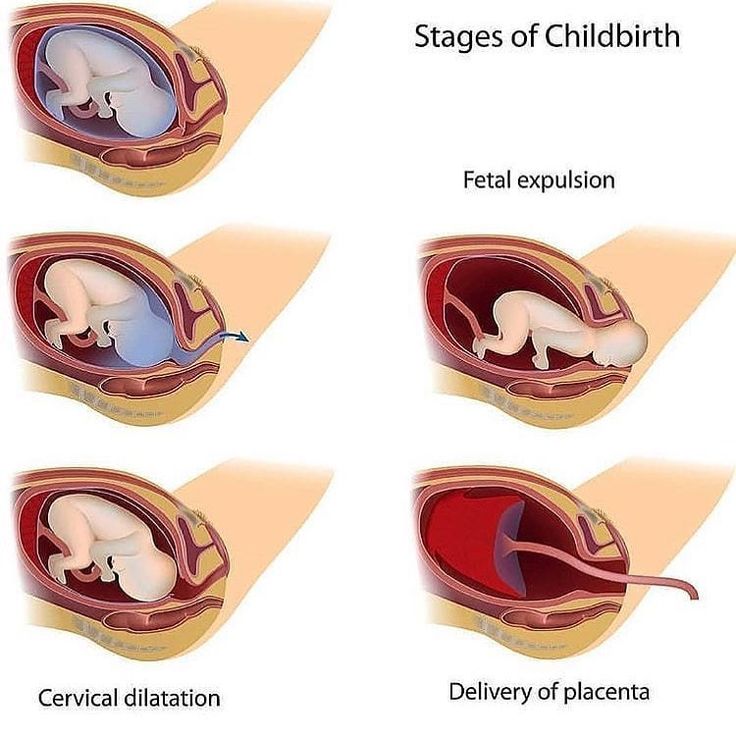
Fourth stage of pregnancy
What is the fourth trimester?
beginning of contentBlog post | 10 Oct 2019
Listen
The fourth trimester is the 12-week period immediately after you have had your baby. Not everyone has heard of it, but every mother and their newborn baby will go through it. It is a time of great physical and emotional change as your baby adjusts to being outside the womb, and you adjust to your new life as a mum.
Helping your newborn adjust to the world
Named by paediatrician Dr Harvey Karp in 2002, the term ‘fourth trimester’ suggests that you should try to recreate, for another 3 or 4 months, the kind of environment your baby had in the womb. But just how do you do that?
Swaddling and swaying
Babies spend 9 months in a confined and constantly moving environment. There are several ways you can re-create the sense of safety and security your baby felt before they were born. By swaddling your baby when you put them down to sleep, you will let them feel secure, and you might find they wake less frequently and sleep for longer.
‘Wearing your baby’ in a sling across your chest can feel familiar to them. But it’s important to make sure you use the sling correctly, since they can cause injury if not properly fitted.
Movement is also a great way to calm your baby. Gently swaying or rocking from side to side, walking whilst carrying them or even taking a quick car trip can settle your baby.
Skin to skin contact
Skin to skin contact is always encouraged in the moments after you give birth, but this type of contact should continue long after you have left the birthing room. Cuddling your newborn on bare skin is a great comfort to them. Your smell and the sound of your heartbeat is warm and familiar. This is also something your partner can do.
Feeding
Whether you are breastfeeding or bottle-feeding, if your baby is hungry, don’t wait for a scheduled time to feed them. Combine feeding your baby with skin to skin contact to reinforce close contact and comfort.
Combine feeding your baby with skin to skin contact to reinforce close contact and comfort.
Bath time
Having a warm bath is often a relaxing and comforting experience for newborns. Floating in the water is like being in the womb. It’s also a great way for you to bond, talk and sing to your baby.
What does the fourth trimester mean for mum?
For you, the fourth trimester is a time of great change. When the baby arrives, quite often the focus shifts to them and as a result, mums can overlook their own health and wellbeing.
Newborns take up lots of time. It’s very easy for new mums to be overwhelmed in the first few weeks by the demands of feeding, sleeping (or lack of), crying and looking after a baby. Combined with the physical recovery after giving birth and the changes to their hormones, it’s no wonder mums can feel exhausted!
Ask for help
In some cultures, new mums spend the first few weeks totally focused on bonding and recovering with their newborn. Other people, usually a family member like a mother, sister or aunty, will stay with them to do the other things around the house and help out with the baby when needed.
Other people, usually a family member like a mother, sister or aunty, will stay with them to do the other things around the house and help out with the baby when needed.
In Australia, however, most women go home from hospital after a couple of days and attempt to continue to do everything as before.
If you have a partner, encourage them to assist and participate in parenting as much as possible. The two of you are in this together and there are lots of things you both can do to share the load.
You don’t want a procession of people coming over, but a few family and friends can help by:
- bringing meals
- helping with household chores
- looking after your other children (if this is not your first child)
- looking after the baby while you rest
Accept help and don’t be afraid to ask.
Eat good, nutritious food
You will need lots of energy in those first few months, so eating a variety of healthy foods will help give you the boost you need.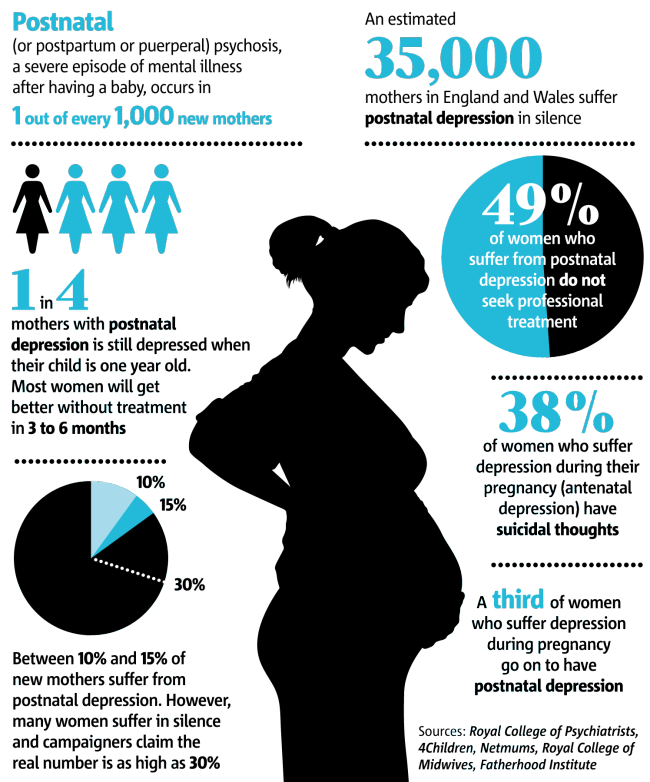 Some some light exercise will also help with your recovery and energy levels. But make sure to give your body time to heal and take it at your own pace.
Some some light exercise will also help with your recovery and energy levels. But make sure to give your body time to heal and take it at your own pace.
Sleep when you can
It might sound obvious, but you need to sleep. It’s going to take a while for your baby to settle into a routine and even then, they will have you up at all hours of the night. If you can, try and sleep when your baby is sleeping, or ask your partner or a family member to look after your baby while you get some rest.
When to see your doctor or midwife
Your body has been through a lot over the past 9 months. Your physical recovery will take time, but it’s important to speak to your doctor or midwife if you have any of the following:
- heavy bleeding or passing of clots
- high temperature or fever
- offensive-smelling vaginal discharge
- a hard or painful lump in your breast
- an area around stitches that is red, hot or oozing
- pain, tenderness or a warm area in your legs
Many women also experience the ‘baby blues’ in the first few days after giving birth, but if these feeling are not going away, it's important you see your doctor as soon as possible.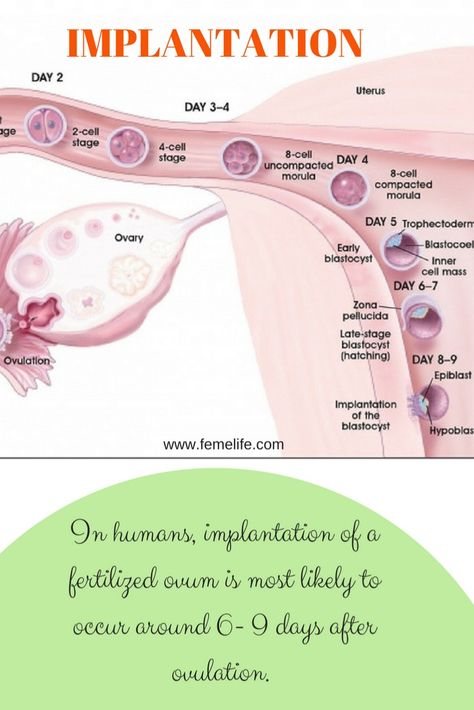 Postnatal depression affects 1 in 7 women in Australia, and it is nothing to be ashamed of, but you need to seek help.
Postnatal depression affects 1 in 7 women in Australia, and it is nothing to be ashamed of, but you need to seek help.
Need help?
- Talk to your doctor or midwife.
- Contact a maternal child health nurse.
- Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436, 7 days a week, from 7am to midnight (AEST).
- Visit the Australian Breastfeeding Association website, or call them on 1800 686 268.
- Call PANDA (Perinatal Anxiety & Depression Australia) on 1300 726 306.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.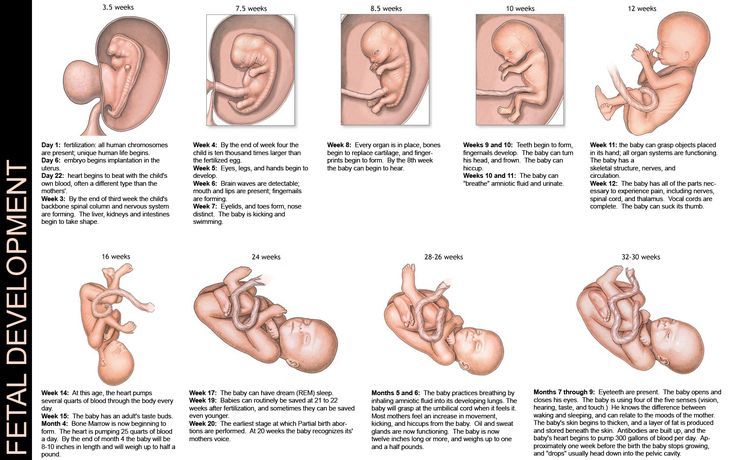
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
A Mother’s Guide to the Fourth Trimester
The fourth trimester—the 12 weeks after giving birth—is just as important for a mother’s health as the first three trimesters. Yet this is often when mothers have the least interaction with their health care team, a time when, some experts argue, mothers need it the most.
