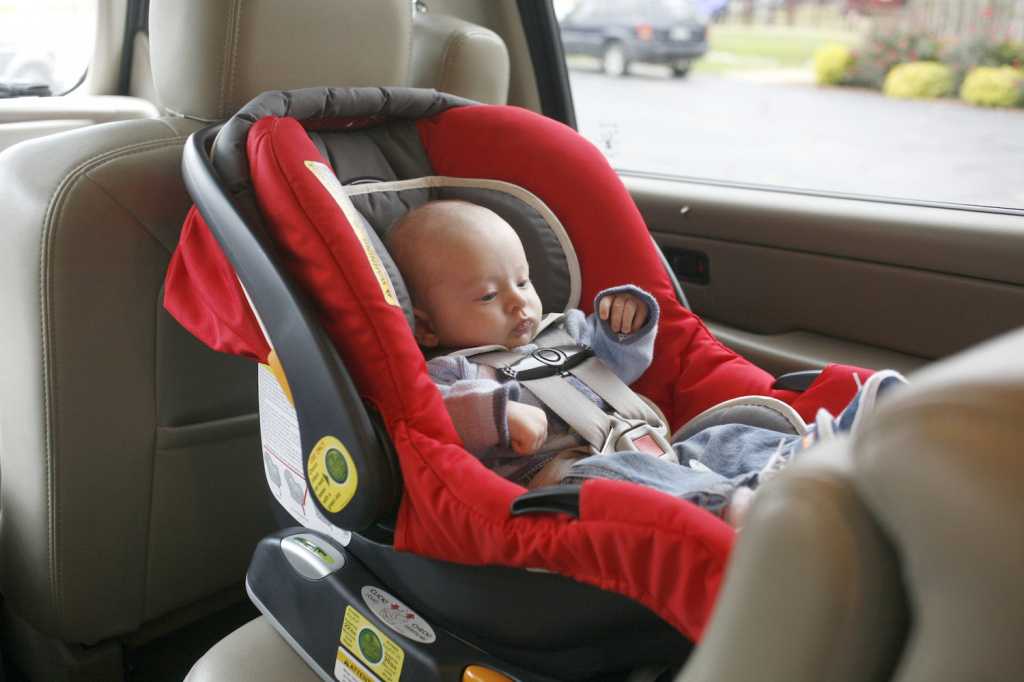 Nearly all passenger vehicles and all car safety seats made on or after September 1, 2002, are equipped to use LATCH. See vehicle owner's manual for highest weight of child allowed to use top tether.
Nearly all passenger vehicles and all car safety seats made on or after September 1, 2002, are equipped to use LATCH. See vehicle owner's manual for highest weight of child allowed to use top tether.
All lower anchors are rated for a maximum weight of 65 pounds (total weight includes car safety seat and child). Parents should check the car safety seat manufacturer's recommendations for maximum weight a child can be to use lower anchors. New car safety seats have the maximum weight printed on their label.
NOTE: Seat belts—If you install a car safety seat by using your vehicle's seat belt, you must make sure the seat belt locks to hold the seat tightly. In most newer cars, you can lock the seat belt by pulling it all the way out and then allowing it to retract to keep the seat belt tight around the car safety seat. In addition, many car safety seats have built-in lock-offs so you can lock the belt without having to lock the seat belt separately as well.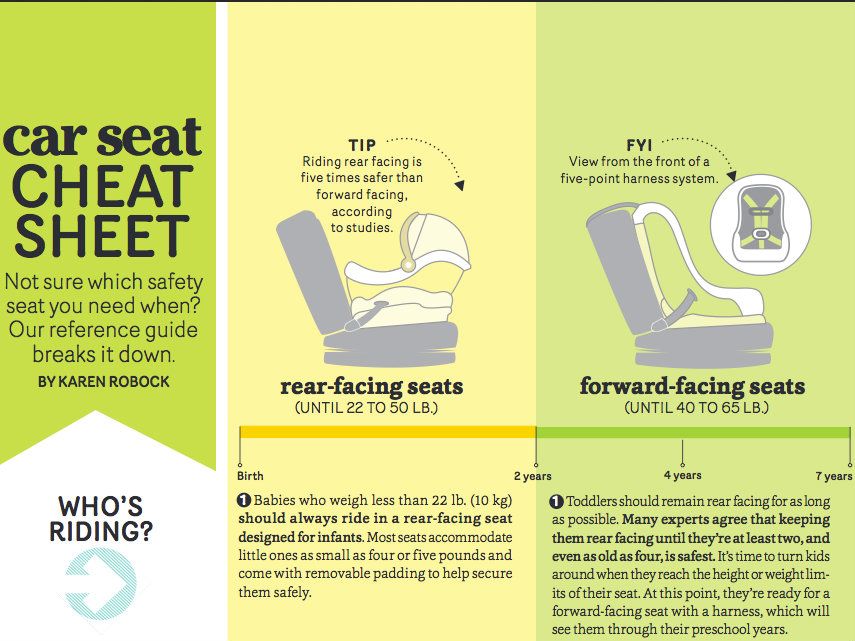 Refer to the vehicle owner's manual for details about how your seat belt locks.
Refer to the vehicle owner's manual for details about how your seat belt locks.
Middle of the back seat—The safest place to ride for all children younger than 13 years is the back seat. If possible, it may be best for the child to ride in the middle of the back seat. However, it is sometimes difficult to install a car safety seat tightly in the middle if the vehicle seat is narrow or uneven. Also, many vehicles do not have lower anchors for the middle seating position. It is safest to put the car safety seat in a position where you can install it tightly with either the lower anchor system or the seat belt; in some cases, this position may be on either side of the back seat rather than in the middle. A child passenger safety technician (CPST or CPS technician) can help you decide which place is best to install your child's car safety seat in your vehicle.
The AAP recommends that all infants ride rear facing starting with their first ride home from the hospital.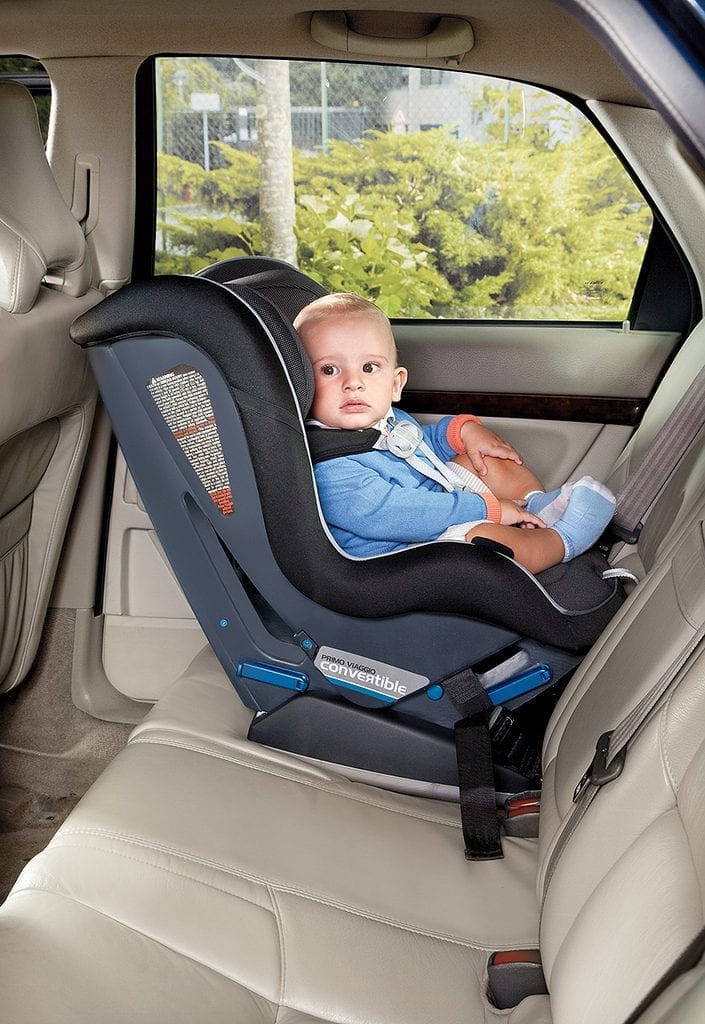 All infants and toddlers should ride in a rear-facing seat as long as possible until they reach the highest weight or height allowed by their car safety seat manufacturer. Most convertible seats have limits that will allow children to ride rear facing for 2 years or more. When infants outgrow their rear-facing–only seat, a convertible seat installed rear facing is needed. All parents can benefit from getting installation help from a CPST to ensure that their child's seat is properly installed.
