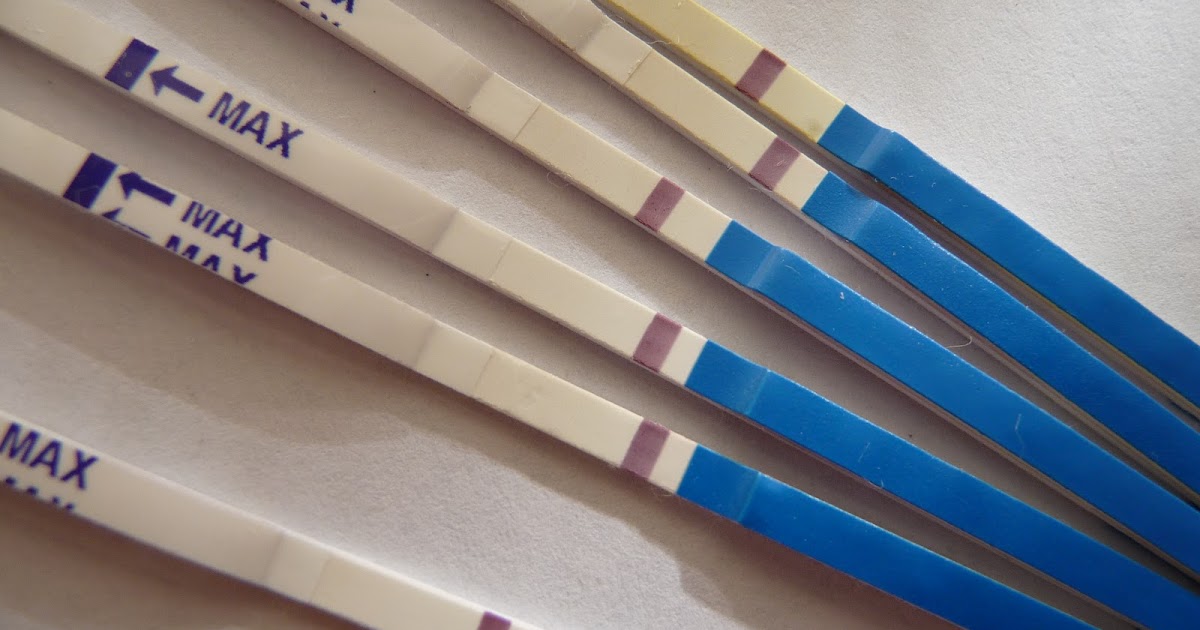
Over 40 pregnancy tests
Genetic Screening Tests for Women 35 or Older
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
Reviewed by Traci C. Johnson, MD on November 10, 2020
In this Article
- Ultrasound
- First Trimester Screen
- Quad Marker Screen
- Amniocentesis
- Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
- Noninvasive Prenatal Diagnosis
If you're 35 or older, you probably know that you have a higher risk for pregnancy problems. To help rule out any concerns, your doctor may offer you some additional prenatal tests. Whether to have these tests is up to you.
Remember that most healthy women aged 35 and into their 40s have healthy pregnancies and healthy babies. But there are several ways genetic tests can be helpful in caring for a pregnancy:
- You'll gain peace of mind about your baby's health.
- You can learn about and prepare for your baby's special needs if a genetic problem is found.
- You can use the information to help make decisions about how best to care for your pregnancy.
Not all tests are without risks, and sometimes tests can have false results. Talk with your doctor about the risks, benefits, and limitations of each test so you can make the best decision for you. Here's an overview of the tests you may be offered.
