Edc calendar pregnancy
Due Date Calculator — Amazingly Accurate Pregnancy Calculator
First day of your
last period:Please choose the day your most recent period started.
Average cycle: 20 days21 days22 days23 days24 days25 days26 days27 days28 days29 days30 days31 days32 days33 days34 days35 days36 days37 days38 days39 days40 days41 days42 days43 days44 days45 days
or
Date you
conceived:Conception is approximately two days after intercourse.
Already know your due date? Click here
Pregnancy Week by Week Universal Header
Pregnancy due date calculator video
Learn how to calculator your pregnancy due date in this video.
When is my baby’s due date?
So you got your positive pregnancy test, you’re feeling some early signs of pregnancy, and now you’re wondering, “when is my baby’s due date?” We’ve got you covered with the Mama Natural due date calculator!
Enter your information in the due date calculator above and discover the best estimate for when your little bundle of joy will make his or her appearance.
How does this due date calculator work?
Because you may not know exactly when you ovulated or conceived, a due date calculator will typically calculate your estimated due date based on your last menstrual period (LMP).
Our online due date calculator uses a simple method to calculate your due date.
- Your due date is estimated to be 40 weeks after the first day of your LMP
- Your cycle is assumed to be 28 days long, with ovulation occurring at day 14
- Therefore the calculator adds 280 days (40 weeks) to your LMP
This method of due date calculation is known as Naegele’s rule (more info on this below).
Due date calculator quote Our standard due date calculator adds 280 days (40 weeks) to the date of your last menstrual period (LMP)
My cycle isn’t 28 days. Will this due date calculator work for me?
Yes. The logic behind our pregnancy calculator works as follows:
- The average cycle length is 28 days
- If your cycle length is shorter, your due date will be earlier
- For every day your cycle is shorter, your due date moves one day earlier
- Similarly, if your cycle is longer, your due date will be later
- For every day your cycle is longer, your due date moves one day later
What is the date of conception due date calculator illustration
How do you calculate due date from conception?
If you know when you conceived, our pregnancy calculator calculates your due date by adding 38 weeks to the date of conception. This method of calculation may be more accurate than a LMP due date calculation if you have irregular or consistently longer or shorter cycles than 28 days.
This method of calculation may be more accurate than a LMP due date calculation if you have irregular or consistently longer or shorter cycles than 28 days.
What exactly
is the date of conception?The date of conception is the day that the egg and sperm meet.
Women who track their ovulation may know their exact date of conception. But for many women, date of conception can be tricky to pinpoint.
Sperm can live in a woman’s body for up to five days, and the ovum (egg) can live for up to 24 hours after being released. In other words, you have a six-day window where you could potentially get pregnant each month.
Do you already know your due date but want to know when you likely conceived? Try our reverse due date calculator.
What is an estimated due date (EDD)?
An estimated due date (EDD) is a “best guess” as to when baby might be born based on a due date calculator like this one.
However, only 4% of babies are born on their due date! Whereas 80% of babies are born within the window of two weeks before and two weeks after your due date calculator results. (See “due month” section below.)
Baby due date on a calendar with pregnant woman background – only 4% of babies are born on their due date
What is “gestational age?” Can it be different than what the calculator shows?
Gestational age (GA) is the term used to describe how far along the pregnancy is and how long baby has been gestating (growing in the uterus).
If you get an ultrasound you may notice a “GA” on the image with a number of weeks and days. This figure is based on how the baby is measuring, not on your LMP, which the due date calculator uses.
It’s normal for these dates to not match up perfectly. If there are significant differences in the dates, your doctor may want to dig deeper to determine conception date. As a result, your midwife or doctor may change your due date based on the ultrasound gestational age.
As a result, your midwife or doctor may change your due date based on the ultrasound gestational age.
Early ultrasounds are very accurate when dating a pregnancy and can be helpful if you don’t know your LMP or your periods are irregular.
Note that you don’t have to have an early ultrasound, especially if you are fairly certain of your cycle length and conception window. This study shows that early dating ultrasounds don’t change the incidence of induction.
How are the weeks of pregnancy calculated?
The 40 weeks of pregnancy begin on the first day of your last menstrual period.
This can be a little confusing because, for most people, conception doesn’t occur until day 14 of the menstrual cycle. So yes, you aren’t actually pregnant during those first two weeks of pregnancy.
Here’s a more in-depth answer to that perennial question of How many weeks pregnant am I?
What is a
“due month?” A “due month” is a more accurate timeframe for when you can expect to deliver your baby. Only 4% of babies are born on their due date. Whereas 80% of babies arrive either two weeks before the due date or two weeks after. Hence the term “due month.”
Only 4% of babies are born on their due date. Whereas 80% of babies arrive either two weeks before the due date or two weeks after. Hence the term “due month.”
The length of a natural pregnancy can vary by as much as five weeks. (source)
A due month helps some mamas reduce the stress and fear of going past their due date.
To calculate your due month, simply subtract two weeks from your EDD given by your practitioner or our due date calculator and also add two weeks to your EDD. Voilà, your due month!
