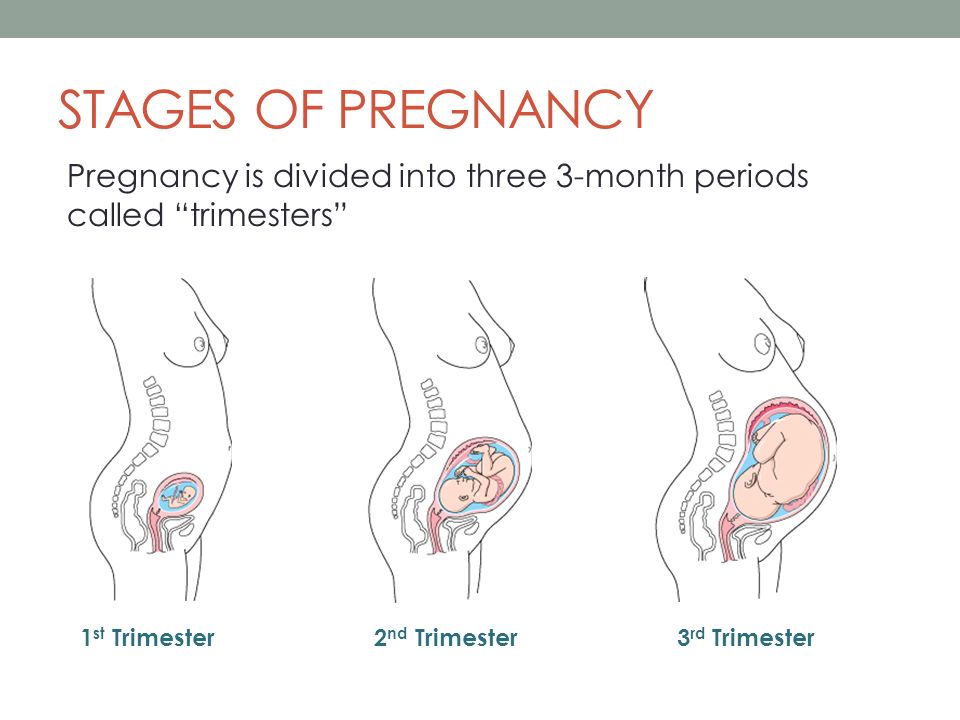
False period pregnancy
Bleeding and/or pain in early pregnancy
- Reference Number: HEY-025/2022
- Departments: Gynaecology
- Last Updated: 31 May 2022
You can translate this page by using the headphones button (bottom left) and then select the globe to change the language of the page. Need some help choosing a language? Please refer to Browsealoud Supported Voices and Languages.
Introduction
This leaflet has been produced to give you general information about your condition. Most of your questions should be answered by this leaflet. It is not intended to replace the discussion between you and your nurse/doctor but may act as a starting point for discussion. If after reading it you have any concerns or require further explanation, please discuss this with a member of the healthcare team.
What is vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy?
Vaginal bleeding is common in early pregnancy and does not always mean there is a problem. However, bleeding can be a warning sign of a miscarriage.
What are the causes of early bleeding?
There are a number of causes of bleeding in early pregnancy which include:
Spotting or bleeding may occur shortly after conception, this is known as an implantation bleed. It is caused by the fertilised egg embedding itself in the lining of the womb. This bleeding is often mistaken for a period, and it may occur around the time your period is due.
Hormonal bleeding is when some women experience a light bleed at around four to eight weeks of pregnancy, or around the time their period would have been due. This can be very confusing for women who are pregnant and is the reason many women do not realise they are pregnant for a while. Again, it is totally normal. This usually settles around the 13th week of pregnancy as by this time the placenta is sufficiently developed to produce all of the hormones needed to sustain the pregnancy.
After the egg is fertilised, the fertilised egg then goes on to implant itself into the lining of the womb (uterus). Sometimes this results in a little bleeding that shows up on an early scan as a haematoma (collection of blood). This is not anything to worry about. When it happens, the woman may notice a small amount of vaginal bleeding, but this is not necessarily the case.
The haematoma will gradually disappear and in most cases, the pregnancy remains safe.
Cervical Erosion (alternatively known as cervical ectropion) may be a source of spotting or bleeding. The blood supply to the womb and cervix is increased during pregnancy and the cervix may bleed harmlessly and painlessly. An erosion may cause bleeding following sexual intercourse; therefore, this type of bleeding must always be reported to your doctor.
Can bleeding indicate a miscarriage?
Not all bleeding in pregnancy is harmless, and it can be the first sign of a miscarriage. As many as 1 in 5 pregnancies are thought to end in miscarriage. The cause of miscarriage is not always known, but researchers have shown that in some cases there is a problem with the developing pregnancy, which means it is unable to develop normally. For most women, miscarriage is a very sad and upsetting experience.
The cause of miscarriage is not always known, but researchers have shown that in some cases there is a problem with the developing pregnancy, which means it is unable to develop normally. For most women, miscarriage is a very sad and upsetting experience.
Experiences of miscarriage vary. In some cases, there may be only very slight spotting, in other cases bleeding may stop and start or heavier bleeding with clots and cramping period type pains can occur. Sometimes there may be no bleeding at all.
For further information relating to miscarriage, please ask your nurse for further details.
What should I do if I experience bleeding during pregnancy?
If you experience bleeding, it is wise to have this checked out. If you have been seen in the Early Pregnancy Assessment Unit (EPAU) during your pregnancy, you may contact us directly, up to 15 weeks + 6 days of pregnancy. Your GP or midwife can also help you.
If you have been seen in the EPAU and you then experience more bleeding contact the EPAU. Depending on how much bleeding and for how long the nursing staff will decide if you need to be seen again. A rescan is not always necessary. Sometimes the nurse will advise that you monitor this bleeding at home. A rescan will only be performed if bleeding heavy with clots. If there is a significant change in your symptoms, then the nurse will make an appointment to come to EPAU and be either rescanned or to be assessed by the doctor. If bleeding is unmanageable, then the nurse may advise to be assessed on ward 30 or the Emergency department depending on your symptoms.
Depending on how much bleeding and for how long the nursing staff will decide if you need to be seen again. A rescan is not always necessary. Sometimes the nurse will advise that you monitor this bleeding at home. A rescan will only be performed if bleeding heavy with clots. If there is a significant change in your symptoms, then the nurse will make an appointment to come to EPAU and be either rescanned or to be assessed by the doctor. If bleeding is unmanageable, then the nurse may advise to be assessed on ward 30 or the Emergency department depending on your symptoms.
What if I experience pain in early pregnancy?
If you experience pain that does not go away, or which you feel is becoming more severe, you should seek advice from your doctor, nurse or midwife. It is important that any serious causes of pain are excluded. For example, there is a need to rule out an ectopic pregnancy (this is where the pregnancy develops outside the womb).
What kind of pain may I feel?
Some women experience abdominal (tummy) pain in early pregnancy. This may be low cramping pain, similar to that felt during a period, or a stitch like or stabbing pain on one or both sides of the tummy. Aches and pains may come and go or be present continuously.