All infants and toddlers should ride in a rear-facing seat as long as possible until they reach the highest weight or height allowed by their car safety seat manufacturer. Most convertible seats have limits that will allow children to ride rear facing for 2 years or more. When infants outgrow their rear-facing–only seat, a convertible seat installed rear facing is needed. All parents can benefit from getting installation help from a CPST to ensure that their child's seat is properly installed.
Types of rear-facing seats
Three types of rear-facing seats are available: rear-facing–only, convertible, and all-in-one. When children reach the highest weight or length allowed by the manufacturer of their rear-facing–only seat, they should continue to ride rear facing in a convertible or all-in-one seat.
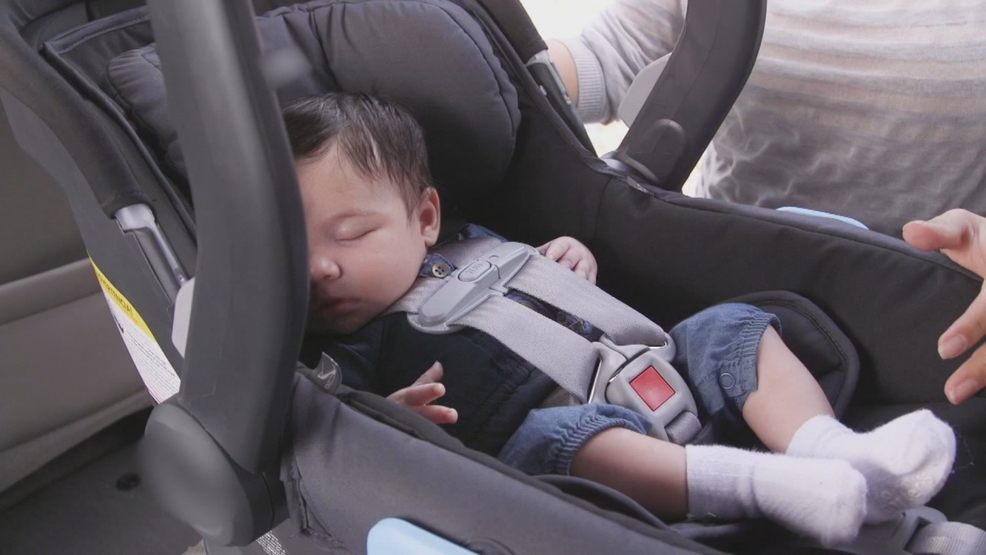
Rear-facing–only seats
Are used for infants up to 22 to 35 pounds and 26 to 35 inches, depending on the model.
Are small and have carrying handles.

Usually come with a base that can be left in the car. The seat clicks into and out of the base so you don't have to install the seat each time you use it. Parents can buy more than one base for additional vehicles.
Should be used only for a child's travel (not sleeping, feeding, or any other use outside the vehicle).
Convertible seats (used rear facing)
Can be used rear facing and, later, "converted" to forward facing for older children when they outgrow either the weight limit or the length limit for rear facing. This means the seat can be used longer by your child. Convertible seats are bulkier than infant seats, however, and they do not come with carrying handles or separate bases and are designed to stay in the car.
Many have higher limits in rear-facing weight (up to 40–50 pounds) and height than those of rear-facing– only seats, a feature that makes convertible seats ideal for bigger babies and toddlers.

Have a 5-point harness that attaches at the shoulders, at the hips, and between the legs.
Should be used only for a child's travel (not sleeping, feeding, or any other use outside the vehicle).
All-in-one seats (used rear facing)
Can be used rear facing, forward facing, or as a belt- positioning booster. This means the seat may be used longer by your child as your child grows.
Are often bigger in size, so it is important to check that they fit in the vehicle while they are rear facing.
Do not have the convenience of a carrying handle or separate base; however, they may have higher limits in rear-facing weight (up to 40–50 pounds) and height than those of rear-facing–only seats, a feature that makes all-in-one seats ideal for bigger babies and toddlers.
Installation tips for rear-facing seats
Always read the vehicle owner's manual and the car safety seat manual before installing the seat.
When using a rear-facing seat, keep the following tips in mind:
Place the harnesses in your rear-facing seat in slots that are at or below your child's shoulders.
Ensure that the harness is snug (you cannot pinch any slack between your fingers when testing the harness straps over the child's shoulders) and that the chest clip is placed at the center of the chest, even with your child's armpits.
Make sure the car safety seat is installed tightly in the vehicle with either lower anchors or a locked seat belt. Many car safety seats have an integrated lock-off system to keep the seat belt locked. If your seat has one, follow the manufacturer's recommendations on how to use it. If you can move the seat at the belt path more than an inch side to side or front to back, it's not tight enough.
Never place a rear-facing seat in the front seat of a vehicle that has an active front passenger airbag. If the airbag inflates, it will hit the back of the car safety seat, right against your child's head, and could cause serious injury or death.

If you are using a convertible or all-in-one seat in the rear-facing position, make sure the seat belt or lower anchor webbing is routed through the correct belt path. Check the instructions that came with the car safety seat to be sure.
Make sure the seat is at the correct angle so your child's head does not flop forward. Check the instructions to find out the correct angle for your seat and how to adjust the angle if needed. All rear-facing seats have built-in recline indicators.
Check the car safety seat instructions and vehicle owner's manual about whether the car safety seat may contact the back of the vehicle seat in front of it.
Still having trouble? Check with a certified CPST in your area who can help.
Common questions
What if my child's feet touch the back of the vehicle seat?
What do I do if my child slouches down or to the side in the car seat?
You can try placing a tightly rolled receiving blanket on both sides of your child.
 Many manufacturers allow the use of a tightly rolled small diaper or cloth between the crotch strap and your child, if necessary, to prevent slouching. Do not place padding under or behind your child or use any sort of car safety seat insert unless it came with the seat or was made by the manufacturer for use with that specific seat.
Many manufacturers allow the use of a tightly rolled small diaper or cloth between the crotch strap and your child, if necessary, to prevent slouching. Do not place padding under or behind your child or use any sort of car safety seat insert unless it came with the seat or was made by the manufacturer for use with that specific seat.
Why should I dress my child in thinner layers of clothing before strapping them into a car safety seat?
Bulky clothing, including winter coats and snowsuits, can compress in a crash and leave the straps too loose to restrain your child, leading to increased risk of injury. Ideally, dress your baby in thinner layers and wrap a coat or blanket around your baby over the buckled harness straps if needed. See Winter Car Seat Safety Tips from the AAP.
Do preemies need a special car seat?
A car safety seat should be approved for a baby's weight. Very small babies who can sit safely in a semi-reclined position usually fit better in rear-facing–only seats. Babies born preterm should be screened while still in the hospital to make sure they can sit safely in a semi-reclined position. Babies who need to lie flat during travel may be able to ride in a car bed that meets Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 213. They should be screened again while in the hospital to make sure they can lie safely in the car bed.
Babies born preterm should be screened while still in the hospital to make sure they can sit safely in a semi-reclined position. Babies who need to lie flat during travel may be able to ride in a car bed that meets Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 213. They should be screened again while in the hospital to make sure they can lie safely in the car bed.
Always read the vehicle owner's manual and the car safety seat manual before installing the seat.
Any child who has outgrown the rear-facing weight or height limit for her convertible seat should use a forward- facing seat with a harness for as long as possible, up to the highest weight or height allowed by her car safety seat manufacturer. It is best for children to ride in a seat with a harness as long as possible, at least to 4 years of age. If your child outgrows a seat before reaching 4 years of age, consider using a seat with a harness approved for higher weights and heights.
