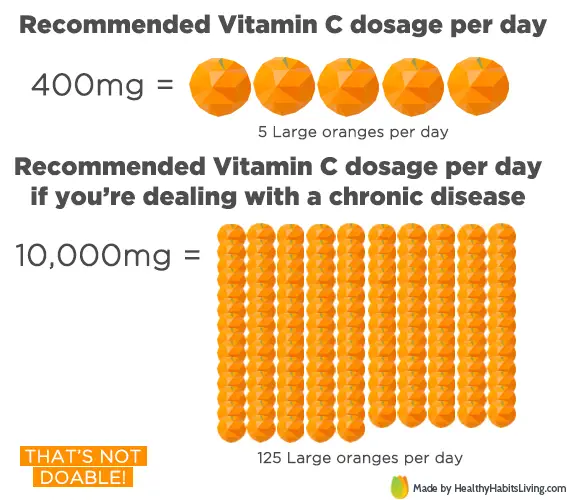
How much vitamin c is safe for a child
What are the side effects and risks?
Vitamin C is usually safe to take even at high dosages. However, people may sometimes experience mild side effects, such as digestive discomfort. Rarely, more serious side effects can occur.
Vitamin C is an essential vitamin for the human body. It is an antioxidant, and it helps with a range of important processes, including lowering blood pressure, fighting inflammation, and creating collagen.
In this article, we look at the recommended upper limits of vitamin C intake, possible side effects of taking too much, and other warnings.
Share on PinterestIt is usually safe to frequently eat foods high in vitamin C.Frequently eating foods high in vitamin C should not lead to any health issues. Taking too much vitamin C through supplements can, however, cause side effects.
In adults, the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) of vitamin C is 90 milligrams (mg) for males and 75 mg for females.
Adults who take more than 2,000 mg of vitamin C per day may experience side effects.
When a person takes more than the recommended limit of vitamin C, they may experience mild digestive disturbances. These can occur if the vitamin C that the body does not absorb irritates the gastrointestinal tract.
Common mild side effects of too much vitamin C include:
- diarrhea
- nausea
- stomach cramping
- bloating
- general abdominal discomfort
The body does not absorb all of the vitamin C that it gets from supplements.
For example, if a person takes 30–180 mg of vitamin C each day, their body absorbs about 70–90% of this vitamin. If a person takes more than 1 gram (g) of vitamin C per day, the body absorbs less than 50% of the vitamin, which reduces the risk of negative side effects. The excess leaves the body in the urine.
As vitamin C can cause unpleasant symptoms if a person takes too much, the Food and Nutrition Board have established “tolerable upper intake levels.”
According to the Office of Dietary Supplements (ODS), the upper limit for vitamin C intake in people aged 19 years and over is 2,000 mg in males and females. The limit remains the same for pregnant or breastfeeding women.
The limit remains the same for pregnant or breastfeeding women.
The upper daily vitamin C levels for children and infants are as follows:
- 400 mg for infants aged 1–3 years
- 650 mg for children aged 4–8 years
- 1,200 mg for children aged 9–13 years
- 1,800 mg for teenagers aged 14–18 years
- 1,800 mg in pregnant or breastfeeding teenagers aged 14–18 years
There are exceptions to these limits, which only apply if a person’s doctor has not specified a different intake. Some people may have to take larger amounts of vitamin C for medical treatments.
Less commonly, people may experience severe side effects from taking too much vitamin C. Long term intake above the recommended levels increases the risk of these negative effects.
Possible health risks of taking too much vitamin C include:
Kidney stones
Share on PinterestKidney stones are a possible consequence of too much vitamin C supplementation.
Doctors believe that too much vitamin C supplementation could result in a person excreting the compounds oxalate and uric acid in their urine. These compounds could lead to kidney stone formation.
These compounds could lead to kidney stone formation.
The authors of a case study in the journal Kidney Internationalreported that a woman developed kidney stones after taking 4 g or more of vitamin C each day for 4 months.
However, researchers have not conducted any larger scale studies on vitamin C intake and kidney stone formation. They do know that people who have a history of kidney stones are more likely to form them if they take large amounts of vitamin C, according to the ODS.
Nutrient imbalances
Another concern regarding excessive vitamin C intake is that it can impair the body’s ability to process other nutrients.
For example, vitamin C may reduce the levels of vitamin B-12 and copper in the body.
The presence of vitamin C can also enhance iron absorption in the body, which could lead to excessively high levels.
Cause bone spurs
According to the Arthritis Foundation, one study found that the presence of very high vitamin C levels in the body increased the likelihood of a person developing painful bone spurs.
However, the Foundation also cited a research study that found that people with low levels of vitamin C had a higher risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis, a painful inflammatory joint condition.
These findings emphasize the need for appropriate vitamin C supplementation that provides neither too much nor too little.
Impair the effectiveness of niacin-simvastatin
Evidence suggests that taking vitamin C supplements may impair the body’s ability to increase high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol in people taking the combination drug niacin-simvastatin. This drug combines the vitamin niacin with the statin simvastatin (Zocor), and people take it to treat high cholesterol.