This may be low cramping pain, similar to that felt during a period, or a stitch like or stabbing pain on one or both sides of the tummy. Aches and pains may come and go or be present continuously.
What are the causes of abdominal and back pain?
Some of the aches and pains experienced during pregnancy are thought to be due to hormonal changes. Large amounts of the hormone progesterone are produced, which are needed to sustain pregnancy. In addition to this, progesterone acts on the muscles, ligaments and joints causing them to become slacker and more flexible. This hormonal effect is thought to be responsible for some of the stitch like pains that some women experience in the lower part of the tummy and in some cases this can be quite severe. The same hormones can be responsible for constipation during pregnancy; this can also cause abdominal pain.
The enlarging womb is made up of layers of muscles and is held in place in the pelvis by supporting ligaments. As the womb expands to accommodate the developing baby, it can pull on the ligaments and muscles, to cause these “growing pains”.
The backache that some women get in early pregnancy is also thought to be due to a hormonal effect, and the supporting muscles are softer.
Abdominal and/or backache can also be a sign of a urine infection. This may also cause burning or stinging when passing urine and the need to pass urine more frequently. You must inform your doctor of these symptoms, so that a urine test can be obtained, and treatment given if needed.
Pain on its own does not mean that a miscarriage will occur. However, if you experience bleeding as well as pain this could indicate a threatened miscarriage and you should always seek advice from your doctor, nurse or midwife.
Can I take pain relief medication during pregnancy?
If you find that you need to take pain relief medication to relieve any pain, it is safest to use something simple such as paracetamol. Drugs such as aspirin and ibuprofen should be avoided. If you find that you need a stronger pain relief medication, you must always check with your doctor, nurse or midwife first.
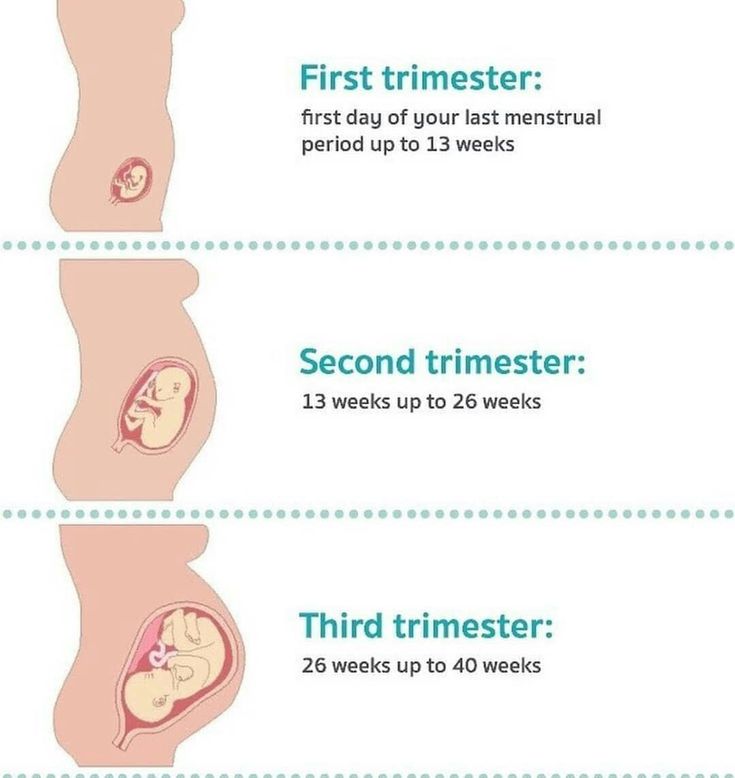
Scanning in early pregnancy
An ultrasound scan is used during pregnancy for a number of reasons. In the first three months of pregnancy, it can be used to check the presence of the baby’s heartbeat, which can be reassuring if you have experienced a problem, such as vaginal bleeding or pain. A scan will also be used to check to see if the pregnancy is in the correct place and to accurately predict the estimated date of delivery (the date the baby is due) by measuring the end points (size) of the embryo or fetus.
Will I have an ultrasound scan?
Yes, if the nurse/doctor thinks it is appropriate for you to have a scan.
What is an ultrasound scan?
Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves that are sent out from a transducer or probe. These sound waves are received back and converted into an image on a screen.
Is it safe to have a scan in early pregnancy?
Yes, it is safe, there is so far no evidence to suggest that an ultrasound scan is unsafe.
What type of scan will I have?
A vaginal scan is the best method in early pregnancy (under 8 weeks) as it gives us a more accurate result at an earlier stage in pregnancy than an abdominal scan. It may be a little uncomfortable, but it is safe to be done, you do not need a full bladder when having a vaginal scan. If you have concerns about a vaginal scan, please let the nurse, midwife doctor know.
What will the scan tell us?
A scan can only tell us how your pregnancy is at that particular time. Unfortunately, it is no guarantee that your pregnancy will continue successfully. If your symptoms persist or become worse, you must contact EPAU, midwife or your GP.
In later pregnancy ultrasound scanning is used to look more closely at the anatomy and organs of the developing baby. This is usually done between 18 – 21 weeks.
What if the scan confirms a miscarriage?
If the scan confirms that you have miscarried, the choices of how we can manage this will be discussed with you.
Occasionally, the scan may pick up an unexpected finding such as a cyst on the ovary. If this is the case, the staff will explain the findings and any necessary follow up.
Common abbreviations used on scans
LMP – Last menstrual period
FH – Fetal heart-rate
EDD – Estimated date of delivery
FM – Fetal movement
USS – Ultrasound scan
YS – Yolk sac
CRL – Crown to rump length (a measurement of the embryo/fetus used in early pregnancy)
BPD – Bi-Parietal Diameter
HC – Head circumference. Both of these measurements of the fetus are used in later pregnancy, after 12-14 weeks.
Should you require further advice on the issues contained in this leaflet, please do not hesitate to contact the:
Early Pregnancy Assessment Unit/Emergency Gynaecology UnitWomen and Children’s Hospital
01482 608767.Gynaecology Ward
Women and Children’s Hospital
01482 604387.