Yet this is often when mothers have the least interaction with their health care team, a time when, some experts argue, mothers need it the most.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that mothers have initial contact with their OB-GYN within three weeks after delivery, followed by ongoing care as needed, and a comprehensive postpartum visit no later than 12 weeks after delivery. They also recommend that a postpartum care plan be developed during pregnancy, so that mothers are better prepared when they go home.
“Those 12 weeks after giving birth are a critical time to focus on Mom and make sure that she is healthy moving forward,” says Mary Rosser, MD, PhD, assistant professor of obstetrics & gynecology at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and an OB-GYN at Columbia University Irving Medical Center/NewYork-Presbyterian. “We want to make sure it is not just a one-off checkup but that we’re giving mothers holistic care and support for their growing family. Postpartum care sets the stage for lifelong health and well-being.”
Postpartum care sets the stage for lifelong health and well-being.”
Postpartum Visits
Just 40% of moms attend their postpartum follow-up visit, says Rosser, who helped develop post-birth recommendations as a member of ACOG’s Presidential Task Force on Redefining the Postpartum Visit. “It’s an overwhelming time, so what often happens is this visit gets pushed aside, but it absolutely should not,” she says. “It impedes the management of chronic health conditions, discussing family planning and contraception, assessing mental health and well-being, and physical recovery.”
Rather than the traditional single checkup at around six weeks, Rosser says that “postpartum care should be an ongoing process, with tailored services to support each mother’s individual needs.”
ACOG recommends a postpartum visit within one to three weeks and another within 12 weeks of giving birth.
Those who are considered high risk should check in within the first week or two, says Rosser.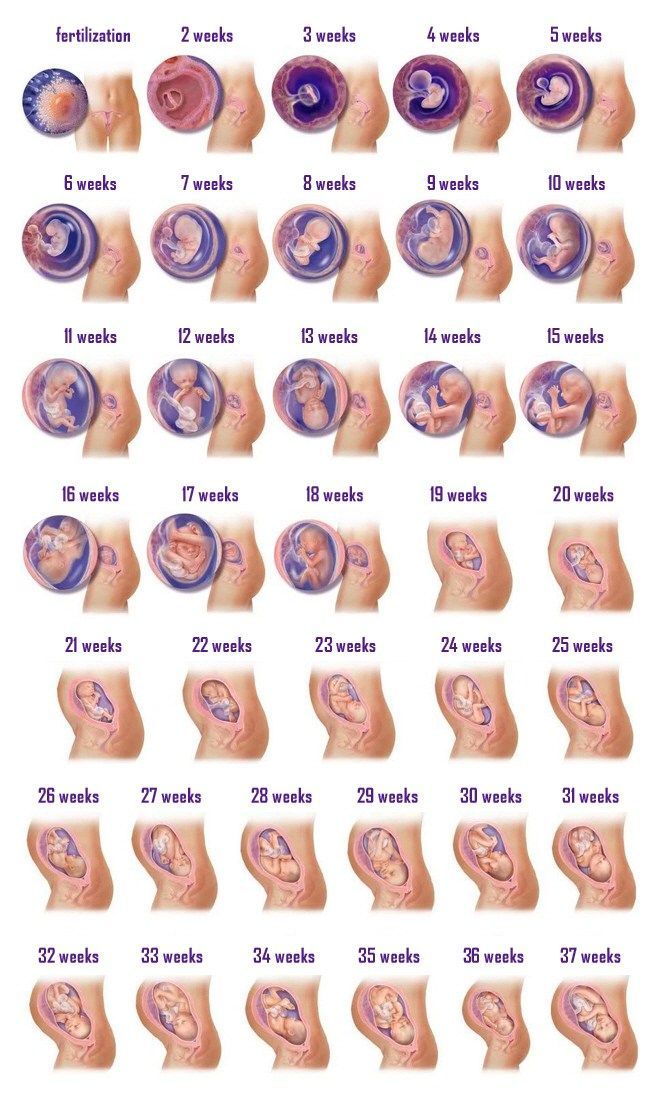 The first check-in—which often can be done over the phone or via telehealth—is to make sure Mom is doing well physically and emotionally and baby is feeding properly and gaining weight. It is important to discuss with your health care provider, Rosser says, whether this initial visit can be done via video or should be in person.
The first check-in—which often can be done over the phone or via telehealth—is to make sure Mom is doing well physically and emotionally and baby is feeding properly and gaining weight. It is important to discuss with your health care provider, Rosser says, whether this initial visit can be done via video or should be in person.
Within 12 weeks mothers should have an in-person, comprehensive care visit to discuss any medical concerns that may need addressing, as well as the mother’s physical health, mental and emotional health, and infant care and feeding. This also is a time when practitioners and patients can develop a road map for future health.
It is important to note that, depending on a mother’s personal history and individual needs, they should receive ongoing postpartum care as needed. “It really is no longer a one-size-fits-all approach,” says Rosser.
A Comprehensive Postpartum Checklist
1. Physical recovery
After delivery, there is a lot of soreness and healing that takes place.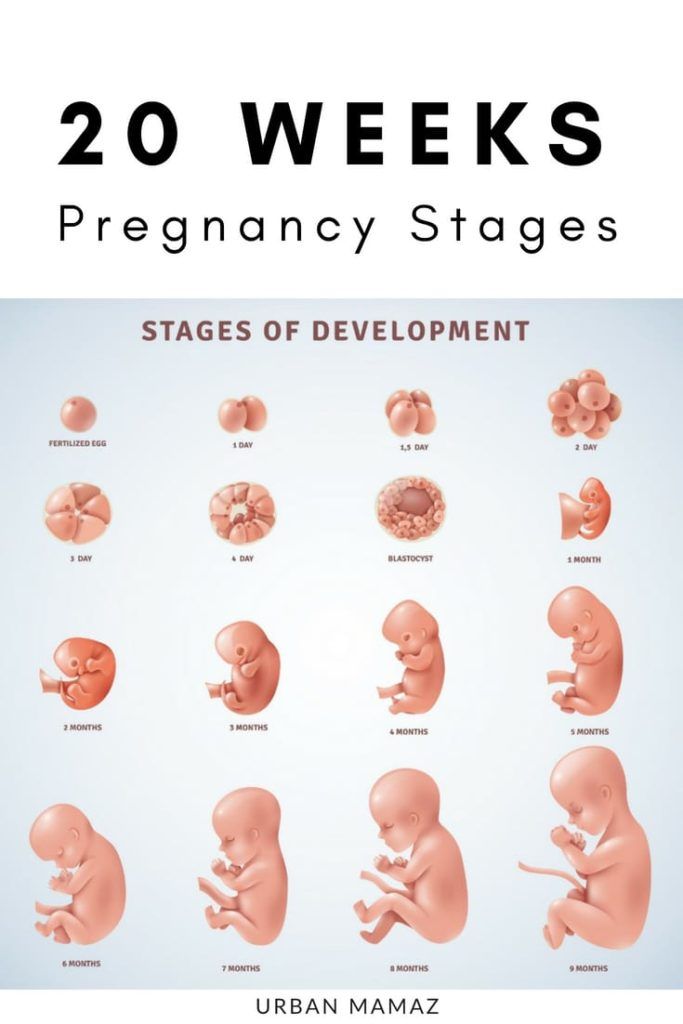 It is important for patients to have a full physical exam during their postpartum visit. A patient who had a tear during a vaginal delivery will need a thorough exam to make sure everything is healed. For C-section deliveries, the stitches need to be looked at to ensure they’re healing. “I’ll listen to the heart and the lungs, especially if they have had hypertension, do an abdominal exam, check to see if their thyroid is OK,” says Rosser. “You’re going from top to bottom, just like you would for any comprehensive exam, but you are targeting and individualizing it to that individual woman.”
It is important for patients to have a full physical exam during their postpartum visit. A patient who had a tear during a vaginal delivery will need a thorough exam to make sure everything is healed. For C-section deliveries, the stitches need to be looked at to ensure they’re healing. “I’ll listen to the heart and the lungs, especially if they have had hypertension, do an abdominal exam, check to see if their thyroid is OK,” says Rosser. “You’re going from top to bottom, just like you would for any comprehensive exam, but you are targeting and individualizing it to that individual woman.”
2. Infant care and feeding
Postpartum appointments also are a chance to assess how a baby is doing and whether they are feeding properly. Breastfeeding is healthy for both infants and moms, but not everyone has instant success. If, after two or three days, there is a lot of pain, Mom is unable to breastfeed, or the baby is not gaining weight, seek support from a lactation consultant.
3.
 Sleep and fatigue
Sleep and fatigueMothers will be very fatigued in the first few weeks after delivering a baby. Experts advise new mothers fit in sleep whenever possible, such as when the baby is sleeping. Resist the urge to do chores around the house when your newborn is sleeping; instead, take a nap yourself. Consider enlisting your partner in nighttime feedings so that you can get a good night’s sleep. Perhaps a family member or friend can help with babysitting once or twice a week or running errands while you get some much-needed rest. Don’t be afraid to ask for help if you are not getting enough sleep to function. Sleep deprivation should slowly get better over time. If it does not and instead gets worse, call your doctor.
