How does ssi work for a child
Apply For A Child (Under Age 18) | Disability Benefits
SSI provides monthly cash payments to help meet the basic needs of children who have a physical or mental disability or who are blind. If you care for a child or teenager with a disability, and have limited income and savings or other resources, your child may be eligible for SSI.
SSI Eligibility for Children
Children under age 18 can get SSI if they meet Social Security's definition of disability for children and there are limited income and resources in the household. Social Security defines a disability as:
- The child must have a physical or mental condition(s) that very seriously limits his or her activities; and
- The condition(s) must have lasted, or be expected to last, at least 1 year or result in death.
How to Apply
Tell us you want to apply for SSI for a child
Get Started
Other Ways to Apply
Apply By Phone1
Call us to make an appointment to file an application at 1-800-772-1213. If you are deaf or hard of hearing, you can call us at TTY 1-800-325-0778.
1 If you are in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and received a letter from the Pennsylvania Department of Human Services with a specific phone number, please use that number for the best service.
Begin the Application Online
Applying for SSI requires 2 steps. You will need to complete the online Child Disability Report AND, with the help of a Social Security representative, complete an Application for SSI.
Step 1
TIP: Before completing the Child Disability Report, use our Child Disability Starter Kit to get answers to commonly asked questions about applying for SSI. The kit also includes a worksheet that will help you gather the information you need.
Fill out the online Child Disability Report
The report usually takes about an hour to complete and collects information about the child's disabling condition and how it affects their ability to function.
We will ask you to sign a form that gives the child's doctor(s) permission to give us information about their disability. We need this information so that we can make a decision on the child's claim. In some cases, if the child is over age 12, he or she must sign his or her own medical release.
Start the Child Disability Report
If you previously started a Child Disability Report for this child but did not finish it, you can use your re-entry number to return to your online Child Disability Report.
Step 2
After you submit a report, we will call you within 3-5 business days. Together, we will:
- Review the completed Child Disability Report.
- Discuss whether the income and resources of the household are within the allowed limits.
- Start the SSI application process.
Related Questions
How can I get ready for the disability interview?
- Review the disability starter kit.
 It includes a checklist and a worksheet to help you gather the information you need. Have this information with you at the time of the interview.
It includes a checklist and a worksheet to help you gather the information you need. Have this information with you at the time of the interview. - You can fill out a Child Disability Report.
- For more information visit Benefits for People with Disabilities or call toll-free 1-800-772-1213 (for the deaf or hard of hearing, call TTY 1-800-325-0778).
How will I know what Social Security has decided?
We will send you a letter. It can take 3 to 5 months for us to make a decision on a child’s SSI disability claim. We may also contact you by phone to ask additional questions. Let us know if your address or telephone number changes so that we can get in touch with you.
What if I am more comfortable speaking in a language other than English?
We provide free interpreter services to help you conduct your Social Security business, including helping you complete the SSI application and answering your questions. NOTE: the Child Disability Report is only available in English.
NOTE: the Child Disability Report is only available in English.
Call our toll-free number, 1-800-772-1213. If you need service in Spanish, press 7 and wait for a Spanish-speaking representative to help you. For all other languages, stay on the line and remain silent during our English voice automation prompts until a representative answers. The representative will contact an interpreter to help with your call. You may access the information on this page in Spanish.
Child Disability Starter Kit Fact Sheet
Child Disability Starter Kit - Fact Sheet
What You Should Know Before You Apply for SSI Disability Benefits for a Child
Children from birth up to age 18 may get Supplemental Security
Income (SSI) benefits. They must be disabled and they must have
little or no income and resources. Here are answers to some questions
people ask about applying for SSI for children.
How does Social Security decide if a child is disabled?
Social Security has a strict definition of disability for children.
- The child must have a physical or mental condition(s) that very seriously limits his or her activities; and
- The condition(s) must have lasted, or be expected to last, at least 1 year or result in death.
A state agency makes the disability decision. They review the information you give us. They will also ask for information from medical and school sources and other people who know about the child.
If the state agency needs more information, they will arrange an examination or test for the child, which we will pay for.
How does Social Security decide if a child can get SSI?
Children can get SSI if they meet Social Security’s definition
of disability for children and if they have little or no income
and resources. We also consider the family’s household
income, resources and other personal information.
We also consider the family’s household
income, resources and other personal information.
How will I know what Social Security has decided?