Useful information
Information on Gynaecology Services at Hull University Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust can be found at:
www.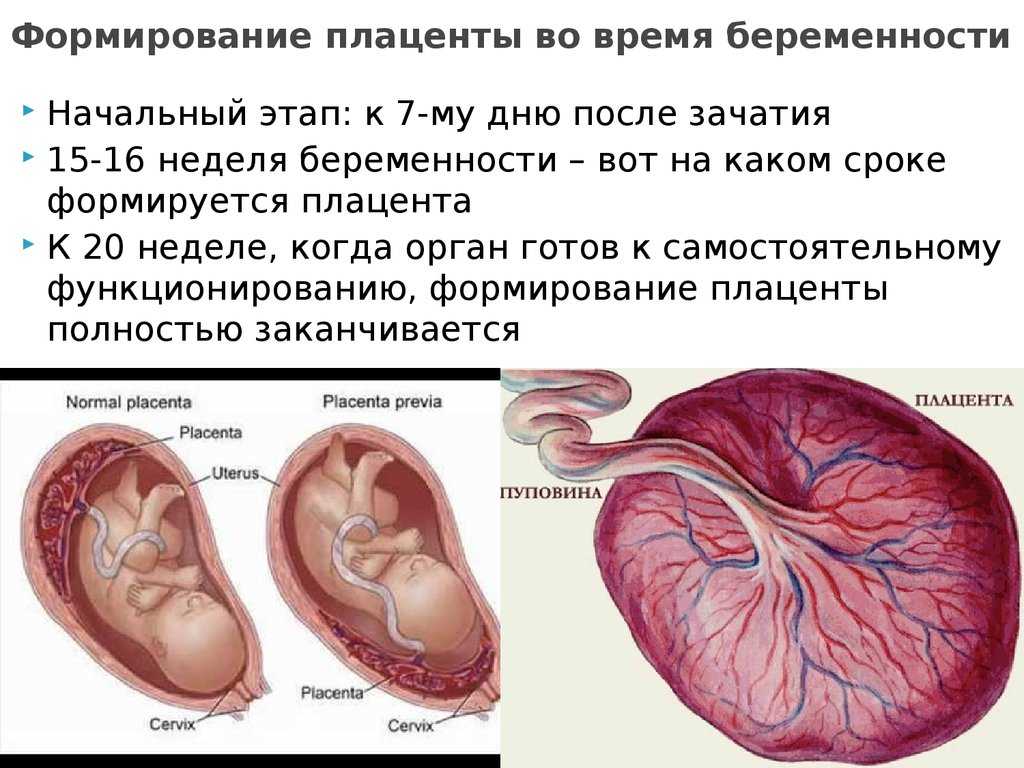 hey.nhs.uk/content/services/gynaecology.
hey.nhs.uk/content/services/gynaecology.
Information on Maternity Services at Hull University Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust can be found at:
www.hey.nhs.uk/maternity
www.womens-health.co.uk
www.nhs.uk
www.earlypregnancy.org.uk
www.patient.org.uk
www.screening.nhs.uk/annbpublications
This leaflet was produced by the Gynaecology Service, Hull and East Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust and will be reviewed in May 2025.
Ref: HEY025/2022
General Advice and Consent
Most of your questions should have been answered by this leaflet, but remember that this is only a starting point for discussion with the healthcare team.
Consent to treatment
Before any doctor, nurse or therapist examines or treats you, they must seek your consent or permission. In order to make a decision, you need to have information from health professionals about the treatment or investigation which is being offered to you.
You should always ask them more questions if you do not understand or if you want more information.
The information you receive should be about your condition, the alternatives available to you, and whether it carries risks as well as the benefits. What is important is that your consent is genuine or valid. That means:
- you must be able to give your consent
- you must be given enough information to enable you to make a decision
- you must be acting under your own free will and not under the strong influence of another person
Information about you
We collect and use your information to provide you with care and treatment. As part of your care, information about you will be shared between members of a healthcare team, some of whom you may not meet. Your information may also be used to help train staff, to check the quality of our care, to manage and plan the health service, and to help with research. Wherever possible we use anonymous data.
We may pass on relevant information to other health organisations that provide you with care. All information is treated as strictly confidential and is not given to anyone who does not need it. If you have any concerns please ask your doctor, or the person caring for you.
Under the General Data Protection Regulation and the Data Protection Act 2018 we are responsible for maintaining the confidentiality of any information we hold about you. For further information visit the following page: Confidential Information about You.
If you or your carer needs information about your health and wellbeing and about your care and treatment in a different format, such as large print, braille or audio, due to disability, impairment or sensory loss, please advise a member of staff and this can be arranged.
Spotting vs. Period: Learn the Signs
Spotting vs. Period: Learn the SignsMedically reviewed by Euna Chi, M.D. — By Stephanie Watson — Updated on March 29, 2019
Overview
If you’re a woman in your reproductive years, you’ll typically bleed every month when you get your period. Sometimes you might notice spots of vaginal bleeding when you’re not on your period. Most of the time, this spotting is nothing to worry about. It can be triggered by a variety of factors, from pregnancy to a switch in birth control methods. It’s always a good idea to have your doctor check out any unexpected vaginal bleeding, especially if you’re not sure of the cause.
Sometimes you might notice spots of vaginal bleeding when you’re not on your period. Most of the time, this spotting is nothing to worry about. It can be triggered by a variety of factors, from pregnancy to a switch in birth control methods. It’s always a good idea to have your doctor check out any unexpected vaginal bleeding, especially if you’re not sure of the cause.
Here’s a guide to help you tell the difference between spotting and your period.
During your period, the flow of blood will usually be heavy enough that you’ll have to wear a sanitary pad or tampon to avoid staining your underwear and clothes. Spotting is much lighter than a period. Usually you won’t produce enough blood to soak through a panty liner. The color may be lighter than a period, too.
Another way to tell whether you’re spotting or starting your period is by looking at your other symptoms. Just before and during your period, you may have symptoms like:
- bloating
- breast tenderness
- cramps
- fatigue
- mood swings
- nausea
If you have spotting that’s due to another condition, you may also have some of these symptoms, either at other times during the month, or at the same time you experience the spotting:
- heavier or longer periods than normal
- itching and redness in the vagina
- missed or irregular periods
- nausea
- pain or burning during urination or sex
- pain in your abdomen or pelvis
- unusual discharge or odor from the vagina
- weight gain
You get your period when your uterine lining sheds at the beginning of your monthly cycle. Spotting, on the other hand, may be caused by one of these factors:
Spotting, on the other hand, may be caused by one of these factors:
- Ovulation. During ovulation, which happens in the middle of your menstrual cycle, an egg is released from your fallopian tubes. Some women notice light spotting when they ovulate.
- Pregnancy. About 20 percent of women have spotting during the first three months of their pregnancy. Often, the blood appears in the first few days of pregnancy, when the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining. Many women mistake this implantation bleeding for a period because it happens so early they don’t realize they’re pregnant.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Irregular bleeding is a symptom of PCOS, a condition in which your ovaries produce extra male hormones. PCOS is common in young women. It leads to the growth of small, fluid-filled sacs in your ovaries.
- Birth control. Birth control pills can cause spotting, especially when you first start using them or you switch to a new one.
 Continuous birth control pills are more likely to cause breakthrough bleeding than 21- or 28-day pills. Spotting is also common in women who have an intrauterine device (IUD).
Continuous birth control pills are more likely to cause breakthrough bleeding than 21- or 28-day pills. Spotting is also common in women who have an intrauterine device (IUD). - Uterine fibroids. Fibroids are small, noncancerous lumps that can form on the outside or inside of the uterus. They can cause abnormal vaginal bleeding, including spotting in between periods.
- Infections. An infection in your vagina, cervix, or another part of your reproductive tract can sometimes make you spot. Bacteria, viruses, and yeast all cause infections. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a serious infection you can get from an STD like chlamydia or gonorrhea.
