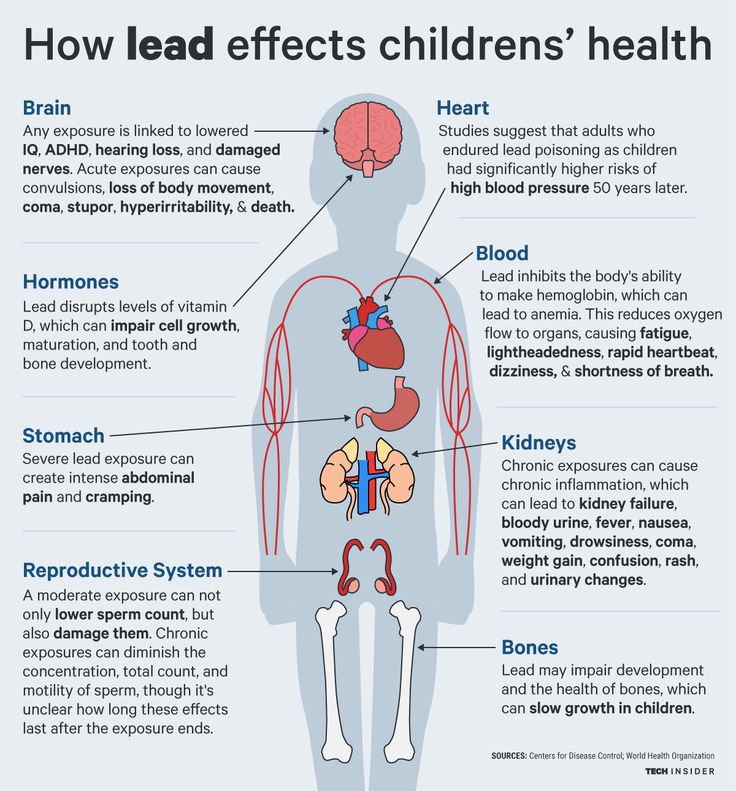
How does technology affect child development
How Does Technology Affect Children?
With media’s expansion to newer formats, including cellphones and tablets, increased portability and access have increased the use of technology – not just for business professionals, but for children. Although TV time is still the main medium for children, clocking in at over four hours per day on average, according to a recent study from the American Academy of Pediatrics, almost a third of that time is spent not in front of the television, but on a computer, tablet or cellphone.
What is also noteworthy is that the cellphone and tablet may not be borrowed from a parent, considering that cellphone ownership among 12- to 17-year-olds has spiked in the past decade, skyrocketing to 45% of teens with their own cell phones in 2004 to an estimated 75%. In addition to watching television programming, preteens and teenagers text and access social media most often.
The question is not if children are increasingly exposed to technology – that’s apparent – but what that technology exposure means for childhood development. Some schools are dolling out smartphones for classroom activities, while others tout an entirely technology-free environment. Although there have been passionate voices both for and against technology in childhood development, it’s important to note that the effect of technology on childhood development may be more nuanced than simply a “good” or a “bad” thing. Instead, by better understanding the overall impact, we can collectively enhance the positive and work to reduce the negative.
1. Harms Attention Spans
Perhaps the concern raised most often when it comes to children and technology is the impact on attention span. The research supports this concern. Jim Taylor, Ph.D., wrote in Psychology Today that heightened technology exposure might actually be changing the way children’s brains are wired. Why? Because, unlike an adult’s brain, a child’s brain is still developing, and as a result, malleable. When children are exposed to technology at high rates, their brain may adopt an internet approach to thinking – quickly scanning and processing multiple sources of information. Developing brains are particularly vulnerable to this, and where previous generations may have spent much more time reading, imagining, or participating in activities that require focus attention, brains in children exposed to high volumes of technology may adapt to frequent visual stimulation, rapid change, and little need for imagination.
Developing brains are particularly vulnerable to this, and where previous generations may have spent much more time reading, imagining, or participating in activities that require focus attention, brains in children exposed to high volumes of technology may adapt to frequent visual stimulation, rapid change, and little need for imagination.
2. Reduces Self-Soothing and Self-Regulation
Anyone who has raised a toddler would acknowledge the beauty of distraction in calming a toddler in a tantrum. But parents today have a tempting distraction always available: technology. And although the immediate handing over of a cellphone or tablet may calm a raging preschooler, the American Academy of Pediatrics states that the distraction of mobile devices may negatively affect children’s opportunity to learn how to self-soothe and regulate in those moments.
