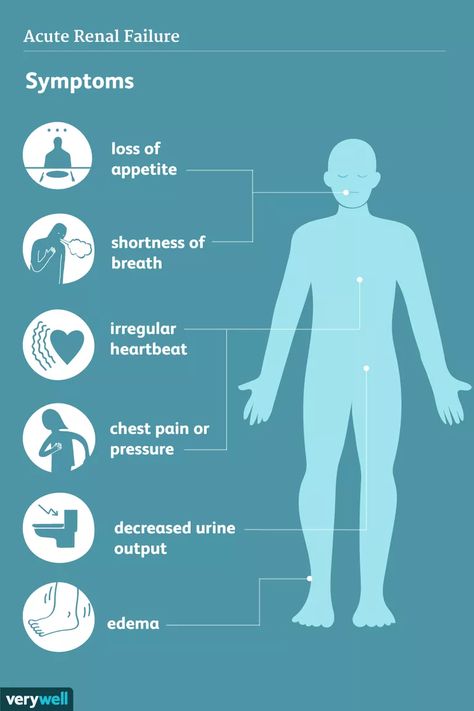
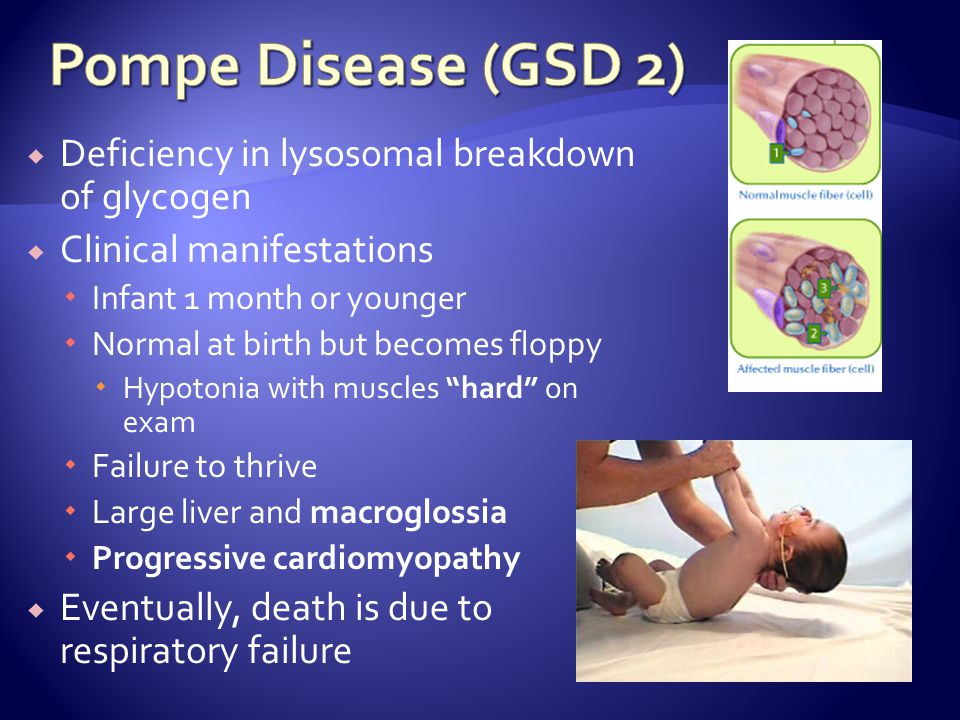
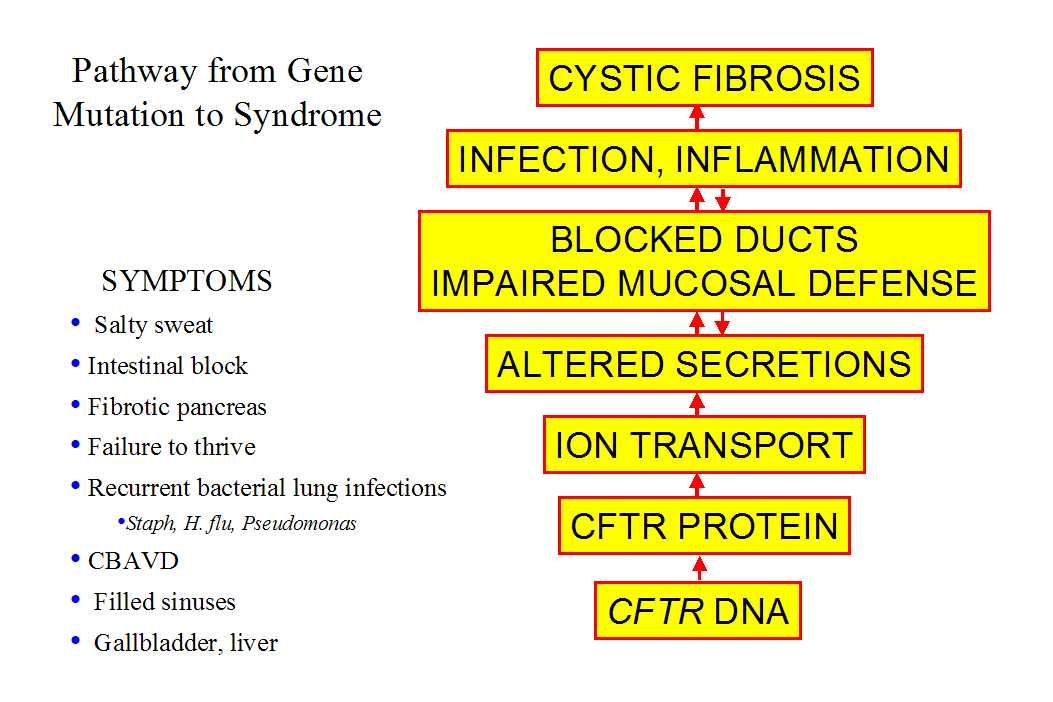
Failure to thrive causes
Failure to Thrive | Johns Hopkins Medicine
Failure to Thrive | Johns Hopkins MedicineHealth
What is failure to thrive?
Children are diagnosed with failure to thrive when their weight or rate of weight gain is significantly below that of other children of similar age and sex. Infants or children that fail to thrive seem to be dramatically smaller or shorter than other children the same age. Teenagers may have short stature or appear to lack the usual changes that occur at puberty. However, there is a wide variation in what is considered normal growth and development.
Symptoms
In general, the rate of change in weight and height may be more important than the actual measurements.
Infants or children who fail to thrive have a height, weight and head circumference that do not match standard growth charts. The person's weight falls lower than the third percentile (as outlined in standard growth charts) or 20 percent below the ideal weight for their height. Growing may have slowed or stopped after a previously established growth curve.
The following are delayed or slow to develop:
Physical skills, such as rolling over, sitting, standing and walking
Mental and social skills
Secondary sexual characteristics (delayed in adolescents)
Diagnosis
It is important to determine whether failure to thrive results from medical problems or factors in the environment, such as abuse or neglect.
There are multiple medical causes of failure to thrive. These include:
Chromosome abnormalities, such as Down syndrome and Turner syndrome
