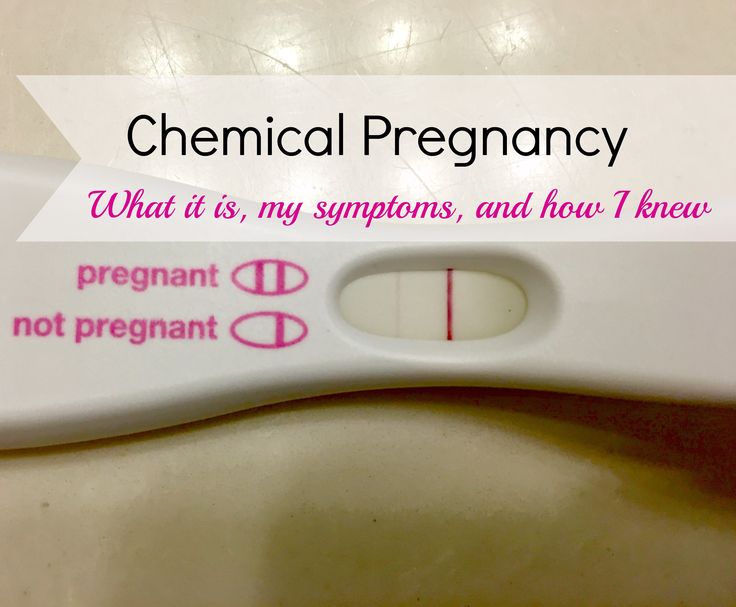
How do you know if your miscarriage is complete
Miscarriage - What happens - NHS
If there's no pregnancy tissue left in your womb, no treatment is required.
However, if there's still some pregnancy tissue in your womb, your options are:
- expectant management – wait for the tissue to pass out of your womb naturally
- medical management – take medicine that causes the tissue to pass out of your womb
- surgical management – have the tissue surgically removed
The risk of complications is very small for all these options. It's important to discuss them all with the doctor in charge of your care.
Expectant management
If you have a miscarriage in your first trimester, you may choose to wait 7 to 14 days after a miscarriage for the tissue to pass out naturally. This is called expectant management.
If the pain and bleeding have lessened or stopped completely during this time, this usually means the miscarriage has finished. You should be advised to take a home pregnancy test after 3 weeks.
If the test shows you're still pregnant, you may need to have further tests.
If the pain and bleeding have not started within 7 to 14 days or are continuing or getting worse, this could mean the miscarriage has not begun or has not finished. In this case, you should be offered another scan.
After this scan, you may decide to either continue waiting for the miscarriage to occur naturally, or have drug treatment or surgery. If you choose to continue to wait, your healthcare professional should check your condition again up to 14 days later.
Contact your hospital immediately if the bleeding becomes particularly heavy, you develop a high temperature (fever) or you experience severe pain.
Medicine
You may choose to have medicine to remove the tissue if you do not want to wait, or if it does not pass out naturally within 2 weeks. This involves taking tablets that cause the cervix to open, allowing the tissue to pass out.
In most cases, you'll be offered tablets called pessaries that are inserted directly into your vagina, where they dissolve.
The tablets usually begin to work within a few hours. You'll experience symptoms similar to a heavy period, such as cramping and heavy vaginal bleeding. You may also experience vaginal bleeding for up to 3 weeks.
In most units, you'll be sent home for the miscarriage to complete. This is safe, but ring your hospital if the bleeding becomes very heavy.
You should be advised to take a home pregnancy test 3 weeks after taking this medicine. If the pregnancy test shows you're still pregnant, you may need to have further tests.
If the pregnancy test shows you're still pregnant, you may need to have further tests.
You may be advised to contact your healthcare professional to discuss your options if bleeding has not started within 24 hours of taking the medicine.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery is used to remove any remaining pregnancy tissue. You may be advised to have immediate surgery if:
- you experience continuous heavy bleeding
- there's evidence the pregnancy tissue has become infected
- medicine or waiting for the tissue to pass out naturally has been unsuccessful
Surgery involves removing any remaining tissue in your womb with a suction device. You should be offered a choice of general anaesthetic or local anaesthetic if both are suitable.
After a miscarriage
A miscarriage can be very upsetting, and you and your partner may need counselling or support. You may also have questions about trying for another baby and what happens to the miscarried foetus.