3. Increases Aggression
Multiple studies, including one by the Seattle Children’s Research Institute and the Journal of Youth and Adolescence, found a correlation between simulated violence, often found in popular video games, and heightened aggression. Exposure to violence was found to make children and teens more likely to argue with peers or teachers, and less empathetic and impacted by actual violence.
Exposure to violence was found to make children and teens more likely to argue with peers or teachers, and less empathetic and impacted by actual violence.
4. Stagnates Physical Activity
Time spent with technology means time spent sitting. Even with portable devices, the activity itself requires users to be mostly still. Given the vast amount of time children are reportedly spending with technology now, this also means that active indoor or outdoor playtime has now largely been replaced by this sedentary activity. In extreme cases, children or teenagers may even forgo other vital activities, likely eating or sleeping, when engaged with a video game or other media.
5. Hurts School Performance
Limited attention spans can also impact how children perform in the classroom. One experienced English teacher told the New York Times that students “lack the attention span to read assignments on their own,” due to cellphones and social media. “You can’t become a good writer by watching YouTube, texting, and e-mailing a bunch of abbreviations,” said Marcia Blondel.
The article also stated that technology habituates brains to constantly switch between tasks, which can lead to reduced attention spans. Michael Rich, executive director of the Center of Media and Child Health in Boston, says that children’s brains get are rewarded for jumping to the next task rather than staying on task, which made lead to “a generation of kids in front of screens whose brains are going to be wired differently.” Anecdotally, some teens admit they prefer the immediate gratification provided by a quick video over slogging through an assigned novel.
Other research suggests the presence of a computer, even if intended for educational purposes, may simply serve as a distraction. In fact, Jacob L. Vigdor, an economics professor at Duke University and researcher, found that when left to themselves, children most often used home computers for entertainment instead of learning. Adult supervision is critical.
6. Limits Interpersonal Interactions
Leaning on a mobile device to distract children can reduce their interpersonal interactions. Whether the need at hand is reconciling with a friend or sibling, entertaining themselves on a long trip, or settling down at night, if children are constantly armed with technology, they’re never to navigate an interaction with a friend, parent, or sibling that may be critical to solving the problem long-term. For older children and teens, technology may serve as a diversion from troubling issues: not fitting in at school, parents arguing at home, etc. But instead of learning to navigate these issues children and teens may find that technology can give the illusion of shelter – without arming them with the interpersonal skills needed to navigate uncomfortable situations in adult life.
Whether the need at hand is reconciling with a friend or sibling, entertaining themselves on a long trip, or settling down at night, if children are constantly armed with technology, they’re never to navigate an interaction with a friend, parent, or sibling that may be critical to solving the problem long-term. For older children and teens, technology may serve as a diversion from troubling issues: not fitting in at school, parents arguing at home, etc. But instead of learning to navigate these issues children and teens may find that technology can give the illusion of shelter – without arming them with the interpersonal skills needed to navigate uncomfortable situations in adult life.
7. Affects Emotional Development
Even in the hands of only parents and caregivers, technology may have an impact on childhood development. Observation is the primary way children learn, as they listen to learn the language, observe conversations, read facial expressions and watch how others navigate emotional situations. Rampant screen time seeps away intentionally, connected time with children that is critical to emotional development. For older children and teens, a heavy reliance on technology to communicate hinders their people skills, and may even develop a sense of detachment from others’ feelings, according to Dr. Gary Small, head of UCLA’s memory and aging research center.
Rampant screen time seeps away intentionally, connected time with children that is critical to emotional development. For older children and teens, a heavy reliance on technology to communicate hinders their people skills, and may even develop a sense of detachment from others’ feelings, according to Dr. Gary Small, head of UCLA’s memory and aging research center.
For young children, the impact may be felt as screen time replaces time previously devoted to playing, peer interaction, and exploration, which are thought to foster empathy, problem-solving skills, curiosity, intelligence, and listening skills, says Catherine Steiner-Adair, a clinical psychologist affiliated with Harvard. Researchers from Boston University also posit that mobile phone use may prevent children from developing empathy, social and problem-solving skills.
8. Helps Visual-Spatial
In particular, video games have been proven to help develop peripheral visual skills, according to Science Daily. More broadly, general visual-motor skills (tracking objects or visually searching for something) may improve with technology use.