Defects in major organ systems
Problems with the endocrine system, such as thyroid hormone deficiency, growth hormone deficiency or other hormone deficiencies
Damage to the brain or central nervous system, which may cause feeding difficulties in an infant
Heart or lung problems, which can affect how oxygen and nutrients move through the body
Anemia or other blood disorders
Gastrointestinal problems that result in malabsorption or a lack of digestive enzymes
Long-term gastroenteritis and gastroesophageal reflux (usually temporary)
Cerebral palsy
Long-term (chronic) infections
Metabolic disorders
Complications of pregnancy and low birth weight
Other factors that may lead to failure to thrive:
Emotional deprivation as a result of parental withdrawal, rejection or hostility
Economic problems that affect nutrition, living conditions and parental attitudes
Exposure to infections, parasites or toxins
Poor eating habits, such as eating in front of the television and not having formal meal times
Many times the cause cannot be determined.
Treatment
The treatment depends on the cause of the delayed growth and development. Delayed growth due to nutritional factors can be resolved by educating the parents to provide a well-balanced diet.
If psychosocial factors are involved, treatment should include improving the family dynamics and living conditions. Parental attitudes and behavior may contribute to a child's problems and need to be examined. In many cases, a child may need to be hospitalized initially to focus on implementation of a comprehensive medical, behavioral and psychosocial treatment plan.
Do not give your child dietary supplements without consulting your physician first.