Types of Forward-Facing Car Seat Restraints
Four types of car safety restraints can be used forward facing:
Convertible seats: Seats can "convert" from rear facing to forward facing.
 These include all-in-one seats.
These include all-in-one seats.Combination seats with harness: Seats can be used forward facing with a harness for children who weigh up to 40 to 65 pounds (depending on the model) or without the harness as a booster (up to 100–120 pounds, depending on the model).
Integrated seats: Some vehicles come with built-in forward-facing seats. Weight and height limits vary. Do not use a built-in seat until your child has reached the highest weight or height allowed for your rear-facing convertible car safety seat. Read your vehicle owner's manual for details about how to use these seats.
Travel vests: Vests can be worn by children 22 to 168 pounds and can be an option to traditional forward- facing seats. They are useful for when a vehicle has lap-only seat belts in the rear, for children with certain special needs, or for children whose weight has exceeded that allowed by car safety seats.
 These vests usually require use of a top tether.
These vests usually require use of a top tether.
Installation tips for forward-facing seats
Always read the vehicle owner's manual and the car safety seat manual before installing the seat.
It is important that the car safety seat is installed tightly in the vehicle and that the harness fits your child snugly.
To switch a convertible or all-in-one seat from rear-facing to forward-facing:
Move the harness shoulder straps to the slots or position that is at or just above your child's shoulders. Check the instructions that came with the seat to be sure you are positioning the shoulder straps correctly.
You may have to adjust the recline angle of the seat so that it sits more upright in your vehicle. Check the instructions to be sure.
If using a seat belt, make sure it runs through the forward-facing belt path (be sure to follow car safety seat instructions) and that the seat belt is locked and tightened.
 Many car safety seats have an integrated lock-off to keep the seat belt locked. If your seat has one, follow the manufacturer's recommendations on how to use it.
Many car safety seats have an integrated lock-off to keep the seat belt locked. If your seat has one, follow the manufacturer's recommendations on how to use it.If using the lower anchors, make sure that the weight of your child plus the weight of the seat does not exceed 65 pounds. Most seats now state in the manual and on the stickers on the side the maximum child weight to use the anchors. If the child weighs too much, caregivers must use the seat belt to install.
Always use the tether when you can. A tether is a strap that is attached to the top part of a car safety seat and holds the seat tightly by connecting to an anchor point in your vehicle (often on the seat back or rear shelf; see your vehicle owner's manual to find where tether anchors are in your vehicle). Tethers give important extra protection by keeping the car safety seat and your child's head from moving too far forward in a crash or sudden stop. All new cars, minivans, and light trucks are required to have tether anchors as of September 2000.
 Forward-facing seats come with tether straps. A tether should always be used as long as your child has not reached the top weight limit for the tether anchor. Check the car safety seat instructions and vehicle owner's manual for information about the top weight limit and locations of tether anchors.
Forward-facing seats come with tether straps. A tether should always be used as long as your child has not reached the top weight limit for the tether anchor. Check the car safety seat instructions and vehicle owner's manual for information about the top weight limit and locations of tether anchors. Watch the Video: How to Install a Forward-Facing Car Seat
Common question
What if I drive more children than those who can be buckled safely in the back seat?
It's best to avoid this, especially if your vehicle has airbags in the front seat. All children younger than 13 years should ride in the back seat. If absolutely necessary, a child in a forward-facing seat with a harness may be the best choice to ride in front. Just be sure the vehicle seat is moved as far back away from the dashboard (and airbag) as possible.
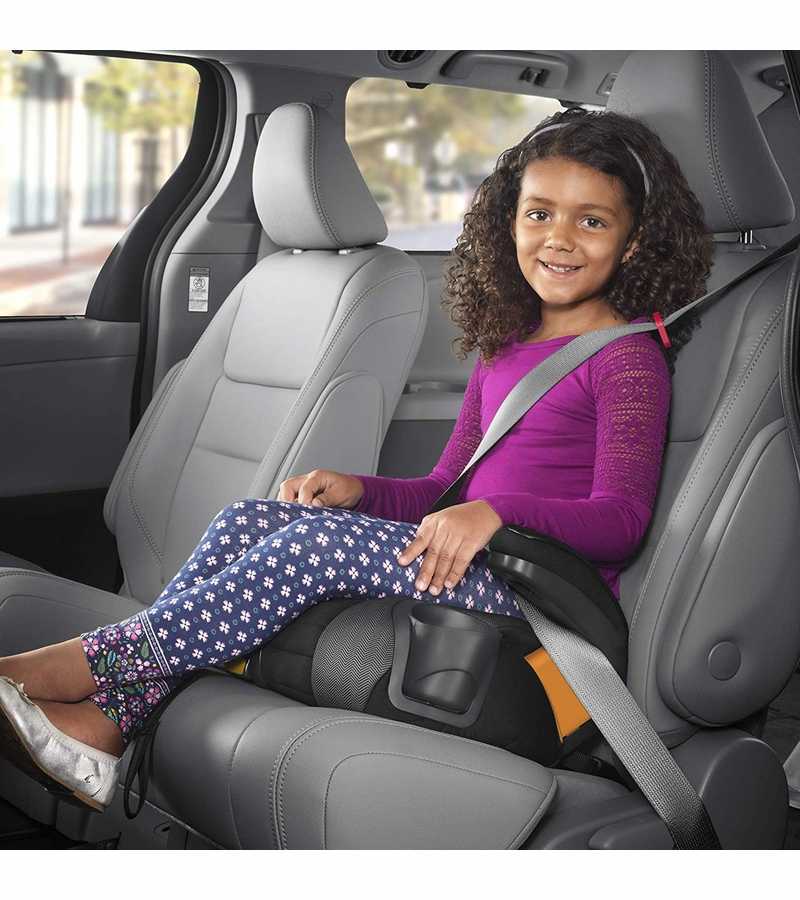
Booster seats are for older children who have outgrown their forward-facing seats. All children whose weight or height exceeds the forward-facing limit for their car safety seat should use a belt-positioning booster seat until the vehicle seat belt fits properly, typically when they have reached 4 feet 9 inches in height and are 8 to 12 years of age. Most children will not fit in most vehicle seat belts without a booster until 10 to 12 years of age. All children younger than 13 years should ride in the back seat. Instructions that come with your car safety seat will tell you the height and weight limits for the seat. As a general guideline, a child has outgrown a forward-facing seat when any of the following situations is true:
All children whose weight or height exceeds the forward-facing limit for their car safety seat should use a belt-positioning booster seat until the vehicle seat belt fits properly, typically when they have reached 4 feet 9 inches in height and are 8 to 12 years of age. Most children will not fit in most vehicle seat belts without a booster until 10 to 12 years of age. All children younger than 13 years should ride in the back seat. Instructions that come with your car safety seat will tell you the height and weight limits for the seat. As a general guideline, a child has outgrown a forward-facing seat when any of the following situations is true:
They reach the top weight or height allowed for his seat with a harness. (These limits are listed on the seat and in the instruction manual.)
Their shoulders are above the top harness slots.
The tops of their ears have reached the top of the seat.