More broadly, general visual-motor skills (tracking objects or visually searching for something) may improve with technology use.
9. Helps Multi-Tasking
When applied appropriately (as opposed to driving and texting, for example) a well-honed ability to multi-task that is brought on with technology use equips children with necessary skill for modern adult life, according to PsychCentral.
10. Aids Learning
Internet users flex their decision-making and problem-solving brain functions more frequently, and are more likely to handle rapid cyber searches well. And, technology may present the next wave of vocational training for students who may not thrive in traditional academic subjects. For example, the New York Times tells the story of Woodside High’s audio class, filled with at-risk students who are engaged, participating and learning. Not only is the technology-driven class inspiring students to show up, but it’s also providing occupational learning, and presents an opportunity to trigger interest in other subjects. Technology can also support education in more traditional ways, with engaging games to boost vocabularies or through electronic books.
Technology can also support education in more traditional ways, with engaging games to boost vocabularies or through electronic books.
As with nearly everything in life, technology is not a problem when used in moderation. However, the numbers suggest most haven’t yet struck a consistent healthy balance, as reported averages are well above what the American Academy of Pediatricians recommends for electronic media. Considering the AAP recommends no exposure before age 2, and a limited 1-2 hours per day with entertainment media, it’s safe to say most children are exceeding the suggested limits. We need to pursue a technology balance for our children, to capitalize on the benefits and alleviate the negative effects of technology in childhood development.
Related Reading:
When Staying Connected Means Staying Stressed
How Smartphones Are Contributing to the Loneliness Epidemic
Why Facebook is Making Us Sad: Social Comparison
Impact of Technology on Kids Today and Tomorrow.

Skip to contentSkip to Live Chat
- Admission Requirements
- Teachers College Admissions Requirements
- College of Business Admissions Requirements
- College of IT Admissions Requirements
- College of Health Professions Admissions Requirements
- Tuition and Fees
- Tuition—College of Business
- Tuition—Teachers College
- Tuition—College of IT
- Tuition—College of Health Professions
- Financial Aid
- Applying for Financial Aid
- State Grants
- Consumer Information Guide
- Your Financial Obligations
- Responsible Borrowing Initiative
- Higher Education Relief Fund
- Scholarships
- Corporate Reimbursement
- Graduate Outcomes
- Our Students & Graduates
- Alumni Services
- Inspiring Stories of Student Success
- Return on Investment
- Diversity
- Learning at WGU
- Accreditation
- How You'll Learn
- Student Reviews
- Partner Organizations
- Paying for School
- Our Faculty
- Military and Veterans
- Tuition and Funding
- Part-Time Options
- Veterans Virtual Resource Center
- Education Outcomes
- Juggling Life and School
- Getting a Raise or Promotion
- Starting a New Career
