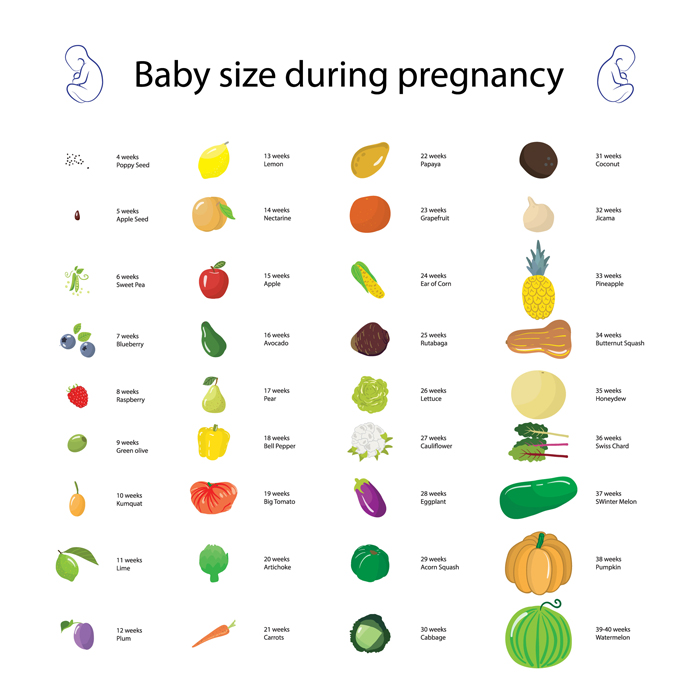
How big is your baby at 1 month
Fetal development: Month-By-Month Stages of Pregnancy
When does a pregnancy start?
The start of pregnancy is actually the first day of your last menstrual period. This is called the gestational age, or menstrual age. It’s about two weeks ahead of when conception actually occurs. Though it may seem strange, the date of the first day of your last period will be an important date when determining your due date. Your healthcare provider will ask you about this date and will use it to figure out how far along you are in your pregnancy.
How does conception work?
Each month, your body goes through a reproductive cycle that can end in one of two ways. You will either have a menstrual period or become pregnant. This cycle is continuously happening during your reproductive years — from puberty in your teen years to menopause around age 50.
In a cycle that ends with pregnancy, there are several steps. First, a group of eggs (called oocytes) gets ready to leave the ovary for ovulation (release of the egg). The eggs develop in small, fluid-filled cysts called follicles. Think of these follicles as small containers for each immature egg. Out of this group of eggs, one will become mature and continue on through the cycle. This follicle then suppresses all the other follicles in the group. The other follicles stop growing at this point.
The mature follicle now opens and releases the egg from the ovary. This is ovulation. Ovulation generally happens about two weeks before your next menstrual period begins. It’s generally in the middle of your cycle.
After ovulation, the opened (ruptured) follicle develops into a structure called the corpus luteum. This secretes (releases) the hormones progesterone and estrogen. Progesterone helps prepare the endometrium (lining of the uterus). This lining is the place where a fertilized egg settles to develop. If you don’t become pregnant during a cycle, this lining is what is shed during your period.
On average, fertilization happens about two weeks after your last menstrual period. When the sperm penetrates the egg, changes occur in the protein coating of the egg to prevent other sperm from entering.
When the sperm penetrates the egg, changes occur in the protein coating of the egg to prevent other sperm from entering.
At the moment of fertilization, your baby’s genetic make-up is complete, including its sex. The sex of your baby depends on what sperm fertilizes the egg at the moment of conception. Generally, women have a genetic combination of XX and men have XY. Women provide each egg with an X. Each sperm can be either an X or a Y. If the fertilized egg and sperm is a combination of an X and Y, it’s a boy. If there are two Xs, it’s a girl.
What happens right after conception?
Within 24 hours after fertilization, the egg begins rapidly dividing into many cells. It remains in the fallopian tube for about three days after conception. Then the fertilized egg (now called a blastocyte) continues to divide as it passes slowly through the fallopian tube to the uterus. Once there, its next job is to attach to the endometrium. This is called implantation.
Before implantation though, the blastocyte breaks out of its protective covering.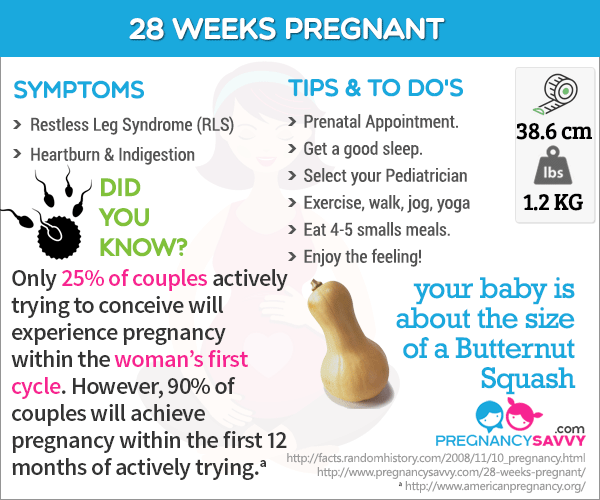 When the blastocyte makes contact with the endometrium, the two exchange hormones to help the blastocyte attach. Some women notice spotting (slight bleeding) during the one or two days when implantation happens. This is normal and isn’t something you should worry about. At this point, the endometrium becomes thicker and the cervix (the opening between your uterus and birth canal) is sealed by a plug of mucus.