You may also have questions about trying for another baby and what happens to the miscarried foetus.
For more information, read what happens after a miscarriage.
Page last reviewed: 09 March 2022
Next review due: 09 March 2025
Miscarriage | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
The loss of a baby through miscarriage can be very distressing. A miscarriage generally occurs for reasons outside your control and nothing can be done to prevent or stop it from happening. Most women who have had a miscarriage will go on to have a healthy pregnancy in the future.
What is a miscarriage?
A miscarriage is the loss of your baby before 20 weeks of pregnancy. The loss of a baby after 20 weeks is called a stillbirth.
Up to 1 in 5 confirmed pregnancies end in miscarriage before 20 weeks, but many other women miscarry without having realised they are pregnant.
Common signs of miscarriage include:
- cramping tummy pain, similar to period pain
- vaginal bleeding
If you think you are having a miscarriage, see your doctor or go to your local emergency department.
Many women experience vaginal spotting in the first trimester that does not result in pregnancy loss.
What are the types of miscarriage?
There are several types of miscarriage — threatened, inevitable, complete, incomplete or missed.
Other types of pregnancy loss include an ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy and a blighted ovum.
Threatened miscarriage
When your body is showing signs that you might miscarry, that is called a 'threatened miscarriage'. You may have light vaginal bleeding or lower abdominal pain. It can last days or weeks and the cervix is still closed.
The pain and bleeding may resolve and you can go on to have a healthy pregnancy and baby. Or things may get worse and you go on to have a miscarriage.
There is rarely anything a doctor, midwife or you can do to prevent a miscarriage. In the past bed rest was recommended, but there is no scientific proof that this helps at this stage.
Inevitable miscarriage
Inevitable miscarriages can come after a threatened miscarriage or without warning. There is usually a lot more vaginal bleeding and strong lower stomach cramps. During the miscarriage your cervix opens and the developing fetus will come away in the bleeding.
There is usually a lot more vaginal bleeding and strong lower stomach cramps. During the miscarriage your cervix opens and the developing fetus will come away in the bleeding.
Complete miscarriage
A complete miscarriage has taken place when all the pregnancy tissue has left your uterus. Vaginal bleeding may continue for several days. Cramping pain much like labour or strong period pain is common — this is the uterus contracting to empty.
If you have miscarried at home or somewhere else with no health workers present, you should have a check-up with a doctor or midwife to make sure the miscarriage is complete.
Incomplete miscarriage
Sometimes, some pregnancy tissue will remain in the uterus. Vaginal bleeding and lower abdominal cramping may continue as the uterus continues trying to empty itself. This is known as an 'incomplete miscarriage'.
Your doctor or midwife will need to assess whether or not a short procedure called a ‘dilatation of the cervix and curettage of the uterus’ (often known as a ‘D&C’) is necessary to remove any remaining pregnancy tissue. This is an important medical procedure done in an operating theatre.
This is an important medical procedure done in an operating theatre.
Missed miscarriage
Sometimes, the fetus has died but stayed in the uterus. This is known as a 'missed miscarriage'.
If you have a missed miscarriage, you may have a brownish discharge. Some of the symptoms of pregnancy, such as nausea and tiredness, may have faded. You might have noticed nothing unusual. You may be shocked to have a scan and find the fetus has died.
If this happens, you should discuss treatment and support options with your doctor.
Recurrent miscarriage
A small number of women have repeated miscarriages. If this is your third or more miscarriage in a row, it’s best to discuss this with your doctor who may be able to investigate the causes, and refer you to a specialist.
A miscarriage can occur suddenly or over a number of weeks. The symptoms are usually vaginal bleeding and lower tummy pain. It is important to see your doctor or go to the emergency department if you have signs of a miscarriage.
The most common sign of a miscarriage is vaginal bleeding, which can vary from light red or brown spotting to heavy bleeding. If it is very early in the pregnancy, you may think that you have your period.
Other signs may include:
- cramping pain in your lower tummy, which can vary from period-like pain to strong labour-like contractions
- passing fluid from your vagina
- passing of blood clots or pregnancy tissue from your vagina
What really happens during a miscarriage?
WARNING — This article contains some graphic descriptions of what you might see during a miscarriage.
What should I do if I think I’m having a miscarriage?
If you are concerned that you are having a miscarriage, call your doctor or midwife for advice and support.
