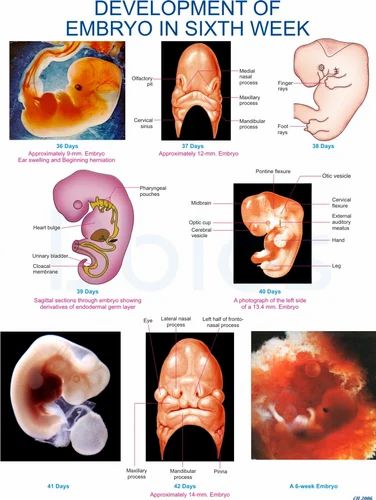
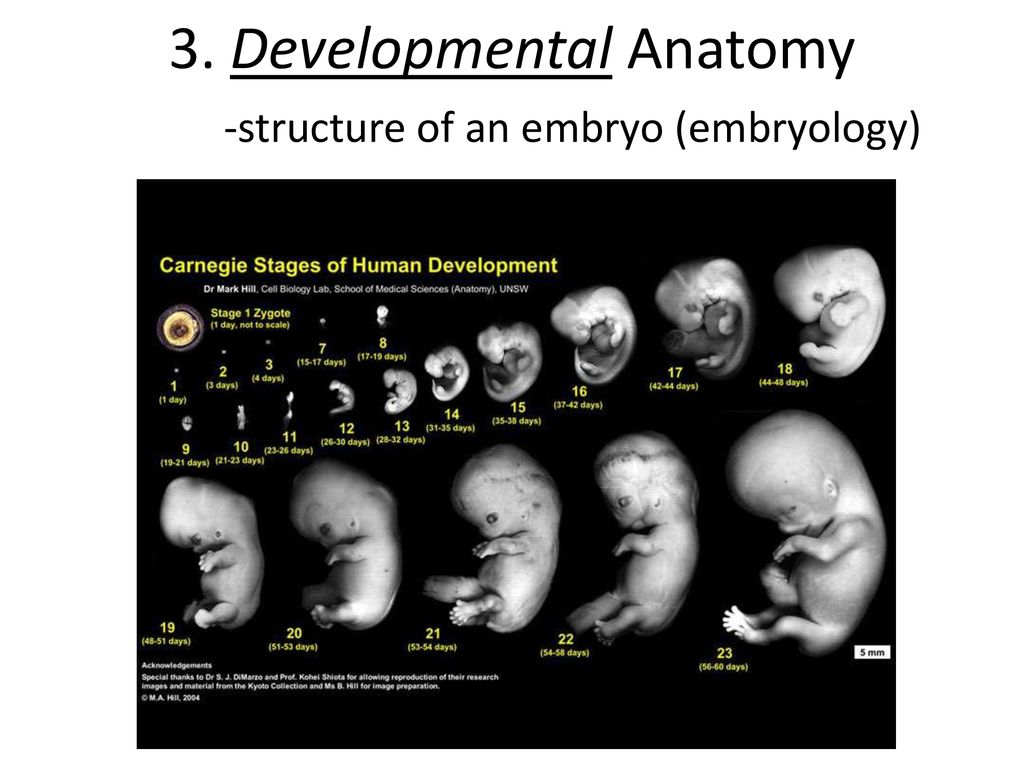
Embryo not growing
Blighted Ovum (Anembryonic Pregnancy): Causes & Symptoms
Overview
A blighted ovum is when the gestational sac containing the embryo is empty.What is a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum (also called an anembryonic pregnancy) is a type of early miscarriage that occurs when a fertilized egg implants into the uterus but does not develop into an embryo. The embryo will stop growing, but the gestational sac (where the embryo would develop) continues to grow. The placenta and empty gestational sac will release pregnancy hormones — even without an embryo present. This causes you to have early symptoms of pregnancy or even have a positive pregnancy test. Sometimes it occurs so early in pregnancy that you don't know you're pregnant.
When does a blighted ovum happen?
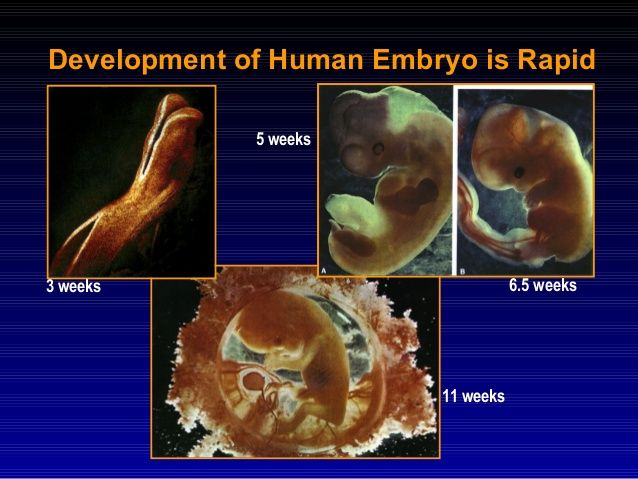
A blighted ovum causes an early miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancy. During fetal development, a fertilized egg turns into a blastocyte. At around four weeks of pregnancy, this blastocyte implants in the wall of the uterus and develops into an embryo. When you have a blighted ovum, the gestational sac that would hold the embryo continues to grow, even without an embryo present. The following can occur:
- A blighted ovum happens so early in pregnancy, that you never realize you are pregnant.
- You have a positive pregnancy test and signs of pregnancy only to discover a blighted ovum at your first ultrasound.
- You have a positive pregnancy test and signs of pregnancy but then experience a miscarriage.
How common is a blighted ovum pregnancy?
A blighted ovum is the number one cause of first trimester miscarriages.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum can occur so early in pregnancy that you never knew you were pregnant. In other cases, you may experience signs of pregnancy such as a missed menstrual period or a positive pregnancy test. You can have symptoms of early pregnancy, such as breast tenderness and morning sickness.
Other times your symptoms will resemble those of a miscarriage:
- Vaginal bleeding: Spotting (light bleeding), bleeding or passing light gray tissue or blood clots.
- Cramping: Mild to moderate cramping in your pelvic and abdominal region.
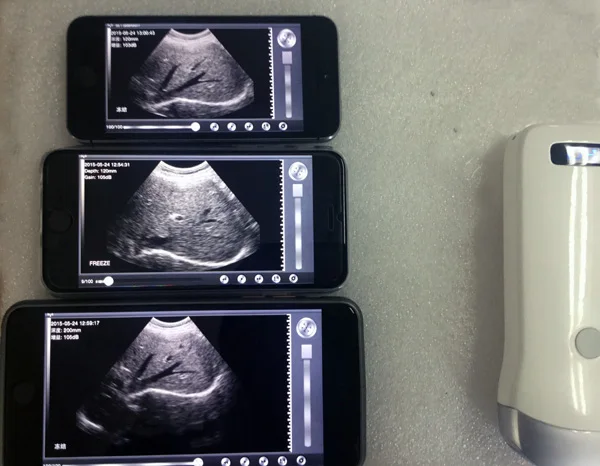
The only way to confirm a blighted ovum is through an ultrasound. It will show a gestational sac that is missing an embryo inside.
What causes a blighted ovum?
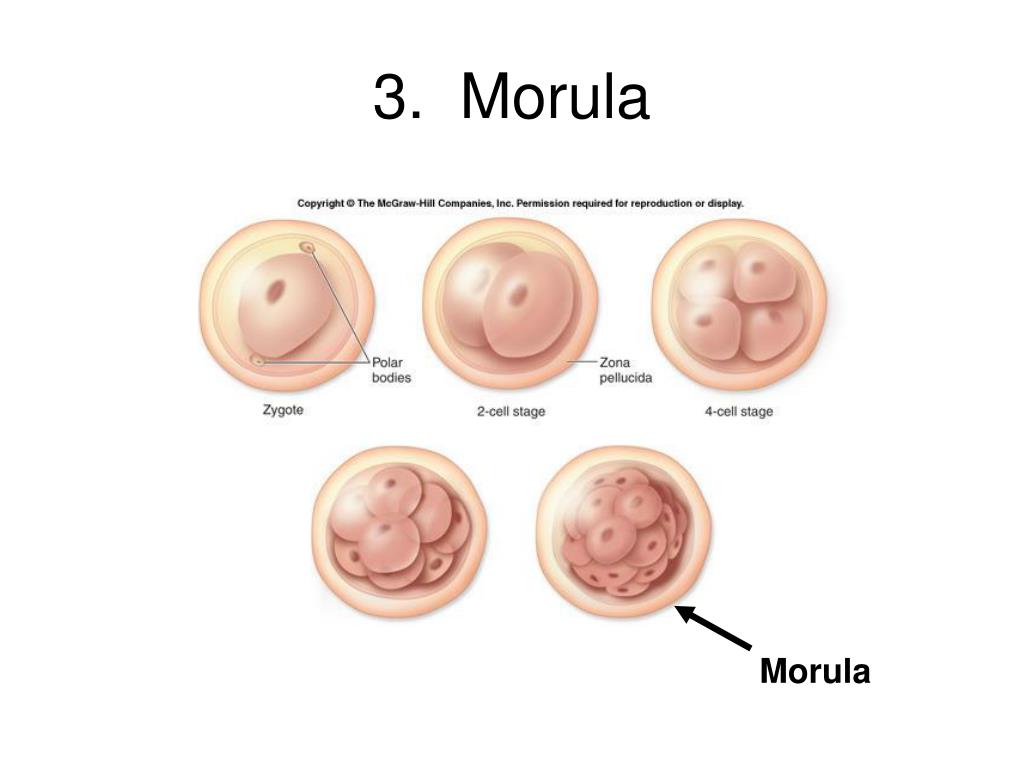
A blighted ovum is usually caused by chromosomal or genetic problems during cell division. During conception, the egg will begin to divide shortly after being fertilized by sperm. Around ten days later, the cells have formed an embryo. With a blighted ovum, the embryo never forms or stops growing after it’s formed.