Related
-
GERD
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) in Children
-
Head and Neck
Head Injury in Children
-
Pediatric
Healthy Sleep Habits
Related Topics
Failure to Thrive (for Parents)
What Is Failure to Thrive?
When growing kids don't gain weight as they should, it is called "failure to thrive.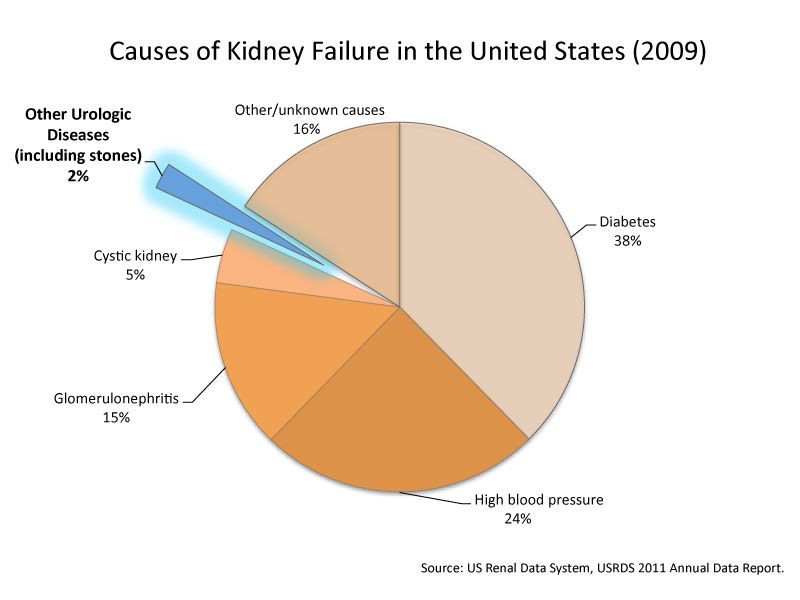 "
"
Failure to thrive is not a disease or disorder itself. Rather, it's a sign that a child is undernourished. In general, kids who fail to thrive are not getting enough calories to grow and gain weight in a healthy way. When kids can't gain weight, they also often may not grow as tall as they should.
Kids need to get enough calories to learn and develop well. So kids with failure to thrive might start to walk and talk later than other kids, and can have trouble learning in school.
What Causes Failure to Thrive?
Different things can cause failure to thrive, including:
- Not enough calories provided. Sometimes a parent or caregiver measures or mixes formula incorrectly, so an infant doesn't get enough calories. Problems with breastfeeding or starting solids also can cause failure to thrive. Some families have trouble affording enough food for their children. And sometimes parents miss their children's hunger cues.
- The child eats too little.
 Some children have trouble eating enough food. This might be due to a developmental delay, being a very picky eater, a medical condition that affects swallowing (like cerebral palsy or a cleft palate), or a condition like autism in which kids don't like eating foods with some textures or tastes.
Some children have trouble eating enough food. This might be due to a developmental delay, being a very picky eater, a medical condition that affects swallowing (like cerebral palsy or a cleft palate), or a condition like autism in which kids don't like eating foods with some textures or tastes. - Health problems involving the digestive system. Problems with the digestive system can prevent a child from gaining weight. Conditions like gastroesophageal reflux (GER), chronic diarrhea, cystic fibrosis, chronic liver disease, and celiac disease can make it harder for kids to absorb enough nutrients and calories to gain weight.
- Food intolerance. A food intolerance means the body is sensitive to some foods. For example, milk protein intolerance means the body can't absorb foods such as yogurt and cheese, which could lead to failure to thrive.
- An ongoing medical condition. Kids with conditions involving the heart, lungs, or endocrine system might need more calories than other kids.
 It can be hard for some to eat enough.
It can be hard for some to eat enough. - Infections. The body can use up a lot of calories as it fights an infection. And kids who don't feel well might eat less than usual.
- Metabolic disorders. These are health conditions that make it hard for the body to break down, process, or take energy from food. They also can cause a child to eat poorly or vomit.
Sometimes a mix of things leads to failure to thrive. For instance, if a baby has severe GER and is reluctant to eat, feeding times can be stressful. The baby may be upset and frustrated, and the caregiver might not be able to get the baby to eat enough.
Other times, doctors aren't sure exactly what causes the problem.
How Is Failure to Thrive Diagnosed?
Many babies and kids go through brief periods when they don't gain as much weight as expected. But if a child continues to not gain enough weight or loses weight, doctors try to find out why.
