How early do cramps start in pregnancy
10 Early Signs That You Might Be Pregnant
Written by Joseph Saling
In this Article
- Do All Women Get Early Symptoms of Pregnancy?
- Spotting and Cramping
- Breast Changes
- Fatigue
- Nausea (Morning Sickness)
- Missed Period
- Other Early Symptoms of Pregnancy
Are you wondering if you might be pregnant? The only way to know for sure is by taking a pregnancy test.
But there are early symptoms of pregnancy that may point to the possibility. Here's what to look for.
Do All Women Get Early Symptoms of Pregnancy?
Every woman is different. So are their experiences of pregnancy. Not every woman has the same symptoms or even the same symptoms from one pregnancy to the next.
Also, because the early symptoms of pregnancy often mimic the symptoms you might experience right before and during menstruation, you may not realize you're pregnant.
What follows is a description of some of the most common early symptoms of pregnancy. You should know that these symptoms may be caused by other things besides being pregnant. So the fact that you notice some of these symptoms does not necessarily mean you are pregnant. The only way to tell for sure is with a pregnancy test.
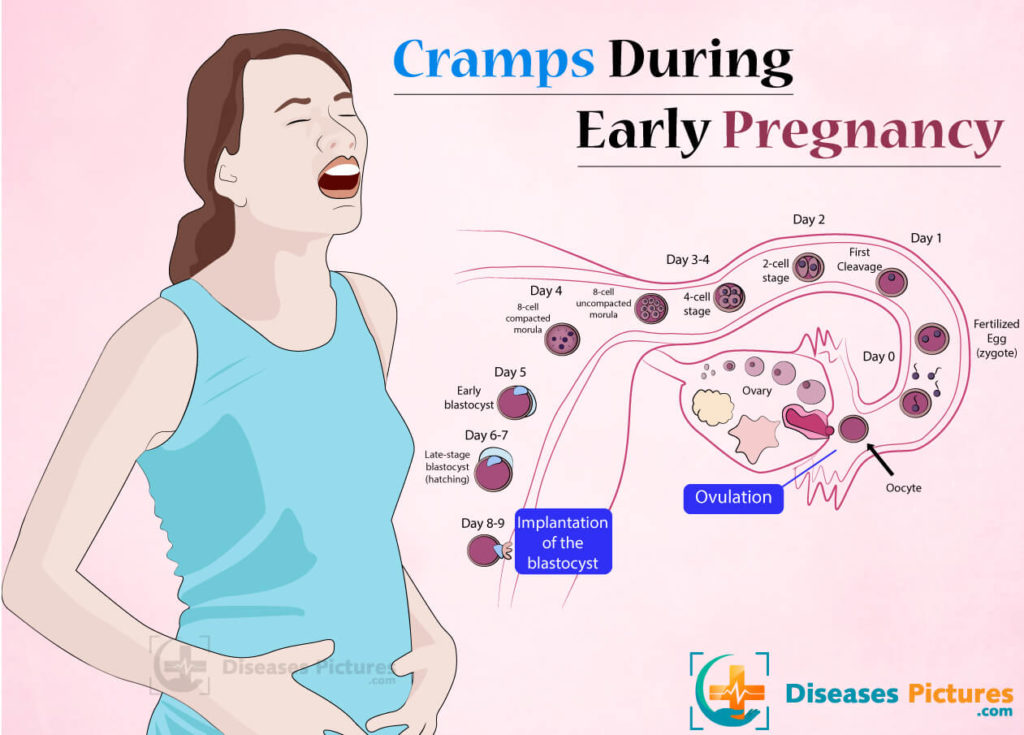
Spotting and Cramping
After conception, the fertilized egg attaches itself to wall of the uterus. This can cause one of the earliest signs of pregnancy -- spotting and, sometimes, cramping.
That's called implantation bleeding. It occurs anywhere from six to 12 days after the egg is fertilized.
The cramps resemble menstrual cramps, so some women mistake them and the bleeding for the start of their period. The bleeding and cramps, however, are slight.