Getty Images4. Mental health and well-being
It is normal to feel a bit of sadness seven to 14 days after birth—as many as 80% of women experience these “baby blues.” After all, a mother’s hormones are shifting, there is lack of sleep, and mothers are adapting to a new baby.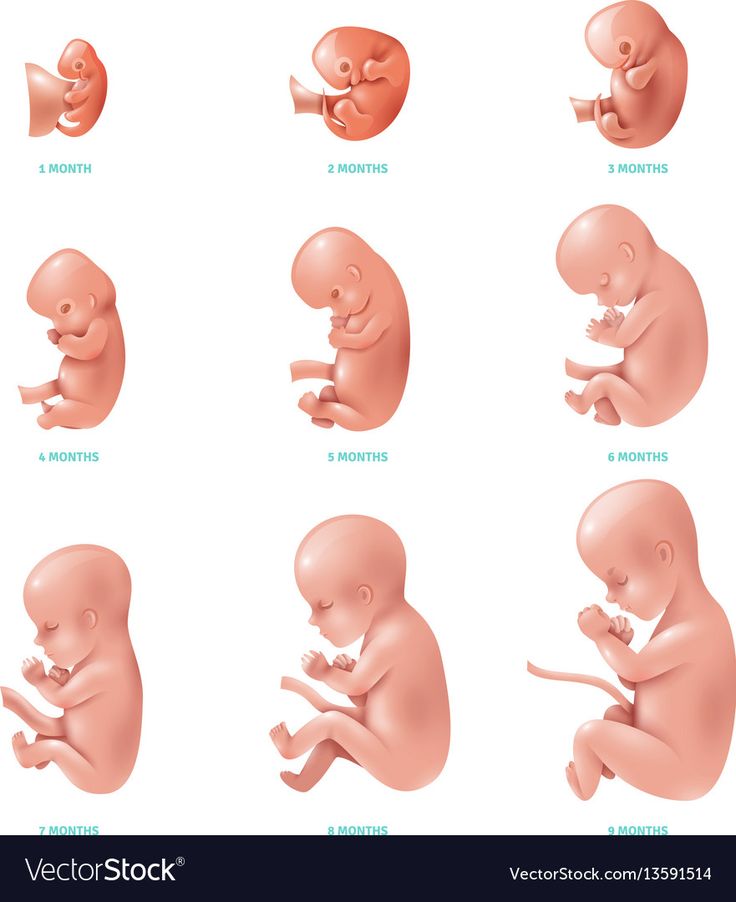 “But if it goes beyond 10 to 14 days and people feel an overwhelming sadness or hopelessness, or a mother has so much anxiety or worry that they even think about not existing anymore, that may be a sign of postpartum depression,” says Rosser. “Those are reasons to get help immediately.”
“But if it goes beyond 10 to 14 days and people feel an overwhelming sadness or hopelessness, or a mother has so much anxiety or worry that they even think about not existing anymore, that may be a sign of postpartum depression,” says Rosser. “Those are reasons to get help immediately.”
5. Sex and family planning
Returning to sex should be a personal decision. “Usually, it’s OK at six to eight weeks if everything is healed, or whenever Mom feels ready,” says Rosser. “What is important is that partners have open communication. Sex may be a bit different, so it is good to be open to it being different and take your time.”
When it comes to contraception and family planning, Rosser urges patients to have a plan in place before the baby arrives. Do not consider breastfeeding a form of contraception. “Before you become sexually active again, talk with your provider about birth control. Many patients will opt for an IUD right after delivery so that they don’t have to worry about an unplanned pregnancy immediately after birth.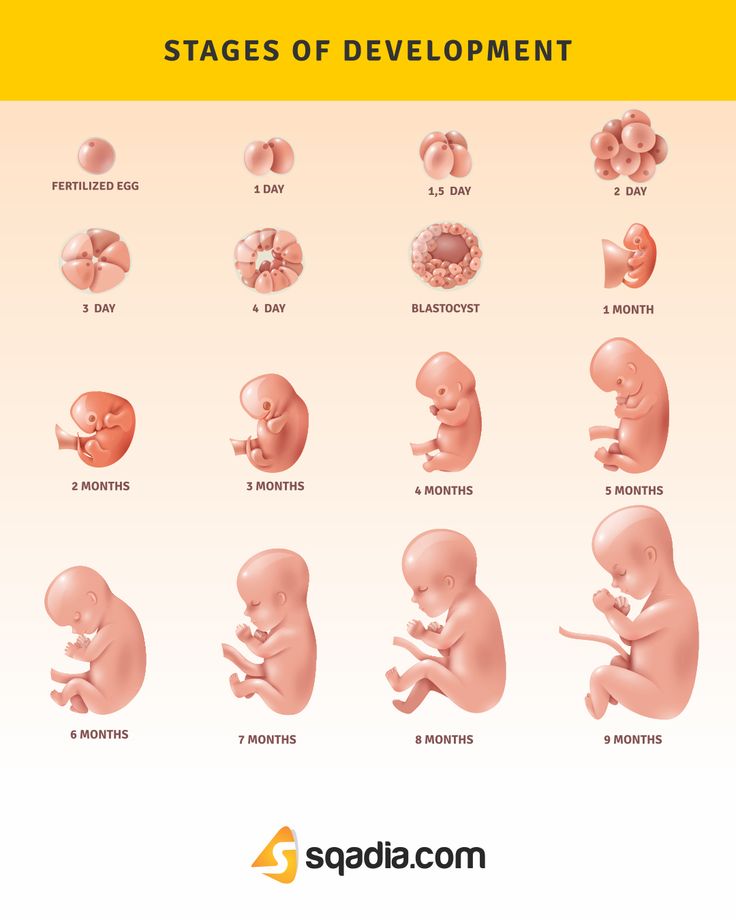 ”
”
6. Diet and exercise
It is important for new moms to nourish their bodies with healthy, whole foods (lots of fresh fruits and vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains), drink plenty of water, and begin moving their bodies as they feel ready. For those who have had a vaginal delivery or a C-section, an excellent place to start is simply walking: Go outside and walk around the block. Ease into it and build up your physical activity. Those who have had a C-section should check with their doctor about when to resume more strenuous physical activity.
Eating well and moving helps the body heal and recover. Healthy babies need healthy, well-adjusted mothers. “If Mom is not well, then she is not going to be able to care for her baby and her family the way that she might want,” says Rosser.
7. Chronic disease management
Postpartum visits are an opportunity to recognize risk factors for conditions like heart disease or obesity and to check that complications during pregnancy such as high blood pressure or diabetes are resolving.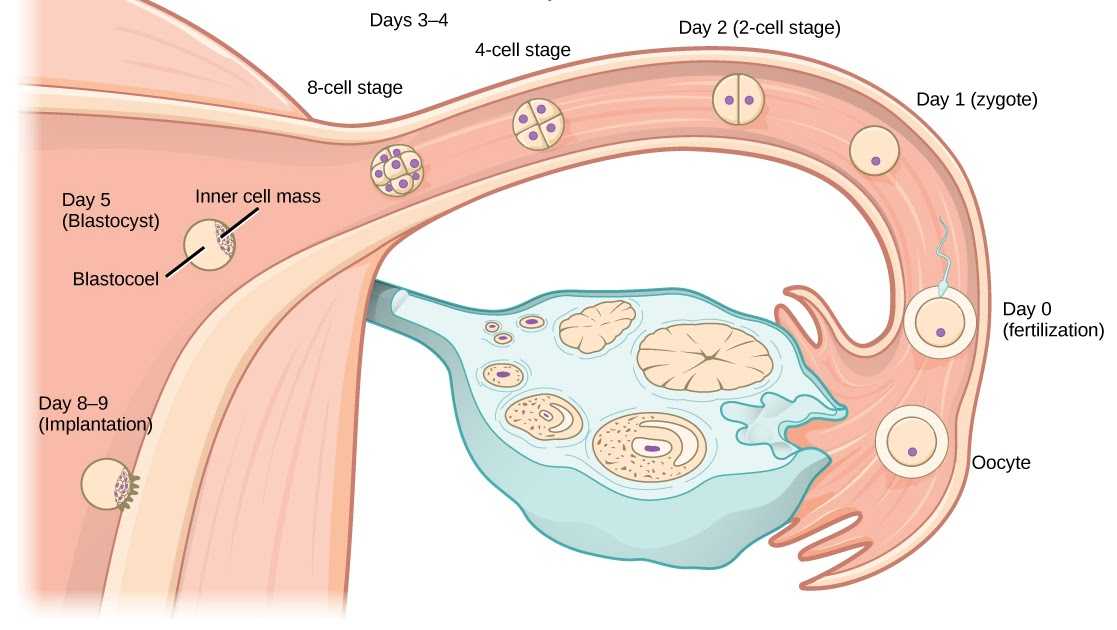 “We can provide risk reduction strategies and early intervention,” Rosser says. “It’s about educating, empowering, and motivating the patient and encouraging a healthy lifestyle that is consistent.”
“We can provide risk reduction strategies and early intervention,” Rosser says. “It’s about educating, empowering, and motivating the patient and encouraging a healthy lifestyle that is consistent.”
8. Know the warning signs
One-third of maternal deaths occur after the birth of the baby, from one week through one year after delivery, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Black women are three to four times more likely to die of a pregnancy-related cause than white women. It’s a sobering statistic that OB-GYN experts are working diligently to change by raising awareness of certain warning signs.
Seek medical attention immediately if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Fever or chills. This could indicate an infection vaginally (if there was a significant tear), in the womb, or of the C-section. Urinary tract infections can also be very common.
- Heavy, brisk, bright-red bleeding. Postpartum women may bleed up to four to six weeks; however, if it is heavy all at once, it could be postpartum hemorrhage.
 “I tell women, if you saturate a pad every hour and that’s consistent for several hours, we want to see you,” says Rosser.
“I tell women, if you saturate a pad every hour and that’s consistent for several hours, we want to see you,” says Rosser. - Dizziness. A symptom associated with loss of blood.
- Shortness of breath or chest pain. This might signal a blood clot like deep venous thrombosis or a pulmonary embolism.