Ultrasound
Moms of all ages usually have one or more ultrasounds during their pregnancy. This safe test uses high-frequency sound waves to produce an image of your baby. An ultrasound may be used to:
- Confirm that you are pregnant
- See if you are carrying more than one baby
- Determine whether your baby's heart is beating
- See if you are carrying more than one baby
- Estimate your baby's due date and see how your baby is growing
- Determine the baby's gender
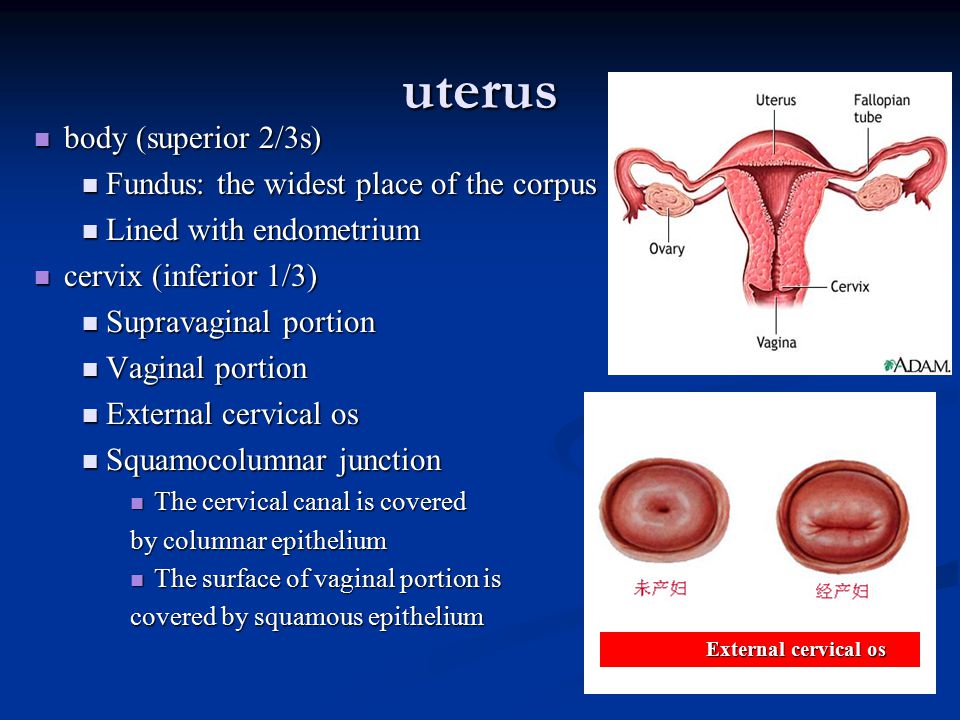
- Examine your ovaries and uterus
- Determine the location of the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid around your baby
- Look for signs of birth defects such as cleft lip, heart defects, spina bifida, and Down syndrome
First Trimester Screen
This test is done between weeks 11 and 14. It involves a blood test and an ultrasound.
It involves a blood test and an ultrasound.
- The blood test measures two markers in your blood.
- The ultrasound measures the thickness of the back of your baby's neck.
Taken together, the results look for problems with your baby's chromosomes, such as Down syndrome.
This test serves the same function as the quad marker screen (below), but allows your doctor to see your baby. It also tends to cause fewer false alarms. Sometimes it's combined with a second blood test like the quad screen, to give a result that is more accurate than either of the individual tests.
Quad Marker Screen
A quad marker screen is a blood test performed between the 15th and 20th weeks of pregnancy. It measures substances in the blood that may show:
- Problems with a baby's brain and spinal cord, called neural tube defects. These include spina bifida and anencephaly. The quad marker screen can detect about 75% to 80% of neural tube defects.
- Genetic disorders such as Down syndrome.
 The test can detect about 75% of Down syndrome cases in women under age 35 and more than 80% of Down syndrome cases in women age 35 and older.
The test can detect about 75% of Down syndrome cases in women under age 35 and more than 80% of Down syndrome cases in women age 35 and older.
It's important to know that the quad screen only indicates your level of risk for birth defects. If the test shows a risk greater than the average risk of a 35-year-old woman, then the test is considered to be positive. The test can't diagnose birth defects, so a positive result doesn't mean that your baby has a birth defect. In most cases, the baby is healthy despite an abnormal test result.