- Taking the Next Step in Education
- Career Guides
- Blog
Online Degrees
-
Admissions
-
Tuition & Financial Aid
- Tuition and Fees
- Tuition—College of Business
- Tuition—Teachers College
- Tuition—College of IT
- Tuition—College of Health Professions
- Financial Aid
- Applying for Financial Aid
- State Grants
- Consumer Information Guide
- Your Financial Obligations
- Responsible Borrowing Initiative
- Higher Education Relief Fund
- Scholarships
- Corporate Reimbursement
-
Student Success
- Graduate Outcomes
- Our Students & Graduates
- Alumni Services
- Inspiring Stories of Student Success
- Return on Investment
- Diversity
- Learning at WGU
- Accreditation
- How You'll Learn
- Student Reviews
- Partner Organizations
- Paying for School
- Our Faculty
- Military and Veterans
- Tuition and Funding
- Part-Time Options
- Veterans Virtual Resource Center
- Education Outcomes
- Juggling Life and School
- Getting a Raise or Promotion
- Starting a New Career
- Taking the Next Step in Education
- Career Guides
- Blog
-
About WGU
October 3, 2019
Hand a smartphone or tablet to a toddler, chances are they’ll figure out how to open it and make some in-app purchases in a matter of seconds.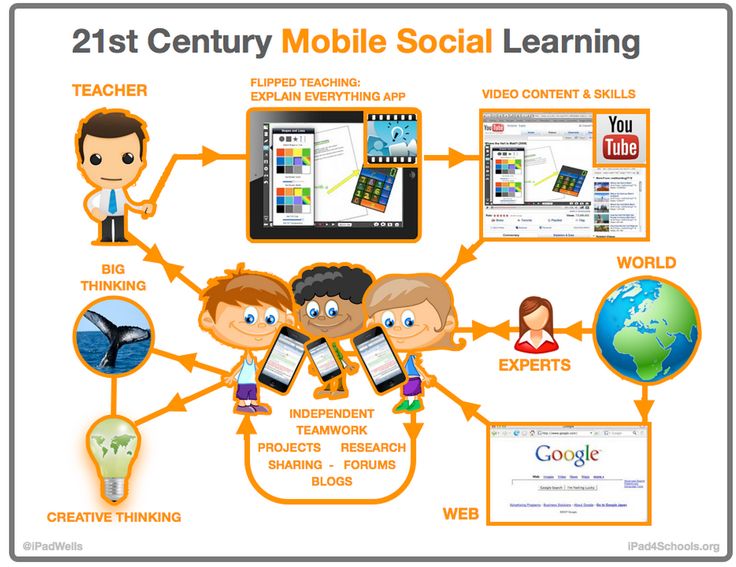 The technological boom means that children are becoming computer experts at a very young age. Elementary school kids have classes on computers, and many of them have been using their computers and tablets at home well before they started school. As kids are learning from a very young age about technology, they’re making huge strides as they grow in being prepared for schooling, future careers, innovation, and more. Your kids may even be able to help you with your online coursework at WGU!
The technological boom means that children are becoming computer experts at a very young age. Elementary school kids have classes on computers, and many of them have been using their computers and tablets at home well before they started school. As kids are learning from a very young age about technology, they’re making huge strides as they grow in being prepared for schooling, future careers, innovation, and more. Your kids may even be able to help you with your online coursework at WGU!
However, with all this constant immersion in technology, there are some very real concerns about how this tech impacts childhood development. We are wandering into unknown territory as generations past have never had this same kind of constant technological immersion. But experts are starting to see what technology at this level can do to children and their future. Many of our WGU students are parents, and we want to help you
Kids have access to screens all around them. Many homes have multiple television sets, computers, tablets, and phones for children to find and play with.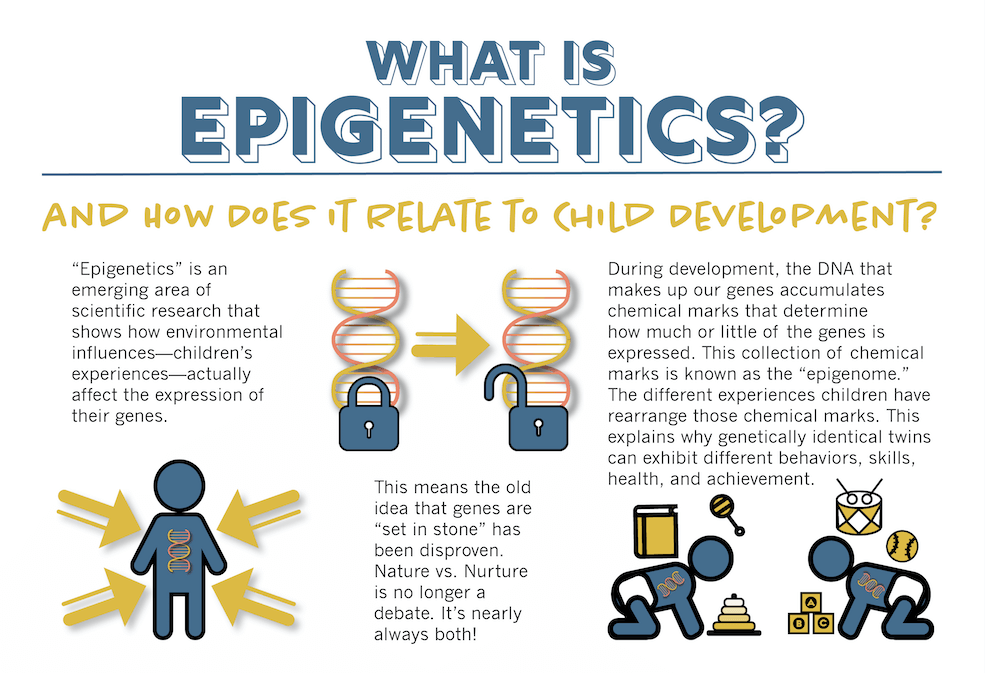 And some children even have access to their own tablet and phone, starting at a young age. Research shows that the average 8- to 10-year-old spends almost 8 hours a day with a variety of media, and older children and teenagers spend around 11 hours per day with media. That time adds up, and young people are spending more time with technology than they do in school.