Yet another way to handle this tricky business of calculating your pregnancy calendar is to add two weeks to the end of your EDD and say, “Baby will be here before [that date].”
What is Naegele’s rule for due date calculation?
Naegele’s rule is what this due date calculator and pregnancy calendar is based on. Named after a German Obstetrician who practiced in the early 1800’s, Naegele’s rule predicts childbirth to occur 280 days after the first day of the last menstrual period.
However, Naegele’s rule assumes that your cycle is 28 days long with ovulation occurring on day 14, which isn’t the case for many women. So other ways of calculating your due date may be more accurate.
(How accurate is your due date? Find out in this post.)
Modern data suggests that women have their babies a few days after their due date on average. Studies like this one found that Naegele’s rule consistently places the due date about 2-4 days too early. So a better estimate may be 40 weeks and 3 days from LMP.
Alternatively, you can use our Advanced Due Date Calculator, which uses the Mittendorf-Williams rule to calculate your due date, which has been shown to be more accurate.
Due date calculator quote 2 Modern data suggests that Naegele’s rule places the due date about 2-4 days too early
What’s the Mittendorf-Williams rule?
This study done in 1990 showed that pregnancy lasted an average of 288 days past LMP for Caucasian first-time moms. For Caucasian women who were not first-time moms, their date of delivery averaged 283 days past LMP (3 days after Naegele’s rule predicted). This finding is known as the Mittendorf-Williams rule.
For Caucasian women who were not first-time moms, their date of delivery averaged 283 days past LMP (3 days after Naegele’s rule predicted). This finding is known as the Mittendorf-Williams rule.
While Naegele’s rule is still the most widely used formula for a due date calculator, the Mittendorf-Williams rule is proving to be more accurate. But it’s a much more complex calculation, taking into account:
- Maternal age
- Race
- Height
- Weight
- Number of pregnancies
- Average luteal phase length
- Maternal education
- Alcohol during pregnancy
- Coffee during pregnancy
Our Advanced Due Date Calculator uses the Mittendorf-Williams rule.
Related Resources
- Our FREE Natural Pregnancy Week-By-Week Series ?
- My Bestselling Natural Pregnancy Guide ?
- Reverse Due Date Calculator ◀️
- Natural Birth Stories ??
- Baby Name Finder ?
Ready to calculate your due date?
First day of your
last period:
Please choose the day your most recent period started.
Average cycle: 20 days21 days22 days23 days24 days25 days26 days27 days28 days29 days30 days31 days32 days33 days34 days35 days36 days37 days38 days39 days40 days41 days42 days43 days44 days45 days
or
Date you
conceived:Conception is approximately two days after intercourse.
Already know your due date? Click here
IVF and FET Due Date Calculator
Please note that Flo Health does not collect, process, or store the data that you enter while using the Tools. All calculations are done exclusively in your browser. Flo Health does not have access to the results. All data will be permanently erased after leaving or closing the page.
You will meet your baby on
date
day
You are pregnant for
weeks and day
Week 1
At 1 week pregnant, you’re actually not pregnant yet.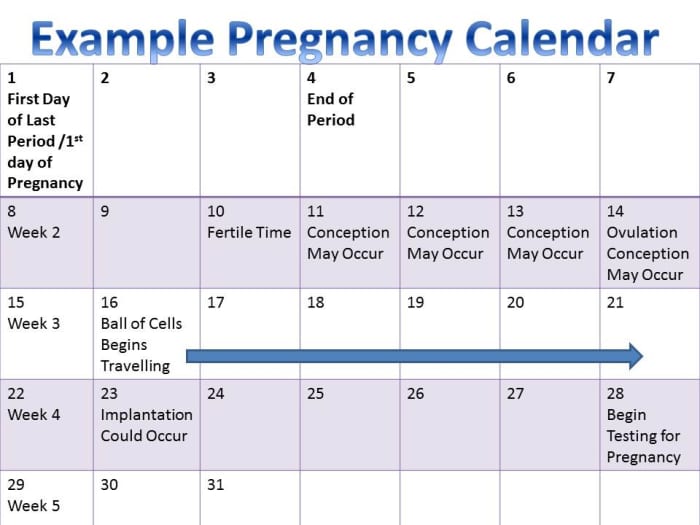 As your pregnancy is calculated from the first day of your last menstruation, your baby does not yet exist, and your body is preparing for the ovulation during which you’ll get pregnant.
As your pregnancy is calculated from the first day of your last menstruation, your baby does not yet exist, and your body is preparing for the ovulation during which you’ll get pregnant.
Read more
Week 2
At 2 weeks pregnant, you’re technically not pregnant yet. Right now there is a lone egg and a whole bunch of anxious sperm eager to fertilize the egg. Your uterus and the entire body are preparing for a big day of ovulation - the stage when you'll get pregnant.
Read more
Week 3
Week 3 of pregnancy is the week when the implantation happens. Your body releases chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which causes an increased production of estrogen and progesterone, and prevents new eggs in the ovaries from ripening. Very soon you'll start experiencing the first symptoms of pregnancy: missed period, nausea, breast changes.