They'll ask for a child's health history, including a feeding history. This helps them see if underfeeding, household stresses, or feeding problems might be causing the problem. A dietitian or other health care professional also may track the calories in a child's diet to make sure the child is getting enough.
This helps them see if underfeeding, household stresses, or feeding problems might be causing the problem. A dietitian or other health care professional also may track the calories in a child's diet to make sure the child is getting enough.
Doctors measure a child's weight, length, and head circumference at each well-child checkup and put the results on a growth chart. Children may have failure to thrive if they weigh less than most kids their age or aren't gaining weight as quickly as they should.
Doctors might order tests (such as blood tests or urine tests) to check for medical problems that could affect a child's weight and growth.
How Is Failure to Thrive Treated?
Treating kids who fail to thrive involves making sure they get the calories needed to grow. The care team also will address any causes for poor weight gain they find. A child's care team may include:
- the primary care doctor
- a registered dietitian
- occupational therapists to help with sensory or coordination problems
- speech therapists to help with any sucking or swallowing problems
- a social worker if a family has trouble getting enough food
- psychologists and other mental health professionals for any behavioral issues
- specialists (such as a cardiologist, neurologist, or gastroenterologist) to treat health conditions that could affect a child's weight
Usually, kids who have failure to thrive can be treated at home. They'll also have regular doctor visits to check on weight gain. Doctors often recommend high-calorie foods and, for babies, a high-calorie formula.
They'll also have regular doctor visits to check on weight gain. Doctors often recommend high-calorie foods and, for babies, a high-calorie formula.
Doctors also might recommend:
- spacing out meals to make sure children are hungry
- avoiding "empty" calories like juices and candies
- offering foods of certain textures if sensory issues are a problem
- other strategies depending what's causing the failure to thrive
Weight gain takes time, so it might be several months before a child is back in the normal range.
Some children with failure to thrive might need care in a hospital. They'll be fed and watched around the clock for several days (or longer) until they gain some weight. After leaving the hospital, the child will continue treatment at home.
How Can Parents Help?
It can be hard to learn that your child has failure to thrive. No matter what's causing it, there are ways to help and support your child. You can:
- Follow the advice from your doctor or the dietitian.

- Take your child to all recommended doctor visits.
- Call the doctor if your child develops new symptoms, like frequent diarrhea or vomiting.
- Learn about any medical conditions that the doctor finds in your child.
- Talk to the doctor or a therapist if you feel stressed or frustrated about problems with feeding your child.
Reviewed by: Larissa Hirsch, MD
Date reviewed: February 2020
Memory problems in young people
Forgetfulness, impaired attention are attributed to the elderly. However, memory problems are increasingly occurring in young people. The reasons for this phenomenon are varied - from an unhealthy lifestyle and overwork to serious disorders in the functioning of the brain and internal organs.
CONTENT OF THE ARTICLE
- 1. Causes of memory impairment at a young age
- 2. Associated symptoms
- 3. How to solve memory problems
Causes of memory impairment at a young age
Memory impairment in older people is usually caused by age-related changes in the body. Atherosclerosis, microstrokes, Alzheimer's disease - these pathologies negatively affect cognitive functions.
Atherosclerosis, microstrokes, Alzheimer's disease - these pathologies negatively affect cognitive functions.
The causes of forgetfulness at a young age are different, they can be divided into 4 groups.
- Brain lesions.
- Diseases of internal organs.
- Unfavorable impact of external factors, violation of the daily routine.
- Chronic intoxication of the body.
Disturbances in the functioning of the brain - the main cause of memory impairment
The cerebral cortex is responsible for the functioning of long-term memory. The hippocampus, which is located in the temporal lobes, starts the processes of translating short-term information into long-term memory. There are other memory centers in the brain. Therefore, any damage to this organ provokes the development of forgetfulness, inattention.
Causes of memory problems in young people:
- Traumatic brain injury. The area affected is irrelevant.
 After any blow, short-term or long-term memory loss, retrograde or antegrade amnesia is observed.
After any blow, short-term or long-term memory loss, retrograde or antegrade amnesia is observed. - Stroke. When blood circulation is disturbed, the functions of the memory centers are disrupted.
- Malignant and benign neoplasms. Tumors affect nearby tissues, including the memory centers located in them.