And some children even have access to their own tablet and phone, starting at a young age. Research shows that the average 8- to 10-year-old spends almost 8 hours a day with a variety of media, and older children and teenagers spend around 11 hours per day with media. That time adds up, and young people are spending more time with technology than they do in school.
Children and teenagers around the country aren’t cutting down their media consumption either. Some teenagers say they send thousands of text messages each month, stay up until 2 AM scrolling social media, and spend hours each day playing video games. And this has continued to get more intense over time, as more apps and options arise to distract kids.
While many people see the negative impact of such technology usage, there also pros. The real question is what can parents and teachers do to harness technology in useful ways, without letting kids become slaves to it and the negative effects it can have on their lives.
Learn about the negative effects of technology on young children and teenagers.
Lower attention span. Teachers, parents, and students themselves find that technology can have a direct impact on attention spans. The immediacy of technological interactions make waiting harder for children. With technology, they aren’t forced to wait. They can have their TV show immediately, they don’t get bored because they always have something to entertain them. Technology moves fast, instant responses and instant gratification are impacting attention spans for young children and teenagers alike.
Increased risk and lack of privacy. Teenagers and children have grown up in a technological world, and the idea of privacy is somewhat foreign to them. Cybersecurity is a huge element of tech today, but it isn’t always perfect. Hackers and criminals can utilize technology to steal identities and harass children. Technology has created an increase of theft, privacy issues, harassment, and more.
 The IT industry is in need of cybersecurity professionals who can help make technology more safe for children, so consider getting started on your degree today.
The IT industry is in need of cybersecurity professionals who can help make technology more safe for children, so consider getting started on your degree today.Risk of depression. Teenagers and children who report more time using media are more likely to also report mental health issues. Depression is a key issue that is correlated with more media use. This has increased suicide rates and has lead to more youth needing mental health interventions like medicine and counseling. Experts believe time spent on social media or using technology can directly be tied to increased depression.
Obesity. Children who spend more time inside on their phones or tablets don’t spend as much time running and playing outside. They establish habits of technology use that doesn’t involve exercise. This can lead to increased obesity rates in children and young adults.
Falling grades. Many students today can see their grades take a hit when they spend more time with technology.
 Increasing technology usage means less time spent on homework, and the kind of developmental changes technology can bring can make students struggle with homework like reading and writing.
Increasing technology usage means less time spent on homework, and the kind of developmental changes technology can bring can make students struggle with homework like reading and writing. Bullying. As technology flourishes, so does bullying. Children and teens are using technology and social media to bully other kids, without having to face them. Often called cyberbullying, this trend is increasing and getting more popular with even younger students.
Social interaction issues. With more time spent on technology, younger children are having issues with face-to-face social interactions. Many seem to prefer to text or talk on social media as opposed to talking to each other in-person. Even when children spend time together, they may spend more time texting or on their phones than actually being together.
While there are many negative impacts that can be connected to technology use, there are many positive impacts as well.
Helping them learn. There are many educational elements of technology that can help children learn. From TV programming to apps on a smartphone or tablet, there are many things that children can be exposed to that can help develop their mind and teach them new things.
Classroom tool. Many teachers have started using technology in classrooms to help students learn. Technology helps teachers reach different kinds of learners, reinforce and expand on concepts, and motivate students in new ways. As more teachers embrace technology, new kinds of learning can take place in classrooms, and more students can be reached in ways that they relate with.
Preparing for future tech careers. As technology continues to grow and flourish, there will be more demand for professionals ready to take on technology careers. When children start getting excited about technology and the potential it offers them from a young age, they’re more prepared for their future and the possibilities it offers.
 Children can start getting technological skills early that they’ll need in the future. If you’re a young student who has the technological background you need for an IT career, consider an IT degree to build your credentials and get you started on the path.