Read more
Week 4
At 4 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a poppy seed.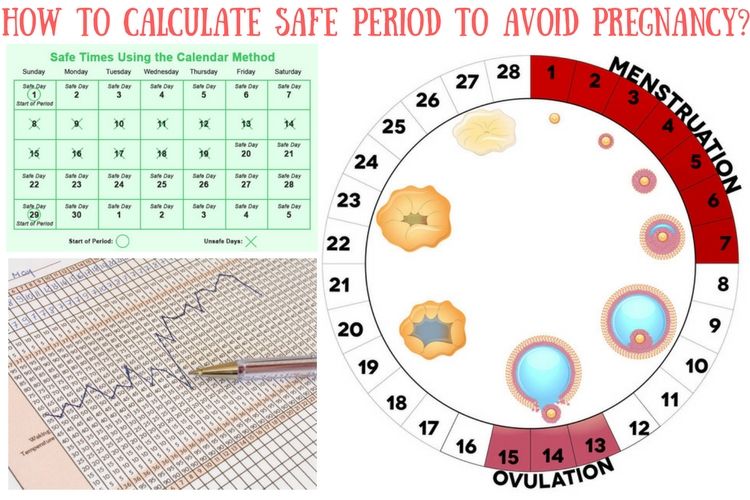
At 4 weeks pregnant, your future baby has finally found his home for the next eight months. The blastocyst has arrived from a fallopian tube to your uterus. You can get a positive pregnancy test result at this stage.
Read more
Week 5
At 5 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a sesame seed.
By week 5, you should have missed your period, which is one of the most obvious signs you're expecting. Under the influence of hormonal changes, you can feel the first signs of pregnancy: breast swelling, fatigue, headache, and back pain.
Read more
Week 6
At 6 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a lentil.
Starting from pregnancy week 6, you may experience morning sickness. This is the result of hormonal changes occurring in your body. Malaise, breast swelling, darkening of the nipple areola, and frequent urination can bother you, too. In case of bleeding, you should consult your doctor.
Read more
Week 7
At 7 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a blueberry.
At 7 weeks pregnant, symptoms start kicking in and your uterus almost doubles in size. Be prepared for a possible increase in nausea, fatigue, heartburn, and other pregnancy symptoms. Morning sickness may give a lot of trouble. Try to find some ways to cope with it.
Read more
Week 8
At 8 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a bean.
At 8 weeks pregnant, you need to plan your first visit to the gynecologist. The doctor will prescribe the necessary tests and examinations for the first trimester of pregnancy. You may feel the growing discomfort of morning sickness. Try to be patient; it usually lasts until the 14th week only.
Read more
Week 9
At 9 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a cherry.
At 9 weeks pregnant, your baby is already about 0. 6–0.7 in (16–18 mm) and weighs about 0.11 oz (3 g). The tail has disappeared; human features are becoming more distinct. The joints of his/her hands and legs can flex; the nipples and hair follicles are developing. Taste buds are beginning to form on the tongue, as well as primary tooth buds in the gums.
6–0.7 in (16–18 mm) and weighs about 0.11 oz (3 g). The tail has disappeared; human features are becoming more distinct. The joints of his/her hands and legs can flex; the nipples and hair follicles are developing. Taste buds are beginning to form on the tongue, as well as primary tooth buds in the gums.
Read more
Week 10
At 10 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a kumquat.
Week 10 of pregnancy is the time when almost all vital organs and tissues of your baby have formed. Now, they are beginning to function and grow rapidly. He or she can swallow amniotic fluid and move their arms and legs. The skin is getting covered with small hair and the fingers have tiny nails. Testes in boys already start to produce testosterone.
Read more
Week 11
At 11 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a fig.
At 11 weeks pregnant, your baby has already reached 2 in (5 cm) in size. Now, his/her head is half the length of the body, but in the coming weeks, the body will grow enough to make up for it. The fetus skin is so thin and translucent that through it you can see an extensive network of vessels. Placental vessels are expanding to provide the fetus with necessary nutrients and oxygen.
The fetus skin is so thin and translucent that through it you can see an extensive network of vessels. Placental vessels are expanding to provide the fetus with necessary nutrients and oxygen.
Read more
Week 12
At 12 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a plum.
At 12 weeks pregnant, your baby weighs about 0.49 oz (14 g). His/her vocal cords are forming, and kidneys are starting to produce urine, filling the bladder. Although you cannot feel it yet, you can see the baby during a sonogram screening (ultrasound).
Read more
Week 13
At 13 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a pea pod.
Welcome to the last week of the first trimester! Most early pregnancy symptoms will soon be left behind. At 13 weeks pregnant, your baby is constantly growing. Now, he/she is more than 2.8 in (7 cm) from the top of his/her head to the coccyx.
Read more
Week 14
At 14 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a peach.
At 14 weeks pregnant, your baby is developing rapidly. In a while, you will be able to feel them moving and kicking. Your body starts actively gaining weight. This occurs due to an increase in blood and lymph volume.
Read more
Week 15
At 15 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of an apple.
At 15 weeks pregnant, your baby is actively drawing in amniotic fluid through his/her nose. Very soon you'll start looking pregnant indeed as your uterus has risen from your pelvic region to your lower abdomen. Time to plan pregnancy shopping!
