Beginning of cradle cap
Cradle Cap (Seborrheic Dermatitis) in Infants (for Parents)
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
en español Costra láctea (dermatitis seborreica) en los bebés
What Is Cradle Cap?
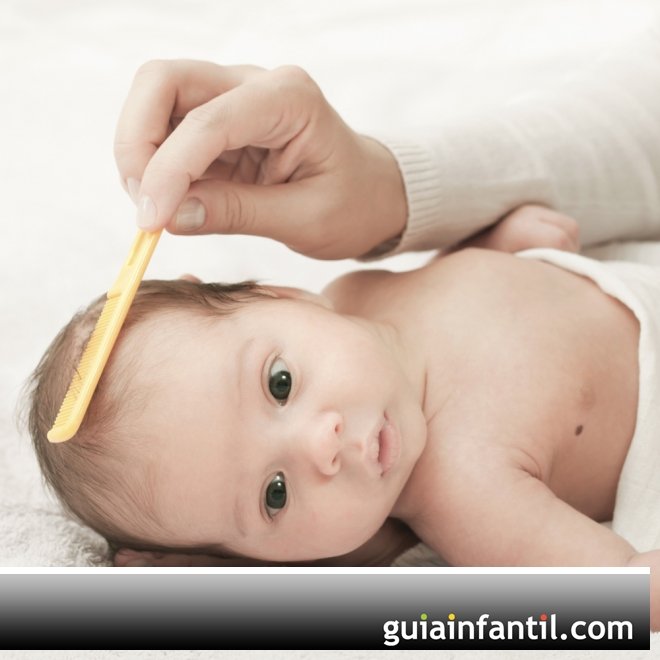
Cradle cap is the common term for seborrheic dermatitis (seb-eh-REE-ik dur-muh-TYE-tis) of the scalp in infants.
Seborrheic dermatitis, also called seborrhea (seb-eh-REE-uh), can show up:
- on the forehead and face
- behind the ears
- in the diaper area, armpits, and other skin folds and creases
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Cradle Cap (Seborrheic Dermatitis)?
Babies can develop seborrheic dermatitis when they're between 2 weeks and 12 months old. It usually starts with cradle cap. A baby with cradle cap will have slightly red scaly or crusty yellow patches on the scalp. It may also start on the face or diaper area and spread to other parts of the body.
Seborrhea looks:
- red and moist in skin creases and folds (like the neck and behind the ears)
- yellowish with greasy patches or crusts
- scaly or flaky
Seborrheic dermatitis might look uncomfortable or irritating to the skin. But it usually isn't itchy and doesn't seem to bother infants.
What Causes Cradle Cap (Seborrheic Dermatitis)?
The exact cause of cradle cap isn't known. It's likely due to a combination of things. Too much skin oil (sebum) in the oil glands and hair follicles and a type of yeast found on the skin called Malassezia may play roles in the development of seborrheic dermatitis.
How Is Cradle Cap (Seborrheic Dermatitis) Diagnosed?
Health care professionals can diagnose cradle cap and seborrheic dermatitis by the way the skin looks and where the rash is. Babies with seborrheic dermatitis are usually well and the condition should get better on its own or with treatment.
How Is Cradle Cap (Seborrheic Dermatitis) Treated?
Cradle cap and seborrheic dermatitis in infants usually clears up on its own in weeks or months. In the meantime, you may want to loosen and remove the scales on your baby's scalp:
- Wash your baby's hair once a day with mild, tear-free baby shampoo.

- Gently remove scales with a soft brush or toothbrush.
- If the scales don't loosen easily, apply a small amount of mineral oil or petroleum jelly to your baby's scalp. Let the oil to soak into the scales for a few minutes to several hours, if needed. Then use a soft brush or toothbrush to remove scales. Shampoo your baby's hair as usual.
If regular shampooing doesn't help, your doctor may recommend a mild steroid cream or antifungal shampoo.
For seborrhea on other parts of the body, your doctor may recommend a mild steroid or antifungal cream.
Do not use over-the-counter steroid or antifungal creams or anti-seborrhea shampoos without checking first with the doctor.
What Else Should I Know?
Sometimes seborrheic dermatitis in the diaper area or skin folds can get infected. Talk to your doctor if the rash gets worse or there are any signs of infection (the skin looks red, starts to drain fluid, or feels warm).