Doctors consider HDL cholesterol the “good” cholesterol because it reduces the amount of harmful cholesterol in the blood.
If a person takes vitamin C supplements and niacin-simvastatin, they should talk to their doctor about ways to make each more effective. Doctors do not know whether vitamin C also affects the ability of other medicines similar to Zocor.
A person’s body cannot make vitamin C, so people need to eat enough foods that contain vitamin C to meet their daily needs. If someone is at risk of a vitamin C deficiency, they can take vitamin C supplements.
The ODS advise aiming for the following RDA of vitamin C each day:
| Age | Male | Female |
| 1–3 years | 15 mg | 15 mg |
| 4–8 years | 25 mg | 25 mg |
| 9–13 years | 45 mg | 45 mg |
| 14–18 years | 75 mg | 65 mg |
| 19+ years | 90 mg | 75 mg |
People who smoke should take 35 mg more vitamin C per day than those who do not smoke.
During pregnancy or when breastfeeding, women should get the following levels of vitamin C per day:
- 14–18 years: 80 mg during pregnancy and 115 mg when breastfeeding
- 19 years and older: 85 mg during pregnancy and 120 mg when breastfeeding
There is not enough research to suggest an RDA for vitamin C in those younger than 1 year of age. As a result, the ODS provide an “adequate intake,” which is the amount that is likely to be sufficient:
As a result, the ODS provide an “adequate intake,” which is the amount that is likely to be sufficient:
- 40 mg for babies aged 0–6 months
- 50 mg for infants aged 7–12 months
Share on PinterestA pregnant woman may wish to take a vitamin C supplement if they have trouble getting enough from their diet.
Some doctors advocate women taking vitamin C supplements when pregnant.
A literature review in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews looked into the effects of vitamin C supplementation during pregnancy.
The authors examined 29 studies that included 24,300 pregnant women. There was insufficient evidence for them to conclude that vitamin C helped prevent problems during pregnancy, such as stillbirth, preterm birth, or preeclampsia.
However, pregnant women should try to get enough vitamin C through their daily diets when pregnant. Foods high in vitamin C include:
- broccoli
- kiwifruit
- oranges
- strawberries
- tomatoes
If a woman has trouble meeting her daily requirements, she should talk to her doctor about supplementation.
Vitamin C has potentially harmful side effects if a person takes too many supplements. Usually, a person will not experience side effects if they eat a lot of foods containing vitamin C.
If a person suspects that their vitamin C intake may be causing side effects, they should talk to their doctor.
Vitamin C for kids and toddlers: How much they need
Vitamin C is an essential nutrient for your child's health and development. It helps repair red blood cells and boosts the immune system. Toddlers ages 1 to 3 years old need 15 mg of vitamin C a day and older children ages 4 to 8 years old need 25 mg a day. Many fruits and vegetables contain vitamin C, especially red and orange-colored ones, like strawberries, red bell peppers, and oranges. Vitamin C deficiencies are rare, but if you're concerned your child isn't getting enough, talk with your doctor about whether or not they need a supplement.
Vitamin C is crucial for children's health and development. The body needs it to form and repair red blood cells, bones, and tissues. It also plays a part in keeping your child's gums healthy and strengthens your child's blood vessels, minimizing bruising from falls and scrapes.
It also plays a part in keeping your child's gums healthy and strengthens your child's blood vessels, minimizing bruising from falls and scrapes.
In addition, vitamin C helps cuts and wounds heal, boosts the immune system, and keeps infections at bay. It also helps the body absorb iron from food sources.
Here's what you need to know about how much vitamin C your child needs, which sources are the best, and how to prevent your child from getting too little or too much.
How much vitamin C kids and toddlers need
Ages 1 to 3 years: 15 milligrams (mg) daily
Ages 4 to 8: 25 mg daily
Vitamin C is available in so many foods that deficiencies are extremely rare. Children who are very picky eaters and don't eat a lot of fruits and vegetables may not get enough vitamin C. And children exposed to secondhand smoke may need more vitamin C to repair cell damage from cigarettes.
If you're concerned that your child isn't getting enough vitamin C, ask your pediatrician whether you need to boost your child's intake.
Your little one doesn't have to get enough vitamin C every day. Instead, aim to get the recommended amount as an average over the course of a few days or a week.
The best sources of vitamin C
In general, a good rule of thumb to remember is that red- and orange-colored fruits and vegetables are great sources of vitamin C. While the amount of vitamin C varies somewhat depending on the size of the fruit or vegetable, here are some foods that are high in vitamin C:
Advertisement | page continues below
- 1/4 cup guava: 94 mg
- 1/2 cup orange juice: 50 mg
- 1/4 cup red bell pepper: 47.5 mg
- 1/4 cup papaya: 35 mg
- 1/4 cup kiwi: 41 mg
- 1/2 medium orange: 35 mg
- 1/2 cup broccoli: 51 mg
- 3 medium strawberries: 21 mg
- 1/4 cup pink grapefruit: 23 mg
- 1/4 cup cantaloupe: 17 mg
- 1/4 cup mango: 15 mg
- 1/4 cup raw tomato: 5 mg
- 1/4 cup spinach: 4.5 mg
- 1/4 cup potato, cooked without skin: 3 mg
Can my child get too much vitamin C?