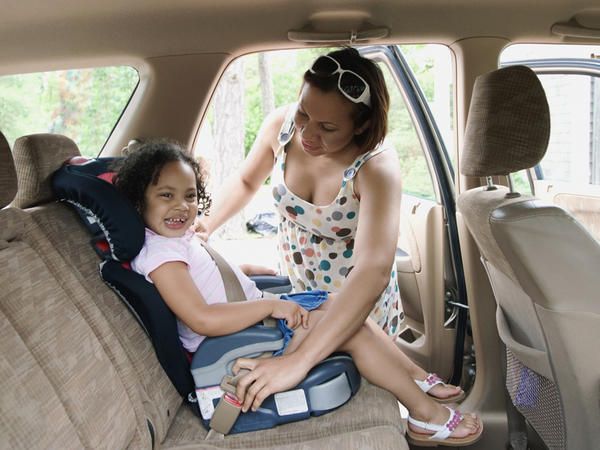
Types of booster seats
High-back and backless are 2 standard types of booster seats.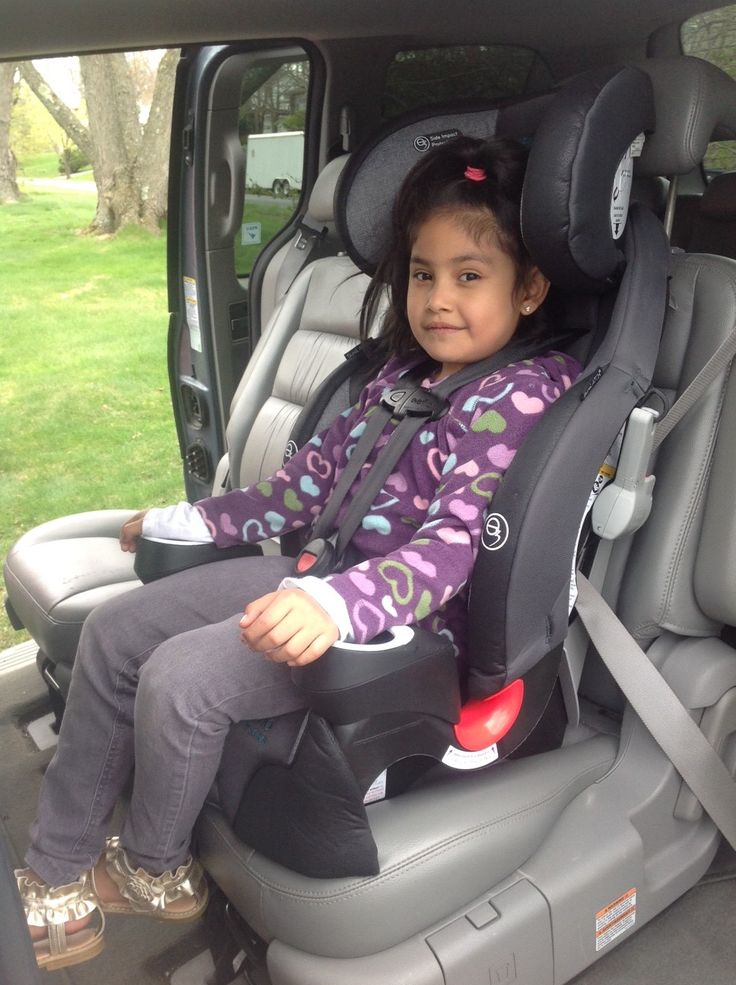 They do not come with a harness but are used with lap and shoulder seat belts in your vehicle, the same way an adult rides. They are designed to raise a child up so that lap and shoulder seat belts fit properly over the strongest parts of the child's body.
They do not come with a harness but are used with lap and shoulder seat belts in your vehicle, the same way an adult rides. They are designed to raise a child up so that lap and shoulder seat belts fit properly over the strongest parts of the child's body.
Most booster seats are not secured to the vehicle seat with the seat belt or lower anchors and tether but simply rest on the vehicle seat and are held in place once the seat belt is fastened over a child. However, some models of booster seats can be secured to the vehicle seat and kept in place by using the lower anchors and tether along with lap and shoulder belts. (Currently, only a few vehicle manufacturers offer integrated booster seats.)
Installation tips for booster seats
When using a booster seat, always read the vehicle owner's manual and the car safety seat manual before installing the seat. Booster seats often have a plastic clip or guide to correctly position vehicle lap and shoulder belts. See the booster seat instruction manual for directions on how to use the clip or guide. Booster seats must be used with lap and shoulder belts. When using a booster seat, make sure:
Booster seats must be used with lap and shoulder belts. When using a booster seat, make sure:
The lap belt lies low and snug across your child's upper thighs.
The shoulder belt crosses the middle of your child's chest and shoulder and is off the neck.
Watch the video: How to Use a Booster Seat
If your booster seat has lower anchors or tether attachments, check its manual for installation instructions.
Common questions about booster seats
What if my car has only lap belts in the back seat?
Lap belts work fine with rear-facing–only, convertible, and forward-facing seats that h av e a harness but can never be used with a booster seat. If your car has only lap belts, use a forward-facing seat that has a harness and higher weight limits. You could also
Check to see if shoulder belts can be installed in your vehicle.
Use a travel vest (check the manufacturer's instructions about the use of lap belts only and about the use of lap and shoulder belts).

Consider buying another car with lap and shoulder belts in the back seat.
What is the difference between high-back boosters and backless boosters?
Both types of boosters are designed to raise your child so seat belts fit properly, and both will reduce your child's risk of injury in a crash. High-back boosters should be used in vehicles without headrests or with low seat backs. Many seats that look like high-back boosters are actually combination seats. They come with harnesses that can be used for smaller children and, later, removed for older children. Backless boosters are usually less expensive and are easier to move from one vehicle to another. Backless boosters can be used safely in vehicles with headrests and high seat backs.
Seat belts are made for adults. Children should stay in a booster seat until adult seat belts fit correctly, typically when children reach about 4 feet 9 inches in height and are 8 to 12 years of age. Most children will not fit in a seat belt alone until 10 to 12 years of age. When children are old enough and large enough to use the vehicle seat belt alone, they should always use lap and shoulder seat belts for the best protection. All children younger than 13 years should ride in the back seat.
Most children will not fit in a seat belt alone until 10 to 12 years of age. When children are old enough and large enough to use the vehicle seat belt alone, they should always use lap and shoulder seat belts for the best protection. All children younger than 13 years should ride in the back seat.
Using a seat belt:
An adult seat belt fits correctly when:
The shoulder belt lies across the middle of the chest and shoulder, not the neck or throat.
The lap belt is low and snug across the upper thighs, not the belly.
Your child is tall enough to sit against the vehicle seat back with her knees bent over the edge of the seat without slouching and can comfortably stay in this position throughout the trip.
Other points to keep in mind when using seat belts include:
Make sure your child does not tuck the shoulder belt under her arm or behind her back. This leaves the upper body unprotected and adds extra slack to the seat belt system, putting your child at risk of severe injury in a crash or with sudden braking.

Never allow anyone to "share" seat belts. All passengers must have their own car safety seats or seat belts.
Common question
I've seen products that say they can help make the seat belt fit better. Should we get one of these?
No, these products are unapproved and should not be used. They may actually interfere with proper seat belt fit by causing the lap belt to ride too high on the stomach or making the shoulder belt too loose. They can even damage the seat belt. This rule applies to car safety seats too; do not use extra products unless they came with the seat or are specifically approved by the seat manufacturer. These products are not covered by any federal safety standards, and the AAP does not recommend they be used. As long as children are riding in the correct restraint for their size, they should not need to use additional devices.
When shopping for a car seat, keep the following tips in mind:
No one seat is the "best" or "safest.
 " The best seat is the one that fits your child's size, is correctly installed, fits well in your vehicle, and is used properly every time you drive.
" The best seat is the one that fits your child's size, is correctly installed, fits well in your vehicle, and is used properly every time you drive.Don't decide by price alone. A higher price does not mean the seat is safer or easier to use.
Avoid used seats if you don't know the seat's history.
Watch the Video: What to Look For When Purchasing a Car Seat
Never use a car seat that:
Is too old. Look on the label for the date the seat was made. Check with the manufacturer to find out how long it recommends using the seat.
Has any visible cracks on it.
Does not have a label with the date of manufacture and model number. Without these, you cannot check to see if the seat has been recalled.
Does not come with instructions.
 You need them to know how to use the seat. Instructions can be found on manufacturer websites or by contacting the manufacturer.
You need them to know how to use the seat. Instructions can be found on manufacturer websites or by contacting the manufacturer.Is missing parts. Used car safety seats often come without important parts. Check with the manufacturer to make sure you can get the right parts.
Was recalled. You can find out by calling the manufacturer or contacting the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) Vehicle Safety Hotline at 888/327-4236. You can also visit the NHTSA Website.
Do not use seats that have been in a moderate or severe crash. Seats that were in a minor crash may still be safe to use, but some car safety seat manufacturers recommend replacing the seat after any crash, even a minor one. The NHTSA considers a crash minor if all the following situations are true:
The vehicle could be driven away from the crash.
The vehicle door closest to the car safety seat was not damaged.

No one in the vehicle was injured.