When the blastocyte makes contact with the endometrium, the two exchange hormones to help the blastocyte attach. Some women notice spotting (slight bleeding) during the one or two days when implantation happens. This is normal and isn’t something you should worry about. At this point, the endometrium becomes thicker and the cervix (the opening between your uterus and birth canal) is sealed by a plug of mucus.
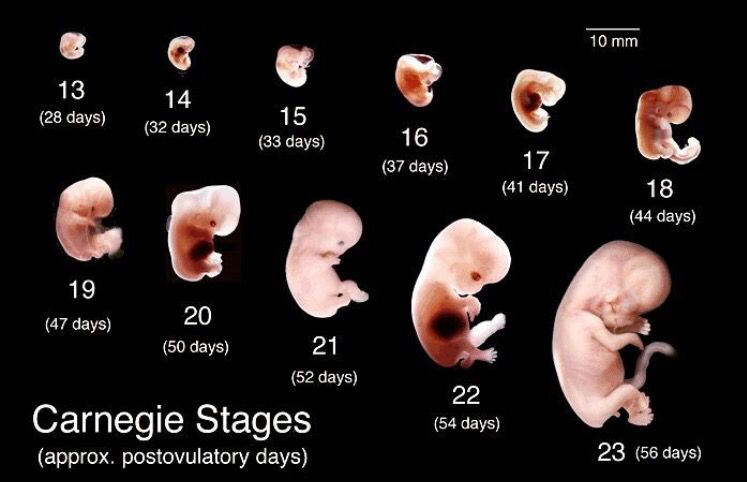
Within three weeks, the blastocyte cells ultimately form a little ball, or an embryo. By this time, the first nerve cells have formed.
Your developing fetus has already gone through a few name changes in the first few weeks of pregnancy. Generally, it's called an embryo from conception until the eighth week of development. After the eighth week, it's called a fetus until it’s born.
How early can I know I’m pregnant?
From the moment of conception, the hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) will be present in your blood. This hormone is created by the cells that form the placenta (food source for the growing fetus). It’s also the hormone detected in a pregnancy test. Even though this hormone is there from the beginning, it takes time for it to build within your body. It typically takes three to four weeks from the first day of your last period for the hCG to increase enough to be detected by pregnancy tests.
It’s also the hormone detected in a pregnancy test. Even though this hormone is there from the beginning, it takes time for it to build within your body. It typically takes three to four weeks from the first day of your last period for the hCG to increase enough to be detected by pregnancy tests.
When should I reach out to my healthcare provider about a new pregnancy?
Most healthcare providers will have you wait to come in for an appointment until you have had a positive home pregnancy test. These tests are very accurate once you have enough hCG circulating throughout your body. This can be a few weeks after conception. It’s best to call your healthcare provider once you have a positive pregnancy test to schedule your first appointment.
When you call, your healthcare provider may ask you if you are taking a prenatal vitamin. These supplements contain folic acid. It’s important that you get at least 400mcg of folic acid each day during a pregnancy to make sure the fetus's neural tube (beginning of the brain and spine) develops correctly. Many healthcare providers suggest that you take prenatal vitamins with folic acid even when you aren’t pregnant. If you weren’t taking prenatal vitamins before your pregnancy, your provider may ask you to start as early as possible.
Many healthcare providers suggest that you take prenatal vitamins with folic acid even when you aren’t pregnant. If you weren’t taking prenatal vitamins before your pregnancy, your provider may ask you to start as early as possible.
What’s the timeline for fetal development?
The fetus will change a lot throughout a typical pregnancy. This time is divided into three stages, called trimesters. Each trimester is a set of about three months. Your healthcare provider will probably talk to you about fetal development in terms of weeks. So, if you are three months pregnancy, you are about 12 weeks.
You will see distinct changes in the fetus, and yourself, during each trimester.
Traditionally, we think of a pregnancy as a nine-month process. However, this isn’t always the case. A full-term pregnancy is 40 weeks, or 280 days. Depending on what months you are pregnant during (some are shorter and some longer) and what week you deliver, you could be pregnant for either nine months or 10 months. This is completely normal and healthy.
This is completely normal and healthy.
Once you get close to the end of your pregnancy, there are several category names you might hear regarding when you go into labor. These labels divide up the last few weeks of pregnancy. They’re also used to look out for certain complications in newborns. Babies that are born in the early term period or before may have a higher risk of breathing, hearing or learning issues than babies born a few weeks later in the full term time frame. When you’re looking at these labels, it’s important to know how they’re written. You may see the week first (38) and then you’ll see two numbers separated by a slash mark (6/7). This stands for how many days you currently are in the gestational week. So, if you see 38 6/7, it means that you are on day 6 of your 38th week.
The last few weeks of pregnancy are divided into the following groups:
- Early term: 37 0/7 weeks through 38 6/7 weeks.
- Full term: 39 0/7 weeks through 40 6/7 weeks.

- Late term: 41 0/7 weeks through 41 6/7 weeks.
- Post term: 42 0/7 weeks and on.
Talk to your healthcare provider about any questions you may have about gestational age and due date.
Stages of Growth Month-by-Month in Pregnancy
First trimester
The first trimester will span from conception to 12 weeks. This is generally the first three months of pregnancy. During this trimester, the fertilized egg will change from a small grouping of cells to a fetus that is starting to have a baby’s features.
Month 1 (weeks 1 through 4)
As the fertilized egg grows, a water-tight sac forms around it, gradually filling with fluid. This is called the amniotic sac, and it helps cushion the growing embryo.