Read more
Week 16
At 16 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of an avocado.
You’re on week 16 of your pregnancy, and things are really starting to gear up! Your tiny baby is not so tiny anymore, and it most definitely looks like a human baby now. By week 16 of your pregnancy, you’re 4 months in. That means you’re nearly halfway there and only have 5 more months to go!
Read more
Week 17
At 17 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a potato.
If you’ve been enjoying a relatively subtle pregnancy with very little belly to show for it, that’s probably over now! Your waist will gradually disappear as your uterus moves upwards and out of your pelvis.
Read more
Week 18
At 18 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a bell pepper.
If you’ve been astonished by your baby’s rapid growth and weight gain over the last few weeks, by week 18 this will start to level off a little — but there’s still lots of big news in your little one’s early life! At this stage, he or she can yawn, stretch, and even make facial expressions like frowning. The baby’s sense of taste is developing, and taste buds can now distinguish between sweet and bitter.
Read more
Week 19
At 19 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a mango.
At 19 weeks pregnant, your rounded belly is very noticeable. The first hair appears on the baby's head, and the brain areas responsible for the senses — tactile, gustatory, olfactory, visual and auditory — are developing rapidly.
Read more
Week 20
At 20 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a grapefruit.
Congratulations! You are halfway to meeting your baby. The baby's legs have almost straightened, so from now on, he/she will be measured from head to toe.
Read more
Week 21
At 21 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a banana.
As a 21 week pregnant woman, you have crossed the halfway line on your journey to becoming a mother. Your baby is getting bigger. You can now definitely feel her presence as she explores the real estate that you’ve prepared for her.
Read more
Week 22
At 22 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a carrot.
If you are entering the 22nd week of your pregnancy, without doubts it is getting crowded in there! Your baby is growing and invading your space. And your uterus stretches to about 2 cm (0.8 in) above your belly button to fit your growing baby.
Read more
Week 23
At 23 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a squash.
For many women, being 23 weeks pregnant is an exciting time because you may finally be showing your baby bump! Among other things, your baby’s eyes and lips are taking shape. They will begin to gain weight more weight which will eventually fill out their wrinkly skin.
Read more
Week 24
At 24 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of an eggplant.
At 24 weeks pregnant, your baby is almost a foot long. You could be experiencing a tingling sensation in your joints, which is known as carpal tunnel syndrome. It is a common condition during pregnancy which occurs due to fluid build-up in your joints which results in compression of the median nerve.
Read more
Week 25
At 25 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a full ear of corn.
Once you reach week 25 of your pregnancy, you’ll be nearing the end of your second trimester. It can feel like times flies! At 25 weeks pregnant, you’re approximately 5 months and 2 weeks along. Your baby has been growing steadily and even though it’s still not ready, it won’t be long before it comes into the world.
It can feel like times flies! At 25 weeks pregnant, you’re approximately 5 months and 2 weeks along. Your baby has been growing steadily and even though it’s still not ready, it won’t be long before it comes into the world.
Read more
Week 26
At 26 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a beetroot.
You’re likely to put on between 16 and 22 pounds by now. At one point during this week, your baby will open his or her eyes for the first time. He or she is not yet able to see anything inside of the uterus but will blink closing and opening his or her eyes when falling asleep and waking up.
Read more
Week 27
At 27 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a cauliflower.
The 27th week of the pregnancy marks the final two weeks of the second trimester. If your baby is more active at night you might suffer from insomnia and have trouble sleeping. Compensate for the lack of sleep time during the night by napping during the day more when the baby is sleeping.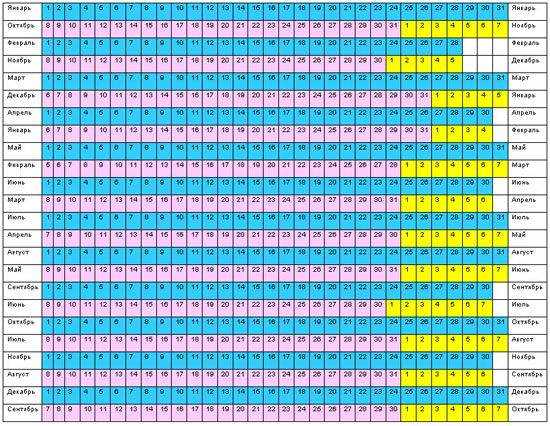
Read more
Week 28
At 28 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a coconut.
At 28 weeks you are now entering the third trimester of your pregnancy. At this stage, your baby is pretty well-developed. Her organs, tissues, and nerves continue to grow, but she already has all of the systems necessary for survival outside the uterus. Towards the end of the pregnancy, babies start to recognize familiar sounds and voices.
Read more
Week 29
At 29 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a pomelo.
At 29 weeks pregnant, you're likely to develop varicose veins like 40 percent of expectant moms. It's also a good time to start doing a kick count. Let your doctor or midwife know if you notice that your baby is becoming less active.
Read more
Week 30
At 30 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a head of cabbage.
At 30 weeks pregnant, you are likely to experience shortness of breath. Your baby is still up high near your rib and is waiting a bit – it is soon expected to drop down into your pelvis.