Keep in mind that many women experience vaginal spotting in the first trimester of pregnancy that does not result in a miscarriage.
If you are alone, consider calling your partner or a friend for help and support.
If you have very heavy bleeding, strong pain or feel unwell, call triple zero (000) or have someone take you to your nearest emergency department.
How is a miscarriage managed?
Unfortunately, nothing can prevent a miscarriage from happening once it has begun. What happens now depends on your own health and what is happening to you.
Each approach has benefits and risks. You should discuss these with your doctor.
Expectant or natural management
Also called ‘watch and wait’, expectant management may be recommended in early pregnancy. This involves going home and waiting until the pregnancy tissue has passed from your womb by itself. This can happen quickly, or it may take a few weeks.
Medical management
You may be offered medication that speeds up the passing of the pregnancy tissue. You may be asked to stay in hospital until the tissue has passed, or you may be advised to go home.
Surgical management
You may be advised to have a form of minor surgery called a 'dilatation and curettage' (also called a D&C or a curette). This procedure is often recommended if you have heavy bleeding, significant pain or signs of infection. It may also be recommended if expectant or medical management has failed. You may also decide that you prefer this option.
This procedure is often recommended if you have heavy bleeding, significant pain or signs of infection. It may also be recommended if expectant or medical management has failed. You may also decide that you prefer this option.
This procedure is done under general anaesthesia in an operating theatre. It takes 5-10 minutes once you are asleep. The doctor opens the cervix and removes the remaining pregnancy tissue.
How is a miscarriage treated?
Once it is confirmed that you are having a miscarriage, your doctor may offer or recommend treatment. There are many options. All have benefits and risks — discuss these with your doctor.
If the miscarriage is complete
If it seems the miscarriage is complete, you should still see your doctor for a check-up. You may be advised to have an ultrasound to make sure your uterus is empty.
If you go to hospital
If you go to your hospital’s emergency department, you will be seen first by a triage nurse, who will assess how urgently you need to be seen by a doctor. Depending on your symptoms, you will either be taken in to see a doctor immediately, or you will be asked to wait.
Depending on your symptoms, you will either be taken in to see a doctor immediately, or you will be asked to wait.
If you are waiting to be seen and your symptoms become worse or you feel like you need to go to the toilet, let the staff know immediately.
What happens if I miscarry at home?
Some women miscarry at home before they have a chance to see their doctor or get to the hospital.
If this happens, then:
- use pads to manage the bleeding
- if you can, save any pregnancy tissue that you pass, as your doctor may recommend it is tested to see why your miscarriage happened
- take medications such as paracetamol if you have pain
- rest
- call your doctor or midwife
There is a chance you may see your baby in the tissue that you pass, but often the baby is too small to recognise, or may not be found at all. It is normal to want to look at the remains, but you may decide you do not want to. There is no right or wrong thing to do.
Some women miscarry while on the toilet. This can also happen if you are out and about, or in hospital. There is no right or wrong way to handle this.
Why do miscarriages happen?
Many women wonder if their miscarriage was their fault. In most cases, a miscarriage has nothing to do with anything you have or have not done. There is no evidence that exercising, stress, working or having sex causes a miscarriage.
Most parents do not ever find out the exact cause. However, it is known that miscarriages often happen because the baby fails to develop properly, usually due to a chromosomal abnormality that was spontaneous, not inherited.
Occasionally, miscarriage is caused by:
- hormonal abnormalities
- immune system and blood clotting problems
- medical conditions such as thyroid problems or diabetes
- severe infections causing high fevers (not common colds)
- physical problems with your womb or cervix
What are the risk factors for miscarriage?
Women are more likely to have miscarriages if they:
- are older
- smoke
- drink alcohol in the first trimester
- drink too much caffeine in coffee, tea or energy drinks
- have had several previous miscarriages
Can you prevent a miscarriage?
Living healthily — no cigarettes, no alcohol and little to no caffeine — can decrease your risk of miscarriage. It’s a good idea to avoid contact with people who have a serious infectious illness when you’re pregnant.
It’s a good idea to avoid contact with people who have a serious infectious illness when you’re pregnant.
Who can I talk to for advice and support?
Talk to your doctor or midwife for information and advice on what do and how to look after yourself if you experience a miscarriage.
Your hospital should be able to provide details of available support services, such as bereavement support.