Cradle cap and seborrheic dermatitis in infants usually get better by 12 months of age.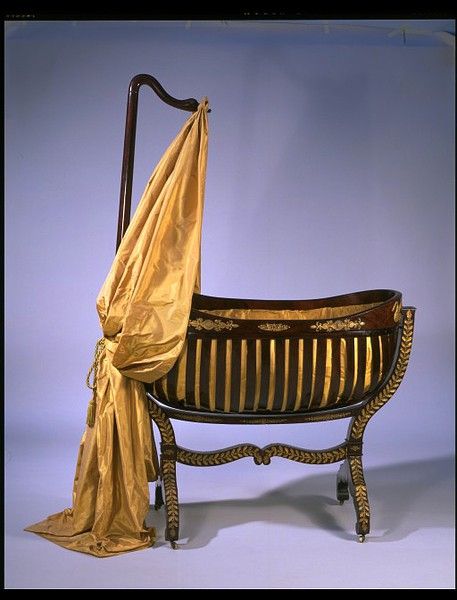 Seborrhea may come back around puberty as dandruff.
Seborrhea may come back around puberty as dandruff.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: February 2019
Cradle Cap
Is this your child's symptom?
- A scaly rash on the scalp that starts in newborns
Symptoms of Cradle Cap
- Yellow scales and crusts attached to the scalp
- Occurs in patches
- Scales can be greasy or dry
- Not itchy or painful
- Begins in the first 2 to 6 weeks of life
Cause of Cradle Cap
- Cradle cap is probably caused by hormones from the mother. These hormones cross the placenta before birth. The hormones cause the oil glands in the skin to become overactive. They then release more oil than normal.
- Dead skin cells normally fall off. The extra oil causes these cells to "stick" to the skin. These cells form yellow crusts and scales on the scalp.
When to Call for Cradle Cap
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Baby less than 1 month old with tiny water blisters or pimples in a cluster
- Your child looks or acts very sick
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- Baby less than 1 month old with any water blisters or pimples
- You think your child needs to be seen
Contact Doctor During Office Hours
- Raw rash behind the ears
- Rash spreads beyond the scalp
- Cradle cap gets worse with treatment
- Cradle cap lasts longer than 12 months
- You have other questions or concerns
Self Care at Home
- Mild cradle cap
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
Care Advice for Cradle Cap
- What You Should Know About Cradle Cap:
- Cradle cap is a common skin condition of newborns.
- It's caused by overactive oil glands in the scalp.
- It's harmless and will go away on its own. But it takes time.
- Here is some care advice that should help.
- Shampoo Daily:
- Wash the hair with an anti-dandruff shampoo (such as Head and Shoulders).
 Do this twice a week. No prescription is needed. Note: The daily use of anti-dandruff shampoo isn't approved until after 2 years old. But, using it twice a week is fine.
Do this twice a week. No prescription is needed. Note: The daily use of anti-dandruff shampoo isn't approved until after 2 years old. But, using it twice a week is fine. - On the other days, wash the hair with baby shampoo.
- Wash the hair with an anti-dandruff shampoo (such as Head and Shoulders).
- Scalp Massage:
- While the hair is lathered, massage the scalp with a soft brush. You can also use a rough washcloth or your fingers for 5 minutes. Don't worry about hurting the soft spot.
- Baby Oil:
- If the scalp has thick crusts (scales), put some baby oil on the scalp. Do this for 15 minutes before shampooing to soften the crusts.
- Wash all the oil off, however, or it may worsen the cradle cap. (Reason: The oil blocks the oil glands on the baby's scalp.)
- Do not use olive oil. (Reason: may increase the growth of yeast)
- Cradle cap lotions for loosening up the scales are also available without a prescription. Apply the lotion 15 minutes before shampooing.
- Steroid Cream:
- If the rash on the scalp is red and irritated, use 1% hydrocortisone cream.
 An example is Cortaid. No prescription is needed.
An example is Cortaid. No prescription is needed. - Put this on once a day.
- After 1 hour, wash it off with soap and water.
- Do this for 7 days or less.
- If the rash on the scalp is red and irritated, use 1% hydrocortisone cream.
- Expected Course:
- Cradle cap will eventually go away on its own between 6 and 12 months of age. Usually, it doesn't cause any symptoms (such as pain or itching).
- Therefore, treatment is optional. It is mainly done for cosmetic reasons.
- Shampoos, lotions and brushing will reduce the thickness of the scales. They will usually make them go away sooner.
- Return to Child Care:
- Cradle cap cannot be spread to others.
- Your child does not need to miss any child care.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Gets worse with treatment
- Lasts over 12 months of age
- You think your child needs to be seen
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.

Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 11/16/2022
Last Revised: 01/13/2022
Copyright 2000-2022. Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Cradle | this... What is the Cradle?