We will send you a letter. It can take 3 to 5 months to decide a child’s SSI disability claim. Let us know if your address or telephone number changes so that we can get in touch with you.
Will my personal information be kept safe?
Yes. Social Security protects the privacy of those we serve. As a federal agency, we are required by the Privacy Act of 1974 (5 U.S.C. 522a) to protect the information we get from you.
What if I am more comfortable speaking in a language other than English?
We provide free interpreter services to help you conduct your
Social Security business.
Other Important Information
SSI is not a medical assistance program. Your state Medicaid agency, local health department, social services office or hospital can help you find your nearest health care agencies. Your Social Security office can also help you find health care agencies.
Medicaid
Medicaid is a health care program for people with low incomes and limited resources. In most states, children who get SSI benefits can also get Medicaid. Even if your child cannot get SSI, he or she may be able to get Medicaid. Your state Medicaid agency, Social Security office or your state or county social services office can give you more information.
State Children's Health Insurance Program (SCHIP)
Children may be able to get health insurance from SCHIP even if
they do not get SSI. SCHIP provides
health insurance to children from working families with incomes
too high to get Medicaid, but who cannot afford private health
insurance. SCHIP provides insurance for prescription drugs and
for vision, hearing and mental health services in all 50 states
and the District of Columbia. Your state Medicaid agency can provide
more information about SCHIP. You can also go to www.insurekidsnow.gov/ or call toll free 1-877-KIDS-NOW (1-877-543-7669) for more information
on your state’s program.
SCHIP provides
health insurance to children from working families with incomes
too high to get Medicaid, but who cannot afford private health
insurance. SCHIP provides insurance for prescription drugs and
for vision, hearing and mental health services in all 50 states
and the District of Columbia. Your state Medicaid agency can provide
more information about SCHIP. You can also go to www.insurekidsnow.gov/ or call toll free 1-877-KIDS-NOW (1-877-543-7669) for more information
on your state’s program.
Other Health Care Services
If the child is under age 16 and we decide he or she is disabled
and can get SSI, we will refer him or her to your state children’s
agencies for social, developmental, educational and medical services.
Even if the child cannot get SSI, these state agencies may be able
to help him or her.
Work Opportunities for Young People Who are Getting SSI
Many young people who get SSI disability benefits want to work. The following information may be helpful.
- We do not count most of a child’s earnings when we figure the SSI payment. We count even less of a child’s earnings if the child is a student.
- We subtract the cost of certain items and services that a child needs to work from his or her earnings in figuring the SSI payment.
- If a child is age 15 or older, he or she can establish a Plan to Achieve Self-Support (PASS). With a PASS, a child can set aside income for a work goal. We will not count this income when we figure the SSI payment.
- A child’s Medicaid coverage can continue even
if his or her earnings are high enough to stop SSI payment,
as long as the earnings are under a certain amount.

Social Security has two programs that can assist young people who get SSI disability benefits and want to go to work:
- Work Incentives Planning and Assistance (WIPA)
- Protection and Advocacy for Beneficiaries of Social Security (PABSS) program
Your local Social Security office can provide more information
about these programs. You can also find more information on our
Work website, www.socialsecurity.gov/work/.
Social Security Administration Rules Regarding Parental Income Credit for a Child with Disabilities to Determine a Child's SSI Eligibility and How Much SSI
This pub will tell you about the "count" rules. This means that a portion of a parent's income and resources are considered in relation to their child when deciding SSI eligibility and benefit amounts. This pub will help you figure out how SSI counts your income. He gives examples. It tells you how to report income.
This pub will help you figure out how SSI counts your income. He gives examples. It tells you how to report income.
Print this publication
Generally, a parent's income and money is "credited" or credited to a child receiving Supplemental Security Income (SSI). This means that a portion of the parent's income and money counts against the child in determining eligibility for SSI. This publication explains the rules for crediting income, namely the rules for determining the amount of a parent's income that is credited to a child with a disability and determining the child's eligibility for any additional social income.