Children can start getting technological skills early that they’ll need in the future. If you’re a young student who has the technological background you need for an IT career, consider an IT degree to build your credentials and get you started on the path. Improved multitasking. Studies show that using technology helps young children learn how to multitask more effectively. While multitasking never allows you to fully focus on one area, students can learn how to listen and type to take notes, or other multitasking activities that can help them succeed in their future.
Improved visual-spatial development. Spatial development can be greatly improved when technology like video games is used to help train young students and children. Practicing visual-spatial skills with video games can be a great way to improve abilities. Visual spatial skills are needed in a variety of things, like map reading, puzzles, and more.
Improved problem solving and decision making.
 Technology often presents children with problems, and helps them learn how to make decisions and solve those problems. Games and apps on tablets or smartphones can help give children the practice they need to find success down the road. When students wisely use technology they can reap huge rewards.
Technology often presents children with problems, and helps them learn how to make decisions and solve those problems. Games and apps on tablets or smartphones can help give children the practice they need to find success down the road. When students wisely use technology they can reap huge rewards.
Parents and adults can help children get the benefits of technology with less of the negative effects. Parents can start by ensuring children under two don’t use screens. They can also play along with children to include face-to-face interactions with technology, and make sure that tech doesn’t interfere for opportunities to play. Parents should also work to set appropriate boundaries including time limits, and model good smartphone use. Cybersecurity software and systems can help ensure that kids stay safe while using technology.
Parents and teachers can watch for quality apps that promote vocabulary, math, literacy, and science. Adults can help make sure kids learn about computer science and IT as part of technology use to give them opportunities for a bright tech future.
Share this:
Subscribe to the WGU Blog
Stay up-to-date with the latest articles, tips, and insights from the team at WGU
Most Popular
Categories
Our focus on your success starts with our focus on four high-demand fields: K–12 teaching and education, nursing and healthcare, information technology, and business. Every degree program at WGU is tied to a high-growth, highly rewarding career path. Which college fits you?
College of Business Online
TEACHERS COLLEGE ONLINE
COLLEGE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY ONLINE
COLLEGE OF HEALTH PROFESSIONS ONLINE
Want to see all the degrees WGU has to offer? View all degrees
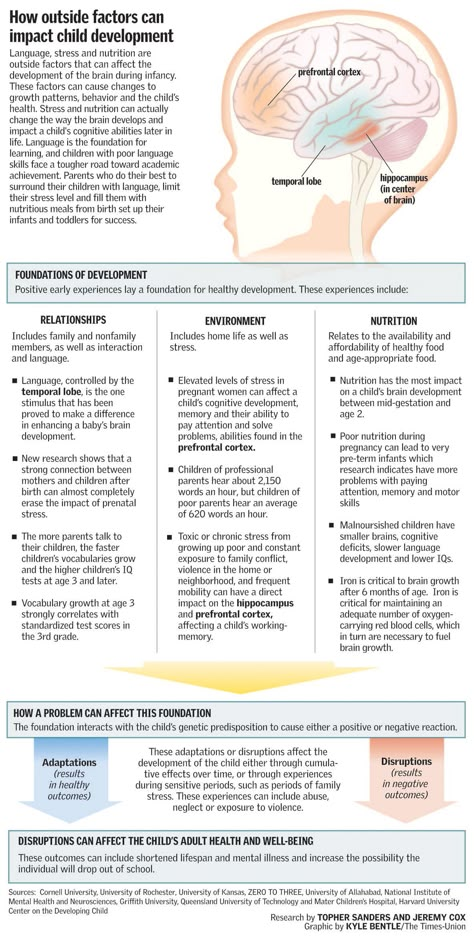
How Technology Affects Children's Development
Reminiscing about the good old days when we were growing up is a memory trip worth taking in trying to understand the challenges children of today face. Just 20 years ago, children played outside all day long, riding bikes, playing sports and building forts. Masters of imaginary play, the children of the past created their own form of play that did not require expensive equipment or parental supervision. The children of the past moved... a lot, and their sensory world was natural and simple. In the past, family time was often spent doing household chores, with children looking forward to seeing each other on a daily basis. The dining table table was the central place where families got together to eat and talk about their day, and after dinner became the center for baking, crafts and homework.
Just 20 years ago, children played outside all day long, riding bikes, playing sports and building forts. Masters of imaginary play, the children of the past created their own form of play that did not require expensive equipment or parental supervision. The children of the past moved... a lot, and their sensory world was natural and simple. In the past, family time was often spent doing household chores, with children looking forward to seeing each other on a daily basis. The dining table table was the central place where families got together to eat and talk about their day, and after dinner became the center for baking, crafts and homework.