During this time, the placenta also develops. The placenta is a round, flat organ that transfers nutrients from the mother to the fetus, and transfers wastes from the fetus. Think of the placenta as a food source for the fetus throughout your pregnancy.
In these first few weeks, a primitive face will take form with large dark circles for eyes. The mouth, lower jaw and throat are developing. Blood cells are taking shape, and circulation will begin. The tiny "heart" tube will beat 65 times a minute by the end of the fourth week.
By the end of the first month, the fetus is about 1/4 inch long – smaller than a grain of rice.
Month 2 (weeks 5 through 8)
Facial features continue to develop. Each ear begins as a little fold of skin at the side of the head. Tiny buds that eventually grow into arms and legs are forming. Fingers, toes and eyes are also forming.
The neural tube (brain, spinal cord and other neural tissue of the central nervous system) is well formed now. The digestive tract and sensory organs begin to develop too. Bone starts to replace cartilage.
The head is large in proportion to the rest of the body at this point. At about 6 weeks, a heartbeat can usually be detected.
After the 8th week, healthcare providers refer to it as a fetus instead of an embryo.
By the end of the second month, the fetus is about 1 inch long and weighs about 1/30 of an ounce.
Month 3 (weeks 9 through 12)
The arms, hands, fingers, feet and toes are fully formed. At this stage, the fetus is starting to explore a bit by doing things like opening and closing its fists and mouth. Fingernails and toenails are beginning to develop and the external ears are formed. The beginnings of teeth are forming under the gums. The reproductive organs also develop, but sex is still difficult to distinguish on ultrasound.
By the end of the third month, the fetus is fully formed. All the organs and limbs (extremities) are present and will continue to develop in order to become functional. The circulatory and urinary systems are also working and the liver produces bile.
At the end of the third month, the fetus is about 4 inches long and weighs about 1 ounce.
Since the most critical development has taken place, your chance of miscarriage drops considerably after three months.
Second trimester
This middle section of pregnancy is often thought of as the best part of the experience. By this time, any morning sickness is probably gone and the discomfort of early pregnancy has faded. The fetus will start to develop facial features during this month. You may also start to feel movement as the fetus flips and turns in the uterus. During this trimester, many people find out whether their baby will be designated male or female at birth. This is typically done during an anatomy scan (an ultrasound that checks physical development) around 20 weeks.
Month 4 (weeks 13 through 16)
The fetal heartbeat may now be audible through an instrument called a doppler. The fingers and toes are well-defined. Eyelids, eyebrows, eyelashes, nails and hair are formed. Teeth and bones become denser. The fetus can even suck his or her thumb, yawn, stretch and make faces.
The nervous system is starting to function. The reproductive organs and genitalia are now fully developed, and your doctor can see on ultrasound if the fetus will be designated male or female at birth.
By the end of the fourth month, the fetus is about 6 inches long and weighs about 4 ounces.
Month 5 (weeks 17 through 20)
At this stage, you may begin to feel the fetus moving around. The fetus is developing muscles and exercising them. This first movement is called quickening and can feel like a flutter.
Hair begins to grow on the head. The shoulders, back and temples are covered by a soft fine hair called lanugo. This hair protects the fetus and is usually shed at the end of your baby's first week of life.
The skin is covered with a whitish coating called vernix caseosa. This "cheesy" substance is thought to protect fetal skin from the long exposure to the amniotic fluid. This coating is shed just before birth.
By the end of the fifth month, the fetus is about 10 inches long and weighs from 1/2 to 1 pound.
Month 6 (weeks 21 through 24)
If you could look inside the uterus right now, you would see that the fetus's skin is reddish in color, wrinkled and veins are visible through translucent skin. The finger and toe prints are visible. In this stage, the eyelids begin to part and the eyes open.
The finger and toe prints are visible. In this stage, the eyelids begin to part and the eyes open.
The fetus responds to sounds by moving or increasing the pulse. You may notice jerking motions if the fetus hiccups.
If born prematurely, your baby may survive after the 23rd week with intensive care.
By the end of the sixth month, the fetus is about 12 inches long and weighs about 2 pounds.
Month 7 (weeks 25 through 28)
The fetus continues to mature and develop reserves of body fat. At this point, hearing is fully developed. The fetus changes position frequently and responds to stimuli, including sound, pain and light. The amniotic fluid begins to diminish.
If born prematurely, your baby would be likely to survive after the seventh month.
At the end of the seventh month, the fetus is about 14 inches long and weighs from 2 to 4 pounds.
Third trimester
This is the final part of your pregnancy. You may be tempted to start the countdown till your due date and hope that it would come early, but each week of this final stage of development helps the fetus prepare for birth. Throughout the third trimester, the fetus gains weight quickly, adding body fat that will help after birth.
Throughout the third trimester, the fetus gains weight quickly, adding body fat that will help after birth.
Remember, even though popular culture only mentions nine months of pregnancy, you may actually be pregnant for 10 months. The typical, full-term pregnancy is 40 weeks, which can take you into a tenth month. It’s also possible that you can go past your due date by a week or two (41 or 42 weeks). Your healthcare provider will monitor you closely as you approach your due date. If you pass your due date, and don’t go into spontaneous labor, your provider may induce you. This means that medications will be used to make you go into labor and have the baby. Make sure to talk to your healthcare provider during this trimester about your birth plan.
Month 8 (weeks 29 through 32)
The fetus continues to mature and develop reserves of body fat. You may notice more kicking. The brain developing rapidly at this time, and the fetus can see and hear. Most internal systems are well developed, but the lungs may still be immature.
The fetus is about 18 inches long and weighs as much as 5 pounds.