- Severe headache. Sometimes associated with preeclampsia, which is a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure or stroke.
- Swelling of the legs and feet. May be a sign of preeclampsia.
- Deep sadness, thoughts of hopelessness, or thoughts about death, suicide, or harming oneself or the baby. Postpartum depression affects one in 10 mothers and is very serious.
“These symptoms can be life-threatening,” says Rosser. “Don’t ignore them or chalk them up to just being tired and postpartum. If it’s something that is out of the ordinary, please contact your doctor or go to the emergency room. ”
”
Mothers who are considered high risk—those with diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, or another chronic health condition—should be extra vigilant about any signs and symptoms that are not normal.
“Just as babies need care and attention during the fourth trimester, so too do mothers,” says Rosser. “Postpartum care is a crucial time to make sure Mom is safe and healthy so that the baby can be supported in the best possible way.”
Pregnancy calendar
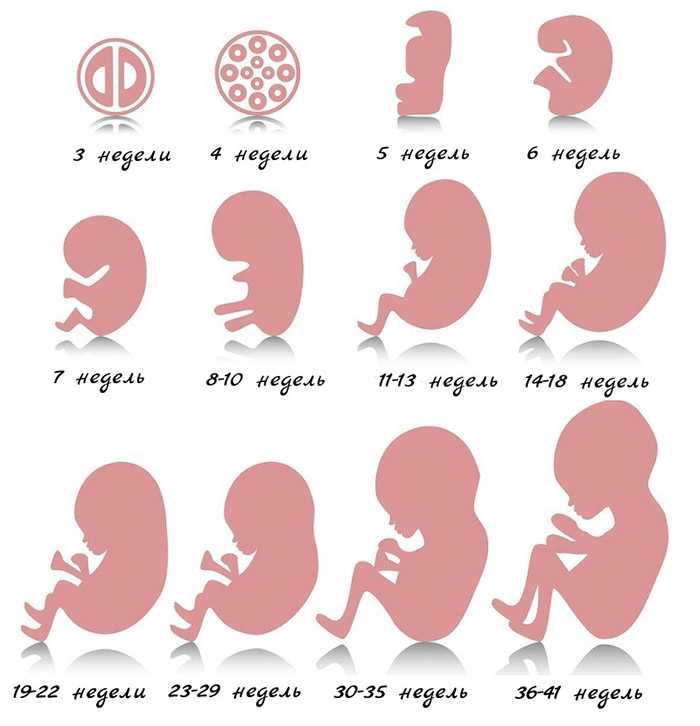
You are pregnant! Your baby will be born in 40 weeks. What changes will occur in your body, how your baby will grow will tell "Calendar of pregnancy".
1-2 weeks
Pregnancy begins at the moment of fertilization or conception.
Fertilization is a complex biological process of the fusion of female and male germ cells (egg and sperm). The resulting cell (zygote) is a new daughter organism. nine0003
A mature egg leaves the ovary approximately on the 12-14th day of the menstrual cycle (ovulation) and enters the fallopian tube, where it remains viable for 24 hours.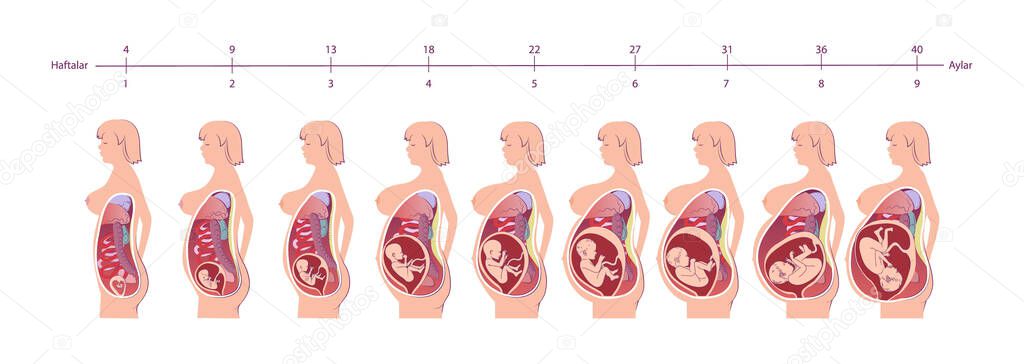 During an orgasm, a man ejects from 200 to 400 million spermatozoa into the woman's vagina. Some of them penetrate through the cervix into the uterine cavity, and from there into the fallopian tubes. Here, spermatozoa retain the ability to fertilize for 48 hours. Thus, within 6-7 days of a woman's menstrual cycle, conception is possible. nine0003
During an orgasm, a man ejects from 200 to 400 million spermatozoa into the woman's vagina. Some of them penetrate through the cervix into the uterine cavity, and from there into the fallopian tubes. Here, spermatozoa retain the ability to fertilize for 48 hours. Thus, within 6-7 days of a woman's menstrual cycle, conception is possible. nine0003
Fertilization of the female egg is performed by a single sperm in the upper part of the fallopian tube. There are two types of sperm: those containing the Y chromosome (“male”) and the X chromosome (“female”). When an egg cell (containing the X chromosome) fuses with a sperm cell, their genetic material is combined and the sex of the child is determined. If there are two X chromosomes in the child's genetic makeup, it's a girl; if an X chromosome and a Y chromosome, it's a boy. It is impossible to change the sex of the child, so you should not follow the "folk beliefs" that guarantee the birth of a child of a given gender. nine0003
The fertilized egg begins to divide with the formation of a multicellular organism and move through the fallopian tube into the uterine cavity.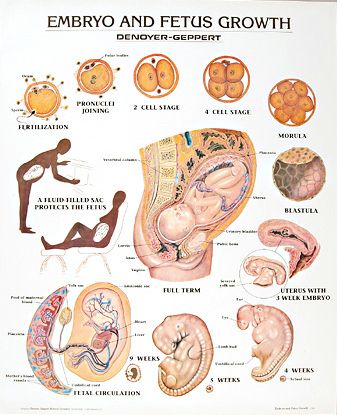 During this period, the nutrition of the embryo is carried out at the expense of those substances that have been accumulated in the egg. If the peristalsis of the tube is slowed down (due to inflammatory diseases), the embryo penetrates the wall of the fallopian tube with the occurrence of an ectopic pregnancy.
During this period, the nutrition of the embryo is carried out at the expense of those substances that have been accumulated in the egg. If the peristalsis of the tube is slowed down (due to inflammatory diseases), the embryo penetrates the wall of the fallopian tube with the occurrence of an ectopic pregnancy.
Implantation (introduction) of the embryo into the uterine wall occurs 7-8 days after fertilization. nine0003
On the seventh day of pregnancy, the outer layer of the embryo (trophoblast) begins to produce a hormone - chorionic gonadotropin. This hormone gives the mother's body information that pregnancy has occurred, and begins its functional restructuring. Diagnostic test strips detect the chorionic gonadotropin in the urine of a pregnant woman, which makes it possible to diagnose pregnancy at an early stage.
3-4 weeks
You do not have the expected menstruation, nausea in the morning, and frequent urination during the day. You become emotionally labile, irritable, whiny. Basal body temperature is above 37°C. nine0025 In appearance, your unborn baby resembles a small auricle measuring 4 mm, surrounded by a small amount of amniotic fluid. On the 21st day after conception, the brain and spinal cord are formed. By the end of the first month, the circulation of embryonic blood is established, the umbilical cord has formed - the connection of the embryo with the future placenta. The eye sockets, the rudiments of arms and legs appeared, the laying and development of other internal organs of the fetus is underway: the liver, kidneys, urinary tract, and digestive organs. nine0003
Basal body temperature is above 37°C. nine0025 In appearance, your unborn baby resembles a small auricle measuring 4 mm, surrounded by a small amount of amniotic fluid. On the 21st day after conception, the brain and spinal cord are formed. By the end of the first month, the circulation of embryonic blood is established, the umbilical cord has formed - the connection of the embryo with the future placenta. The eye sockets, the rudiments of arms and legs appeared, the laying and development of other internal organs of the fetus is underway: the liver, kidneys, urinary tract, and digestive organs. nine0003
5-6 weeks
You no longer doubt that you are pregnant. Regardless of how you feel, all pregnant women need to visit a antenatal clinic and undergo an examination that will allow you to identify and correct existing health problems in time.
Starting from the 5th week, there may be a threat of termination of pregnancy. This will be evidenced by: periodic pain in the lower abdomen and in the lumbar region, a feeling of pressure on the rectum, an increased amount of mucus. If you experience these symptoms, you should consult a doctor. nine0003
If you experience these symptoms, you should consult a doctor. nine0003
By week 6, the face is formed in the embryo: eyes, nose, jaws and limbs.
7-8 weeks
From the 7th week of pregnancy, the yellow body of pregnancy undergoes reverse development, the production of hormones begins to be carried out by the forming placenta.
The baby develops large blood vessels, the heart becomes four-chambered. Bile ducts appear in the liver. There is a development of the endocrine glands, the brain. The auricles are already formed, fingers have appeared on the limbs. The embryo begins to move. At week 8, under the influence of the Y chromosome, the formation of male gonads (testicles) occurs. They begin to produce testosterone - the male sex hormone, which will lead to the formation of the sexual characteristics of the boy. nine0003
9-10 weeks
Your metabolism is changing significantly to provide the growing body with all the necessary "building materials" - amino acids, energy. Disadaptation to such a restructuring can result in toxicosis of the 1st half of pregnancy. It is characterized by nausea, vomiting, salivation, weight loss. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
Disadaptation to such a restructuring can result in toxicosis of the 1st half of pregnancy. It is characterized by nausea, vomiting, salivation, weight loss. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
At the tenth week, the development of the oral cavity, intestines, rectum, and bile ducts ends in the embryo. The formation of the face and hemispheres of the brain was completed. The development of the cerebellum, the main coordinator of movements, begins. nine0003
11-12 weeks
The body has adapted to the new conditions. By this time, nausea, vomiting, salivation practically disappear. You become balanced, calm.