- Encephalitis, meningitis. The infection negatively affects the functioning of the brain and memory.
- Post-surgical asthenic syndrome.
After any injuries and diseases of the brain, it is necessary to be constantly monitored by a neurologist. This will help to timely identify memory impairment and cognitive disorders.
What diseases of the internal organs negatively affect memory
The normal functioning of the brain largely depends on the well-coordinated work of the whole organism. Many dysfunctions can indirectly affect concentration and memory.
The hormonal background influences the memorization process.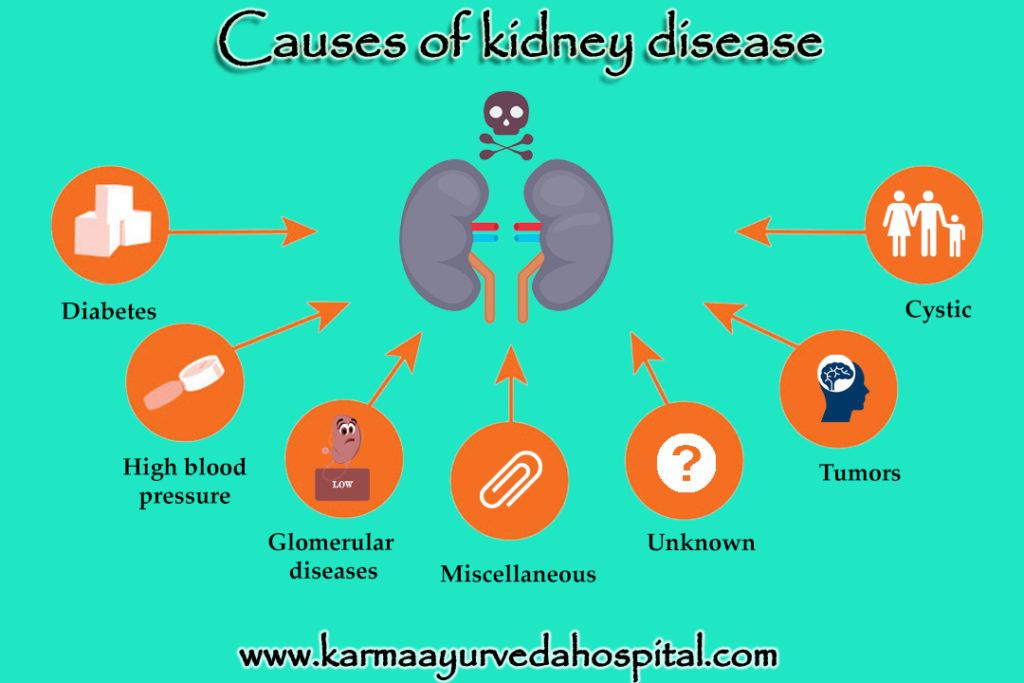 Testosterone, vasopressin, prolactin, estrogen help convert short-term memory into long-term memory. Oxytocin impairs the memory process.
Testosterone, vasopressin, prolactin, estrogen help convert short-term memory into long-term memory. Oxytocin impairs the memory process.
Main diseases:
- Hypertension, other diseases of the cardiovascular system. Provoke a deterioration in the blood supply to the brain.
- Violation of exchange processes. When metabolism fails, brain tissue suffers from nutritional deficiencies. Resources are allocated to vital areas, and the memory center is not a priority in this list.
- Angiopathy - pathology develops against the background of diabetes mellitus. Vascular walls thicken, small vessels overlap and stop working. Blood circulation is disturbed in all organs, the brain also suffers.
- Hypothyroidism - lack of thyroid hormone leads to the development of iodine deficiency.
- Mental disorders - schizophrenia, epilepsy, depression.
- Cervical osteochondrosis. Deformed vertebrae compress blood vessels, the brain suffers from a lack of oxygen and nutrients.

In diseases of the kidneys, verbal memory deteriorates. Cognitive functions decrease with an increase in creatinine levels, a decrease in glomerular filtration rate. The study was carried out for 5 years by scientists from the United States.
Adverse environmental influences, lifestyle
If young people have memory problems, the causes are often associated with unconscious brain dysfunction. But these causes, unlike diseases, are easier to eliminate. With a change in lifestyle, forgetfulness will gradually disappear.