How does a blighted ovum miscarriage start?
A blighted ovum miscarriage will cause vaginal bleeding and abdominal cramping. A miscarriage usually feels more intense than your regular menstrual period. You can take an over-the-counter medicine like acetaminophen to relieve cramping. Avoid lifting anything heavy or any strenuous exercise as it can increase your bleeding. You may experience spotting for several weeks after a miscarriage.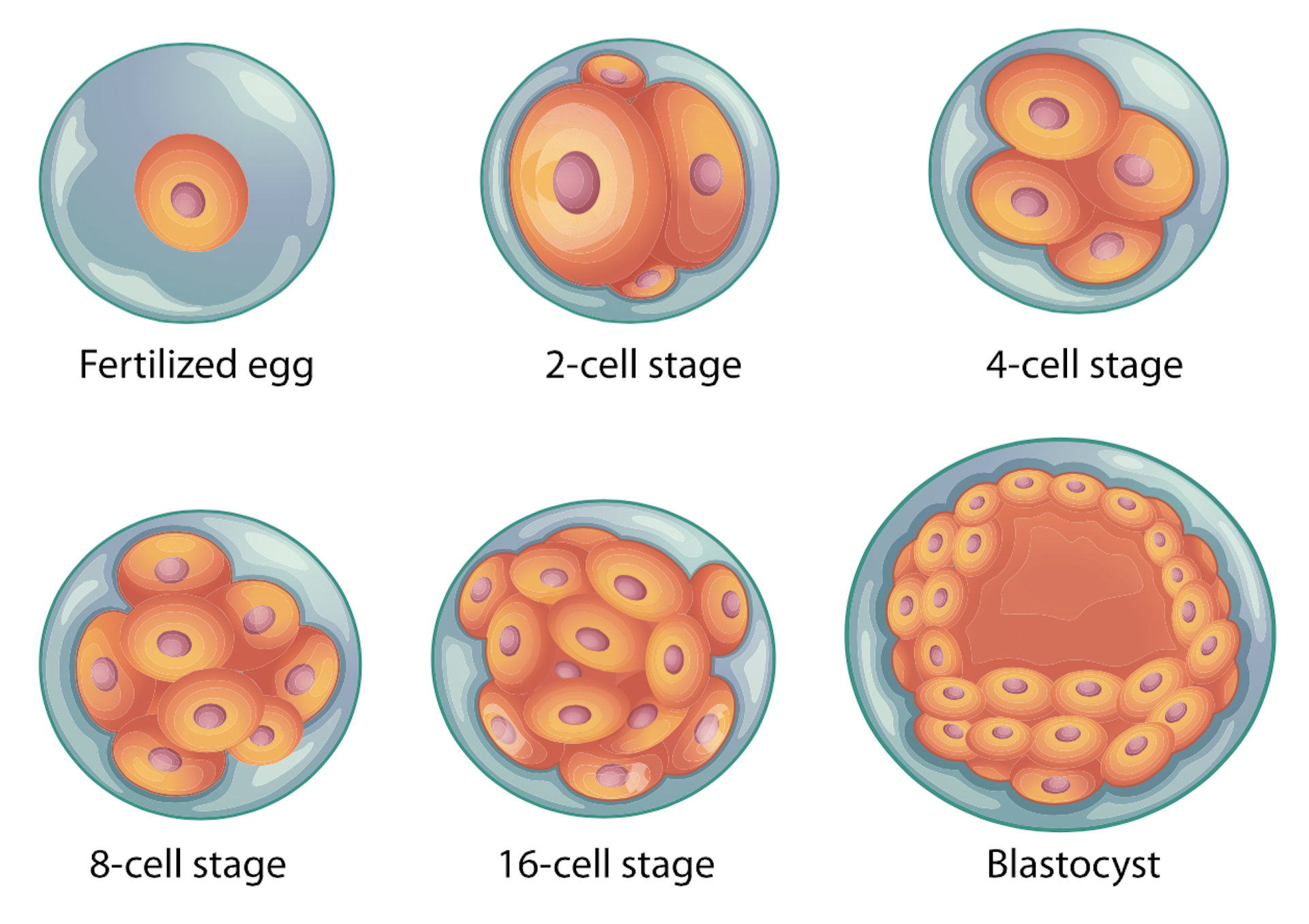
Diagnosis and Tests
How is a blighted ovum diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will diagnose a blighted ovum using transvaginal ultrasound. This happens in the first trimester, usually between seven and nine weeks of pregnancy. An embryo should be visible at this time in pregnancy. With a blighted ovum, the gestational sac will be empty.
- You will lie back on an exam table and place your feet in stirrups like you do for a pelvic exam. Your healthcare provider will put an ultrasound wand into your vagina to see the contents of your uterus.
- A blighted ovum will appear as an empty sac — almost like a bubble.
A blighted ovum is when the gestational sac containing the embryo is empty.
People are often unaware that they have a blighted ovum. This is because your placenta continues to give off hormones, making your body think you are pregnant. This is also why you can still have symptoms of pregnancy, including a positive pregnancy test.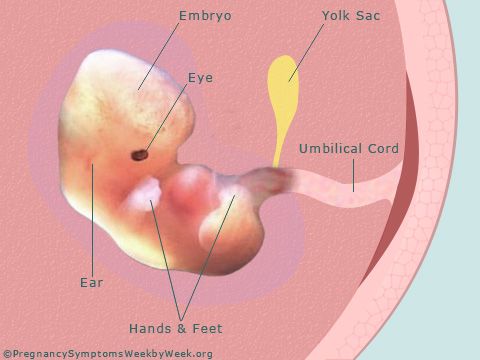
If you’ve already experienced bleeding or signs of a miscarriage, your healthcare provider will use ultrasound to look at the contents of your uterus to diagnose a blighted ovum.
Some healthcare providers will collect a series of blood samples that check the levels of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in your body. HCG is known as the pregnancy hormone because it's only produced if you are pregnant. The level of hCG in your blood increases rapidly in early pregnancy and reaches its peak around weeks eight to ten. If it's not rising quickly, it can indicate a miscarriage or other complication. Your provider may decide to test your hCG levels over the course of several days to evaluate how your hCG levels are rising. This can be an effective tool for diagnosing blighted ovum.
Management and Treatment
How is a blighted ovum treated?