- Cervical polyps. A polyp is a growth that forms on the cervix. It isn’t cancerous, but it can bleed. During pregnancy, polyps are more likely to bleed because of changing hormone levels.
- Menopause. The transition to menopause can take several years.
 During this time, your periods will likely be more unpredictable than usual. This is due to fluctuating hormone levels. The bleeding should taper off once you’re in full menopause.
During this time, your periods will likely be more unpredictable than usual. This is due to fluctuating hormone levels. The bleeding should taper off once you’re in full menopause. - Rough sex or sexual assault. Any damage to the lining of the vagina can make you bleed a little bit.
You’re more likely to notice spotting in between periods if you:
- are pregnant
- recently switched birth control methods
- just started to get your period
- have an IUD
- have an infection of the cervix, vagina, or other part of the reproductive tract
- have PID, PCOS, or uterine fibroids
Although spotting is usually not a sign of something serious, it isn’t normal. Any time you notice bleeding outside of your period, you should mention it to your primary care doctor or OB-GYN. It’s especially important to call your doctor if you’re pregnant and notice spotting. Spotting could be a sign of a serious complication, such as an ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage.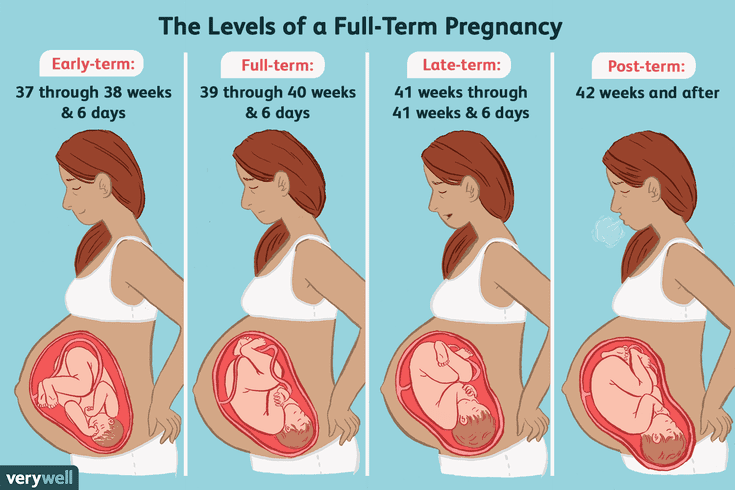
During your visit your doctor will ask about your symptoms and do a physical exam to try to identify the cause of your spotting. The physical exam will likely include a pelvic exam. Tests that can help diagnose the cause include:
- blood tests
- Pap smear
- pregnancy test
- ultrasound of your ovaries and uterus
The treatment for spotting will depend on what condition is causing it. You might need:
- an antibiotic or antifungal drug to treat an infection
- birth control or other hormones to regulate your menstrual cycle
- a procedure to remove polyps or other growths in your uterus or cervix
The outlook depends on the cause of your spotting. Spotting during pregnancy and from a birth control switch will usually stop after a few weeks or months. Spotting that’s due to an infection, polyps, fibroids, or PCOS should go away once the condition is under control with treatment.
Usually spotting is nothing serious, but it can be inconvenient, especially when you’re not prepared for the bleeding. One way to figure out whether you’re spotting or menstruating is to track your periods. Keep a diary or use a period app on your phone to record when your monthly bleeding starts and ends each month, and when you have spotting. Share it with your doctor to see if you can find any patterns.
One way to figure out whether you’re spotting or menstruating is to track your periods. Keep a diary or use a period app on your phone to record when your monthly bleeding starts and ends each month, and when you have spotting. Share it with your doctor to see if you can find any patterns.
Ask your doctor about hormone treatments that can help regulate your periods and prevent spotting. During pregnancy you can manage bleeding by getting as much rest as possible and by not lifting anything heavy.
Until you can get your spotting under control, always keep panty liners close by. Have a box at home and carry a few in your purse, just in case you start to bleed.
Last medically reviewed on September 12, 2016
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Abnormal uterine bleeding: Diagnosis & tests. (2014, February)
familydoctor.org/familydoctor/en/diseases-conditions/abnormal-uterine-bleeding/diagnosis-tests.html - Intra uterine device (IUD). (n.d.)
familyplanning.org.nz/advice/contraception/intra-uterine-device-iud - Laughlin-Tommaso, S. K. (2014, November 27). Is breakthrough bleeding more common with extended-cycle birth control pills, such as Seasonale and others? Retrieved from
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/birth-control/expert-answers/seasonale-side-effects/faq-20058109 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2014, September 3). Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Tests and diagnosis
mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pcos/basics/tests-diagnosis/con-20028841 - Menstruation and the menstrual cycle fact sheet. (2014, December 23)
womenshealth.gov/publications/our-publications/fact-sheet/menstruation.html - Ovulation frequently asked questions.
 (2016, September 2)
(2016, September 2)
americanpregnancy.org/getting-pregnant/ovulation-faq/ - PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome): General information. (2016, May 25)
youngwomenshealth.org/pcos-all-guides/ - Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) – CDC fact sheet. (2016, May 23)
cdc.gov/std/pid/stdfact-pid.htm - Periods. (2015, February 21)
nhs.uk/Conditions/Periods/Pages/Symptoms.aspx - Spotting during pregnancy. (2015, August)
americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-concerns/spotting-during-pregnancy/ - Uterine fibroids and abnormal bleeding. (n.d.)
uofmhealth.org/conditions-treatments/abnormal-bleeding-uterine-fibroids
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Mar 29, 2019
Written By
Stephanie Watson
Edited By
Judy Lee
Sep 12, 2016
Medically Reviewed By
Euna Chi, M. D.
D.
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Euna Chi, M.D. — By Stephanie Watson — Updated on March 29, 2019
Read this next
Why Am I Spotting Between Periods?
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
You might have spotting before your period due to changes in medication, pregnancy, infection, or another underlying condition. Learn when to get help.
READ MORE
What Causes Your Period to Be Shorter or Lighter Than Normal?
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
Everyone's menstrual cycle is different. A "normal" period can last anywhere from three to seven days. If your periods usually last five or six days…
READ MORE
Is It Normal to Not Have Discharge Before Your Period?
Medically reviewed by Carolyn Kay, M.
 D.
D.It might be alarming to find that you have little or no vaginal discharge before your period, but vaginal discharge varies from person to person. This…
READ MORE
Should You Be Worried if Your Period Is Light?
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI
Learn when a light period is nothing to worry about, and when it may be the sign of something more serious.
READ MORE
Why Is My Period Late? 8 Possible Reasons
Worried about a late period, but know you aren't pregnant? Missed or late periods can happen for plenty of reasons. Read on to learn about them.
READ MORE
Here’s Why You Missed Your Period While on Birth Control
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
The birth control pill introduces different hormones into your system.
 Learn how this may affect your menstrual cycle.