The airbags did not go off.
You can't see any damage to the car safety seat.
If you have specific questions about the car seat, contact the manufacturer.
Front airbags are installed in all new cars. When used with seat belts, airbags work well to protect teenagers and adults; however, airbags can be very dangerous to children, particularly to those riding in rear-facing seats and to preschoolers and young school-aged children who are not properly restrained. If your vehicle has a front passenger airbag, infants in rear-facing seats must ride in the back seat. Even in a relatively low-speed crash, the airbag can inflate, strike the car safety seat, and cause serious brain injury and death.
Vehicles with no back seat or a back seat that is not made for passengers are not the best choice for traveling with small children; however, the airbag can be turned off in some of these vehicles if the front seat is needed for a child passenger.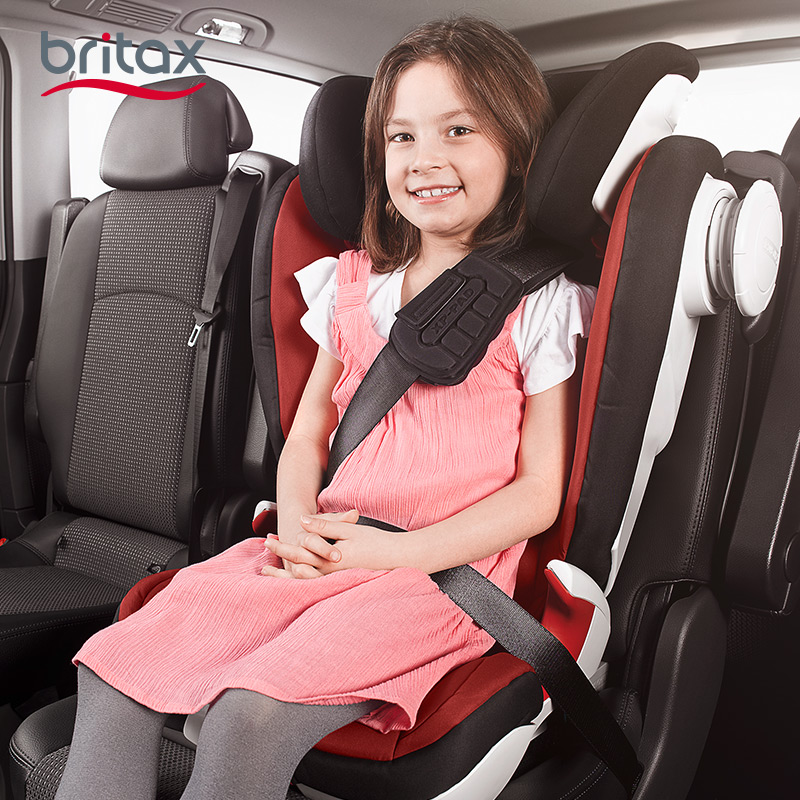 See your vehicle owner's manual for more information.
See your vehicle owner's manual for more information.
Side airbags are available in most new cars. Side airbags improve safety for adults in side-impact crashes. Read your vehicle owner's manual for more information about the airbags in your vehicle. Read your car safety seat instructions and the vehicle owner's manual for guidance on placing the seat next to a side airbag.
About carpooling
If your child is being driven by someone else, make sure:
The car safety seat your child will be using fits properly in the vehicle used for transport.
The car safety seat being used is appropriate for the age and size of your child.
The person in charge of transporting your child knows how to install and use the car safety seat correctly.
Child care programs and schools should have written guidelines for transporting children, including
All drivers must have a valid driver's license.
 In some states, school bus drivers need to have a special type of license.
In some states, school bus drivers need to have a special type of license.Staff to child ratios for transport should meet or exceed those required for the classroom.
Every child should be supervised during transport, either by school staff or a parent volunteer, so the driver can focus on driving.
School staff, teachers, and drivers should know what to do in an emergency, know how to properly use car safety seats and seat belts, and be aware of other safety requirements.
About car safety seats on airplanes
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and the AAP recommend that children less than 40 pounds be securely fastened in certified child restraints when flying. This will help keep them safe during takeoff and landing or in case of turbulence. Most rear-facing, convertible, and forward-facing seats can be used on airplanes , but booster seats and travel vests cannot.
Read your seat's instruction manual and look for a label on the car safety seat that says, "This restraint is certified for use in motor vehicles and aircraft. " You can also consider using a restraint made only for use on airplanes and approved by the FAA. Larger children may use the airplane seat belt or continue to use their car safety seat on the airplane as long as it is labeled for use on aircraft and the child has not exceeded the seat's weight or height limit. Remember that your child will need an appropriate car safety seat to use at your destination. For more information, visit the
FAA Website or the
CARES (Airplane Safety Harness for Children) Website.
" You can also consider using a restraint made only for use on airplanes and approved by the FAA. Larger children may use the airplane seat belt or continue to use their car safety seat on the airplane as long as it is labeled for use on aircraft and the child has not exceeded the seat's weight or height limit. Remember that your child will need an appropriate car safety seat to use at your destination. For more information, visit the
FAA Website or the
CARES (Airplane Safety Harness for Children) Website.
If you need installation help
If you have questions or need help with installing your car safety seat, find a certified child passenger safety technician (CPST or CPS technician). Lists of certified CPSTs and child seat–fitting stations are available on the following websites:
National Child Passenger Safety Certification (Click on "Find a Tech" or call 877-366-8154.) – Includes list of CPSTs fluent in Spanish and other languages or with extra training in transportation of children with special needs.

NHTSA Parents & Caregivers
Important reminders
Be a good role model. Make sure you always wear your seat belt. This will help your child form a lifelong habit of buckling up.
Make sure that everyone who transports your child uses the correct car safety seat or seat belt on every trip, every time. Being consistent with car safety seat use is good parenting, reduces fussing and complaints, and is safest for your child.
Never leave your child alone in or around cars, and lock your vehicle when it is not in use. Any of the following situations can happen when a child is left alone in or around a vehicle. A child can
Die of heatstroke because temperatures can reach deadly levels in minutes.
Be strangled by power windows, retracting seat belts, sunroofs, or accessories.
Knock the vehicle into gear, setting it into motion.

Be backed over when the vehicle backs up.
Become trapped in the trunk of the vehicle.
Always read and follow the manufacturer's instructions for your car safety seat. If you do not have those, write or call the company's customer service department. Staff will ask you for the model number, name of seat, and date of manufacture. The manufacturer's address and phone number are on a label on the seat. Also, be sure to follow the instructions in your vehicle owner's manual about using car safety seats. Some manufacturers' instructions may be available on their websites.
Remember to fill out and mail in the registration card that comes with the car safety seat. You can also register your seat on the manufacturer's website. It will be important in case the seat is recalled.
Follow manufacturer directions for cleaning car seats. Cleaning but not disinfecting is usually permitted. That's because disinfectant products may decrease the protection provided by the seat and harness.
That's because disinfectant products may decrease the protection provided by the seat and harness.
More information
-
Ask the Pediatrician: Is it safe for my baby to travel in a car seat a few hours at a time?
- Car Seats: Product Listing
- Car Seat Checkup
- Car Seats and Obese Children: Suggestions for Parents
- Prevent Child Deaths in Hot Cars
- Travel Safety During COVID-1 9
Although the AAP is not a testing or standard-setting organization, this article sets forth the AAP recommendations based on the peer-reviewed literature available at the time of its publication and sets forth some of the factors that parents should consider before selecting and using a car seat.
Figure 1 adapted from US Department of Transportation, National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). LATCH Makes Child Safety Seat Installation as Easy as 1-2-3. Washington, DC: NHTSA; 2011. DOT HS publication 809 489.
Washington, DC: NHTSA; 2011. DOT HS publication 809 489.
Figure 4 from Bull MJ, Engle WA; American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention and Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Safe transportation of preterm and low birth weight infants at hospital discharge. Pediatrics. 2009;123(5):1424–1429.
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
When to change car seats for children
Last updated May 2020
One of the most common questions we are receiving is: “when is the right time for my child to change to the next car seat?” – and this is a great and very important question! Different regulations focussing on weight, height and age and can make it quite confusing.