Vitamin C is water-soluble, so any excess is flushed from the body in your child's urine. However, megadoses can still cause nausea, diarrhea, kidney stones, and gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining).
However, megadoses can still cause nausea, diarrhea, kidney stones, and gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining).
For children ages 1 to 3,a megadose would be more than 400 mg of vitamin C in a day. For children ages 4 to 8, a megadose is more than 650 mg a day. Be careful before giving a child chewable supplements meant for adults, since each tablet can contain up to 500 mg.
For most children and adults, eating a well-rounded diet provides an adequate amount of nutrients, including vitamin C. In fact, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) doesn't recommend vitamin supplements for kids unless your child's doctor thinks they need one.
Some neurodivergent kids with sensory processing disorders or autism may be especially picky eaters who struggle to eat foods rich in vitamin C. Talk with your child's pediatrician if you're worried about your child's diet to see if a vitamin supplement is right for them.
Learn more: Ten important nutrients for children
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
properties and benefits, which products contain
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is a water-soluble organic compound, one of the main substances necessary for a person to maintain life. Vitamin C is not synthesized by the body, but comes only from the outside with food. A micronutrient deficiency can lead to the development of serious diseases, so it is important to monitor your diet to ensure that you are getting enough ascorbic acid. nine0003
Vitamin C is not synthesized by the body, but comes only from the outside with food. A micronutrient deficiency can lead to the development of serious diseases, so it is important to monitor your diet to ensure that you are getting enough ascorbic acid. nine0003
Properties of vitamin C
Vitamin C was first isolated almost a hundred years ago, in 1928. Since then, scientists have conducted a huge amount of research that helped to establish the physicochemical properties of the micronutrient, find out its benefits for the human body and sources of intake.
Ascorbic acid is a white powdery substance with a sour taste and a neutral odor. It is highly soluble in water and alcohol, quickly destroyed at high and low temperatures, exposure to ultraviolet rays. nine0003
From a chemical point of view, vitamin C is an electron donor or reducing agent. It is precisely this ability of it that explains most of the physiological effects known to science 1 .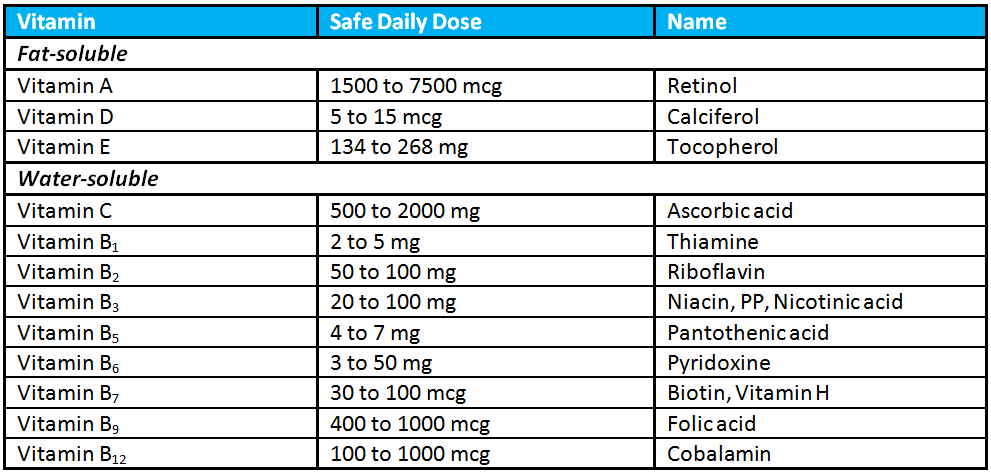 Entering into biological reactions, vitamin C acts as a coenzyme, promotes the regeneration of bone and connective tissue cells, acts as an antioxidant, helping the body fight free radicals.
Entering into biological reactions, vitamin C acts as a coenzyme, promotes the regeneration of bone and connective tissue cells, acts as an antioxidant, helping the body fight free radicals.
Only L-ascorbic acid, which is called vitamin C or biological supplement E 300, is capable of participating in biochemical reactions. It does not accumulate in the body and is excreted by the kidneys. The compound is very unstable, easily destroyed during heat treatment and long-term storage, which often leads to its deficiency. nine0003
Physiological need for vitamin C
Currently, there is no accurate information on the need for vitamin C depending on body weight and data on the characteristics of its metabolism, which creates some difficulties in substantiating differentiated recommendations regarding micronutrient intake norms.
According to the methodological recommendations of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare, the physiological need for vitamin C for adults is 100 mg / day, for children - from 30 to 90 mg/day 2 . However, these are very average indicators, since in different periods of life and under different conditions, the need for a micronutrient changes.
However, these are very average indicators, since in different periods of life and under different conditions, the need for a micronutrient changes.