If the test is positive, your doctor may suggest having diagnostic tests, such as:
- Amniocentesis to check your baby’s chromosomes
- Ultrasound to look for signs of birth defects
Amniocentesis
Unlike blood testing, which only shows whether you are at risk, amniocentesis is used to make a diagnosis. During the test, your doctor will insert a needle through the abdomen wall, using ultrasound images to help guide the needle into the uterus. They will remove a small amount of amniotic fluid from the sac surrounding your baby. This sample is then used to check the baby's chromosomes and test for genetic diseases. In addition to the most common chromosome problems, including Down syndrome, trisomy 18, trisomy 13, and Turner syndrome, the sample can be tested for:
They will remove a small amount of amniotic fluid from the sac surrounding your baby. This sample is then used to check the baby's chromosomes and test for genetic diseases. In addition to the most common chromosome problems, including Down syndrome, trisomy 18, trisomy 13, and Turner syndrome, the sample can be tested for:
- Sickle cell disease
- Cystic fibrosis
- Muscular dystrophy
- Tay-Sachs disease
- Neural tube defects, such as spina bifida and anencephaly
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
CVS is an alternative to amniocentesis, and it can be performed earlier in the pregnancy. Like amniocentesis, CVS can diagnose some diseases. If you have certain risk factors, you may be offered CVS as a way to detect birth defects during early pregnancy.
During this test, a small sample of cells, called chorionic villi, is taken from the placenta. Chorionic villi are tiny parts of the placenta that are formed from the fertilized egg, so they have the same genes as your baby. To get the cells, a doctor passes a needle through the vagina or the abdomen, depending on the location of the placenta. The cells are used to check your baby's chromosomes, just like amniocentesis.
To get the cells, a doctor passes a needle through the vagina or the abdomen, depending on the location of the placenta. The cells are used to check your baby's chromosomes, just like amniocentesis.
CVS and amniocentesis usually involve genetic counseling, where you speak with a counselor about your risk for genetic disorders. You will also learn about the risks and benefits of the procedures. CVS isn’t usually done when you’re carrying twins because of the risks.
Noninvasive Prenatal Diagnosis
This newer blood test, also called cell-free DNA testing, is used to show whether you are at risk for having a baby with chromosome problems. Because it's done by using a sample of your blood, it's less invasive than amniocentesis or CVS.
The test is done between 10 and 22 weeks of pregnancy. It finds DNA from your baby floating around in your blood. The result determines the chance that your baby could be born with Down syndrome, trisomy 18, or trisomy 13.
Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis can detect about 99% of Down syndrome and trisomy 18 cases, which is much better than other blood tests. The majority of trisomy 13 cases can also be detected with this test.
The majority of trisomy 13 cases can also be detected with this test.
If the test shows an increased risk for chromosome problems, your doctor may recommend CVS or amniocentesis to confirm the diagnosis.
Because this is a new test, not all insurers cover it. Check with your insurance company to see whether the cost of the test will be covered.
Being pregnant after 40 | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Being pregnant after 40 | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
If you’re over 40 years of age and you’re having a baby, there’s plenty to look forward to. There is also a lot to think about.
Some of the benefits of being an older mother might be:
- knowing yourself better than you did when you were younger
- having more life experience
You are also more likely to already have a healthy diet.
Mothers over 40 are less likely to punish and scold their children.
Children of older mothers are also less likely to have:
- behavioural difficulties
- social difficulties
- emotional difficulties
Most people over 40 have healthy pregnancies and healthy babies. But there are some things you need to think about. You’ll want to be sure to get good antenatal care.
What is antenatal care?
Antenatal care is the care you get while you’re pregnant. It’s an important way to keep yourself and your baby healthy.
Antenatal tests are an important part of your care. Different types of tests are used to check your and your baby’s health. These include blood tests, urine tests and ultrasound scans.
Seeing a doctor or midwife regularly lets them check both your health and your baby’s health.
Your doctor or midwife can also:
- provide you with advice
- answer your questions
- deal with any fears you may have
- help you to prepare for the birth
How is antenatal care different for mothers aged over 40?
Good antenatal care is important for both you and your baby. Your antenatal care is the same as that for younger people.
Your antenatal care is the same as that for younger people.
What pregnancy complications happen in mothers aged over 40?