 We have therefore collected an overview of when to change car seats for your child.
We have therefore collected an overview of when to change car seats for your child.At BeSafe, we categorize the different child car seat stages in a child’s life into three groups:
1) Car seats from birth
2) Car seats for toddlers
3) Car seats for older children
When choosing a seat for your newborn, there are two paths you can choose from: either to use an infant carrier from approx. 0-1 year, followed by a toddler seat until approx. 4 years; or to use a 2-in-1 seat from 0 to approx. 4 years.
When using such a 2-in-1 seat, it is only relevant in this article for you to know when to change to a seat for older children. When to remove the baby insert of your 2-in-1 seat is defined by the user manual of your seat.
INFANT CARRIERS
If you choose the path of having a “classic” infant carrier for your newborn, these are typically used to approximately 12 months and feature a carrying handle that makes it easy to bring with you outside of the car. Infant carriers are always installed rear facing in the car. They can be installed either with the vehicle belt or for some seats with an additional ISOfix base, both being equally safe when fitted correctly.
Infant carriers are always installed rear facing in the car. They can be installed either with the vehicle belt or for some seats with an additional ISOfix base, both being equally safe when fitted correctly.
When to change the earliest from an infant carrier to a toddler seat?
We at BeSafe recommend you to use an infant carrier for as long as possible, as it gives you as a parent flexibility and offers your baby great side protection. However, you might consider changing to a toddler car seat earlier. In these cases, we recommend you to only change to a toddler car seat when your baby can sit by themselves, as toddler car seats typically are more upright and give a bit less stability than infant carriers.
Depending on which toddler seat you are choosing, make sure that your child has reached the minimum requirement of that seat. Based on its regulation, this can either be a minimum weight or a minimum height.
When to change the latest from an infant carrier to the toddler seat?
Step 1: Check the weight/height limitation of your seat
If your infant carrier is approved to ECE R44-04, then your seat has a maximum weight based on its approval. This maximum weight must not be exceeded. But this does not mean that you can always use your infant carrier until you have reached this maximum weight, often babies outgrow their seat in height before they reach the weight. For this, check step 2!
This maximum weight must not be exceeded. But this does not mean that you can always use your infant carrier until you have reached this maximum weight, often babies outgrow their seat in height before they reach the weight. For this, check step 2!
If your infant carrier is approved to UN R129, then it has a maximum height given by its approval. This maximum height must not be exceeded. In most cases, the maximum height marks the end of when you can use the seat, but in addition also check step 2!
Step 2: Check the shoulder belts and distance to the top of the seat
When the uppermost point of the baby’s head is approx. 2 fingers away from the highest point of the seat shell, you should change to a toddler seat. Ideally, you should look for toddler seats already some time before your baby has reached this point. This 2-finger-distance is recommended since it includes a “buffer” for upwards movement in case of an accident. Such a movement can happen if the belts are not perfectly tightened. Even though we know that parents do their best to always tighten the belts correctly, it can happen – when in a rush or if the baby moves a lot – that the belts are not as tight as they should be.
Even though we know that parents do their best to always tighten the belts correctly, it can happen – when in a rush or if the baby moves a lot – that the belts are not as tight as they should be.
Additionally, check how the shoulder belts are sitting on your baby’s shoulders and what your seat’s user manual advises about this. Most manufacturers say that the shoulder belts should not come from below your baby’s shoulders. So if the shoulder belts are not coming straight onto the shoulders anymore when having the headrest/belts in the highest setting, then it’s time to change as well.
TODDLER CAR SEATS
If you chose the “classic path” and had an infant carrier before, the toddler car seat is the second car seat for your child. It can be used from approximately 6 months of age up to approx. four years, depending on the height and weight of your child. According to the regulation UN R129 (i-Size), children must remain rear facing for at least 15 months, but we at BeSafe recommend to keep your child rear facing until at least 4 years of age, preferably longer.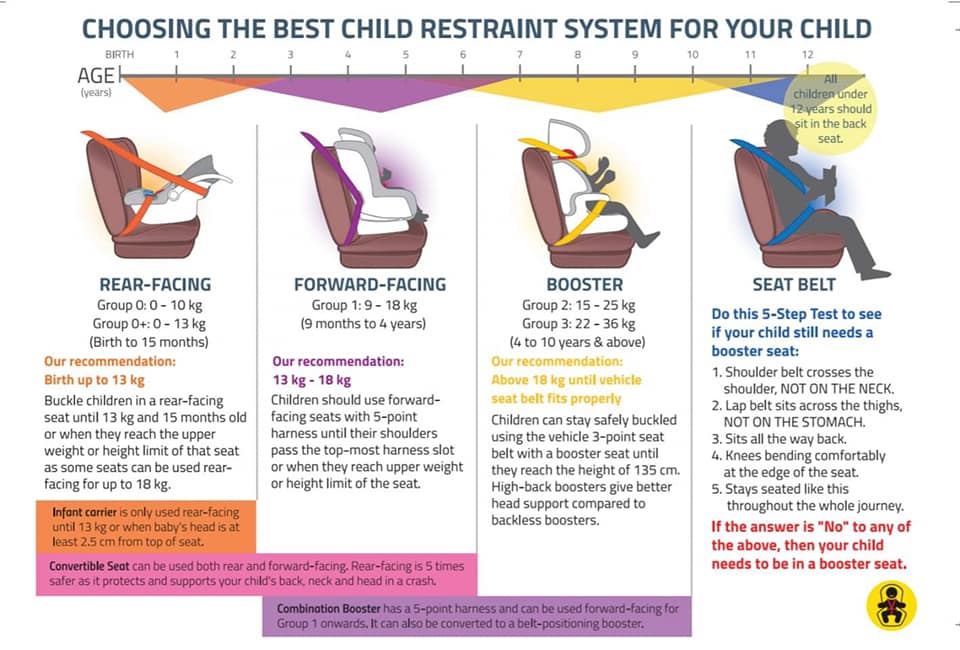 Some seats in this group can be used both rear or forward facing.
Some seats in this group can be used both rear or forward facing.
We at BeSafe advise you to keep your child rear facing for as long as possible or at least until the age of four. Therefore, we recommend you to move your child to a booster seat only when all three of the following conditions are met:
- Your child should be at least four years old
- Your child has reached the minimum requirement of the seat (15kg when approved to ECE R44 or 100cm when approved to UN R129) – this is legally binding by the regulations
- Your child has the mental maturity to sit still in the high back booster seat. When leaning forwards a lot, your child is outside of the seat’s protection zone, so the seat would not protect your child as intended.
Step 1: Check the weight/height limitation of your seat
If your toddler seat is approved to UN R129, you have to stop using your seat once the maximum height of your seat according to its approval is reached. In addition, ISOfix-installed UN R129 seats also have a weight limitation which you can find on your seat’s approval sticker and/or user manual. It is time to change to another seat once your child has reached one of the two limitations, whichever comes first.
In addition, ISOfix-installed UN R129 seats also have a weight limitation which you can find on your seat’s approval sticker and/or user manual. It is time to change to another seat once your child has reached one of the two limitations, whichever comes first.
If your toddler seat is approved to ECE R44-04, the seat has a maximum weight which you can find on your seat’s approval sticker and user manual. Once your child has reached this maximum, you have to change. However, practically you might not always be able to use the seat until the maximum weight as your child can outgrow the seat in height before. Check step 2 for this!
Step 2: Check the shoulder belts and ear-to-headrest level
When the top of child’s ears reaches the highest point of the headrest, it is high time to change.
Additionally, check how the shoulder belts are sitting on your child’s shoulders and what your seat’s user manual advises about this. Many manufacturers say that the shoulder belts should not come from below your child’s shoulders. So if the shoulder belts are not coming straight onto the shoulders anymore when having the headrest/belts in the highest setting, then it’s time to change as well.
So if the shoulder belts are not coming straight onto the shoulders anymore when having the headrest/belts in the highest setting, then it’s time to change as well.
CHILD CAR SEATS/BOOSTER SEATS
This is the car seat that your child will use for the longest time – from approx. 4 years until 12 years. Using a high back booster seat instead of only a booster cushion ensures that your child is provided with a side impact protection during the whole period of use. We recommend you to use a high back booster seat for as long as possible, even if not required by national law anymore to give your child the best kind of protection.