So, per kilogram of body weight, the need for L-ascorbic acid in children is higher than in adults, which is explained by the rapid development of organs and structures of a growing organism. Women need higher doses of vitamin C during pregnancy and lactation.
Environmental conditions and the diet associated with them also have a great influence on the need for ascorbic acid. The greatest deficiency of vitamin C is experienced by residents of the Far North. Additional intake of ascorbic acid at low temperatures and a poor diet reduces the risk of developing meteoneurosis, accelerates acclimatization, and increases the body's resistance to infections. nine0003
The results of some studies indicate a possible relationship between vitamin C and the energy needs of the body, so the individual level of consumption of ascorbic acid is determined at the rate of 25 mg per 1000 kcal, for example:
-
a man aged 20 to 40 who lives in an urban environment and performs mental work needs 2800 kcal and, accordingly, 70 mg of ascorbic acid per day; nine0003
-
a worker of the same age, engaged in physical labor and living in the same conditions, requires 3700 kcal and 93 mg of vitamin C per day;
-
a person whose activity is associated with heavy manual labor, other things being equal, needs at least 4500 kcal and 120 mg of ascorbic acid daily.
The need for vitamin C also increases during a cold, with chronic infectious processes, reduced immunity, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by impaired absorption of nutrients. nine0003
Benefits for the body and consumption rates
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant. It protects cells and tissues of internal organs from damage, regulates redox processes, promotes the synthesis of collagen, procollagen, steroid and neurohormones, mediators, and participates in the metabolism of folic acid and iron. And this is not a complete list of the properties of ascorbic acid. Vitamin C performs a number of other equally important functions: nine0003
- regulates blood clotting;
- strengthens the vascular wall;
- has an anti-inflammatory effect;
- reduces the body's sensitivity to allergens;
- strengthens the immune system;
- supports higher nervous activity;
- is involved in the breakdown of fats;
- accelerates the processes of tissue regeneration; nine0034
- prevents malignant transformation of cells 3 .

The debate about the exact amount of vitamin C that a person needs to maintain normal life is still ongoing, and scientists do not yet have a consensus on this matter. The minimum daily norms of ascorbic acid for people of different ages are presented in the table below.
| Population category nine0003 | Minimum amount of vitamin C, mg/day |
| Newborns up to 6 months | 40 |
| Infants 7 to 12 months | 50 |
| Children from 1 to 3 years old | 40 |
| Children from 4 to 8 years old | 45 |
| Children from 9 to 13 years old | 50 | nine0085
| Girls from 14 to 18 years old | 65 |
| Youth from 14 to 18 years old | 75 |
| Women over 18 | 75 nine0080 |
| Men over 18 | 90 |
| Pregnant and lactating women | 90 |
The greatest need for vitamin C is experienced by children in the period of active growth, pregnant and lactating women, athletes, people involved in heavy physical labor, residents of the northern regions. The consumption of ascorbic acid increases with acute infections, oral contraceptives, during periods of severe stress. Vitamin C supplementation is recommended during this time to avoid micronutrient deficiencies. nine0003
The consumption of ascorbic acid increases with acute infections, oral contraceptives, during periods of severe stress. Vitamin C supplementation is recommended during this time to avoid micronutrient deficiencies. nine0003
Signs of vitamin C deficiency
A deficiency in the body of one or more vitamins is called hypovitaminosis, an acute shortage is called beriberi. Hypovitaminosis is accompanied by a decrease in the concentration of vitamin C, as evidenced by the following signs:
- bruising without injury;
- slow healing of wounds and abrasions;
- bleeding gums; nine0031 dry skin;
- fragility of nails;
- hair loss;
- decreased immunity, frequent colds;
- pain in the joints;
- fast fatiguability;
- emotional instability;
- depressed mood.
Vitamin C deficiency is more often observed in the autumn-winter period. To some extent, this is due to a change in the diet, as well as the high activity of viruses, the fight against which the body consumes a large amount of micronutrient. nine0003
nine0003
If symptoms of hypovitaminosis appear, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination. If the test results confirm a vitamin C deficiency, the specialist may prescribe supplements containing ascorbic acid.
Symptoms of vitamin C surplus
An excess of ascorbic acid is extremely rare, since the micronutrient does not accumulate in the body, it is easily excreted by the kidneys. However, uncontrolled intake of the vitamin can cause side effects: nine0003
-
from the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, heartburn, bloating, intestinal cramps, diarrhea;
-
from the nervous system: sleep disturbance, headache, dizziness;
-
on the part of the immune system: allergic reactions in the form of a rash, itching, redness of the skin, swelling;
- nine0002 from the urinary system: the appearance of kidney stones, back pain.
These symptoms can be dangerous to health, so when they appear, you should immediately stop taking ascorbic acid and seek medical help.
Features of taking vitamin C in various diseases and conditions
Despite the relative safety of ascorbic acid, vitamin C supplements for a number of diseases should be taken with caution and only with the permission of the attending physician, as it can enhance the effect of certain drugs and cause side effects. For example: nine0003
-
Simultaneous intake of salicylic acid (aspirin) and vitamin C can increase the acidity of gastric juice, which increases the risk of gastritis and stomach ulcers.