Before looking at the method of calculating the amount of parental income credited to a child and the amount of SSI a child is entitled to, you need to understand how the Social Security Administration's Retrospective Monthly Accounting system works and how are your reporting obligations. The Social Security Administration only considers the income and money of the parent with whom the child on SSI lives. The Social Security Administration does not count the income or money of a parent with whom a child receiving SSI does not live. The income of a foster parent with whom a child receiving SSI lives is counted.1
The Social Security Administration does not count the income or money of a parent with whom a child receiving SSI does not live. The income of a foster parent with whom a child receiving SSI lives is counted.1
Retrospective monthly calculation
The Social Security Administration uses the retrospective monthly calculation system for the period of eligibility for SSI benefits. Section 20 of the Code of Federal Regulations (C.F.R., Code of Federal Regulations), part 416.420. This means that any month's income determines your SSI benefit two months later. For example, income received in January affects the amount of the March SSI check. If, however, any month's income exceeds the maximum amount for any Supplemental Social Income, SSI for that month will be suspended. Therefore, if January's income is so high that your child is no longer eligible for SSI, January's SSI will be suspended. Your child is eligible for automatic reinstatement of benefits without filing a new petition if your income is low enough to make your child eligible for SSI in any of the next 11 months. 2 Title 20 CFR Part 416.1323(b). If within 12 months your income does not drop enough for your child to be eligible for any additional social income, the suspension becomes a cessation of benefits. Title 20 CFR Part 416.1335. If your child's eligibility has been terminated, you will need to file a new petition in order for your child to be eligible for SSI again.
2 Title 20 CFR Part 416.1323(b). If within 12 months your income does not drop enough for your child to be eligible for any additional social income, the suspension becomes a cessation of benefits. Title 20 CFR Part 416.1335. If your child's eligibility has been terminated, you will need to file a new petition in order for your child to be eligible for SSI again.
Obligation to report changes in parental income
In order for the Retrospective Monthly Calculation system to work, the Social Security Administration has a rule that you must notify the Social Security Administration of changes in your income by the 10th of the month following the month in which the change occurred. Section 20 CFR 416.708(c), 416.714.3 If your January income was higher or lower than your December income, you must report the change so that the Social Security Administration is aware of it by the 10th February - or better if before the 5th. You do not need to report if your income for January is the same as your income for December. When the Social Security Administration receives your January income statement, the Social Security Administration must enter the changes into the computer so that your March SSI check will be increased or decreased to reflect the change in your January income.
When the Social Security Administration receives your January income statement, the Social Security Administration must enter the changes into the computer so that your March SSI check will be increased or decreased to reflect the change in your January income.
Below is a sample income statement form to help you meet your reporting obligations. We recommend that you partially complete the report form with the address of your department of the Social Security Administration and all the information in the heading "regarding". And then make more photocopies of the partially completed form.
For each month you have a change in income, write the date you signed the document, the month you are reporting for, and your income information at the bottom of the form. Then sign the form. Only one parent must sign the report form. Make a photocopy of the completed form or complete the second form and keep it as a copy. Attach photocopies of pay stubs or check stubs to the report form you send to the Social Security Administration. Attach the originals to the copy you keep. Do not send the originals of your pay stubs to the Social Security Administration, only photocopies.4 The Social Security Administration often loses items sent in the mail. Keep the original pay stubs and check stubs with a copy of your report form so that the Social Security Administration can review the originals during your annual review. Write the date the letter was sent on the copy of the income statement you keep.5 Keep a copy of any paperwork you send to the Social Security Administration.
Attach the originals to the copy you keep. Do not send the originals of your pay stubs to the Social Security Administration, only photocopies.4 The Social Security Administration often loses items sent in the mail. Keep the original pay stubs and check stubs with a copy of your report form so that the Social Security Administration can review the originals during your annual review. Write the date the letter was sent on the copy of the income statement you keep.5 Keep a copy of any paperwork you send to the Social Security Administration.
In addition, keep a record of all your conversations with the Social Security Administration. Write down the date of the conversation, the name of the person you spoke to, and the content of your conversation. We recommend that you bind the documents you receive from the Social Security Administration with a 3-hole punch and make copies of all documents you send to the Social Security Administration. Keep all documents in a notebook or folder.
Cash and income not credited to children
The Social Security Administration does not count the following funds in the context of determining a child's eligibility for SSI benefits: these funds can be converted into cash. Title 20 CFR Part 416.1202(b).
The Social Security Administration does not count the following income in determining a child's eligibility for SSI:
- Income received by a parent for providing In-Home Supportive Services (IHSS) to a child with a disability. Income earned from IHSS Services does not count towards determining SSI eligibility. Title 20 CFR Part 416.1161(a)(16).
- Income received through the IHSS Community First Choice Option (CFCO) program provided by a parent to a child is covered by Medi-Cal and income received by the parent is not considered in determining eligibility for Medi-Cal.