After 12 weeks, the growth of the uterus becomes noticeable
13-14 weeks
By this time, the formation of the main organs of the unborn child is completed. In appearance, the fetus resembles a small person.
15-16 weeks
A change in skin pigmentation is possible - the midline of the abdomen, nipples and the skin around them have darkened.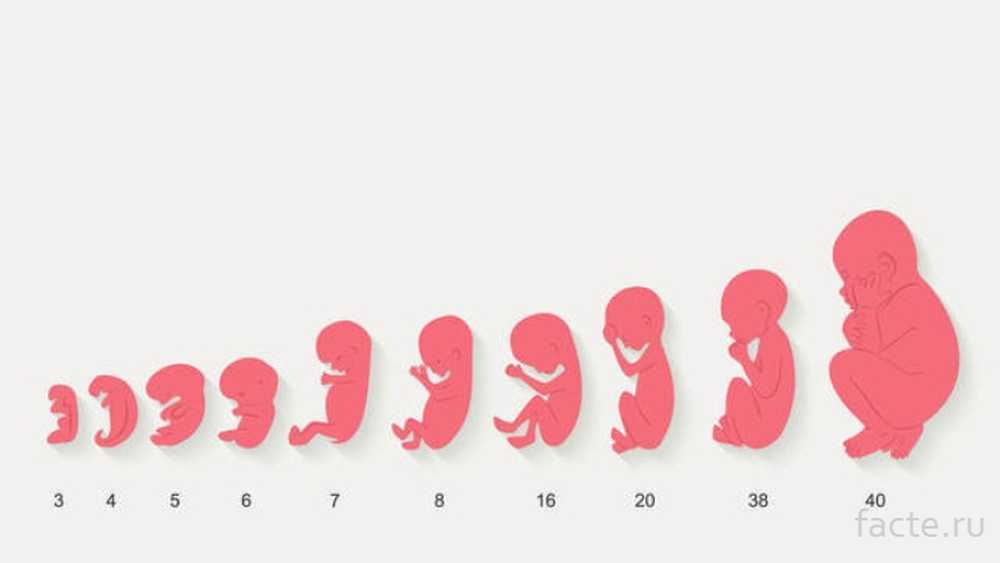 These phenomena should pass soon after childbirth. nine0025 The formation of the placenta ends. The fetus and placenta represent a single functional system. During this period of pregnancy, the fetus floats freely in the amniotic fluid. The composition of the amniotic fluid can determine the condition of the fetus.
These phenomena should pass soon after childbirth. nine0025 The formation of the placenta ends. The fetus and placenta represent a single functional system. During this period of pregnancy, the fetus floats freely in the amniotic fluid. The composition of the amniotic fluid can determine the condition of the fetus.
17-18 weeks
These days, your unborn child begins to move. His limbs, ligamentous apparatus, cerebellum have already developed enough. By this time, the formation of the immune system is completed.
19-20 weeks
There have been big changes in your body. The pulse quickened, cardiac output increased significantly (40% higher than the initial level) and the volume of circulating blood (almost 500 ml). nine0003
Due to the increased volume of plasma compared to the mass of red blood cells, hemoglobin decreases in blood tests.
Some women during this period experience frequent and painful urination, pain in the lumbar region on the right or left, weakness.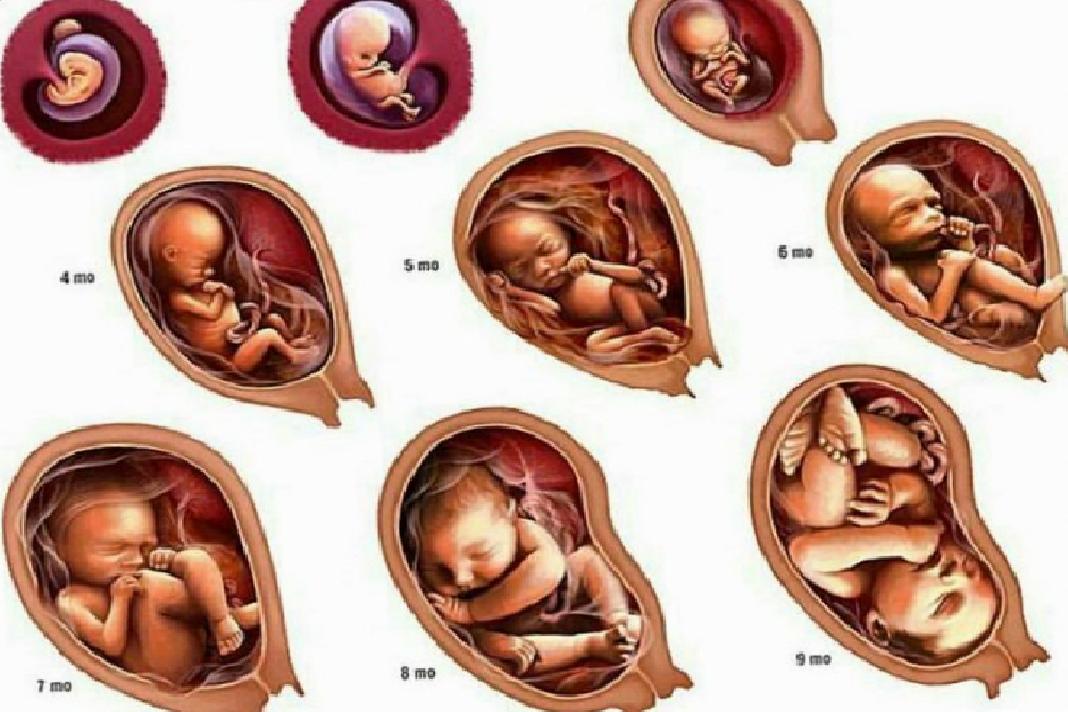 A large uterus presses down on the bladder, the mouth of the ureters, disrupting the outflow of urine. Stagnation of urine and incomplete emptying of the renal pelvis create conditions for the development of infection. Bacteriuria develops and pyelonephritis of pregnant women may occur. If there is any suspicion of pyelonephritis, you should immediately consult a doctor, because this disease is not only dangerous for your health, but also for the further growth and development of the fetus. nine0003
A large uterus presses down on the bladder, the mouth of the ureters, disrupting the outflow of urine. Stagnation of urine and incomplete emptying of the renal pelvis create conditions for the development of infection. Bacteriuria develops and pyelonephritis of pregnant women may occur. If there is any suspicion of pyelonephritis, you should immediately consult a doctor, because this disease is not only dangerous for your health, but also for the further growth and development of the fetus. nine0003
The weight of the baby is 300-350 grams, he often and quite actively moves, swallows amniotic fluid, begins to open his eyes.
21-22 weeks
In these weeks, the fetus already has a mass of 400-500 grams, and it develops very intensively bones and muscles, which require calcium from your body. Therefore, if you do not want to lose your white-toothed smile, then, on the advice of your obstetrician-gynecologist, start taking calcium supplements regularly. This will help save your teeth and get rid of leg cramps. They appear for the same reason of calcium deficiency. nine0003
They appear for the same reason of calcium deficiency. nine0003
23-24 weeks
At this time, the weight of the fetus is 500-600 g. It already has all the organs and systems fully formed. Until that time, only his lungs remained immature. And now, by 24 weeks, they begin to ripen. And the cells lining the lung alveoli produce surfactant, a substance that, by lubricating the alveoli, prevents them from sticking together during breathing. However, the amount of surfactant is so small that a child born at this time will not be able to breathe on its own. To survive outside the uterus, he needs sophisticated breathing equipment, incubators, a control system, infusors for nutrition, infusion media, artificial surfactant. nine0003
There are perinatal centers where children born during these terms of pregnancy are nursed. It is very difficult. And therefore, the longer the pregnancy is prolonged, the more likely the birth of a healthy and viable child. Therefore, try to do everything so that the child is born on time, full-term and healthy.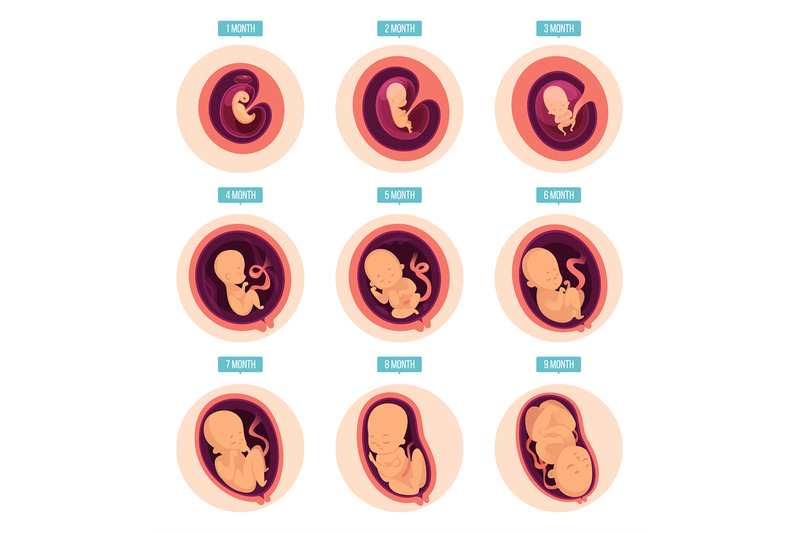
By this gestational age, the uterus is at a height of about 24 cm above the pubic bone, and now it not only builds up muscles, but is also stretched by the fetus that completely filled its cavity. nine0003
25-26 weeks
The fetus already has a mass of 700-750 g. Due to the improvement of the brain structures in his body, a connection is established with the adrenal cortex and they begin to produce corticoids - hormones necessary for adaptation. The pituitary gland of the fetus reaches such a degree of maturity that the production of adrenocorticotropic hormone begins, which also stimulates hormonal production by the adrenal glands. In short, all forces are thrown to the upcoming "publication". But the most obvious changes in these weeks occur in the lungs - there is an increased maturation of cells that produce surfactant. However, a fetus born during this period can only survive in incubators with artificial lung ventilation, artificial feeding with special infusion media.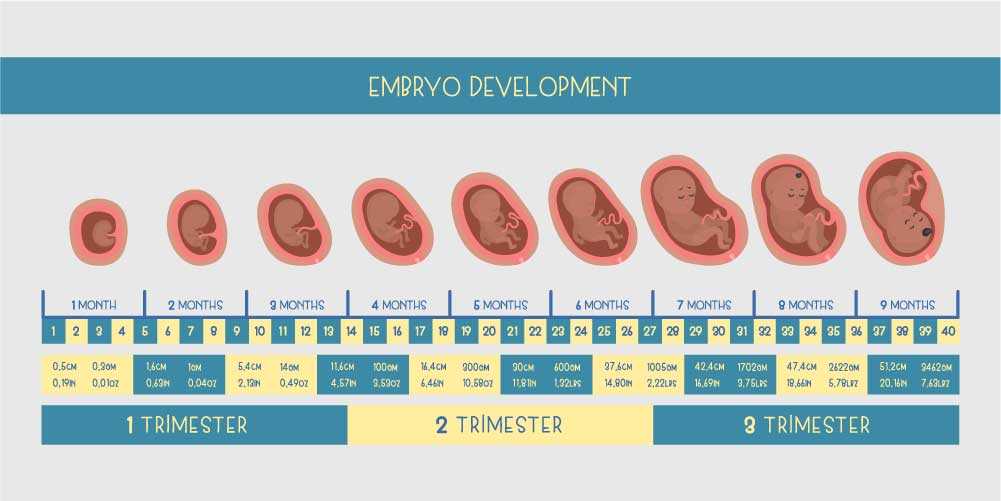 Therefore, try to keep both him and yourself from rash steps. nine0003
Therefore, try to keep both him and yourself from rash steps. nine0003
At this time, it's time to start preparing for the future feeding of the child. Under the influence of placental lactogen, your breasts, that is, the mammary glands, are growing rapidly. From time to time, droplets of colostrum may appear on the nipples. Daily air baths, washing with cool water, rubbing the nipples with a rough towel will help prepare the nipples for feeding. If the nipples are flat, start to stretch them little by little.