SANDS is an independent organisation that provides support for miscarriage, stillbirth and newborn death. You can call them on 1300 072 637 or visit www.sands.org.au.
You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436, 7am to midnight (AET) to speak to a maternal child health nurse for advice and emotional support.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Miscarriage, symptoms - Health Clinic 365 Yekaterinburg
Causes of miscarriage
Questions to the doctor about miscarriage
Diagnosis of miscarriage
Treatment and prevention of miscarriage
According to statistics, 10 to 20% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, the real numbers could be much higher, as a large number of miscarriages happen very early, and women are not even aware of their pregnancy. Most miscarriages happen due to abnormal development of the fetus.
Miscarriage is quite common, but this fact does not make things any easier. It is always difficult to cope with the realization that there was a pregnancy, but no child. Try to deal with the situation psychologically and understand what could be causing the miscarriage, what increases the risk of it, and what type of treatment might be needed.
Miscarriage symptoms .
Most miscarriages occur before 12 weeks. Signs and symptoms of a miscarriage include:
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting (although quite common in early pregnancy)
- Pain or cramps in the abdomen or lower back
- Fluid vaginal discharge or tissue fragments
It is important to consider the fact that in early pregnancy, spotting or vaginal bleeding is quite common. In most cases, women who experience light bleeding during the first three months have an uneventful pregnancy thereafter. In some cases, even with heavy bleeding, the pregnancy does not end in a miscarriage.
In most cases, women who experience light bleeding during the first three months have an uneventful pregnancy thereafter. In some cases, even with heavy bleeding, the pregnancy does not end in a miscarriage.
Some women who have a miscarriage develop an infection in the uterus. This infection, also called septic miscarriage, can cause:
- Fever (feeling hot, chills)
- Body pains
- Thick, foul-smelling vaginal discharge
When to see a doctor.
Call your doctor if:
- Bleeding, even if only light spotting occurs
- Profuse, liquid vaginal discharge without pain or bleeding
- Isolation of tissue fragments from the vagina
You can put a piece of tissue to be isolated in a clean container and take it to your doctor for examination. It is unlikely that the study will give any accurate results, but if it is determined that the fragments of the excreted tissue are from the placenta, the doctor will be able to conclude that the symptoms that appear are not associated with the presence of a tubal (ectopic) pregnancy.
You can get more detailed information about miscarriage from the gynecologists of the Health 365 clinic in Yekaterinburg.
Prices
Gynecologist, initial appointment
2300 i
Cleansing after a miscarriage
When the body experiences early fetal loss, it is subjected to tremendous stress. Tune in to bear a child, he issues a failure of internal programs, due to which the embryo dies. Before you figure out how the 9 goes0011 cleaning of a missed pregnancy , provoking a spontaneous miscarriage with medications and how the recovery period goes after these procedures, let's dwell a little on the pregnancy itself, which is called undeveloped.
Every woman has heard stories of missed pregnancy, but few go into details. The less you know, the stronger and more confident you sleep. Following this principle, future women in labor consciously protect themselves from unnecessary knowledge that can negatively affect their mood and inspire unnecessary fears before conception. However, many women experience fetal freezing firsthand, purging, preparing to become mothers again. To ensure that materials for studying the anomalous state are always at hand, we tried to collect all the necessary information in one article.
However, many women experience fetal freezing firsthand, purging, preparing to become mothers again. To ensure that materials for studying the anomalous state are always at hand, we tried to collect all the necessary information in one article.
Define the terminology
Before moving on to cleansing a missed pregnancy, let's define the term itself. Why does a fetus that develops normally in the womb freeze? How does a child that is being formed yesterday stop living under the influence of external factors? Does the mother make mistakes in the process of bearing? And can the father cause miscarriage? About everything in order.
Missed pregnancy is usually called the state of death of the embryo due to the impossibility of its further development. Many women mistakenly confuse this concept with lagging fetal development. However, these are completely different phenomena. With a developmental delay, the doctor can prescribe competent timely treatment that will allow the baby to be born healthy and strong. With an undeveloped pregnancy, the child dies in the mother's womb, there is no chance of saving him. At the same time, a woman does not always understand that the pregnancy is terminated. This can only be diagnosed by a doctor and a prescribed health examination.