 In addition, income and funds that are considered in determining a child's financial eligibility for SSI benefits and the amount of the child's SSI check cannot be secondary to determining eligibility of other family members for Medi-Cal.6
In addition, income and funds that are considered in determining a child's financial eligibility for SSI benefits and the amount of the child's SSI check cannot be secondary to determining eligibility of other family members for Medi-Cal.6
For more information about the IHSS (IHSS Fair Hearing and Self-Assessment) program, see our IHSS Fair Hearing and Self-Assessment Information Pack: http://www.disabilityrightsca.org/pubs/501301.htm
Child Benefit Calculation
For instructions on calculating parental child benefit income, see 20 CFR 416.1160, 416.1161, and 416.1165. “Employed income” includes wages and salaries or income from self-employment.7 Everything else is considered “unearned income”: gifts, unemployment benefits, state disability benefits, and social security benefits are examples of unearned income. You pool your parents' unearned income. You also combine the parents' earned income. Earned income is considered gross income, not what you bring home. Gross income is the amount you earn before any deductions.8
Gross income is the amount you earn before any deductions.8
The Social Security Administration begins by deducting contributions for every child in the family who does not have a disability, except for a child on SSI or children with disabilities. Contributions are deducted first from any unearned income and then from earned income to the extent of the unused share of the contributions (see examples). The term "child" for deductions includes children under 21 living in the same household and 21-year-olds who are full-time students under the standards of Title 20 CFR Part 416.1861. The contribution for each non-disabled child is the difference between the individual Federal Benefit Rate (FBR) and the spousal FBR. (The federal benefit rate is the portion of the SSI check amount received from the federal government; the remainder of the SSI check amount is money received from the state.)9The own income of a child who does not qualify for benefits will reduce the amount of the contribution. However, if the ineligible child is a full-time student, the money earned will not be counted to the same extent as for a child or young adult under 22 receiving SSI benefits. Title 20 CFR 416.1112(c)(3), 416.1160(d), 416.1161(c), 416.1163(b), 416.1165, 416.1861.
However, if the ineligible child is a full-time student, the money earned will not be counted to the same extent as for a child or young adult under 22 receiving SSI benefits. Title 20 CFR 416.1112(c)(3), 416.1160(d), 416.1161(c), 416.1163(b), 416.1165, 416.1861.
After deductions for children without disabilities living in the home, there will be a deduction of $20.00 from any income not included in the income assessment. It is deducted first from unearned income (if any or remaining), and then from earned income to the extent of the deduction unused by unearned income. This is followed by special deductions from earned income - first $65.00 and then 50% of the balance. Then you add the remaining amounts of unearned and earned income. From the amount received, you deduct either individual FBR (for a single parent) or spousal FBR (if both parents or a parent and a foster parent are at home). The remaining amount is credited to the child with a disability as his or her unearned income. If there is more than one child with a disability in the family, the amount credited is divided between them.
If there is more than one child with a disability in the family, the amount credited is divided between them.
A child's SSI benefit is determined in the same way as any other SSI recipient, with two exceptions. First, only two-thirds of the amount of child support is counted. Title 20 CFR Part 416.1124(c)(11). Second, if the child is a student and does not reach age 22 in 2016, the Social Security Administration does not credit the first $1,780.00 of earned income for each month up to an annual maximum of $7,180.00. 20 CFR 416.1112(c)(3).10 This is in addition to the deductions normally applicable to earned income.
Examples of applying the rules for calculating child credit
This note includes a worksheet template (see below). You are encouraged to make several copies of this worksheet and use them to calculate your child's SSI benefit amount. In addition to this, we have attached two worksheets completed according to examples "A" and "B". These calculations are based on 2016 benefit amounts. The numbers and letters below correspond to the numbers and letters on the Child Benefit Income Worksheet.
| The January 2016 Individual Federal Benefit Rate is $733.00. | The January 2014 Individual Federal Benefit Rate was $721.00. | The January 2015 Individual Federal Benefit Rate is $733.00. |
| The January 2016 Spousal Federal Benefit Rate is $1,100.00. | The Spousal Federal Benefit Rate for January 2014 was $1,082.00. | The January 2015 Spousal Federal Benefit Rate is $1,100.00. |
| January 2016 income deduction for a non-disabled child is $367.00. | The income deduction for a child without a disability for January 2014 was $361.00. | January 2015 income deduction for a non-disabled child is $367.00. |
The January 2016 SSI benefit rate for a child with a disability is $796. 40. 40. | The SSI benefit rate for a child with a disability for January 2014 was $784.40. | The January 2015 SSI benefit rate for a child with a disability is $796.40. |
| The January 2016 SSI benefit rate for a child with blindness is $944.40. | January 2014 SSI benefit rate for a child with blindness was $932.40. | The January 2015 SSI benefit rate for a child with blindness is $944.40. |
Example A: Mr. and Mrs. Apple have three children, including Adam, who is ill. Mr. Apple's gross earned income is $2,000.00 per month. Ms. Apple works part-time and earns $1,000.00 per month. They also receive an income of $30 per month from oil field leases.