27-28 weeks
This period completes the second trimester of pregnancy. By this time, the fetus weighs up to 1000 g and has a height of up to 35 cm. However, he still cannot live on his own, because. his lungs are not mature enough and special equipment is still needed to nurse him. During these periods of pregnancy, there is an intensive growth of the fetus, the formation of muscles. His movements become more active. Periods of movement alternate with its relatively calm state when the fetus is sleeping. With an ultrasound, you can see that he already knows how to suck his thumb and even smile! nine0003
With an ultrasound, you can see that he already knows how to suck his thumb and even smile! nine0003
The fundus of the uterus stands on average at a height of 27-28 cm above the womb.
29-30 weeks
The third trimester of pregnancy begins. The uterus stands at a height of 29-30 cm, it becomes more difficult for you to breathe. Now one of the most serious complications can develop - toxicosis of the second half of pregnancy, which is characterized by the appearance of edema, increased blood pressure and the appearance of protein in the urine. For early diagnosis of this complication, it is necessary to carefully observe an obstetrician-gynecologist and follow all his recommendations, incl. strict weight control. In the III trimester of pregnancy, the daily weight gain should be no more than 50 g, i.e. no more than 300 g per week. You should also monitor the ratio of drunk and secreted fluid. nine0003
31-32 weeks
Have you asked your doctor how the fetus is? Find out now it's very important.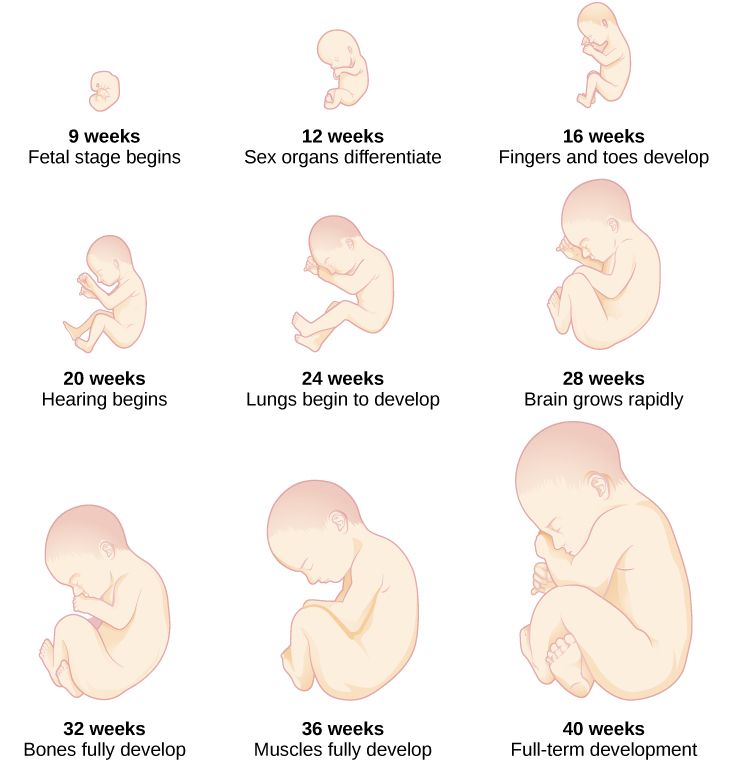 Its position can be longitudinal, transverse, oblique. Correct, normal is the longitudinal position of the fetus. Childbirth is safer with cephalic presentation. From this period of pregnancy, it is necessary to wear a prenatal bandage that will support the anterior abdominal wall and help maintain the correct position and presentation of the fetus. If the presentation of the fetus is breech, i.e. above the entrance to the pelvis is the pelvic end of the fetus, then the bandage should not be worn yet. There is gymnastics to correct the presentation of the fetus. nine0003
Its position can be longitudinal, transverse, oblique. Correct, normal is the longitudinal position of the fetus. Childbirth is safer with cephalic presentation. From this period of pregnancy, it is necessary to wear a prenatal bandage that will support the anterior abdominal wall and help maintain the correct position and presentation of the fetus. If the presentation of the fetus is breech, i.e. above the entrance to the pelvis is the pelvic end of the fetus, then the bandage should not be worn yet. There is gymnastics to correct the presentation of the fetus. nine0003
In the morning and evening for 1 hour, do the following: lie down on the bed on your left side and lie quietly for 15 minutes, then turn over to your right side and lie for the next 15 minutes, and then repeat these turns 2 more times.
Pregnant women with Rh-negative blood and with O (I) blood type need blood tests for Rh - or group immune antibodies. Immunization of pregnant women with Rh-negative blood is carried out from 28 weeks and within 72 hours after childbirth according to the indications, which will be discussed by the doctor observing you in the antenatal clinic.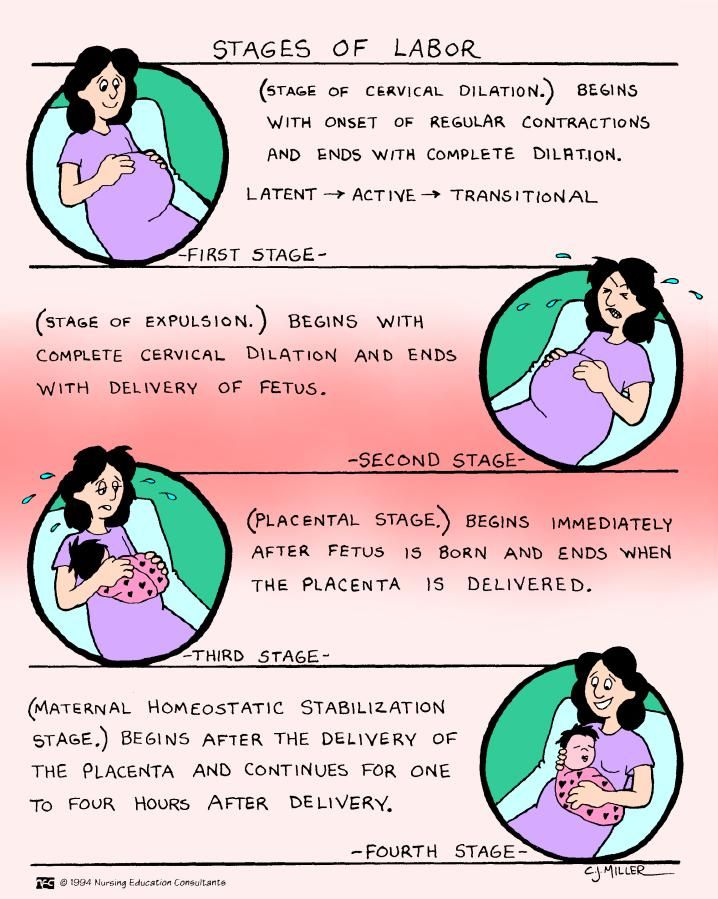 nine0003
nine0003
33-34 weeks
The fetus already has a mass of 1800-2100 g, a height of 40-41 cm. By the end of this period, its lungs will begin to produce surfactant in full and will be able to breathe without special equipment. The fetus is fully developed, its chances of surviving in case of preterm birth are greatly increased. However, there is still extremely little subcutaneous fat, so his skin is thin and has a red color. Such a newborn retains heat very poorly and at birth needs an incubator or a heating pad. His body is still covered with fluff and cheese-like grease, the auricles are still very small, but they are already beginning to straighten out, the boy's testicles descend into the scrotum. nine0003
Caring for a premature baby is the hardest work for the whole family, associated with high material costs, physical overload of parents, and this work is not always rewarded, since a child can be born and remain sick. Therefore, up to 37 weeks of pregnancy, a woman should be especially attentive to her condition and, at the slightest suspicion of an increase in the tone of the uterus, starting frequent and regular contractions, immediately consult a doctor.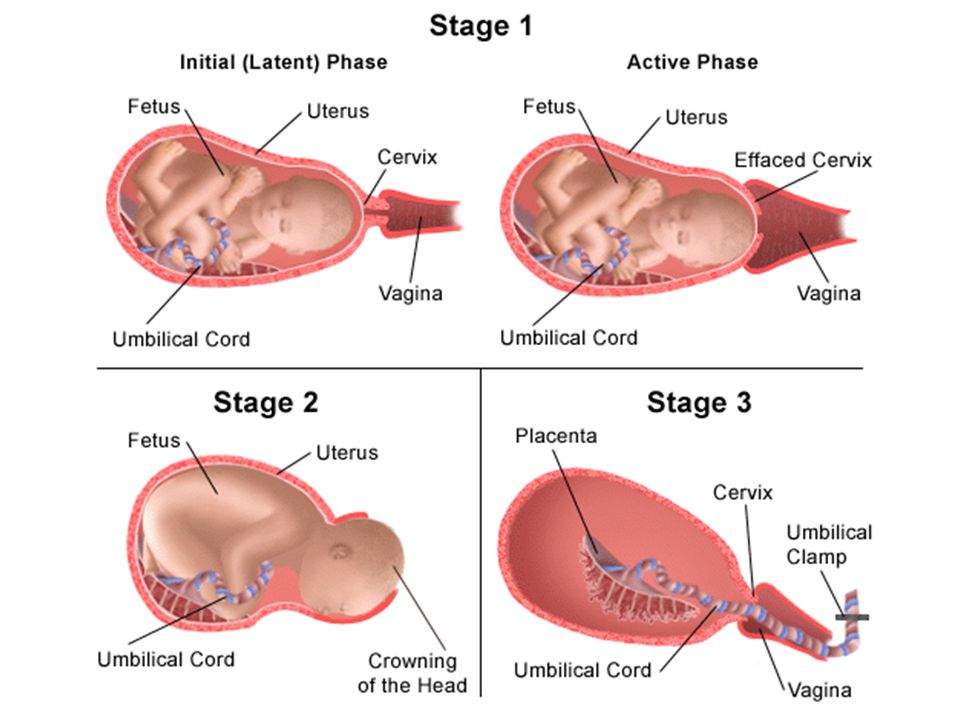
Doctors know that women, in anticipation of the arrival of a new person in the house, begin to glue walls and paint ceilings during this period. Don't take unnecessary risks. For this, prenatal leave is provided from 30 weeks, so that you can avoid overwork, do not push in transport, and have the opportunity to sleep. So repairs, stuffy shops, queues are no longer for you. nine0003
35-36 weeks
The fetus already has a mass of 2100-2700 g and a height of 44-45 cm. It is advisable to see a doctor during this period of pregnancy at least once every 10 days.