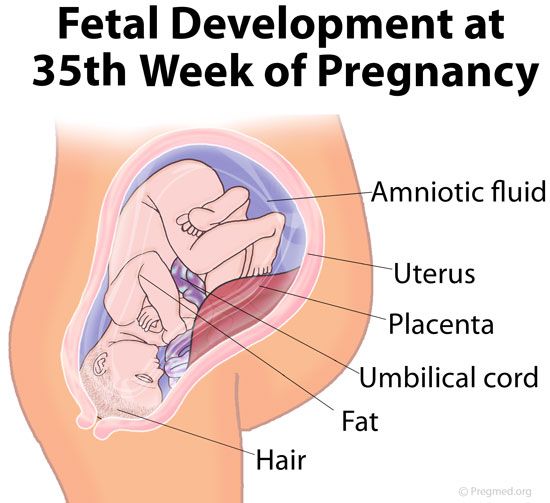
Month 9 (weeks 33 through 36)
During this stage, the fetus continues to grow and mature. The lungs are close to being fully developed at this point.
The fetus has coordinated reflexes and can blink, close the eyes, turn the head, grasp firmly, and respond to sounds, light and touch.
The fetus is about 17 to 19 inches long and weighs from 5 ½ pounds to 6 ½ pounds.
Month 10 (Weeks 37 through 40)
In this final month, you could go into labor at any time. You may notice that less movement because space is tight. At this point, The fetus's position may have changed to prepare for birth. Ideally, it's head down in your uterus. You may feel very uncomfortable in this final stretch of time as the fetus drops down into your pelvis and prepares for birth.
Your baby is ready to meet the world at this point. They are about 18 to 20 inches long and weigh about 7 pounds.
1 Month Pregnant: Symptoms and Fetal Development
You might have noticed some changes in your body and started to wonder, “Could I be … pregnant!?” Or, you might not have observed any signs of pregnancy other than your period being late. If you have your suspicions, you'll probably want to take a home pregnancy test. If the result is positive, congratulations! Read on to find out more about early pregnancy symptoms, how your baby is developing when you’re one month pregnant, and what else is in store for you this month.
Common Pregnancy Symptoms at 1 Month Pregnant
At one month pregnant, you may not experience many — or any — symptoms. However, some of the early signs of pregnancy at one month pregnant can include:
A missed period. If you have a regular menstrual cycle, this is perhaps the most telling sign of pregnancy. You might first suspect you could be pregnant when your period is late, and then when it never arrives at all.
Mood changes. When you become pregnant, your hormone levels start to rise dramatically, and this can sometimes leave you feeling more emotional than usual. It’s also common to experience a range of moods — anything from being anxious and overwhelmed to feeling excited and ecstatic — when you find out you are pregnant. Talk to your loved ones about your feelings, and talk to your healthcare provider if you have any concerns.
Bloating. The surge of pregnancy hormones can lead to bloating, which you might even mistake for a normal symptom of PMS. Eating more fiber and getting regular exercise can help relieve bloating.
Cramps. Some moms-to-be get light uterine cramping in the early days and weeks of pregnancy. These sensations can sometimes feel like menstrual cramps, so you might think you're about to get your period. If cramps are painful or are bothering you, ask your healthcare provider to recommend suitable pain relief options.

Spotting. If you notice some spots of blood on your underwear, it could be what’s called implantation bleeding. This light spotting can happen when the fertilized egg implants itself in the uterine lining in early pregnancy. Wearing a panty liner can help prevent any accidental leaks or stains.
Frequent urination. When you become pregnant, the amount of blood in your body starts increasing. This means your kidneys have to work overtime to process the extra fluid, which then ends up in your bladder. Although some early symptoms of pregnancy may ease up over time, this might not be one of them. Don’t cut back on your fluid intake — it’s important to stay hydrated — but think about trying to pee before you leave your home or any time you might be away from a restroom for any length of time, such as before a meeting or a car trip.
Sore or tender breasts. Your breasts may be sensitive or even sore right now, but this symptom may subside in a few weeks as your body gets used to the hormonal changes taking place.

Fatigue. It’s not uncommon to feel a little more tired than usual, and the hormone progesterone may be to blame. Take it easy as much as you can, and know that many moms-to-be experience a burst of energy once they enter the second trimester.
Nausea. The dreaded morning sickness (nausea with or without vomiting) often doesn’t hit until after the first month of pregnancy, but some moms-to-be may get it a bit sooner, and some lucky women may never experience any queasiness associated with early pregnancy at all. Try to stay hydrated, take a multivitamin, and sip ginger ale or ginger tea to help soothe your stomach.
Constipation. If you’re feeling a bit blocked up, chalk it up to those rising levels of hormones, which can slow down your digestive system. Prenatal vitamins, which typically contain iron, may also be a factor. Ask your healthcare provider for advice on how to help get things going again.
Food aversions.
 When you’re newly pregnant, you might find that certain odors and flavors aren’t quite as appealing as they used to be. Feeling nauseous when you encounter certain foods and smells can sometimes go hand in hand with morning sickness. Use a kitchen fan when cooking, and ask your partner to take out the garbage if certain smells start to bother you.
When you’re newly pregnant, you might find that certain odors and flavors aren’t quite as appealing as they used to be. Feeling nauseous when you encounter certain foods and smells can sometimes go hand in hand with morning sickness. Use a kitchen fan when cooking, and ask your partner to take out the garbage if certain smells start to bother you.
How Is Your Baby Developing This Month?
After conception, the fertilized egg travels along the fallopian tube to the uterus, where it will implant in the uterine lining.