Besides bleeding, a woman may notice a white, milky discharge from their vagina. That's related to the thickening of the vagina's walls, which starts almost immediately after conception. The increased growth of cells lining the vagina causes the discharge.
This discharge, which can continue throughout pregnancy, is typically harmless and doesn't require treatment. But if there is a bad smell related to the discharge or a burning and itching sensation, tell your doctor so they can check on whether you have a yeast or bacterial infection.
But if there is a bad smell related to the discharge or a burning and itching sensation, tell your doctor so they can check on whether you have a yeast or bacterial infection.
Breast Changes
Breast changes are another very early sign of pregnancy. A woman's hormone levels rapidly change after conception. Because of the changes, their breasts may become swollen, sore, or tingly a week or two later. Or they may feel heavier or fuller or feel tender to the touch. The area around the nipples, called the areola, may also darken.
Other things could cause breast changes. But if the changes are an early symptom of pregnancy, keep in mind that it is going to take several weeks to get used to the new levels of hormones. But when it does, breast pain should ease up.
Fatigue
Feeling very tired is normal in pregnancy, starting early on.
A woman can start feeling unusually fatigued as soon as one week after conceiving.
Why? It's often related to a high level of a hormone called progesterone, although other things -- such as lower levels of blood sugar, lower blood pressure, and a boost in blood production -- can all contribute.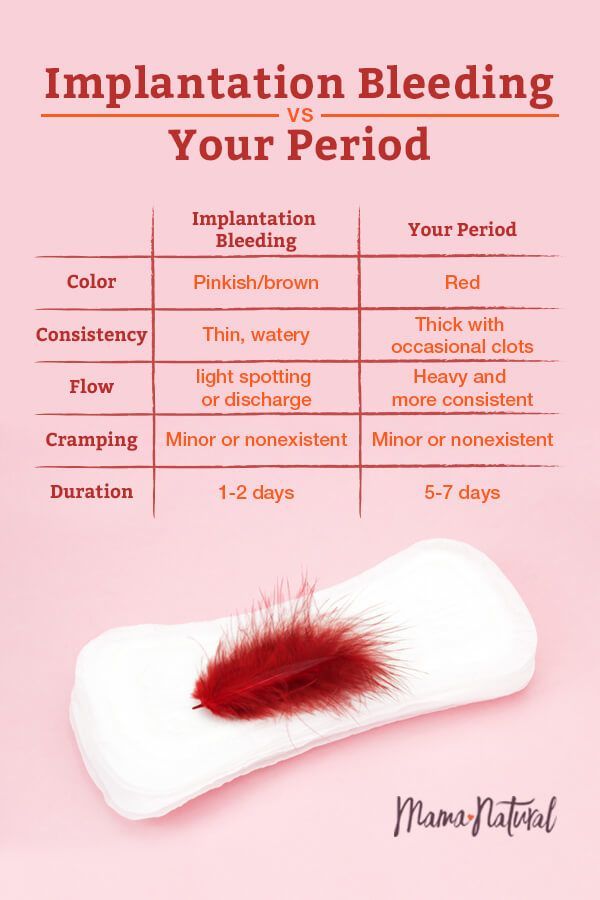
If fatigue is related to pregnancy, it's important to get plenty of rest. Eating foods that are rich in protein and iron can help offset it.
Nausea (Morning Sickness)
Morning sickness is a famous symptom of pregnancy. But not every pregnant woman gets it.
The exact cause of morning sickness is not known but pregnancy hormones likely contribute to this symptom. Nausea during pregnancy may occur at any time of the day but most commonly in the morning.
Also, some women crave, or can't stand, certain foods when they become pregnant. That's also related to hormonal changes. The effect can be so strong that even the thought of what used to be a favorite food can turn a pregnant woman's stomach.
It's possible that the nausea, cravings, and food aversions can last for the entire pregnancy. Fortunately, the symptoms lessen for many women at about the 13th or 14th week of their pregnancy.
In the meantime, be sure to eat a healthy diet so that you and your developing baby get essential nutrients. You can talk to your doctor for advice on that.