Your baby is still up high near your rib and is waiting a bit – it is soon expected to drop down into your pelvis.
Read more
Week 31
At 31 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a head of a zucchini.
At 31 weeks pregnant, your breasts can get leaky producing the first baby’s food – colostrum. This is one of the symptoms that your body is getting ready for the big day. You are likely to experience shortness of breath. This week your baby is going through major nerve and brain development.
Read more
Week 32
At 32 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a head of lettuce.
At 32 weeks pregnant, your body may start flexing its muscles preparing for the big day. Your baby is also preparing for her debut mastering the skills she’ll need to thrive outside your womb: swallowing, breathing, sucking.
Read more
Week 33
At 33 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a pineapple.
At 33 weeks pregnant, you may notice that your baby’s movements are affected by your daily routine. Your belly continues to grow and it’s getting even more troublesome to find a comfortable sitting or sleeping position.
Read more
Week 34
At 34 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a butternut squash.
At 34 weeks pregnant, your breasts could start leaking small amounts of yellowish colostrum. Your baby is already the size of a school bag and weighs as a melon. If you’re worried about your safety at work, time to talk to your employer about maternity benefits.
Read more
Week 35
At 35 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a honeydew melon.
At 35 weeks pregnant, you may know how your baby’s moving in your womb just by looking at your bump. It can you give you some discomfort and make you a bit breathless. At this point, many moms can’t wait for the baby to get here, while others are feeling a bit anxious about giving birth. Both feelings are completely normal!
Both feelings are completely normal!
Read more
Week 36
At 36 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a papaya.
At 36 weeks pregnant, your baby is sleeping between 60 and 80% of the time. It has finally moved into your pelvic cavity, the pressure on your diaphragm is released, and lightening happens. Your baby can now open its eyes, suck its thumb, breathe, and recognize voices!
Read more
Week 37
At 37 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a head of romaine lettuce.
Welcome to your 37th week of pregnancy, and congratulations! The baby moves further into the pelvis. It is considered to be ‘at-term’ and can actually arrive any day now. Make sure you are ready for the arrival of a new family member.
Read more
Week 38
At 38 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of Swiss chard.
At 38 weeks pregnant, you can find yourself spending the whole life peeing. The pressure on your bladder is tremendous. Your baby is a fully functioning little human and your placenta is fully grown.
The pressure on your bladder is tremendous. Your baby is a fully functioning little human and your placenta is fully grown.
Read more
Week 39
At 39 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a small watermelon.
Welcome to the week 39 of pregnancy! Your baby is full term, meaning that it is fully developed and is only waiting for the right time to make an entrance into the world. Have you prepared everything that is needed to welcome your baby?
Read more
Week 40
At 40 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a mini watermelon.
At 40 weeks pregnant, you may feel disappointed that your due date has come and gone. Don’t panic and make the last preparations for a new human who’ll soon join the world.
Read more
Week 41
At 41 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a pumpkin.
At week 41 of pregnancy, you might be dying out of the desire to give birth and see your baby. But rest assured that plenty of moms-to-be go past their due date and everything turns out just fine.
But rest assured that plenty of moms-to-be go past their due date and everything turns out just fine.
Read more
Week 42
At 42 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a watermelon.
When a pregnancy lasts for 42 weeks or more it is referred to as a post-term pregnancy. While not many studies exist that prove why some women’s pregnancy lasts for 42 weeks, medical experts believe that factors such as hormones, genetics, and even obesity can be the cause.
Read more
Take a quiz
Find out what you can do with our Health Assistant
How many weeks pregnant are you?
Typically, pregnancy lasts for about 40 weeks, or 280 days. If you conceive naturally, the estimated due date is usually determined based on the first day of your last period, not from the date of conception. Why is this?
The reason is that most people don’t know exactly when they ovulated or conceived. Someone with a regular 28-day menstrual cycle usually ovulates around day 14.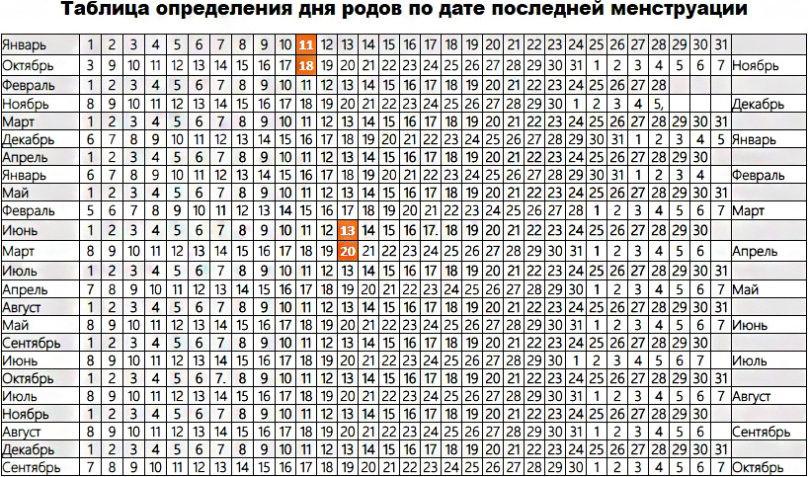
However, this date isn’t 100-percent accurate, as ovulation can occur earlier or later. This is why a due date is just a rough estimate of the day the baby is likely to arrive.