When to stop using a booster seat?Step 1: Check the weight/height limitation of your seat
If your booster seat is approved to ECE R44-04, you have to stop using your seat once the maximum weight has been reached, which is 36 kg based on the regulation.
If your booster seat is approved to UN R129, you have to stop using the seat once the maximum height has been reached, which is 150 cm based on the regulation.
Step 2: Check your national laws
Each country has different regulations in their national laws for how long a child must use a child car seat. In most countries, the minimum is 135 cm or the age of 12.
Step 3: Check how your child sits in the car without a child car seat
In addition to step 1 and 2, you can do the “5-point check” to see if your child’s body would be ready to sit in your car without a child car seat. If one of these 5 points is not reached yet, your child should still sit in a booster seat:
- Can they sit with their back flush against the backrest of the vehicle seat?
- While doing that, do their knees bend over the edge of the vehicle seat
- Does the lapbelt sit low over the pelvis bones and not in their tummy area?
- Does the shoulderbelt lay well on their shoulder and is not too close to their neck or sliding off over the shoulder?
- Does your child understand and manage to sit properly on the vehicle seat without slouching or leaning over?
car seat selection guide - magazine Behind the wheel
What is a combined group? What ratings should be trusted? Along the way or against? When to switch to a booster and how to understand that the child is already big enough to do without restraints, fastening with standard seat belts? “Behind the wheel” answered these and other questions.
To choose a car seat for a child, you need to know three parameters - age, height and weight. It's understandable with age. And parents of very young children know exactly the height and weight, as a rule. Parents of kindergarteners and younger schoolchildren know approximately. Exactly - only if the child has recently undergone medical examination.
0 and 0+
Newborns and infants under six months of age are transported in category 0 or 0+ seats, often referred to as "car seats" or "carriers". Children are in them in a lying position (they still do not know how to sit). And they put them against the direction of movement, since babies do not hold their heads, their neck muscles are not developed, which prevent serious injuries in the event of a sudden braking of the car or in an accident. So, against the move, it is recommended to carry children for at least a year. The Swedes, who have made a cult out of road safety, carry children backwards up to 3 years! Maybe right.
Children under the age of one (and according to Swedish recommendations - up to 3 years) can only be transported backwards.
Children under one year of age (and according to Swedish recommendations up to 3 years old) can only be carried backwards.
Related materials
How to carry a child: forward or backward?
Installing the infant carrier in the direction of travel, across the car (in the back seat), loose fasteners - these are all serious, if not potentially fatal mistakes. It is clear that it may be more convenient for you. But imagine (even though it's hard) what will happen to the baby in an accident. Frivolity can kill.
It is believed that the safest place in the car to install a child seat is behind the driver's seat, as the driver instinctively protects himself and exposes the other side of the car to the impact. But there are no supporting statistics to be found. If you imagine all possible impacts, it turns out that the safest place is in the middle of the back seat. But when installing a child car seat (or car seat), you need to fix it as rigidly as possible so that the seat (and the child with it) do not fly off upon impact. Of course, the child must also be securely fastened in the seat. Teach him to use belts from day one - despite the tears.
If you imagine all possible impacts, it turns out that the safest place is in the middle of the back seat. But when installing a child car seat (or car seat), you need to fix it as rigidly as possible so that the seat (and the child with it) do not fly off upon impact. Of course, the child must also be securely fastened in the seat. Teach him to use belts from day one - despite the tears.
You can use your favorite toy to teach your child how to buckle up without whims.
You can use your favorite toy to teach your child how to buckle up without whims.
The most important point: if you decide to put a child seat in the front seat, turn off the passenger airbag - otherwise, in the event of an accident, it can shoot into the back of the seat, break it and injure the child. And try not to be distracted by the child while driving.
Combined groups 0+/1, 0+/1/2, 0/1/2/3
Category 0+ seats are designed for children weighing up to 13 kg. On sale there are also chairs of the combined group 0+/1, designed for weights up to 18 kg. But they tend to be very large for babies, and even padded inserts don't always make up for the extra space. In addition, the child is in such a chair in a semi-sitting position, which is bad for newborns. So if we use such devices, then only when the child learns to sit. At the same time, long trips should be avoided in order to reduce the load on the spine.
On sale there are also chairs of the combined group 0+/1, designed for weights up to 18 kg. But they tend to be very large for babies, and even padded inserts don't always make up for the extra space. In addition, the child is in such a chair in a semi-sitting position, which is bad for newborns. So if we use such devices, then only when the child learns to sit. At the same time, long trips should be avoided in order to reduce the load on the spine.
Universal seats (combined groups) are usually quite bulky, expensive and not always comfortable for the child.
Universal chairs (combined groups) are usually quite bulky, expensive and not always comfortable for the child.
This is especially true for the seats of combined groups 0+/1/2 and 0+/1/2/3. Yes, there are some. The former are designed for weights from 2.2 to 30 kg, the latter - from 2.2 to 55 kg. Wow ranger! Of course, it's tempting to buy one car seat for your entire childhood rather than changing it out every couple of years. But, firstly, such a chair will be very large for the child at first, despite all the inserts, and then it may turn out to be small (for short, for example, the legs will hang in the air). Both are bad, the chair should be "fit". Secondly, before buying, the model you like must be checked for compliance with safety standards. After all, the seat is bought specifically to ensure the safety of the child. Ratings you can trust - for example, the German ADAC Automobile Club. The Germans annually conduct crash tests of current models of child seats. Unfortunately, not all models presented on the Russian market are found in these ratings. And thirdly, universal chairs are very expensive - despite the nuances mentioned above.
But, firstly, such a chair will be very large for the child at first, despite all the inserts, and then it may turn out to be small (for short, for example, the legs will hang in the air). Both are bad, the chair should be "fit". Secondly, before buying, the model you like must be checked for compliance with safety standards. After all, the seat is bought specifically to ensure the safety of the child. Ratings you can trust - for example, the German ADAC Automobile Club. The Germans annually conduct crash tests of current models of child seats. Unfortunately, not all models presented on the Russian market are found in these ratings. And thirdly, universal chairs are very expensive - despite the nuances mentioned above.
Armchairs groups 1, 2, 3
Related materials
These are the children! Main rules for choosing a car seat
Seats of the first group are designed for children weighing from 9 to 18 kg (conditionally from 9 months to 4 years). The second - from 15 to 25 kg (from 3 to 7 years), the third - from 22 to 36 kg (from 6 to 12 years). Recommendations for selection are given above. If your car is equipped with Isofix mounts (and most modern cars have these), it is better to choose the “isofix” model - these hold better than those that are fastened with standard belts. And therefore, safer.
The second - from 15 to 25 kg (from 3 to 7 years), the third - from 22 to 36 kg (from 6 to 12 years). Recommendations for selection are given above. If your car is equipped with Isofix mounts (and most modern cars have these), it is better to choose the “isofix” model - these hold better than those that are fastened with standard belts. And therefore, safer.
Armchairs of the second group are quite rare. More often devices of group 2/3 are sold. Five-point harnesses, as a rule, are no longer in them. Such seats are fastened with standard car seat belts. And they are often disassembled into two parts - a back and a booster (seat with armrest). Booster is already the third group.
Boosters
It is sometimes said that boosters can be used from the age of four. But in this case, it is better to focus not on age, but on height and use a booster when the child outgrows 130 cm. Then regular seat belts will be able to protect the child, and not threaten him with injuries in an accident.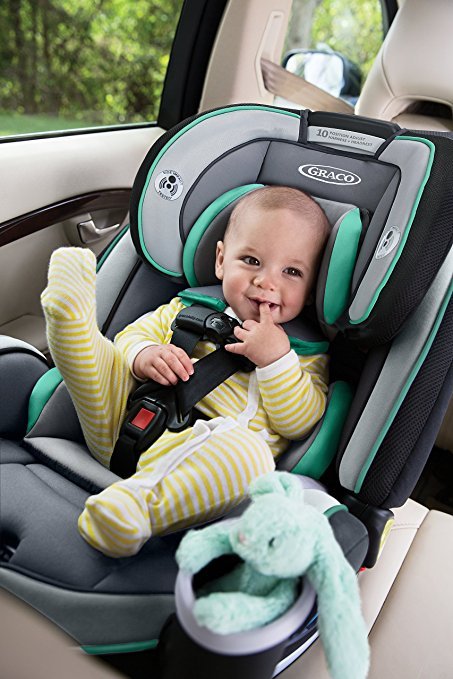
According to WHO, for boys, normal height at four years is from 94.9 to 111.7 cm, for girls - from 94.1 to 111.3 cm. 130 cm is quite a lot even for seven-year-olds.