For some people, there may be no treatment needed, because your body passes the embryo through your vagina (a miscarriage).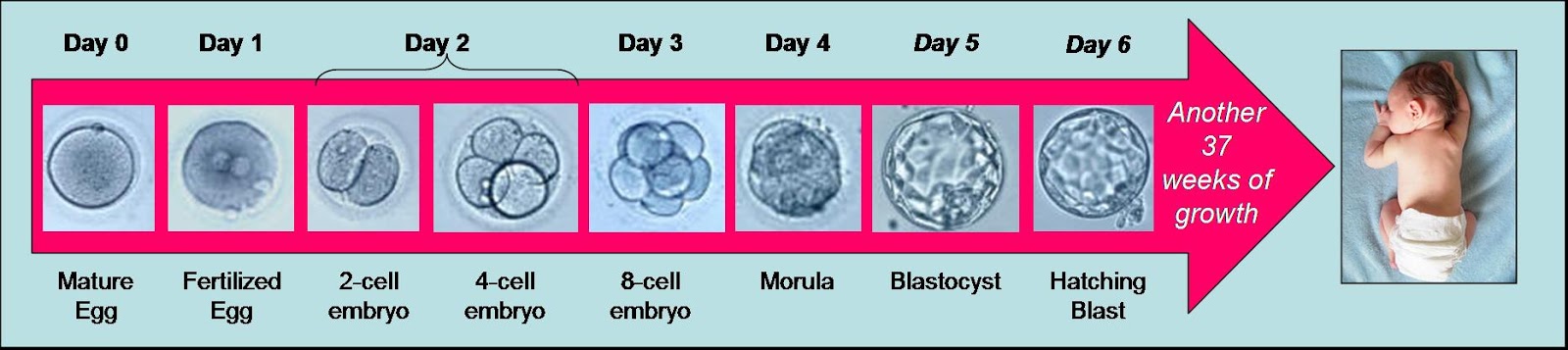 If your body does not miscarry the embryo, there are other options to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will talk you through possible treatments:
If your body does not miscarry the embryo, there are other options to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will talk you through possible treatments:
- Dilation & Curettage (D&C): This is a surgical procedure to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will dilate, or open, the cervix and use medical tools and suction to remove the pregnancy tissues from your uterus. This is done under sedation or general anesthesia.
- Natural miscarriage: If it's safe, you may be able to watch and wait to see if your body eventually releases the pregnancy tissues. It can sometimes take days or weeks for this to start. Your healthcare provider will let you know if this is an option for you. You will experience cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding once the miscarriage begins.
- Medication-induced miscarriage: You may be given a medication called misoprostol to trigger your body to miscarry.
 This moves the process along and eliminates the time waiting for a miscarriage to start on its own. You will have cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding within 30 minutes to ten hours of taking the medication.
This moves the process along and eliminates the time waiting for a miscarriage to start on its own. You will have cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding within 30 minutes to ten hours of taking the medication.
A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled four to six weeks after a miscarriage or D&C. You may be given another ultrasound to confirm the uterus is empty. Your healthcare provider will check for signs of infection and make sure there were no complications.
What are the complications of a blighted ovum?
Complications of a blighted ovum are uncommon, but the possible complications could include:
- Excessive bleeding or hemorrhage.
- Infection.
- Scarring (from the D&C procedure).
- Tears in the uterus (from the D&C procedure).
How long does it take to recover from a blighted ovum?
Recovering from a blighted ovum miscarriage or D&C can last from one or two weeks to a month. Cramping generally lasts up to a week, but bleeding can last several weeks. Your bleeding should get lighter until it stops completely.
Your bleeding should get lighter until it stops completely.
You can resume normal activities when you feel comfortable. Bleeding can increase with strenuous activity or exercise. Hormones may remain in your body and delay your menstrual cycle. Most people will get their period within four to six weeks after a blighted ovum.
It may take longer to recover emotionally from a blighted ovum miscarriage. You may have feelings of sadness, anger or confusion. It’s OK to take time to grieve. Ask your friends and family for support.
Prevention
Can a blighted ovum be prevented?
A blighted ovum can’t be prevented. Some couples may want to do genetic testing on the tissue inside the uterus. This checks for underlying causes of your miscarriage and can be helpful to couples who have experienced multiple pregnancy losses.
Outlook / Prognosis
How soon after a blighted ovum can I get pregnant again?
Most healthcare providers recommend having one or two regular menstrual cycles before trying to conceive again after any type of miscarriage.
What are my chances of having another blighted ovum?
Your chances of having another blighted ovum are low. Most people go on to have healthy, full-term pregnancies. If you experience more than one blighted ovum, your healthcare provider may suggest testing to determine if there is an underlying cause.
Living With
When should I see my healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- Excessive bleeding from your vagina.
- Dizziness or fainting.
- Fever that does not go away.
- Symptoms that get worse over time.
- Severe pain that isn’t helped with pain medicine.
When should I go to the ER?
Go to the nearest ER If you experience heavy vaginal bleeding — more than two pads per hour for two consecutive hours — or have symptoms of anemia like dizziness, palpitations or paleness.
What questions should I ask my doctor?
Losing a pregnancy is upsetting and confusing. Do not be embarrassed to ask any questions you have. It's completely normal to have questions and feel emotional during this time. Some questions you may ask are:
Do not be embarrassed to ask any questions you have. It's completely normal to have questions and feel emotional during this time. Some questions you may ask are:
- Can I let my body miscarry or should I take medication to induce a miscarriage?
- What are the risks of miscarriage?
- Do I have to have a D&C?
- What are the risks of a D&C?
- How long can I expect to bleed or have cramping?
- Is there any indication this will happen again?
- When can I start trying to conceive?
- Do I need to come back for another ultrasound?
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a blighted ovum considered a miscarriage?
Yes, a blighted ovum is a miscarriage. A miscarriage is a loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks. A blighted ovum is considered an early miscarriage because it occurs before 13 weeks of pregnancy.
How long can you carry a blighted ovum?
The amount of time you can carry a blighted ovum varies.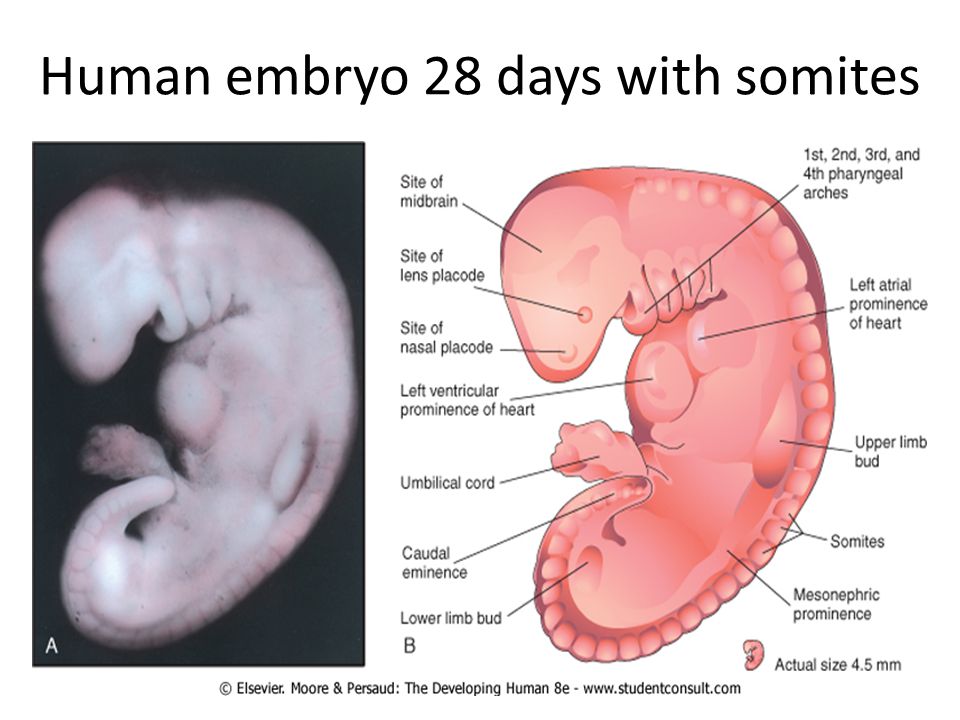 Your placenta will continue to grow and release hormones without an embryo. For some people, a miscarriage can occur within a few days or weeks. Others may still believe they are pregnant only to discover a blighted ovum at their first ultrasound.
Your placenta will continue to grow and release hormones without an embryo. For some people, a miscarriage can occur within a few days or weeks. Others may still believe they are pregnant only to discover a blighted ovum at their first ultrasound.
Can a blighted ovum turn into a baby?
No, an empty gestational sac will not turn into an embryo. The formation of the embryo occurs within two weeks of conception. By the time the gestational sac is formed, the cells should have already formed the embryo. Your healthcare provider will be able to examine your gestational sac to confirm that no embryo has developed.
Do hCG levels rise with blighted ovum?
Yes, most of the time hCG levels will rise, giving you a positive pregnancy test and symptoms of pregnancy. This is because the placenta continues to give off hCG even if an embryo is not present. The hormone hCG is sometimes called the pregnancy hormone because it is only produced if you are pregnant.
Is a blighted ovum more common with IVF?