The egg divides into a bunch of cells, some of which become the embryo and some of which eventually become the placenta, which will provide nourishment for your baby during your pregnancy. The umbilical cord also forms between the embryo and the placenta, delivering nutrients and removing waste.
The upcoming month is a time of rapid growth for your little one, as internal organs, bones, and tiny limbs are beginning to form. One quick note on the terminology you might see when reading up on baby development: During the first eight weeks, your little one may be referred to as an embryo in medica circles, whereas after this point your baby may be called a fetus until she is born.
One quick note on the terminology you might see when reading up on baby development: During the first eight weeks, your little one may be referred to as an embryo in medica circles, whereas after this point your baby may be called a fetus until she is born.
How Big Is Your Baby When You’re 1 Month Pregnant?
At this stage your baby is teeny-tiny, but by the start of the second month of pregnancy your little one will be about ¼ of an inch long – or about the size of a pumpkin seed.
What Does an Embryo Look Like at 1 Month?
For a glimpse at how your little one might be looking inside your belly at 4 weeks, take a look at this illustration:
Changes to Your Body at 1 Month Pregnant
You probably won’t be noticing any changes to your body just yet, but that doesn’t mean there isn’t a lot going on under the surface.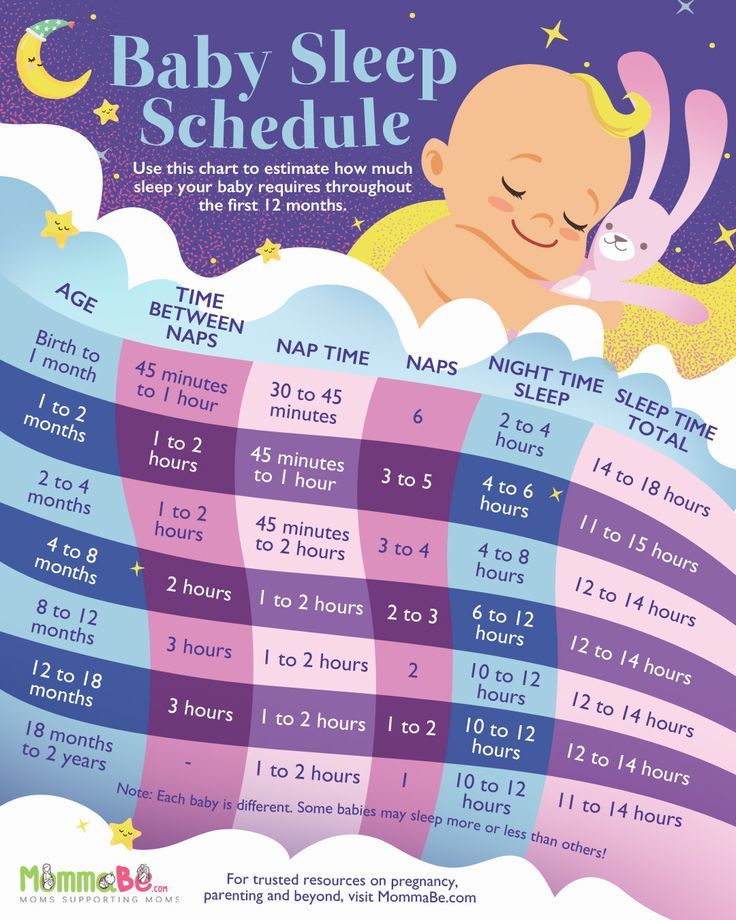 At this point, it’s important to prepare your body for pregnancy and childbirth by paying attention to your overall health and nutrition. This often means taking a multivitamin supplement to make sure you have all the nutrients you and your little one will need for the months ahead.
Talk to your healthcare provider at your first prenatal visit to make sure you’re getting the right amounts of the right vitamins.
It can also be helpful to begin or continue an exercise routine this month. Check in with your provider to make sure your favorite activities are safe during pregnancy, but in general, getting regular exercise can help build the strength and endurance you’ll need throughout your pregnancy.
At this point, it’s important to prepare your body for pregnancy and childbirth by paying attention to your overall health and nutrition. This often means taking a multivitamin supplement to make sure you have all the nutrients you and your little one will need for the months ahead.
Talk to your healthcare provider at your first prenatal visit to make sure you’re getting the right amounts of the right vitamins.
It can also be helpful to begin or continue an exercise routine this month. Check in with your provider to make sure your favorite activities are safe during pregnancy, but in general, getting regular exercise can help build the strength and endurance you’ll need throughout your pregnancy.
How Far Along Are You at 1 Month Pregnant?
At one month pregnant, you’re at the start of the first trimester. Though there is no standard way of grouping pregnancy weeks into months (as they don't fit evenly), the first month usually includes week one through week four of pregnancy. The breakdown of weeks into trimesters also varies; here is a common method we'll follow:
First trimester: 1 to 13 weeks
Second trimester: 14 to 27 weeks
Third trimester: 28 to 40 weeks (or until you give birth)
The breakdown of weeks into trimesters also varies; here is a common method we'll follow:
First trimester: 1 to 13 weeks
Second trimester: 14 to 27 weeks
Third trimester: 28 to 40 weeks (or until you give birth)
How Is Your Due Date Calculated?
At one month pregnant, you’ll be eager to know when your newborn will arrive. Our Due Date Calculator can give you an estimate, but your healthcare provider may be able to give you a more accurate date.