Causes of memory impairment:
- Information overload. The human brain freezes if it is not able to process all the information received. The principle of multitasking has already been recognized as ineffective, since it leads to a deterioration in memory capabilities, attentiveness, and nervous disorders.
- Avitaminosis. For the normal functioning of the brain, it is necessary to constantly replenish the reserves of B vitamins.
 These substances protect cells from aging and overload, participate in oxygen metabolism and the synthesis of certain neurotransmitters, and ensure the normal functioning of the central nervous system.
These substances protect cells from aging and overload, participate in oxygen metabolism and the synthesis of certain neurotransmitters, and ensure the normal functioning of the central nervous system. - Stress, nervous and emotional overwork. Under such conditions, the physiological processes associated with memory are blocked. With prolonged stress, information is not remembered at all.
- Chronic sleep deprivation. During sleep, new cells are synthesized. If a person constantly does not get enough sleep, the brain does not have time to recover, the process of memorizing and reproducing information is disrupted.
- Abuse of junk food. Foods with food coloring contain aluminum. The substance accumulates in the body, is poorly excreted. The result is a deterioration in memory, thinking, attention.
- Caffeinated drinks. Constant stimulation of the brain leads to a decrease in memory.
- Poisoning with lead, mercury, other heavy metals.
- Long-term and uncontrolled use of tranquilizers, sedatives and antihistamines, neuroleptics.
 Anticholinergics, antidepressants, barbiturates negatively affect brain function.
Anticholinergics, antidepressants, barbiturates negatively affect brain function.
Smoking destroys the brain. Heavy smokers suffer from memory problems, the ability to perceive new information, logical thinking is deteriorating. Equally dangerous active and passive smoking, memory performance is reduced by 25-30%.
Daily consumption of 36 g of pure alcohol leads to early memory impairment. But the complete rejection of alcohol negatively affects the functioning of the brain. It is safe to consume up to 4 glasses of dry red wine per week.
Drugs are neurotoxic substances that disrupt the process of receiving, processing and sending information. Even with a single use, irreversible damage often occurs in the serotonin system of the brain.
Associated symptoms
Forgetfulness, inability to remember and reproduce information are not the only signs of poor memory.
What symptoms should you see a doctor for?

Often, memory problems are accompanied by migraine attacks, tinnitus, hearing and vision impairment, heart rhythm disturbance, and chronic fatigue.
How to deal with memory problems
If memory often fails, it is necessary to visit a neurologist. After examination, history taking and primary diagnosis, consultation with a general practitioner, neuropsychologist, psychotherapist, oncologist may be required.
Neuromonitoring begins with an assessment of the neurological status. The doctor checks the work of the cranial nerves, determines the amplitude of the movement of the eyeballs, the symmetry of the tongue and dental grin, evaluates facial and voluntary movements.
Assesses hearing, vision, smell, reflexes, speech. To diagnose memory disorders, tests are used that show the ability to remember and reproduce new information. To detect cognitive impairment, the doctor prescribes a general and biochemical blood test, a study of cerebrospinal fluid, EEG, MRI and CT of the brain. Based on the results of the diagnosis, treatment methods and drugs are selected.
Based on the results of the diagnosis, treatment methods and drugs are selected.
Prevention
Memory needs to be trained daily. Exercises according to the method of Lawrence Katz will help improve brain function.
How to avoid memory problems:
- Perform habitual activities with your eyes closed, walk in the dark.
- Combing, brushing teeth with non-dominant hand. Right-handed left, left-handed right.
- Learn poems, foreign languages, solve crossword puzzles and logic problems, play chess.
- Limit the time of watching TV, working at the computer.
- Increase stress resistance - yoga, meditation, regular physical activity have a positive effect on the psycho-emotional state.
- Eat right, refuse fatty and salty foods, sweets.
- Timely vaccinate, treat viral and bacterial diseases, strengthen the immune system.
- Observe the drinking regimen. The brain is 70-80% water, so it reacts sharply to the slightest dehydration.
 The optimal volume in the absence of contraindications is 1.5-2 liters of pure water per day.
The optimal volume in the absence of contraindications is 1.5-2 liters of pure water per day.
Memory problems do not always indicate serious illnesses at a young age. Try to have a good rest, sleep, not be nervous, get rid of bad habits. Include foods high in vitamin B in your diet, and remember to drink plenty of water. If no improvement is observed, consult a specialist, do not select drugs for treatment on your own.