You can talk to your doctor for advice on that.
Missed Period
The most obvious early symptom of pregnancy -- and the one that prompts most women to get a pregnancy test -- is a missed period. But not all missed or delayed periods are caused by pregnancy.
Also, women can experience some bleeding during pregnancy. If you are pregnant, ask your doctor what you should be aware of with bleeding. For example, when is bleeding normal and when is it a sign of an emergency?
There are reasons, besides pregnancy, for missing a period. it might be that you gained or lost too much weight. Hormonal problems, fatigue, or stress are other possibilities. Some women miss their period when they stop taking birth control pills. But if a period is late and pregnancy is a possibility, you may want to get a pregnancy test.
Other Early Symptoms of Pregnancy
Pregnancy brings changes in your hormonal balance. And that can cause other symptoms that include:
- Frequent urination.
 For many women, this starts around the sixth or eighth week after conception. Although this could be caused by a urinary tract infection, diabetes, or using diuretics, if you're pregnant, it's most likely due to hormonal levels.
For many women, this starts around the sixth or eighth week after conception. Although this could be caused by a urinary tract infection, diabetes, or using diuretics, if you're pregnant, it's most likely due to hormonal levels. - Constipation. During pregnancy, higher levels of the hormone progesterone can make you constipated. Progesterone causes food to pass more slowly through your intestines. To ease the problem, drink plenty of water, exercise, and eat plenty of high-fiber foods.
- Mood swings. These are common, especially during the first trimester. These are also related to changes in hormones.
- Headaches and back pain. Many pregnant women report frequent mild headaches, and others experience back pain.
- Dizziness and fainting. These may be related to dilating blood vessels, lower blood pressure, and lower blood sugar.
A pregnant woman could have all of these symptoms, or maybe have only one or two. If any of these symptoms become bothersome, talk with your doctor about them so you can make a plan to offset them.
Health & Pregnancy Guide
- Getting Pregnant
- First Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Labor and Delivery
- Pregnancy Complications
- All Guide Topics
Implantation Bleeding: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Written by Lisa Fields
In this Article
- What Is Implantation Bleeding?
- When Does Implantation Bleeding Happen?
- Implantation Bleeding Symptoms
- How Long Does Implantation Bleeding Last?
- Implantation Bleeding Treatment
- Other Causes of Bleeding During Pregnancy
- When to See a Doctor
What Is Implantation Bleeding?
Implantation bleeding is light bleeding from the vagina that happens in some women 10 to 14 days after conceiving a baby.
You may think it’s just a light period, but it’s an early sign of pregnancy. It’s not dangerous, and you don’t need treatment.
It’s not dangerous, and you don’t need treatment.
But heavy bleeding (more than you’d have with a typical period) can be a sign of a problem. Call your doctor if you bleed a lot, with or without fever, chills, or have cramps that get worse.
When Does Implantation Bleeding Happen?
After a sperm fertilizes your egg, the combination becomes an embryo. It travels to your uterus, where it implants itself into the lining.
Sometimes, as the embryo attaches, it causes a little bleeding. This usually happens about the time you would have your period. You may even confuse it with your period and not realize you’re pregnant. Implantation bleeding is normal and doesn’t mean you or your baby will have problems.
Implantation Bleeding Symptoms
Implantation bleeding tends to happen before you notice morning sickness. You might have:
- Blood that’s brown or pinkish
- Blood that’s lighter in flow and doesn’t last as long as your period
- Mild or no cramping
- Unlike your period, you won’t see any blood clots or tissue in the blood
It’s probably implantation bleeding if you have some of the other signs of early pregnancy, including:
- Tender, swollen breasts or nipples
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Upset stomach
- Vomiting (morning sickness)
- Food cravings or aversions
- Mood swings
- Peeing more than usual
If you’re not sure whether you’re having implantation bleeding or your period, take a pregnancy test or talk to your doctor.
How Long Does Implantation Bleeding Last?
Unlike most periods, it usually stops after 1 or 2 days.