Learn how this may affect your menstrual cycle.READ MORE
Why Is My Period So Heavy?
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
Heavy flows and cramps can be a common experience during your periods. A period so heavy that it prevents you from doing everyday activities isn’t…
READ MORE
False pregnancy - causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
I confirm More
- INVITRO
- Library
- Disease Handbook
- False pregnancy
Pseudocyesis
nine0002 Pseudo-pregnancyAmenorrhea
Toxicosis
1643 February 17
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0027 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.
False pregnancy, or pseudocyesis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
Definition
False pregnancy is a psychophysiological disorder characterized by a woman's mistaken belief that she is pregnant based on her neuroendocrine symptoms, which resemble those of a true pregnancy. nine0003
Pseudo-pregnancy occurs in one in 22,000 pregnancies.
Causes of false pregnancy
The development of this pathology is based on mental, psychological and emotional factors that provoke endocrine, vegetative and somatic disorders. Experts note that women who experience a false pregnancy are very eager to experience the state of pregnancy and become mothers.
At the heart of mental causes development of false pregnancy are functional neurological disorders: neurosis, anxiety, personality disorders, schizophrenia, dementia praecox, manic-depressive psychosis, hysteria, frontotemporal degeneration.
Psychological reasons often go in addition to mental ones. False pregnancy is more likely in women with an unstable nervous system, in the presence of psychopathic character traits and traumatic situations.
False pregnancy is more likely in women with an unstable nervous system, in the presence of psychopathic character traits and traumatic situations.
The risk group is women over 35 years old, especially suspicious and impressionable. nine0003
The psychological reasons for the development of a false pregnancy are the desire to have a child, a large number of abortions or spontaneous abortion at different stages of gestation, fear of bearing a child, the death of an already born child, envy towards people who have children, the desire to keep a husband in the family, approaching menopause . In young women, pseudopregnancy can develop as a result of amenorrhea, anxiety associated with unprotected intercourse, tubal ligation (surgical sterilization), and hysterectomy (removal of the uterus). nine0003
Stress, emotional experiences and increased anxiety are accompanied by increased production of pituitary hormones. Against the background of hormonal imbalance, a woman has a partial or full range of manifestations of pregnancy, with the exception of the presence of a fetus.
It is assumed that the disease can be caused by trauma (physical or mental), hormone imbalance and some diseases. The appearance of symptoms of false pregnancy is noted with hormone-secreting tumors (ovarian cyst, uterine myoma, etc.), hypothyroidism (a disease caused by a decrease in thyroid function and insufficient hormone production), alcoholic liver disease, cholecystitis (including gallstones), infections urinary tract (complicated by urinary retention), tumors of the abdominal cavity, hyperprolactinemia, esophageal achalasia. nine0003
There are a number of studies that focus on the neuroendocrine mechanism underlying pseudopregnancy. Changes in plasma levels of prolactin, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, growth hormone, estradiol, progesterone, and testosterone can cause amenorrhea, galactorrhea (milk production outside the breastfeeding period), and diurnal and/or nocturnal hyperprolactinemia, which are found in most women with false pregnancies . nine0003
nine0003
I.P. Pavlov in the development of false pregnancy attached great importance to cortical impulses under the influence of self-hypnosis. He believed that an ultraparadoxical phase state develops in the cerebral cortex.
Somatic changes are probably also explained by endocrine disorders (hypothalamic-pituitary, ovarian, adrenal).
Increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system causes apparent fetal movements and contractions on the day of the expected birth. The sympathetic system increases the contractility of the diaphragm, chronic contraction of the diaphragmatic muscle pushes the intestines down in the abdominal cavity, the intestines are stretched, constipation, pain and a characteristic lordotic posture occur (the head is pushed forward, the chest is flat, turning into a protruding abdomen, the shoulders are pushed forward, and the legs are spread apart in knee joints). nine0003
False pregnancy syndrome can also be experienced by men (Couvade syndrome, or sympathetic pregnancy) whose partners are currently carrying a child. Such a disorder can develop in men of an infantile-hysterical psychotype against the background of strong empathy for the condition of a woman. At the same time, men feel many of the symptoms that characterize the course of pregnancy in a partner.
Such a disorder can develop in men of an infantile-hysterical psychotype against the background of strong empathy for the condition of a woman. At the same time, men feel many of the symptoms that characterize the course of pregnancy in a partner.
Disease classification
In the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), false pregnancy is a disorder with somatic symptoms. The disease is listed as "not elsewhere classified", meaning that it is in a separate category from other somatic symptom disorders such as functional neurological symptomatic disorder. nine0003
Symptoms of a false pregnancy
In case of pseudo-pregnancy, a woman does not pretend her condition, but is really convinced of the presence of pregnancy, experiences and feels its signs.
False pregnancy is accompanied by vegetative and endocrine symptoms that mimic the changes that occur in the female body after fertilization.
In women with pseudo-pregnancy, there may be slight discharge during menstruation or amenorrhea, signs of toxicosis (nausea, increased salivation, vomiting, fatigue, drowsiness, mood swings, perversion of food addictions, etc. ) may appear. nine0003
) may appear. nine0003
In case of false pregnancy, the mammary glands increase, breast milk is secreted, nipples are hyperpigmented, in rare cases, changes in the external genitalia and cervix are noted, the stomach enlarges as a result of excessive development of subcutaneous tissue on the anterior abdominal wall and flatulence, weight is added. The woman feels the movement of the "fetus" associated with increased peristalsis.
Diagnosis of false pregnancy
An objective examination of the patient can provide a number of valuable data, such as the degree of protrusion of the navel, the degree of development of subcutaneous fat. The diagnosis is usually made during a gynecological examination. In patients with false pregnancy, objective changes in the genital organs, such as cyanosis of the cervix and vagina, enlargement and softening of the uterus, are not detected. nine0003
Modern possibilities of pregnancy detection make it possible to reliably exclude a true pregnancy.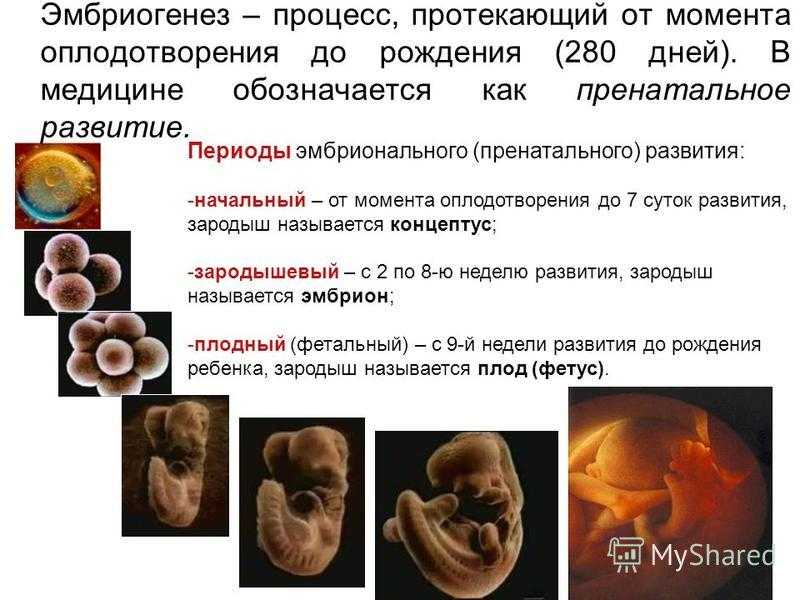 To confirm the diagnosis, a woman is prescribed:
To confirm the diagnosis, a woman is prescribed:
- ultrasound examination;
Fetal ultrasound according to indications (before the 20th week)
Additional ultrasound, which is prescribed in the presence of concomitant pathologies to monitor the condition of the fetus.