SIGNS OF MENTAL DISORDERS (WHEN TO SEE A DOCTOR)
Signs of mental disorders, and also the frequency of their occurrence is a common question, exciting people in recent years. This is especially true in connection with the fact that the pace of life is steadily growing, and the resources of human nervous system remain unchanged. Very often mental violations develop gradually, stepwise, introducing features into the psyche a person who was previously not peculiar to him, respectively, there are good chances to notice them in time and provide proper medical care.
According to the latest data, mental disorders are detected in 25-30% of the population, that is, one in four in the world. However, it is noteworthy that while 75-80% are sick non-psychotic, mild mental disorders. serious mental illnesses such as schizophrenia occur in 6-17% cases. Alcoholism - in 60%.
It must be remembered that mental disorder is not a sentence, because with sufficient and timely treatment by a specialist, as well as a responsible attitude and attention to their condition, the symptoms of mental disorders can be stopped, (and often the disorder itself can be completely cured), which will help to maintain the former social, professional status and quality of life.
SIGNS
Asthenic syndrome.
This condition may accompany any mental disorders and many of the somatic diseases. Asthenia expressed in weakness, low performance, mood swings, increased sensitivity. A person starts crying easily, instantly gets irritated and loses his temper. Often asthenia is accompanied sleep disturbances, feeling of weakness, increased fatigue, inability to cope with the usual workload, study.
Often asthenia is accompanied sleep disturbances, feeling of weakness, increased fatigue, inability to cope with the usual workload, study.
Obsessive states.
A wide range of obsessions includes many manifestations: from constant doubts, unpleasant thoughts, "stuck, spinning in the head", fears with which a person does not able to cope, to an irresistible desire for purity or performing certain unusual actions. Under the control of the obsessive state, a person can return home several times in order to check whether he turned off the iron, gas, water, whether he closed the door with a key. An obsessive fear of an accident can force the patient to perform some rituals that, according to the sufferer, can avert trouble. If you notice that your friend or relative washes his hands for hours, became overly squeamish and is always afraid of getting infected with something - this also obsession. The desire not to step on cracks in the asphalt, joints tiles, avoidance of certain modes of transport or people in clothing a certain color or type is also an obsessive state.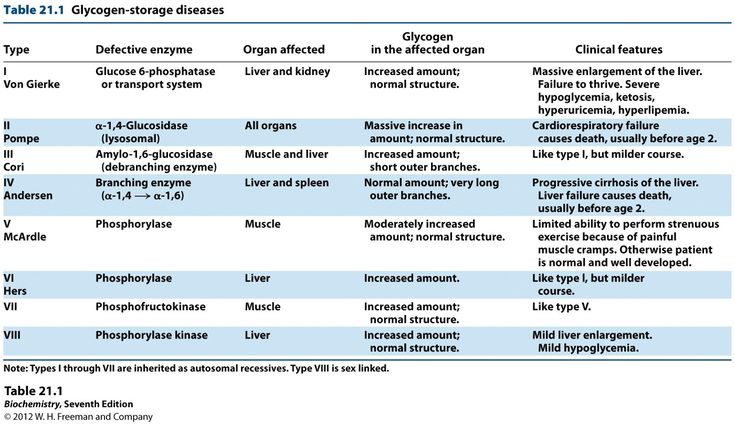
Mood changes.
It is especially important to pay attention not to how much for short-term changes under the influence of momentary factors, how much for mood changes that were not previously characteristic a person, long-term, from 2 weeks or more.
- Longing, depression, longing for self-accusations, talk about their own worthlessness, sinfulness, about death, lack of future, hope for the best, etc.
- Unnatural frivolity, carelessness.
- Foolishness, not characteristic of age and character.
- Euphoric state, optimism without any basis.
- Apathy, painful feeling of lack of emotions.
- Fussiness, talkativeness, inability to concentrate, confused thinking.
- Irritability, anger, aggressiveness
- Inability to restrain emotions, tearfulness, slight breakdowns in conversation
- Strengthening of sexuality, extinction natural bashfulness, inability to restrain sexual desires or vice versa, the disappearance of libido, the absence of a morning erection in men
Unusual body sensations.
Stinging, burning in the skin, sensations burning, “twisting” pressure in the body, stirring “something inside”, "rustling in the head", the presence of foreign objects in the body - can signal disturbances in the nervous system.