Your due date is calculated as 40 weeks, or 280 days, from the first day of your last menstrual period. Keep in mind that your due date is just an estimate. You may not remember the date of your last period; the length of your menstrual cycle may be shorter or longer than the 28-day average; and it’s very difficult to know exactly when ovulation or fertilization occurred.
Keep in mind, only a small percentage of babies are born exactly on their due date and most babies are born in the two weeks either side of their due date.
Checklist for When You’re 1 Month Pregnant
Research and select a prenatal healthcare provider.
Confirm your pregnancy by taking a home pregnancy test. Read about the pregnancy hormone hCG as it’s what most home pregnancy tests work to detect.
Arrange a doctor’s checkup. Your healthcare provider will confirm your pregnancy and give you guidance on the appointments you’ll need to keep over the coming months.
Speak to your provider about pregnancy nutrition and whether you need to take any prenatal vitamins, such as folic acid.
Download our complete guide to exercising while pregnant, which is brimming with helpful tips, and ask your healthcare provider about what type of exercise is right for your situation. Exercise can help you get a better night’s sleep and can also help with pregnancy body aches and pains.
Quit unhealthy habits like smoking and drinking, and try to reduce stress.
Although rare, it’s a good idea to read up on the signs of an ectopic pregnancy – just in case.
Rest up whenever you can.
If your partner doesn’t know you are pregnant yet, check out our fun ideas for how to announce your pregnancy to your partner.
Speak to your loved ones about how you are feeling. This can be an emotional time, and you might be feeling all kinds of physical symptoms and pregnancy emotions that it may be best to share.
Sign up for even more weekly pregnancy tips here:
Size charts - AnnyBaby
Sizes of baby's undershirts
Large stores sort clothes according to the height of the child. In the department for newborns, undershirts, bodysuits, panties, overalls are hung or laid out in accordance with growth. The European dimensional grid of children's clothing is more and more widely used in Russian everyday life. The European size grid corresponds to the height of the baby in centimeters, a new size is every 6 cm. In the department for newborns, you will find sizes 50, 56, 62, 68. Most newborns start wearing clothes from size 56, and after one and a half to two months they grow up from it and move on to the next size. nine0005
In the department for newborns, you will find sizes 50, 56, 62, 68. Most newborns start wearing clothes from size 56, and after one and a half to two months they grow up from it and move on to the next size. nine0005
It is difficult to accurately measure the height of a newborn. The easiest way to remember what height was measured at the doctor's appointment, but for this you need to help the nurse measure the growth of your child, put the newborn evenly, not in a hurry, fix it for a second so that the measurement is reliable.
Each manufacturer of children's clothing has its own standards. But since for newborns the cut of clothes is wide, free, the difference is not significant and it is enough to focus on the growth of the newborn. If we talk about the standards of manufacturers, then European manufacturers do not have a single standard and each company sews according to its own standard. Pants are sewn with the diaper in mind. Large Russian manufacturers of children's clothing sew in accordance with GOST. You will find a table of standard sizes according to GOST below, in the section about sliders for newborns. Here is a table of average standard sizes for a variety of manufacturers. I repeat, due to the wide cut of undershirts, bodysuits, overalls for newborns, differences in standards do not greatly affect the result, the main indicator when choosing the size of clothes for a newborn is the growth of the baby. nine0005
You will find a table of standard sizes according to GOST below, in the section about sliders for newborns. Here is a table of average standard sizes for a variety of manufacturers. I repeat, due to the wide cut of undershirts, bodysuits, overalls for newborns, differences in standards do not greatly affect the result, the main indicator when choosing the size of clothes for a newborn is the growth of the baby. nine0005
| Size | 50 | 56 | 62 | 68 | 74 | 80 | 86 | 92 |
| Height in cm | to 50 | 51-56 | 57-62 | 63-68 | 69-74 | 75-80 | 81-86 | nine0013 87-92|
| Chest in cm | 40-43 | 42-45 | 44-47 | 46-49 | 48-51 | 50-53 | 51-55 | 52-56 |
| Waist in cm | 40-43 | 42-45 | 44-47 | 46-48 | 47-50 | 49-51 | 50-52 | 51-53 |
| Hips in cm | 42-44 | 44-46 | 46-48 | 48-50 | 50-52 | 52-54 | 54-56 | 56-58 |
| Estimated age | 0 months | 0-1. 5 months 5 months | 1.5-3 months | 3-6 months | 6-9 months | 9-12 months | 1-1.5 years | 2 years |
Newborn overall sizes
Winter and demi-season overalls for newborns are sized by height in centimeters. They are sewn loose enough to wear blouses, pants, a diaper under the overalls. When choosing a size, keep in mind that a newborn and a baby up to a year old grows very quickly, and the cold season lasts several months, therefore, when buying an expensive thing for growth, it is easy to make a mistake with the size. We recommend buying a jumpsuit for a newborn on the eve of the season.
Baby size 9 sliders0003
Most mothers first come across the Russian dimensional grid when choosing rompers, panties, T-shirts. The Russian dimensional grid of children's clothing differs from the European one not only in standard metric indicators, but also in the main size. If you see size 18, 20, 22 on Russian-made clothes, then this is a Russian dimensional grid. You can find a table with the Russian dimensional grid of clothes for newborns here, just below.
You can find a table with the Russian dimensional grid of clothes for newborns here, just below.
