How long do you bleed after ectopic pregnancy
Bleeding And Periods - The Ectopic Pregnancy Trust
Is the bleeding after treatment/monitoring of my ectopic pregnancy my period?
The bleeding you have after surgery, after treatment with methotrexate, or if you are managed expectantly, is not actually classed as your first period after the ectopic pregnancy. This is your body expelling the thickened lining of the uterus because you are, sadly, no longer pregnant.
Once the beta hCG levels (pregnancy hormones) in your body have dropped, the chemical signals to retain the thickened uterine lining that has built up in preparation for pregnancy, are no longer being produced and so the lining of the uterus is shed. The process involves vaginal bleeding and the material may be clotty, heavy, dark in appearance or appear just like one of your normal period bleeds.
Back to top
Share thisHow long will the bleeding last?
The length of time anyone bleeds varies greatly, as the bleeding is from the lining of the womb and is hormonally controlled. It will probably last a week or two, changing in colour from red to brown and diminishing. Some women report bleeding and spotting on and off for up to six weeks.
Provided you are not soaking a pad in less than an hour or the pain is so severe you can’t manage it with over-the-counter pain relief, such as paracetamol, you should try not to worry. If you have any concerns, you should seek a reassessment.
Back to top
Share thisShould my bleeding have all these clots in it?
The bleeding that follows an ectopic pregnancy, particularly when treated with methotrexate, can be very heavy and clotty and result in the passing of what we call a decidual cast. This decidual cast can cause confusion and worry and it can often be mistaken for the tissue of their baby.
The lining of the uterus when we are pregnant, other than that which is taken up by the placenta, is called the decidua. The appearance of the normal lining of the uterus by the presence and action of progesterone (hormone that prepares the uterus for a fertilised egg) becomes decidualised.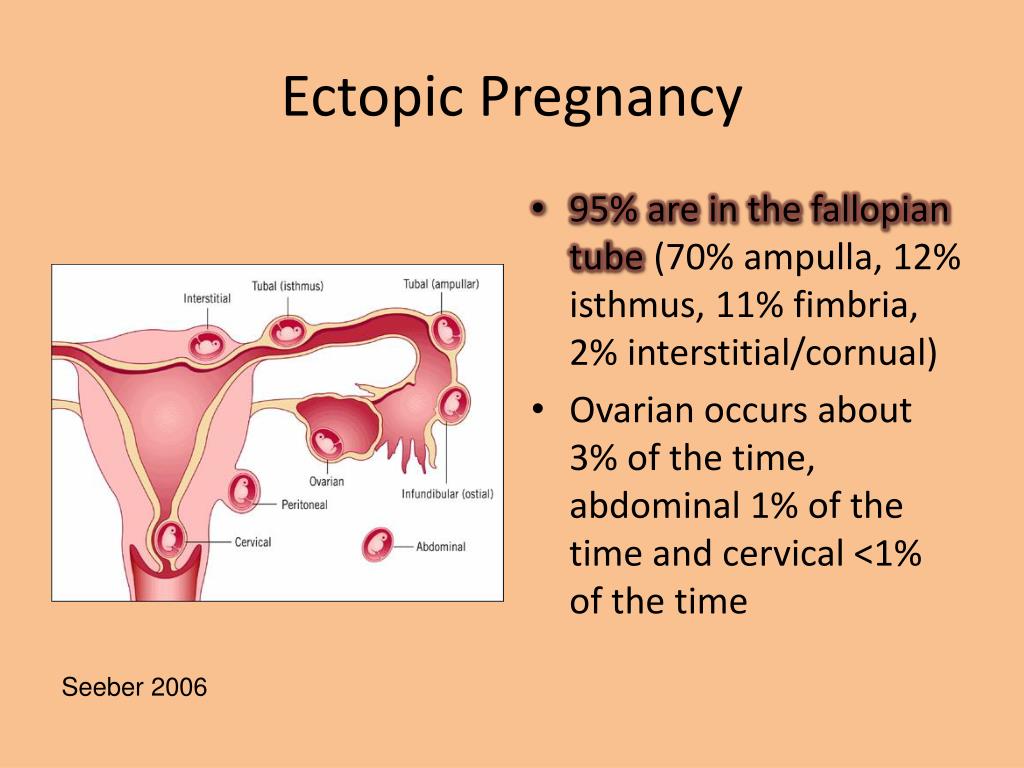 When an area of the decidua is shed we call it a decidual cast. It is thought to occur as a result of the lack of stability of the integrity of the lining and this lack of stability is because the hormones aren’t functioning properly in an ectopic pregnancy.