A blighted ovum is not more common with IVF (In Vitro Fertilization).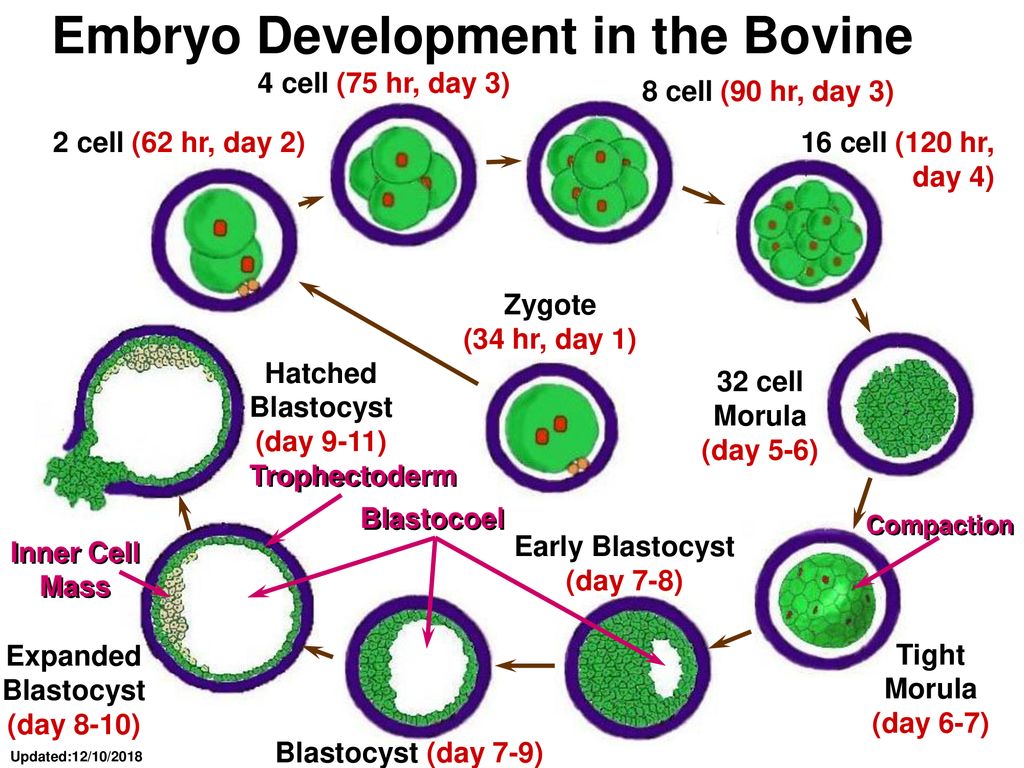 Your chances of having a blighted ovum with IVF treatment are about the same as they would be with a natural conception.
Your chances of having a blighted ovum with IVF treatment are about the same as they would be with a natural conception.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Losing a pregnancy is difficult. If you are struggling after a miscarriage, speak with your healthcare provider so they can recommend support groups or counselors. Finding support may help you get through this hard time. Most people who have had a blighted ovum will go on to have a healthy pregnancy.
Blighted Ovum (Anembryonic Pregnancy): Causes & Symptoms
Overview
A blighted ovum is when the gestational sac containing the embryo is empty.What is a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum (also called an anembryonic pregnancy) is a type of early miscarriage that occurs when a fertilized egg implants into the uterus but does not develop into an embryo. The embryo will stop growing, but the gestational sac (where the embryo would develop) continues to grow. The placenta and empty gestational sac will release pregnancy hormones — even without an embryo present. This causes you to have early symptoms of pregnancy or even have a positive pregnancy test. Sometimes it occurs so early in pregnancy that you don't know you're pregnant.
This causes you to have early symptoms of pregnancy or even have a positive pregnancy test. Sometimes it occurs so early in pregnancy that you don't know you're pregnant.
When does a blighted ovum happen?
A blighted ovum causes an early miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancy. During fetal development, a fertilized egg turns into a blastocyte. At around four weeks of pregnancy, this blastocyte implants in the wall of the uterus and develops into an embryo. When you have a blighted ovum, the gestational sac that would hold the embryo continues to grow, even without an embryo present. The following can occur:
- A blighted ovum happens so early in pregnancy, that you never realize you are pregnant.
- You have a positive pregnancy test and signs of pregnancy only to discover a blighted ovum at your first ultrasound.
- You have a positive pregnancy test and signs of pregnancy but then experience a miscarriage.
How common is a blighted ovum pregnancy?
A blighted ovum is the number one cause of first trimester miscarriages.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum can occur so early in pregnancy that you never knew you were pregnant. In other cases, you may experience signs of pregnancy such as a missed menstrual period or a positive pregnancy test. You can have symptoms of early pregnancy, such as breast tenderness and morning sickness.
Other times your symptoms will resemble those of a miscarriage:
- Vaginal bleeding: Spotting (light bleeding), bleeding or passing light gray tissue or blood clots.
- Cramping: Mild to moderate cramping in your pelvic and abdominal region.
The only way to confirm a blighted ovum is through an ultrasound. It will show a gestational sac that is missing an embryo inside.
What causes a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum is usually caused by chromosomal or genetic problems during cell division. During conception, the egg will begin to divide shortly after being fertilized by sperm.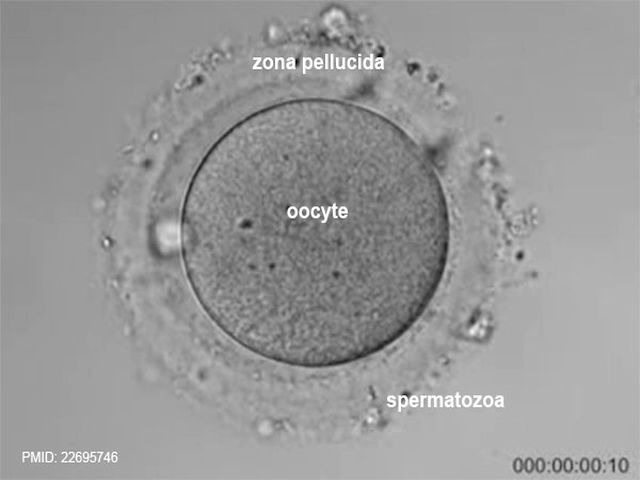 Around ten days later, the cells have formed an embryo. With a blighted ovum, the embryo never forms or stops growing after it’s formed.
Around ten days later, the cells have formed an embryo. With a blighted ovum, the embryo never forms or stops growing after it’s formed.
How does a blighted ovum miscarriage start?
A blighted ovum miscarriage will cause vaginal bleeding and abdominal cramping. A miscarriage usually feels more intense than your regular menstrual period. You can take an over-the-counter medicine like acetaminophen to relieve cramping. Avoid lifting anything heavy or any strenuous exercise as it can increase your bleeding. You may experience spotting for several weeks after a miscarriage.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is a blighted ovum diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will diagnose a blighted ovum using transvaginal ultrasound. This happens in the first trimester, usually between seven and nine weeks of pregnancy. An embryo should be visible at this time in pregnancy. With a blighted ovum, the gestational sac will be empty.
- You will lie back on an exam table and place your feet in stirrups like you do for a pelvic exam.
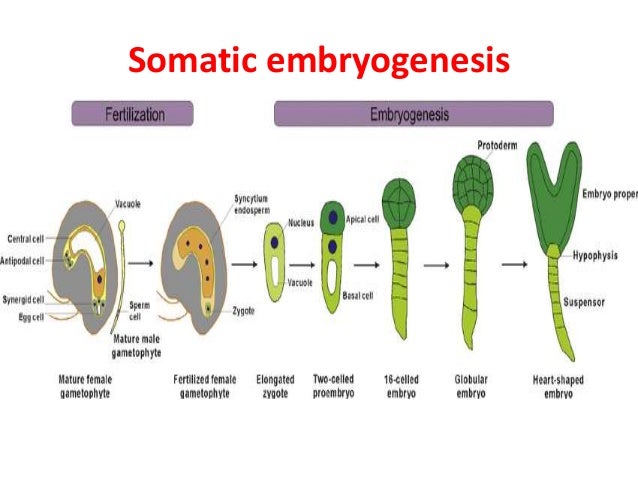 Your healthcare provider will put an ultrasound wand into your vagina to see the contents of your uterus.
Your healthcare provider will put an ultrasound wand into your vagina to see the contents of your uterus. - A blighted ovum will appear as an empty sac — almost like a bubble.
A blighted ovum is when the gestational sac containing the embryo is empty.
People are often unaware that they have a blighted ovum. This is because your placenta continues to give off hormones, making your body think you are pregnant. This is also why you can still have symptoms of pregnancy, including a positive pregnancy test.
If you’ve already experienced bleeding or signs of a miscarriage, your healthcare provider will use ultrasound to look at the contents of your uterus to diagnose a blighted ovum.