37-38 weeks
From this point on, your pregnancy is considered full-term. And if you have a baby in these weeks, he will live. Its development is complete. Now he has a mass of approximately 2700-3000 g. Height is 49-50 cm. The remaining two weeks he will add a little in weight and height.
It becomes easier for you to breathe, as the fetal head is pressed tightly against the entrance to the pelvis, the uterus pulls the anterior abdominal wall more, and therefore its bottom sank lower.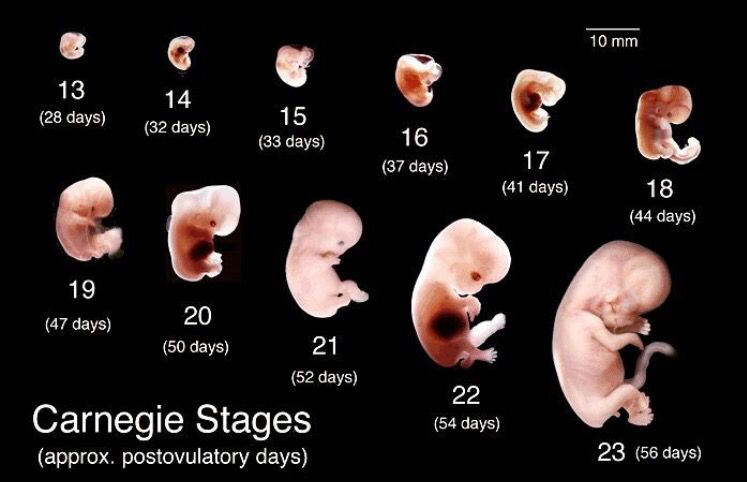 Tension of the uterus; small sharp pulling pains in the lumbar region. nine0003
Tension of the uterus; small sharp pulling pains in the lumbar region. nine0003
With an exacerbation of extragenital diseases, the appearance of signs of toxicosis in the second half of pregnancy, with an incorrect position of the fetus, with some gynecological diseases, against which pregnancy develops, a scar on the uterus, etc., early prenatal hospitalization is required. Do not forget to take an exchange card, passport, medical insurance policy and birth certificate to the hospital.
39-40 weeks
You can find out the approximate day of delivery by the date of the last normal menstruation - count back three months and add 7 days. The resulting number will be the estimated date of birth. More precisely, according to many parameters, ultrasound data, additional studies, the date of the first fetal movement, the date of the first visit to the obstetrician-gynecologist, especially if the visit was before 11-12 weeks of pregnancy. nine0003
The child already has all the signs of maturity. His weight is more than 3000 g, and his height is more than 50 cm, he has fair skin, a sufficient amount of subcutaneous fat, he retains heat and does not need special heating. He will scream loudly, breathe, suck. There is a very small amount of lubricant on the skin, which will no longer be able to protect it from the effects of amniotic fluid.
His weight is more than 3000 g, and his height is more than 50 cm, he has fair skin, a sufficient amount of subcutaneous fat, he retains heat and does not need special heating. He will scream loudly, breathe, suck. There is a very small amount of lubricant on the skin, which will no longer be able to protect it from the effects of amniotic fluid.
For you, regular contractions (1 contraction every 10 minutes) will become an indicator of the beginning of the birth process, or you will feel the outflow of amniotic fluid, you will see scanty bloody discharge - do not panic, call an ambulance, the telephone number for transportation for pregnant women is written on the margins of your exchange card. While she is driving, change your clothes, prepare your passport, exchange card, medical insurance policy and birth certificate. nine0003
1-4 weeks of pregnancy
From a tiny fetus to a small person, a child's body develops in just 9 months. What changes are happening to the expectant mother and what changes are observed inside her during this difficult and joyful period of life?
Each new life begins with the union of the egg and sperm.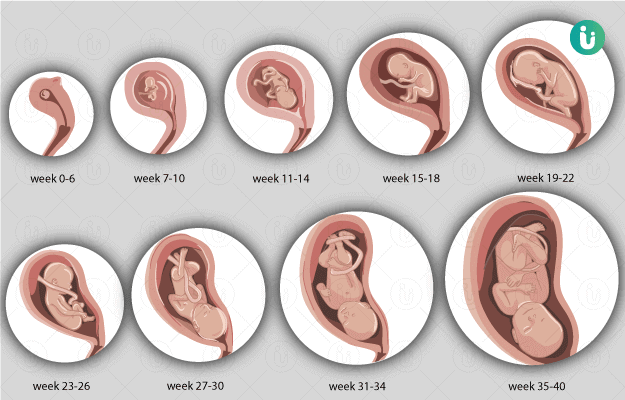 Conception is the process by which a sperm enters an egg and fertilizes it.
Conception is the process by which a sperm enters an egg and fertilizes it.
It should be noted that the embryonic and obstetric terms are different. The thing is that among specialists it is customary to consider the period from the first day of the last menstruation, that is, the obstetric period includes the period of preparation for pregnancy. So it turns out that the embryo has just appeared, and the gestation period is already two weeks. It is the obstetric period that is indicated in all the documents of a woman and is the only reporting period for specialists. nine0003
Until the moment of the meeting, the spermatozoon and the ovum lived for a certain time, being in the stage of development and maturation. The development of the future fetus significantly depends on the quality of these processes.
First week
Growth and maturation of the egg starts from the first day of the cycle. A mature egg contains 23 chromosomes as the genetic material for the future embryo, and also contains all the nutrients necessary to start its development. It contains reserves of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, designed to support the embryo during the first days after its occurrence. nine0003
It contains reserves of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, designed to support the embryo during the first days after its occurrence. nine0003
A certain number of eggs are laid in each ovary of a girl before she is born. During the childbearing period, they only grow and develop, the process of their formation does not occur. By the time a girl is born, the number of cells from which eggs can develop in the future reaches a million, but this number decreases significantly over the course of life. So, by the time of puberty, there are several hundred thousand of them, and by maturity - about 500.
The ovary each month gives the opportunity to develop most often one egg, the maturation of which occurs inside a vesicle with a liquid called a follicle. From the first day of the cycle, the uterine mucosa begins to prepare for a possible pregnancy. For implantation, i.e., the introduction of the resulting embryo into the wall of the uterus, an optimal environment is created. To do this, due to the influence of hormones, the endometrium thickens, it becomes covered with a network of vessels and accumulates the nutrients necessary for the future embryo. nine0003
nine0003
Male reproductive cells are formed in the gonads - in the testicles or testes. The maturation of spermatozoa occurs in the epididymis, into which they move after formation. The liquid structure of semen is formed due to the secretion of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland. A liquid medium is necessary for storing mature spermatozoa and creating favorable conditions for their life.
The number of spermatozoa is quite large: tens of millions in one milliliter. Despite such a significant number, only one of them will be able to fertilize the egg. In spermatozoa, there is exclusively genetic material - 23 chromosomes, which are necessary for the appearance of the embryo. nine0003
Spermatozoa are characterized by high motility. Once in the female genital tract, they begin their movement towards the egg. Only half an hour or an hour passes from the moment of ejaculation, when sperm enter the uterine cavity. It takes one and a half to two hours for spermatozoa to penetrate into the widest part, which is called the ampulla. Most spermatozoa die on the way to the egg, meeting the folds of the endometrium, getting into the vaginal environment, cervical mucus.
Most spermatozoa die on the way to the egg, meeting the folds of the endometrium, getting into the vaginal environment, cervical mucus.