When an area of the decidua is shed we call it a decidual cast. It is thought to occur as a result of the lack of stability of the integrity of the lining and this lack of stability is because the hormones aren’t functioning properly in an ectopic pregnancy.
The sudden drop in hormones can cause the material inside the uterus to be shed in layers and the material that is passed can be grey, pink or white as well as appear like a clot or dark or frank red blood.
Back to top
Share thisI haven't bled following my treatment with methotrexate.
Not experiencing bleeding after being treated with methotrexate is not uncommon. Some do not have bleeding with this type of treatment.
Back to top
Share thisWhen can I expect a period after my ectopic and will it be painful?
Your periods can take a while to re-establish and they can re-start anything between four and ten weeks after treatment. Most find that their period arrives sometime around week six or seven after surgery, or, if treated without surgery, at some time in the four weeks after their hCG levels have fallen to below 100 mIU/mL.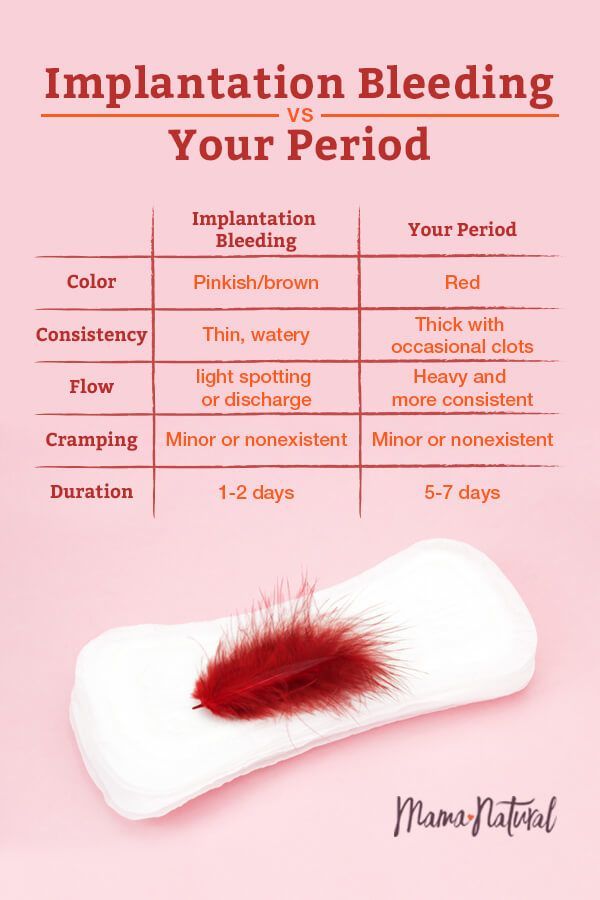
Before you can have a period, you would usually have to ovulate. It is perfectly possible to ovulate 14 days after surgical treatment and almost as soon with methotrexate treatment, so it is important to be aware that it is possible to become pregnant without having a period first if you are not using some form of contraception. You can read more about contraception using the link below.
The first period may be more painful or less so than usual, heavier or lighter, last for longer or shorter than usual – there really is no set pattern. You should be able to manage the discomfort with over-the-counter pain relief and should not be soaking a pad in less than an hour. If this is not the case, you should seek medical attention.
Contraception
Back to top
Share thisWill my period cycle return to normal after my ectopic?