Some healthcare providers will collect a series of blood samples that check the levels of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in your body. HCG is known as the pregnancy hormone because it's only produced if you are pregnant. The level of hCG in your blood increases rapidly in early pregnancy and reaches its peak around weeks eight to ten. If it's not rising quickly, it can indicate a miscarriage or other complication. Your provider may decide to test your hCG levels over the course of several days to evaluate how your hCG levels are rising. This can be an effective tool for diagnosing blighted ovum.
If it's not rising quickly, it can indicate a miscarriage or other complication. Your provider may decide to test your hCG levels over the course of several days to evaluate how your hCG levels are rising. This can be an effective tool for diagnosing blighted ovum.
Management and Treatment
How is a blighted ovum treated?
For some people, there may be no treatment needed, because your body passes the embryo through your vagina (a miscarriage). If your body does not miscarry the embryo, there are other options to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will talk you through possible treatments:
- Dilation & Curettage (D&C): This is a surgical procedure to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will dilate, or open, the cervix and use medical tools and suction to remove the pregnancy tissues from your uterus. This is done under sedation or general anesthesia.
- Natural miscarriage: If it's safe, you may be able to watch and wait to see if your body eventually releases the pregnancy tissues.
 It can sometimes take days or weeks for this to start. Your healthcare provider will let you know if this is an option for you. You will experience cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding once the miscarriage begins.
It can sometimes take days or weeks for this to start. Your healthcare provider will let you know if this is an option for you. You will experience cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding once the miscarriage begins. - Medication-induced miscarriage: You may be given a medication called misoprostol to trigger your body to miscarry. This moves the process along and eliminates the time waiting for a miscarriage to start on its own. You will have cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding within 30 minutes to ten hours of taking the medication.
A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled four to six weeks after a miscarriage or D&C. You may be given another ultrasound to confirm the uterus is empty. Your healthcare provider will check for signs of infection and make sure there were no complications.
What are the complications of a blighted ovum?
Complications of a blighted ovum are uncommon, but the possible complications could include:
- Excessive bleeding or hemorrhage.
- Infection.
- Scarring (from the D&C procedure).
- Tears in the uterus (from the D&C procedure).
How long does it take to recover from a blighted ovum?
Recovering from a blighted ovum miscarriage or D&C can last from one or two weeks to a month. Cramping generally lasts up to a week, but bleeding can last several weeks. Your bleeding should get lighter until it stops completely.
You can resume normal activities when you feel comfortable. Bleeding can increase with strenuous activity or exercise. Hormones may remain in your body and delay your menstrual cycle. Most people will get their period within four to six weeks after a blighted ovum.
It may take longer to recover emotionally from a blighted ovum miscarriage. You may have feelings of sadness, anger or confusion. It’s OK to take time to grieve. Ask your friends and family for support.
Prevention
Can a blighted ovum be prevented?
A blighted ovum can’t be prevented. Some couples may want to do genetic testing on the tissue inside the uterus. This checks for underlying causes of your miscarriage and can be helpful to couples who have experienced multiple pregnancy losses.
Some couples may want to do genetic testing on the tissue inside the uterus. This checks for underlying causes of your miscarriage and can be helpful to couples who have experienced multiple pregnancy losses.
Outlook / Prognosis
How soon after a blighted ovum can I get pregnant again?
Most healthcare providers recommend having one or two regular menstrual cycles before trying to conceive again after any type of miscarriage.
What are my chances of having another blighted ovum?
Your chances of having another blighted ovum are low. Most people go on to have healthy, full-term pregnancies. If you experience more than one blighted ovum, your healthcare provider may suggest testing to determine if there is an underlying cause.
Living With
When should I see my healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- Excessive bleeding from your vagina.
- Dizziness or fainting.
- Fever that does not go away.
- Symptoms that get worse over time.
- Severe pain that isn’t helped with pain medicine.
When should I go to the ER?
Go to the nearest ER If you experience heavy vaginal bleeding — more than two pads per hour for two consecutive hours — or have symptoms of anemia like dizziness, palpitations or paleness.
What questions should I ask my doctor?
Losing a pregnancy is upsetting and confusing. Do not be embarrassed to ask any questions you have. It's completely normal to have questions and feel emotional during this time. Some questions you may ask are:
- Can I let my body miscarry or should I take medication to induce a miscarriage?
- What are the risks of miscarriage?
- Do I have to have a D&C?
- What are the risks of a D&C?
- How long can I expect to bleed or have cramping?
- Is there any indication this will happen again?
- When can I start trying to conceive?
- Do I need to come back for another ultrasound?
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a blighted ovum considered a miscarriage?
Yes, a blighted ovum is a miscarriage.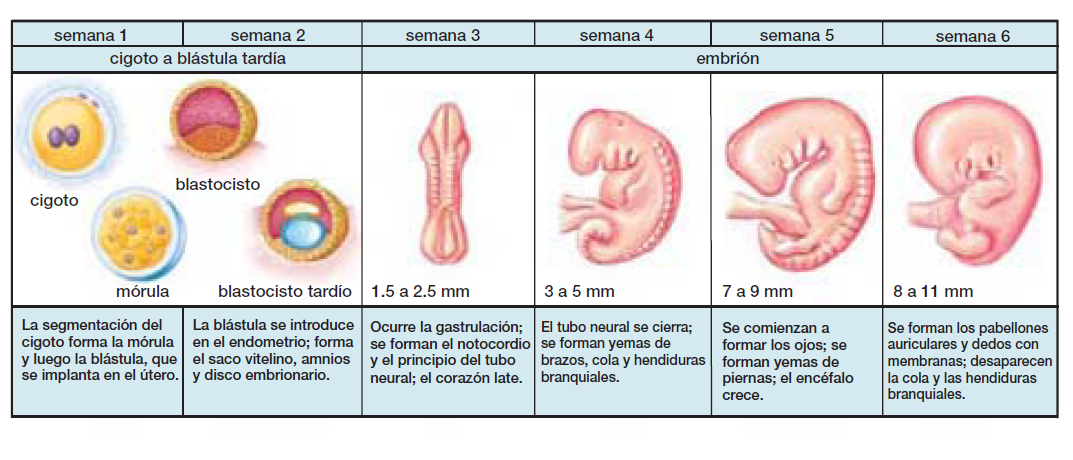 A miscarriage is a loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks. A blighted ovum is considered an early miscarriage because it occurs before 13 weeks of pregnancy.
A miscarriage is a loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks. A blighted ovum is considered an early miscarriage because it occurs before 13 weeks of pregnancy.
How long can you carry a blighted ovum?
The amount of time you can carry a blighted ovum varies. Your placenta will continue to grow and release hormones without an embryo. For some people, a miscarriage can occur within a few days or weeks. Others may still believe they are pregnant only to discover a blighted ovum at their first ultrasound.
Can a blighted ovum turn into a baby?
No, an empty gestational sac will not turn into an embryo. The formation of the embryo occurs within two weeks of conception. By the time the gestational sac is formed, the cells should have already formed the embryo. Your healthcare provider will be able to examine your gestational sac to confirm that no embryo has developed.
Do hCG levels rise with blighted ovum?
Yes, most of the time hCG levels will rise, giving you a positive pregnancy test and symptoms of pregnancy. This is because the placenta continues to give off hCG even if an embryo is not present. The hormone hCG is sometimes called the pregnancy hormone because it is only produced if you are pregnant.
This is because the placenta continues to give off hCG even if an embryo is not present. The hormone hCG is sometimes called the pregnancy hormone because it is only produced if you are pregnant.
Is a blighted ovum more common with IVF?
A blighted ovum is not more common with IVF (In Vitro Fertilization). Your chances of having a blighted ovum with IVF treatment are about the same as they would be with a natural conception.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Losing a pregnancy is difficult. If you are struggling after a miscarriage, speak with your healthcare provider so they can recommend support groups or counselors. Finding support may help you get through this hard time. Most people who have had a blighted ovum will go on to have a healthy pregnancy.