RUB 2,540 Sign up nine0003
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, beta-hCG, b-hCG, Human Chorionic)
Synonyms: Beta-hCG generic. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin; hCG; Pregnancy Quantitative hCG; Beta hCG; Total beta hCG. Brief description of the analyte Human Chorionic Gonadotropin...
Up to 1 business day
Available with home visit
RUB 685
In garbage

Plain X-ray of the abdominal organs
X-ray examination that allows to detect pathological changes in the abdominal cavity, including foreign bodies and neoplasms.
RUB 2,440 Sign up nine0003
Differential diagnosis in pseudopregnancy is carried out with simulated pregnancy, missed pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy, tumor processes in the pelvic region.
Which doctors to contact
To confirm pregnancy, a woman usually goes to gynecologist. If endocrine disorders are suspected in a patient with a false pregnancy, a gynecologist-endocrinologist or endocrinologist. nine0003
In the event that a woman stubbornly refuses to believe in a false pregnancy and inadequately perceives reality, she needs the help of a psychologist or psychotherapist.
Treatment of false pregnancy
As a rule, the condition of false pregnancy does not require special treatment.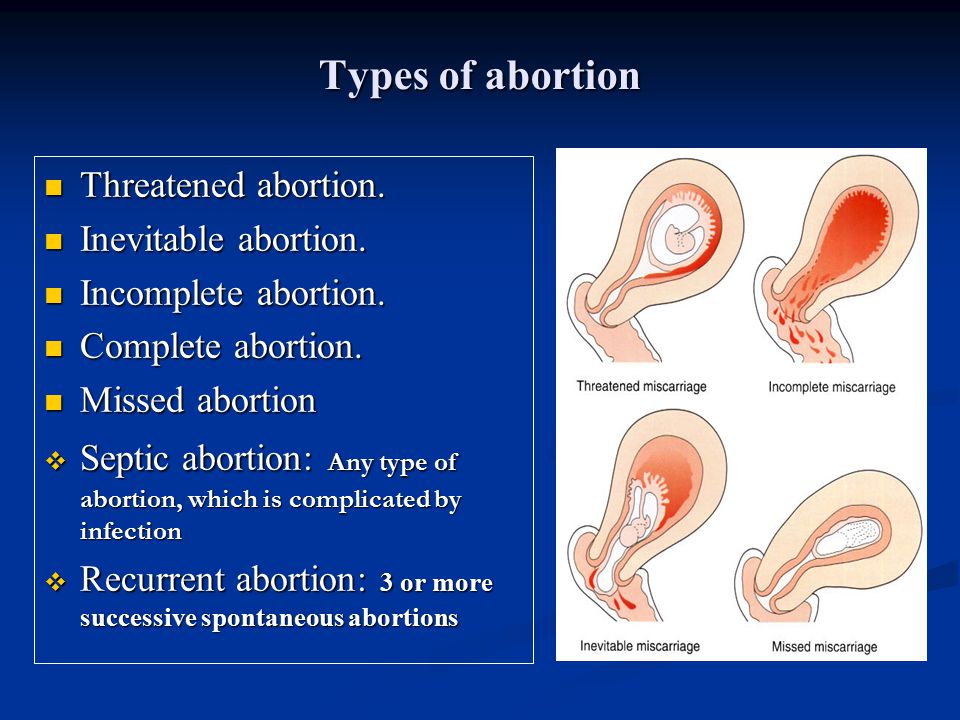 In most cases, to eliminate imaginary sensations, a competent and sympathetic explanation of the situation by a gynecologist, as well as understanding and support from close people, is sufficient. In the absence of self-hypnosis, the woman's menstrual cycle is restored, and the symptoms of toxicosis and other signs of pregnancy also disappear. nine0003
In most cases, to eliminate imaginary sensations, a competent and sympathetic explanation of the situation by a gynecologist, as well as understanding and support from close people, is sufficient. In the absence of self-hypnosis, the woman's menstrual cycle is restored, and the symptoms of toxicosis and other signs of pregnancy also disappear. nine0003
If a woman is diagnosed with a depressive disorder, drugs are prescribed that increase the formation and release of dopamine. Normalization of dopamine levels leads to adequate work of the adrenal glands, a decrease in the excessive activity of the sympathetic nervous system.
If a false pregnancy manifested itself in hormone-secreting tumors, hypothyroidism, alcoholic liver disease, cholecystitis, urinary tract infections, etc., then these pathologies are treated. It is necessary to identify the causes of psychogenic and neuroendocrine disorders, possible mental illnesses. In this case, the woman needs the appointment of psychiatric treatment. Psychotherapy, pharmacotherapy with antidepressants or antipsychotics, hormonal therapy, and uterine curettage are sometimes needed as treatment. As a rule, after treatment, the state of false pregnancy in women no longer occurs. nine0003
Psychotherapy, pharmacotherapy with antidepressants or antipsychotics, hormonal therapy, and uterine curettage are sometimes needed as treatment. As a rule, after treatment, the state of false pregnancy in women no longer occurs. nine0003
It happens that a false pregnancy is caused on purpose - for example, if the uterus or mammary glands are underdeveloped. In this case, the woman is prescribed a certain dose of estrogens and progestins for 8-12 weeks. In order for the therapeutic effect to persist for a long time, an ointment is used, which includes progesterone and estradiol.
Complications
False pregnancy syndrome can lead to pathological hyperprolactinemia. It has been shown that the symptoms of false pregnancy are caused by the secretion of prolactin with a simultaneous decrease in the secretion of luteinizing hormone and an increase in follicle-stimulating hormone. Perhaps hormonal disorders in some women can serve as a background for the development of mental disorders. nine0003
nine0003
Sometimes it is extremely difficult to convince a woman that she is not pregnant. Psychopathic personalities can live in this delusion for years. In women with neurosis-like reactions and mental disorders, the news of a false pregnancy can cause depression and suicidal thoughts.
Prevention of false pregnancy
Due to the fact that the causes of false pregnancy are not well understood, it is not possible to prevent its development. nine0003
Sources:
- Clinical guidelines "Hyperprolactinemia". Developed by: Russian Association of Endocrinologists. – 2016.