We would like to draw your attention to the fact that the Russian dimensional grid is focused on not very well-fed children. Today, most newborns are larger than 30-50 years ago, when GOST was created. Therefore, when choosing a size according to the table below, pay attention not only to height, but also to the circumference of your child's chest. First, according to the height of the newborn, find the appropriate size in the table, then compare what chest girth in the table and the baby. If the newborn has a smaller bust than in the table, choose the size corresponding to the height. If the newborn has a larger chest circumference than indicated in the table, take a larger size. nine0005
| Size | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 |
| Height in cm | 50-56 | 62-68 | 74 | 80 | 86-92 |
| Chest in cm | 40 | 44 | 44 | 48 | 52 |
| Waist in cm | 40 | 44 | 45 | 48 | 52 |
| Hips in cm | 42 | 46 | 50 | 54 | 56 |
| Estimated age | 0-1.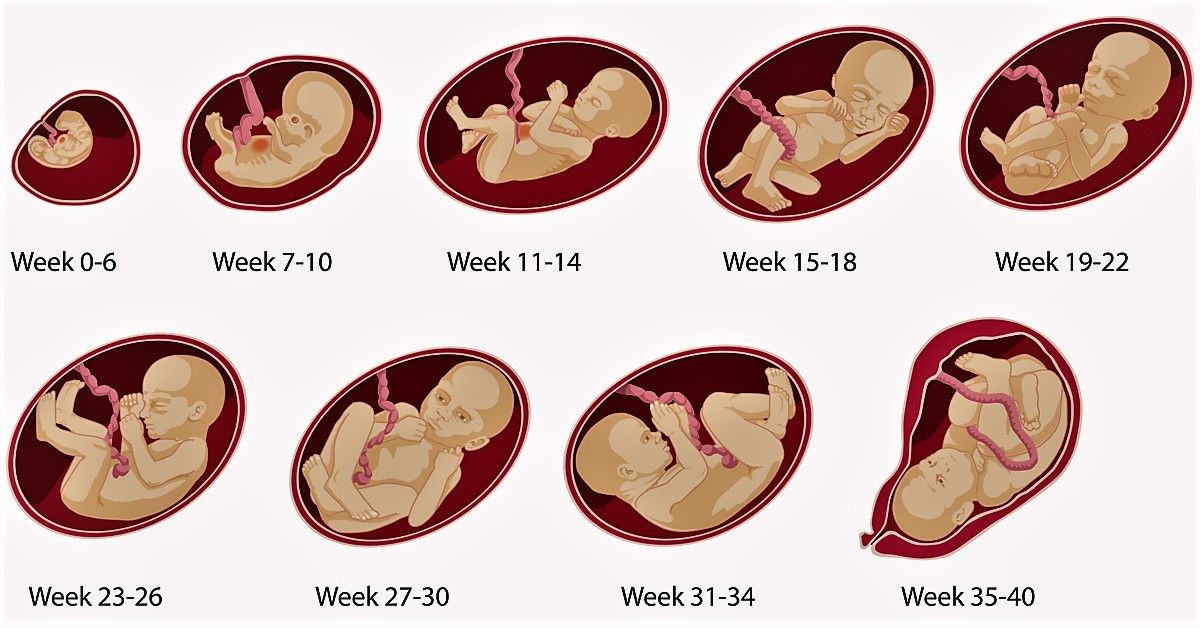 5 months 5 months | 1.5-6 months | 6-9 months | 9-12 months | 1-2 years |
Sizes of socks for newborns and toddlers up to two years
The size of socks is determined by the length of the foot in centimeters. Foot length is measured from heel to toe. It is convenient for a newborn to measure the leg when he sleeps. For the most reliable measurement, try tracing the outline of the foot on paper and measure the length of the foot on the paper.
Children's socks have different sizes. Most often there is a grid after 2 cm for even values, for example, in most Russian manufacturers. Some manufacturers produce socks according to the size grid in 1 cm.
| Size | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| Russian size | 10 | 12 | 14 | ||||||
| Foot length in cm | to 6. | 6.5-7.4 | 7.5-8.4 | 8.5-9.4 | 9.5-10.4 | 10.5-11.4 | 11.5-12.4 | 12.5-13.4 | 13.5-14.4 |
| Estimated age | 0-1 months | 0-1.5 months | 0-3 months | 1.5-3 months | 3-6 months | 6-9 months | 9-12 months | 1-1.5 years | nine0013 1.5-2 years|
Children's tights sizes
Children's tights are sized according to height in centimeters. Manufacturers provide a standard foot length (see size chart). If the baby has a large leg, take stretchy tights. For a chubby newborn, choose tights for the next size chart.
Tights are double sized, but sizes vary from manufacturer to manufacturer. Some manufacturers sew children's tights in sizes 50-56, 62-68, 74-80, 86-92. Others - 56-62, 68-74, 80-86. Which is very convenient, because. allows you to choose the size of the newborn tights. Large children's stores sell tights in both sizes.
Large children's stores sell tights in both sizes.
In the table we present both dimensional grids of children's tights at the same time, in sizes for newborns and babies up to two years old.