Non-developing pregnancy - Official website of the FGBUZ KB No. 85 FMBA of Russia
General brief information
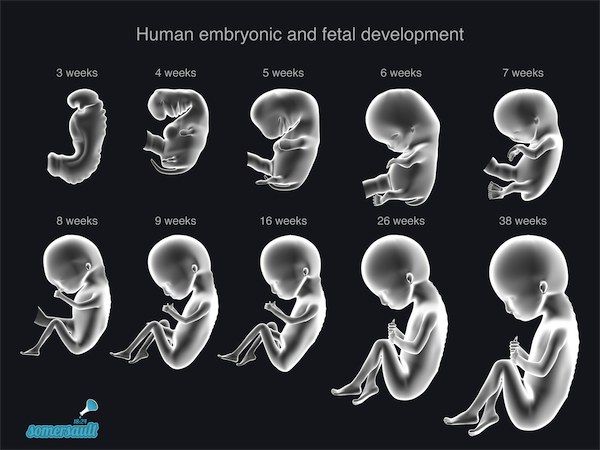
Non-developing or missed pregnancy is a cessation of fetal development due to its death, in which there are no signs of miscarriage. Most often, this pathology occurs in the early stages - in the 1st trimester. Another variety of it is a non-developing pregnancy of the type of anembryony. This is a situation in which fertilization has occurred and the fetal membranes have begun to form, but there is no embryo in the fetal egg. nine0005
Most often, this pathology occurs in the early stages - in the 1st trimester. Another variety of it is a non-developing pregnancy of the type of anembryony. This is a situation in which fertilization has occurred and the fetal membranes have begun to form, but there is no embryo in the fetal egg. nine0005
Symptoms
Unfortunately, in most cases, a woman does not know that her child has already died, since an early pregnancy that does not develop does not have the bright symptoms that are characteristic of a miscarriage. With this pathology, the placenta does not stop producing hormones, which is why the woman continues to feel pregnant. However, in some cases, a woman may notice that her symptoms such as breast tenderness, nausea, and fatigue have disappeared. At later stages, the fading of pregnancy is characterized by the absence of fetal movements in the uterus. nine0005
Causes
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to determine why a woman has an undeveloped pregnancy. If embryonic death occurs during the 1st trimester, it is usually caused by problems in the unborn child. Approximately 3/4 of miscarriages occur during this period. If the fetus dies during the 2nd or 3rd trimester, this may be due to the presence of diseases in the mother.
If embryonic death occurs during the 1st trimester, it is usually caused by problems in the unborn child. Approximately 3/4 of miscarriages occur during this period. If the fetus dies during the 2nd or 3rd trimester, this may be due to the presence of diseases in the mother.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of non-progressing pregnancy is most often established after an ultrasound examination, which detects the absence of a heartbeat in the fetus. Ultrasound is performed through the anterior abdominal wall or transvaginally. The latter technique is more accurate, but its implementation is accompanied by some discomfort. To exclude errors with a diagnosis, at least two examination procedures are performed. The doctor can detect the absence of a heartbeat in the fetus later in pregnancy with the help of auscultation with an obstetric stethoscope. Cardiotocography, a technique for recording the fetal heartbeat and uterine tone, will help confirm the fears. Also, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin and progesterone, hormones associated with pregnancy, can be determined. In some cases, the diagnosis is not immediately possible. For example, a non-developing pregnancy before a gestational age of 6-7 weeks is difficult to confirm, since only at this time does the fetus develop a heartbeat. In this case, doctors usually recommend a re-examination in 1-2 weeks. Sometimes fetal death is discovered by chance during a screening ultrasound examination. After a case of pregnancy fading, a man and a woman need to undergo a complete examination, with the help of which specialists will try to identify possible causes of fetal death. Unfortunately, in half of the cases, the etiology of a non-developing pregnancy cannot be detected. nine0005
In some cases, the diagnosis is not immediately possible. For example, a non-developing pregnancy before a gestational age of 6-7 weeks is difficult to confirm, since only at this time does the fetus develop a heartbeat. In this case, doctors usually recommend a re-examination in 1-2 weeks. Sometimes fetal death is discovered by chance during a screening ultrasound examination. After a case of pregnancy fading, a man and a woman need to undergo a complete examination, with the help of which specialists will try to identify possible causes of fetal death. Unfortunately, in half of the cases, the etiology of a non-developing pregnancy cannot be detected. nine0005
Methods of treatment
As a rule, a woman is offered one of the following options: Expectant management. In the early stages of pregnancy, with intrauterine death of the embryo, it is possible to expect a natural rejection of its tissues by the woman's body. At this time, careful monitoring and observation is carried out. However, you can't wait too long - it's dangerous. As a rule, active treatment can be delayed only up to 2 weeks from the diagnosis. Doctors are not too fond of expectant management during a missed pregnancy. Surgical tactics. After establishing and clarifying the diagnosis, a small obstetric operation is performed - dilation of the cervix and curettage (curettage of the uterine cavity). During this surgical intervention, the tissues of the fetus, its membranes and the placenta are removed from the uterine cavity. The operation is usually performed under general anesthesia. medical tactics. Termination of an undeveloped pregnancy in the early stages (up to 8 weeks of gestation) can also be carried out by a conservative method. For this purpose, drugs are used that cause the uterus to contract and push the fetal tissues and placenta out of its cavity. With intrauterine death of the fetus in the 3rd trimester, delivery is necessary. To this end, doctors either induce labor through the birth canal or perform a caesarean section.
However, you can't wait too long - it's dangerous. As a rule, active treatment can be delayed only up to 2 weeks from the diagnosis. Doctors are not too fond of expectant management during a missed pregnancy. Surgical tactics. After establishing and clarifying the diagnosis, a small obstetric operation is performed - dilation of the cervix and curettage (curettage of the uterine cavity). During this surgical intervention, the tissues of the fetus, its membranes and the placenta are removed from the uterine cavity. The operation is usually performed under general anesthesia. medical tactics. Termination of an undeveloped pregnancy in the early stages (up to 8 weeks of gestation) can also be carried out by a conservative method. For this purpose, drugs are used that cause the uterus to contract and push the fetal tissues and placenta out of its cavity. With intrauterine death of the fetus in the 3rd trimester, delivery is necessary. To this end, doctors either induce labor through the birth canal or perform a caesarean section.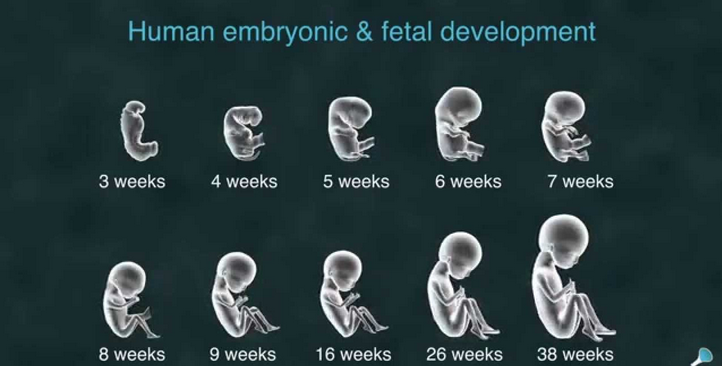 nine0005
nine0005
Anembryonic - pregnancy or not?
Unfortunately, not all pregnancies end in childbearing. Reproductive losses in this case can be due to various reasons. And one of them is a non-developing or missed pregnancy. The proportion of this pathology accounts for up to 15-20% of reproductive losses. Currently, there are 2 variants of missed pregnancy: death of the embryo and anembryony. It is important to understand that the differential diagnosis between them does not affect the subsequent treatment tactics, but is taken into account when assessing the prognosis. Anembryony is more often determined, and this condition in many cases is not accompanied by spontaneous abortion and therefore requires artificial termination of a missed pregnancy. nine0005
Anembryony – what is it?
Anembryony - is the absence of an embryo in a developing fetal egg. This condition is also called the empty gestational sac syndrome.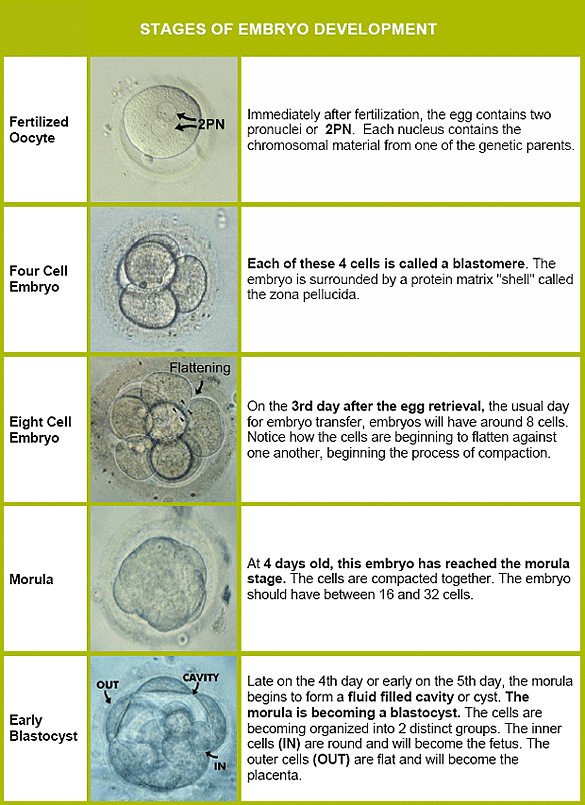 This is by no means a rare pathology that can be diagnosed in primigravida and in women who already have healthy children.