Today's families are different. The impact of technology on the 21st century family is breaking its foundation and causing the disintegration of core values that have long been a theme that has held families together. Juggling school, work, home and community life, parents now rely heavily on communication, information and transportation technology to make their lives faster and more efficient. Entertainment technologies (television, internet, video games, iPads, cell phones) have developed so rapidly that families have hardly noticed significant impact and changes in their family structure and lifestyle. A 2010 Kaiser Foundation study found that young children use an average of 7.5 hours of entertainment technology per day, 75 percent of these children have TVs in their bedrooms, and 50 percent of homes in North America have a TV all day long. . The conversation in the dining room left, replaced the "big screen" and took it out.
Entertainment technologies (television, internet, video games, iPads, cell phones) have developed so rapidly that families have hardly noticed significant impact and changes in their family structure and lifestyle. A 2010 Kaiser Foundation study found that young children use an average of 7.5 hours of entertainment technology per day, 75 percent of these children have TVs in their bedrooms, and 50 percent of homes in North America have a TV all day long. . The conversation in the dining room left, replaced the "big screen" and took it out.
Children today use technology for much of their play, making it extremely difficult for them to be creative and imaginative, and limiting their challenges to achieve optimal sensory and motor development. Sedentary bodies bombarded with chaotic sensory stimulation lead to delays in reaching a child's developmental life stages, with a subsequent negative impact on the basic basic skills for achieving literacy. Tough cables for high speed, today's young people enter school struggling with the self-regulation and attention skills needed for learning, ending up as significant behavior management challenges for teachers in the classroom.
So what is the impact of technology on the developing child? The development of children's sensory, motor, and attachment systems has not biologically evolved to accommodate this sedentary but frantic and chaotic nature of modern technology. The impact of rapidly advancing technology on the developing child has led to an increase in physical, psychological and behavioral disorders that health and education systems are only beginning to detect, much less understand. Obesity and diabetes are currently national epidemics in both Canada and the United States, causally linked to technology overload. The diagnosis of ADHD, autism, impaired coordination, developmental delays, slurred speech, learning difficulties, sensory processing disorder, anxiety, depression, and sleep disorders are associated with technology overuse and are increasing at an alarming rate. Taking a closer look at the critical factors for achieving milestones and the subsequent impact of technology on these factors would help parents, teachers and health professionals better understand the complexity of this problem and help create effective strategies to reduce technology use.
The four important factors necessary for the healthy development of a child are movement, touch, connection with man, and exposure to nature. These types of sensory materials provide normal postural development, bilateral coordination, optimal states of arousal, and self-regulation required to achieve the basic skills for eventual school entry. Young children require 2-3 hours per day of active rough and drum play to achieve adequate sensory stimulation of their vestibular, proprioceptive, and tactile systems. The tactile stimulation received by touch, hugging and playing is critical to the development of practice or planned movements. Touch also activates the parasympathetic systems, which reduce cortisol, adrenaline, and anxiety. Nature and "green space" not only have a calming effect on children, but also attract attention and promote learning.
Further analysis of the impact of technology on the developing child indicates that while the vestibular, proprioceptive, tactile and attachment systems are stimulated, the visual and auditory sensory systems are in "overload". This sensory imbalance creates huge problems in overall neurological development as brain anatomy, chemistry and pathways become constantly altered and weakened. Young children who are abused through television and video games are in a high state of adrenaline and stress because the body does not know that what they are watching is not real. Children who misuse technology report constant body sensations of general "shaking", increased breathing and heart rate, and a general state of "restlessness". It can best be described as a permanent hypervigilant sensory system that is still "warning" when an attack is coming. While the long-term effects of this chronic stress on the developing child are unknown, we do know that chronic stress in adults leads to a weakened immune system and a host of serious illnesses and diseases. disorders. Gaming and children
This sensory imbalance creates huge problems in overall neurological development as brain anatomy, chemistry and pathways become constantly altered and weakened. Young children who are abused through television and video games are in a high state of adrenaline and stress because the body does not know that what they are watching is not real. Children who misuse technology report constant body sensations of general "shaking", increased breathing and heart rate, and a general state of "restlessness". It can best be described as a permanent hypervigilant sensory system that is still "warning" when an attack is coming. While the long-term effects of this chronic stress on the developing child are unknown, we do know that chronic stress in adults leads to a weakened immune system and a host of serious illnesses and diseases. disorders. Gaming and children
It is important to bring parents, teachers, and therapists together to help society “wake up” and see how disruptive technologies affect not only our child’s physical, psychological, and behavioral health, but also their ability to learn and maintain personal and family relationships. While technology is a train that will constantly move forward, knowledge of its detrimental effects and actions to balance the use of technology with critical developmental factors will be directed towards sustaining our children. While no one can argue about the benefits of cutting-edge technology in today's world, plugging into these devices could lead to disconnection from what society should value most, children. Instead of cuddling, playing, rough housing, and talking to kids, parents are increasingly resorting to providing their kids with more TVs, video games, and the latest iPads and cell phones, creating a deep and irreversible chasm between parent and child.