-
The use of ascorbic acid with increased blood clotting increases the risk of thrombosis, so people with high levels of prothrombin and platelets need to coordinate the micronutrient intake with their doctor. nine0003
-
High doses of vitamin C are contraindicated in patients with type 2 diabetes, as high doses (above 1000 mg/day) inhibit insulin production. On the contrary, prophylactic doses of ascorbic acid can help strengthen blood vessels, which often suffer from diabetes.
-
For people who are prone to stone formation, additional intake of vitamin C may be contraindicated due to the high risk of developing urolithiasis. In this case, it is enough to diversify your diet with foods rich in this micronutrient. nine0003
-
Long-term joint use of ascorbic acid and drugs containing estrogens can lead to menstrual irregularities, weight gain, deterioration of the skin and hair. Therefore, women taking oral contraceptives should limit themselves to short-term courses of the vitamin.
Healthy people can take vitamin C prophylactically at the recommended dosages without fear of harming the body. However, as with any vitamin/mineral supplement, it is advisable to seek the advice of a physician or nutritionist before starting to take ascorbic acid. nine0003
Vitamin C sources
Vegetables, fruits, berries, greens are rich in ascorbic acid. The advantage of these products is that most of them can be consumed fresh without being subjected to heat treatment, which destroys vitamin C.
Contrary to popular belief, citrus fruits are not leaders in the content of ascorbic acid - they only close the top twenty. In addition to vegetables and fruits, dried porcini mushrooms and beef liver are rich in vitamin C. nine0003
The TOP 20 foods high in ascorbic acid are shown in the table below. Adding them to your daily diet will be an excellent prevention of hypovitaminosis.
| Product | Quantity, mg/100 g | Percentage of Daily Value |
| Rose hip | 650 | 929 |
| Sea buckthorn | 200 | 286 |
| Before Sweet (Bulgarian) nine0003 | 200 | 286 |
| Black currant | 200 | 286 |
| Kiwi | nine0078 180 | 257 |
| Dried white mushrooms | 150 | 214 |
| parsley | 150 nine0003 | 214 |
| Brussels sprouts | 89 | 127 |
| Cauliflower | 70 | nine0077 |
| Papaya | 61 | 87 |
| pomelo | 61 | 87 nine0080 |
| Orange | 60 | 86 |
| strawberries | 60 | 86 |
| nine0002 red cabbage | 60 | 86 |
| Spinach | 55 | 79 |
| Grapefruit nine0003 | 45 | 64 |
| White cabbage | 45 | 64 |
| Lemon | nine0078 40 | 57 |
| Mandarin | 38 | 54 |
| Beef liver | 33 nine0080 | 47 |
When calculating the intake of vitamin C, it should be borne in mind that the amount of nutrients depends on the method of processing products and the duration of their contact with oxygen. In order to preserve the maximum of vitamins in vegetables and fruits, it is recommended to cut them immediately before eating, and put them in boiling water during cooking without peeling.
In order to preserve the maximum of vitamins in vegetables and fruits, it is recommended to cut them immediately before eating, and put them in boiling water during cooking without peeling.
Therapeutic and prophylactic use of vitamin C
Ascorbic acid is used for the treatment and prevention of hypovitaminosis, viral infections, some vascular pathologies, strengthening the immune system 4 . With a slight decrease in the level of vitamin in the blood, the doctor can give recommendations for correcting nutrition, with severe hypovitaminosis, prescribe a course of vitamin C in the form of soluble tablets, dragees or powders. In case of an acute shortage of ascorbic acid, as a rule, intramuscular injections of vitamin preparations are prescribed. nine0003
The prophylactic dose of vitamin C is 50–100 mg for adults, 25–75 mg for children, and 25–100 mg for pregnant and lactating women. Therapeutic dosages depend on the severity of the disease and are calculated individually. The duration of the course and the regimen are determined by the attending physician.
The duration of the course and the regimen are determined by the attending physician.
In severe viral infections in the acute period of the disease, patients may be given loading doses of vitamin C. According to studies, high doses do not affect the duration and severity of viral infections, but allow maintaining a sufficient level of ascorbic acid in conditions when the body consumes it most actively 5 .
How to take vitamin C correctly?
Vitamin C is available in pharmacies in single form and as part of complex dietary supplements, but regardless of the form of release, it is best to take it during or immediately after a meal. Together with food, ascorbic acid itself is absorbed better and promotes the absorption of nutrients that come with it. After taking a dietary supplement in the form of chewable lozenges or lozenges, it is recommended to rinse your mouth thoroughly so that the acid does not destroy tooth enamel. nine0003
When using ascorbic acid, it is also necessary to take into account its interaction with other vitamins and minerals. Remember that vitamin C:
Remember that vitamin C:
- enhances the activity of vitamins A, E, B 5 , B 9 ;
- accelerates the absorption of iron and calcium;
- destroyed by vitamins B 1 , B 12 and K;
- promotes the excretion of copper from the body. nine0034
If you do not want to remember the rules of interaction, choose multivitamin complexes and dietary supplements for prophylactic use, in which the optimal combinations and dosages are selected to provide a person's daily need for micronutrients.