| Size | 50-56 | 56-62 | 62-68 | 68-74 | 74-80 | 80-86 | 86-92 |
| Foot length in cm | 7 | 8 | 9 | 9-10 | 11-12 | 12-13 | 13-14 |
| Estimated age | 0-1.5 months | 0-3 months | 1.5-6 months | 3-9 months | 6-12 months | 9-18 months | nine0013 1-2 years
Sizes of baby caps and caps
Sizes of baby caps and caps are determined by the head circumference in centimeters. You need to measure your head exactly along the eyebrows, above the ears and further to the back of the head. We measure the newborn when he lies, then lower the centimeter from the eyebrows to the back of the head vertically. If the newborn is already holding the head, it is better to measure the circumference of the head when someone is holding it. If the baby is already sitting, measure while sitting. Then we clasp the head with a centimeter strictly horizontally. nine0005
You need to measure your head exactly along the eyebrows, above the ears and further to the back of the head. We measure the newborn when he lies, then lower the centimeter from the eyebrows to the back of the head vertically. If the newborn is already holding the head, it is better to measure the circumference of the head when someone is holding it. If the baby is already sitting, measure while sitting. Then we clasp the head with a centimeter strictly horizontally. nine0005
Caps for newborns and children's hats are very different in size: letter and number, single and double, according to size grids in 1, 2 or 4 cm. Most manufacturers sew caps and hats according to size grids with double sizes 36-38, 40 -42 or 38-40, 42-44 or according to the size grid after 2 cm, for example, 36, 38, 40, 42. Sometimes, along with the volume of the head, the height of the newborn is indicated, for example, 36/56, 40/62, 44 / 68, or the age of the child.
For the sake of safety and health, we recommend wearing bonnets and caps, especially for newborns, in size. nine0005
nine0005
| Age of boys | 0 months | 1 month | 2 months | 3 months | 6 months | 9 months | 1 year | 1.5 years | 2 years |
| Medium head circumference | 34-39 | 37-41 | 39-43 | 41-45 | 43-47 | 45-48 | 47-49 | 48-50 | 48-51 | nine0049
| Age of girls | 0 months | 1 month | 2 months | 3 months | 6 months | 9 months | 1 year | 1.5 years | 2 years |
| Medium | 32-38 | 35-40 | 37-42 | 39-44 | 41-46 | 43-47 | 45-48 | 47-49 | 48-50 |
If you have come across the letter designation of the cap size for a newborn or baby hat, then the table below will help you determine the appropriate size:
| XXS | XS | S | M | |
| Head circumference | 40-43 | 44-46 | 47-49 | 50-52 |
Sizes of mittens for babies and toddlers
The Russian size of children's mittens and mittens is determined by the girth of the palm, excluding the thumb in centimeters. Correspondence with international size is shown in the table below. It is very difficult to find mittens for newborns on sale, and sometimes it is not necessary, because. modern overalls for newborns cover the entire handles. For one-year-olds, it is also not easy to buy gloves in size, in such a situation they buy the smallest ones.
Correspondence with international size is shown in the table below. It is very difficult to find mittens for newborns on sale, and sometimes it is not necessary, because. modern overalls for newborns cover the entire handles. For one-year-olds, it is also not easy to buy gloves in size, in such a situation they buy the smallest ones.
| International size | 0 | 1 | |
| Russian size | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Estimated age | 0-6 months | 6-12 months | 1-2 years |
How to determine the size of clothes for a newborn baby
Finding the first clothes for a baby is very difficult. If everything is more or less clear with the set: baby diapers, bonnet, socks, etc. , then determining the size sometimes confuses young parents. Experienced mothers of LOLOCLO will tell you how to choose clothes for someone who appeared in this world just a couple of days ago. nine0005
, then determining the size sometimes confuses young parents. Experienced mothers of LOLOCLO will tell you how to choose clothes for someone who appeared in this world just a couple of days ago. nine0005
Clothing parameters
The main parameter by which the size of clothes for a newborn is selected is the height of the baby. Most often, children are born with a height of 48-54 cm, on average - about 52 centimeters. No two babies are exactly alike, even if they are twins. When creating children's clothing, fashion designers are guided not only by the growth of the baby. It is important to take into account the girth of the chest and tummy in order to surely hit the target. Approximate volumes of newborns (children up to 1 month old) are as follows:
- bust: 38-40cm
- tummy circumference: 42 cm
- head circumference - 33-35 cm
- height: 51-56 cm
Carefully study the information on the tag and compare it with the parameters of your baby.
Types of clothing sizes
There are several size ranges on the market: Russian, European and standard. The most popular is the standard one, and we'll talk about it first. The smallest size in this line is the 50th. It is designed for newborn babies, and also suitable for babies who were born prematurely. The step of the size range is not 2, as in adults, but 6, respectively, the next size is the 56th. This is one of the most “running” and popular sizes, which is suitable for both girls and boys from 50 cm tall and in the first month of life. Clothes of the 62nd size are worn on heroes who were born with a height of 53 cm, as well as for children aged 1 to 2 months. nine0005
The Russian system of clothing sizes for newborns is established by GOST and starts from the 18th size. It is suitable for babies in the first days of life, as well as for premature babies. The 20th size is intended for children under the age of 1 month, as well as strong men who were born very large. The next size - the 22nd - is suitable for those who are about to turn 1.5 months old. The European grid is perhaps the easiest to remember and the most unpredictable when trying on. For a new family member, you need the size indicated by the numbers “0/3”. It is suitable for babies aged 0 to 3 months. nine0005
The next size - the 22nd - is suitable for those who are about to turn 1.5 months old. The European grid is perhaps the easiest to remember and the most unpredictable when trying on. For a new family member, you need the size indicated by the numbers “0/3”. It is suitable for babies aged 0 to 3 months. nine0005
Cap size
We've sorted out the undershirts, now we need to determine the size of the first cap. It is important to know the approximate girth of the baby's head. In ordinary newborns, this is usually about 33-35 cm, in large babies - up to 37-40 cm. The size of the cap, which will surely be a crumb at the time in the first month of life, is the 35th. For the second month, and for the heroes, a bonnet of the 40th size is suitable.
Sock size
This is perhaps one of the most touching pieces of children's wardrobe. The smallest socks you can find on the market, only 6 cm long! Such clothes are worn on the smallest children who were born before term.