Implantation Bleeding Treatment
It will stop on its own. If you're worried that you've bled a lot, call your doctor. They may want to know how much blood you saw and what color it was.
Other Causes of Bleeding During Pregnancy
Many things can cause bleeding in pregnant women, some of them harmless and some serious. If you’re bleeding a lot, with or without pain or cramping at any time, call your doctor.
If you’re pregnant and see blood in your underwear, it may be caused by:
Sex. Hormonal and physical changes may be to blame for this. It should stop on its own.
Fibroids and polyps. Your doctor might do some tests to check for these growths on your uterus.
Cervical problems. Conditions like infection or growths on your cervix can also cause bleeding.
Infection.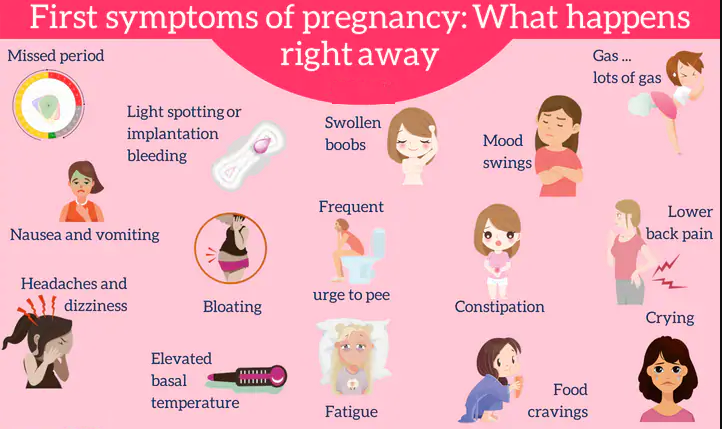 Sexually transmitted diseases like trichomoniasis can cause light bleeding as well as more serious problems. Starting treatment as soon as possible will keep your baby healthy.
Sexually transmitted diseases like trichomoniasis can cause light bleeding as well as more serious problems. Starting treatment as soon as possible will keep your baby healthy.
Ectopic pregnancy. This is when an embryo implants outside your uterus. You may have bleeding with pain and cramps. It’s dangerous and needs medical care right away.
Miscarriage. About 15% of known pregnancies end during the first few months. Most women bleed and cramp afterward. Call your doctor right away if you know that you're pregnant and you have these symptoms.
When to See a Doctor
Call your doctor if the bleeding doesn’t stop after a few days or if you’re worried about how much you are bleeding.
Interventions for leg cramps during pregnancy
What is the problem?
Leg cramps manifest themselves as sudden, intense involuntary contractions of the leg muscles. This is a common problem during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester. They are painful and can interfere with daily activities, disrupt sleep, and reduce quality of life. Various types of interventions are used to treat leg cramps during pregnancy, including medications, electrolytes (magnesium, calcium, sodium) and vitamins, as well as non-drug therapies such as muscle stretching. nine0005
They are painful and can interfere with daily activities, disrupt sleep, and reduce quality of life. Various types of interventions are used to treat leg cramps during pregnancy, including medications, electrolytes (magnesium, calcium, sodium) and vitamins, as well as non-drug therapies such as muscle stretching. nine0005
Why is this important?
The aim of this review was to find out which treatment for leg cramps during pregnancy is effective and safe.
What evidence did we find?
In September 2019, we searched for evidence and identified eight randomized controlled trials in 576 women 14 to 36 weeks pregnant comparing magnesium, calcium, calcium with vitamin D or B vitamins versus placebo or no treatment, and compared vitamin C with calcium. All drugs were given as tablets to chew or swallow. nine0005
Magnesium supplements may reduce the incidence of leg cramps in women compared with placebo or no treatment, although studies have not been consistent. Different studies have assessed the effect of magnesium supplementation differently. Some studies have shown magnesium to help reduce the incidence of leg cramps, while others have shown little or no effect. Data on the effect of magnesium on pain reduction was also inconclusive, with only one study showing a reduction in pain intensity, while others showed no difference. Differences in the occurrence of side effects such as nausea and diarrhea were negligible or non-existent. nine0005
Different studies have assessed the effect of magnesium supplementation differently. Some studies have shown magnesium to help reduce the incidence of leg cramps, while others have shown little or no effect. Data on the effect of magnesium on pain reduction was also inconclusive, with only one study showing a reduction in pain intensity, while others showed no difference. Differences in the occurrence of side effects such as nausea and diarrhea were negligible or non-existent. nine0005
Calcium did not always reduce the incidence of leg cramps in women after treatment compared to those who did not receive any treatment. It also found that the evidence was of very low quality, so we cannot be sure of the results.