According to Russian traffic rules, a child can be carried without a special device in the back seat from the age of seven. But it's still better to use a booster.
According to Russian traffic rules, a child can be transported without a special device in the back seat from the age of seven. But it's still better to use a booster.
What the SDA say
According to our Traffic Rules (in force since July 12, 2017), children under 12 years old can only be transported in the front seat when using a special restraint device (car seat or infant carrier). In the back seat, a car seat (or booster) is mandatory up to seven years. From 7 to 12 years old, parents can either use a restraint or fasten their child with standard seat belts.
From 7 to 12 years old, children in the front seat can only be transported in a car seat (or with a booster seat).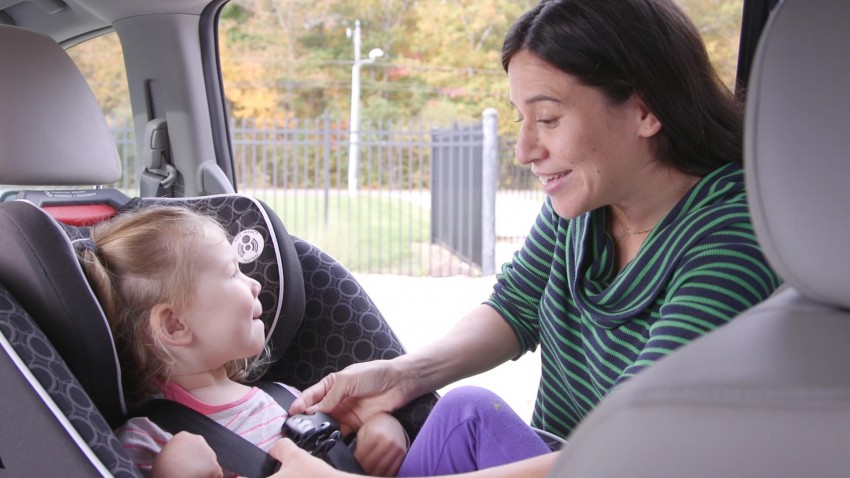
From 7 to 12 years old, children in the front seat can only be transported in a car seat (or with a booster seat).
Our recommendations
- Use car seats from reputable manufacturers, focusing not only on price and design, but also, first of all, on places in safety ratings.
- Do not chase universal models, but choose a seat according to the height and weight of the child so that it is comfortable.
- Use booster from 7 to 12 years old. Earlier - only if the child is significantly ahead of peers in growth.
Baby in the car: guide to choosing a car seat
What is a shared group? What ratings should be trusted? Along the way or against? When to switch to a booster and how to understand that the child is already big enough to do without restraints, fastening with standard seat belts? “Behind the wheel” answered these and other questions.
Child in the car: guide to choosing a car seat
- Comfort in the rear seats is achieved by reducing the volume of the trunk.
 Install the crossbars on the roof and you will be able to transport bicycles, boats or just cargo in baskets or boxes!
Install the crossbars on the roof and you will be able to transport bicycles, boats or just cargo in baskets or boxes!
“How long can an infant be in a car seat?”
Health
- Photo
- Getty Images
In our “Ask the Expert” section, reader Elizaveta asks:
“We went to another city with our child for the holidays. Drive approximately 10 hours. Daughter is 3 months old. He tolerates short trips well, falls asleep immediately. How long can you keep a child in a car seat without a break? Can you sleep in it?
Founder and director of the BabySleep Center for Children's Sleep and Development, author of a unique methodology for teaching self-sleeping, mother of three children
www.baby-sleep.ru/
not for long stay and sleep.
Infants under 4 weeks old should be in a car seat for no more than 30 minutes at a time, up to 2 years for no more than 1.5 hours at a time.
Leaving the child for longer increases the risk of positional asphyxia, where the child's head falls forward onto the chest. This makes breathing difficult, lowers oxygen levels in the blood, and can lead to brain damage and even death.
If you have a long trip with your baby, take regular breaks and take your baby out of the car seat to warm up. The duration of the stops depends on the age and purpose (feed, change a diaper, walk, play).
The shape of the car seat for babies is specially designed. Although some are embarrassed that it is not flat, you want to put something under the back, you don’t need to do this. The position in which the baby lies in the chair is physiological and safe. If you put something extra, the position of the child becomes less safe in the event of an accident.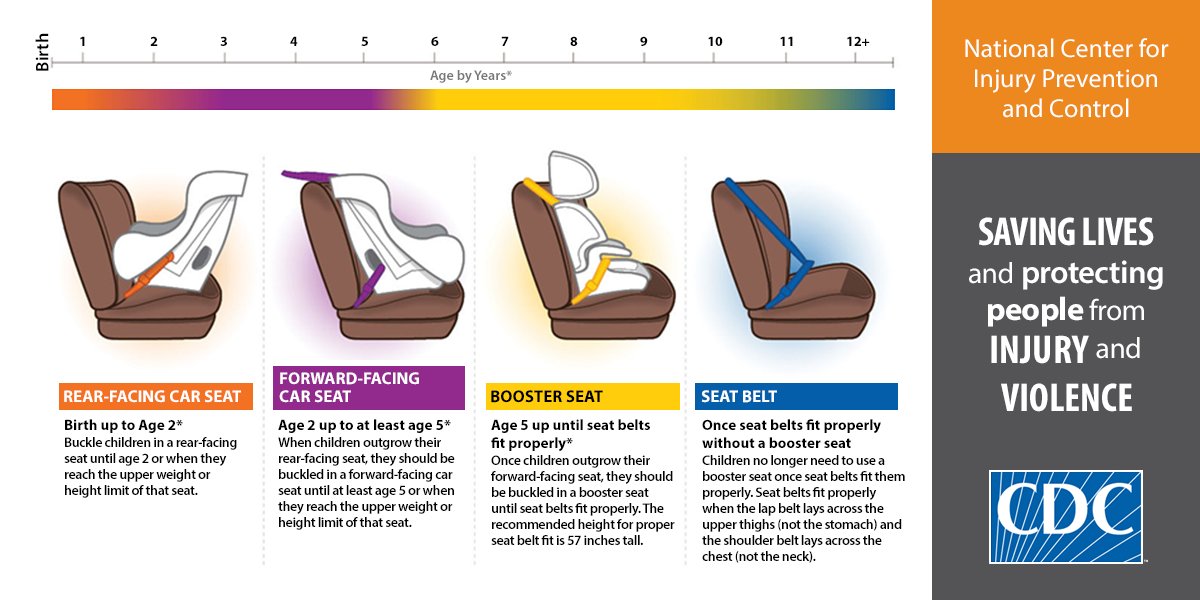 Still, it is protection in the event of an impact that is the main function of a car seat.
Still, it is protection in the event of an impact that is the main function of a car seat.
It is important not only to choose the right car seat for your age, but also to install it correctly in your car.
Always remove your child's outer clothing so that they can be securely fastened with seat belts.
Periodically check on the condition of the baby during the trip. And never leave your child alone in the car, even if he is fast asleep.
There are children who fall asleep as soon as they are in the car. Noise, swaying, restriction of movements soothe them, lull them to sleep. For some children, traveling in a car becomes an association with sleep. It also happens that parents specifically put their children to sleep in the car. In such cases, it is important, firstly, to observe all the listed safety rules. And secondly, try to ensure that the baby still sleeps at home in the crib too.
 Many seats can accommodate children up to 65 pounds or more.
Many seats can accommodate children up to 65 pounds or more.