Disclaimer: This publication is for legal information only and does not constitute legal advice regarding your individual situation. It is current as of the date of publication. We try to update our content regularly. However, laws change regularly. If you want to make sure the law hasn't changed, contact the DRC or another legal office.
However, laws change regularly. If you want to make sure the law hasn't changed, contact the DRC or another legal office.
- 1. Although the Social Security Administration considers a foster parent's income and money when determining SSI eligibility, the state agency's Medi-Cal (Medicaid) agency does not. Section 42 of the United States Code, Part 1396a(a)(17)(D). For a child, Medi-Cal only considers the income and money of the parent and child. If your child is ineligible for SSI because of the income and money of the foster parent, apply for Medi-Cal under the Federal Aging Program and for Children and Adults with Disabilities Living Below the Poverty Line (A&D FPL) , Federal Poverty Level for aged and for children and adults with disabilities). If your child is not eligible for Medi-Cal under the A&D FPL program, apply for Medi-Cal under the Aged, Blind, and Medically Needed Disability (ABD, aged-blind-disabled). You can apply for Medi-Cal at your county department of social assistance.
 To ensure that the appropriate rules are applied, explain that your child is subject to the Sneede case (title of lawsuit).
To ensure that the appropriate rules are applied, explain that your child is subject to the Sneede case (title of lawsuit). - 2. To renew your child's SSI benefits, write or go to your local Social Security Administration office and let them know that your income has decreased or that your money is now within the Social Security Administration limits to qualify for benefits. . Attach proof that your income has decreased or that your money is now within the limits set by the Social Security Administration to qualify for benefits. You must specifically request a reinstatement of SSI benefits. If you are requesting recovery by mail, we advise you to do so by certified mail.
- 3. You must report more than just income changes. See Title 20 CFR § 416.708. You must also tell the Social Security Administration if you move, if your child with a disability or children without a disability moves house, if a parent gets married or a parent moves out of home, or if your child with a disability moves to a residential facility.
 institution.
institution. - 4. Some parents told us that they were told at the local offices that the Social Security Administration does not accept photocopies. This is not true. In the income change letter, you swear under penalty of perjury that the photocopies are exact copies of the original documents
- 5. Some families tell us that they were told at their local office of the Social Security Administration that they were not required to submit monthly income statements, that the Social Security Administration would make adjustments after the fact during the annual review. This is sometimes true, in cases where the Social Security Administration arranges for your benefits to be adjusted according to anticipated changes in your income. If you receive benefits once a week, you will receive five checks in some months instead of four; if you get biweekly benefits, twice a year you will get three checks a month instead of two. During the annual review, the Social Security Administration may make anticipated changes in your income for the following year in its program.
 However, if you do not receive written approval from the Social Security Administration that you do not need to report changes in your income, you must report changes in your income. If you don't and end up with extra pay, the Social Security Administration will blame you because you didn't notify them of the change in your income.
However, if you do not receive written approval from the Social Security Administration that you do not need to report changes in your income, you must report changes in your income. If you don't and end up with extra pay, the Social Security Administration will blame you because you didn't notify them of the change in your income. - 6. Title 42 of the United States Code, Part 1309, C.C.R., California Code of Regulations, Title 22, Part 50555.1. In the case of the Apple family members in Example A on page 8, the other two children would be eligible for Medi-Cal benefits from zero income. Parents may not be eligible if both of them are working. If there is only one parent in the family, or if one of the parents is unemployed or underemployed, or has a disability, including a temporary one, the parents may also be eligible for Medi-Cal coverage. If a parent receives an IHSS program to care for a child with a disability, that income is not considered in determining the child's financial eligibility for SSI, and under the IHSS First Choice of the Public program, this income is also not considered in determining Mediation eligibility.
 -Cal of any other members of this household.