More women who received B-vitamin supplements made a full recovery compared to those who received no treatment; however, these results were based on a small sample size and the study had design limitations. nine0005
Frequency of leg cramps did not differ between women receiving calcium and women receiving vitamin C. with placebo.
with placebo.
What does this mean?
The quality of the evidence was low to very low. This was mainly due to small study sample sizes and study design weaknesses. Four studies were well-conducted and presented their reports. The remaining four had flaws in their design: in several studies, women were not best assigned to different treatment groups, and in two studies, women knew whether they were receiving treatment or not. Adverse effects, such as the effect of treatment on complications of pregnancy, childbirth and child, were not reported. Several studies have focused primarily on serum calcium and magnesium levels. The frequency and intensity of seizures and duration of pain were not uniformly reported, and there was often no information on whether they were assessed during treatment, at the end of treatment, or after treatment was discontinued. nine0005
It is not clear from the evidence reviewed whether any oral interventions (magnesium, calcium, calcium with vitamin D, B vitamins, vitamin D, or vitamin C) are an effective and safe treatment for leg cramps during pregnancy. Supplements can have different effects depending on how women usually take them. None of the trials looked at forms of treatment such as muscle stretching, massage, relaxation, or heat therapy.
Supplements can have different effects depending on how women usually take them. None of the trials looked at forms of treatment such as muscle stretching, massage, relaxation, or heat therapy.
Translation notes:
Translation: Luzan Maria Alexandrovna. Editing: Yudina Ekaterina Viktorovna. Russian translation project coordination: Cochrane Russia - Cochrane Russia, Cochrane Geographic Group Associated to Cochrane Nordic. For questions related to this transfer, please contact us at: [email protected]
Leg cramps - should I be worried? :: ACMD
Short-term painful localized (limited to one muscle or group of muscles) spasms are called crumpy . They can occur in any muscle group but are most common in the calf muscles. And it looks like this: we lie on our back and after a slight movement of the toes, “ convulsive pains in the calf muscles ” appear, tightening and squeezing, extremely unpleasant. Such pain can also occur when we take off our shoes. By its nature, this is a long tonic contraction of the muscle, lasting from a few seconds to minutes.
By its nature, this is a long tonic contraction of the muscle, lasting from a few seconds to minutes.
Most often, krampi is associated with diseases of the lumbar spine (for example, osteochondrosis), in which, sooner or later, the nutrition of the nerve endings and muscles in the legs is disturbed, so they do not receive all the necessary nutrients and begin to work “wrongly”. Such cramps occur after physical exertion or at night in the supine position. nine0005
Separately, stenosolia are distinguished - these are compressive pains in the soleus muscle (it is located deeper under the calf), also very unpleasant pains, but a little weaker than cramps. This muscle has a special structure and is very sensitive to microcirculation disturbances in it. Stenosolia often occurs when we lie on our side or stand for a long time, walk around, sit down.
Cramps in the calf muscles (cramps) causes
Cramps can occur as a symptom of circulatory disorders in stenosing diseases of the vessels of the legs (may be one of the symptoms of intermittent claudication). Patients with diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism fall into the risk group for the development of diseases of the vessels of the legs, since these diseases will always develop a violation of cholesterol metabolism and atherosclerotic plaques will form on the vessels of the legs as well. This also includes "malicious smokers". nine0005
Patients with diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism fall into the risk group for the development of diseases of the vessels of the legs, since these diseases will always develop a violation of cholesterol metabolism and atherosclerotic plaques will form on the vessels of the legs as well. This also includes "malicious smokers". nine0005
Cramps can occur after active physical exertion on the legs, when squatting, and in the muscles of the hands, repetitive spasms can occur during prolonged use of the mouse.