This is by no means a rare pathology that can be diagnosed in primigravida and in women who already have healthy children.
Many possible causes of anembryony have now been identified. These include:
- Genetic anomalies , which are observed in almost 80% of the pathological condition. They are usually associated with gross and/or multiple chromosomal abnormalities. Moreover, with anembryony, such anomalies are of a qualitative nature, and with the death of the embryo and its abortion, they are predominantly quantitative. Unviable combinations of parental genes or mutations in key areas responsible for the early stages of embryogenesis and the synthesis of the main structural proteins of cell membranes are also possible. nine0052
- Some acute viral and bacterial diseases occurring in early pregnancy and leading to damage to embryonic tissues or trophoblast. The most dangerous in this regard are TORCH infections, although other pathogens can also be embryotropic.

- Persistent viral and bacterial infections of the reproductive system, leading to the development of chronic endometritis . And in most cases, such a pathology occurs without obvious clinical symptoms and is detected after a frozen pregnancy. nine0052
- Radiation exposure of to a developing embryo.
- Exogenous intoxications : taking drugs with embryotoxic action, drug addiction, exposure to certain industrial and agricultural poisons (toxins).
- Endocrine disorders in a pregnant woman. And the most critical is the deficiency of progesterone and disorders of its metabolism, which is the main cause of the pathology of endometrial decidualization and abnormal implantation of the fetal egg. nine0052
In general, the causes of pathology in most cases remain undiagnosed. Usually it is possible to determine only a presumptive etiology.
Genetic diagnosis of aborted tissues can reveal obvious anomalies of hereditary material.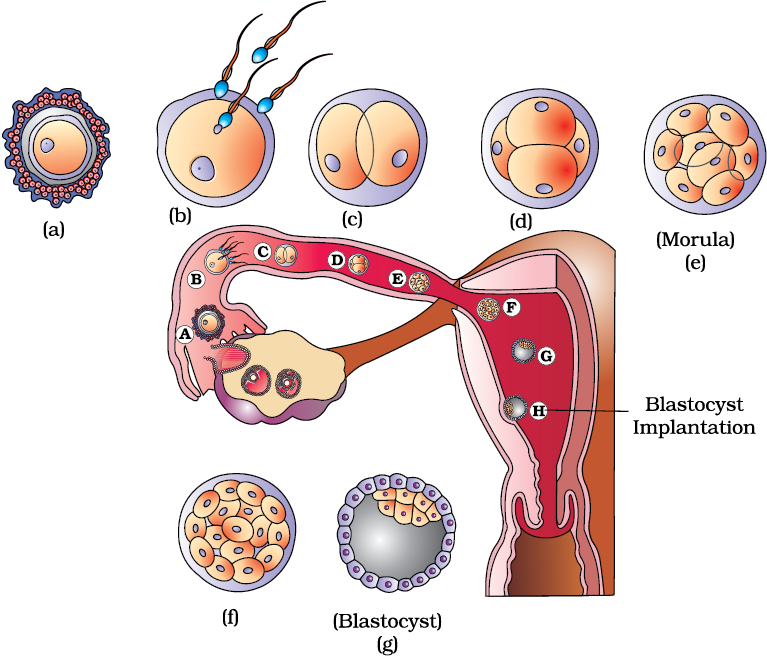 But such a study, unfortunately, is carried out in a very small percentage of cases. Basically, it is indicated with a burdened obstetric history in a woman, when she already had frozen or spontaneously interrupted in the early stages of gestation in the past. But even such a diagnosis is not always informative enough, which is associated with the limited possibilities of modern genetics and the high probability of the impact of other etiological factors. nine0005
But such a study, unfortunately, is carried out in a very small percentage of cases. Basically, it is indicated with a burdened obstetric history in a woman, when she already had frozen or spontaneously interrupted in the early stages of gestation in the past. But even such a diagnosis is not always informative enough, which is associated with the limited possibilities of modern genetics and the high probability of the impact of other etiological factors. nine0005
Pathogenesis
Anembryony is a consequence of the cessation of reproduction and differentiation of the embryoblast or inner cell mass - a group of cells that normally give rise to fetal tissues. And this happens at the earliest stages of pregnancy (usually at 2-4 weeks of gestation), and without disturbing the development of the fetal membranes from the trophoblast. As a result, a so-called empty fetal egg is formed, which continues to grow even in the absence of an embryo in it.
Pathogenetically important factors in the development of the disease include:
- Inherited or acquired chromosome aberrations and other genetic abnormalities.
 They can lead to a gross desynchronization of the development of embryonic tissues, critical changes in the structure of collagen and other proteins, disruption of the induction of differentiation and migration of dividing cells. The most common autosomal trisomy, monosomy, triploidy, tetraploidy.
They can lead to a gross desynchronization of the development of embryonic tissues, critical changes in the structure of collagen and other proteins, disruption of the induction of differentiation and migration of dividing cells. The most common autosomal trisomy, monosomy, triploidy, tetraploidy. - Excessive formation of circulating immune complexes in a woman's body . Their deposition in the walls of small vessels leads to thromboembolism and other critical microcirculation disorders in the area of the implanting egg. Antiphospholipid antibodies are of the greatest clinical importance.
- Excessive activation of T-helpers with an increase in the concentration and aggression of the cytokines secreted by them. These substances are able to have a direct and indirect damaging effect on embryonic tissues with a violation of their proliferation and differentiation. In fact, the fetal egg in this case acts as a target for the cellular link of immunity.
 The reason for such an abnormal immune response of a woman's body may be a chronic infection of the endometrium, hormonal abnormalities, and some other endogenous factors. nine0052
The reason for such an abnormal immune response of a woman's body may be a chronic infection of the endometrium, hormonal abnormalities, and some other endogenous factors. nine0052
It is important to understand that with anembryony, the woman's body produces substances that help prolong pregnancy. Therefore, in a significant proportion of cases, spontaneous abortion does not occur. The patient develops and maintains signs of pregnancy, there is an increase in hCG in the blood serum. Therefore, the basal temperature during anembryony usually does not have characteristic features. And on the first early ultrasound, the fact of successful implantation of the fetal egg in the uterine cavity is confirmed. After all, pregnancy does occur, but it develops without a key component - the embryo. nine0005
In the future, rejection of the abnormal fetal egg is possible. In this case, the threat of termination of pregnancy (including with the formation of exfoliating retrochorial hematomas) or spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) can be diagnosed. But often anembryony is diagnosed only during a routine examination, in which case the diagnosis is absolutely unexpected and shocking news. Such a pregnancy requires an artificial interruption.
But often anembryony is diagnosed only during a routine examination, in which case the diagnosis is absolutely unexpected and shocking news. Such a pregnancy requires an artificial interruption.
How does this manifest itself?
Anembryony does not have its own clinical symptoms , all emerging disorders are usually associated with the threat of termination of such a pathological pregnancy. And the warning signs include the presence of clinical manifestations of relative progesterone deficiency, which creates the prerequisites for spontaneous abortion. Therefore, pain in the lower abdomen and bloody discharge can become a reason for contacting a doctor; with anembryony, they can appear at almost any time during the 1st trimester. But often a woman learns about the existing pathology only when conducting a screening ultrasound for a period of 10-14 weeks. nine0005
Diagnosis
Like other forms of miscarriage, anembryony is detected in the first trimester of gestation. And the main diagnostic tool in this case is ultrasound , because it is this study that allows you to visualize the existing deviations.
And the main diagnostic tool in this case is ultrasound , because it is this study that allows you to visualize the existing deviations.
At the same time, symptoms can be reliably detected only after the 8th week of gestation. At earlier dates, visualization is often insufficient due to the too small size of the ovum, so an erroneous diagnosis is not ruled out. Therefore If a missed pregnancy and anembryony are suspected, it is recommended to conduct an examination several times, repeating the procedure on expert-class equipment with an interval of 6-8 days. At the same time, the initial diagnosis of an empty fetal egg can be removed if subsequent ultrasound scans can visualize an embryo with signs of a heartbeat and sufficient developmental dynamics.
The main echographic features:
- absence of the yolk sac when the diameter of the fetal egg is 8-25 mm; nine0052
- the absence of an embryo in a fetal egg with a diameter of more than 25 mm.