There are a few pregnancy complications that are more common in people over 40.
Pregnant people over 40 years are more likely to:
- have high blood pressure or gestational diabetes
- have twins or even triplets
- go into premature labour
- have placenta praevia, in which the placenta develops in the wrong part of the uterus
- have a miscarriage
People over 40 years are also more likely to experience heartburn when they are pregnant. This risk is likely to increase if you:
- had heartburn before you got pregnant
- put on a lot of weight during pregnancy
Your doctor or healthcare professional will give you advice on lifestyle changes you can make.
Your doctor will probably organise a blood test to check your rubella immunity. This is because rubella immunity decreases as you get older.
If you are not immune to rubella, your doctor will recommend that you avoid people with symptoms of rubella. They will also organise for you to vaccinated against rubella once you have had this baby.
Are there other tests or investigations I should have?
Genetic conditions
Routine antenatal tests for genetic conditions are offered to all pregnant people. However, chromosomal conditions are more common in babies of people aged 40 years or older.
They include:
- Down syndrome (trisomy 21)
- Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18)
- Patau syndrome (trisomy 13)
Prenatal screening tests assess the risk of your baby having one of these conditions.
These screening tests are tests you can choose to have. None of them are compulsory — they're a personal choice. It’s worth talking to your doctor or midwife to help you decide.
If the screening tests show that the risk of your baby having a chromosomal disorder is high, you can have a diagnostic test. These include:
These include:
- chorionic villus sampling
- amniocentesis
You can also arrange to have genetic counselling with a specialist counsellor. They will discuss with you what might happen with your baby, and how you might handle the situation.
Resources and support
For more information and advice, call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436. You can speak to a maternal child health nurse for advice and support.
Sources:
Australian Government Department of Health (Clinical Practice Guidelines Pregnancy Care 2020 Edition), Tea Trillingsgaard & Dion Sommer (Associations between older maternal age, use of sanctions, and children's socio-emotional development through 7, 11, and 15 years)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: July 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Pregnancy checkups, screenings and scans
- Exercising during pregnancy
- Healthy diet during pregnancy
Need more information?
What are the current multiple pregnancy and birth trends?
There has been an overall increasing trend in multiple births in the last two decades in Australia. Attributed largely to the increased use of fertility drugs and assisted reproduction technology and the growing number of older mothers.
Attributed largely to the increased use of fertility drugs and assisted reproduction technology and the growing number of older mothers.
Read more on Twins Research Australia website
Pregnancy tests – chorionic villus sampling - Better Health Channel
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a pregnancy test that checks the baby for some abnormalities.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Placental abruption - Better Health Channel
Placental abruption means the placenta has detached from the wall of the uterus, starving the baby of oxygen and nutrients.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Getting pregnant - MyDr.com.
 au
au Getting pregnant is easy for some women, but for others it can be a difficult. Women are most fertile between 20 and 24 years of age, after which fertility declines.
Read more on myDr website
Risk factors for Perinatal Anxiety - Gidget Foundation
Risk Factors Perinatal depression and anxiety can strike anyone: first-time parents, experienced parents, older parents, younger parents, and parents from all socioeconomic backgrounds and cultures
Read more on Gidget Foundation Australia website
Causes of autism | Autism Awareness Australia
While we know there is no one single cause for autism, genetics play a major role as well as environmental factors.
Read more on Autism Awareness Australia website
Trisomy 13 or Patau syndrome | Raising Children Network
Trisomy 13 or Patau syndrome is a chromosomal disorder. It often results in miscarriage or stillbirth. Babies born with trisomy 13 have severe disability.
It often results in miscarriage or stillbirth. Babies born with trisomy 13 have severe disability.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Trisomy 18 or Edwards syndrome | Raising Children Network
Trisomy 18 or Edwards syndrome is a chromosomal disorder that causes severe disability. Most babies with trisomy 18 die in the first weeks of life.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
When to do a pregnancy test? Maternity hospital Leleka | Blog
Pregnancy in the life of every woman is a significant event and most often unexpected.