Before, they were 25/26 days but this time it has been 30 days and I have checked and am not pregnant.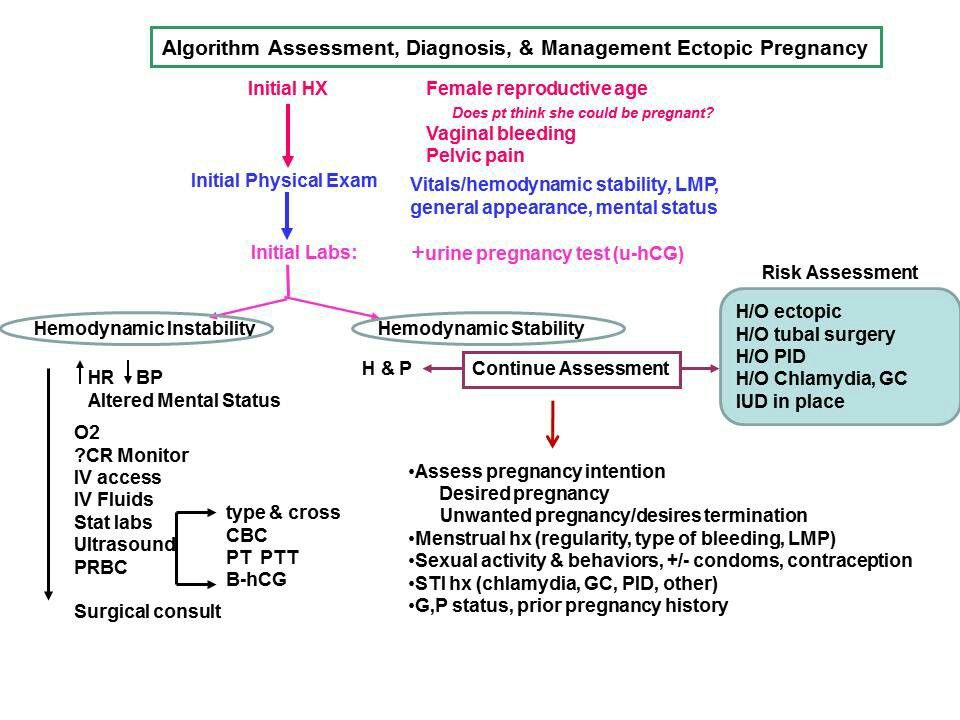 Is my changed menstrual cycle length ok?
Is my changed menstrual cycle length ok?
The first period can occur up to ten weeks after the ectopic pregnancy although it may not be like your normal period. It might be heavier or lighter and it may be more painful than expected. The period after that is usually more like your usual pattern. However, although there is no medical reason for it, women do very often report some irregularity to their cycle for several months after an ectopic pregnancy.
Broadly speaking, doctors consider menstrual (period) cycles of between 23 to 42 days to be within normal parameters. If the first day of your last period was more than 42 days ago, make an appointment with your doctor to discuss the possible reasons for this.
Back to top
Share thisWill I still have a period every month after removal of one/both of my Fallopian tubes?
You will continue to have normal periods every month after the removal of one or both Fallopian tubes. The menstrual cycle is controlled by hormones produced in different sites in the body, predominantly in the ovaries, and a period is the shedding of the lining of the womb. The Fallopian tubes play no part in controlling your period cycle. Periods usually continue normally even in the very rare cases when one of the ovaries is removed as part of the surgical process.
The Fallopian tubes play no part in controlling your period cycle. Periods usually continue normally even in the very rare cases when one of the ovaries is removed as part of the surgical process.
Back to top
Share thisIs it normal to have pain during ovulation after my ectopic?
After surgery for an ectopic pregnancy, you may have some adhesions which might cause some pelvic pain and pain at ovulation but this usually settles. Some do report that they can feel themselves ovulate, often because there is more awareness of sensations within our bodies after suffering an ectopic pregnancy.
Back to top
Share thisEctopic Pregnancy | Cedars-Sinai
ABOUT CAUSES DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT NEXT STEPS
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
A pregnancy that develops outside the uterus is called an ectopic pregnancy. It almost always happens in a fallopian tube. Because of this, it’s often called a tubal pregnancy. In rare cases, an ectopic pregnancy will happen in an ovary, in the cervix, or the belly (abdomen).
Because of this, it’s often called a tubal pregnancy. In rare cases, an ectopic pregnancy will happen in an ovary, in the cervix, or the belly (abdomen).
What causes an ectopic pregnancy?