-Cal of any other members of this household. - 7. If you are self-employed, the Social Security Administration will want to know your adjusted gross income. Title 20 CFR Part 416.1110(b). Bring last year's income tax return to the Social Security Administration along with your gross income for this year. The Social Security Administration will count your income tax return for last year along with your gross income for this year. The Social Security Administration will use your last year's income tax return as the basis for estimating your adjusted gross income for this year. If your gross income for the past year was $40,000 and your adjusted gross income (the amount you paid in taxes after IRS-allowed business deductions) was $18,000, or 45% of your gross income, the Social Security Administration calculates that your adjusted gross income this year will be 45% of your gross income for that year. Because self-employment income is determined on an annual basis and then spread out evenly over 12 months under section 20 CFR 416.
 1111(b), you will be using adjusted estimates when filing your tax return. The Social Security Administration does not consider real estate necessary to cover costs from proceeds, including for employees, as a monetary resource. Section 42 of the United States Code, Part 1382b(a)(3). This may include inventory, computers, farm equipment and livestock, agricultural land, separate business trading accounts, buildings, a fishing boat, and a car you use to work or need to commute to work. and back.
1111(b), you will be using adjusted estimates when filing your tax return. The Social Security Administration does not consider real estate necessary to cover costs from proceeds, including for employees, as a monetary resource. Section 42 of the United States Code, Part 1382b(a)(3). This may include inventory, computers, farm equipment and livestock, agricultural land, separate business trading accounts, buildings, a fishing boat, and a car you use to work or need to commute to work. and back. - 8. Some employers have benefit plans that allow you to put money into a special account to pay for child care or medical care under Section 125 of the Internal Revenue Code. Such plans are often referred to as "cafeteria plans". Money set aside in these accounts and used to pay for eligible benefits is not considered "income" because you don't pay Social Security taxes on it. Title 20 CFR Part 404.1054. To determine your eligibility for SSI benefits, your gross earned income is your gross income minus money set aside in the Benefits Cafeteria.
 However, cash receipts deposited in a tax-exempt retirement account are considered income. The money in the parent's retirement account is a deductible resource that is not credited to the child. Title 20 CFR Part 416.1202(b).
However, cash receipts deposited in a tax-exempt retirement account are considered income. The money in the parent's retirement account is a deductible resource that is not credited to the child. Title 20 CFR Part 416.1202(b). - 9. Because of the retrospective monthly calculation (see pages 1-2), the November and December income calculations must use the following year's Federal Benefit Rate. This is because the SSI check received in January and February must reflect income received and credited to the child in November and December of the previous year.
- 10. Annual and monthly maximums increase each year by the amount of the annual cost of living allowance. Title 20 CFR Part 416.112(c)(3)(B). Regulations provide flexibility and accommodation for health conditions in defining a child or young adult as a student in the context of a deduction from earned income. Title 20 CFR Part 416.1861. These legal acts can be found in state libraries. They can also be found on the Social Security Administration website: www.
 ssa.gov. Once on the Social Security Administration website, click on the "Our Program Rules" link on the right side of the page.
ssa.gov. Once on the Social Security Administration website, click on the "Our Program Rules" link on the right side of the page.
social payments and unemployment
Author Aleksey Pitelin Reading 8 min Views 75k. Published
Content
- Unemployment benefits
- Size and benefits of benefits
- Children's benefits
- Social
- Social allowance for poor elderly people and disabled people 900,
- Social insurance for the occasion SSDI)
- Heating Assistance Program (HEAD)
- Illegal immigrants
Under the existing social support system in 2021, several categories of people are distinguished. They are eligible for various benefits in the US. Benefits can be in cash or in kind. For example, food cards, free meals, help with utility bills, and so on.
Almost everyone who is legally in the country is entitled to benefits. Everyone, without exception, is issued a social security card with an individual number. It can always be used to check how carefully a person pays taxes, and what social benefits he receives.
Everyone, without exception, is issued a social security card with an individual number. It can always be used to check how carefully a person pays taxes, and what social benefits he receives.
Unemployment benefit
This type of social support can be received by an adult able-bodied adult citizen. In addition, not reached retirement age. To assign unemployment benefits, you will have to collect a lot of documents. And also to prove that the need is real. Unemployment benefits in the US are greater than the average salary in some countries.
In general, to receive unemployment benefits, you need:
- Work in the country for at least 6-12 months (depending on the state).