Use of vitamin C in cosmetology
Ascorbic acid has antioxidant and anti-aging properties, so it is often included in cosmetics and anti-aging complexes. Oral vitamin supplements can have a systemic effect, and topical treatments can help: nine0003
- relieve inflammation;
- improvement of cellular metabolism and microcirculation;
- stimulation of collagen synthesis;
- alignment of color and increase of skin turgor;
- strengthening local immunity;
- improve blood circulation;
- reduce the appearance of wrinkles 6 .

Care products with ascorbic acid are available in the form of creams, gels, peels, masks, patches. Homemade masks based on berries and fruits also have a healing and rejuvenating effect. nine0003
1 Vitamin C: the known and the unknown and Goldilocks. Padayatti C . D ., Levin M . OralDis. 2016 Sep; 22(6):463-93. doi: 10.1111/odi.12446 . Epub 2016 Apr 14. PMID: 26808119; PMCID: PMC4959991.
2 Norms of physiological needs for energy and nutrients for various groups of the population of the Russian Federation: Guidelines. - M.: Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare, 2021. - 72 p.
3 Vitamin C/ Vitamin C . Likkesfeldt J., Michels A. D., Frei B. Adv Nutr . 2014 Jan 1;5(1):16-8. doi : 10.3945/ an .113.005157 . PMID : 24425716; PMCID : PMC 3884093.
Adv Nutr . 2014 Jan 1;5(1):16-8. doi : 10.3945/ an .113.005157 . PMID : 24425716; PMCID : PMC 3884093.
0648 Vitamin C as an antioxidant: evaluation of its role in disease prevention. Padayatti S. D., Katz A., Wang Y., Ek P., Kwon O., Lee D. H., Che S., Corp. K., Datta A., Datta S. K., Levin M. J Am Coll Nutr. 2003 Feb;22(1):18-35. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2003.10719272 . PMID: 12569111.
6 Evaluation individual parameters skin after application 5% vitamin concentrate C / Evaluation of selected skin parameters following the application of 5% vitamin C concentrate. Jarosh A ., Zasada M ., Budzis E ., Dembovska R ., Giembczynska - Rzepka M ., Rothstein X . J Cosmetic Dermatol. 2019 Feb;18(1):236-241. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12562 . Epub 2018 Apr 30. PMID: 29707883.
Jarosh A ., Zasada M ., Budzis E ., Dembovska R ., Giembczynska - Rzepka M ., Rothstein X . J Cosmetic Dermatol. 2019 Feb;18(1):236-241. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12562 . Epub 2018 Apr 30. PMID: 29707883.
Vitamin C for children. Is your child getting enough?
The information in this blog has not been verified by your country's public health authority and is not intended for diagnosis, treatment or medical advice. Read more
I am a certified paediatrician, and children and their parents often come to me for preventive check-ups. At these checkups, we often talk about diet and the body's need for nutrients. I am often asked about the norms of vitamin intake and the need for nutritional supplements.
Many parents wonder if they should give their children nutritional supplements in addition to their normal diet.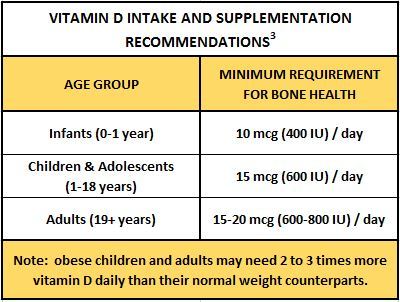 This is certainly an important topic and a key issue to discuss with the pediatrician at every visit. Let's talk about this in more detail. nine0003
This is certainly an important topic and a key issue to discuss with the pediatrician at every visit. Let's talk about this in more detail. nine0003
How do I know if my child is getting enough vitamins?
The American Academy of Pediatrics does not recommend supplementation in excess of the recommended nutrient intake for children who are on a balanced diet. The daily intake of each vitamin is different. Diet and nutrient recommendations also differ by age. Keep this in mind when discussing supplementation with your pediatrician.
Can my child overdose on vitamins? nine0903
This is a less common but important question! High doses of certain vitamins, such as A or D, can lead to dangerous symptoms. That's why it's so important to check with your pediatrician before giving vitamins to your child.
If your child takes a huge dose of vitamin C for any reason, they will most likely develop mild symptoms like gastrointestinal upset. Vitamin C is water soluble, so excess is excreted from the body without the toxic burden seen with accidental overdose of other vitamins. nine0003
Vitamin C is water soluble, so excess is excreted from the body without the toxic burden seen with accidental overdose of other vitamins. nine0003
How is it recommended to take vitamin C?