A fertilized egg normally moves down a fallopian tube and into the uterus. But the egg can get stuck in the tube if the tube is blocked. This might be from an infection or scar tissue. If the fertilized egg can't reach the uterus, it begins to develop in the tube.
Who is at risk for an ectopic pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy is more common in women who:
- Have had trouble getting pregnant (infertility)
- Have endometriosis. This is when uterine tissue grows in other areas of the pelvis.
- Have a sexually transmitted disease. This can cause infection and scarring in the pelvis.
- Had tubal surgery
- Use an IUD
- Had an ectopic pregnancy in the past
- Have multiple sex partners
- Smoke
- Are older
What are the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy?
Women with an ectopic pregnancy may have irregular bleeding and pelvic or belly (abdominal) pain.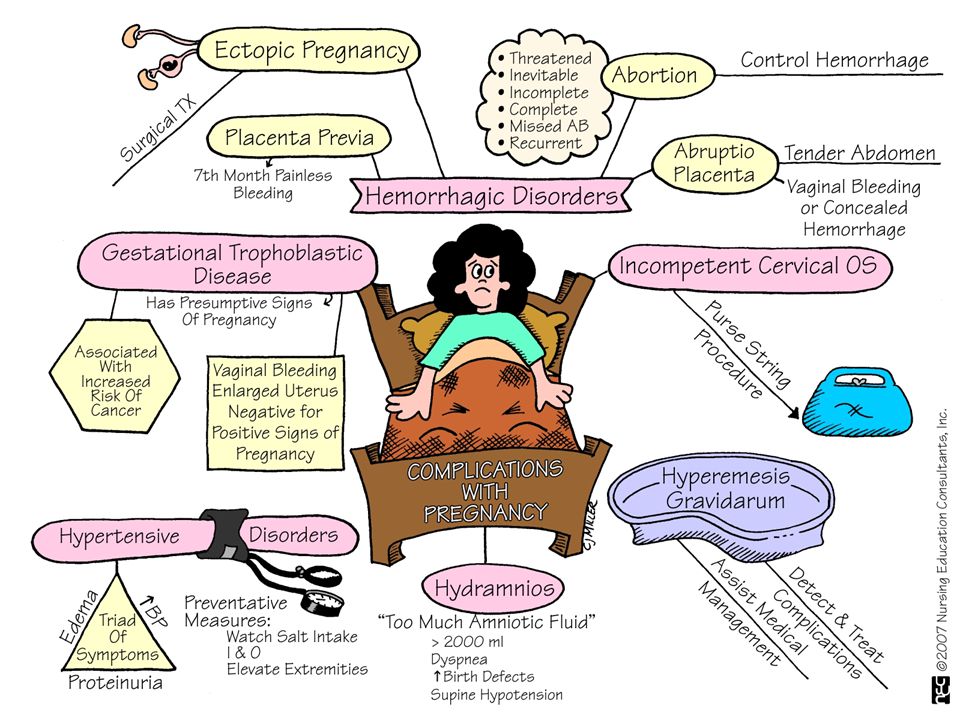 The pain is often just on 1 side. Symptoms often happen 6 to 8 weeks after the last normal menstrual period. If the ectopic pregnancy is not in the fallopian tube, symptoms may happen later. The classic symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are:
The pain is often just on 1 side. Symptoms often happen 6 to 8 weeks after the last normal menstrual period. If the ectopic pregnancy is not in the fallopian tube, symptoms may happen later. The classic symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are:
- Belly (abdominal) pain
- No recent period
- Vaginal bleeding not related to a period
How is an ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will measure the level of the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in your blood. They will use ultrasound to check the uterus for a fetus or other pregnancy tissue. In some cases, your healthcare provider will use laparoscopy to diagnose and treat an ectopic pregnancy. This is surgery that uses a lighted tube inserted into your abdomen to check inside the pelvis. It often gives the most accurate diagnosis.
It often gives the most accurate diagnosis.
How is an ectopic pregnancy treated?
Ectopic pregnancy may be treated in several ways. This depends on whether the fallopian tube has broken open (ruptured), how far along the pregnancy is, and your hormone levels. Treatments may include:
- Letting the ectopic pregnancy heal and the body absorb it on its own. This is only for certain cases.