- Be registered for a permanent place of work, and not under a fixed-term contract or work contract.
- Work full-time and earn at least the minimum wage.
- To be dismissed due to redundancy or in connection with the liquidation of the enterprise, and not of their own free will or for failure to fulfill their official duties.

These are the main criteria that apply throughout the country. More detailed questions concerning the social security of the population are being worked out at the local level. Also, they may vary by state.
In one county, the presence of dependents may be taken into account, but in another county it will not matter. Accordingly, the amount of unemployment benefits depends on the place of residence (as, indeed, the minimum wage).
Benefit amounts and payments
Unemployment benefits are a maximum of 49% of a person's average earnings at their last job and a maximum of $2,700 per month. Payments are made for 6.5 months and then stop. And this is regardless of whether the unemployed got a job.
During the entire period of receiving unemployment benefits, a citizen must communicate closely with state authorities. Also, meet weekly with social workers. And also make every effort to get back to work as soon as possible.
Social workers also offer him vacancies from their database. Attendance at interviews is mandatory, refusal can only be on the part of the employer.
Attendance at interviews is mandatory, refusal can only be on the part of the employer.
In case of violation of the rules, the payment of unemployment benefits is suspended or completely canceled.
An unemployed person can be sent to some courses so that he can acquire a new profession that is in demand.
Due to such strict requirements for the recipient of unemployment benefits, not everyone receives it. In 2021, one in four applicants was deemed ineligible. According to statistics, women receive unemployment benefits more often than men. In addition, their allowance is usually slightly higher.
According to the latest data, the minimum unemployment benefit is fixed in Oklahoma ($65), the maximum - in the state of Washington ($2,000).
Child Benefit
Child Benefit as we know it does not exist in the US. Benefits in the United States are only targeted, to a specific needy family, and not always in money. There is also no concept of maternity leave.
There is also no concept of maternity leave.
A mother may not work after giving birth for a maximum of 4 months, and after this period she must return to work or quit. True, the child will not have to be left unattended - in every city there is a system of early nurseries and kindergartens. You can also get a discount on their payment.
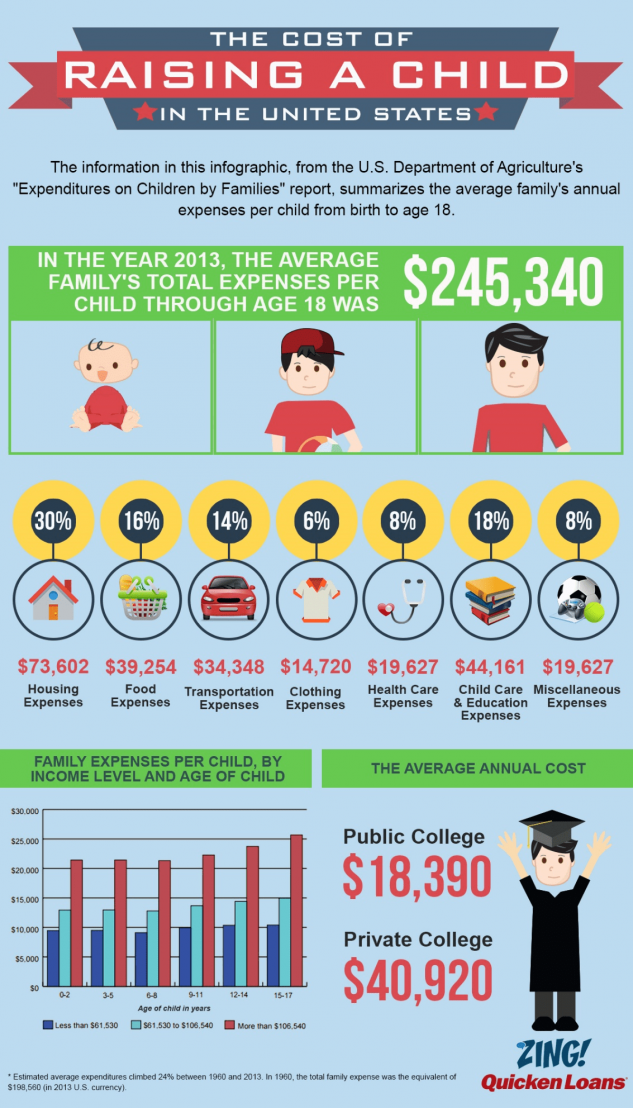
A poor family will not be allowed to die of hunger either. If the parents' income is below the subsistence level, they are paid the missing amount - in cash or various kinds of coupons or benefits. These can be food cards, free school breakfasts and lunches, transportation costs, tax breaks.