- Sholokhova V.R. Pathology of pseudocyesis as a psychosomatic disorder / V.R. Sholokhova, O.V. Minaev. // Medicine: today's challenges: materials of the IV Intern. scientific conf. (Moscow, November 2017). - Moscow: Buki-Vedi, 2017. - S. 64-68.
- Tarin et al. Endocrinology and physiology of pseudocyesis (Review). Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology 2013, 11:39.

IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes. nine0003
Recommendations
-
Myxedema
13566 26 December
-
Pick's disease (frontotemporal degeneration)
13541 23 December
nine0011
Schizotypal disorder
13523 21 December
Show more
Hypervitaminosis D
Hypervitaminosis A
nine0002 AnemiaDysbacteriosis
Malabsorption syndrome
Celiac disease
Lactase deficiency
nine0002 Cystic fibrosisToxicosis
Preeclampsia
Fetal hypoxia
Underweight
Hypotrophy (protein-energy malnutrition (PEM))
Hypotrophy: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
More
Cyst
Abscess
Cystitis
nine0002 UrethritisFistula
Bartholinitis
Bartholinitis is an inflammation of the Bartholin gland, which is located in the vestibule of the vagina, with blockage of its excretory duct and the development of an abscess.
More
ECO
nine0002 Diabetes mellitusThrush
Mastopathy
Mastopathy: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
More
Fungus
Diabetes mellitus
Gout
Atherosclerosis
Iron deficiency
HIV
Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment. nine0003
More
Allergen
Immunoglobulin
Quincke's edema
Angioedema
nine0002 Anaphylactic shockAtopic dermatitis
Urticaria
Pollinosis
Rhinitis
nine0002 ConjunctivitisItching
Sneezing
Lachrymation
Edema
Rash
Allergies
Allergies: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
More
Nothing found
Try changing your query or select a doctor or service from the list.
Doctor not found
Try changing your query or select doctor from the list
Medical office not found
Try changing the query or select medical office from the list
Therapist Traumatologist-orthopedist Endocrinologist Urologist Gynecologist Ultrasound doctor Cardiologist Pediatrician
Nothing found
Please try editing your query
Thank you!
You have successfully made an appointment
Detailed information has been sent to your e-mail
Subscribe to our newsletters
Enter e-mail
I consent to processing of personal data nine0003
Subscribe
False pregnancy: symptoms and causes
Consultation with a specialist:
Causes of false pregnancy
The exact mechanisms and causes of the development of a false pregnancy are unknown, but scientists have several assumptions. It is believed that this phenomenon is based on psycho-emotional changes in a particular personality, which lead to hormonal, vegetative and somatic disorders. As a rule, women who have been diagnosed with a false pregnancy actually want a child very much and dream of becoming a mother. Sometimes scientists also find an inverse relationship. Those girls who are very afraid of getting pregnant, there are signs of a false pregnancy. They can also occur at a time when a close friend or relative is carrying a child. nine0003
It is believed that this phenomenon is based on psycho-emotional changes in a particular personality, which lead to hormonal, vegetative and somatic disorders. As a rule, women who have been diagnosed with a false pregnancy actually want a child very much and dream of becoming a mother. Sometimes scientists also find an inverse relationship. Those girls who are very afraid of getting pregnant, there are signs of a false pregnancy. They can also occur at a time when a close friend or relative is carrying a child. nine0003
Risk factors for false pregnancy have also not been established. However, it is known that this condition is more often detected in women with high suspiciousness and associated psycho-emotional disorders (neurosis, hysteria, psychosis, etc.). With regular exposure to stressful situations, as well as if a woman constantly experiences anxiety or other vivid emotions, the secretion of pituitary hormones increases. Exactly the same hormones are released during natural pregnancy. Therefore, these conditions can also be related to predisposing factors. Finally, the risk group for false pregnancy includes women aged 35-40 years and older who have: nine0003
Therefore, these conditions can also be related to predisposing factors. Finally, the risk group for false pregnancy includes women aged 35-40 years and older who have: nine0003
-
diagnosed with infertility;
-
there is a panic fear of pregnancy;
-
lost a child as a result of termination of pregnancy at different times;
-
they really want to have children.
In some cases, signs of a false pregnancy may develop due to various endocrine or gynecological diseases, for example, with uterine fibroids or ovarian cysts. nine0003
Call right now
+7 (495) 215-56-90
Sign up
Symptoms of false pregnancy
With a false pregnancy, the same symptoms are noted as with a natural one. These include:
-
cessation of menstruation;
-
an increase in the size of the abdomen;
-
breast enlargement; nine0003
-
secretion of milk from the nipples;
-
weight gain;
-
sensation of fetal movement;
-
nausea in the morning;
-
a sharp change in mood;
-
craving for inedible; nine0003
-
fatigue and constant weakness.

In addition, if you take a pregnancy test, it may turn out to be false positive, and in some cases, a woman may even develop false contractions. All these symptoms can be present for several months, so the woman has no doubt that she is carrying a child. However, if you do an ultrasound, then the developing fetus in the uterus will not be visible. nine0003
All these signs of a false pregnancy can be explained from a medical point of view. For example, fetal movements are the result of active peristalsis, and an increase in the size of the abdomen is associated with excessive deposition of subcutaneous fat and increased gas formation in the intestines. A false pregnancy test and some other symptoms are explained by hormonal disruptions.
Diagnosis of false pregnancy
Women with suspected false pregnancy should consult a gynecologist. Already after a routine examination on the chair, the doctor may suspect the disease. The fact is that with an imaginary pregnancy there are no characteristic changes in the genital and reproductive organs. With a true pregnancy, the uterus increases in size and acquires a softer texture, and moderate cyanosis (“blueness”) is noted in the cervical and vaginal mucosa. In the case of an empty pregnancy, there will be no such changes. nine0003
With a true pregnancy, the uterus increases in size and acquires a softer texture, and moderate cyanosis (“blueness”) is noted in the cervical and vaginal mucosa. In the case of an empty pregnancy, there will be no such changes. nine0003
An ultrasound of the uterus and laboratory tests (determination of hCG in the urine or in the blood) can put a point in the diagnosis of the disease. But even with conclusive evidence, a woman may still continue to think that she is actually pregnant.
On the other hand, the gynecologist should also not always be skeptical about the words of the patient. Other diseases, such as ectopic pregnancy or abdominal tumors, may look like a false pregnancy. Therefore, in each case, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination and exclude similar diseases. nine0003
Treatment of false pregnancy
In most cases, specific treatment for false pregnancy is not required. It is enough for a gynecologist to talk to a woman, show the results of examinations, explain why she developed this disease. To improve the psycho-emotional state, the help of a psychologist may be required. In this case, you can eliminate internal experiences and other risk factors, as well as find a way out of existing psychological problems. After a woman realizes that she is not pregnant, all existing symptoms will gradually disappear. After some time, her menstrual cycle normalizes, signs of toxicosis disappear, body weight decreases and the size of the abdomen returns to its original value. nine0003
To improve the psycho-emotional state, the help of a psychologist may be required. In this case, you can eliminate internal experiences and other risk factors, as well as find a way out of existing psychological problems. After a woman realizes that she is not pregnant, all existing symptoms will gradually disappear. After some time, her menstrual cycle normalizes, signs of toxicosis disappear, body weight decreases and the size of the abdomen returns to its original value. nine0003
If this approach proved to be ineffective, then another approach is used, which involves the appointment of non-drug and drug treatments. the first group includes:
-
Relaxing massage. It can be performed manually or on special devices. Massage helps to improve overall well-being, helps to get rid of stress and irritation.