Due date calculation for IVF pregnancies
In-vitro fertilization (IVF) is the only case in which your health care provider will know exactly when you conceived. Enter this date in the “Date of transfer” field of the calculator.
You can calculate your due date by using different formulas depending on the type of IVF you had. Choose your IVF type in the “Type of transfer” field of the calculator.
This is how Flo’s calculator formulas work based on your IVF type (these formulas are set automatically in the calculator for each option you choose):
- IVF with own eggs (with or without ICSI) — Egg retrieval date + 266 days (or 38 weeks)
- IVF with fresh donor egg cycle (with or without ICSI) — Egg retrieval date + 266 days (or 38 weeks)
- Fresh donor embryo cycle — Egg retrieval date + 266 days (or 38 weeks)
- 3 day FET — Transfer date + 266 days (or 38 weeks) – 3 days (for embryos)*
*Sometimes your embryos’ age is more than 3 days, so it’s important to subtract the exact age of the embryos.
- 5 day FET — Transfer date + 266 days (or 38 weeks) – 5 days (for blastocysts)*
*If the blastocysts’ age is more than 5 days, you need to subtract their exact age.
How accurate are IVF due dates?
Due date calculations may vary regardless of whether you conceived naturally or via IVF. Even with IVF and ultrasound measurements, no due date is a guarantee. It’s just a way to provide a window of time in which you are likely to go into labor.
Try some of Flo's other online tools, including our due date calculator (for non-IVF pregnancies), hCG calculator, our pregnancy test calculator, and our period calculator.
Updated December 01 2022
Pregnancy calendar
Asked the question "How to determine the gestational age?" We suggest you use our pregnancy calendar, which will easily and quickly determine the duration of pregnancy by week.
Extremely important information for a gynecologist - knowledge of the gestational age. All this is necessary in order to correctly prescribe the necessary tests and examinations for the quality management of pregnancy.
Knowing the gestational age, you can accurately calculate the date of delivery. With this information, the attending physician will inform you about the date of maternity leave. Therefore, correctly determining the gestational age is a very important procedure for all pregnant women. nine0003
Our interactive pregnancy calculator helps you determine your due date. Below is a step-by-step instruction on how to determine the gestational age.
Step 1. Determine the date of conception
It is important to know the date of conception if you want to determine the exact timing of pregnancy. It coincides with the date of the last ovulation. Enter your data in the pregnancy calendar and click on the "Calculate!" button. If you know the date of conception, you can skip this step.
Calculate the date of conception
Last menstruation
The average cycle duration
(from 22 to 45 days - by default 28)
The average duration of the second phase
(from 9 to 16 days - by default 14)
The estimated date
Pregnancy video calendar
1 month pregnant 2 month pregnant 3 month pregnant 4 month pregnant 5th month of pregnancy 6 month pregnant 7 month pregnant 8 month pregnant ninemonth of pregnancy
Pregnancy: week by week
Every week of pregnancy is special. It is important for every expectant mother not only to be observed during pregnancy by a doctor, but also to engage in self-education. And it doesn't matter what week of pregnancy you have - our guide for expectant mothers describes the development of pregnancy by week . Each week of pregnancy includes useful tips and recommendations from the CIR doctors. You will have a clear idea of what what happens from the 1st to the 40th week of pregnancy, how the child's developmental norms change (weight, height, formation of body parts, skeleton). This section describes pregnancy by week .
Each week of pregnancy includes useful tips and recommendations from the CIR doctors. You will have a clear idea of what what happens from the 1st to the 40th week of pregnancy, how the child's developmental norms change (weight, height, formation of body parts, skeleton). This section describes pregnancy by week .
So, about all the features of the development of the fetus and pregnancy by week , about what happens with your body in the first weeks of pregnancy and how you will change week by week, our pregnancy guide will help you find out. Just follow us. nine0030
-
1-4 weeks
Before conception, the growth and maturation of the egg begins in the ovary. In the middle of the menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs: the egg leaves the ovary into the abdominal cavity, and then moves into the fallopian tube. The egg and sperm combine: fertilization has occurred, the pregnancy begins to develop.

The size of the embryo at 4 weeks of gestation is 2-4 mm.
Read about the first weeks of pregnancy...
nine0073 -
5-8 weeks
By the end of 7 weeks, the embryo is already about 1 centimeter long. It will grow by forming a million new cells every minute! By the end of the 8th week of pregnancy, your baby will grow to 1.5-2 cm. During an ultrasound scan with a coccyx-parietal size (CTE) of more than 4 mm, you can determine the heartbeat. Around this time, the nerve cells in your child's brain begin to form primitive neural pathways.
Read about 5-8 weeks of pregnancy...