The amount of such benefits is calculated individually each time. At school, your child will definitely be fed a free breakfast, and possibly lunch. In the summer, during vacations and holidays, a network of free food sections operates. A mother with a child less than a year old can receive additional healthy nutrition.
Single parents have an advantage when granting child support. Recently, this leads to the fact that people are in no hurry to enter into an official marriage, or fictitiously divorced.
Recently, this leads to the fact that people are in no hurry to enter into an official marriage, or fictitiously divorced.
The only category of children guaranteed to receive benefits are children left without parents and raised in families of relatives.
Low-income families with a child are eligible for free American Medicaid, free public education, and social housing. However, the level of these services leaves much to be desired, so the state encourages parents to still find a permanent job with an acceptable income.
Welfer
Not only the unemployed and families with a child are entitled to receive assistance from the state. The so-called welfare is theoretically available to all those in need. It is a number of different benefits assigned to persons who, for one reason or another, are not provided with a minimum income.
In 2021, any US permanent resident can apply for welfare. That is, you do not even need to wait for citizenship. The social service will carefully check all your income and assign the necessary amount of payments. Assistance other than cash may also be offered. Benefits in the US protect citizens from living without food and clothes.
The social service will carefully check all your income and assign the necessary amount of payments. Assistance other than cash may also be offered. Benefits in the US protect citizens from living without food and clothes.
Benefits are checked monthly and will stop when your income reaches the required amount.
For its part, the state encourages a person to get a job or go to school as soon as possible in order to get a profession that is in demand on the labor market. Theoretically, with a certain resourcefulness, you can sit on welfare for years. Therefore, many taxpayers are unhappy with the existence of this kind of social support.
The Mexican and African-American families most often given this type of benefit are believed to deliberately have many children and not get a job. And they can even work illegally without paying taxes.
In 2015, the Arizona government, with a budget deficit of $1 billion, decided to revise the terms of the welfare program. Now residents of the state will be able to apply for the appointment of this benefit only once in a lifetime, and payments will be made no more than 12 months. It is possible that over time, other states will follow the example of Arizona.
Now residents of the state will be able to apply for the appointment of this benefit only once in a lifetime, and payments will be made no more than 12 months. It is possible that over time, other states will follow the example of Arizona.
Social Security for the Indigent Elderly and Disabled (SSI)
SSI is another program that supports disadvantaged people. Both citizens and legal immigrants can apply for it. It is required that the person be disabled (due to age or illness), have a low income and do not own expensive property. Another condition is that it must already be included in all possible social assistance programs.
The SSI program in 2020 is funded by the federal budget and is designed to be an additional income for people with disabilities.
Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)
This assistance is for those who have worked in the US and paid Social Security taxes. SSDI requires one year of disability or blindness. It does not matter whether you have property or other income - only seniority is taken into account.
It does not matter whether you have property or other income - only seniority is taken into account.
Your dependents (spouse, child) are also eligible for this benefit in 2019.
Despite numerous social benefits, in the end it is profitable to work and pay taxes to the state.
Heating Assistance Program (HEAD)
Another interesting form of social assistance in the US is heating assistance. It is eligible for people with low incomes if they run out of fuel or are not going to turn on the heat supply due to debt. They can apply in a prescribed manner and receive an allowance to pay for these services.
Its size is determined annually. It can range from $20 to $600 per year. In order to receive benefits, you will have to prove that you are in an emergency and cannot handle it on your own. The funds allocated for this type of social assistance are usually limited, so it makes sense to apply as early as possible in order to receive this benefit as early as 2020.
Illegal immigrants
This category of the US population is quite numerous. They are not entitled to receive any cash benefits. However, they can participate in various social programs.
Reduced travel for pensioners and the disabled, tax deductions for dependents, free meals for children and women, assistance for primiparas and many others. Medical services in emergencies, as well as for children and pregnant women, are available to them through the Medicaid program.
It is worth noting that if the child is a US citizen (for example, by birthright) and his parents are illegal immigrants, they can legally apply on behalf of their child for any applicable benefits.
The structure of social benefits in the US is quite complex and branched. In each state, there are various charitable organizations that help those in need without the participation of the state.
Recently, due to the budget deficit, the state is revising the conditions for assigning various kinds of assistance in the direction of tightening.