- Using the medicine methotrexate to stop the pregnancy from growing further
- Using surgery (usually laparoscopy) to make a small opening in the fallopian tube. The surgeon removes the pregnancy and sometimes the tube.
In rare cases, healthcare providers must make a larger incision in the abdomen to remove the ectopic pregnancy or damaged fallopian tube.
What are possible complications of an ectopic pregnancy?
When the embryo implants in the fallopian tube, it does not have enough room to grow or enough blood flow to keep it healthy, so it dies.
The tube may start to let out some of the tissues or bleed. Some embryos do keep growing and may become large enough to burst the fallopian tube. This can cause severe bleeding and shock.
Ectopic pregnancy is the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths during the first 3 months of pregnancy in the U.S.
When should I call the healthcare provider?
Don’t ignore symptoms of ectopic pregnancy. Call your healthcare provider if you have any bleeding or pain in pregnancy.
Key points about ectopic pregnancy
- Pregnancy that develops outside the uterus is called ectopic pregnancy.
- Women with an ectopic pregnancy may have irregular bleeding and pelvic or abdominal pain, often on one side.
- Symptoms most often appear 6 to 8 weeks after the last normal menstrual period.
- Ectopic pregnancy may be treated in several ways, depending on whether the fallopian tube has burst.
- Don’t ignore symptoms of ectopic pregnancy. Call your healthcare provider if you have any bleeding or pain in pregnancy.
Next steps
Tips to help you get the most from a visit to your healthcare provider:
- Know the reason for your visit and what you want to happen.
- Before your visit, write down questions you want answered.
- Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your provider tells you.
- At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. Also write down any new instructions your provider gives you.
- Know why a new medicine or treatment is prescribed, and how it will help you.
 Also know what the side effects are.
Also know what the side effects are. - Ask if your condition can be treated in other ways.
- Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
- Know what to expect if you do not take the medicine or have the test or procedure.
- If you have a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for that visit.
- Know how you can contact your provider if you have questions.
Medical Reviewer: Irina Burd MD PhD
Medical Reviewer: Donna Freeborn PhD CNM FNP
Medical Reviewer: Heather M Trevino BSN RNC
© 2000-2022 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.
Menstruation after treatment of ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a dangerous complication of pregnancy when a fertilized egg does not enter the uterus, but is fixed outside its cavity. In 98% of cases, this occurs in the fallopian tubes.
In 98% of cases, this occurs in the fallopian tubes.
Ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency. Otherwise, internal bleeding can endanger a woman's life.
Many women are concerned about the question - how soon after the operation will the normal menstrual cycle be restored and when is it possible to plan pregnancy again?
Menstruation usually occurs 30 days after the termination of an ectopic pregnancy. A delay of more than 40 days may indicate a hormonal failure.
Let's note right away: termination of pregnancy is a stress for the body. Even if an ectopic pregnancy was detected at an early stage and removed with a light laparoscopic operation, the body does not immediately return to normal. Changed hormonal levels, endometrium and ovarian function require sufficient time to recover.
For the same reason, the use of oral contraceptives after termination of an ectopic pregnancy is not recommended. There is a known practice when, under normal conditions, a course of oral contraceptives is prescribed to stabilize the menstrual cycle. However, after termination of pregnancy due to hormonal failure, taking oral contraceptives can lead to a deep suppression of ovarian function.
There is a known practice when, under normal conditions, a course of oral contraceptives is prescribed to stabilize the menstrual cycle. However, after termination of pregnancy due to hormonal failure, taking oral contraceptives can lead to a deep suppression of ovarian function.
Physiotherapy has a good therapeutic effect after operations on the fallopian tubes. If you have concomitant diseases (endometriosis, polyps, etc.), you should consult with your doctor. Physiotherapy can be a catalyst for these undesirable pathologies.
Restoration of the menstrual cycle and pregnancy planning
Many women tend to consider the normalization of the menstrual cycle as an opportunity to plan a pregnancy again. However, the state of the fallopian tubes and endometrium of the uterus may be unsatisfactory even when the cycle is restored. It is generally not recommended to become pregnant during the first 3 months after the termination of an ectopic pregnancy. It is better to plan a second pregnancy after consultation with your doctor.