-
Reflexology. It implies an impact on biologically active points. For this, classical acupuncture or alternative methods may be prescribed.
 Reflexology can affect the condition of almost all organs, including the organs of the reproductive system. nine0003
Reflexology can affect the condition of almost all organs, including the organs of the reproductive system. nine0003 -
Aromatherapy. Another non-drug treatment that has a calming effect, helps relieve tension and anxiety, and eliminate the effects of stress.
-
Electrosleep. It affects the nerve connections in the structures of the brain. It is used to normalize the function of the organs of the endocrine system, improve metabolism, and normalize the psychological state. nine0003
Drug therapy involves the appointment of various drugs. In this case, the treatment plan is selected individually and involves a stepwise approach. If a woman is shown sedatives, then herbal preparations are first prescribed. They have a minimal risk of side effects and at the same time help to effectively deal with anxiety, sleep disturbance and psycho-emotional stress. If such drugs were ineffective, then more "strong" drugs from the group of tranquilizers are prescribed.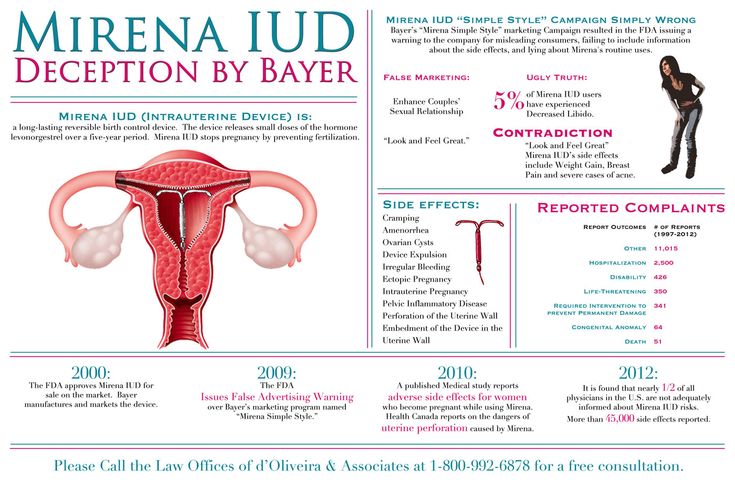 With their help, you can eliminate fear and anxiety, as well as other psychological disorders. Tranquilizers are quite serious drugs, so they should not be used uncontrollably. If a false pregnancy has developed against the background of depression or anxiety disorders, then antidepressants are included in the treatment plan. At the same time, various methods of psychotherapy are used. nine0003
With their help, you can eliminate fear and anxiety, as well as other psychological disorders. Tranquilizers are quite serious drugs, so they should not be used uncontrollably. If a false pregnancy has developed against the background of depression or anxiety disorders, then antidepressants are included in the treatment plan. At the same time, various methods of psychotherapy are used. nine0003
You can restore the menstrual cycle with the help of various hormonal drugs. The most popular of these are combined oral contraceptives. Also, the gynecologist may prescribe other medications, depending on the characteristics of the hormonal background of the patient.
After the treatment, some women wonder if a false pregnancy can be repeated? This disease is not prone to recurrence, therefore, after the treatment, it does not return. Medicine knows only isolated cases of repeated false pregnancy. nine0003
Prevention of false pregnancy
It is difficult to carry out effective prevention of false pregnancy in women, since the exact mechanism for the development of this disease has not been established.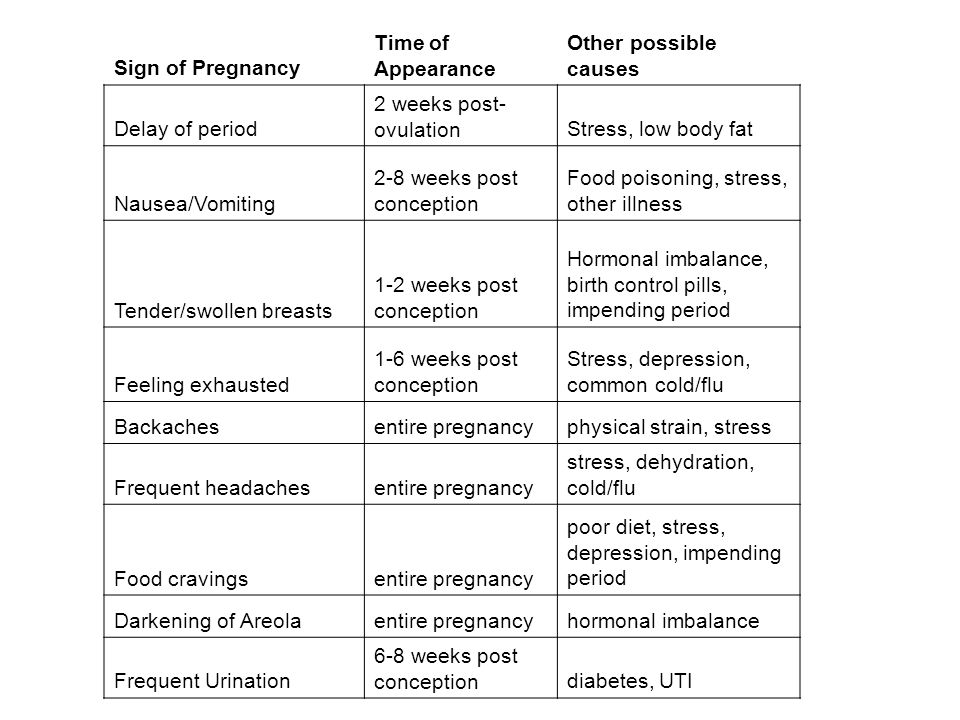 At the same time, you can follow simple recommendations that will help reduce the risk of developing this condition:
At the same time, you can follow simple recommendations that will help reduce the risk of developing this condition:
-
In the presence of violations in the psycho-emotional sphere, it is necessary to seek the help of a psychologist in time. The help of a specialist will not be superfluous for those women who are regularly exposed to stress, have a busy work schedule, or who have experienced psychological trauma. nine0003
-
If a woman has signs of gynecological diseases (irregular menstrual cycle, pain in the lower abdomen, abnormal vaginal discharge, discomfort during intimacy, etc.), you should consult a gynecologist. The specialist will conduct an examination, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe an effective treatment.
-
If a woman is terribly afraid of becoming pregnant, then in this case she may need the help of both specialists. The gynecologist will be able to tell you how the process of bearing a child goes, what needs to be done at different stages of pregnancy, how childbirth goes, etc.