But, even if the pregnancy came as a “surprise”, you must definitely confirm your suspicions or refute them. And you can do this with the help of an instant express pregnancy test, in a matter of seconds.
| Express pregnancy test is a very convenient, fast and inexpensive device that determines pregnancy (if any) as accurately as possible. The erroneous result is reduced to a minimum and is only 1%. |
The most informative are digital and tablet tests (the strip is placed on a plastic device with two "windows"). However, strip tests remain the most popular, which means that the price of the test does not affect the result.
If there is any doubt after the test, you should make an appointment with a gynecologist.
How the pregnancy test works
Despite the whole range of pregnancy tests, the principle of action is the same for everyone - to determine the level of hCG (the first hormone of pregnancy) in the urine.
| hCG - secreted by the villi of the embryo from the period of attachment of the fertilized egg to the uterine wall. May be detected in the urine and blood of a pregnant woman. |
Pregnancy test procedure
Pregnancy test is performed no earlier than the first day of missed period or approximately 2 weeks after the expected day of conception. Until the zygote attaches to the wall of the uterus, hCG is not released, which means that before ten days of pregnancy, it is not advisable to carry out a test or any other tests.
At the beginning of the test, you should carefully study the instructions for its use. Although the principle of operation is always identical: one part of the test (paper) is immersed in a container with urine, the other (with a chemical indicator) determines the result in the form of red / blue stripes, the symbols “+” / “-” or the words “yes” / “no” ". The result is evaluated after the time specified in the instructions (from 1 to 5 minutes).
Sometimes there are mini-pipettes for metered distribution of urine in the tests, which are very convenient to use.
But putting the test under the urinary stream is not recommended, since this method can technically disrupt the express screening and give an error.
| You cannot rely on the result of a single test; for complete certainty, you need to repeat the express test in 1-3 days. If two stripes are determined each time, it is mandatory to make an appointment with a gynecologist. |
When to take a pregnancy test
In order not to be confused by the numbers, dates and know exactly when it is appropriate to take a pregnancy test, you need to keep a calendar, control your well-being and know the basic process of how the egg is fertilized .
In every woman with a regular monthly cycle, the egg goes through several physiological stages of development, one of which is called “ovulation”.
Ovulation is the process where a mature egg is released from the ovary into the fallopian tube to join the sperm. If there is no sperm in the tube, the egg dies and menstruation occurs.
If there is no sperm in the tube, the egg dies and menstruation occurs.
| Ovulation lasts approximately 2 days. All this time the egg is active. |
If during ovulation the spermatozoa were inside the woman's genitals and conception did occur, the fertilized egg (zygote) begins to "move" into the uterine cavity, with the help of the ciliated epithelium and the muscles of the fallopian tube itself.
This whole process takes about 1 week.
After a fertilized egg enters the uterine cavity, it attaches there, hCG rises in the blood, cells divide and further development of the fetus occurs.
| The level of hCG (the first hormone of pregnancy) rises only after the fixation of a fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. Therefore, a reliable result of pregnancy can be obtained only on the seventh to tenth day of conception. In this case, the result must be supported by a doctor's opinion. |
Some rapid tests can determine the presence of the hormone as early as the fourth day, but it is still better to check after at least 1.5 weeks. Then the level of the hormone becomes high enough to confidently determine the condition of the woman.
| Delayed periods do not always indicate pregnancy, but it is better to immediately check the cause and take a test on the first day. |
When is a pregnancy test false?
Two strips on the test do not always cause delight in women, since pregnancy is not a cherished dream for all women, for most it is a surprise.
However, if you really do not plan a child and your test suddenly becomes “striped”, do not rush to panic, since a result error is not ruled out here.
False-positive or false-negative responses can range from a technical failure of a screening test to the identification of serious gynecological pathologies.
As you can see, pregnancy is not the most “terrible” thing that a test can determine, so we once again emphasize the importance of a gynecological examination.
| Gynecologists of the private maternity hospital "Leleka" strongly recommend not to be limited to the results of a rapid test to establish pregnancy.