With an undeveloped pregnancy, the child dies in the mother's womb, there is no chance of saving him. At the same time, a woman does not always understand that the pregnancy is terminated. This can only be diagnosed by a doctor and a prescribed health examination.
Spontaneous fading of pregnancy is most common in the early stages of a baby's development. It includes up to 80% of the total number of applications. Despite the fact that the mother is not able to understand that the pregnancy has stopped, she can feel something is wrong, carefully listening to her own body. What criteria should be given special attention?
- Toxicosis - normally, toxicosis gradually stops by the second trimester of pregnancy or becomes much weaker than the initial one. But if the feeling of nausea disappears suddenly and for good, there is reason to be wary - is everything okay with the child. Contact your obstetrician-gynecologist who is observing you, describing to him the symptoms that bother you in as much detail as possible.

- Breast - during pregnancy, it is filled with heaviness, swells, increases in volume, becomes like a bulk apple, more precisely, a larger fetus. All this is about them, about the mammary glands. This is how the hormonal background of a woman's body affects the chest. As soon as these symptoms have disappeared, visit a specialist. Talk about what happened and share your own concerns.
- Pain and discharge from the vagina - if the pulling pain in the sacrum and lower abdomen does not give you rest, rolls in waves and is accompanied by bloody discharge - it's bad. This is not an accurate indication of the need for subsequent cleaning of a missed pregnancy, but it signals an impending disaster. Start bed rest immediately and call an ambulance. Do without the hassle, stress and any activity. It is possible that you will be allowed to go home after the examination. If it is possible to save the child, you can be placed in the outpatient department at the antenatal clinic for preservation.

Diagnosis of a missed pregnancy before cleaning
Only a specialist is able to determine the need for cleaning a missed pregnancy, as well as the pregnancy itself. To do this, the obstetrician-gynecologist carefully examines the pregnant woman, using diagnostic tools:
- Manual examination is the most common reason for determining a miscarriage when the mother is not yet aware of the misfortune that has occurred. Examining the woman who turned to him manually, the doctor notes the discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the expected life span of the embryo.
- Blood test - the amount of pregnancy hormones with an increase in its duration should increase and show a positive trend. If this does not happen, and hormones reduce the level, a serious problem can be stated in the form of an undeveloped pregnancy.
- Ultrasound diagnosis of the uterus is a mandatory procedure in a comprehensive examination of a woman.
 The uterus itself, the fetal egg, and the embryo are examined. The doctor carefully examines the fetus, notes its activity or passivity, listens to the heartbeat. If no movements are noted, no heartbeat is heard, we can talk about a missed pregnancy.
The uterus itself, the fetal egg, and the embryo are examined. The doctor carefully examines the fetus, notes its activity or passivity, listens to the heartbeat. If no movements are noted, no heartbeat is heard, we can talk about a missed pregnancy.
When the diagnosis is made, it remains to be decided what is best to do to remove the embryo - cleaning the miscarriage or waiting for spontaneous expulsion of the fetus, which may not occur.
Cleansing a missed pregnancy or how to expel a fetus from the body
When confirming a diagnosis, it is very important for a woman to get immediate medical attention. If this is not done in a timely manner, there is a high risk of developing complications associated with a fetal egg left in the uterus. There are many options for the development of events - from the inflammatory process to the strongest blood poisoning. Task number 1 for the near future is the cleaning of a missed pregnancy in order to eliminate the fetal egg from the body.
Abroad, there is a widespread practice, according to which a failed childbirth is given a period of time to expel the egg from the cavity on her own. To prevent negative events, a woman is recommended to do an ultrasound weekly and visit a gynecologist's office. If a miscarriage does not occur, and an inflammatory process begins to appear in the tissues, the cleaning of a missed pregnancy is used to eliminate the remnants of the embryo in the uterus and stop the infection developing in the body. There are three main methods of treatment used in Russia:
- A drug effect that terminates a miscarriage. The patient takes pills and after 1-3 days she has a miscarriage. The method resembles medical abortion, but is not 100% reliable. The doctor will not give any guarantee that there will be no excess tissue left in the uterine cavity, which can later cause inflammation. It is not uncommon for technology to be supplemented by cleaning a missed pregnancy in order to completely scrape out all foreign bodies from the uterine cavity.

- Vacuum aspiration - when, under great directed pressure, a tube inserted into the uterine cavity sucks out the remains of the dead body of the embryo. The method is used only in the early stages of pregnancy.