The Recommended Daily Allowance for Vitamin C ranges from 15 to 45 mg for ages 1-13 and 65 to 75 mg for ages 14-18. Recommended doses within these age ranges vary slightly, so be sure to discuss the details and the correct dosage for your child's particular age with your pediatrician. As a rule, the need for vitamin C increases with infectious diseases or inflammatory processes, as well as during pregnancy and lactation in adult women. nine0003
The upper limit of the acceptable intake level differs from the recommended daily intake. The maximum allowable level for different age groups is usually higher than the daily intake. Higher doses of vitamin C may be used to treat vitamin C deficiency.
Why is vitamin C important?
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is important for the normal functioning of the immune system. It strengthens muscles and skin, promotes healing of wounds and bones. Vitamin C also helps the body absorb another important micronutrient, iron. Iron carries oxygen throughout the body so cells can produce energy. When iron levels are low, children may feel tired or weak. nine0003
It strengthens muscles and skin, promotes healing of wounds and bones. Vitamin C also helps the body absorb another important micronutrient, iron. Iron carries oxygen throughout the body so cells can produce energy. When iron levels are low, children may feel tired or weak. nine0003
Vitamin C is also involved in the production of collagen, a protein that helps a child's body form healthy ligaments and tendons, bones and teeth. Collagen is also important for the skin.
Is it true that vitamin C helps with colds?
Many researchers have noted a link between vitamin C intake and improved immunity, which in turn may help the body fight off infections or cold symptoms. However, this link has not been definitively proven, and physicians or the American Academy of Pediatrics do not provide clear guidelines for increasing vitamin C intake during illness. nine0003
To help prevent colds and flu, some doctors recommend taking at least 200 mg of vitamin C daily. Studies have shown a 14% reduction in colds in children taking this amount of vitamin C. Many children already consume 200 mg of vitamin C through their meals, so supplementation may not be necessary. However, when children feel unwell, they usually eat and drink less, so supplements should be taken in such situations.
Studies have shown a 14% reduction in colds in children taking this amount of vitamin C. Many children already consume 200 mg of vitamin C through their meals, so supplementation may not be necessary. However, when children feel unwell, they usually eat and drink less, so supplements should be taken in such situations.
Are there natural sources of vitamin C? nine0903
Of course! Since your body does not produce or store vitamin C, it is important to include foods that contain this vitamin in your diet. Vitamin C is found in many foods, especially fruits and vegetables. For example, there is a lot of vitamin C in citrus fruits (oranges) and pineapples, it is also in melon, strawberries and tomatoes. Vitamin C is also present in vegetables: sweet potatoes, spinach, green tomatoes, yellow bell peppers, broccoli, etc. Vitamin C can be destroyed by light and heat, so fresh and raw fruits and vegetables contain more vitamin C. nine0003
It would be useful to remind you that it is important to eat well.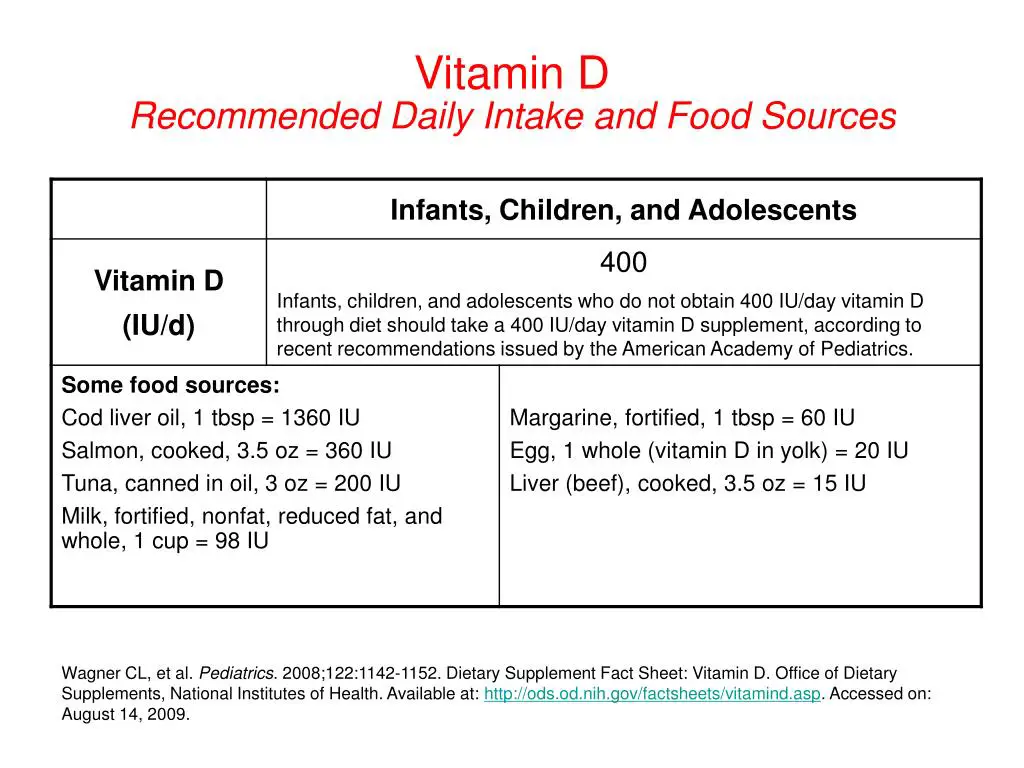 A balanced diet should include fruits and vegetables. However, it is not a secret for anyone that children are capricious little ones and do not always eat vegetables and fruits in the quantity that we would like. There are two ways to discreetly introduce these food groups into your child's diet: you can make fruit and vegetable smoothies or fresh fruit ice cream.