Since today there is a growing trend of ectopic pregnancies, which lead to serious complications and gynecological pathologies in the future. |
Be that as it may, a positive test result is only the first step towards determining pregnancy. The second step is a visit to the gynecologist, who must confirm / refute the information received. Since there are situations when express screening gives a false positive answer.
Main causes of a false positive result
A false positive result is a result that indicates the presence of pregnancy, in the absence of it.
Causes:
1. Incorrect express test.
Incorrect use of the test is the main cause of a false positive response. Therefore, you always need to read the instructions and follow the specified algorithm of actions. The evaluation of the result should be carried out strictly within the specified time range, from 3 to 10 minutes. After this period, a weak second strip may appear on the test (due to evaporation of urine), and the woman will perceive the result as a pregnancy.
2. Marriage.
A defective test is a very rare occurrence, but no one is immune from such a situation. Knowing this, women buy several tests from different brands and thus the problem is leveled.
3. Postpartum period.
Pregnancy test remains positive throughout pregnancy and 3-4 weeks after delivery. Therefore, if the test after the recent birth of a child shows a positive answer, and you are not planning children of the same age, you should not worry. However, you still need to check with your doctor about the absence of pregnancy.
However, you still need to check with your doctor about the absence of pregnancy.
4. Miscarriage, abortion.
After a miscarriage, miscarriage or medical abortion, the level of hCG cannot immediately decrease, it takes time. And, as a rule, this process takes from 2 to 4 weeks. Therefore, doing a pregnancy test during this period simply does not make sense, since the result will be false positive.
| If in doubt, a blood test for hCG levels or a follow-up abdominal ultrasound should be done. |
5. Preparation for IVF.
Some women dream of pregnancy so much that they take tests even when they don't have to. As, for example, when preparing for IVF.
During this period, ovulation is stimulated with hormonal preparations, which also increase the level of hCG, although there is no pregnancy itself yet. Therefore, a pregnancy test done during this period can misinform a woman.
6. Oncopathology.
Sometimes a positive pregnancy test, in its absence, indicates serious pathological processes that increase the level of hCG. These are ovarian tumors, lung, brain, breast or stomach cancer.
| To dispel all suspicions and fears, with a positive pregnancy test result, you should immediately contact a gynecologist to rule out ectopic pregnancy and oncopathology. |
Main causes of a false negative test
A false negative is a result that indicates no pregnancy, if any.
Causes:
- Fertilization occurred before the start of menstruation, and the level of hCG did not have time to rise to the desired concentration.
- There is a threat of miscarriage.
- A woman is taking diuretics (diuretics).
- Technical damage to the test.
If a pregnancy test shows a negative result, but the woman has specific pregnancy symptoms (morning sickness, dizziness, frequent urination, pain in the lower abdomen and chest), you need to see a doctor.
What to do if in doubt?
There are situations that make a woman doubt the correctness of a pregnancy test. For example, different tests give different results, spotting is present (similar to menstruation), screening gave a positive response, and there are no specific symptoms of pregnancy.
What to do in this case?
- Do not look for the cause yourself, but go for a consultation with a gynecologist and approach the solution of the problem comprehensively.
- Do not dispose of unwanted and unconfirmed pregnancies yourself.
- Find the exact reason why the test showed a false positive result in the absence of pregnancy.
| Note! Leading gynecologists of the private maternity center "Leleka" strongly recommend that after passing the test with a positive response, immediately contact a medical institution. Even if you do not plan to give birth to a child, pregnancy in any case must be confirmed or denied. You should not rely only on the test result, and in no case should you resort to criminal abortions, buy the “necessary” pills in a pharmacy on your own, use folk methods to terminate a pregnancy. All this is fraught with serious consequences and complications, even death. |
The Leleka maternity hospital is a modern medical institution where you will always receive specialized, highly qualified obstetric-gynecological and neonatological medical care at the level of world standards.
Only timely diagnosis and competent treatment will help preserve the reproductive health of a woman and there are no other options here.