-
9-12 weeks
At 9 weeks, the period when your unborn baby is called an "embryo" has ended. It is now a "fetus" as it looks like a miniature replica of a human. By 11-12 weeks, many internal organs are formed, the heart has four chambers. Hands, fingers, feet and toes, mouth, nose and nostrils, eyes and earlobes are already visible. The expectant mother has a feeling of fatigue, signs of toxicosis should change in the near future to a good and stable state of health.
 nine0003
nine0003 Read about 9-12 weeks of pregnancy...
-
13-16 weeks
From 14 weeks - the second trimester of pregnancy.
The first hair appears on the little man. By the 16th week, the nervous and muscular systems of the fetus are well developed enough for the first movements of the facial muscles to begin to appear. The eyes become sensitive to light stimuli. Baby grows up to 16 cm.
Read about 13-16 weeks of pregnancy...
nine0064 -
21-24 weeks
From 21 weeks, sensory receptors begin to form: taste buds (tongue), the brain is now able to process the sensation of touch.

By the end of 22 weeks, the baby will be about 25 cm long and weigh about 500 grams. The brain and nervous system continue to mature.
Read about 21-24 weeks of pregnancy...
-
25-28 weeks
The end of the period of the most active growth. From weeks 20 to 30, a baby's weight doubles in 4 weeks. By the end of this month, the weight is from 1 to 1.5 kg. nine0003
Eyelids were not tightly closed until the 28th week. It is necessary for the development of the retina.
At this time, the child begins to hear, to distinguish between tastes. It often moves in response to touch and sound. The brain and nervous system are undergoing rapid growth and development.
Read about 25-28 weeks of pregnancy...
-
29-32 weeks
The third trimester of pregnancy has come.
During this last trimester of pregnancy, your baby grows, accumulates fat, and his organs slowly mature. By 32 weeks pregnant, your baby will be about 40 centimeters long and weigh up to 2 kg.
 nine0003
nine0003 At this time, the child may show high motor activity and even “hiccups” (so-called hiccup-like movements)! So the child practices breathing, trains the respiratory muscles.
Read about 29-32 weeks of pregnancy...
-
33-36 weeks
By the end of 36 weeks, the fetus will be about 48 cm tall and weigh about 2.4 - 2.8 kg. Over the next three weeks, the baby's weight will increase by about 200 grams per week. Facial features are rounded due to the layer of fat cells. The muscles of the cheeks and jaws are adapted for sucking. It can be seen on ultrasound how the baby sucks his finger or tries to put his fist in his mouth. nine0003
Read about 33-36 weeks of pregnancy...
-
37-40 weeks
The weight of the child by the 40th week of pregnancy is on average 3-4 kg. Height is 51-53 cm. The kid is happy to move inside, using the capabilities of the arms and legs. He can already suck, swallow, blink, grasping skills are developed.
 He turns his head with interest, stretches his legs. You may notice fairly distinct periods of activity and sleep. The sucking reflex is extremely pronounced, so everything that swims near the mouth makes you want to try it. nine0003
He turns his head with interest, stretches his legs. You may notice fairly distinct periods of activity and sleep. The sucking reflex is extremely pronounced, so everything that swims near the mouth makes you want to try it. nine0003 Read about 37-40 weeks of pregnancy...
17-20 weeks
Your child is growing and developing.
By the end of the 20th week, the skin is no longer as translucent as it used to be, because fat is now accumulating under the skin. Developed motor neurons of the brain enable the unborn child to make many movements, for example, even “put your thumb in your mouth”!
The body is getting bigger. The head no longer looks so bulky relative to the body.
Read about 17-20 weeks of pregnancy...
Work and Children - A Handbook on Human Rights Education with Youth
Instructions
- Explain that the theme of the role-play is women's reproductive rights in relation to their place of work. Brainstorm on the topic of women's reproductive rights so that the participants understand what is at stake.
- Divide participants into small groups (maximum 5 people per group). nine0073
- Read out the role-play scenario.
- Give participants 20 minutes to think of an ending to the story in small groups and act it out. The role play should begin with a meeting between Maria and Mr. Vladstock and should not last more than 5 minutes.
- Then all the small groups take turns presenting their dramatizations.
 Leave comments before the debriefing stage.
Leave comments before the debriefing stage.
Analysis and Evaluation
Start by asking small groups how they came up with their role play scenarios, and let others have their say. Then talk about the consequences of this situation and think about how you can fight this kind of discrimination. nine0003
- Was anyone surprised by this situation? Has this happened in your country?
- How did the groups decide how to proceed with this situation?
- Were the suggested endings realistic? In what situations did Maria behave well (or not so confidently)? How much more difficult is it to be assertive in such a situation than to be aggressive or submissive?
- What rights do women in your country have in the workplace if they are pregnant? nine0064 Why does the company want to put such a condition on Maria? Is it fair? Why? Why not?
- Were human rights violated? If so, which ones?
- If Mary were a man, could the situation be the same? Why? Why not?
- How does a man's view of this problem differ from a woman's view?
- What do you think can be done to promote and protect women's reproductive rights?
Tips for presenters
Consider whether to include an equal number of boys and girls in small groups. Experience has shown that same-sex group activities often lead to more provocative plot twists and a livelier discussion.
Experience has shown that same-sex group activities often lead to more provocative plot twists and a livelier discussion.