Hypochondria.
Expressed in an obsessive, obsessive search for themselves of serious illnesses and disorders, painful "listening" to the slightest change in the state of your body. At the same time, the patient often does not trust doctors, requires repeated and deeper research, completely focused on finding difficult diseases, requires to be treated as a patient.
Appetite disorders.
It is important to note how sudden increased appetite - "wolfish appetite", and its sharp decrease and perversion of taste preferences. The reason may be as in the disease gastrointestinal tract, and in the general depression of the state, or painful conviction of excessive fullness in its absence. Also it is important if previously tasty food has lost its taste, has become bland, tasteless, "like cardboard."
Also it is important if previously tasty food has lost its taste, has become bland, tasteless, "like cardboard."
Illusions
Do not confuse illusions with hallucinations. Illusions force a person to perceive real objects and phenomena in distorted form, while in hallucinations a person feels something that in reality does not exist.
Examples of illusions:
- the pattern on the wallpaper seems to be an interweaving of snakes or worms;
- sizes of objects are perceived in a distorted form;
- the sound of raindrops on the windowsill seems to be the cautious steps of someone terrible;
- the shadows of the trees turn into terrible creatures crawling up with frightening intentions, etc.
Hallucinations not guess, then susceptibility to hallucinations can manifest itself more noticeable. Hallucinations can affect all the senses, that is be visual and auditory, tactile and gustatory, olfactory and common, as well as combined in any combination. To the sick all he is sees, hears and feels, seems completely real. He may not believe that all this is not felt, not heard, not seen by others. Them he can perceive bewilderment as a conspiracy, deceit, mockery, get irritated at not being understood.
To the sick all he is sees, hears and feels, seems completely real. He may not believe that all this is not felt, not heard, not seen by others. Them he can perceive bewilderment as a conspiracy, deceit, mockery, get irritated at not being understood.
- For auditory hallucinations a person hears various kinds of noise, fragments of words or coherent phrases. Voices can give commands or comment on every action of the patient, laugh at him or discuss his thoughts.
- Taste and olfactory hallucinations often cause a sensation of an unpleasant quality: a disgusting taste or smell.
- For tactile hallucinations, the patient it seems that someone is biting him, touching him, strangling him, that they are crawling on him insects that some creatures are introduced into his body and there move or eat the body from the inside.
- Outwardly susceptibility to hallucinations expressed in conversations with an invisible interlocutor, sudden laughter or constant intense listening to something.
 The patient can always to shake off something, to cry out, to examine oneself with preoccupied look or ask others if they see something on his body or in the surrounding space.
The patient can always to shake off something, to cry out, to examine oneself with preoccupied look or ask others if they see something on his body or in the surrounding space.
Changes in thinking
Previously uncharacteristic overestimation own abilities or abilities, confidence in one's own exclusivity, passion for esotericism, magic, suddenly appeared belief in the supernatural. The rate at which thoughts flow in the head can also change, or become uncomfortably slow, or so fast that sometimes it is very difficult to concentrate on one thought.
Delusional thoughts.
Delusional states often accompany psychoses. Delusion is based on erroneous judgments, and the patient stubbornly maintains its false belief, even if there are obvious contradictions with reality. Crazy ideas acquire significance that determines everything behavior. Delusional disorders can be expressed in an erotic form, or in the conviction of one's great mission, in descent from a noble kind or aliens. It may seem to the patient that someone is trying to kill or poison, rob or kidnap. Sometimes the development of delusional state is preceded by a feeling of unreality of the surrounding world or own personality.
It may seem to the patient that someone is trying to kill or poison, rob or kidnap. Sometimes the development of delusional state is preceded by a feeling of unreality of the surrounding world or own personality.
Desocialization.
There are people who are unsociable and unsociable in strength of his character. This is normal and should not arouse suspicion. mental disorders. But if a born merry fellow, the soul company, a family man and a good friend suddenly begins to destroy social connections, becomes unsociable, shows coldness towards those who have recently was dear to him - this is a reason to worry about his mental health. A person becomes sloppy, stops taking care of himself, maybe quit your job for no good reason, abandon your career, former goals and interests, in society can begin to behave shockingly - commit acts that are considered indecent and unacceptable.
Gathering or excessive generosity
Yes, any collector can be suspicion.