While technology is a train that will constantly move forward, knowledge of its detrimental effects and actions to balance the use of technology with critical developmental factors will be directed towards sustaining our children. While no one can argue about the benefits of cutting-edge technology in today's world, plugging into these devices could lead to disconnection from what society should value most, children. Instead of cuddling, playing, rough housing, and talking to kids, parents are increasingly resorting to providing their kids with more TVs, video games, and the latest iPads and cell phones, creating a deep and irreversible chasm between parent and child.
How does technology affect your child's development? - Club for moms. All about pregnancy, baby and toddler development
Tablets and smartphones can be found in every home. It is natural that the baby will show interest in them. The question of whether technologies benefit or harm the development of the baby is very relevant, because there is not yet a sufficiently long time period that would allow us to evaluate this and draw clear conclusions. Parents, teachers, doctors and scientists are and will continue to argue bitterly about this. In this article, we will consider different opinions and let you draw your own conclusions.
Parents, teachers, doctors and scientists are and will continue to argue bitterly about this. In this article, we will consider different opinions and let you draw your own conclusions.
First, the positive aspects of using technology.
One of the arguments is that the world is changing, the baby will have to be included in it. Depriving a child of the opportunity to develop skills in a timely manner can cause problems in the future.
Speaking about specific arguments, an interesting idea was expressed by one researcher from the USA. While the child is very young and can not yet cope with different objects, the excitement that the movement of a finger on the touch screen can achieve a certain result gives the child confidence in his abilities and makes him want to learn new skills. As a result, the baby develops faster.
Another positive aspect that can be used for educational purposes is children's amazing fascination with the screen. There is one little-studied phenomenon of brain activity associated with mirror neurons. In principle, they are responsible for the ability to learn from others, repeating after them, and for the opportunity to be in "someone else's shoes." The most interesting thing is that when observing some action, mirror neurons convince the observer for half a second that he himself is performing the action, and even send signals to the corresponding muscle groups.
In principle, they are responsible for the ability to learn from others, repeating after them, and for the opportunity to be in "someone else's shoes." The most interesting thing is that when observing some action, mirror neurons convince the observer for half a second that he himself is performing the action, and even send signals to the corresponding muscle groups.
Whatever the reason for the screen craze, kindergarten and elementary school teachers recognize that doing different tasks on a tablet keeps a child attentive longer, and it can be a great supplementary material for gaining new knowledge and skills. There are also studies that show that children who use technology learn writing and literacy earlier. We now turn to arguments reflecting the opposite view.
The biggest worries are related to the fact that the child gets used to the "screen society" and does not develop the ability to communicate with people around him. If parents use technology to calm the baby, the child may have problems with self-control, the ability to cope with their emotions in the future. As a negative aspect of the use of smartphones, the fact that the child's creativity is suppressed is also mentioned. Information is presented in a ready-made, attractive form. There is no need to imagine or create anything.
While learning to write and read is a positive development, there is evidence that a child may have problems with science and logic later on. It is also said that when a child gets used to strong stimulation of the senses, his perception changes. In the future, difficulties may arise with the perception of a stream of monotonous information, for example, reading long texts without visual effects and audio effects can cause difficulty.
Summarizing the above, I would like to highlight one thing - in order for the baby to develop comprehensively, it is necessary to occupy him comprehensively. If you get too carried away with monotonous activities, skills from other areas of activity will suffer from this. In relation to technology, parents need to evaluate and intuitively feel what will be the most correct solution for the baby.