Striving for excellence: Criteria for the perfect pregnancy test
The need for accurate diagnosis of pregnancy has always existed, which is why our ancestors found ways to solve this problem that are somewhat unusual for modern women. For example, in a book written over 4,000 years ago, an Egyptian doctor describes the first pregnancy test: “Wrap wheat and barley with a piece of cloth. Every day a woman should urinate on it. Then everything is mixed with dates and sand. If both grains germinate, she will give birth, if only wheat germinates, she will give birth to a boy, and if barley germinates, she will give birth to a girl. If nothing sprouts, she won't give birth at all." Other diagnostic methods were of the same empirical nature and had low reliability until the era of evidence-based medicine and accurate diagnosis came.
For example, in a book written over 4,000 years ago, an Egyptian doctor describes the first pregnancy test: “Wrap wheat and barley with a piece of cloth. Every day a woman should urinate on it. Then everything is mixed with dates and sand. If both grains germinate, she will give birth, if only wheat germinates, she will give birth to a boy, and if barley germinates, she will give birth to a girl. If nothing sprouts, she won't give birth at all." Other diagnostic methods were of the same empirical nature and had low reliability until the era of evidence-based medicine and accurate diagnosis came.
In 1929, German scientists Selmar Aschheim and Bernhard Zondek published a work in which they proved the presence in the urine of pregnant women of a substance that, when injected under the skin of a mouse, can cause maturation of the genital organs in 4 days. They suggested using this method to determine pregnancy in women, which made it possible to achieve more reliable and accurate results.
Subsequently, a hormone was discovered that is determined in the urine during pregnancy - human chorionic gonadotropin (CGT). The first home pregnancy test appeared in 1971, its result had to wait about 2 hours. In the 80s of the twentieth century. the first tests to quickly determine pregnancy appeared. These were paper strips impregnated with a reagent. Soon the paper was replaced with latex, which made it possible to increase the accuracy of the result.
Modern test systems have allowed women to independently determine pregnancy at home with great certainty. But the more diverse they became, the higher the requirements for quality, convenience and speed of diagnosis began to be made by consumers.
The marketing department of Pharmasco conducted a survey, the purpose of which was to determine the main criteria for an ideal pregnancy test from the point of view of the fair sex. We present its results below.
Determination of pregnancy at the minimum time after conception
It is known that the “pregnancy hormone” (CHT) is found in the urine only after the implantation of the ovum has occurred - namely, 6-7 days after fertilization. Accordingly, even the most sensitive tests (10 mIU/ml) will be able to detect pregnancy no earlier than 7 days after sexual intercourse, and tests with normal sensitivity (25 mIU/ml) - only from the first day of missed menstruation.
Accordingly, even the most sensitive tests (10 mIU/ml) will be able to detect pregnancy no earlier than 7 days after sexual intercourse, and tests with normal sensitivity (25 mIU/ml) - only from the first day of missed menstruation.
Diagnosis possible at any time of the day
Conventional pregnancy tests have a low sensitivity (25 mIU/ml), so morning urine should be used for testing, because it contains the highest content of HCG. At the same time, for highly sensitive tests (10 mIU/ml), a threshold concentration of HCG is sufficient, which makes it possible to detect this hormone in urine collected at any time of the day.
Ease of diagnosis
For comfortable testing, the inkjet test format is optimal, because the study is possible not only at home and there is no need to collect urine in a container.
Quality of information provided to the consumer
The women interviewed indicated that when buying a test, it is important for them to have the necessary information on the package, its accessible presentation, as well as detailed instructions for the test.
Brand awareness and expert references
Consumers are more likely to choose the products they have bought before and also pay attention to the opinion of experts. For pregnancy tests, such an expert organization is the Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists of Ukraine.
Visual appeal of the package
Of the variety of pregnancy tests on the domestic pharmaceutical market, not many fully meet the needs of demanding customers.
Pharmasco, well known to pharmacists for pregnancy tests such as DUET TM , SEZAM TM , ULTRA TM and SECRET TM , has committed itself to create the so-called "International Women's Day" pregnancy test".
This test was based on a well-known brand - test DUET TM . It has an inkjet format, the recommendations of the Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, its packaging is highly informative and contains detailed instructions.