- Curettage - reliable cleaning of missed pregnancy by surgical intervention. The uterus is cleaned by the surgeon and carefully released by hand from the placenta and fetus.
Specifies which method to use, specialist. Self-treatment is unacceptable here.
How is a missed pregnancy cleaned by scraping
For some reason, the female half of society is terrified of cleaning a missed pregnancy by scraping, although the procedure has been used in gynecological practice for a long time. It is so developed that it is almost impossible for a professional doctor to disrupt the operation. Specially conducted studies have shown that the main factor of fear in anticipation of curettage is the expectation of pain. However, modern medicine has reached such heights that discomfort and pain at the time of cleaning a missed pregnancy are completely absent.
For this purpose, general anesthesia is used, which blocks pain and neutralizes the body's sensitivity for the duration of the operation. Before being admitted to a hospital, an anesthesiologist conducts a conversation with a woman, who determines which drug to use during the procedure and what dose to calculate so that anesthesia does not harm the health and well-being of the patient. In addition, her gynecologist communicates with the woman, whose task is to exclude possible contraindications to the procedure. Among them:
- infections;
- inflammation of the uterus;
- inflammation of the appendages;
- suspicion of violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes of the uterus.
The operation to clean a miscarriage is performed in a gynecological chair after a dose of general anesthesia is administered. The patient comes to her senses upon completion of all procedures performed in the ward. Therefore, he cannot remember the smallest details of what happened. And the woman does not feel severe pain. The situation is slightly different when the patient cannot be anesthetized. In this case, the cleaning of a frozen pregnancy takes place under local anesthesia.
And the woman does not feel severe pain. The situation is slightly different when the patient cannot be anesthetized. In this case, the cleaning of a frozen pregnancy takes place under local anesthesia.
The doctor carefully injects the uterus with specialized drugs that block sensitivity, treats the genital area with iodine solution, covers the vagina with medical alcohol to exclude the possibility of infection. It is important to observe the measure in processing, otherwise aggressive disinfecting solutions can burn the mucous membrane. This will affect the patient's discomfort in the vagina over the next few days.
The procedure for cleaning a missed pregnancy normally takes no more than 20 minutes, if complications can be avoided. The doctor expands the cervix with a special tool and removes the fetal egg from the cavity with a curette.
What complications can occur
Surgery does not always go smoothly. In a minimal percentage of cases, complications after surgery are possible. Among them:
Among them:
- Damage to the integrity of the walls of the uterus - a kind of perforation, recognized as a very serious complication with serious consequences. According to statistics, such a pathology occurs in 1% of cases after an unsuccessful operation.
- Opening bleeding after cleaning a dead pregnancy - this phenomenon must be reported to the doctor immediately, even if the discharge is of a slight smearing nature. There is a danger of blood clots accumulating in the uterine cavity, which will require a second curettage operation.
- Inflammation - occurs when an infection enters a wound. After cleaning a frozen pregnancy, high fever, chills, pain symptoms of a pulsating nature should alert.
- Adhesions - this abnormality may appear several years after the operation. The adhesive process negatively affects the stability of menstruation, fertilization and many other functions of the female body.
After the cleaning of a miscarriage is completed, you must carefully follow the doctor's recommendations. Body temperature should be closely monitored. From the second day, she should return to normal. It is necessary to control the separation from the vagina - there should be no heavy bleeding and discharge with an unpleasant odor. If a woman feels well after cleaning a missed pregnancy, after a couple of days the doctor draws up an extract and allows her to leave the hospital to continue treatment at home.
Body temperature should be closely monitored. From the second day, she should return to normal. It is necessary to control the separation from the vagina - there should be no heavy bleeding and discharge with an unpleasant odor. If a woman feels well after cleaning a missed pregnancy, after a couple of days the doctor draws up an extract and allows her to leave the hospital to continue treatment at home.
At home, monitoring of well-being should be continued for at least another 2-3 weeks. According to the recommended schedule of visits to the gynecologist, pay a visit to the consultation to see the attending physician and make sure that the normal course of affairs. After the end of the rehabilitation period, it is necessary to find out the causes of a missed pregnancy in order to eliminate them in the future. It is necessary to plan conception no earlier than in a year. There is no need to fear that after a failed pregnancy and cleansing, you will not be able to become a mother.