There are also spontaneous cramps in the muscles of the arms and legs. They may be due to a hereditary feature and do not require special treatment.
But cramps, which occur spontaneously and often in adolescence, should be closely looked at, since they may be the first sign of a hereditary enzyme defect in McArld's disease (Type V glycogenosis, myophosphorylase deficiency). nine0005
And in adults, spontaneous cramps can be the first symptom of a severe neurological disease - amyotrophic lateral sclerosis .
Leg cramps and Magnesium
Although cramps can be a simple manifestation of metabolic disorders in the muscle, for example, with chronic magnesium deficiency.
Perhaps this is a very common cause of . Magnesium is a unique mineral, it takes part in hundreds of biochemical processes in the body (according to modern concepts, about 300 biochemical processes in the human body occur with the participation of magnesium). This element is needed everywhere, but it comes with food in insufficient quantities, since we eat foods rich in magnesium in small quantities (bran, nuts, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds). But magnesium is consumed intensively during stressful conditions (it goes to the work of the nervous system), during heavy physical exertion and in the heat (excreted with sweat), when drinking a large amount of liquid (excreted in the urine) and with frequent intake of alcoholic beverages. And if a muscle lacks magnesium, it is more prone to tension and spasms. For the same reason (magnesium deficiency), the eyelid may “twitch” - the circular muscle of the eye is tender and very sensitive to a lack of magnesium. nine0005
For the same reason (magnesium deficiency), the eyelid may “twitch” - the circular muscle of the eye is tender and very sensitive to a lack of magnesium. nine0005
I was recently asked if there is an alternative to magnesium replenishment other than using Magne B6. There are other preparations containing magnesium: magnerot, magnicum. It is believed that magnesium is well absorbed from the intestine in the presence of pyridoxine (vitamin B6) or in the form of a salt of orotic acid, but in food magnesium often comes with calcium or phosphorus, and they prevent magnesium from being absorbed in the intestine. With the culinary processing of products, its amount is significantly reduced. Yes, and in food it is contained less and less due to the rapid development of "new technologies". You can, of course, provide yourself with magnesium with the help of proper nutrition, but this must be really wanted. nine0005
Leg cramps and Calcium
Calcium is also responsible for muscle contraction. And calcium deficiency (hypocalcemia) can be a metabolic cause of leg cramps.
And calcium deficiency (hypocalcemia) can be a metabolic cause of leg cramps.
Calcium in the daytime is spent on the work of muscles, and at night it goes to build bones.
As a rule, it is difficult to diagnose hypocalcemia in the initial stages. Small muscle spasms can occur both in the muscles in the legs and in the muscles of the back, and sometimes even in the muscles of the face. There may be a parallel sensation of "tingling" in the tip of the tongue, lips and fingers. Only in the already advanced stages does “carpopedal spasm” develop (prolonged and very painful strong flexion of the muscles of the flexors of the foot and fingers) and tetany attacks (with the presence of laryngospasm and generalized convulsive seizures that threaten life). nine0005
But calcium deficiency can be caused by many different diseases. The most common include hypoparathyroidism (deficiency of the parathyroid hormone of the parathyroid gland leads to a violation of the level of calcium in the blood), vitamin D deficiency (impaired absorption of calcium in the intestine), with chronic kidney disease (due to a decrease in calcium reabsorption in the kidneys, it is intensively excreted, except in addition, the synthesis of vitamin D in the kidneys decreases), with acute pancreatitis (with fatty necrosis, calcium binds to fatty acids, the secretion of glucagon and calcitonin also increases), and taking certain medications (antacids, rifampicin, phenobarbital, phenytoin, agents to lower calcium levels in blood).