Additional signs of a missed pregnancy include an irregular shape of the fetal egg, an insufficient increase in its diameter in dynamics, a weak severity of the decidual reaction, and the absence of a heartbeat at a gestational age of 7 or more weeks. And signs of the threat of its interruption are a change in the tone of the uterus and the appearance of areas of chorion detachment with the appearance of subchorial hematomas.
Anembryony can also be suspected by a dynamic assessment of the level of hCG in the blood. An increase in the level of this hormone along the lower limit of the norm should be the basis for further examination of a woman with an ultrasound scan. It is important to understand that hCG is also produced in the syndrome of an empty ovum. Moreover, its level in this pathology will be almost normal, in contrast to a frozen pregnancy with the death of a normally developing embryo. Therefore, monitoring of indirect signs of pregnancy and the growth of hCG during anembryony cannot be attributed to reliable diagnostic methods.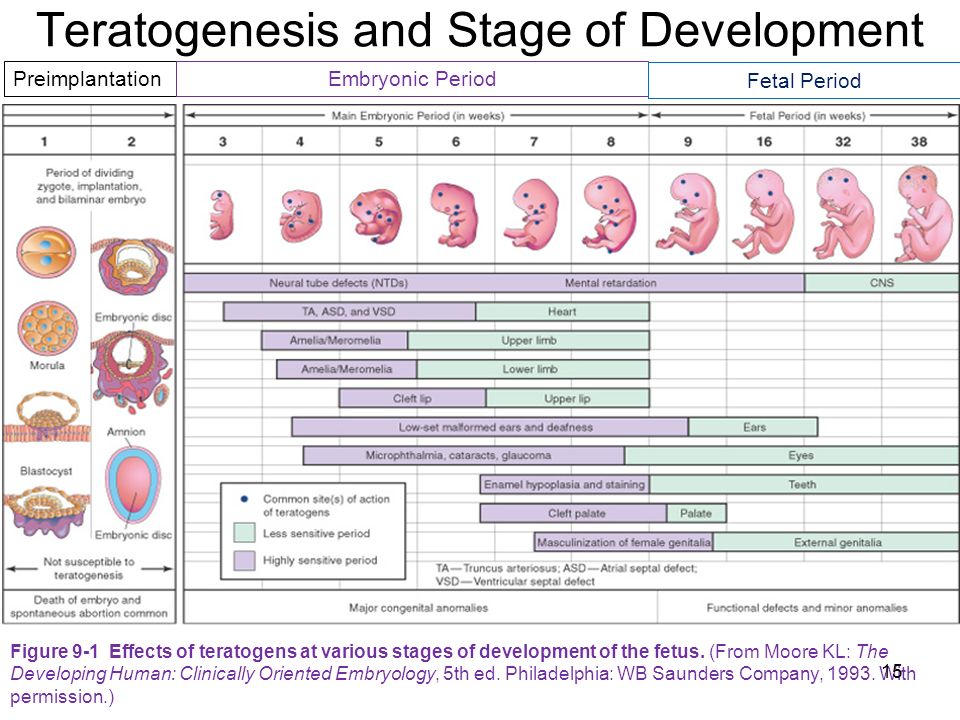 nine0005
nine0005
Varieties
There are several variants of empty ovum syndrome:
- Type I anembryony. The embryo and its remains are not visualized, the size of the fetal egg and uterus does not correspond to the expected gestational age. The diameter of the egg is usually no more than 2.5 mm, and the uterus is enlarged only up to 5-7 weeks of gestation.
- Type II anembryony. There is no embryo, but the fetal egg and uterus correspond to the gestational age. nine0052
- Resorption of one or more embryos in multiple pregnancies. At the same time, normally developing and regressing fetal eggs are visualized. According to this type, anembryony often occurs after IVF, if several embryos were implanted in a woman.
All these varieties are determined only with the help of ultrasound, they do not have characteristic clinical features .
What to do?
Confirmed anembryony is an indication for abortion. This does not take into account the gestational age, the woman's well-being and the presence of signs of a possible spontaneous abortion. An exception is the situation when the anembryony of the second fetal egg is diagnosed in a multiple pregnancy. In this case, a wait-and-see strategy is taken, evaluating the dynamics of the development of the preserved embryo. nine0005
This does not take into account the gestational age, the woman's well-being and the presence of signs of a possible spontaneous abortion. An exception is the situation when the anembryony of the second fetal egg is diagnosed in a multiple pregnancy. In this case, a wait-and-see strategy is taken, evaluating the dynamics of the development of the preserved embryo. nine0005
Termination of a missed pregnancy is carried out only in a hospital. After the procedure for the evacuation of the fetal egg, the woman should be under medical supervision. In many cases, after it, additional medication and sometimes physiotherapy are prescribed, aimed at normalizing the hormonal background, preventing inflammatory and hemorrhagic complications, and eliminating the detected infection.
Several techniques can be used to perform a medical abortion for this pathology. Can be used:
- medical abortion - termination of pregnancy with the help of hormonal drugs that provoke rejection of the endometrium along with an implanted fetal egg;
- vacuum aspiration of the contents of the uterine cavity;
- curettage is an operation involving the mechanical removal of the ovum and endometrium with a special instrument (curette) after the forced expansion of the cervical canal with bougie.
Medical abortion for anembryos is possible only after 6-8 weeks. In later periods of gestation, preference is given to mechanical methods, which requires the use of general anesthesia. The choice of the method of artificial abortion depends on whether the stomach hurts after an abortion, the length of the rehabilitation period, the likelihood of early and late complications. nine0005
Examination after induced abortion necessarily includes ultrasound control. This allows you to confirm the complete evacuation of the membranes and endometrium, to exclude undesirable consequences of abortion in the form of hematomas, perforation and endometritis.
Prediction
Can anembryony recur? Can I still have children? These questions concern all patients who have undergone this pathology. Fortunately, in most cases, the condition does not recur, the woman subsequently manages to safely become pregnant and bear the child. But at the same time, she is classified as a risk group for the possible development of complications of pregnancy and childbirth. Therefore, in the first trimester, she is usually assigned dynamic ultrasound control of the development of the fetal egg, determination of the hormonal profile and assessment of the state of the hemostasis system. nine0005
Therefore, in the first trimester, she is usually assigned dynamic ultrasound control of the development of the fetal egg, determination of the hormonal profile and assessment of the state of the hemostasis system. nine0005
Pregnancy after anembryos is theoretically possible already in the next ovarian-menstrual cycle. But it is desirable to let the body recover. Therefore, it is recommended to start planning for re-conception not earlier than 3 months after the induced abortion . If it proceeded with complications, the rehabilitation period, while maintaining reproductive rest, is extended for up to six months. If a woman has chronic endometritis and various infections, 2 months after the completion of treatment, a control examination is carried out and only then the possible timing of re-conception is determined. nine0005
Barrier method and hormonal contraception are preferred to prevent pregnancy. The selection of funds in this case is carried out individually.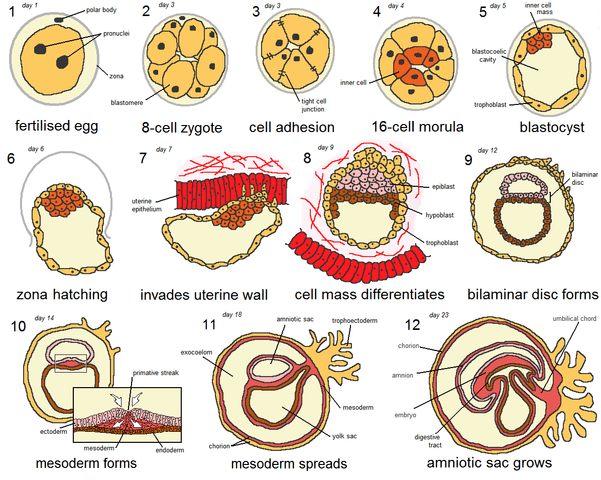 Intrauterine devices immediately after a frozen pregnancy are not used in order to avoid the development of endometritis.
Intrauterine devices immediately after a frozen pregnancy are not used in order to avoid the development of endometritis.
Prevention
Primary prevention of anembryonia includes careful planning of pregnancy with a comprehensive examination. If deviations are found, they are corrected. Of course, such preparation does not allow 100% to exclude the possibility of pathology, but reduces the risk of its development. nine0005
Secondary prophylaxis is carried out if the woman has a history of spontaneous abortions and anembryos. The first pregnancy with empty ovum syndrome is a reason for a subsequent examination of a woman for infections and hemostasis disorders. When the situation repeats, a genetic examination of the spouses is also shown to exclude anomalies in their hereditary material. In some cases, subsequent conception is preferably carried out using IVF, which will allow the use of preimplantation diagnosis to detect chromosomal abnormalities in embryos.