A balanced diet should include fruits and vegetables. However, it is not a secret for anyone that children are capricious little ones and do not always eat vegetables and fruits in the quantity that we would like. There are two ways to discreetly introduce these food groups into your child's diet: you can make fruit and vegetable smoothies or fresh fruit ice cream.
What will my child suffer from vitamin C deficiency?
Chronic vitamin C deficiency results in a disease called scurvy. It is relatively rare because most children get enough vitamin C from their diet. Some diseases can reduce the amount of vitamin C that the body can absorb or increase the need for vitamin C.
What are the symptoms of a vitamin C deficiency?
Initial symptoms of vitamin C deficiency may include irritability, loss of appetite, and bruising. Another symptom of vitamin C deficiency is bleeding gums. Children may develop joint inflammation or joint pain. Since vitamin C helps the body absorb iron, it is common for people with iron deficiency to be deficient in vitamin C.
Since vitamin C helps the body absorb iron, it is common for people with iron deficiency to be deficient in vitamin C.
The treatment for vitamin C deficiency is to increase its intake. Your pediatrician can help you monitor your child's vitamin C levels.
Is my child at increased risk of vitamin C deficiency?
Children with gastrointestinal disorders or some forms of cancer may be at increased risk of vitamin C deficiency. Chronic hemodialysis in patients with kidney disease or a strict ketogenic diet in patients with refractory seizures can also result in low vitamin C concentrations. Tobacco smoking and nicotine exposure increase vitamin C requirements by up to 40%, which is important to keep in mind, especially if your children are exposed to passive smoking. nine0003
What should I look for when choosing a vitamin C supplement?
When choosing a supplement, it is important to consider the additional ingredients that may be undesirable.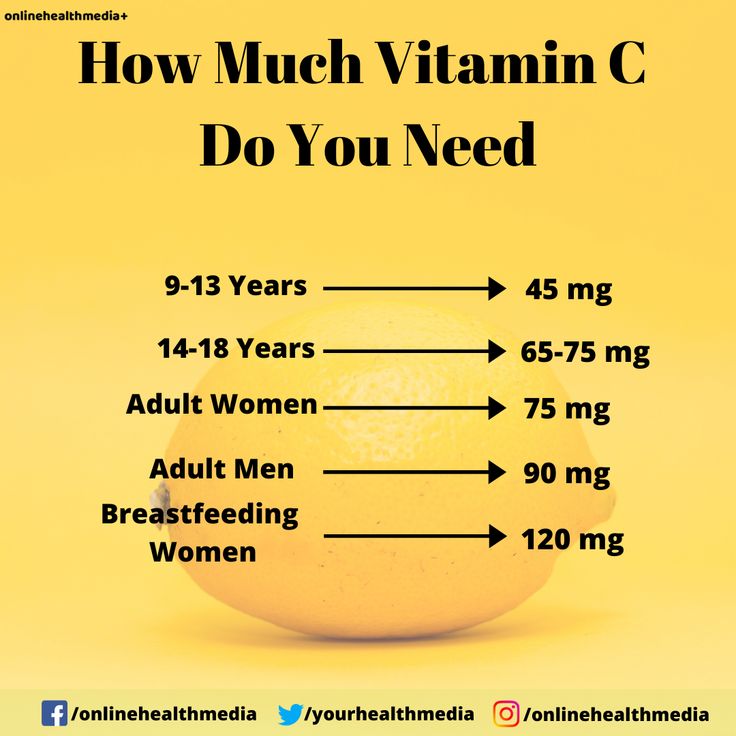 For example, natural and artificial colors or sweeteners are unnecessary and can be avoided when choosing a vitamin C supplement. Look for products without artificial ingredients or fillers. On sale there are preparations with vitamin C that do not contain gluten, genetically modified organisms and gelatin. nine0003
For example, natural and artificial colors or sweeteners are unnecessary and can be avoided when choosing a vitamin C supplement. Look for products without artificial ingredients or fillers. On sale there are preparations with vitamin C that do not contain gluten, genetically modified organisms and gelatin. nine0003
Another important factor when choosing a vitamin supplement for children is its taste. Children usually like fruity or citrus scents. These are the flavors most commonly used in vitamin C supplements.
When shopping for vitamins, consider whether your child likes chewables or gummy bears. Vitamin C is also available in liquid form, in case your child is not yet able to chew or swallow teddy bears or tablets. Vegetarian vitamin C supplements are also available in case an older child chooses a vegetarian diet. nine0003
Look for supplements that are manufactured under Good Manufacturing Practices. This system guarantees constant control at all stages of production and its compliance with quality standards.