If the fallopian tubes are preserved, the possibility of spontaneous pregnancy cannot be ruled out. If one of the tubes was removed during the operation, the possibility of natural conception due to the second fallopian tube is allowed. However, it is worth remembering that after a tubeectomy, the remaining tube also needs therapy, especially if intra-abdominal bleeding has been observed.
| service | price |
| Reception | 3000 rub |
| ultrasound | 2100 rub |
| Operation cost | from 20,000 rubles |
see all prices
You can also
Get an examination and treatment on credit or in installments!
For more information, please contact the clinic managers by phone:
+7 (495) 979-00-00, +7 (495) 211-71-78, 8-800-234-17-10 order a call
our advantages
Low prices and
impeccable service
No queues
Positive reviews
and best results
Convenient
free parking
step by step
leave a request
Our operator
will advise you
by phone
and make an appointment
at a convenient time for you
consultation
Come for a consultation
with all available test results
and everything you need to show to the doctor
surveys
In our clinic
you will be given all the
necessary tests
repeated
consultation
after
test results are ready,
to evaluate the received data and prescribe
treatment
sign up
media about us
Reviews
video reviews guest book
all reviews
Ectopic pregnancy - American Medical Clinic
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition. This complication is very dangerous for a woman. If an ectopic pregnancy is not removed on time, there is a risk of intra-abdominal bleeding. And this, in turn, threatens the health and life of the patient. Therefore, noticing the early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, you should immediately see a doctor. This condition requires urgent medical attention.
This complication is very dangerous for a woman. If an ectopic pregnancy is not removed on time, there is a risk of intra-abdominal bleeding. And this, in turn, threatens the health and life of the patient. Therefore, noticing the early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, you should immediately see a doctor. This condition requires urgent medical attention.
The uterus is a muscular organ that exists to bear a child. However, sometimes the egg, having been fertilized, does not enter the uterine cavity, but is fixed in the ovaries, tubes or abdominal cavity. As a result, there are pains during an ectopic pregnancy and a rupture of an organ (for example, a fallopian tube) is possible.
Why does an ectopic pregnancy occur?
Causes of ectopic pregnancy may be as follows:
- pelvic inflammatory disease, especially chronic
- endometriosis
- congenital malformation of the tubes
- IVF complication
The question of why an ectopic pregnancy occurs worries many women. However, it is possible to establish the true causes of an ectopic pregnancy only after a laparoscopic operation to remove it.
However, it is possible to establish the true causes of an ectopic pregnancy only after a laparoscopic operation to remove it.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
Many women wonder how to distinguish an ectopic pregnancy from a normal one. Doctors recommend to carefully monitor your condition and pay attention to the main symptoms of ectopic pregnancy:
- pain in ectopic pregnancy
- bleeding
Pain during an ectopic pregnancy is aching, cramping in nature. Painful sensations appear from the moment of attachment of the fetal egg. If a rupture occurs, bleeding begins, pain radiates to the anus, and can spread throughout the abdomen, a woman may feel pain during an ectopic pregnancy while urinating or trying to empty the intestines.
Bleeding during an ectopic pregnancy occurs in the abdominal cavity. However, due to a drop in hormone levels, uterine bleeding is often observed. The volume of allocations is usually meager. Bleeding during an ectopic pregnancy lasts a long time.
Bleeding during an ectopic pregnancy lasts a long time.
Both of these symptoms require immediate medical attention. Rarely, bleeding during an ectopic pregnancy is accompanied by fever, which signals the onset of the inflammatory process.
Early ectopic pregnancy: treatment
There is only one possible way to treat pathology - the removal of an ectopic pregnancy by surgery. However, before proceeding with the operation, doctors conduct a diagnosis. External signs of ectopic pregnancy must be confirmed by laboratory and instrumental methods of examination.
There are three ways that help to make a diagnosis:
1) pregnancy can be diagnosed if menstruation is delayed by 2-3 days. To do this, conduct a test for hCG. There are no signs of an ectopic pregnancy yet.
2) After one and a half to two weeks from the start of the delay, an ultrasound examination can be performed. If a fetal egg is not visualized in the area of \u200b\u200bthe uterus, a second appointment will be scheduled in a few days.