Peasant cradle (late 19th — early 20th century)
Cradle (F. Riss. Lullaby. Earlier 1886)
Cradle — a small bed or basket for infants, which allows you to rock the baby. In a figurative sense - hothouse conditions in which something or someone developed. For example, Egypt is the cradle of civilization.
|
Contents
|
Symbolism
Due to the fact that the cradle itself was a powerful pagan amulet, in Russia the priests tried to ensure that the child was placed in the cradle for the first time with a special prayer: “Prayer, put the child in the cradle”, which was introduced in the ancient Ritual Books, only after baptism.
Most of the peoples of the European part of Russia and Siberia believed that in a suspended (raised above the floor) cradle the child is under the cover of heavenly powers.
Types of cradles
The cradle (cradle, pitching, carriage, cradle, baby) is known to most peoples of the world. Cradles were made from a wide variety of materials: wood (hollowed out, plank cradles), willow twigs, rattan, leather, bark, ropes (hammock cradles). There are cradles on a rocking chair and suspended. A type of cradle is a stroller.
In royal cradles, beds and feather beds were stuffed with swan's down. Small icons or crosses were placed inside the cradle.
Zybka - in the East Slavic languages, the dialect or regional name of a cradle (crib suspended from the ceiling) for rocking infants.
Light unsteady (body), woven from pine shingles, was hung on bird-cherry shackles to the eyelet and had a step for swinging. Ochep is a flexible pole attached to the ceiling mat. On a good eyelet, the shaking fluctuated quite strongly, sometimes a fathom from the floor. Perhaps such a swing from the very birthday, followed by swinging on a swing, developed a special hardening: sailors, who came from peasants, were very rarely prone to seasickness. Later, instead of an eyeglass, they began to use a spring. Modern cradles are most often made of wicker, wood, and even plastic.
On a good eyelet, the shaking fluctuated quite strongly, sometimes a fathom from the floor. Perhaps such a swing from the very birthday, followed by swinging on a swing, developed a special hardening: sailors, who came from peasants, were very rarely prone to seasickness. Later, instead of an eyeglass, they began to use a spring. Modern cradles are most often made of wicker, wood, and even plastic.
In the ethnology of North America, the device to which a child was attached in the first months of life was called a cradle. It served both as a cradle and for carrying the child, even more so for the latter.
Sayings
- To rock an empty cradle is to call a child for a quick death (Russian everywhere) [1] .
See also
- Lullaby
Notes
- ↑ Folk traditions. Pregnancy
Literature
- Ivan Zabelin Home life of Russian tsars in the 16th and 17th centuries - M .
 : Tranzitkniga Publishing House, 2005. - p. 555-558. ISBN 5-9578-2773-8
: Tranzitkniga Publishing House, 2005. - p. 555-558. ISBN 5-9578-2773-8 - Listova T. L. Rituals and customs associated with the birth of children. The first year of life // Russians / Resp. ed. V. A. Aleksandrov, I. V. Vlasova, N. S. Polishchuk. — M.: Nauka, 1999. — ISBN 5-88590-309-3.
Links
- Cradle // sv-class.com
- Cradle, cradle, cradle // Look ahead
- CPSC crib safety standards
- Crib safety information
Exhibit of the day. Russian cradle - Museum of history and ethnography of the city of Yugorsk
In MBU "Museum of history and ethnography" is ready to open the exhibition "Shaking the Cradle", organized jointly with the Institution of Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug - Yugra "Museum of Nature and Man".