Participants may not be familiar with the term "reproductive rights", so you may need to introduce them to some ideas so they can get the big picture. Reproductive rights include the right to:
- pleasurable sexual relations without fear of infection or disease; nine0073
- choice to have or not to have children;
- family planning services with the option of abortion in a manner that is respectful, sensitive and confidential;
- sex education.
Remember that when discussing the case of violation of the rights of Mary, such a controversial issue as abortion and the opposition of the woman's right to choose and the right of the fetus to life may arise. This topic is especially important in the context of human rights education because it requires the trainees to be open-minded, to reject stereotypes and preconceived notions, and to use critical thinking skills. It well illustrates the inherent complexity of human rights. If such a question arises, you can organize a separate discussion of this issue at another time. nine0003
It well illustrates the inherent complexity of human rights. If such a question arises, you can organize a separate discussion of this issue at another time. nine0003
Variations
Use forum theater methods. Instead of dividing all the participants into small groups, you can ask two volunteers to act out the skit between Maria and Mr. Vladstock in front of the rest of the participants who will act as observers. You can periodically interrupt the game and ask the audience for their opinions and suggestions about what should happen next. Alternatively, the observers can simply switch places with the actors in order to present the situation from a different angle and change the plot of the role-play. nine0003
Other characters can be added to the game. For example, Maria's husband, who may be a trade union representative, then the situation will go beyond a meeting with an employee of the personnel department.
You can replace the names of the characters with other names that are more common in your country.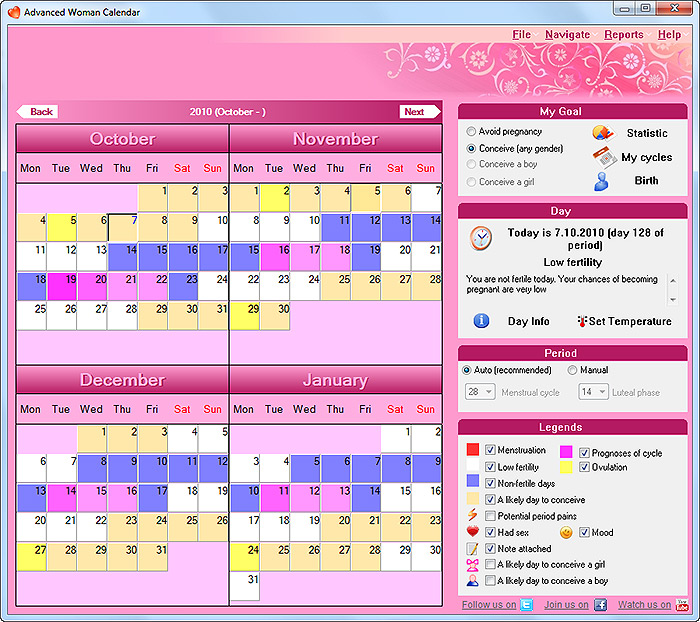
Some participants find it difficult to role-play, then invite them to tell stories instead. Divide the participants into small groups, give each a piece of paper with a story, ask them to discuss it and write their own version of the ending. Then bring the groups together in plenary and compare the different endings. nine0003
Suggestions for follow-up
If sex education is included in your school's curriculum, ask your fellow teacher to include the Work and Children activity in one of your lesson plans. Alternatively, this exercise can be done in a civics or history class, or in conjunction with International Women's Day (March 8) or International Family Day (May 15).
The team could do some research on reproductive rights in your country. After that, a survey could be conducted among both women and employers to see how the legislation is implemented in practice. The Panel may also consider how European Union legislation on this matter has influenced national laws. nine0003
nine0003
Participants can also study the situation of sex education in their country. Does it cover all aspects of reproductive rights?
If you want to look at other types of discrimination in the workplace, you can do the exercise “Different wages”.
Ideas for Action
Ideas for Action Discuss reproductive rights in your school or organization.
Find out which local NGOs advocate for women's reproductive rights and get involved in their debates and campaigns. nine0003
More information
Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women
In addition to protecting human rights, the Convention also focuses on an issue that is of vital importance to women, namely reproductive rights. The preamble states that "the role of women in procreation should not be a reason for discrimination."
The Convention continually draws attention to the link between discrimination against women and their role in procreation. For example, in Article 5, the Convention defends the “correct understanding of motherhood as a social function” by requiring the joint responsibility of both sexes for the upbringing of children. nine0003
For example, in Article 5, the Convention defends the “correct understanding of motherhood as a social function” by requiring the joint responsibility of both sexes for the upbringing of children. nine0003
Accordingly, provisions for the protection of motherhood and the upbringing of children are declared essential rights and are included in all sections of the Convention relating to employment, family law, health and education.
Commitment on the part of society includes the organization of social services, especially childcare, to enable citizens to combine family responsibilities with work and participation in public life.
Adoption of special maternity protection measures recommended, which “shall not be discriminatory” (Article 4) “The Convention also affirms a woman's right to reproductive choice. It is noteworthy that this is the only human rights convention that addresses the issue of family planning. nine0003
It states that the parties undertake to provide access to educational information, including information and advice on family planning (Article l0.