Second week
In the middle of the cycle, the egg fully matures and leaves the ovary. It enters the abdominal cavity. This process is called ovulation. With a regular cycle of 30 days, ovulation occurs on the fifteenth. The egg is unable to move on its own. When she leaves the follicle, the fimbriae of the fallopian tube ensure her penetration inside. The fallopian tubes are characterized by longitudinal folding, they are filled with mucus. The muscular movements of the tubes have a wave-like character, which, with a significant number of cilia, creates optimal conditions for transporting the egg. nine0003
Through the tubes, the egg enters their widest part, which is called the ampulla. This is where fertilization takes place. If there is no meeting with the sperm, the egg dies, and the female body receives the appropriate signal to start a new cycle. There is a rejection of the mucous membrane, which was created by the uterus. The manifestation of such rejection is bloody discharge, which is called menstruation.
There is a rejection of the mucous membrane, which was created by the uterus. The manifestation of such rejection is bloody discharge, which is called menstruation.
The waiting period for fertilization by the egg is short. On average, it takes no more than a day. Fertilization is likely on the day of ovulation and maximum on the next. Sperm have a longer lifespan, averaging three to five days, in some cases seven. Accordingly, if a spermatozoon enters the female genital tract before ovulation, there is a possibility that it will be able to wait for the appearance of an egg. nine0003
When the egg is in a state of waiting for fertilization, certain substances are released that are designed to detect it. If spermatozoa find an egg, they begin to secrete special enzymes that can loosen its shell. As soon as one of the spermatozoa penetrates the egg, the others can no longer do this due to the restoration of the density of its shell. Thus, one egg can only be fertilized by one sperm.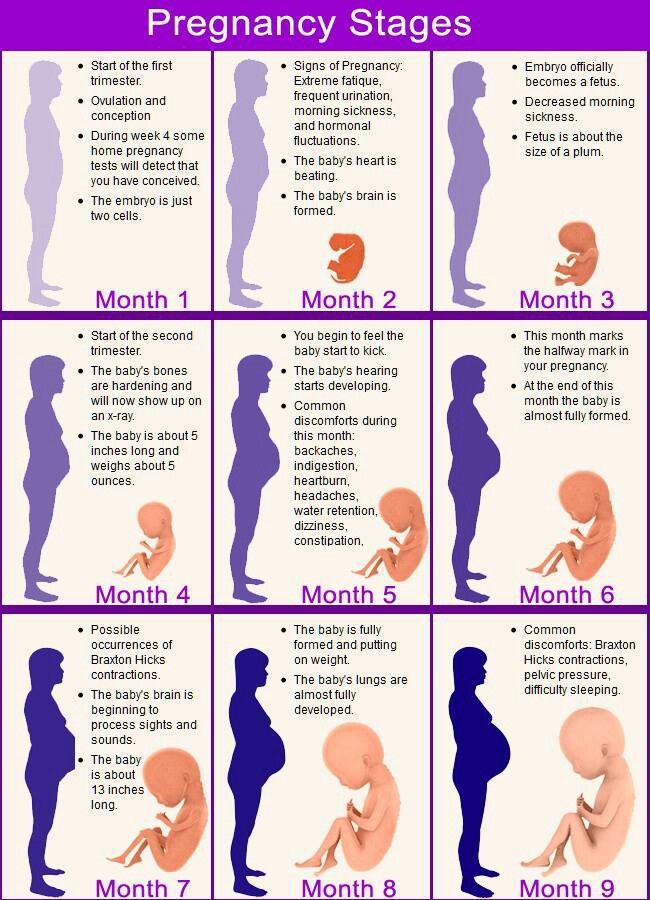 nine0003
nine0003
After fertilization, the chromosome sets of the parents merge - 23 chromosomes from each. As a result, one cell is formed from two different cells, which is called a zygote. The sex of the unborn child depends on which of the chromosomes, X or Y, was in the sperm. Eggs contain only X chromosomes. When XX is combined, girls are born. If the spermatozoon contains a Y chromosome, that is, with a combination of XY, boys are born. As soon as a zygote is formed in the body, a mechanism is launched in it aimed at maintaining pregnancy. There are changes in the hormonal background, biochemical reactions, immune mechanisms, and the receipt of nerve signals. The female body creates all the necessary conditions for the safe development of the fetus. nine0003
Third week
As soon as a day has passed after the formation of the embryo, he will need to make his first journey. The movements of the cilia and the contraction of the muscles of the tube direct it into the uterine cavity.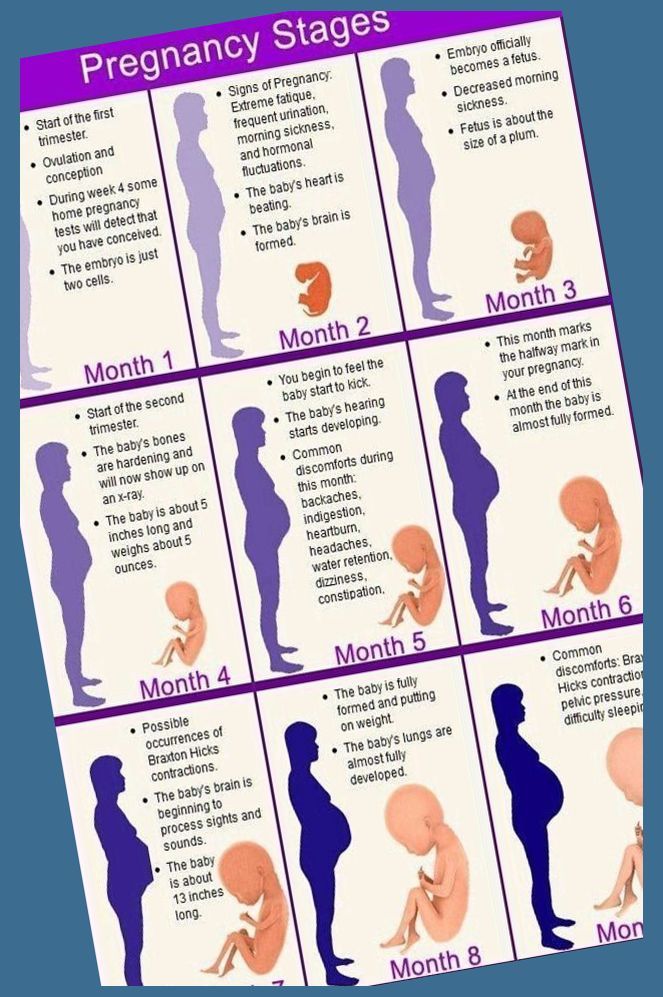 During this process, inside the egg, fragmentation into identical cells occurs.
During this process, inside the egg, fragmentation into identical cells occurs.
After four days, the appearance of the egg changes: it loses its round shape and becomes vine-shaped. This stage is called morula, embryogenesis begins - an important stage in the development of the embryo, during which the formation of the rudiments of organs and tissues occurs. Cleavage of cells continues for several days, on the fifth day their complexes are formed, which have different functions. The central cluster forms directly the embryo, the outer one, called the trophoblast, is designed to melt the endometrium - the inner layer of the uterus. nine0003
It takes 5-7 days for the embryo to reach the uterus. When implantation occurs in its mucous membrane, the number of cells reaches one hundred. The term implantation refers to the process of implantation of the embryo into the endometrial layer.
After fertilization on the seventh or eighth day, implantation takes place. The first critical period of pregnancy is this stage, since the embryo will have to demonstrate its viability for the first time.
During implantation, the outer cells of the embryo actively divide, and the process itself takes about forty hours. The number of cells outside the embryo increases dramatically, they stretch, they penetrate into the uterine mucosa, and the thinnest blood vessels are formed inside, which are necessary for the supply of nutrients to the embryo. Time will pass, and these vessels will be transformed first into the chorion, and subsequently into the placenta, which will be able to supply the fetus with everything necessary until the baby is born. nine0003
The embryo at this stage of life is called a blastocyst. It contacts with the endometrium, melts the cells of the endometrium with its activity, creates a path for itself to the deeper layers. The blood vessels of the embryo intertwine with the mother's body, which allows it to immediately begin to extract useful and necessary substances for development. This is vital, because by this time the stock that the mature egg carried in itself is exhausted.
Next, the production of the trophoblast cells, i.e., the outer cells of human chorionic gonadotropin, the hCG hormone, begins. The distribution of this hormone throughout the body notifies it of the onset of pregnancy, which causes the launch of active hormonal changes and the beginning of corresponding changes in the body. nine0003
After fertilization and before the start of hCG, it usually takes eight or nine days. Therefore, already from the tenth day after fertilization, it becomes possible to determine this hormone in the mother's blood. Such an analysis is the most reliable confirmation of the onset of pregnancy. The tests that are offered today to determine pregnancy are based on the detection of this hormone in the urine of a woman. After the first day of delayed menstruation with its regular cycle, it is already possible to determine pregnancy using a test on your own. nine0003
What happens to a woman in the third week of pregnancy
If a woman is planning a pregnancy, 21-24 days, subject to a regular cycle, should become important for her. This is a period of possible implantation, when you should pay special attention to your own lifestyle. During this period, thermal effects and excessive physical exertion are undesirable, and the influence of various kinds of radiation should also be prevented.
This is a period of possible implantation, when you should pay special attention to your own lifestyle. During this period, thermal effects and excessive physical exertion are undesirable, and the influence of various kinds of radiation should also be prevented.
The woman does not feel anything at this stage, because implantation has no external signs. If you adjust your lifestyle in accordance with the simple rules listed above, you will be able to create optimal conditions for successful implantation. nine0003
Fourth week
At the fourth obstetric week or the second week of the fetus's life, its body consists of two layers. Endoblast - cells of the inner layer - will become the beginning of the digestive and respiratory systems, ectoblast - cells of the outer layer - will start the development of the nervous system and skin.
The size of the embryo at this stage is 1.5 mm. The flat arrangement of the cells determined the name of the embryo of this age - the disc.