The first exhibit of the day in October will be the Russian cradle "ZYBKA" (body), presented at the exhibition "Swinging Cradle". This unique cradle, recreated by the museum staff, fully conveys the culture and traditions of the Russian people.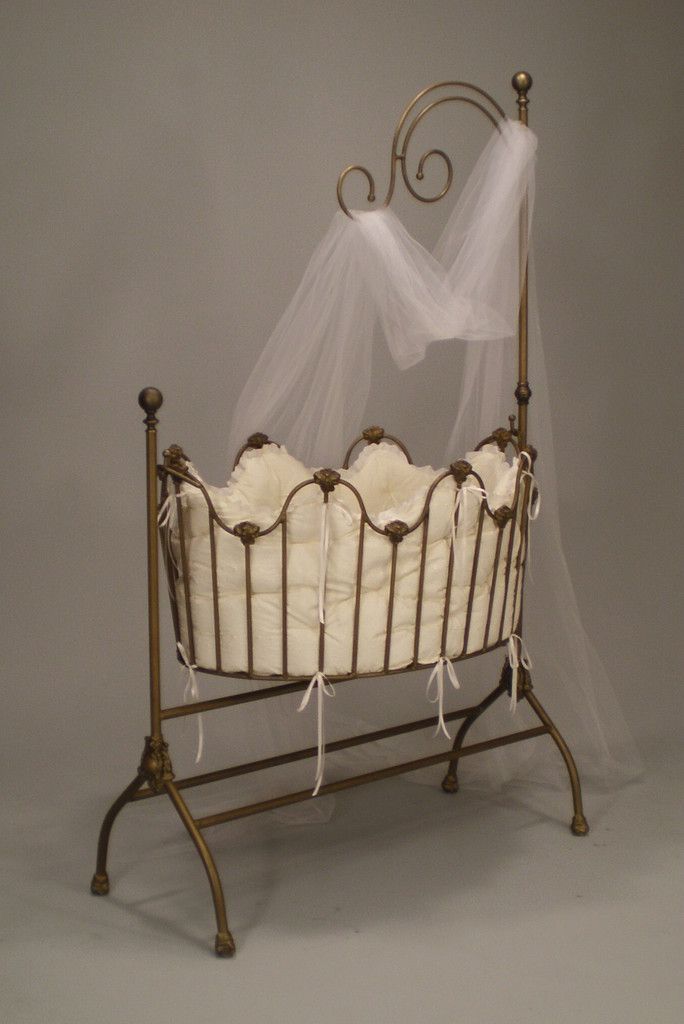
There were several types of baby cribs in Russia. One of them is unsteady (used by the peasants of Northern Russia).
Light unsteady (body), hung from the eyelet. An ochep is a long, flexible and strong pole attached to a ceiling mat. On a good eyelet, the shaking fluctuated quite strongly, sometimes a fathom from the floor.
Fathers and grandfathers made the hanging bed themselves lovingly and crossing themselves. From dry thin (better - spruce) boards, a shallow box (box) was knocked together end-to-end, without nails. The bottom was burlap or homespun cloth. The panel was fastened firmly: holes were drilled along the bottom of the planks, which made it possible to sew fabric and wood together.
The expectant mother, meanwhile, was preparing the canopy for the shaky: not only picked up the beautiful fabric, but also made decorations - embroidery, appliqué, lace. The following protective symbols were depicted on the canopy of the bulge. In the center is the Tree of Life, a symbol of growth, strength, and power. There are squirrels and sprouts on the sides - after all, the teeth are still very young! On the upper edge - Radinets, the sign of babies. Our ancestors carved it on the cradles of babies. What a wonderful word - Radinets! Here is birth, and joy, and the Sun (Ra among the ancient Slavs)! If the family was very poor or the mother was tired of the repeated production of canopies, they could simply put on a grandmother's sundress on the unsteady. The canopy is a must! This is not just a shield from light and flies. It is also an obstacle for evil spirits. It was forbidden to pump an empty shank: supposedly the child would then sleep restlessly.
There are squirrels and sprouts on the sides - after all, the teeth are still very young! On the upper edge - Radinets, the sign of babies. Our ancestors carved it on the cradles of babies. What a wonderful word - Radinets! Here is birth, and joy, and the Sun (Ra among the ancient Slavs)! If the family was very poor or the mother was tired of the repeated production of canopies, they could simply put on a grandmother's sundress on the unsteady. The canopy is a must! This is not just a shield from light and flies. It is also an obstacle for evil spirits. It was forbidden to pump an empty shank: supposedly the child would then sleep restlessly.
Toys were fastened to the shank - shreds of fabric, painted spoons (a sign of share, prosperity, happiness).
In Rus', they believed that children laughing in their sleep see magical gardens of Eden. So the cradles were decorated: on the sides are “paradise” trees, royal birds, azure flowers. In the head part of the bulge they depicted a red sun in the rays, and in the legs - a clear month about the stars. This cradle was passed down from generation to generation.
This cradle was passed down from generation to generation.
If the baby had difficulty falling asleep, the mother, the nanny or the grandmother put the Nanny doll in the cradle. Soft, bright and full-breasted beauty gave joy, warmth and comfort to babies up to the age of three. In the northern villages, two weeks before the birth, the expectant mother made a swaddling doll and hung it over the cradle of the unborn child. The diaper was placed in the cradle, and then next to the baby, so that she would protect him from evil spirits. A doll was made of such a size as to fit in the baby's hand, then it could be the first toy that he would hold and examine. Among the Russians, to treat children from night crying and from fright, they put an ax under the cradle of a boy, and a spinning wheel for a girl; to cure the girl's insomnia, they stuck a spinning wheel with a tow and a spindle under the mat with a sentence and said: “Midnight Office, Tickler! Do not play with my child, play with a spinning wheel, a spindle and a spatula!
In the north of Russia, a shark was traditionally given as a gift for the birth of a child.